Misc Bacteria
Diunggah oleh
Ashamdeep AntaalHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Misc Bacteria
Diunggah oleh
Ashamdeep AntaalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
sl 2013
Bacteria
Mycobacteriu
m
tuberculosis
Mycobacteriu
m leprae
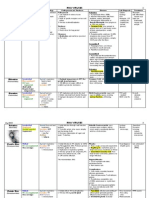
MISCELLANEOUS BACTERIA
Characteristics
Epidemiology
Pathogenesis and Virulence
Weakly Gram +
Strongly Acid
Fast
Aerobic
Cell wall:
peptidoglycan
&
lipoarabinogal
actan
Spread: aerosol
Location:
patients with
active TB
infection
Risk Factors:
1. Geographic
(Asia, Eastern
Europe)
2. Exposure to
infected group
At Risk:
1. Immunocomp
2. Drug/Alcohol
abuser,
homeless
3. Exposed
individuals
Virulence
1. Trehalose mycolate or cord
factor: induces granuloma
formation
2. Establishes lifelong infection:
intracellular pathogen
3. Prevent phagolysosome fusion:
sulphatide secretion
4. Phagosome fuses with other
intracellular vesicles for nutrient
access
5. Oxidant inactivation: evade
macrophage killing
6. Stimulate IL-12 and TNF-
release: TH1 CD4+ response
IFN- and nitric oxide release
Weakly Gram +
Strongly Acid
Fast
Aerobic
Spread: aerosol
or personperson contact
Location:
armadillo, soil,
contaminated
Pathogenic Development
1. Macrophages and lymphocytes
are attracted to infectious focus
2. Fuse to form Langhan giant
cells
3. Granuloma formation to
prevent further spread of
bacteria
4. TH1 CD4+ cells attempt to
control and eradicate the
infection via pro-inflammatory
and cell-mediated cytokines
5. Depending on the size of the
focus, the bacteria can either get
eradicated or remain dormant
1. Prolonged contact required
2. Low infectivity: longer duration
for disease development
Diseases
Primary (children): Initial focus
in subpleural part of lung
activate cellular immunity
replication ceases
1. Pneumonia, abscess
formation, cavitation in upper
lobes and hilar
lymphadenopathy
2. Ghons complex: Calcification
of healed primary lesion
(scarring)
3. Nonspecific complaints of
weight loss, cough and night
sweats
4. Sputum: scant or bloody and
purulent; can be associated
with tissue destruction
Secondary (adults):
Reactivation of dormant
tubercle bacilli or reinfection
spread to upper lobe apex
1. Fibrocaseous cavitary lesion
near apex of upper lobe
Miliary: Hematogenous
widespread dissemination of
tubercle bacilli
1. Millet-like seeding in lung
Extrapulmonary:
hematogenous spread of
tubercle bacilli causing tissue
destruction at lymph nodes,
pleura, urogenital tract, bones,
kidneys
Chronic granulomatous lesion of
peripheral nerves and
mucocutaneous tissue (nasal
mucosa)
1. Tuberculoid leprosy: few
skin lesions in cooler body
Lab
Diagnosis
Culture
collection
Acid Fast
Stain
PCR
Various
media: LJ,
Middlebroo
k, BACTEC
460
Chest X-ray
Treatment
RIPE:
Rifampin,
Isoniacid,
Pyrazinami
de,
Ethambutol
BCG vaccine
DOT:
Directed
Observed
Treatment
Tuberculin
(Mantoux
) skin
test:
injection of
PPD intradermally
>5mm: HIV
px,
immunosu
pp,
contact
with TB px
>10mm:
immigrant
s, IV drug
users,
hospital
workers
>15mm: no
risk factors
for TB
Quantiferon
Gold Test:
detect whole
blood IFN-;
immune
reactivity
Acid-fast in
lepromato
us leprosy
Dapsone
Rifampin
Clofazamine
sl 2013
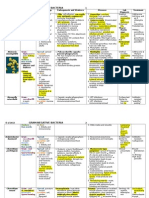
MISCELLANEOUS BACTERIA
persons
At Risk:
1. Contact with
infected person
Mycobacteriu
m avium
complex
(MAC)
Weakly Gram +
Strongly Acid
Fast
Aerobic
Mycoplasma
pneumoniae
Cell-wall has no
peptidoglycan
but contains
sterol (requires
cholesterol!)
Aerobic
Pleomorphic
Spread: aerosol
At Risk:
1. HIV patients
2.
Chemotherapy
Spread: aerosol
Location:
ubiquitous
Risk Factors:
1. Schools,
prisons, military
settings (close
contact)
At Risk:
1. Children and
young adults
Asymptomatic colonization in
immunocompetent
Dissemination in
immunocompromised
1. P1 adhesion protein: adherence
to ciliated respiratory epithelia
2. Eventual loss of ciliated
epithelia: facilitate bacterial
spread to lungs
**Fried egg appearance!!
tissues (nose, ears, fingers,
testicles), CMI, low infectivity,
lepromin +
2. Lepromatous leprosy:
extensive destruction of skin,
immunity is depressed, high
infectivity, lepromin 1. Development of single
infected nodule: disseminates
in immunocompromised
1. Upper Respiratory Tract
Infection: low grade fever,
headache, dry, non-productive
cough
2. Lower Respiratory Tract
Infection: primary atypical
pneumonia (walking
pneumonia) mild, diffuse
interstitial pneumonia;
tracheobronchitis
**Pneumococcal pneumonia
(Strep) is consolidate, lobar
pneumonia
Other Miscellaneous Bacteria:
U. urealyticum: causes non-gonococcal urethritis
M. hominis: causes pyelonephritis, PID, post-partum fever
Macrolides
Cold
agglutinin
test: Ab
that lyses
RBC in 4C
PCR
Erythomycin
Doxycycline
**Penicillin
resistant
(no cell
wall)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Goljan SlidesDokumen383 halamanGoljan Slidesusmle196% (23)
- Sulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMDokumen10 halamanSulfonamides: Wednesday, 1 October 2014 10 Am - 12 PMAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Step 1 Study Schedule BlogDokumen11 halamanStep 1 Study Schedule BlogAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology High YieldDokumen13 halamanPhysiology High YieldAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio OsceDokumen7 halamanCardio OsceAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Brachial Plex How ToDokumen21 halamanBrachial Plex How ToAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine ComprehensiveDokumen43 halamanEndocrine ComprehensiveAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- USMLE 100 Essential DrugsDokumen15 halamanUSMLE 100 Essential DrugsAnnTranBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology High YieldDokumen13 halamanPhysiology High YieldAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- 2015samples Step1Dokumen45 halaman2015samples Step1katherineBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine ComprehensiveDokumen43 halamanEndocrine ComprehensiveAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Anti TB DrugsDokumen18 halamanAnti TB DrugsAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- RespiratoryDokumen26 halamanRespiratoryAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio-Comprehensive: - AnatomyDokumen51 halamanCardio-Comprehensive: - AnatomyAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Rna VirusesDokumen4 halamanRna VirusesAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- GI ComprehensiveDokumen22 halamanGI ComprehensiveAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Renal ComprehensiveDokumen54 halamanRenal ComprehensiveAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Negative BacteriaDokumen11 halamanGram Negative BacteriaAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Dna VirusesDokumen3 halamanDna VirusesAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Negative BacteriaDokumen11 halamanGram Negative BacteriaAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Heart MurmursDokumen18 halamanHeart MurmursRobby Wiranata WijayaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory PathDokumen6 halamanRespiratory PathAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Miscellaneous VirusDokumen2 halamanMiscellaneous VirusAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Negative BacteriaDokumen11 halamanGram Negative BacteriaAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- Lung Cancer ChartDokumen2 halamanLung Cancer ChartAshamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- 033 Auditory Part 1Dokumen17 halaman033 Auditory Part 1Ashamdeep AntaalBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Hse Statistics Report Pp701 Hse f04 Rev.bDokumen1 halamanHse Statistics Report Pp701 Hse f04 Rev.bMohamed Mouner100% (1)
- Demography Using Cemetery DataDokumen5 halamanDemography Using Cemetery DatamjbdobleuBelum ada peringkat
- Tony Gaddis Python BookDokumen5 halamanTony Gaddis Python BookArslan AliBelum ada peringkat
- ISC Class 12 Biology Syllabus: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18Dokumen18 halamanISC Class 12 Biology Syllabus: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18HemantBelum ada peringkat
- Holi With Natural ColoursDokumen1 halamanHoli With Natural Coloursankush014Belum ada peringkat
- # Category Image Product Name Producer Package Hs Code Remark Key FeaturesDokumen9 halaman# Category Image Product Name Producer Package Hs Code Remark Key Featuresiq_dianaBelum ada peringkat
- Proceedings GRANADA 1Dokumen70 halamanProceedings GRANADA 1wingsskyBelum ada peringkat
- Gingival Inflammation in Mouth Breathing PatientsDokumen5 halamanGingival Inflammation in Mouth Breathing PatientsCamiLunaBelum ada peringkat
- Factory Farming in The Developing WorldDokumen10 halamanFactory Farming in The Developing WorldDaisyBelum ada peringkat
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDokumen11 halamanRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamBelum ada peringkat
- Disability EssayDokumen7 halamanDisability Essayapi-459529771Belum ada peringkat
- 1273655379alkem Annual Report FY 2015-16 PDFDokumen212 halaman1273655379alkem Annual Report FY 2015-16 PDFShalako45Belum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Ultrasound Report TemplatesDokumen8 halamanDiagnostic Ultrasound Report TemplatesJay Patel100% (10)
- Ultimate Guide To Surviving in The WildDokumen175 halamanUltimate Guide To Surviving in The WildSal Ot100% (1)
- Department of Vegetable Science N.D. University of Agriculture & Technology Kumarganj, Faizabad-224229Dokumen35 halamanDepartment of Vegetable Science N.D. University of Agriculture & Technology Kumarganj, Faizabad-224229Ujjwal UpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- DNS ENT Case Write UpDokumen8 halamanDNS ENT Case Write UpShafiq ZahariBelum ada peringkat
- Belgian MalinoisDokumen9 halamanBelgian MalinoislordnrBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Self-Stimulation of The BrainDokumen7 halamanElectrical Self-Stimulation of The BrainKris VacyBelum ada peringkat
- FNCP (Open Drainage) For Soft BoundDokumen3 halamanFNCP (Open Drainage) For Soft BoundSean Maghinay BanicoBelum ada peringkat
- A Drug Study On PrednisoneDokumen5 halamanA Drug Study On PrednisonePrincess Alane MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- TOX-SICK by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptDokumen19 halamanTOX-SICK by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group100% (1)
- RevalidaDokumen5 halamanRevalidajbmyworlddaenna1Belum ada peringkat
- Medsurg 3 Exam 1Dokumen55 halamanMedsurg 3 Exam 1Melissa Blanco100% (1)
- RRL Local and ForeignDokumen2 halamanRRL Local and ForeignArjelyn Loquisan MonsalesBelum ada peringkat
- 9 Steps To Reverse DementiaDokumen36 halaman9 Steps To Reverse DementiaLavinia PirlogBelum ada peringkat
- Rickey Dixon Letter To The Court On NFL Concussion Settlement FeesDokumen9 halamanRickey Dixon Letter To The Court On NFL Concussion Settlement FeesRobert Lee100% (1)
- Reconocimiento Del Acv CLINISC 2012Dokumen21 halamanReconocimiento Del Acv CLINISC 2012Camilo GomezBelum ada peringkat
- SteroidsDokumen3 halamanSteroidsapi-236946512Belum ada peringkat
- Book 28Dokumen56 halamanBook 28Er Sana WarsiBelum ada peringkat
- A Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Dokumen32 halamanA Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Abdulaziz AbdullahiBelum ada peringkat