Diarrhea E
Diunggah oleh
abdalballah11510 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
81 tayangan1 halamanAcute diarrhea is a common illness in children that usually lasts less than one week. It is often caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. While most cases do not require antibiotics, replacing lost fluids is important to prevent dehydration, especially in young infants. Oral rehydration solutions are recommended for severe or prolonged diarrhea, and hospitalization may be necessary in serious cases to monitor hydration and allow the infection to pass.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniAcute diarrhea is a common illness in children that usually lasts less than one week. It is often caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. While most cases do not require antibiotics, replacing lost fluids is important to prevent dehydration, especially in young infants. Oral rehydration solutions are recommended for severe or prolonged diarrhea, and hospitalization may be necessary in serious cases to monitor hydration and allow the infection to pass.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
81 tayangan1 halamanDiarrhea E
Diunggah oleh
abdalballah1151Acute diarrhea is a common illness in children that usually lasts less than one week. It is often caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. While most cases do not require antibiotics, replacing lost fluids is important to prevent dehydration, especially in young infants. Oral rehydration solutions are recommended for severe or prolonged diarrhea, and hospitalization may be necessary in serious cases to monitor hydration and allow the infection to pass.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
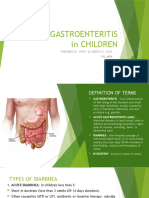
Acute Diarrhea in Children
What is acute diarrhea? How is diarrhea treated?
Acute diarrhea stops when the body clears the infection
D iarrhea, an increase in the
number of stools per day
and/or an increase in their loose-
or toxin causing it. Most viruses and bacteria do not
require treatment with antibiotics. If the diarrhea persists
ness, is a common problem that for longer than one or two weeks, stool and blood tests
generally lasts only a few days. will help determine the most likely cause of the problem
Diarrhea that has lasted for less and guide treatment.
than one week is called “acute”.
Children with acute diarrhea should continue to eat
their regular diet, unless the diarrhea is severe or
accompanied by vomiting. Sometimes, restriction of
How common is diarrhea? milk and dairy products might be helpful. Excessive fluid
loss can result in dehydration which can be avoided by
Acute diarrhea is one of the most common illnesses in making sure the child is drinking.
children and a common reason for doctor visits. Often it
can occur in several members of a family or a classroom Infants under 3 months of age and those who are
at the same time. The average child under 3 years of vomiting are at the highest risk for dehydration. High
age will have 1 to 3 episodes of diarrhea every year, and fever increases the body fluid losses and should
acute diarrhea accounts for almost 10% of all childhood therefore be controlled. A decrease in the number of wet
hospital admissions. Although diarrhea occurs year diapers, lack of tears when crying, and excessive
round, it is more common during the winter months. sleepiness are all signs of dehydration and require
medical attention.
What causes acute diarrhea?
When the diarrhea is severe or there is vomiting,
The most common causes of acute diarrhea are: replacement fluid mineral drinks such as Pedialyte,
l Viruses, bacteria and parasites Infalyte, Cerealyte, Naturalyte and Rehydralyte are
recommended. These are also available in popsicles.
l Food poisoning
l Medications, especially antibiotics If the child cannot keep enough fluid in, hospitalization is
l Food allergies recommended to prevent serious dehydration and to
l Enzyme deficiencies (as in lactose intolerance)
allow “bowel rest” while the infection runs its course.
l Toxic substances Feedings by mouth will be started as soon as the
condition improves and while the child’s response can be
How does the doctor/nurse determine the watched more closely.
cause of my child’s diarrhea? For more information or to locate a pediatric gastroen-
terologist in your area please visit our website at:
Your description of the problem often provides the most www.naspghan.org
useful clues to help determine the possible cause of your
IMPORTANT REMINDER: This information from the North American Society for
child’s diarrhea. For example, has your child come in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) is intended
contact with other people with similar symptoms? Has only to provide general information and not as a definitive basis for diagnosis or
treatment in any particular case . It is very important that you consult your doctor
he/she eaten food that was not properly cooked? Were about your specific condition.
antibiotics used?
When the history clearly suggests the cause, tests for
SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONS:
viruses and bacteria are often not needed. Exceptions
include children with bloody diarrhea or very severe diar-
rhea. Children with bloody diarrhea or other serious ill-
nesses should be evaluated promptly by a health care
professional.
NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY,
HEPATOLOGY AND NUTRITION
NASPGHAN • PO Box 6 • Flourtown, PA 19031
215-233-0808 • Fax: 215-233-3939
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- DOH Control of Diarrheal DiseasesDokumen16 halamanDOH Control of Diarrheal DiseasesNielArmstrongBelum ada peringkat
- Food PoisoningDokumen24 halamanFood PoisoningSena AjahBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen45 halamanCase Studymejul100% (2)
- DiarrheaDokumen3 halamanDiarrheaSusana Lopez MontoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Education - Acute Diarrhea in Children (Beyond The Basics) - Uptodate FreeDokumen12 halamanPatient Education - Acute Diarrhea in Children (Beyond The Basics) - Uptodate Freekhaled khaterBelum ada peringkat
- Acute GastroenteritisDokumen11 halamanAcute GastroenteritisrubyjoysasingBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1makalah BigDokumen6 halamanChapter 1makalah BigrizqiBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea ATPDokumen42 halamanDiarrhea ATPsoni syangboBelum ada peringkat
- Case For Acute GastroenteritisDokumen26 halamanCase For Acute GastroenteritisSheana TmplBelum ada peringkat
- GastroenteritisDokumen2 halamanGastroenteritisabhieghailBelum ada peringkat
- Update On Diarrhea - Peds in Rev 2016Dokumen12 halamanUpdate On Diarrhea - Peds in Rev 2016TriLightBelum ada peringkat
- Influenza Nausea and Vomiting Fever Dehydration: Salmonella and Campylobacter Bacteria HoweverDokumen16 halamanInfluenza Nausea and Vomiting Fever Dehydration: Salmonella and Campylobacter Bacteria HoweverMark Bin S. DilangalenBelum ada peringkat
- AGE ReadingDokumen7 halamanAGE ReadingyasiraBelum ada peringkat
- Update On DiarrheaDokumen12 halamanUpdate On DiarrheantnquynhproBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Diarrhea?: Contaminated Food Flu Norovirus RotavirusDokumen3 halamanWhat Is Diarrhea?: Contaminated Food Flu Norovirus RotavirusMardie ArcesBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 109 Case Study - Sir JesusDokumen25 halamanNCM 109 Case Study - Sir JesusLance RaphaelBelum ada peringkat
- Case (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4Dokumen36 halamanCase (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4EljhayrosBelum ada peringkat
- Influenza Nausea and Vomiting FeverDokumen5 halamanInfluenza Nausea and Vomiting Feverjayne_saulogBelum ada peringkat
- GastroenteritisDokumen2 halamanGastroenteritisTiara Sekar AyudhipashaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is DiarrheaDokumen4 halamanWhat Is Diarrheasanozuke02Belum ada peringkat
- 4 FoodborneillnessesDokumen25 halaman4 Foodborneillnessesapi-232909671Belum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen8 halamanPDFmovow71424Belum ada peringkat
- Clinical Presentation On ADDDokumen39 halamanClinical Presentation On ADDSREEDEVI T SURESHBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDokumen5 halamanPathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15Belum ada peringkat
- AGE ReadingsDokumen6 halamanAGE ReadingseljhayrosBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Gastroenteritis 1Dokumen2 halamanAcute Gastroenteritis 1chenglibagBelum ada peringkat
- 6DehydrationRefArticle6 PDFDokumen11 halaman6DehydrationRefArticle6 PDFMaya LarasBelum ada peringkat
- DiarrheaDokumen19 halamanDiarrheaShaffy UngaBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea: On This PageDokumen6 halamanDiarrhea: On This PageKristine AlejandroBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Diarrhoeal DiseaseDokumen3 halamanAcute Diarrhoeal DiseaseBINIJA 2020Belum ada peringkat
- Gastrointestinal Case Study: INTIA, Crisset O. Iii-Bn Professor Ralph PecoDokumen6 halamanGastrointestinal Case Study: INTIA, Crisset O. Iii-Bn Professor Ralph PecoCrisset IntiaBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenteritis in ChildrenDokumen4 halamanGastroenteritis in ChildrenDennifer MadayagBelum ada peringkat
- Case2 AnswerDokumen5 halamanCase2 AnswerKATHERINE CANCIOBelum ada peringkat
- The Vomiting Child PDFDokumen4 halamanThe Vomiting Child PDFJos ArnoBelum ada peringkat
- National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC)Dokumen12 halamanNational Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC)yeolteaBelum ada peringkat
- Update On Diarrhea 2016Dokumen12 halamanUpdate On Diarrhea 2016sanlupinBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 Investigation of Chronic DiarrhoeaDokumen10 halaman2016 Investigation of Chronic DiarrhoeaDanielaRojasBelum ada peringkat
- Klasifikasi Diare Pada AnakDokumen15 halamanKlasifikasi Diare Pada AnakTia UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Diarrhea in Adults and ChildrenDokumen30 halamanAcute Diarrhea in Adults and ChildrenM Isyhaduul IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013Dokumen9 halamanDiarrhea: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Politeknik Kesehatan Palembang Jurusan Keperawatan 2012-2013emmi_valentinaBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenteritis CausesDokumen6 halamanGastroenteritis CausesMikael AlmstrongBelum ada peringkat
- ColasDokumen2 halamanColasKhris Sy-HandumonBelum ada peringkat
- Healthtalkdiarrhoea 211002091117Dokumen8 halamanHealthtalkdiarrhoea 211002091117Dinesh Kumar SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study 2Dokumen52 halamanCase Study 2mejulBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea: DefinitionDokumen13 halamanDiarrhea: Definitionudaybujji100% (1)
- What Causes Diarrhea After EatingDokumen6 halamanWhat Causes Diarrhea After Eatingyushendra putraBelum ada peringkat
- AGE From NelsonDokumen9 halamanAGE From NelsonKristine Jade OdtujanBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenteritis Pregnancy July 2019Dokumen2 halamanGastroenteritis Pregnancy July 2019Tochukwu IgboanugoBelum ada peringkat
- Strointestinal / GastroenterologyDokumen6 halamanStrointestinal / GastroenterologyLeizel ApolonioBelum ada peringkat
- FINALDokumen36 halamanFINALSakshi GargBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenteritis HandoutDokumen5 halamanGastroenteritis HandoutAndrea Jane T GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea Written OutputDokumen5 halamanDiarrhea Written Outputrobertvaliente471Belum ada peringkat
- Viral Gastroenteritis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDokumen4 halamanViral Gastroenteritis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsMars TorrecampoBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Gastroenteritis in Children: Prepared By: Prof. Elizabeth D. Cruz RN, ManDokumen12 halamanAcute Gastroenteritis in Children: Prepared By: Prof. Elizabeth D. Cruz RN, ManChaii De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea Is One of The Most Common Health ComplaintsDokumen8 halamanDiarrhea Is One of The Most Common Health ComplaintsnurBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Clinical Types of Diarrhea: (Define) Pakidagdagan HeheDokumen4 halaman3 Clinical Types of Diarrhea: (Define) Pakidagdagan Hehekristelaaa guevarraBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic DiarrheaDokumen2 halamanChronic DiarrheasimbawulaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Final OutputDokumen42 halamanCase Study Final Outputroizen bagamaspadBelum ada peringkat
- Food Poisoning, (Gastroenteritis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandFood Poisoning, (Gastroenteritis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- What Your Doctor Didn't Tell You About Childhood Constipation: What Your Doctor Didn't Tell YouDari EverandWhat Your Doctor Didn't Tell You About Childhood Constipation: What Your Doctor Didn't Tell YouBelum ada peringkat
- Capital Expenditure Approval Process - CapEx FlowDokumen1 halamanCapital Expenditure Approval Process - CapEx Flowabdalballah1151Belum ada peringkat
- Advanced Product Quality Planning For New Product DevelopmentDokumen1 halamanAdvanced Product Quality Planning For New Product Developmentabdalballah1151Belum ada peringkat
- Hazard Analysis FormDokumen1 halamanHazard Analysis Formabdalballah1151Belum ada peringkat
- Hidden Dairy "Cheat Sheet": FromDokumen1 halamanHidden Dairy "Cheat Sheet": Fromabdalballah1151Belum ada peringkat
- Cornell Leadership Skills For Success: VisionaryDokumen2 halamanCornell Leadership Skills For Success: Visionaryabdalballah1151Belum ada peringkat
- General Informtion For Chemistry - :: Logarithm Hydrogen IonDokumen12 halamanGeneral Informtion For Chemistry - :: Logarithm Hydrogen Ionabdalballah1151Belum ada peringkat
- Acute Diarrhea in Children Thomas G. DeWittDokumen10 halamanAcute Diarrhea in Children Thomas G. DeWittabdalballah1151Belum ada peringkat
- Ways To Lead A Healthy LifeDokumen3 halamanWays To Lead A Healthy Lifesirthana697547Belum ada peringkat
- Sanitary PermitDokumen1 halamanSanitary PermitCPDOlucena100% (1)
- External MBR Vs Internal MBRDokumen8 halamanExternal MBR Vs Internal MBRwacsii ccasullaBelum ada peringkat
- Health and Safety Policy-BeremontDokumen3 halamanHealth and Safety Policy-BeremontAdibe ChukwudiBelum ada peringkat
- CDC - O&O - Single-Dose and Multi-Dose Vial InfographicDokumen6 halamanCDC - O&O - Single-Dose and Multi-Dose Vial Infographicrobin hasanBelum ada peringkat
- Indikasi SCDokumen11 halamanIndikasi SCLutfiAnny Rahman HakimBelum ada peringkat
- Form A - Checklist For Temporary Living Quarters in Factory/Office SpaceDokumen10 halamanForm A - Checklist For Temporary Living Quarters in Factory/Office SpaceWanping TangBelum ada peringkat
- Maternity and Women Chapter 21Dokumen7 halamanMaternity and Women Chapter 21Sam JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Pengetahuan, Sikap Dan Etika Batuk Pada Penderita Tuberkulosis ParuDokumen8 halamanPengetahuan, Sikap Dan Etika Batuk Pada Penderita Tuberkulosis ParuNurafni LativamcbBelum ada peringkat
- Case Analysis - DOH GP ProgramDokumen3 halamanCase Analysis - DOH GP ProgramRobxn GrciaBelum ada peringkat
- ABETDokumen9 halamanABETAndrea CoptoBelum ada peringkat
- Paracetamol Use With Bexsero: in Children Aged Under 2 YearsDokumen1 halamanParacetamol Use With Bexsero: in Children Aged Under 2 YearswindiBelum ada peringkat
- Water Treatment Plant PDFDokumen14 halamanWater Treatment Plant PDFArul Vanan100% (2)
- Food Fortification The Evidence, Ethics, and PoliticsDokumen276 halamanFood Fortification The Evidence, Ethics, and PoliticsSandor GOMBOSBelum ada peringkat
- Obesity in UK, Alexandra VelescuDokumen15 halamanObesity in UK, Alexandra VelescuGabriela AlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Safety On Accident Site:: Bloodborne Pathogen AwarenessDokumen69 halamanSafety On Accident Site:: Bloodborne Pathogen Awarenessdaily absurdBelum ada peringkat
- Msoga 1Dokumen73 halamanMsoga 1gabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes Week 8Dokumen17 halamanLecture Notes Week 8Kartik MuppirisettyBelum ada peringkat
- BHF CVD Statistics Global FactsheetDokumen12 halamanBHF CVD Statistics Global FactsheetRobby Paguh TariganBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan - Harga - Jual & No. RakDokumen22 halamanLaporan - Harga - Jual & No. RakVanny Swantika Minanda AlsiBelum ada peringkat
- Association Between Prenatal Smoking and Gestational Diabetes MellitusDokumen11 halamanAssociation Between Prenatal Smoking and Gestational Diabetes Mellitusนีล ไบรอันBelum ada peringkat
- COVID 19 Risk AssessmentDokumen3 halamanCOVID 19 Risk AssessmentMajaga MabhenaBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Exp4Dokumen7 halamanContoh Exp4Salsabila DindaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care of The Community CHP 1Dokumen26 halamanNursing Care of The Community CHP 1Hanwell Keith SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Icesu Updates Covid19 Confirmed Cases: Morbidity Week 13 January 1 - April 2, 2022Dokumen15 halamanIcesu Updates Covid19 Confirmed Cases: Morbidity Week 13 January 1 - April 2, 2022Jeremae VentarBelum ada peringkat
- Muguni Brandan ProposalDokumen31 halamanMuguni Brandan ProposalbonfaceBelum ada peringkat
- Accidents in ConstructionDokumen3 halamanAccidents in ConstructionmelvermoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Q3 EXAM MAPEH10 No Answer KeyDokumen5 halamanQ3 EXAM MAPEH10 No Answer KeyNivlem AyartBelum ada peringkat
- Health Care To Rural Population in Russian FederationDokumen8 halamanHealth Care To Rural Population in Russian FederationbrightagbotuiBelum ada peringkat
- Legionella - A Reemerging PathogenDokumen9 halamanLegionella - A Reemerging PathogenBam ManBelum ada peringkat