Library Creation
Diunggah oleh
enggeng7Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Library Creation
Diunggah oleh
enggeng7Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
When a C program is compiled, the compiler generates object code.
After generating the object
code, the compiler also invokes linker. One of the main tasks for linker is to make code of library
functions (eg printf(), scanf(), sqrt(), ..etc) available to your program. A linker can accomplish this
task in two ways, by copying the code of library function to your object code, or by making some
arrangements so that the complete code of library functions is not copied, but made available at runtime.
Static Linking and Static Libraries is the result of the linker making copy of all used library
functions to the executable file. Static Linking creates larger binary files, and need more space on
disk and main memory. Examples of static libraries (libraries which are statically linked) are, .a
files in Linux and .lib files in Windows.
Steps to create a static library Let us create and use a Static Library in UNIX or UNIX like OS.
1. Create a C file that contains functions in your library.
/* Filename: lib_mylib.c */
#include <stdio.h>
void fun(void)
{
printf("fun() called from a static library");
}
We have created only one file for simplicity. We can also create multiple files in a library.
2. Create a header file for the library
/* Filename: lib_mylib.h */
void fun(void);
3. Compile library files.
gcc -c lib_mylib.c -o lib_mylib.o
4. Create static library. This step is to bundle multiple object files in one static library (see ar for
details). The output of this step is static library.
ar rcs lib_mylib.a lib_mylib.o
5. Now our static library is ready to use. At this point we could just copy lib_hello_static.a
somewhere else to use it. For demo purposes, let us keep the library in the current directory.
Let us create a driver program that uses above created static library.
1. Create a C file with main function
/* filename: driver.c */
#include "lib_mylib.h"
void main()
{
fun();
}
2. Compile the driver program.
gcc -c driver.c -o driver.o
3. Link the compiled driver program to the static library. Note that -L. is used to tell that the static
library is in current folder (See this for details of -L and -l options).
gcc -o driver driver.o -L. -l_mylib
4. Run the driver program
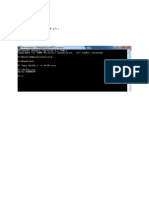
./driver
fun() called from a static library
Following are some important points about static libraries.
1. For a static library, the actual code is extracted from the library by the linker and used to build the
final executable at the point you compile/build your application.
2. Each process gets its own copy of the code and data. Where as in case of dynamic libraries it is
only code shared, data is specific to each process. For static libraries memory footprints are larger.
For example, if all the window system tools were statically linked, several tens of megabytes of
RAM would be wasted for a typical user, and the user would be slowed down by a lot of paging.
3. Since library code is connected at compile time, the final executable has no dependencies on the
the library at run time i.e. no additional run-time loading costs, it means that you dont need to carry
along a copy of the library that is being used and you have everything under your control and there
is no dependency.
4. In static libraries, once everything is bundled into your application, you dont have to worry that
the client will have the right library (and version) available on their system.
5. One drawback of static libraries is, for any change(up-gradation) in the static libraries, you have
to recompile the main program every time.
6. One major advantage of static libraries being preferred even now is speed. There will be no
dynamic querying of symbols in static libraries. Many production line software use static libraries
even today.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- 7GCBC PohDokumen75 halaman7GCBC PohEyal Nevo100% (1)
- Centaour 50 Solar TurbineDokumen2 halamanCentaour 50 Solar TurbineTifano KhristiyantoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Compressed Air SystemDokumen23 halamanIntroduction To Compressed Air SystemMohd Zulhairi Mohd NoorBelum ada peringkat
- BDM DriverDokumen16 halamanBDM DrivervolvodiagBelum ada peringkat
- Superscalar ArchitectureDokumen9 halamanSuperscalar Architectureenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Sr. Number: Name of Participant: Email ID: Mobile NumberDokumen5 halamanSr. Number: Name of Participant: Email ID: Mobile Numberenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Architecture of The Pentium MicroprocessorDokumen12 halamanArchitecture of The Pentium Microprocessorenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Subject:-Engineering Mathematics III Class: - SE-IT Subject Code:-ITC 301 Module Number: - 3 Fourier SeriesDokumen19 halamanSubject:-Engineering Mathematics III Class: - SE-IT Subject Code:-ITC 301 Module Number: - 3 Fourier Seriesenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Sec8 1Dokumen16 halamanSec8 1enggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Course File Programming and Problem Solving in CDokumen10 halamanCourse File Programming and Problem Solving in Cenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Pillai HOC College of Engineering and Technology, RasayaniDokumen1 halamanPillai HOC College of Engineering and Technology, Rasayanienggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Te CN Lab ManualDokumen58 halamanTe CN Lab Manualenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Mapping 1 PracticalDokumen12 halamanMapping 1 Practicalenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Poiuytteewqqasdfghgjlol, MNNCBBVBF Hfghtyu654256758787685634 Efyhf Tughjghdxfx BCGNH GFDGDGFGH GJGHDXGFHGJH FGDGFJHKGHDFG FHGFD FGD GFDH FG SDGJH G JDFGFSHDFHJ FGJ SF FHDF GJDF GHDFH GDokumen1 halamanPoiuytteewqqasdfghgjlol, MNNCBBVBF Hfghtyu654256758787685634 Efyhf Tughjghdxfx BCGNH GFDGDGFGH GJGHDXGFHGJH FGDGFJHKGHDFG FHGFD FGD GFDH FG SDGJH G JDFGFSHDFHJ FGJ SF FHDF GJDF GHDFH Genggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- List of Experiments OOPM16Dokumen3 halamanList of Experiments OOPM16enggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- #Include Void Main (Printf ("Hello SANDEEP/n") )Dokumen1 halaman#Include Void Main (Printf ("Hello SANDEEP/n") )enggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Diagram: Use Case Diagram Page 1Dokumen1 halamanDiagram: Use Case Diagram Page 1enggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Vehicle Management SystemDokumen3 halamanVehicle Management Systemenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- Exp 10 DFSDokumen4 halamanExp 10 DFSenggeng7Belum ada peringkat
- REST Society For Research International: Rsri Membership Application FormDokumen1 halamanREST Society For Research International: Rsri Membership Application FormmeenasarathaBelum ada peringkat
- Man Ssa Ug en 0698Dokumen43 halamanMan Ssa Ug en 0698Andy LBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Science Ram PresentationDokumen11 halamanComputer Science Ram Presentationapi-268896185100% (3)
- 08 PrimingDokumen6 halaman08 PrimingJose RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Template Extended-AbstractDokumen3 halamanTemplate Extended-AbstractGraita PurwitasariBelum ada peringkat
- CM Line Catalog ENUDokumen68 halamanCM Line Catalog ENUdmugalloyBelum ada peringkat
- Solid Desiccant DehydrationDokumen5 halamanSolid Desiccant Dehydrationca_minoBelum ada peringkat
- Amendment No. 3 June 2018 TO Is 15658: 2006 Precast Concrete Blocks For Paving - SpecificationDokumen3 halamanAmendment No. 3 June 2018 TO Is 15658: 2006 Precast Concrete Blocks For Paving - Specificationraviteja036Belum ada peringkat
- Model 7691Dokumen1 halamanModel 7691Khiết trầnBelum ada peringkat
- REVIEWDokumen12 halamanREVIEWGoka Agbesi GokaBelum ada peringkat
- The 'X' Chronicles Newspaper - August 2010Dokumen50 halamanThe 'X' Chronicles Newspaper - August 2010Rob McConnell100% (1)
- Capilares Diferentes GasesDokumen14 halamanCapilares Diferentes GasesWalter RuedaBelum ada peringkat
- Reckitt Benkiser (Case Study) For SCMDokumen13 halamanReckitt Benkiser (Case Study) For SCMDiptiman GuhaBelum ada peringkat
- Dutch Cone Penetrometer Test: Sondir NoDokumen3 halamanDutch Cone Penetrometer Test: Sondir NoAngga ArifiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 50 Monitoring Performance GuideDokumen86 halamanVsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 50 Monitoring Performance GuideZeno JegamBelum ada peringkat
- Brendan JoziasseDokumen2 halamanBrendan Joziasseapi-255977608Belum ada peringkat
- Dungeon Siege Game GuideDokumen21 halamanDungeon Siege Game GuideJesse StillBelum ada peringkat
- Orkot® TLM & TXM Marine Bearings: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionsDokumen7 halamanOrkot® TLM & TXM Marine Bearings: Trelleborg Se Aling Solutionsprodn123Belum ada peringkat
- Bus Bar Schemes: Submitted By: Under Guidance ofDokumen26 halamanBus Bar Schemes: Submitted By: Under Guidance ofHumeraBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Plate Fin Heat Sink Calculator - MyHeatSinksDokumen2 halamanAdvanced Plate Fin Heat Sink Calculator - MyHeatSinksHarsh BhardwajBelum ada peringkat
- CL21C650MLMXZD PDFDokumen45 halamanCL21C650MLMXZD PDFJone Ferreira Dos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogue SocorexDokumen40 halamanCatalogue Socorexdomitian88100% (1)
- Lab 01 IntroductionDokumen4 halamanLab 01 IntroductiontsikboyBelum ada peringkat
- Shivani Singhal: Email: PH: 9718369255Dokumen4 halamanShivani Singhal: Email: PH: 9718369255ravigompaBelum ada peringkat
- Kyabin Studio Pricelist 2021Dokumen18 halamanKyabin Studio Pricelist 2021BudiBelum ada peringkat
- System SizingDokumen50 halamanSystem SizingVictor mulotaBelum ada peringkat