Chapter 1 Revision
Diunggah oleh
sadyehHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 1 Revision
Diunggah oleh
sadyehHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
Chapter 1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
1. Define the following and in each case give two examples:
(a) base quantity; (b) base unit; (c) derived quantity; (d) derived unit
2. Give four further examples of a base quantity beyond those you gave in Q1(a).
3. What type of quantities are these? Derived quantity or base quantity ?
Period
Energy
Power
Current
Frequency
Resistance
4. Put these derived units into BASE units Joule, Watt, Volt, Ohm.
Hint : Joule is the unit for work done, WORK DONE = Force X Distance
Watt is the unit for power, POWER = Work done Time
Volt is the unit for potential difference, P.d = Work done Charge
Ohm is the unit for resistance, RESISTANCE = P.dCurrent
5. An equation is said to be homogeneous. What does homogeneous mean?
4. What are the base units of ; work, pressure, frequency?
5. What are the units of constant k in this equation ?
Force = k X density X velocity 2
6. Show whether this equation is HOMOGENOUS.
Period = 4 X mass
Acceleration
7. (a) What is the difference between a vector and a scalar?
(b) State whether the following are vectors or scalars:
force
momentum
distance
Kinetic energy
Copyright Reserved2015
Potential energy
work
displacement
mass
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
speed
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
8. Calculate:
(a) the vertical and horizontal components of a force of 50N that acts at an angle of 30o
upwards
from the horizontal.
(b) the resultant of two velocities if one is 5m/s north and the other 8m/s east.
9.
10.
11.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
12.
13. (a) State what is meant by an equation is homogeneous with respect to its units.
(b) Show that the equation x = ut + at2 is homogeneous with respect to its units.
(c) Explain why an equation may be homogeneous with respect to its units but still be
incorrect.
14. (a) A candidate in a physics examination has worked out a formula for the kinetic energy, E
of a solid sphere spinning about its axis. His formula is
1 2 2
2
where is the density of the sphere, r is its radius and f is the rotation frequency. Show
that this formula is homogeneous with respect to base units.
=
(b)
Why might the formula still be incorrect?
15. Complete the following equations by writing the correct physical quantities, in words, on the
dotted lines.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
16. (a) Many physical quantities are defined from two other physical quantities. The
diagram shows how a number of different quantities are defined by either multiplying
or dividing two other quantities. Write correct quantities in the two blank ellipses
below.
(b) Explain what is special about the physical quantities in the shaded ellipses.
17. (a) The diagram shows two forces acting on a body.
(a) On the grid (next page) draw a scale diagram to determine the resultant force acting on
the body. Use a scale of 1 cm to 1 N.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
(b) State the magnitude of the resultant force.
(c) What name is given to physical quantities which add by the same rule as forces?
(d) Name two other examples of such physical quantities.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
18. Listed below are six physical quantities:
energy
force
moment
momentum
power
velocity
Hint : Moment = Force X Displacement
Select from this list the quantity or quantities fitting each description below. You
may use each quantity once, more than once or not at all.
(i)
A quantity which can be measured in newton second (N s).
(ii)
A quantity which equals the rate of change of another quantity in the list.
(iii)
A quantity which equals the product of two other quantities in the list.
(iv)
A quantity with base units kg m2 s3.
(v)
Two quantities which have the same base units.
19. Complete the table to show the missing physical quantity for each unit.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
20. Name the physical quantity represented by the area under each of the following graphs. Give
your answers in the table below.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
21. What physical quantity does the gradient of each of the following graphs represent? Give
your answers in the table below the graphs.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
22.
23. A microphone has a weight W of 6.0 N. It is suspended by wire X from the ceiling in a radio
studio. Fig. 1.1 shows the microphone held in the correct position by a horizontal wire Y.
The tension T in wire Y is 8.0 N. Use a vector diagram to determine the magnitude and
the direction of the resultant of W and T.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
24. A student studies some equations.
power
= work / time
force
= mass acceleration
velocity
= displacement / time
How many vector quantities are contained in the equations?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
25.
26.
27.
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
10
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
28.
29.
30.
Write the value and symbols of the following prefixes :
Prefix
Value
Symbol
tera
nano
giga
deci
centi
31.
Write the following physical quantities using the suggested standard prefix.
(i) Wavelength of light
= 0.000 000 55 m = .. nm
(ii) Radio wave frequency = 91 000 000 Hz
Copyright Reserved2015
= MHz
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
11
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
32. State if each of the following physical quantities is a scalar quantity or a vector quantity.
(i)
Temperature
:______________________
(ii)
Force
: _____________________
(ii)
Electric current
: _____________________
(iii)
Momentum
: ______________________
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
12
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
ans:
q13
q14
q18
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
13
Chap1 : Physical Quantities & Unit (REVISION)
q23
Copyright Reserved2015
by : Mr Sathya Seelan(0103775698)
14
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 5: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #5Dari EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 5: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #5Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Physical World and Measurement by Er Rammohan MudgalDokumen9 halamanChapter 1 Physical World and Measurement by Er Rammohan MudgalRammohan MudgalBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 11 Word.Dokumen23 halamanPhysics 11 Word.Michael John C UrpianoBelum ada peringkat
- Physical World and Measurement: Fundamental Quantities Are Raised To Represent That Physical QuantityDokumen9 halamanPhysical World and Measurement: Fundamental Quantities Are Raised To Represent That Physical QuantityFull Masti and EntertainmentBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Study Material For Class Xi PDFDokumen208 halamanPhysics Study Material For Class Xi PDFAbhishek UpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- Grade XI - Phys. T2 Ans KeyDokumen7 halamanGrade XI - Phys. T2 Ans Keyrohan fernandesBelum ada peringkat
- Physic Xi 2011Dokumen230 halamanPhysic Xi 2011Ashok PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge International As and A Level Physics Revision Guide Cambridge Education Cambridge Uni SamplesDokumen5 halamanCambridge International As and A Level Physics Revision Guide Cambridge Education Cambridge Uni SamplesNalaka Abeysekera50% (6)
- FORM TP 21228: Caribbean Examinations Counci Advanced Proficiency Examination Physics UNIT 02 - Paper 0LDokumen18 halamanFORM TP 21228: Caribbean Examinations Counci Advanced Proficiency Examination Physics UNIT 02 - Paper 0LRaymond ScottBelum ada peringkat
- Important Question For Annual ExamDokumen4 halamanImportant Question For Annual Examallen77georgesBelum ada peringkat
- MIT8 04S13 ps9Dokumen5 halamanMIT8 04S13 ps9Yul LopeBelum ada peringkat
- TAN Activity2 Section5.1Dokumen16 halamanTAN Activity2 Section5.1ceferinotanBelum ada peringkat
- 1973 - Journal of Structural Mechanics - 1 - 497-518 - WITTRICKW-An Algorithm For Computing Critical Buckling Loads of Elastic StructuresDokumen23 halaman1973 - Journal of Structural Mechanics - 1 - 497-518 - WITTRICKW-An Algorithm For Computing Critical Buckling Loads of Elastic StructuresZhangJiayongBelum ada peringkat
- Physics AssignmentDokumen17 halamanPhysics AssignmentAadrija PaullBelum ada peringkat
- Switching Power Supplies:: Analysis of Waveform Distortion and Absorbed PowersDokumen6 halamanSwitching Power Supplies:: Analysis of Waveform Distortion and Absorbed PowersRaj ChavanBelum ada peringkat
- Vedcpast Exams Additional Questions-SolvedDokumen14 halamanVedcpast Exams Additional Questions-Solvedapi-202182511Belum ada peringkat
- H2 Measurement 2012Dokumen21 halamanH2 Measurement 2012Ronnie QuekBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Lab5 TheveninDokumen5 halaman3 Lab5 TheveninBrett HendricksBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On StaticsDokumen121 halamanLecture Notes On StaticsМарко Шилобод75% (4)
- 01-ES202 - Topic1Dokumen18 halaman01-ES202 - Topic1Moguri OwowBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Topic 1Dokumen5 halamanTutorial Topic 1Suraya SariBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On StaticsDokumen121 halamanLecture Notes On StaticsAhmet BenliBelum ada peringkat
- Steven Miller and Jonathan Tennyson - First Principles Calculation of The Molecular Constants of H3 +, H2D +, D2H + and D3 +Dokumen10 halamanSteven Miller and Jonathan Tennyson - First Principles Calculation of The Molecular Constants of H3 +, H2D +, D2H + and D3 +TreaxmeABelum ada peringkat
- Physics NotesDokumen34 halamanPhysics NotesWeipeng LumBelum ada peringkat
- Ustani Jee 1ST Year Physics Preparation Paper 2024-2Dokumen12 halamanUstani Jee 1ST Year Physics Preparation Paper 2024-2ismailmaster62Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1A (Engineering Science)Dokumen5 halamanTutorial 1A (Engineering Science)Niveshini SuntharBelum ada peringkat
- د - سفيان فاضل -مبادئ هندسة كيمياوية1-مرحلة اولىDokumen74 halamanد - سفيان فاضل -مبادئ هندسة كيمياوية1-مرحلة اولىAbdla DoskiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Circuit Variables Study Guide: ObjectivesDokumen3 halamanChapter 1 - Circuit Variables Study Guide: ObjectivesRalph SomersBelum ada peringkat
- BPhO 2014 - 15 - A2 Challenge 2014Dokumen8 halamanBPhO 2014 - 15 - A2 Challenge 2014Mohar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- الميكانيك الهندسيDokumen175 halamanالميكانيك الهندسيkraralbsyrawyBelum ada peringkat
- SpecSimVR MEGDokumen6 halamanSpecSimVR MEGMatthew GarnerBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Activity 2Dokumen12 halamanLaboratory Activity 2Johaira Maute100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDokumen37 halamanChapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsTutor_KLBelum ada peringkat
- Tos III Lesson 3Dokumen18 halamanTos III Lesson 3Kendi KoomeBelum ada peringkat
- Section 1. 0 Physical Quantities and UnitsDokumen140 halamanSection 1. 0 Physical Quantities and Unitsgarikaishumba2005Belum ada peringkat
- ExamDokumen12 halamanExamapi-312236075Belum ada peringkat
- Physical World: Year 10 Science Common Assessment Task 2011Dokumen11 halamanPhysical World: Year 10 Science Common Assessment Task 2011Aimee Ta G LeBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Student'sDokumen10 halamanForm 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Student'sPavithiranBelum ada peringkat
- محاضرة مبادئ الهندسة الكيمياوية PDFDokumen121 halamanمحاضرة مبادئ الهندسة الكيمياوية PDFKING of DARKNESSBelum ada peringkat
- Force in A Statically Indeterminate Cantilever TrussDokumen7 halamanForce in A Statically Indeterminate Cantilever TrussOlivia Sim0% (1)
- Expt. No.7-Series Circuit (Manual and Tabulation)Dokumen3 halamanExpt. No.7-Series Circuit (Manual and Tabulation)Ryan S. BudionganBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Lab ManualDokumen17 halamanCivil Lab ManualShakil KhanBelum ada peringkat
- M-Power Iit and Neet Academy: MV MGHDokumen9 halamanM-Power Iit and Neet Academy: MV MGHVenu GopalBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 F16 CVL313 PDFDokumen25 halamanLecture 3 F16 CVL313 PDFAndres De CamposBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Coursework EdexcelDokumen4 halamanPhysics Coursework Edexcelbcrqs9hr100% (2)
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureDari EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11Dari EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11Belum ada peringkat
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 4: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #4Dari EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 4: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #4Belum ada peringkat
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2Dari EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2Belum ada peringkat
- Barron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewDari EverandBarron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewBelum ada peringkat
- Formula List ProgressionDokumen1 halamanFormula List ProgressionsadyehBelum ada peringkat
- 170S1Dokumen22 halaman170S1sadyeh100% (1)
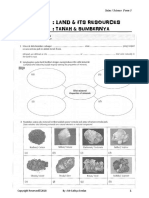
- Chapter 6: Land & Its Resources: Bab 6: Tanah & SumbernyaDokumen13 halamanChapter 6: Land & Its Resources: Bab 6: Tanah & SumbernyasadyehBelum ada peringkat
- NO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan JawapanDokumen1 halamanNO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan Jawapan NO. Soalan JawapansadyehBelum ada peringkat
- EXERCISE CHAPTER 6: Land & Its Resources: Latihan Bab 6: Tanah & SumbernyaDokumen20 halamanEXERCISE CHAPTER 6: Land & Its Resources: Latihan Bab 6: Tanah & SumbernyasadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Formula List ProgressionDokumen1 halamanFormula List ProgressionyindichonBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 1 - Bab 1-5 - Ting 2Dokumen20 halamanModul 1 - Bab 1-5 - Ting 2sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- QuadraticDokumen22 halamanQuadraticsadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 2.2Dokumen14 halamanModul 2.2sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Preservation & Conservationof Environment: By: MR Sathya SeelanDokumen26 halamanChapter 3: Preservation & Conservationof Environment: By: MR Sathya SeelansadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Microorganisms & Their Effects On Living Things: Science Form 5Dokumen14 halamanMicroorganisms & Their Effects On Living Things: Science Form 5sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 The Importance of Nutrition & Good Eating HabitsDokumen22 halaman2.1 The Importance of Nutrition & Good Eating HabitssadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 2.3Dokumen10 halamanModul 2.3sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise Chapter 4: Reproduction (Part 1) : Latihan Bab 4: Pembiakan (BHG 1)Dokumen20 halamanExercise Chapter 4: Reproduction (Part 1) : Latihan Bab 4: Pembiakan (BHG 1)sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Ujian Bab 2Dokumen21 halamanUjian Bab 2sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Nota Bab 4 - Part 1Dokumen16 halamanNota Bab 4 - Part 1sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Ujian Bab 3Dokumen12 halamanUjian Bab 3sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3: Perkumuhan: Sains/Science Form 3Dokumen4 halamanBab 3: Perkumuhan: Sains/Science Form 3sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Dokumen6 halamanChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925Belum ada peringkat
- Exercise Chapter 4: Reproduction (Part 2) : Latihan Bab 4: Pembiakan (BHG 2)Dokumen12 halamanExercise Chapter 4: Reproduction (Part 2) : Latihan Bab 4: Pembiakan (BHG 2)sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Sains / Science Form 3: By: MR Sathya SeelanDokumen5 halamanSains / Science Form 3: By: MR Sathya SeelansadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Nota - Bab 2Dokumen11 halamanNota - Bab 2sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Bab 3Dokumen19 halamanLatihan Bab 3sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Bab 2Dokumen19 halamanLatihan Bab 2sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Form 5: By: MR Sathya Seelan 1Dokumen12 halamanMathematics Form 5: By: MR Sathya Seelan 1sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Analisis 2017Dokumen5 halamanAnalisis 2017sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Science / Sains Form 3 Chapter 1: Respiration (Respirasi) : By: MR Sathya Seelan 1Dokumen7 halamanScience / Sains Form 3 Chapter 1: Respiration (Respirasi) : By: MR Sathya Seelan 1sadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Test 1: Home Tuition With Tutor SathyaDokumen9 halamanDiagnostic Test 1: Home Tuition With Tutor SathyasadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Topics & ImportanceDokumen1 halamanTopics & ImportancesadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Pusat Tuisyen Meka Bestari & Indera: Bab 3: Daya & Tekanan Chapter 3: Force & PressureDokumen11 halamanPusat Tuisyen Meka Bestari & Indera: Bab 3: Daya & Tekanan Chapter 3: Force & PressuresadyehBelum ada peringkat
- Grand Canonical EnsembleDokumen10 halamanGrand Canonical EnsembleDanny WebbBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Behavior of Materials - I - Meyers PDFDokumen684 halamanDynamic Behavior of Materials - I - Meyers PDFAamir RazaBelum ada peringkat
- ASBMB Science Book List: Title Author Publisher IsbnDokumen4 halamanASBMB Science Book List: Title Author Publisher IsbnjitendramataBelum ada peringkat
- Colloidal DispersionDokumen5 halamanColloidal DispersionCarlo HafallaBelum ada peringkat
- SurgeProtectionforACMachinery PrintDokumen8 halamanSurgeProtectionforACMachinery PrintAldy R OpccBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Reaction ReviewDokumen3 halamanNuclear Reaction ReviewSeyi Martins ObandoBelum ada peringkat
- L-1 Introduction To MechanicsDokumen10 halamanL-1 Introduction To Mechanicspinku kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Mis Ce2201Dokumen2 halamanMis Ce2201Ashan ShamikaBelum ada peringkat
- Science 7 Third Quarter ExamDokumen7 halamanScience 7 Third Quarter ExamKenny Ann Grace Batiancila100% (1)
- Thermistor 50KDokumen2 halamanThermistor 50Kfredjbps@gmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- Profile LevelingDokumen3 halamanProfile LevelingShealtiel Regine Cinco-AyalaBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Harmonic MotionDokumen4 halamanSimple Harmonic MotionNuyara VithanageBelum ada peringkat
- Mock Board Examination Licensure Examination For Chemical Engineers (April 2006) Subject: Chemical EngineeringDokumen4 halamanMock Board Examination Licensure Examination For Chemical Engineers (April 2006) Subject: Chemical EngineeringMinnie InarapmasBelum ada peringkat
- sm1 014Dokumen2 halamansm1 014Paulo Henrique D. FavarettoBelum ada peringkat
- 004-The Stability of A Floating BodyDokumen10 halaman004-The Stability of A Floating BodyHafizah Fadil100% (1)
- Robotics Sensors N Transducers AcckDokumen5 halamanRobotics Sensors N Transducers AcckSumixam AureliusBelum ada peringkat
- Stiffness Matrix Based Form-Finding Method of Tensegrity Structures-Zhang & Liyuan 2014Dokumen14 halamanStiffness Matrix Based Form-Finding Method of Tensegrity Structures-Zhang & Liyuan 2014Angel SullyvanBelum ada peringkat
- Horizontally Connected High-Rise Buildings Under Earthquake LoadingsDokumen15 halamanHorizontally Connected High-Rise Buildings Under Earthquake LoadingsMaulana Nur IkhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Ferranti EffectDokumen2 halamanFerranti EffectVaibhav Singh RajputBelum ada peringkat
- Vapor Liquid Equilibrium Densities and Interfacial Tensions For The System Benzene Propan 1 OlDokumen17 halamanVapor Liquid Equilibrium Densities and Interfacial Tensions For The System Benzene Propan 1 OlLorena AgudeloBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Pom - Sem 1Dokumen21 halamanChapter 1 - Pom - Sem 1Ami MorakhiaBelum ada peringkat
- UnificationDokumen318 halamanUnificationoperationmanagerBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Worksheet On MotionDokumen2 halamanRevision Worksheet On Motionsohil khattarBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions # 8: Department of Physics IIT Kanpur, Semester II, 2022-23Dokumen9 halamanSolutions # 8: Department of Physics IIT Kanpur, Semester II, 2022-23darshan sethiaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual of Basic Air Flow BenchDokumen24 halamanManual of Basic Air Flow BenchPung Kang Qin100% (1)
- Measurement of Yield Stress of Cement Pastes Using The Direct Shear TestDokumen10 halamanMeasurement of Yield Stress of Cement Pastes Using The Direct Shear TestAlbert PontusBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 - III - SummativeDokumen3 halamanGrade 8 - III - Summativemenchie ismael100% (4)
- MRI PrinciplesDokumen140 halamanMRI PrinciplesRuth CohlerBelum ada peringkat
- Course Outline SPH4UDokumen6 halamanCourse Outline SPH4UKaXin CheahBelum ada peringkat
- A New Phase in ND, Fe,,B Magnets. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of ND, Fe,,SiDokumen7 halamanA New Phase in ND, Fe,,B Magnets. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of ND, Fe,,SiAlberto JimenezBelum ada peringkat