9-) Simple Conduction Example PDF
Diunggah oleh
scs1720Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
9-) Simple Conduction Example PDF
Diunggah oleh
scs1720Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/Conduction/Conduction....
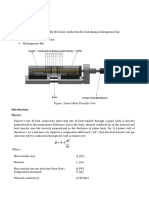
Simple Conduction Example
Introduction
This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple conduction problem.
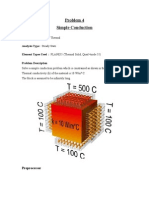
The Simple Conduction Example is constrained as shown in the following figure. Thermal conductivity (k) of
the material is 10 W/m*C and the block is assumed to be infinitely long.
Preprocessing: Defining the Problem
1. Give example a Title
2. Create geometry
Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Areas > Rectangle > By 2 Corners > X=0, Y=0, Width=1,
Height=1
BLC4,0,0,1,1
3. Define the Type of Element
Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/Delete... > click 'Add' > Select Thermal Solid, Quad
4Node 55
ET,1,PLANE55
Copyright 2001 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/Conduction/Conduction....
For this example, we will use PLANE55 (Thermal Solid, Quad 4node 55). This element has 4 nodes and
a single DOF (temperature) at each node. PLANE55 can only be used for 2 dimensional steady-state or
transient thermal analysis.
4. Element Material Properties
Preprocessor > Material Props > Material Models > Thermal > Conductivity > Isotropic > KXX =
10 (Thermal conductivity)
MP,KXX,1,10
5. Mesh Size
Preprocessor > Meshing > Size Cntrls > ManualSize > Areas > All Areas > 0.05
AESIZE,ALL,0.05
6. Mesh
Preprocessor > Meshing > Mesh > Areas > Free > Pick All
AMESH,ALL
Solution Phase: Assigning Loads and Solving
1. Define Analysis Type
Solution > Analysis Type > New Analysis > Steady-State
ANTYPE,0
2. Apply Constraints
For thermal problems, constraints can be in the form of Temperature, Heat Flow, Convection, Heat Flux,
Heat Generation, or Radiation. In this example, all 4 sides of the block have fixed temperatures.
{
Solution > Define Loads > Apply
Note that all of the -Structural- options cannot be selected. This is due to the type of element
(PLANE55) selected.
Thermal > Temperature > On Nodes
Click the Box option (shown below) and draw a box around the nodes on the top line.
Copyright 2001 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/Conduction/Conduction....
The following window will appear:
Fill the window in as shown to constrain the side to a constant temperature of 500
Using the same method, constrain the remaining 3 sides to a constant value of 100
Orange triangles in the graphics window indicate the temperature contraints.
3. Solve the System
Solution > Solve > Current LS
SOLVE
Copyright 2001 University of Alberta
University of Alberta ANSYS Tutorials - www.mece.ualberta.ca/tutorials/ansys/IT/Conduction/Conduction....
Postprocessing: Viewing the Results
1. Results Using ANSYS
Plot Temperature
General Postproc > Plot Results > Contour Plot > Nodal Solu ... > DOF solution, Temperature
TEMP
Note that due to the manner in which the boundary contitions were applied, the top corners are held at a
temperature of 100. Recall that the nodes on the top of the plate were constrained first, followed by the
side and bottom constraints. The top corner nodes were therefore first constrained at 500C, then
'overwritten' when the side constraints were applied. Decreasing the mesh size can minimize this effect,
however, one must be aware of the limitations in the results at the corners.
Command File Mode of Solution
The above example was solved using a mixture of the Graphical User Interface (or GUI) and the command
language interface of ANSYS. This problem has also been solved using the ANSYS command language
interface that you may want to browse. Open the file and save it to your computer. Now go to 'File > Read
input from...' and select the file.
Copyright 2001 University of Alberta
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Sudharsan Engineering College: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokumen34 halamanSudharsan Engineering College: Department of Mechanical EngineeringOmar BouledrouaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-071Dokumen31 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-071NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR100% (5)
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCDari EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap12-001Dokumen34 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap12-001NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR50% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-001Dokumen21 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-001NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR100% (3)
- Non Linear AnalysisDokumen53 halamanNon Linear AnalysisdpksobsBelum ada peringkat
- ANSYS Mechanical APDL for Finite Element AnalysisDari EverandANSYS Mechanical APDL for Finite Element AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Transient Thermal Conduction ExampleDokumen14 halamanTransient Thermal Conduction ExampleDevendra BangarBelum ada peringkat
- Digital LED Thermometer with Microcontroller AVR ATtiny13Dari EverandDigital LED Thermometer with Microcontroller AVR ATtiny13Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Monday Test UEPTDokumen1 halamanMonday Test UEPThodeegits9526Belum ada peringkat
- Iec 60287 Grouping TableDokumen2 halamanIec 60287 Grouping TableAnas Yousuf100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap14-001Dokumen87 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap14-001NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR50% (4)
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap06-058Dokumen18 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap06-058NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR100% (4)
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-043Dokumen20 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-043NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR33% (3)
- Broiler Farm Production ManualDokumen46 halamanBroiler Farm Production ManualAbdul Rahman Selamat100% (2)
- Module 7: Thermal Buckling of A 2D Beam Fixed at Both EndsDokumen17 halamanModule 7: Thermal Buckling of A 2D Beam Fixed at Both Endsnanduslns07Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Fea and AnsysDokumen24 halamanIntroduction To Fea and AnsysParameswara RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Transient Thermal ExampleDokumen5 halamanAnsys Transient Thermal ExampleMaciejBlokBelum ada peringkat
- Cryogenic Vacuum Insulation For Vessels and Piping: Blank Line !jlonk Line IJ/ank LineDokumen7 halamanCryogenic Vacuum Insulation For Vessels and Piping: Blank Line !jlonk Line IJ/ank LineAchmadda FebiyonoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics - A Course in Fluid Mechanics With Vector FieldDokumen198 halamanMathematics - A Course in Fluid Mechanics With Vector FieldprashanthreddyhBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics - A Course in Fluid Mechanics With Vector FieldDokumen198 halamanMathematics - A Course in Fluid Mechanics With Vector FieldprashanthreddyhBelum ada peringkat
- 11 - Thermal - Mixed Boundary ExampleDokumen5 halaman11 - Thermal - Mixed Boundary ExampleMuhammad Saad Khan TareenBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal - Mixed Boundary Example (Conduction/Convection/Insulat Ed)Dokumen6 halamanThermal - Mixed Boundary Example (Conduction/Convection/Insulat Ed)Ahmad BaltajiBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal - Mixed Boundary Example (Conduction/Convection/Insulated)Dokumen5 halamanThermal - Mixed Boundary Example (Conduction/Convection/Insulated)Amit PalaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Give Example A Title 2. Open Preprocessor Menu: /PREP7Dokumen4 halamanGive Example A Title 2. Open Preprocessor Menu: /PREP7api-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- Give Example A Title 2. Open Preprocessor Menu: /PREP7Dokumen5 halamanGive Example A Title 2. Open Preprocessor Menu: /PREP7api-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal AnsysDokumen5 halamanThermal Ansysrajeshkumar247500Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal - Mixed Boundary Example (Conduction/Convection/Insulated)Dokumen21 halamanThermal - Mixed Boundary Example (Conduction/Convection/Insulated)Srini RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Conduction Example: 1. Give Example A Title 2. Create GeometryDokumen4 halamanSimple Conduction Example: 1. Give Example A Title 2. Create GeometrysandeepBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal-Conduction: 1. Give Example A TitleDokumen12 halamanThermal-Conduction: 1. Give Example A Titleapi-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- WK 16 - Thermal Analysis in ANSYS APDLDokumen4 halamanWK 16 - Thermal Analysis in ANSYS APDLMian AsimBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys ExperimentsDokumen10 halamanAnsys ExperimentsASIST MechBelum ada peringkat
- Convection PDFDokumen3 halamanConvection PDFChenna KeshoBelum ada peringkat
- Transient Thermal Conduction ExampleDokumen7 halamanTransient Thermal Conduction Exampledr_ar_marwatBelum ada peringkat
- EX04. Simple ConductionDokumen4 halamanEX04. Simple ConductionvarshiniBelum ada peringkat
- Problem 4 Simple ConductionDokumen4 halamanProblem 4 Simple ConductionRaghu KothaBelum ada peringkat
- Give Example A TitleDokumen10 halamanGive Example A Titleapi-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- Simulation Lab - M.E Thermal (Converted1)Dokumen94 halamanSimulation Lab - M.E Thermal (Converted1)சதீஷ் குமார்100% (1)
- Tutorials - Nonlinear & Eigenvalue Buckling ProblemDokumen20 halamanTutorials - Nonlinear & Eigenvalue Buckling Problemmanuel_9_4Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A TitleDokumen6 halamanApplication of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A Titlesilverknights007Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A TitleDokumen6 halamanApplication of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A TitleSebastian GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Hbti Ansys Cadcam Centre, KapnurDokumen5 halamanHbti Ansys Cadcam Centre, KapnurAjay Kumar OjhaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Using P-ElementsDokumen9 halaman5 - Using P-ElementsBaljinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Eigenvalue: Nonlinear TutorialDokumen16 halamanEigenvalue: Nonlinear Tutorialapi-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- Give Example A TitleDokumen8 halamanGive Example A Titleapi-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- 2 - Design OptimizationDokumen14 halaman2 - Design OptimizationBaljinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Keypoint Coordinates (X, Y, Z) : /title, Effects of Self Weight For A Cantilever BeamDokumen5 halamanKeypoint Coordinates (X, Y, Z) : /title, Effects of Self Weight For A Cantilever BeamjasimabdBelum ada peringkat
- Give Example A Title: /title, Effects of Self Weight For A Cantilever BeamDokumen5 halamanGive Example A Title: /title, Effects of Self Weight For A Cantilever Beamapi-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- ANSYSPrac-9c PDFDokumen4 halamanANSYSPrac-9c PDFtoshugoBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial: Solving A Conjugate Heat Transfer Problem Using Ansys FluentDokumen30 halamanTutorial: Solving A Conjugate Heat Transfer Problem Using Ansys FluentThiagarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys TutorialDokumen4 halamanAnsys TutorialborchecBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Ansys ExperimentsDokumen32 halamanThermal Ansys ExperimentsRajesh BapuBelum ada peringkat
- Distributed LoadingDokumen6 halamanDistributed LoadingJean David ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Conjugate Heat TransferDokumen30 halamanConjugate Heat Transferteguh hady aBelum ada peringkat
- U of A ANSYS Tutorials - Effect of Self WeightDokumen5 halamanU of A ANSYS Tutorials - Effect of Self WeightJean David ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Exercise PDFDokumen14 halamanAnsys Exercise PDFRajesh Choudhary0% (1)
- Plate With HOLE Stress AnalysisDokumen12 halamanPlate With HOLE Stress AnalysisquadmagnetoBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Lab ExcerciseDokumen3 halamanAnsys Lab ExcercisebaranirajBelum ada peringkat
- Buckling Analysis in Ansys: Ex. No: 22 DateDokumen17 halamanBuckling Analysis in Ansys: Ex. No: 22 DatedpksobsBelum ada peringkat
- Preprocessing: Defining The Problem: Keypoint Coordinates (X, Y, Z)Dokumen5 halamanPreprocessing: Defining The Problem: Keypoint Coordinates (X, Y, Z)dsathiyaBelum ada peringkat
- ANSYS Tutorials For MTECH StudentsDokumen49 halamanANSYS Tutorials For MTECH StudentsSubbu SuniBelum ada peringkat
- Design OptimizationDokumen15 halamanDesign Optimizationakroma123Belum ada peringkat
- ConvectionDokumen2 halamanConvectionRaden Ahmad ThohirBelum ada peringkat
- TP 9 - BucklingDokumen17 halamanTP 9 - BucklingFatima FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- T1 2D HeatsinkDokumen13 halamanT1 2D HeatsinkKhusi1Belum ada peringkat
- Effect of Self Weight On A Cantilever Beam: 1. Give Example A TitleDokumen5 halamanEffect of Self Weight On A Cantilever Beam: 1. Give Example A TitleMaulik PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Give Example A TitleDokumen11 halamanGive Example A Titleapi-3833671Belum ada peringkat
- 7 - Modal Analysis of A Cantilever BeamDokumen9 halaman7 - Modal Analysis of A Cantilever BeamRASHMI SAHOOBelum ada peringkat
- Coupled Structural/Thermal AnalysisDokumen259 halamanCoupled Structural/Thermal AnalysisARNABI100% (4)
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionDari EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionBelum ada peringkat
- 14-) NonLinear Analysis of A Cantilever Beam PDFDokumen7 halaman14-) NonLinear Analysis of A Cantilever Beam PDFscs1720Belum ada peringkat
- 12-) Coupled Structural PDFDokumen4 halaman12-) Coupled Structural PDFscs1720Belum ada peringkat
- Modelling Using AxisymmetryDokumen8 halamanModelling Using AxisymmetryNalla PaiyanBelum ada peringkat
- 12 - Transient Thermal Conduction ExampleDokumen13 halaman12 - Transient Thermal Conduction ExampleBaljinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 13-) Contact Problem PDFDokumen5 halaman13-) Contact Problem PDFscs1720Belum ada peringkat
- Ansys Tutorial-6Dokumen11 halamanAnsys Tutorial-6Amit PalaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Solid Model CreationDokumen19 halamanAnsys Solid Model CreationRodrigo GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Plane Stress BracketDokumen24 halamanPlane Stress BracketDevendra BangarBelum ada peringkat
- Alberta University EfficycleDokumen25 halamanAlberta University EfficycleVaibhav MadamshettyBelum ada peringkat
- ViewingDokumen7 halamanViewingKushagra shivamBelum ada peringkat
- ANSYS Assignments-2d TrussDokumen20 halamanANSYS Assignments-2d TrusssandeshlikesBelum ada peringkat
- 5-) Effect of Self Weight On A Cantilever Beam PDFDokumen5 halaman5-) Effect of Self Weight On A Cantilever Beam PDFscs1720Belum ada peringkat
- 0-) Introduction ANSYS PDFDokumen12 halaman0-) Introduction ANSYS PDFscs1720Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A TitleDokumen6 halamanApplication of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A TitleSebastian GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap06-001Dokumen27 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap06-001NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR100% (6)
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap06-044Dokumen12 halamanFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap06-044NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJARBelum ada peringkat
- FM Sol Chap03-001Dokumen34 halamanFM Sol Chap03-001scs1720Belum ada peringkat
- FM Sol Chap02-001Dokumen41 halamanFM Sol Chap02-001drifter712Belum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics 4-29Dokumen44 halamanFluid Mechanics 4-29Hakan_KURU100% (5)
- FM Sol Chap04-001Dokumen74 halamanFM Sol Chap04-001Brijal Patel100% (2)
- Final Hmt-1Dokumen210 halamanFinal Hmt-1ERRAMESH1989Belum ada peringkat
- An Infrared Thermography Study On The Thermal Load PDFDokumen14 halamanAn Infrared Thermography Study On The Thermal Load PDFalialbadryBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Fields (ECEG-2122) : Electric Fields in Material BodyDokumen33 halamanElectromagnetic Fields (ECEG-2122) : Electric Fields in Material BodyjemalBelum ada peringkat
- Physics - Transfer of Thermal EnergyDokumen8 halamanPhysics - Transfer of Thermal Energyjason deruloBelum ada peringkat
- LAB10 Heat Conduction ReportDokumen8 halamanLAB10 Heat Conduction ReportSyfBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Analysis of Fins With Modified Tips: M. Rajagurunathan & Vishnu. VDokumen8 halamanThermal Analysis of Fins With Modified Tips: M. Rajagurunathan & Vishnu. VTJPRC PublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrotherapy 0910 StudentDokumen54 halamanHydrotherapy 0910 Studentkrissh20Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal Unit Operation Lecture NoteDokumen214 halamanThermal Unit Operation Lecture Notegebreslassie gereziherBelum ada peringkat
- Artigo Microondas Review Alimentos PDFDokumen11 halamanArtigo Microondas Review Alimentos PDFgugaaiexlopesBelum ada peringkat
- HW6 SolutionDokumen9 halamanHW6 SolutionMuhammad Saqib IrshadBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal EngineeringDokumen11 halamanThermal EngineeringParasBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation CFD Comparison MatrixDokumen2 halamanSimulation CFD Comparison MatrixtalabizBelum ada peringkat
- Dielectric, Ohmic, and Infrared HeatingDokumen22 halamanDielectric, Ohmic, and Infrared HeatingSuheel HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering ReferenceDokumen1.767 halamanEngineering ReferencecloubuBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Conduction in Solid ExperimentDokumen4 halamanHeat Conduction in Solid ExperimentNo MIBelum ada peringkat
- HeatDokumen82 halamanHeatLUVAI KIOKOBelum ada peringkat
- Maths IGCSE Quick RevisionDokumen16 halamanMaths IGCSE Quick Revisionlindy musekaBelum ada peringkat
- Test Question 1: Matching Items Column A 1.1 What TypeDokumen3 halamanTest Question 1: Matching Items Column A 1.1 What TypeMadikgetlad376Belum ada peringkat
- CHP 11Dokumen104 halamanCHP 11Francisco Jesús Infante PérezBelum ada peringkat
- Hyperthermia SystemicDokumen21 halamanHyperthermia Systemicataraix22Belum ada peringkat
- SS3 1st Further MathsDokumen14 halamanSS3 1st Further MathsoluwafemiabdulsemiuBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 01 - Conduction Through CopperDokumen13 halamanLab 01 - Conduction Through CopperMuhammad FarhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter One Heat and MassDokumen29 halamanChapter One Heat and MassBK MKBelum ada peringkat
- Transient Heat ConductionDokumen47 halamanTransient Heat Conductionbaruaole100% (2)
- Thermal Physics NotesDokumen34 halamanThermal Physics Notesswcaptain2008Belum ada peringkat