Emanufacturing With SAP
Diunggah oleh
SultanJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Emanufacturing With SAP
Diunggah oleh
SultanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
E-MANUFACTURING &
SAP-CREATING
RESPONSIVE SHOP FLOOR
IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN
Traditionally, the shop floor was isolated from the rest of the
supply chain and within the organization. Businesses that harness
the power of the Internet are making huge gains in efficiency,
both by reducing the friction inside their own business and by
binding suppliers more tightly into the supply chain.
E-Manufacturing covers a single, complete set of operational
capabilities including rapid plant design and deployment,
real-time ERP connectivity, comprehensive asset management of
people, products and processes, and a seamless coupling to the
entire supply chain via the Web.
WHITEPAPER
E-manufacturing integrates customers, e-commerce systems, and
suppliers into the manufacturing process to provide an Internetbased strategic framework for the factory. This white paper
discusses the concept, history & evolution of e-manufacturing,
implementation footprint, SAP and e-manufacturing. The concept
of e-manufacturing is extended to using SAP as the vehicle to get
the business integrated to the whole of the supply chain.
SUDHINDRA KULKARNI
VINAYAK OAK
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................................................ 3
MANUFACTURING TRANSFORMATION ................................................................................................................. 4
E-MANUFACTURING FOOTPRINT .................................................................................................................... 4
REQUIREMENTS FOR E-MANUFACTURING SUCCESS ....................................................................................... 5
TCO FOR E-MANUFACTURING ............................................................................................................................... 10
ROADMAP FOR E-MANUFACTURING .................................................................................................................. 12
CONCLUSION .............................................................................................................................................................. 13
GLOSSARY ................................................................................................................................................................... 13
REFERENCES ................................................................................................................................................................ 13
ABOUT THE AUTHORS .............................................................................................................................................. 13
ABOUT WIPRO TECHNOLOGIES ............................................................................................................................. 14
Page: Table of Contents
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
INTRODUCTION
ITraditionally, the visibility of the shop floor was very limited in the supply chain and within the organization. With the
evolution of e-commerce, there is a constant urge of business managers to quickly respond to the customer demand than
ever. These managers attempt to balance customers demands for shorter lead times, smaller batches and lower costs with
the need to understand the true capacity of the plant and so find ways to make it more efficient.
In todays tightly integrated supply chains, the factory floor is still where the value is added in every manufacturing enterprise.
In these models, it is essential to make the connection from the shop floor to the top floor where management decisions are
made. And this connection has to be very quick in response to the changes in the markets. The answer for this lies in bringing
the shop floor in limelight and therein lays the opportunity in e-manufacturing.
What then does e-manufacturing mean? The core of [a] manufacturing strategy is the technology roadmap for information
transparency between the customer, manufacturing operations, and suppliers. An e-Manufacturing strategy takes e-business
processes, such as build to order and reliability centered maintenance, and generates guidelines for implementing plant
systems. The e-manufacturing strategy takes the e-business and manufacturing strategies and creates a roadmap for system
development and implementation in the plant. (AMR Research, August 2000).
Enormous amount of data is generated in todays factory. But the problem managers faced in the past was haystack
syndrome i.e. finding the useful information. But with the modern industrial automation hardware, powered by advanced
control software and inter-connected by open networks, it is possible to provide a wealth of information on the manufacturing
process whenever required. On one level, e-manufacturing bridges the gap between shop floor and top floor systems, yet it
is a concept much greater than the sum of its parts. It covers a single, complete set of operational capabilities including rapid
plant design and deployment, real-time ERP connectivity, comprehensive asset management of people, products and processes,
and a seamless coupling to the entire supply chain via the Web. Businesses that harness the power of the Internet are making
huge gains in efficiency, both by reducing the friction inside their own business and by binding suppliers more tightly into
the supply chain.
E-manufacturing integrates customers, e-commerce systems, and suppliers into the manufacturing process to provide an
Internet-based strategic framework for the factory. Most prevalent in the high-tech industry, e-manufacturing is gaining
ground in other industries as companies integrate the Internet into their manufacturing operations, leading to increased
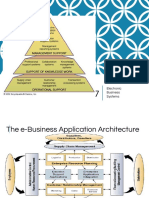
agility and profitability as well as reduced lead times. The essentials of e-manufacturing are shown in Figure 1 which
represents the structure built with various components.
E-business
SCM
ERP
CRM
Service & enterprise asset management
Product life cycle management & CAD
Figure 1: The essentials of e-manufacturing
Wipro Technologies
Page: 03 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
MANUFACTURING TRANSFORMATION
As the older manufacturing models do not allow for the heightened flexibility and modularity necessary to meet the demands
of customers and their changing needs, manufacturing is moving from make to forecast to make to order scenarios. The
foundation for e-manufacturing is based on a pull system in which products are made to order, thereby allowing companies
to customize their offerings to meet specific demands. Companies can manufacture their products more efficiently by
moving away from building work-in-process and finished goods in excess of actual demand. Though manufacturing forecasts
still play a role in the process and unforeseen swings will still cause disparity between supply and demand, E-manufacturing
helps to minimize these situations.
In a true make-to-order system with Web-based order-entry, forecasting accuracy is still relevant to anticipate big-picture
future demand. But all systems and resources must allow for - and actually promote - significant daily swings in production.
A companys strategy must include a notification system that utilizes the correct amount of human, machine, and material
resources. For many years, models like lean manufacturing, agile manufacturing, and constraint management have led the
effort to convert mass production to more flexible, responsive, and cost-effective methods. Both lean and agile manufacturing
promote the idea of producing only whats needed - no more, no less - while maintaining minimal or zero finished-goods
inventory. Constraint management focuses on eliminating production holdups by optimizing the material flow through
bottlenecks. Success depends on the ability to forecast future demand and produce to that forecast.
The solution is e-manufacturing, the next logical stage in the manufacturing evolution, which applies Web-based applications,
emerging technologies, and new developments in enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to the manufacturing models.
This new model integrates customers, e-commerce systems, suppliers, PLM and CAD into the manufacturing process to
provide an Internet-based strategic framework for the factory.
e-Manufacturing Footprint
e-manufacturing is all about the increasing need for communications to and from the factory floor. Manufacturers need
systems that can reveal available capacity, status of orders, and quality of a product - not just after it comes off the line, but
while it is in process. The e-manufacturing journey begins by recognizing the need for creating a seamless flow of information
from the factory floor. While electronic management of manufacturing functions such as maintenance offers big cost and
time savings, the greater strategic value may lie in the new options electronic information provides to executives. For
example, collecting plant data centrally also facilitates the ability of managers to assign work based on which a plant can
deliver the quickest response time or the lowest cost of production at a particular point in time. By pushing data from circuit
monitors and PLCs scattered across multiple plant sites to a central location, companies now can do a better job of assigning
energy expenses to individual cost centers, analyzing energy usage trend data, and assigning orders to plants to take advantage
of hourly fluctuations in utility rates.
Success in Web enabling the factory also hinges on the work cultures familiarity with e-business. A company that isnt using
the Web for purchasing, for example, is unlikely to embrace the idea of e-enabling its plants. Manufacturers should start
small and build the success that will bring support. The greatest culture challenge lies in closing the cultural chasm between
IT and the production floor.
A company today can now have a single, complete set of operational capabilities including rapid plant design and deployment,
real-time ERP connectivity, comprehensive asset management (of people, products, and processes), and a seamless coupling
to the entire supply chain via the Web. Thats what e-manufacturing really is about.
Wipro Technologies
Page: 04 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
E-manufacturing works best in situations in which a company can manufacture a small number of base products to an
intermediate step, postponing the completion of the manufacturing process until the customer orders the customized
product. As a result, most current manufacturing efforts are concentrated in the technology sector, where product customization
is the norm.
e-manufacturing growth is slow, due in large part the change-resistant nature of the manufacturing industry overall. According
to Gartner, only 1% of U.S. companies currently have full e-manufacturing implementations, although that number is
expected to increase to 15% by 2004. There are a few exceptions though, Companies such as Dell and Hewlett-Packard,
along with their major suppliers, have long utilized e-manufacturing to meet their customer needs. Once a consumer has
chosen and ordered a customized PC, final production begins and the product is shipped. By postponing final assembly by
waiting to load software and memory into certain networking devices until it receives a customer order, Cisco Systems
minimizes finished-goods inventory and maximizes flexibility.
REQUIREMENTS FOR E-MANUFACTURING SUCCESS
ocesses & pr
1. Bu
Bussiness pr
processes
production
must
ynchronized.
oduction mu
st be ssynchr
ynchr
onized. E-manufacturers must raise the visibility of manufacturing
information to optimize performance, enhance responsiveness, and manage costs. Those who leverage manufacturing data
to continuously improve their own operations and to enhance those of their suppliers and customers will be the winners.
ation of supply chain. Plants need to utilize supply chain planning systems and procurement systems to improve
2. Collabor
Collaboration
their overall supply chain performance. The goal is to leverage this information in real time to work against actual demand
rather than forecasts of anticipated demand. Marketplaces and trading exchanges, he believes, are the frontier for collaboration
and the real-time exchange of information across trading networks.
se bu
ocesses and workflow
3.. Inter & extr
extraa enterpri
enterprise
bussiness pr
processes
workflowss automation. Manufacturing managers need new tools that
allow them to have visibility into events as they occur, and the ability to impact those events to add value. The business
processes and workflows within the enterprise and across the value chain needs to be automated.
hboar
d. New Internet-based tools allow e-manufacturing managers to visualize
4. Plant information and analy
analyssis tool
toolss das
dashboar
hboard.
information from a variety of systems throughout the enterprise, and interpret the results in conjunction with established
performance metrics.
ate the des
ign pr
ocess among all collabor
ating parties
5. Integr
Integrate
design
process
collaborating
parties.. The manufacturing process begins well before the line ever
starts to run. New internet-based tools are emerging to support collaborative design and engineering processes.
age bi-dir
ectional information with cu
stomer
6. Lever
Leverage
bi-directional
customer
stomerss & supplier
supplierss . The essence of collaboration is the ability for individual
plants to schedule their work in real time based on accepted orders, and to coordinate the delivery of component materials
needed at the production level to meet those schedules. That involves sharing not only with suppliers, but providing visibility
into the manufacturing process to customers, while gaining visibility into real-time demand from customers.
e-manufacturing & SAP Solution:
The components of e-manufacturing are:
a) PLM
b) E-business
c) SCM
d) CRM
e) Service & EAM
Wipro Technologies
Page: 05 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
Now lets discuss how these components, to a great extent, are mapped to the various integrated components of one of the
widely used software viz. SAP.
SAP & e-manufacturing
SAP today offers following components for implementation of e-manufacturing concept.
PLM
R/3-ERP
APO for SCM
CRM
SRM for e-procurement.
Following diagram can represent the holistic view of the above components. In following sections we will discuss each of
these components.
SAP R/3
SRM
CRM
Customers
Firewall
CAD
Firewall
Vendors
PLM
Automation
Control
Execution
SCM
Figur
Figuree 2: The component
componentss of e-manufacturing
Wipro Technologies
Page: 06 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
At the core of this diagram are the shop floor automation systems viz. PLCs, Sensors, field devices etc. which can be integrated
with the core SAP component viz. R/3. On the next layer is the Saps core software i.e. R/3. The next layer consists of SRM
(Supplier relationship management), CRM (Customer relationship management) & SCM (Supply chain management).
Design
Sales & Production
Service
Customer Relationship
Management
Supply Chain Management
Product Life-Cycle
Management
First Product
idea
Production
start
Production
end
Production
obsolescence
Figur
ole of each component in variou
Figuree 3: The rrole
variouss stages of e-manufacturing
Product lifecycle management encompasses all these components as it exists from the inception of the idea of a new product
till its death. PLM can be integrated with the CAD systems. There are two most important entities exists in e-manufacturing
viz. the vendors systems & customers systems. With the help of the firewalls the systems of vendor & customer can be
integrated easily.
Interplay of SCM, CRM & PLM
R/3
Material Master
Product Master
mySAP SCM
mySAP PLM
Demand
information
Technical information
& Drawings
ATM information
mySAP CRM
Figur
Figuree 4: Interplay of SCM, CRM & PLM
Wipro Technologies
Page: 07 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
The typical business flow will be as follows in an e enabled manufacturing environment.
The R&D and marketing department will work closely to develop a product using SAP PLM. During the development the
vendor development also takes place using SAP SRM. Once the product comes in to manufacturing then the SCM starts
planning according to the Make-to-Order strategy. The CRM now gets the inputs like drawing/photos of the products
which can be accessed by the potential customer for ordering purpose. Any changes or modification required can be immediately
carried out by using CRM-PLM-CAD interface.
mySAP PLM overview
PLM handles following areas:
a) New product development & document management
b) Product change management & gearing up the production
c) Maintenance management including service management
d) Asset lifecycle management
e) Asset operation
f) Asset replacement
PLM helps in
a) Reducing cost-to-market by efficiently managing the cost of changes & project management of new product
developments.
b) Improved availability of assets within the given maintenance & service budget.
c) Reduced total cost of ownership through integration with CAD, CRM, SCM & SRM.
mySAP SCM overview
SAP SCM has following components.
a) APO Advance planning & optimization.
b) EM: Event management
c) ICH: Inventory collaboration hub
APO has following component
s:
components:
a) Demand planning: In this, component system identifies and analyzes patterns and fluctuations in demand, and creates
accurate, dynamic demand forecasts.
b) Supply Network planning: Matches purchasing, production and transportation processes to demand, and balances and
optimizes your entire supply network.
c) Production Planning & detailed scheduling: Optimizes the use of resources and creates accurate plant-by-plant production
schedules in order to shorten production life-cycles and responds rapidly to changes in market demands forecasts.
d) Global available-to-promise: Matches supply to demand on a truly world-wide scale, and gives your customers reliable
delivery commitments by means of both real-time checks and sophisticated simulation methods.
Wipro Technologies
Page: 08 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
mySAP SRM overview
mySAP SRM has following components to take care of the e-business side of the procurement function in e-manufacturing.
a) EBP Enterprise buyer
b) Catalog engine
c) Supplier self service
d) Bidding engine
Due to SRM it is very easy to automate the entire procurement process and reduce the paper work drastically e.g., there is no
need to send the fax or physical copy of PO to vendor. It can be mailed to him in his mailbox. Also supplier can login into the
system to check the status. The security of the data can be taken care by firewall between the vendors system and the SRM.
In a nutshell, SRM offers the following:
Efficient procurement process
Optimal supplier management
Focus on sourcing strategy
mySAP CRM overview
mySAP CRM offers following components to take care of the customer angle of the e-manufacturing.
Internet sales
Telesales
Mobile sales & service
Customer interaction centre
Integration with other systems like R/3, APO & BW.
Due to CRM the complete sales process is covered via internet. This internet sales takes care of marketing, order management,
fulfillment etc. CIC (Customer interaction centre) provides inbound and outbound call processing, e-mail management,
activity management to track, monitor and enhance all customer contact. It supports multiple channels for customer
communication, including telephony and Web. The other component of CRM i.e. mobile sales delivers key customer and
prospect information to sales personnel at any place, at any time; facilitates planning and maintenance of sales activities,
such as appointments, visits, and calls; and provides activity reports. It creates quotations and takes orders; includes support
for mobile and wireless devices. Thus the customer angle of e-manufacturing is taken care by CRM.
Wipro Technologies
Page: 09 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
TCO FOR E-MANUFACTURING
If we observe the evolution of SAP it can be seen that in the past SAP systems have been integrated with other legacy
systems e.g. using middleware tools to legacy systems. This has increased the total cost of ownership of the systems. With the
new concept of separating the application & the Technology layers, SAPs NetWeaver helps in reducing the TCO drastically. So
the effect is companies can implement the e-manufacturing concept with the help of SAP system with lesser & lesser TCO.
TCO today
10%
TCO 3 years
from now
30%
In large enterprises
up to 75% are
personnel or
services costs
Hardware, software
and infrastructure
only 25%
Cost drives:
custom
code
interfaces
number of
(integrated)
systems
testing
end user
training
60%
40%
INNOVATION
20-25%
CONSOLIDATION
35-40%
OPERATION
We need to move
to a sustainable
costs structure!
Figur
CO for e-manufacturing
Figuree 5: TTCO
Integration Platform
Business
Intelligence
Portal
Exchange
Infrastructure
Knowledge
Mgmt
SAP
R/3
---
Mobile
Infrastructure
Partner
SAP
R/3
CRM
Legacy
Applications
Figur
stry
Figuree 6: IMplementation
IMplementationss of SAP in the indu
industry
Wipro Technologies
Page: 10 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
We can observe that there are many other legacy systems integrated with the SAP systems. This increases the maintenance
of these systems and the TCO for implementing e-manufacturing. But with SAPs NetWeaver the typical scenario will change
as indicated below.
Integration Platform
Other
SAP
NetWeaver
Portal
Bl, KM,
Mobile, ...
mySAP ERP
ERP
SAP
R/3
Partner
CRM
Legacy
Applications
Figur
eaver
Figuree 7: SAP NetW
NetWeaver
As one can see the integration with other legacy system can be done through one tool i.e. NetWeaver - be it any legacy
system. The major benefits of SAP NetWeaver from e-manufacturing point of view are:
It leverages the SAPs core strength and existing investments in SAP
Its an integrated out of box tool
Its a foundation to serve all application needs
Integration with non-SAP system is easy
So with NetWeaver coming into picture the implantation of e-manufacturing is made further achievable in the time to
come.
Wipro Technologies
Page: 11 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
ROADMAP FOR E-MANUFACTURING
1. Embr
ace the Internet.
Embrace
All parties in the company must recognize the organizational change required to adopt an e-manufacturing strategy
and the greater influence of the Internet and of customer demand.
ocess
2. Plant engineer
engineerss have an important place in deci
decission-making pr
process
ocess..
Plant engineers bring expertise in plant-floor processes, as well as the information available (and required) for seamless
integration. Their plant floor experience and perspective will prove to be invaluable as e-manufacturing efforts proceed.
3. Build an internal team, and dr
aw the company
oadmap for e-manufacturing.
draw
companyss rroadmap
Draw from various departments and functions within the organization, and discuss the common and specialized benefits
each would receive from information transparency. Each segment of the organization should have a vision for success
reliant on information transparency.
4. Find a company leader to serve as champion.
Whenever possible, secure the CEO as the e-manufacturing driver for the enterprise. If an e-business strategy is in place
for the company, its especially critical to be sure that e-manufacturing is a key element of that broader strategy. Thus,
the e-commerce director or CIO is another good champion to enlist.
5. Take one step at a time on the rroadmap.
oadmap.
Dont attempt to do everything at once that is a lesson to be learned from the original ERP implementations. It took
many years for plant floor, front office, and supply chain to evolve to where they are today; take a logical path to evolve
them via e-manufacturing, and measure successes along the way.
6. Measur
oadmap.
Measuree the success and failur
failuree of the rroadmap.
Put metrics in place to determine the real savings and efficiencies from a transparent enterprise.
7. Evaluate your tr
aditional channel
sten to their needs
traditional
channelss and lilisten
needs..
Analyze the ways the company works with customers, suppliers, distributors, and others to determine their effectiveness,
and find ways to streamline relationships and processes.
8. Build on your exi
sting foundation
emental successes along the way
existing
foundationss, and on your incr
incremental
way..
An e-manufacturing strategy will help your organization embrace information transparency that will foster operational
excellence, while not creating more work, major overhauls, or enormous investments. It wont happen all at once, but
once you begin, your organization can build upon the successes until the full e-manufacturing approach is realized and
the organization excels in its own design, operations, maintenance, and synchronizes competencies.
9. Get help fr
om an expert.
from
Consider the outsourcing trend in manufacturing. When competition and pressure for bottom-line performance are
high, companies outsource basic production, manufacturing engineering, automation engineering and other capabilities
to suppliers that specialize in these competencies. Employ experts for the implementation.
Wipro Technologies
Page: 12 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
CONCLUSION
The companies embarking on the e-manufacturing journey can make a start from their existing stage. The companies already
having implemented the SAP ERP system can be the forerunners of the e-manufacturing journey. However they should plan
their journey carefully and follow a step by step approach to succeed in the strategy. Given below is the Roadmap for emanufacturing.
GLOSSARY
TCO: Total cost of ownership
PLC: Programmable logic controllers
PLM: Product life cycle management
SCM: Supply chain management
CRM: Customer relationship management
EAM: Enterprise asset management
APO: Advance planning & optimization
SRM: Supplier relationship management
EM: Event management
ICH: Inventory collaboration hub
EBP: Enterprise buyer professional
BW: Business Information warehouse
REFERENCES
1. E-Manufacturing: Made to Order - by James A. Tompkins, Ph.D.
2. White paper Making Sense of e-manufacturing: A Roadmap for Manufacturers Rockwell Automation
3. The seven requirements of e-manufacturing - Modern Materials Handling (mmh.com)
4. http://service.sap.com
ABOUT THE AUTHORS
Sudhindra Kulkarni AND Vinayak Oak are Senior Consultants at the SAP Division of Wipro Technologies.
Wipro Technologies
Page: 13 of 14
E-manufacturing & SAP-Creating Responsive Shop Floor in the Supply Chain
ABOUT WIPRO TECHNOLOGIES
Wipro is the first PCMM Level 5 and SEI CMMi Level 5 certified IT Services Company globally. Wipro provides comprehensive
IT solutions and services (including systems integration, IS outsourcing, package implementation, software application
development and maintenance) and Research & Development services (hardware and software design, development and
implementation) to corporations globally.
Wipros unique value proposition is further delivered through our pioneering Offshore Outsourcing Model and stringent
Quality Processes of SEI and Six Sigma.
For more whitepapers logon to: http://www.wipro.com/insights
Copyright 2004. Wipro Technologies. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without express written permission from Wipro Technologies. Specifications subject to change without notice. All other trademarks mentioned
herein are the property of their respective owners. Specifications subject to change without notice.
Worldwide HQ
Wipro Technologies,
Sarjapur Road,
Bangalore-560 035,
India.
Tel: +91-80-844 0011.
U.S.A.
Wipro Technologies
1300 Crittenden Lane,
Mountain View, CA 94043.
Tel: (650) 316 3555.
U.K.
Wipro Technologies
137 Euston Road,
London, NW1 2 AA.
Tel: +44 (20) 7387 0606.
France
Wipro Technologies
91 Rue Du Faubourg,
Saint Honor, 75008 Paris.
Tel: + 33 (01) 4017 0809.
Germany
Wipro Technologies
Am Wehr 5,
Oberliederbach,
Frankfurt 65835.
Tel: +49 (69) 3005 9408.
Japan
Wipro Technologies
# 911A, Landmark Tower,
2-1-1 Minatomirai 2-chome,
Nishi-ku, Yokohama 220 8109.
Tel: +81 (04) 5650 3950.
Tel: +97 (14) 3913480.
U.A.E.
Wipro Limited
Office No. 124,
Building 1, First Floor,
Dubai Internet City,
P.O. Box 500119, Dubai.
www.wipro.com
eMail: info@wipro.com
Wipro Technologies
Page: 14 of 14
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- How To Guide For Transferring Data in SAPDokumen66 halamanHow To Guide For Transferring Data in SAPSultanBelum ada peringkat
- Tax Jurisdiction - ERP SD - SCN WikiDokumen25 halamanTax Jurisdiction - ERP SD - SCN Wikigouthamdms1979Belum ada peringkat
- Software ENG Original PDFDokumen20 halamanSoftware ENG Original PDFJongky PekokBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Accounts Receivable AccountingDokumen29 halamanSAP Accounts Receivable AccountingSultanBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Implementation Tools Overview: Version 1.0 Page 1/32Dokumen32 halamanSAP Implementation Tools Overview: Version 1.0 Page 1/32SultanBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Accounts Payable AccountingDokumen22 halamanSAP Accounts Payable AccountingSultan100% (1)
- ECA SAP Validation GMP ComplianceDokumen4 halamanECA SAP Validation GMP Compliancesophian ninawiBelum ada peringkat
- ERP Implementation ChecklistDokumen2 halamanERP Implementation ChecklistNorth W.rawdBelum ada peringkat
- Sap Full IntroductionDokumen74 halamanSap Full Introductionsmart sriniBelum ada peringkat
- DNVGL-CG-0508 Smart VesselDokumen47 halamanDNVGL-CG-0508 Smart VesselDui BuiBelum ada peringkat
- Central Finance - Solution Overview: Sap S/4HanaDokumen9 halamanCentral Finance - Solution Overview: Sap S/4HanabarathBelum ada peringkat
- PMO Setup Chapter 3Dokumen36 halamanPMO Setup Chapter 3camiloBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise On ERPnextDokumen4 halamanExercise On ERPnextVikas KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Sap Data Archiving MethodDokumen3 halamanSap Data Archiving MethodSultanBelum ada peringkat
- SAP AccountingDokumen2 halamanSAP AccountingSultanBelum ada peringkat
- SAP ABAP Quiz 1Dokumen5 halamanSAP ABAP Quiz 1SultanBelum ada peringkat
- Frequenlty Asked Questions - ABAP/4 Reporting: Sy-IndexDokumen2 halamanFrequenlty Asked Questions - ABAP/4 Reporting: Sy-IndexSultanBelum ada peringkat
- TestDokumen46 halamanTestdaillmatikBelum ada peringkat
- AX2009 Introduction (80020)Dokumen322 halamanAX2009 Introduction (80020)vagrantfxBelum ada peringkat
- PPC SyllabusqDokumen1 halamanPPC SyllabusqKannan MuthusamyBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Managing Information Technology 7 e 7th EditionDokumen38 halamanSolution Manual For Managing Information Technology 7 e 7th Editionilvaitekabassou7k10t100% (15)
- Auditing in Erp EnvironmentDokumen32 halamanAuditing in Erp Environmentjoseph davidBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 1 - Information System Concepts: Definition of A SystemDokumen30 halamanChap 1 - Information System Concepts: Definition of A SystemdoshirutuBelum ada peringkat
- COGI and It's Cohesion With SAP EWM - PP-EWM-Integration - Delivery BasedDokumen9 halamanCOGI and It's Cohesion With SAP EWM - PP-EWM-Integration - Delivery BasedVictor HUNGBelum ada peringkat
- Sap Erp Training Material PDF: Download: DownloadDokumen2 halamanSap Erp Training Material PDF: Download: DownloadajaychattaBelum ada peringkat
- Warehouse Number: Goods MovementsDokumen2 halamanWarehouse Number: Goods MovementsGLOBAL TEQBelum ada peringkat
- Good Practices in Government Resource Planning, Developed Vs Developing CountriesDokumen11 halamanGood Practices in Government Resource Planning, Developed Vs Developing CountriesFreeBalanceGRPBelum ada peringkat
- Business and Info Systems-Midterm Exam Question Answers!Dokumen5 halamanBusiness and Info Systems-Midterm Exam Question Answers!rajnitBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To AisDokumen9 halamanChapter 1 - Introduction To AisHychell Mae Ramos DerepasBelum ada peringkat
- Industrialised Building System (IBS) Plan of Work (#355659) - 367367Dokumen7 halamanIndustrialised Building System (IBS) Plan of Work (#355659) - 367367Hazz Julean HamzzBelum ada peringkat
- Enterprise Resource Planning Text and Cases Rajesh Ray, Tata MC Graw Hill Education PVT LTD New Delhi 2011Dokumen2 halamanEnterprise Resource Planning Text and Cases Rajesh Ray, Tata MC Graw Hill Education PVT LTD New Delhi 2011sharukh taraBelum ada peringkat
- ERP Software Company - ACG Infotech Ltd.Dokumen4 halamanERP Software Company - ACG Infotech Ltd.ACG ILBelum ada peringkat
- APS - Qccs Profile - V1Dokumen5 halamanAPS - Qccs Profile - V1faca9883Belum ada peringkat
- c7 Electronic Business System.gDokumen20 halamanc7 Electronic Business System.gMd Hasibul Karim 1811766630Belum ada peringkat
- BD - Unit - I - Introduction To Big DataDokumen18 halamanBD - Unit - I - Introduction To Big DataPrem KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Teamcenter CMS in PLMDokumen11 halamanTeamcenter CMS in PLMVenkateshKamepalliBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation of ERP For Steel IndustryDokumen3 halamanImplementation of ERP For Steel Industryganesh gowthamBelum ada peringkat
- Bihar School Examination EditDokumen20 halamanBihar School Examination EditrocketspeedBelum ada peringkat