Various Influencing Factors of Photosynthesis
Diunggah oleh
Swopnil Kalika0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
18 tayangan2 halamanThe process of photosynthesis is affected by various factors- both external (environmental) factors and internal factors.
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThe process of photosynthesis is affected by various factors- both external (environmental) factors and internal factors.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
18 tayangan2 halamanVarious Influencing Factors of Photosynthesis
Diunggah oleh
Swopnil KalikaThe process of photosynthesis is affected by various factors- both external (environmental) factors and internal factors.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Various influencing factors of photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis is affected by various factors- both external
(environmental) factors and internal factors.
A. The external factors are:
i.
Light: Light is an essential factor in photosynthesis as it supplies the
energy necessary for photosynthesis. Although leaves absorb about 80%
of light incident on them, only 0.5 to 4% are utilized in the
photosynthesis process. These characteristics of light cast significant
effects on the rate of photosynthesis:
Quality of light: Photosynthesis can take place only in the
wavelengths of visible spectrum (390 to 760nm). However, the rate of
photosynthesis is not equal in all the wavelengths of visible spectrum. The
rate is highest at the wavelength of 700-900 nm and it is minimum at 470600nm, as green light is reflected by the chlorophyll.
Intensity of light: Generally, the rate of photosynthesis is
greater in intense light than in diffused light. However, extremely intense
light may cause a phenomenon called solarization which results in decrease
in photosynthesis rate.
Duration of light: Photosynthesis rate is higher in intermittent
light than in continuous light.
ii.
Carbon-dioxide: CO2 concentration is quite low in nature, which is much
below the requirement for high photosynthesis rate. So, in laboratory or
in green houses, the CO2 concentration could be increased to bring about
an increase in the rate of photosynthesis. However, very high
concentration of CO2 is toxic and inhibits the photosynthesis rate.
iii.
Temperature: Generally, the optimum temperature range for
photosynthesis is 10 to 35 degree Celsius. The rate of photosynthesis
increases with the increase in temperature in this range. However, the
optimum range varies with the plant habitat. The plants of cold climates
(e.g., conifers) carry photosynthesis at much lower temperature than
those of warm climates (e.g., xerophytes). Extremely high temperature
has harmful effects on photosynthetic enzymes and thus, it may inhibit
photosynthesis.
iv.
Water: Water is an essential raw material for photosynthesis. The rate of
photosynthesis falls down if the water isnt adequately supplied.
v.
Oxygen: Increase in oxygen concentration results in decline of
photosynthesis rate. This phenomenon is seen mostly in C3 plants and not
in C4 plants.
B) The internal influencing factors are:
i.
Chlorophyll content: Chlorophyll is very essential in photosynthesis
as it traps light required for producing energy required in the process.
There is a direct relationship between chlorophyll concentration of
leaves and rate of photosynthesis.
ii.
Protoplasmic factors: For proper rate of photosynthesis, protoplasm
should be sufficiently hydrated.
iii.
Leaf anatomy: The anatomical features of leaves like thickness of
cuticle and epidermis, structure and frequency of stomata, structure
and distribution of vascular tissues, proportion of chlororphyllous and
non-chlorophyllous tissues etc. cast impact on the photosynthesis rate.
This is because these anatomical features influence important factors
like the intensity of light reaching the chlorophyllous tissues, entrance
of CO2, turgidity of cells etc.
iv.
Accumulation of CO2 and other end products: If CO2 or other end
products of photosynthesis accumulate at the photosynthesizing parts
of plants, rate of photosynthesis is inhibited.
v.
Frequency and distribution of stomata: Stomata affects the CO2 intake,
ascent of sap etc. and hence, they are very influential in
photosynthesis.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Original RT-PCR ReportDokumen1 halamanOriginal RT-PCR ReportVishva IyerBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Bored Cast-in-Situ Pile Foundation DetailsDokumen3 halamanBored Cast-in-Situ Pile Foundation DetailsSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Dornier 228 PDFDokumen27 halamanDornier 228 PDFSwopnil Kalika100% (2)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- 2010 FulltextDokumen410 halaman2010 FulltextNajam Din SahitoBelum ada peringkat
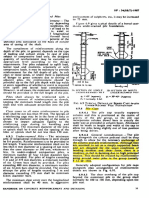
- Typical Section of RCC Road Rigid Pavement: SCALE 1:50Dokumen4 halamanTypical Section of RCC Road Rigid Pavement: SCALE 1:50Swopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- FAARFIELD Pavement Design SampleDokumen2 halamanFAARFIELD Pavement Design SampleSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Aerodrome Width RequirementDokumen1 halamanAerodrome Width RequirementSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- TRB Poster PDFDokumen1 halamanTRB Poster PDFSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- General Rules For Measurement of Civil WorksDokumen3 halamanGeneral Rules For Measurement of Civil WorksSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- TRB PosterDokumen1 halamanTRB PosterSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- FAA Pavement Design CurveDokumen1 halamanFAA Pavement Design CurveSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- CodeeDokumen1 halamanCodeeSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- 9150 Stolport Cons enDokumen54 halaman9150 Stolport Cons enSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
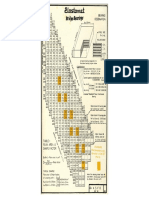
- Standard For Pedestal Below Bridge BearingsDokumen2 halamanStandard For Pedestal Below Bridge BearingsSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Minimum Dia of Bridge Piles As Per IRC78Dokumen1 halamanMinimum Dia of Bridge Piles As Per IRC78Swopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Specifications For Concrete PavementDokumen43 halamanSpecifications For Concrete PavementSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Determining Mean Diameter of Particles (Required For Calculating Silt Factor)Dokumen1 halamanDetermining Mean Diameter of Particles (Required For Calculating Silt Factor)Swopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Size of Coarse Aggregates For Various ComponentsDokumen1 halamanSize of Coarse Aggregates For Various ComponentsSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Control Tests For Subbase and BaseDokumen1 halamanQuality Control Tests For Subbase and BaseSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Reccommended Dose of Anti Stripping AgentDokumen1 halamanReccommended Dose of Anti Stripping AgentSwopnil Kalika100% (1)
- Quality Control Tests For Bituminous WorksDokumen5 halamanQuality Control Tests For Bituminous WorksSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- RWY LengthDokumen1 halamanRWY LengthSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- I II RoutineDokumen3 halamanI II RoutineSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- A Design Manual For Small Bridges UK 1992 2000 PDFDokumen236 halamanA Design Manual For Small Bridges UK 1992 2000 PDFAbdul SalamBelum ada peringkat
- Highway Engineering Assignment For IOE MSc. I/IDokumen7 halamanHighway Engineering Assignment For IOE MSc. I/ISwopnil Kalika100% (1)
- Typical Elastomeric BearingsDokumen1 halamanTypical Elastomeric BearingsSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Viking Twin Otter Series 400 Technical Specifications 10-15 RevisionDokumen14 halamanViking Twin Otter Series 400 Technical Specifications 10-15 RevisionSwopnil Kalika100% (1)
- FY2018-38 FAA Aerospace ForecastDokumen101 halamanFY2018-38 FAA Aerospace ForecastSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- ORN 16 Road Engineering in Mountainous Regions PDFDokumen166 halamanORN 16 Road Engineering in Mountainous Regions PDFSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Entrance 2075 ResultDokumen12 halamanMSC Entrance 2075 ResultSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Global Economic Prospects: South Asia AnalysisDokumen9 halamanGlobal Economic Prospects: South Asia AnalysisSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Bhawan Nirman KaryabidhiDokumen9 halamanBhawan Nirman KaryabidhiSwopnil KalikaBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Environmental Science Free-Response QuestionsDokumen6 halamanAp Environmental Science Free-Response Questionsapi-234419767Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanDokumen7 halamanChemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanSkyle VoBelum ada peringkat
- Bioinformatic Analysis of HBBDokumen1 halamanBioinformatic Analysis of HBBfrank2689Belum ada peringkat
- Effects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiDokumen7 halamanEffects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiAngela ValdiviesoBelum ada peringkat
- Cu EnzymesDokumen8 halamanCu EnzymesVINEESHA VKBelum ada peringkat
- 10th Standard Tamilnadu State Board Science (English Medium)Dokumen283 halaman10th Standard Tamilnadu State Board Science (English Medium)Karthick NBelum ada peringkat
- Biology of Implant OsseointegrationDokumen11 halamanBiology of Implant OsseointegrationAmIrBelum ada peringkat
- Biofuels Bioprod Bioref - 2022 - Souza - Bioenergy Research in Brazil A Bibliometric Evaluation of The BIOEN ResearchDokumen16 halamanBiofuels Bioprod Bioref - 2022 - Souza - Bioenergy Research in Brazil A Bibliometric Evaluation of The BIOEN Researchdeborah151Belum ada peringkat
- Colon 2014597 D FHTDokumen4 halamanColon 2014597 D FHTyoohooBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan No 5Dokumen6 halamanLesson Plan No 5hafeez ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Life in The Deserts Worksheet 2Dokumen2 halamanLife in The Deserts Worksheet 2Uma TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- 1oksidative Stress TestDokumen34 halaman1oksidative Stress TestDian WijayantiBelum ada peringkat
- UAS Writing For Discourse - 4 Pagi OkDokumen1 halamanUAS Writing For Discourse - 4 Pagi Oksalwa syabinaBelum ada peringkat
- MR Spectroscopy: Technical Aspects and Clinical ApplicationsDokumen5 halamanMR Spectroscopy: Technical Aspects and Clinical ApplicationsNotariana Kusuma ABelum ada peringkat
- The "Five Families" College Essay ExampleDokumen1 halamanThe "Five Families" College Essay ExampleKishor RaiBelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Técnica SpotcheckDokumen5 halamanFicha Técnica SpotcheckJuan PazBelum ada peringkat
- Stress BreakerDokumen7 halamanStress BreakerEshan Verma33% (3)
- Daftar PustakaDokumen3 halamanDaftar PustakaAdnanBelum ada peringkat
- Protein Structure and Function Book ReviewDokumen1 halamanProtein Structure and Function Book ReviewBrunoBelum ada peringkat
- Significance of 4D Printing For Dentistry: Materials, Process, and PotentialsDokumen9 halamanSignificance of 4D Printing For Dentistry: Materials, Process, and PotentialsMohamed FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- Everyday Sports Injuries The Essential Step-By-Step Guide To Prevention, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDokumen274 halamanEveryday Sports Injuries The Essential Step-By-Step Guide To Prevention, Diagnosis, and TreatmentAnonymous f6goFflg3T100% (10)
- Thephysiologyofincarnationprocess PDFDokumen14 halamanThephysiologyofincarnationprocess PDFGabriel OzórioBelum ada peringkat
- Brigitte King - InformativeDokumen2 halamanBrigitte King - Informativeapi-262025468Belum ada peringkat
- 2 Part 1Dokumen99 halaman2 Part 1m_luchianBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Level Biology 2015 Marking SchemeDokumen29 halamanAdvanced Level Biology 2015 Marking SchemeAngiee FBelum ada peringkat
- Adolescent Reproductive and Sexual HealthDokumen42 halamanAdolescent Reproductive and Sexual HealthMuhammad Abbas WaliBelum ada peringkat
- MOKUSAKU APPLICATIONS (Version 1)Dokumen1 halamanMOKUSAKU APPLICATIONS (Version 1)api-19621568Belum ada peringkat
- Regular Evaluation Test I Maths+Sc IXDokumen7 halamanRegular Evaluation Test I Maths+Sc IXB.L. Indo Anglian Public School, Aurngabad, BiharBelum ada peringkat