pg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case Study
Diunggah oleh
ikemasDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
pg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case Study
Diunggah oleh
ikemasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2.
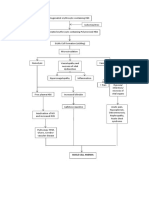
Schematic Diagram: Client Based Pathophysiology:
Precipitating/Modifiable
Non Modifiable / Any Chest Injury
factors
Predisposing Factors
• Environment
• Age
• Exposure to
• Immunocompromised Allows air to enter Pathologic
• Common Colds the pleural space Microorganism
• aspiration of foods or
fluids
• Lung Disease
Manifestations:
Depends on its size and the
integrity of the underlying lung.
Pneumothorax
Penetration into the pleural Internal Mechanism (such as broken
space by an object external to rib or bleb rupture of the lung) air or
the chest wall (such ash Increase intrathoracic blood enters the pleural space.
knife/needle) pressure and reduction in
vital capacity
Open Pneumothorax Closed
Pneumothorax
Large Pneumothorax
Penetrating Injury to the chest Air filled bleb/blister
/Non or respiratory Hypoxemia on the lung surface
penetrating structures ruptures
injuries 36
Vasoconstriction of the
blood vessels in the
affected lung.
Manifestations:
Aug. 24,09
Fractured/ • CHEST: (+) rales and retractions
dislocated Chest Medical Cardio August 27, 09
ribs Trauma Procedure pulmonary • (+) nasal flaring
that such as resuscitation • RR= 96
penetrates intra (CPR) • diminished breath sounds on right lung field
the pleura thoracic Aug. 28,09
Air enters the
needle • (+) nasal flaring
pleural space but
aspirations,
Other does not leave • RR=92
intubation,
Complication • diminished breath sounds on right lung field
and
Hemothorax positive
Rapid increase of
pressure
pressure in chest
ventilation Spontaneous
with compression
atelectasis of Pneumothorax
unaffected lung
Unknown cause Lung Disease History of
Traumatic Shift in mediastinum to the endometriosis
Pneumothorax opposite side of the chest and
Air filled Trapping
compression of the vena cava
blebs rupture of gases &
with impairment of venous Air may gain access
on TOP of Destruction
return to the heart to the peritoneal
the lungs. of lung Cavity during
tissue menstruation and
Intrapleural pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure. then enter the pleural
Primary Secondary cavity through
Spontaneous Spontaneous diaphragmatic
Pneumothorax Pneumothorax Defect.
Tension
Pneumothorax
Catamenial
Partial/total Pneumothorax
loss of lung
Manifestations: function
• Structures in the mediastinal space shift toward
the opposite side of the chest. Hypoxemia
• Distention of neck veins
37
• Subcutaneous emphysema Life threatening
Intrapleural pressure
• Clinical signs of shock
exceeds atmospheric
pressure.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- To Be African or Not To Be: An Autoethnographic Content Analysis of The Works of Dr. Asa Grant Hilliard, III (Nana Baffour Amankwatia, II) - by Qiana M. CuttsDokumen283 halamanTo Be African or Not To Be: An Autoethnographic Content Analysis of The Works of Dr. Asa Grant Hilliard, III (Nana Baffour Amankwatia, II) - by Qiana M. Cutts☥ The Drop Squad Public Library ☥100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMarynette MapaBelum ada peringkat
- The Seven Seals of Revelation and The SevenDokumen14 halamanThe Seven Seals of Revelation and The Sevenyulamula100% (2)
- Bread Machine Sunbeam 5891Dokumen44 halamanBread Machine Sunbeam 5891Tyler KirklandBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumothorax (Collapsed Lung)Dokumen34 halamanPneumothorax (Collapsed Lung)james garcia100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniaJesselle LasernaBelum ada peringkat
- ScreenwritingDokumen432 halamanScreenwritingkunalt09100% (4)
- A Strategic Management PaperDokumen7 halamanA Strategic Management PaperKarll Brendon SalubreBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PneumothoraxDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of PneumothoraxDizah Faye OsboroBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure Due to Myocardial DysfunctionDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Heart Failure Due to Myocardial DysfunctionabbeeyyBelum ada peringkat
- Qtsoi Concept MapDokumen5 halamanQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoBelum ada peringkat
- pg.38-78 of Pnemothorax Case StudyDokumen43 halamanpg.38-78 of Pnemothorax Case StudyikemasBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsDokumen1 halamanPneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsJoshua Villarba80% (5)
- (Patho) PTB COPDDokumen1 halaman(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and AnemiaDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and Anemiapa3kmedina100% (2)
- Pathophysiology and Management of COPDDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology and Management of COPDNeil Andro Marcelo100% (1)
- Electrical Burn PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanElectrical Burn PathophysiologydanicaBelum ada peringkat
- Chest Tube Drainage of The Pleural SpaceDokumen10 halamanChest Tube Drainage of The Pleural SpaceFernandaBelum ada peringkat
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDokumen3 halaman"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaFirenze Fil100% (21)
- Intestinal Obstruction A Case StudyDokumen44 halamanIntestinal Obstruction A Case StudyikemasBelum ada peringkat
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramDokumen3 halamanMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramJessica Peñamora100% (1)
- Rules & Guidelines of Elliott WaveDokumen12 halamanRules & Guidelines of Elliott WaveNd Reyes100% (2)
- PneumothoraxDokumen57 halamanPneumothoraxCamille Marquez100% (9)
- Acute Renal FailureDokumen76 halamanAcute Renal Failureikemas100% (7)
- Chest Tube Thoracostomy and Water Sealed DrainageDokumen50 halamanChest Tube Thoracostomy and Water Sealed DrainagegraceriaaBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyDokumen4 halamanAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionCharina Aubrey100% (1)
- Patho of Pott's DiseaseDokumen2 halamanPatho of Pott's DiseaseIris Balino100% (1)
- Mafia Bride by CD Reiss (Reiss, CD)Dokumen200 halamanMafia Bride by CD Reiss (Reiss, CD)Aurniaa InaraaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDokumen8 halaman1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorBelum ada peringkat
- Iv. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing FactorsDokumen2 halamanIv. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing Factorsikemas67% (6)
- Pathophysiology ARDSDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology ARDSRoderick Agbuya100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisMaria Socorro Sismundo DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Patho Pleural EffusionDokumen2 halamanPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Osteomyelitis, PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanOsteomyelitis, Pathophysiology4kscribdBelum ada peringkat
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen3 halamanDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Septic Shock Secondary To PyelonephritisDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Septic Shock Secondary To PyelonephritisShirlyn100% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen4 halamanNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Dokumen2 halamanPathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Jamie HaravataBelum ada peringkat
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDokumen1 halamanSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaBelum ada peringkat
- Tuberculosis PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanTuberculosis Pathophysiologymiss RN100% (15)
- Medical Management For PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanMedical Management For PneumoniaSue Elaine100% (1)
- Assessing and Treating Impending Thyroid StormDokumen4 halamanAssessing and Treating Impending Thyroid StormRenie SerranoBelum ada peringkat
- Postpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestDokumen8 halamanPostpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestLei OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia OverviewDokumen3 halamanAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia OverviewKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaTine GuibaoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen3 halamanNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoBelum ada peringkat
- CeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanCeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyJjessmar Bolivar FamaBelum ada peringkat
- Congestive Heart FailureDokumen4 halamanCongestive Heart FailureAnnie Grace PoliranBelum ada peringkat
- Myocardial InfarctionDokumen6 halamanMyocardial InfarctionMaicie Rose Bautista VallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care for Cholera DiarrheaDokumen2 halamanNursing Care for Cholera DiarrheaMichael Angelo Garcia RafananBelum ada peringkat
- Thrombophlebitis Pathophysiology ExplainedDokumen2 halamanThrombophlebitis Pathophysiology ExplainedKartika YuliantiBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan #1: IndependentDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan #1: IndependentMaria ThereseBelum ada peringkat
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDokumen4 halamanAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologyteddydeclines1467% (6)
- Breathing Difficulties Pleural EffusionDokumen3 halamanBreathing Difficulties Pleural EffusionErickson OcialBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Meniere FinalDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Meniere Final1S VILLEGAS GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokumen3 halamanImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliBelum ada peringkat
- CHOLElithiasisDokumen93 halamanCHOLElithiasisfranciscomaricris13Belum ada peringkat
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Dokumen3 halamanElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliBelum ada peringkat
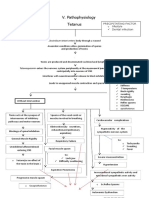
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumothorax Key PointsDokumen2 halamanPneumothorax Key PointsJose UringBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of pneumothorax and hemothoraxDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of pneumothorax and hemothoraxAllana RayosBelum ada peringkat
- ADAZA BSND 3 OR REQS Concept MAP 3 PDFDokumen1 halamanADAZA BSND 3 OR REQS Concept MAP 3 PDFKrizle AdazaBelum ada peringkat
- Thorax Anatomy Review: Lungs, Mediastinum & PneumothoraxDokumen84 halamanThorax Anatomy Review: Lungs, Mediastinum & PneumothoraxAlvikhaabieber Alvinosztarisegfc Stuarst'gBelum ada peringkat
- Hafizah Hoshni PneumothoraxDokumen47 halamanHafizah Hoshni PneumothoraxhafizahhoshniBelum ada peringkat
- PneumothoraxDokumen30 halamanPneumothoraxnorhazirah hassanBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives 1. Anatomy of The LungsDokumen5 halamanLearning Objectives 1. Anatomy of The LungslaurenBelum ada peringkat
- To CTTDokumen51 halamanTo CTTMaryasi PanjaitanBelum ada peringkat
- C StudyDokumen18 halamanC StudyikemasBelum ada peringkat
- Homework Problems - Chi-Square Test of IndependenceDokumen42 halamanHomework Problems - Chi-Square Test of IndependenceikemasBelum ada peringkat
- pg1-33 of Pneumothorax Case StudyDokumen36 halamanpg1-33 of Pneumothorax Case StudyikemasBelum ada peringkat
- Restaurant Social Media GuideDokumen30 halamanRestaurant Social Media GuideHoàng gia NghiêmBelum ada peringkat
- Limit Switch 1LX7001-J AZBILDokumen8 halamanLimit Switch 1LX7001-J AZBILHoàng Sơn PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- College Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Solutions ManualDokumen36 halamanCollege Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Solutions Manualshippo.mackerels072100% (22)
- Chapter 12Dokumen52 halamanChapter 12Mr SaemBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study On Global Branding - DuluxDokumen18 halamanCase Study On Global Branding - DuluxAakriti NegiBelum ada peringkat
- Schedule FinalDokumen6 halamanSchedule FinalJamora ManilynBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneDokumen10 halamanMaterials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneVikrant Saumitra mm20d401Belum ada peringkat
- Datasheet AD549Dokumen14 halamanDatasheet AD549Trần Hồng VănBelum ada peringkat
- Synetek Controls Inc.: Ds1-S: Installation InstructionsDokumen2 halamanSynetek Controls Inc.: Ds1-S: Installation Instructionsdgd_electromecBelum ada peringkat
- Radial Drill Catalog-110620Dokumen14 halamanRadial Drill Catalog-110620Anto SiminBelum ada peringkat
- Viscosity IA - CHEMDokumen4 halamanViscosity IA - CHEMMatthew Cole50% (2)
- X32 Digital Mixer: Quick Start GuideDokumen28 halamanX32 Digital Mixer: Quick Start GuideJordán AstudilloBelum ada peringkat
- LSAP 423 Tech Data 25kVA-40KVA - 3PH 400VDokumen1 halamanLSAP 423 Tech Data 25kVA-40KVA - 3PH 400Vrooies13Belum ada peringkat
- Single-phase half-bridge inverter modes and componentsDokumen18 halamanSingle-phase half-bridge inverter modes and components03 Anton P JacksonBelum ada peringkat
- Polifur 1K Synthetic Top Coat MSDS Rev 2 ENDokumen14 halamanPolifur 1K Synthetic Top Coat MSDS Rev 2 ENvictorzy06Belum ada peringkat
- Radiant Tube BurnersDokumen18 halamanRadiant Tube BurnersRajeshBelum ada peringkat
- CVR College of Engineering: UGC Autonomous InstitutionDokumen2 halamanCVR College of Engineering: UGC Autonomous Institutionshankar1577Belum ada peringkat
- NotesTransl 108 (1985) Larsen, Who Is This GenerationDokumen20 halamanNotesTransl 108 (1985) Larsen, Who Is This GenerationluzuBelum ada peringkat
- Master of Advanced Nursing Practice degreeDokumen2 halamanMaster of Advanced Nursing Practice degreeAgusfian Trima PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Captive Screws - Cap Head: Hex. SocketDokumen5 halamanCaptive Screws - Cap Head: Hex. SocketvikeshmBelum ada peringkat
- Psyclone: Rigging & Tuning GuideDokumen2 halamanPsyclone: Rigging & Tuning GuidelmagasBelum ada peringkat
- NVH PDFDokumen3 halamanNVH PDFSubhendu BarisalBelum ada peringkat
- Feyzin Oil Refinery DisasterDokumen8 halamanFeyzin Oil Refinery DisasterDavid Alonso Cedano EchevarriaBelum ada peringkat