Guiding Flange Prosthesis For Early Management of Reconstructed Hemi Mandibulectomy - A Case Report
Diunggah oleh
IOSRjournalJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Guiding Flange Prosthesis For Early Management of Reconstructed Hemi Mandibulectomy - A Case Report
Diunggah oleh
IOSRjournalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
e-ISSN: 2279-0853, p-ISSN: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 8 Ver. I (Aug. 2015), PP 01-02
www.iosrjournals.org
Guiding flange prosthesis for early management of reconstructed
hemi mandibulectomy - a case report
Dr. M. Rajakumar1, Dr .C.Sabarigirinathan2, Dr K.Vinayagavel3,
Dr.P.Rupkumar4, Dr.G.Sriramaprabu5, Dr. T. Jeyanthikumari6,
6
Dr.S.Vinayakam7, Dr.V.Parimala8, Dr J.Gandhimathy9
1, 4, 5
Associate Professor, 2 Professor and HOD, 3 Professor, 6,7. 8,9 Senior Assistant Professor Department of
Prosthodontics, Tamilnadu Government Dental College & Hospital, Chennai.
Abstract: Ameloblastoma is a locally aggressive tumor commonly arising from the Mandibular Surgical
resection of the neoplasm is the treatment of choice1. Mandibular resection and resulting loss of mandibular
continuity is inevitable in such cases. Mandibular deviation towards the defective side results in loss of
masticatory function, defective control of salivary secretions and disfigurement of face. Mandibular Guiding
prosthesis helps the patient to achieve normal occlusion of teeth2. This case report describes simple mandibular
Guiding flange prosthesis for a patient with a hemi mandibulectomy defect to restore function.
Keywords - Guidingflange Prosthesis, Ameloblstoma, Mandibular deviation
I.
Introduction
Ameloblastoma is a commonly occurring odentogenic tumour in mandible. The treatment for
ameloblastoma is the surgical resection of involved portion of mandible. As a result of this, loss of mandibular
continuity causes deviation of the mandible towards the resection side, rotation of mandible inferiorly and
inability of patient to stabilize the occlusion. Guidingflange prosthesis is a conventional management for the
patient to achieve mediolateral position of the mandible.4
II.
Case Report
A 42year old male patient was referred to the department of prosthodontics for management after
hemimandibular resection. Patient history revealed that hemimandibular resection was carried out following
diagnosis of ameloblastoma in right side mandible. No reconstructive procedure during surgery.
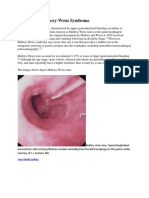
Intraoral examination revealed thick buccal mucosa with mucosa scar formation and obliteration of
alveolar ridge buccal and lingual sulcus in the region of defect. Mouth opening restricted. The mandible deviates
to the resection side and rotation of mandible inferiorly. Centric occlusion does not exist. Midline shift is present
when the patient in occlusion position .He is not able to close the mandible in occlusion and also not able to
control dropping of saliva.
A decision was made to fabricate Guiding flange prosthesis to with wrought wire clasps and
substructure and acrylic resin guide flange prosthesis ,Primary impression of maxillary and mandiblular arches
were obtained using perforated stainless steel impression trays with irreversible hydrocolloid . The cast were
made by using type IV dental stone. The bite block was done by using modeling wax, bite registration done and
mounted on a mean value articulator with type II dental plaster. Teeth selection was made on the basis of age,
color and sex of the patient and wax trail was done. A 21 gauge stainless steel wire was manipulated between
33, 35 to produced retention of the denture. The Guiding prosthesis was fabricated by using acrylic resin, where
the buccal flange was extended between 34 to 36 and the height extended up to buccal sulcus of the maxilla
between 24 to 26.
DOI: 10.9790/0853-14810102
www.iosrjournals.org
1 | Page
Guiding flange prosthesis for early management of reconstructed hemi mandibulectomy
Guiding flange was tried in patients mouth and the initial stability and retention was checked.The
inclination of the Guiding flange was adjusted by selective trimming the teeth contacting surface and adding self
cure acrylic resin. The Guiding flange surface was created intraorally to guide the mandible in a definite
occlusion. The flange height was altered that it guided the Mandible from opening position to maximum
intercuspation in a smooth and unhindered path. The Guidingprosthesis was delivered and post insertion
instructions were given
III.
Conclusion
Depending upon the location and extent of the tumour in the mandible various surgical treatment
modalities like marginal, segmental, hemi, subtotal or total mandibulectomy can be done. Due to loss of
mandibular continuity, causes deviation towards the defect side and rotation of the mandibule on the defect
occurs. Vertical extention from the buccal aspects of a mandibular prosthesis extends to contact the buccal
surface of the opposing maxillary arch. This extention maintains the mandible in proper mediolateral position
for vertical chewing it is usually recommended to improve both facial asymmetry and masticatory
During this initial healing period early prosthodontic intervention by mandibular Guidingflange serves
the purpose of managing the mandibular deviation, preventing inferior rotation of mandible and improving the
masticatory efficiency.
References
[1].
[2].
[3].
[4].
[5].
Shafer wg ,hine mk,LEVY Bo TOMICH CE, a textbook of oral pathology ,4 th ed philadelphia: w.B saunders 1993 pp 86-229
Aramany MA,Myers EN. Intermaxillary Fixatation following Mandibular resection J prosthet dent 1977:37:437-444
Beumer iii j. Marunick MT,Esposito SJ Maxillofacial rehabilitation,3 rd ed,2011,Quintessence page87-89,118-120
Curtis TA TAYLOR RC, Rositano SA, physical in obtaining records of the maxillofacial patients J prosthet dent 1975:34:539-554
Prakash v prosthetic rehabilitation of edentulous mandibulectomy Indian j dent res2008:19:257-260
DOI: 10.9790/0853-14810102
www.iosrjournals.org
2 | Page
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Socio-Ethical Impact of Turkish Dramas On Educated Females of Gujranwala-PakistanDokumen7 halamanSocio-Ethical Impact of Turkish Dramas On Educated Females of Gujranwala-PakistanInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- A Review of Rural Local Government System in Zimbabwe From 1980 To 2014Dokumen15 halamanA Review of Rural Local Government System in Zimbabwe From 1980 To 2014International Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- The Role of Extrovert and Introvert Personality in Second Language AcquisitionDokumen6 halamanThe Role of Extrovert and Introvert Personality in Second Language AcquisitionInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- "I Am Not Gay Says A Gay Christian." A Qualitative Study On Beliefs and Prejudices of Christians Towards Homosexuality in ZimbabweDokumen5 halaman"I Am Not Gay Says A Gay Christian." A Qualitative Study On Beliefs and Prejudices of Christians Towards Homosexuality in ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Attitude and Perceptions of University Students in Zimbabwe Towards HomosexualityDokumen5 halamanAttitude and Perceptions of University Students in Zimbabwe Towards HomosexualityInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- A Proposed Framework On Working With Parents of Children With Special Needs in SingaporeDokumen7 halamanA Proposed Framework On Working With Parents of Children With Special Needs in SingaporeInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Technologies On Society: A ReviewDokumen5 halamanThe Impact of Technologies On Society: A ReviewInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)100% (1)
- Relationship Between Social Support and Self-Esteem of Adolescent GirlsDokumen5 halamanRelationship Between Social Support and Self-Esteem of Adolescent GirlsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Investigation of Unbelief and Faith in The Islam According To The Statement, Mr. Ahmed MoftizadehDokumen4 halamanInvestigation of Unbelief and Faith in The Islam According To The Statement, Mr. Ahmed MoftizadehInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment of The Implementation of Federal Character in Nigeria.Dokumen5 halamanAssessment of The Implementation of Federal Character in Nigeria.International Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- An Evaluation of Lowell's Poem "The Quaker Graveyard in Nantucket" As A Pastoral ElegyDokumen14 halamanAn Evaluation of Lowell's Poem "The Quaker Graveyard in Nantucket" As A Pastoral ElegyInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Edward Albee and His Mother Characters: An Analysis of Selected PlaysDokumen5 halamanEdward Albee and His Mother Characters: An Analysis of Selected PlaysInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Comparative Visual Analysis of Symbolic and Illegible Indus Valley Script With Other LanguagesDokumen7 halamanComparative Visual Analysis of Symbolic and Illegible Indus Valley Script With Other LanguagesInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Importance of Mass Media in Communicating Health Messages: An AnalysisDokumen6 halamanImportance of Mass Media in Communicating Health Messages: An AnalysisInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Topic: Using Wiki To Improve Students' Academic Writing in English Collaboratively: A Case Study On Undergraduate Students in BangladeshDokumen7 halamanTopic: Using Wiki To Improve Students' Academic Writing in English Collaboratively: A Case Study On Undergraduate Students in BangladeshInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Women Empowerment Through Open and Distance Learning in ZimbabweDokumen8 halamanWomen Empowerment Through Open and Distance Learning in ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Human Rights and Dalits: Different Strands in The DiscourseDokumen5 halamanHuman Rights and Dalits: Different Strands in The DiscourseInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Classical Malay's Anthropomorphemic Metaphors in Essay of Hikajat AbdullahDokumen9 halamanClassical Malay's Anthropomorphemic Metaphors in Essay of Hikajat AbdullahInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- The Lute Against Doping in SportDokumen5 halamanThe Lute Against Doping in SportInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Role of Madarsa Education in Empowerment of Muslims in IndiaDokumen6 halamanRole of Madarsa Education in Empowerment of Muslims in IndiaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Beowulf: A Folktale and History of Anglo-Saxon Life and CivilizationDokumen3 halamanBeowulf: A Folktale and History of Anglo-Saxon Life and CivilizationInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Transforming People's Livelihoods Through Land Reform in A1 Resettlement Areas in Goromonzi District in ZimbabweDokumen9 halamanTransforming People's Livelihoods Through Land Reform in A1 Resettlement Areas in Goromonzi District in ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Designing of Indo-Western Garments Influenced From Different Indian Classical Dance CostumesDokumen5 halamanDesigning of Indo-Western Garments Influenced From Different Indian Classical Dance CostumesIOSRjournalBelum ada peringkat
- Substance Use and Abuse Among Offenders Under Probation Supervision in Limuru Probation Station, KenyaDokumen11 halamanSubstance Use and Abuse Among Offenders Under Probation Supervision in Limuru Probation Station, KenyaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- An Exploration On The Relationship Among Learners' Autonomy, Language Learning Strategies and Big-Five Personality TraitsDokumen6 halamanAn Exploration On The Relationship Among Learners' Autonomy, Language Learning Strategies and Big-Five Personality TraitsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Motivational Factors Influencing Littering in Harare's Central Business District (CBD), ZimbabweDokumen8 halamanMotivational Factors Influencing Littering in Harare's Central Business District (CBD), ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- A Study On The Television Programmes Popularity Among Chennai Urban WomenDokumen7 halamanA Study On The Television Programmes Popularity Among Chennai Urban WomenInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Micro Finance and Women - A Case Study of Villages Around Alibaug, District-Raigad, Maharashtra, IndiaDokumen3 halamanMicro Finance and Women - A Case Study of Villages Around Alibaug, District-Raigad, Maharashtra, IndiaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Kinesics, Haptics and Proxemics: Aspects of Non - Verbal CommunicationDokumen6 halamanKinesics, Haptics and Proxemics: Aspects of Non - Verbal CommunicationInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Design Management, A Business Tools' Package of Corporate Organizations: Bangladesh ContextDokumen6 halamanDesign Management, A Business Tools' Package of Corporate Organizations: Bangladesh ContextInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Overview of MalloryDokumen10 halamanOverview of MalloryVivi Maulidatul AzizahBelum ada peringkat
- Coronary Artery Disease-Willerson 2015-Pg 228-254Dokumen27 halamanCoronary Artery Disease-Willerson 2015-Pg 228-254Muthu KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Sandeep 35y M 20240328 Report 1Dokumen2 halamanSandeep 35y M 20240328 Report 1rishabmohitkiidBelum ada peringkat
- International Patient Safety Goals PDFDokumen36 halamanInternational Patient Safety Goals PDFHarsya Parma PhastikaBelum ada peringkat
- Format For Manuscript Submission: ReviewDokumen26 halamanFormat For Manuscript Submission: ReviewMariaBelum ada peringkat
- Central Venous Line CareDokumen13 halamanCentral Venous Line CarePaul Henry RoxasBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Equipment List: For Cataract SurgeryDokumen10 halamanEssential Equipment List: For Cataract SurgeryAditya Angga DharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Corticotomy For Orthodontic Tooth MovementDokumen8 halamanCorticotomy For Orthodontic Tooth MovementGissellePantojaBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthetic Drugs Cheat SheetsDokumen2 halamanAnaesthetic Drugs Cheat SheetsPkern100% (3)
- Critical Care NursingDokumen10 halamanCritical Care Nursingianecunar100% (10)
- PIIS0889540612002740Dokumen13 halamanPIIS0889540612002740Aly OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Infections Associated With Surgical ImplantsDokumen8 halamanTreatment of Infections Associated With Surgical ImplantsDiego Bedón AscurraBelum ada peringkat
- Suture Anchor Fixation For Scaphoid Nonunions With Small Proximal Fragments - Report of 11 CasesDokumen6 halamanSuture Anchor Fixation For Scaphoid Nonunions With Small Proximal Fragments - Report of 11 CasesLUIS SALVADOR FLORESBelum ada peringkat
- 220200320sathiya PrakashDokumen95 halaman220200320sathiya Prakashpriya selvaraj100% (1)
- Patelpriya InterventionalresumeuncDokumen2 halamanPatelpriya Interventionalresumeuncapi-356366193Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomia de Puntos Craneometricos PDFDokumen35 halamanAnatomia de Puntos Craneometricos PDFAlberto SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Periosteal Pocket Flap Technique. A Comparative StudyDokumen10 halamanPeriosteal Pocket Flap Technique. A Comparative StudyosiglesiBelum ada peringkat
- Topographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisDokumen11 halamanTopographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisJohn NinBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)Dokumen7 halamanBasic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)Rizki YuliantoBelum ada peringkat
- Retromuscular Repairs For Ventral HerniaDokumen76 halamanRetromuscular Repairs For Ventral HerniaROUNAK MEHROTRABelum ada peringkat
- Ophthalmology For The Veterinary Practitioner - Revised and ExpandedDokumen272 halamanOphthalmology For The Veterinary Practitioner - Revised and ExpandedJulia Martinez PottierBelum ada peringkat
- Olympus Largest Business Domain: From Early Diagnosis To Minimally Invasive TherapyDokumen2 halamanOlympus Largest Business Domain: From Early Diagnosis To Minimally Invasive TherapyЭнхЗаяаBelum ada peringkat
- MedetomidineDokumen4 halamanMedetomidineHanifa Agus SetyawanBelum ada peringkat
- Extirpation of Eye - DoxcDokumen2 halamanExtirpation of Eye - Doxckushal NeupaneBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Cardiovascular Disease and MedicineDokumen5 halamanJournal of Cardiovascular Disease and MedicineMarci Z. FultsBelum ada peringkat
- Amniocentesis ProcedureDokumen6 halamanAmniocentesis ProcedureswetaBelum ada peringkat
- JD Fs Papilla Preservation FlapDokumen7 halamanJD Fs Papilla Preservation FlapReshmaa RajendranBelum ada peringkat
- 38 AnswersDokumen8 halaman38 AnswersJasmine Nicole EnriquezBelum ada peringkat
- Male Genitals and Inguinal AreaDokumen33 halamanMale Genitals and Inguinal AreabianqueeBelum ada peringkat
- Motatility ReviewDokumen68 halamanMotatility Reviewndifor bonnyBelum ada peringkat