Phytohormones
Diunggah oleh
rustyryan770 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
36 tayangan3 halamanPlant hormones
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniPlant hormones
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
36 tayangan3 halamanPhytohormones
Diunggah oleh
rustyryan77Plant hormones
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
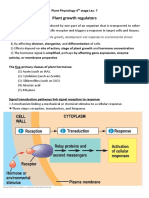
Phytohormones
HORT 3000
Phytohormones
Naturally occurring organic (C-H-O based) substance that influences physiological
processes
Chemical messenger within the plant
Provides communication between different areas within the plant
Site of action is often different from site of synthesis
Six main types in plant
Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Abscisic Acid, Ethylene, Brassinosteriods
Auxin
Indole-3-acetic acid
First hormone to be discovered
Ubiquitous throughout the plant
Synthesized in embryos and shoots
Concentration varies highest in actively growing regions
Stimulates cell elongation
Auxin Polar Transport
Preferential movement in one direction
Predominately basipetal auxin movement in the shoot auxin moves from morphological
apex towards morphological base
Auxin moves from shoot apex down stem
Path of transport not totally clear travels in cells near vascular tissue
Basipetal and acropetal movement occur in roots
Basipetal auxin moves away from root tip via epidermal and cortical cells
Acropetal auxin moves towards root tip through stele
Auxin Polar Transport
Auxin Polar Transport
Auxin Acid Growth Hypothesis
Auxin-activated proton pump in cell membrane acidifies cell wall space
Pumps in protons from cytosol
Phytohormones, 1
Lower pH activates wall-loosening enzymes, extensins
Extensins loosen glycan bonds between microfibrils within cell wall
Turgor then causes micofibrils to be displaced, allowing elongation
Auxin Acid Growth Hypothesis
Auxin Vascular Differentiation
IAA-induced xylem regeneration
Polar auxin transport visible in accumulation above wound
Xylem regeneration occurs first above wound
Auxin Root Initiation
Auxin Axillary Bud Break
Auxin Tropic Curvature and Growth
Gibberellins
Gibberellic Acid, GA3
Synthesized in seeds, fruits, and young leaves
Modified in roots
Stem elongation
Flower and fruit development
Gibberellins Internode Elongation
Gibberellins Seed Germination
Helps to mobilize endosperm reserves
Gibberellins Flower and Fruit Development
Cytokinins
Kinetin
Benzyladenine
Zeatin
Synthesized in root
Important for cell division
Cytokinesis division of cytoplasm during mitosis
Used in tissue culture to encourage shoot proliferation
(auxin used to promote root proliferation)
Cytokinin Witchs Broom
Phytohormones, 2
Fungal infection causes overproduction of cytokinin and uncontrolled axillary bud
development
Abscisic Acid
ABA
Synthesized mostly in mature leaves
Not actually directly involved in abscission
Important signal for plant water relations, stomatal activity
Active during seed germination
Ethylene
H2C=CH2 (gas)
Synthesized
In all plant organs
In tissues experiencing stress
In tissues experiencing senescence and/or ripening
MCP = ethylene blocker used to preserve cut flowers
Methylcyclopropene
Phytohormones
Brassinosteriods
Brassinolide is active component
Newly discovered group of hormones
Stimulate shoot growth and inhibit root growth
Involved in stem elongation and leaf morphogenesis
Play a role in vascular differentiation
Phytohormones
HORT 3000
Phytohormones, 3
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Plant Hormones - DR - FQDokumen47 halamanPlant Hormones - DR - FQUmarBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDokumen33 halamanPlant Growth RegulatorsShalini MBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth Hormonesbotany 2.4Dokumen7 halamanPlant Growth Hormonesbotany 2.4nitesh.th15005Belum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen36 halamanPlant HormonesDesy YusriyyahBelum ada peringkat
- The Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentDokumen29 halamanThe Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentbeneBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Physiology Lec. 7 Growth RegulatorsDokumen4 halamanPlant Physiology Lec. 7 Growth RegulatorsMuhamad MuhamadBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen40 halamanPlant HormonesSakina26100% (1)
- Plant Growth Regulators (2014)Dokumen34 halamanPlant Growth Regulators (2014)matthewBelum ada peringkat
- HORMONE ROLEDokumen39 halamanHORMONE ROLEMuhammad Naufal IndriatmokoBelum ada peringkat
- Macronutrients, Micronutrients, and Plant HormonesDokumen28 halamanMacronutrients, Micronutrients, and Plant HormonesHERSHELL KETASH CAPACITEBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - Plant HormonesDokumen49 halamanChapter 8 - Plant Hormonessayidah nafisah100% (2)
- Auxin: Greek Auxein, Meaning "To Increase" or "To Grow."Dokumen31 halamanAuxin: Greek Auxein, Meaning "To Increase" or "To Grow."gouthami shivaswamyBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3908Dokumen42 halamanCH 3908ridhi424Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones Ch. 39Dokumen43 halamanPlant Hormones Ch. 39Peter MathewBelum ada peringkat
- Plant GrowthDokumen33 halamanPlant GrowthDave SmtBelum ada peringkat
- Regulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesDokumen30 halamanRegulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesMoath EnnabBelum ada peringkat
- Biotechnology BookDokumen30 halamanBiotechnology BookAshrita PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 6 FITOHORMONEDokumen23 halamanBab 6 FITOHORMONEnormaBelum ada peringkat
- Kingdom: Plants: Domain EukaryaDokumen24 halamanKingdom: Plants: Domain Eukaryapeterr1022Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDokumen37 halamanPlant Growth RegulatorsKaran RavalBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormone PhysiologyDokumen61 halamanPlant Hormone PhysiologyKarylle Chloe MarceloBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen39 halamanPlant HormonesSaffira AzzahraBelum ada peringkat
- BIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesDokumen48 halamanBIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesJet DelimaBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones Guide Growth and ResponsesDokumen28 halamanPlant Hormones Guide Growth and Responseslilly kitBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDokumen29 halamanPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Organismal Biology ConceptsDokumen97 halamanOrganismal Biology ConceptsDaryl PansoyBelum ada peringkat
- The Discovery and Functions of Auxin, the First Plant Growth HormoneDokumen33 halamanThe Discovery and Functions of Auxin, the First Plant Growth HormoneAyushi MandloiBelum ada peringkat
- Phytohormone Functions and InteractionsDokumen3 halamanPhytohormone Functions and InteractionsNur Anisha Binti Mohd AzmyBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen25 halamanPlant HormonesikaBelum ada peringkat
- UG - Sem-VI-BOTHC-14-Biotechnology - Tissue CultureDokumen95 halamanUG - Sem-VI-BOTHC-14-Biotechnology - Tissue CultureJaishree RawatBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones Lecture on Growth RegulatorsDokumen9 halamanPlant Hormones Lecture on Growth RegulatorsPreen SanmukBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDokumen30 halamanPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 PLANTDokumen3 halamanChapter 4 PLANTSedsed QuematonBelum ada peringkat
- 3.3 Plant ResponsesDokumen50 halaman3.3 Plant ResponsesIrfan 21Belum ada peringkat
- 9.plant HarmonesDokumen6 halaman9.plant HarmonesRAVINDRA PRASADBelum ada peringkat
- P3 OrganogenesisDokumen13 halamanP3 OrganogenesisPanca Ayu VirgirlBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDokumen55 halamanPlant Growth RegulatorsXimena Libano0% (1)
- Plant HormonesDokumen19 halamanPlant HormonesWu YiruiBelum ada peringkat
- CRP 101 Lecture No 27Dokumen9 halamanCRP 101 Lecture No 27AnandKuttiyanBelum ada peringkat
- PLANT HORMONES: KEY REGULATORS OF GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENTDokumen40 halamanPLANT HORMONES: KEY REGULATORS OF GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENTAhmed ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth Regulators GuideDokumen6 halamanPlant Growth Regulators GuideSenthilkumar PalanisamyBelum ada peringkat
- 481 - Plant Growth Substances and Their Roles in Crop Ppcp202Dokumen19 halaman481 - Plant Growth Substances and Their Roles in Crop Ppcp202SALAUDEEN SAEFULLAHBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen3 halamanPlant HormonesAbdullah Al MamunBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth Regulators Lecture on Auxins, GibberellinsDokumen16 halamanPlant Growth Regulators Lecture on Auxins, GibberellinsAnandKuttiyanBelum ada peringkat
- Crop - Lecture - Growth HormonesDokumen9 halamanCrop - Lecture - Growth HormonesCynel DelaBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen38 halamanPlant Hormonesbaha hafizBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Harmons PDFDokumen15 halamanPlant Harmons PDFRahul GauravBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones NXPowerLiteDokumen25 halamanPlant Hormones NXPowerLiteZionne TanafrancaBelum ada peringkat
- Auxin Plays Key Roles in Plant Growth and DevelopmentDokumen29 halamanAuxin Plays Key Roles in Plant Growth and DevelopmentRajamma GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Tissue Culture... PPTX 1Dokumen12 halamanPlant Tissue Culture... PPTX 1Pooja ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Response To The Environemnt (Hormones and Defence)Dokumen30 halamanPlant Response To The Environemnt (Hormones and Defence)api-202349222Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Hormones SummaryDokumen11 halamanPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyBelum ada peringkat
- CONTROL AND COORDINATION IN PLANTS 2 Plant Hormones 2 The Role ofDokumen2 halamanCONTROL AND COORDINATION IN PLANTS 2 Plant Hormones 2 The Role ofSevara KazimovaBelum ada peringkat
- AuxinsDokumen16 halamanAuxinsICPH 2021Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Notes NEET Botany (PDF)Dokumen10 halamanPlant Growth and Development Class 11 Notes NEET Botany (PDF)tswrs jaffargadhBelum ada peringkat
- Organ and Organ Systems: Structure, Growth, Development and ReproductionDokumen26 halamanOrgan and Organ Systems: Structure, Growth, Development and ReproductionTrixie Santos100% (1)
- Folio 1 Biology STPM Sem 2Dokumen5 halamanFolio 1 Biology STPM Sem 2陈凯雯Belum ada peringkat
- Ass in Gen BioDokumen4 halamanAss in Gen BioDivine PadillaBelum ada peringkat
- Just Grow Mushrooms: Guide to growing mushrooms at home, in the basement or in garden. Mushroom gardening and cultivation for beginners.Dari EverandJust Grow Mushrooms: Guide to growing mushrooms at home, in the basement or in garden. Mushroom gardening and cultivation for beginners.Belum ada peringkat
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersDari EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersBelum ada peringkat
- 249 FullDokumen3 halaman249 Fullrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- 4623 FullDokumen8 halaman4623 Fullrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- 0615Dokumen6 halaman0615rustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Blood Lead Levels in Children From Primary Schools of BangladeshDokumen4 halamanBlood Lead Levels in Children From Primary Schools of Bangladeshrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- 04 Terpenoides CompilationDokumen209 halaman04 Terpenoides Compilationrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Theoncologistv 7 I Supplement 4 P 31 F2Dokumen1 halamanTheoncologistv 7 I Supplement 4 P 31 F2rustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen59 halamanBiochemistryrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- AnitAgingTips SmithDokumen107 halamanAnitAgingTips Smithrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDokumen11 halamanProkaryote Vs Eukaryoterustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Use of The Cefepime-Clavulanate Esbl Etest For Detection of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases in Ampc Co-Producing BacteriaDokumen6 halamanUse of The Cefepime-Clavulanate Esbl Etest For Detection of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases in Ampc Co-Producing Bacteriarustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- AspirinDokumen25 halamanAspirinApurba Sarker ApuBelum ada peringkat
- Theoncologistv 7 I Supplement 4 P 31 F2Dokumen1 halamanTheoncologistv 7 I Supplement 4 P 31 F2rustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Biological BackgroundDokumen15 halamanBiological Backgroundrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- RNA Modification: Post-Transcriptional Processing of RNADokumen4 halamanRNA Modification: Post-Transcriptional Processing of RNArustyryan770% (1)
- Central Dogma Still StandDokumen7 halamanCentral Dogma Still Standrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- 4 R DNADokumen22 halaman4 R DNArustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and AdipocytesDokumen5 halamanObesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Adipocytesrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Why Genes Persist in Organelle GenomesDokumen6 halamanWhy Genes Persist in Organelle Genomesrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Hybrid Rice Adoption in Bangladesh - 2Dokumen6 halamanHybrid Rice Adoption in Bangladesh - 2rustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Anti SenseDokumen2 halamanAnti SenseMalkit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The Plant CellDokumen14 halamanAnatomy of The Plant Cellrustyryan77100% (1)
- Understanding Hereditary HaemochromatosisDokumen26 halamanUnderstanding Hereditary Haemochromatosisrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Cloning DNA Recombination ProcessDokumen44 halamanCloning DNA Recombination Processrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Hybrid Rice Adoption in Bangladesh - 2Dokumen6 halamanHybrid Rice Adoption in Bangladesh - 2rustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Islamic Law - Sharia and FiqhDokumen8 halamanIslamic Law - Sharia and Fiqhmohsinemahraj100% (1)
- Methods & MaterialsDokumen1 halamanMethods & Materialsrustyryan77Belum ada peringkat
- Soilrens, Volume 16 No. 2, Juli - Desember 2018Dokumen8 halamanSoilrens, Volume 16 No. 2, Juli - Desember 2018Purwita Sari NugrainiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction Lesson (2) - 6Dokumen21 halamanIntroduction Lesson (2) - 6Jamal KerkhofBelum ada peringkat
- GHXHJVJGJDokumen541 halamanGHXHJVJGJAngad KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Nip Material ComparsionDokumen1 halamanNip Material ComparsionRob WillestoneBelum ada peringkat
- Position Quantity DescriptionDokumen7 halamanPosition Quantity Descriptionshidik hossenBelum ada peringkat
- Bonsai Cendrawasih How To GrowDokumen2 halamanBonsai Cendrawasih How To GrowariefprotonBelum ada peringkat
- Past McqsDokumen37 halamanPast McqsNaveed IrshadBelum ada peringkat
- 03 01 30 - Maintenance of Cast-in-Place ConcreteDokumen11 halaman03 01 30 - Maintenance of Cast-in-Place ConcreteHardeo Dennis ChattergoonBelum ada peringkat
- Sugar Beet Development Plan 2020-21Dokumen52 halamanSugar Beet Development Plan 2020-21WaqasBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly construction report for 2B + G + 4Floors + Gym projectDokumen13 halamanWeekly construction report for 2B + G + 4Floors + Gym projectHANNA LAYOUSBelum ada peringkat
- CV-Praveen SharmaMDDokumen5 halamanCV-Praveen SharmaMDsandeepgawadeBelum ada peringkat
- Blockwork Marking SchemeDokumen2 halamanBlockwork Marking SchemeAbok AduogoBelum ada peringkat
- Basil (O. Basilicum)Dokumen22 halamanBasil (O. Basilicum)rdineshBelum ada peringkat
- Manual4 PDFDokumen66 halamanManual4 PDFelmer francescoBelum ada peringkat
- Vascular Flora of Bardača ComplexDokumen22 halamanVascular Flora of Bardača Complextomislavgaljbo88Belum ada peringkat
- Customer Price List: Certified Code Compliant Steel Stud Manufacturer Manufacturer of Supreme Framing SystemsDokumen5 halamanCustomer Price List: Certified Code Compliant Steel Stud Manufacturer Manufacturer of Supreme Framing SystemsRamonBelum ada peringkat
- Mannings Formula SpreadsheetDokumen18 halamanMannings Formula SpreadsheetparthivBelum ada peringkat
- Imp of MicronutrientsDokumen5 halamanImp of MicronutrientsDanish S MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Lime - SpecificationDokumen2 halamanLime - SpecificationKokila Gayashi SooriyagodaBelum ada peringkat
- Spec 820 Concrete 24 Nov 2016.RCN-D1623749976Dokumen30 halamanSpec 820 Concrete 24 Nov 2016.RCN-D1623749976virajBelum ada peringkat
- List of Common Ornamental Plants in The PhilippinesDokumen29 halamanList of Common Ornamental Plants in The PhilippinesAnonymous HXLczq378% (69)
- Century of Progress 161008Dokumen20 halamanCentury of Progress 161008Cheong Ying ZhiBelum ada peringkat
- Plant HormonesDokumen40 halamanPlant HormonesSakina26100% (1)
- Sterkel Park OverviewDokumen1 halamanSterkel Park Overviewemills11Belum ada peringkat
- How To Propagate Succulents From LeavesDokumen4 halamanHow To Propagate Succulents From LeavesBulan CahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Individual Worksheet - Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDokumen3 halamanIndividual Worksheet - Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsHarmanjot KaurBelum ada peringkat
- NBS TASIK - Remove Duckweed From LakeDokumen9 halamanNBS TASIK - Remove Duckweed From LakeBen ConnahBelum ada peringkat
- Proposed 2-Storey House ProjectDokumen19 halamanProposed 2-Storey House ProjectErnane Rita100% (4)
- Irrigation and Fertigation SoybeanDokumen1 halamanIrrigation and Fertigation Soybeanvhfdz1175Belum ada peringkat
- Awc Dca3 FRR Assemblies 1907Dokumen28 halamanAwc Dca3 FRR Assemblies 1907Lê Anh ĐứcBelum ada peringkat