Q8 IM13DFinal
Diunggah oleh
Jb MacarocoJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Q8 IM13DFinal
Diunggah oleh
Jb MacarocoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
This is file Q8IM13D - The fourth of five files for solutions to this
chapter.
23.
The sample means and standard deviations gathered in a calibration project by the
Weighrite Corporation were observed for sample sizes of 10, as show in worksheet Prob.
13-23. Construct x - and s-charts and discuss the results.
Answer
23.
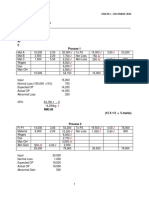
See data and control charts below and spreadsheet Prob.1323XSWeigh.xls for details.
For the Weighrite Corporation, the center line, CL x : x = 8.659; CLs : s =
7.474
a. Control limits for the x - s charts are:
x
A3 s = 8.659 0.975 (7.474) = 1.372 to 15.946
For the s-chart: UCLs = B4 s = 1.716 (7.474) = 12.825
LCLs = B3 s = 0
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
b. The process appears to be in statistical control, because values are distributed
randomly about the mean, all values lie within control limits, and there are no unusual
patterns on the x or s-charts.
24.
The temperature in a computer lab at Coyote University is very important for proper
functioning of the computer equipment. The data in the worksheet Prob.13-24 shows the
results of 30 samples of 5 each, taken at random at different times of day over a three
month time period. Construct x - and s charts and discuss the results.
Answer
24.
See data and control charts below and spreadsheet Prob.1324XSCoyote.xls for details.
For the Coyote University computer lab, the center line, CL x : x = 72.071;
CLs : s = 1.159
a. Control limits for the x - s charts are:
x
A3 s = 72.071 1.43 (1.159) = 70.414 to 73.728
For the s-chart: UCLs = B4 s = 2.09 (1.159) = 2.422
LCLs = B3 s = 0
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
b. The process appears to be in statistical control, although there seems to be a tendency
for values to hug the center lines on both the x and s-charts. However, all values
lie within control limits.
25.
Calculate the process capability statistics for the outside diameters of the bottles made on
the injection molding machine at the Moby Molding Co. (from Prob. 13-22). Use 0.12 as
the upper tolerance limit and -0.10 as the lower tolerance limit for this important measure
of process performance. What recommendation would you make to management
concerning the process, based on these findings?
Answer
25.
The process is not capable at this point. None of the values of Cp, Cpu, Cpl, Cpk are greater
than 1.0
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
Note that the spreadsheet uses an actual standard deviation of =
0.047 calculated from all of the sample values. Although this numeric
value happens to be the same, this is the overall standard deviation for
all sample values, and is not the same average statistic as s .
Process Capability
Upper specification
0.12
Lower specification
- 0.10
Cp
Cpu
Cpl
Cpk
0.789
0.795
0.784
0.784
Management should be advised that, the capability is not good, so they should work to
reduce variability, so as to approach a Cp = 2.0.
26.
Calculate the process capability statistics for the temperature in the computer lab at
Coyote University (from Prob. 13-24). Use 76 as the upper tolerance limit and 68 as the
lower tolerance limit for this important measure. What recommendation would you make
to management concerning the process, based on these findings?
Answer
26.
The process is capable at this point. All of the values of Cp, Cpu, Cpl, Cpk are greater than 1.0,
although the process is slightly skewed to the left.
Note that the spreadsheet uses an actual standard deviation of =
1.268 calculated from all of the sample values. This numeric value is
the overall standard deviation for all sample values, and is not the
same average statistic as s .
Process Capability
Upper specification
76.0
Lower specification
68.0
Cp
Cpu
Cpl
Cpk
1.051
1.033
1.070
1.033
Management should be advised that, while the capability is minimally acceptable, they
should work to reduce variability, so as to approach a Cp = 2.0.
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
27.
Chief Henry Batter of the Gotham City Police Department is trying to reduce the time
required to answer the phone at police headquarters (in fractions of a minute). The data in
the worksheet for Prob. 13-27 represent time in fractions of minutes for 3 individual
readings taken at random for 25 days.
a. Compute control limits for an x-chart (chart for individuals) using the statistic R / d2
with a 3-period moving range, as an estimate of the standard deviation.
b. Construct an x - chart for individuals, using the data. Interpret the results.
Answer
27.
See spreadsheet Prob.13-27IVGotham.xls for details. Values, below, for
x and R were obtained from the spreadsheet calculations.
a) Preparing a chart for individuals: Center Lines, CL x : x = 0.759; CLR :
R = 0.037
Estimated = R / d2 = 0.037 / 1.693 = 0.022; actual = 0.021
x - 3 est = 0.759 3 (0.021) = 0.696 to 0.822;
x - 3 actual = 0.759 3 (0.022) = 0.693 to 0.825
These limits apply to individual items only. In this case, the estimated
standard deviation was based on a three period moving range, and
was only 0.001 different from the actual standard deviation. This small
variation will not happen in every case, because = R / d2 is only an
estimator for the population standard deviation. Individual items can
only be plotted on x-charts, as shown below.
Control limits - R: UCLR = D4 R = 2.574 (0.037) = 0.095
LCLR = D3 R =
0 (0.037) = 0
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
b) The individual values should be plotted on x-charts, but students need
to understand how x - chart and R-chart results differ in comparison
with the above. The chart for individuals and the moving range chart
seem to be under control.
28.
Charlie Plato owns Charlies China Emporium, which sells inexpensive cups, dishes, and
bric-a-brack in a seaside resort. She has three checkout stations, which she would like to
test to see if they are under control and capable. She considers sales of $36.50 per hour,
per station, to be a representative average. Consider the data for 75 individual results of
sales dollars per hour, per unit, shown in the worksheet Prob.13-28.
a. Compute control limits for an x-chart (chart for individuals) using the statistic R / d2
as an estimate of the standard deviation with a 3-period moving range.
b. Construct an x - chart for individuals, using the data. Interpret the results.
Answer
28.
See spreadsheet Prob13-28IVCharlie.xls for details. Values, below, for
x and R were obtained from the spreadsheet calculations.
a) Preparing a chart for individuals: Center Lines, CL x : x = 36.58; CLR :
R = 20.64
x 3 est = 36.58 3 (12.19) = 0.01 to 73.15;
x 3 actual = 36.58 3 (11.38) = 2.44 to 70.72
These limits apply to individual items only.
Control limits - R: UCLR = D4 R = 2.574 (20.64) = 53.13
LCLR = D3 R =
0 (20.64) = 0
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
10
b) The individual values should be plotted on x-charts, but students need
to understand how x - chart and R-chart results differ in comparison
with the above. The chart for individuals and the moving range chart
seem to be under control.
29.
Ricardos Widgets makes a critical part for a popular brand of cell phones. Consider the
data for 60 observations of a key dimension for the part, shown in the worksheet
Prob.13-29.
a. Compute control limits for an x-chart using the statistic R /d2 as an estimate of the
standard deviation, with a 4-period moving average for the range calculation.
b. Construct an x- chart for individuals using the data. Interpret the results.
Ans
29.
a) See spreadsheet Prob.13-29IVRick.xls (X and MR chart template) for
details. Values, below, for x and R were obtained from the
spreadsheet calculations.
CLx : x = 0.112; CLR : R = 0.011 (with a 4-period moving average)
Estimated = R / d2 = 0.011 / 2.059 = 0.0053
3 est = 0.112 3 (0.0053) = 0.096 to 0.128;
for x 3 = 0.112 3 (0.0055) = 0.096 to 0.129
x
The limits above apply to individual items only. Individual items can
only be plotted on x-charts. See the chart on individuals, below.
Control limits - R: UCLR = D4 R = 2.282 (0.011) = 0.025
LCLR = D3 R =
0 (0.011) = 0
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
11
b) The individual values should be plotted on x-charts, but students need
to understand how x - chart and R-chart results differ in comparison
Chapter 13 - Statistical Process Control
12
with the above. The chart for individuals and the moving range chart
seem to be under control.
See file Q8IMC13E.DOC - the last file, for more solutions to end-ofchapter problems for Chapter 13.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Comprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire TruckDokumen79 halamanComprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire Truckbhupendra singh sengarBelum ada peringkat
- Harmonica IntroDokumen5 halamanHarmonica Introapi-26593142100% (1)
- AEC 34 - ACB Assignment: Module 1: Problem 1-1.TRUE OR FALSEDokumen5 halamanAEC 34 - ACB Assignment: Module 1: Problem 1-1.TRUE OR FALSEDrew BanlutaBelum ada peringkat
- Piezometers: Types, Functions, & How It Works?Dokumen38 halamanPiezometers: Types, Functions, & How It Works?Encardio RiteBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Childrenswear Safety Manual 2009 - ClothingDokumen57 halaman01 Childrenswear Safety Manual 2009 - Clothingmorshed_mahamud705538% (8)
- Q8 IM02 FinalDokumen21 halamanQ8 IM02 FinalJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Q8 IM13CFinalDokumen21 halamanQ8 IM13CFinalJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Fin 320 - Individual AssignmentDokumen14 halamanFin 320 - Individual AssignmentAnis Umaira Mohd LutpiBelum ada peringkat
- Q8 IM08 FinalDokumen59 halamanQ8 IM08 FinalJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Action Research Intervention in English 9Dokumen6 halamanAction Research Intervention in English 9Rey Kris Joy ApatanBelum ada peringkat
- John Macaroco MIS 315 ERP: Dynamics 5/8/15: Microsoft Enterprise Resource Planning Software Microsoft DynamicsDokumen2 halamanJohn Macaroco MIS 315 ERP: Dynamics 5/8/15: Microsoft Enterprise Resource Planning Software Microsoft DynamicsJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Q8 IM13BFinalDokumen31 halamanQ8 IM13BFinalJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Q8 IM03 FinalDokumen42 halamanQ8 IM03 FinalJb Macaroco100% (1)
- Q8 IM05 FinalDokumen35 halamanQ8 IM05 FinalJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Q8 IM04 FinalDokumen34 halamanQ8 IM04 FinalJb Macaroco100% (1)
- Q8 IM07 FinalDokumen39 halamanQ8 IM07 FinalJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Q8 IM06 FinalDokumen39 halamanQ8 IM06 FinalJb MacarocoBelum ada peringkat
- Q8 IM11 FinalDokumen53 halamanQ8 IM11 FinalJb Macaroco100% (1)
- Q8 IM12 FinalDokumen60 halamanQ8 IM12 FinalJb Macaroco100% (1)
- Q8 IM13EFinalDokumen44 halamanQ8 IM13EFinalJb Macaroco100% (1)
- Thermo Exam QuestionsDokumen4 halamanThermo Exam QuestionssiskieoBelum ada peringkat
- 1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018Dokumen5 halaman1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018PRO ECUBelum ada peringkat
- Nava LunchDokumen3 halamanNava LuncheatlocalmenusBelum ada peringkat
- Times Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Dokumen49 halamanTimes Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Joseph HoukBelum ada peringkat
- The USP AdvantageDokumen30 halamanThe USP AdvantageGabriel A. RamírezBelum ada peringkat
- Fractal Approach in RoboticsDokumen20 halamanFractal Approach in RoboticsSmileyBelum ada peringkat
- Report On Sonepur MelaDokumen4 halamanReport On Sonepur Melakashtum23Belum ada peringkat
- Advertisement For Recruitment of Non-Teaching StaffDokumen3 halamanAdvertisement For Recruitment of Non-Teaching StaffGoogle AccountBelum ada peringkat
- Swot Ananlysis of Fintech CompaniesDokumen7 halamanSwot Ananlysis of Fintech CompaniesUyen Le VuBelum ada peringkat
- Contemporary ArtsDokumen16 halamanContemporary Artsantoinette100% (2)
- MAF 451 Suggested Solutions - A) I) Process 1Dokumen9 halamanMAF 451 Suggested Solutions - A) I) Process 1anis izzatiBelum ada peringkat
- PESTEL AnalysisDokumen2 halamanPESTEL AnalysisSayantan NandyBelum ada peringkat
- Noten - Detective Conan - Case ClosedDokumen2 halamanNoten - Detective Conan - Case ClosedBLU-NYTE GamingBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Spent Engine Oil On The Internal Structure of Corchorus OlitoriusDokumen55 halamanEffect of Spent Engine Oil On The Internal Structure of Corchorus Olitoriusanon_568621284Belum ada peringkat
- MNHS Annex G10 Q4 LC1Dokumen10 halamanMNHS Annex G10 Q4 LC1angelinebianesBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Water On Quality and Preservation of FoodDokumen10 halamanEffect of Water On Quality and Preservation of FoodrupinisinnanBelum ada peringkat
- Monster Energy v. Jing - Counterfeit OpinionDokumen9 halamanMonster Energy v. Jing - Counterfeit OpinionMark JaffeBelum ada peringkat
- KC CVDokumen2 halamanKC CVVishal KeshriBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Dokumen4 halamanA Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Tîrban Pantelimon FlorinBelum ada peringkat
- Ed508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Severe Weather EventsDokumen3 halamanEd508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Severe Weather Eventsapi-526575993Belum ada peringkat
- Mock MeetingDokumen2 halamanMock MeetingZain ZulfiqarBelum ada peringkat
- Harvester Main MenuDokumen3 halamanHarvester Main MenuWonderboy DickinsonBelum ada peringkat
- Research InstrumentsDokumen28 halamanResearch InstrumentsAnjeneatte Amarille AlforqueBelum ada peringkat