Projectile Investigation
Diunggah oleh
xbox4life007Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Projectile Investigation
Diunggah oleh
xbox4life007Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Miami Dade College North Campus
PHY1025 w Calculus
Projectile Motion Investigation
We will use a computer Animation to study the properties of a Projectile:
Projectiles move along the horizontal and along the vertical at the same time. They will have
vertical and horizontal components of the velocities. The range of the projectile depends on the
initial velocity and the angle made with the horizontal.
I. Go online and go to the Animation Page by typing:
http://www3.interscience.wiley.com:8100/legacy/college/halliday/0471320005/simulations6e/ind
ex.htm
II. Choose projectile motion from the animation menu.
Part A: Range versus the launch angle.
III. Set the initial velocity to 10 m/s and set the launch angle to 5. Complete the corresponding
row on the table:
IV. Change the angle by five and repeat step 3 until you reach 85.
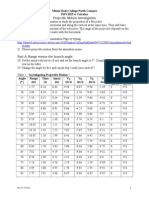
Table 1: Investigating Projectile Motion.
Angle Range
Time
hmax
V0x
(m)
(s)
(m)
(m/s)
( )
V0y
(m/s)
Vfx
(m/s)
Vfy
(m/s)
ax
ay
2
(m/s2)
-9.8
1.77
0.16
0.04
9.96
-0.87
9.96
-1.49
(m/s )
0
10
3.49
0.34
0.15
9.85
-1.74
9.85
-3.03
-9.8
15
5.10
0.52
0.34
9.66
-2.59
9.66
-4.43
-9.8
20
6.56
0.68
0.60
9.40
-3.42
9.40
-4.71
-9.8
25
7.82
0.86
0.91
9.06
-4.23
9.06
-6.64
-9.8
30
8.84
1.02
1.28
8.66
-5.00
8.66
-7.5
-9.8
35
9.59
1.16
1.68
8.19
-5.74
8.19
-8.1
-9.8
40
10.05
1.30
2.11
7.66
-6.43
7.66
-8.61
-9.8
45
10.20
1.44
2.55
7.07
-7.07
7.07
-9.11
-9.8
50
10.05
1.56
2.99
6.43
-7.66
6.43
-9.42
-9.8
55
9.59
1.66
3.42
5.74
-8.19
5.74
-9.56
-9.8
60
8.84
1.76
3.83
5.00
-8.66
5.00
-9.75
-9.8
65
7.82
1.84
4.19
4.23
-9.06
4.23
-9.82
-9.8
70
6.56
1.90
4.51
3.42
-9.40
3.42
-9.8
-9.8
75
5.10
1.96
4.76
2.59
-9.66
2.59
-9.89
-9.8
80
3.49
2.00
4.95
1.74
-9.85
1.74
-9.91
-9.8
85
1.77
2.02
5.06
0.87
-9.96
0.87
-9.87
-9.8
By JC Catala
V.
Miami Dade College North Campus
PHY1025 w Calculus
Projectile Motion Investigation
Calculate the average acceleration along the horizontal and vertical axes.
VI. What do your results mean?
VII. How does the Range changes with the launch angles?
a.What is the launch angle that gives you the farthest range?
b. Find angles that would give you the same range?
c.What conditions do these angles meet?
Part B: Range versus initial speed.
VIII. Set the launch angle so that you get the maximum range possible. Change the initial speed
from 1m/s to 10 m/s. Complete the following table.
Table 2: Range vs. initial speed.
Vinital
1
2
3
4
(m/s)
Range 0.10
0.41
0.92
1.63
(m)
10
2.55
3.67
5.00
6.53
8.27
10.20
IX. Graph of Range vs. initial speed. Use Logger Pro to graph and determine the regression
equation that fits this dependence. Write the equation on the graph. Graph 2
X.
What conclusion can you reach? How does the range changes with the initial speed?
Part C: Horizontal and Vertical velocities as function of time.
XI. Choose seven different times by clicking step back and step forward keys. Complete the
following table.
Table 3: Velocities as function of time.
Trial
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Time (s)
0.08
0.36
0.40
0.78
1.06
1.24
1.32
Vx (m/s)
7.07
7.07
7.07
7.07
7.07
7.07
7.07
Vy (m/s)
6.29
3.74
3.13
-0.57
-3.32
-5.08
-5.86
XII. Graph of Horizontal velocity vs. time, using Logger Pro find the equation that best fits this
dependence. Write the equation on the graph. Graph 1
XIII. Graph of Vertical velocity vs. time. Use Logger Pro to find the equation that best fits this
dependence. Write the equation on the graph. Graph 1
XIV. Explains your results.
By JC Catala
Miami Dade College North Campus
PHY1025 w Calculus
Projectile Motion Investigation
Part D: Conclusions.
XV. Review all your results and describe the properties of Projectile Motion. Support your
conclusions.
By JC Catala
Miami Dade College North Campus
PHY1025 w Calculus
Projectile Motion Investigation
By JC Catala
Miami Dade College North Campus
PHY1025 w Calculus
Projectile Motion Investigation
By JC Catala
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mathemeatical Model of Glider TrajectoryDokumen6 halamanMathemeatical Model of Glider TrajectoryAyanilBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Analysis of Forklift During Load Lifting Using Modeling and SimulationsDokumen6 halamanDynamic Analysis of Forklift During Load Lifting Using Modeling and SimulationsMahmoudMaherBelum ada peringkat
- BME - Nahla - Almeamar - Labreport1and2Dokumen9 halamanBME - Nahla - Almeamar - Labreport1and2NaN GamingBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2.projectile MotionDokumen9 halamanProblem Set 2.projectile MotionChristian OconBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2.projectile MotionDokumen9 halamanProblem Set 2.projectile MotionCriZhae OconBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2.projectile MotionDokumen9 halamanProblem Set 2.projectile MotionCriZhae OconBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2.projectile MotionDokumen9 halamanProblem Set 2.projectile MotionChristian OconBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2.projectile MotionDokumen9 halamanProblem Set 2.projectile MotionChristian OconBelum ada peringkat
- 11ap T1 Sec BDokumen3 halaman11ap T1 Sec Bmahsan abbasBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Exercise 006BDokumen6 halamanLab Exercise 006BEDWIN KHANBelum ada peringkat
- WTFDokumen6 halamanWTFDerek BowermanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter2pp010 020 PDFDokumen11 halamanChapter2pp010 020 PDFInderMaheshBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Shaker Control SystemDokumen5 halamanVibration Shaker Control SystemtripathijohnBelum ada peringkat
- Practica de Laboratorio 1 Alumno Fir115 2023 Clave ADokumen8 halamanPractica de Laboratorio 1 Alumno Fir115 2023 Clave AMatematica Fisica EstadisticaBelum ada peringkat
- One-Dimensional Motion With A Constant Acceleration LabDokumen5 halamanOne-Dimensional Motion With A Constant Acceleration LabJoseph zBelum ada peringkat
- Topographical Surveying & Earthwork CalculationsDokumen4 halamanTopographical Surveying & Earthwork CalculationsLeah Pérez100% (1)
- Projectile Motion Lab Report Yasmeen6432Dokumen7 halamanProjectile Motion Lab Report Yasmeen6432yesBelum ada peringkat
- Projectile MotionDokumen6 halamanProjectile MotionArseniojakejr FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual LaboratoryDokumen20 halamanVirtual LaboratoryMelissa Álvarez UrregoBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3: Projectile Motion Part 1: Equipment Computer Capable of Running HTML SimulationDokumen8 halamanExperiment 3: Projectile Motion Part 1: Equipment Computer Capable of Running HTML SimulationKulendran AnushanBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 102 Kinematics: III. ProcedureDokumen4 halamanExperiment 102 Kinematics: III. ProcedureRisha SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- MotionDokumen14 halamanMotionteerapong onogkBelum ada peringkat
- Newton Second LawDokumen4 halamanNewton Second LawLester ParadilloBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Image Correlation For Tensile TestDokumen9 halamanDigital Image Correlation For Tensile TestAli AbbarBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab ProjectDokumen4 halamanMatlab ProjectaliroomanqBelum ada peringkat
- Uniform Acceleration: Objective: To Study The Kinematics of Uniformly Accelerated Motion. DiscussionDokumen6 halamanUniform Acceleration: Objective: To Study The Kinematics of Uniformly Accelerated Motion. DiscussionAlfred LacandulaBelum ada peringkat
- Dps - Mis, Doha-Qatar Weekly Test - I (2011-12) Class: XI Subject: Physics Date: 15 - 05 - 2011Dokumen3 halamanDps - Mis, Doha-Qatar Weekly Test - I (2011-12) Class: XI Subject: Physics Date: 15 - 05 - 2011Viren PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Coefficient of Kinetic Friction and Drag ForceDokumen7 halamanCoefficient of Kinetic Friction and Drag ForcejhhjjhBelum ada peringkat
- Murciano A 2Dokumen5 halamanMurciano A 2AaronBelum ada peringkat
- Angle Inclination & Acceleration (2.1 Linear Motion)Dokumen1 halamanAngle Inclination & Acceleration (2.1 Linear Motion)wengsungBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Unit Iii: Worksheet 2A: Clock Starts The Instant You See The HazardDokumen4 halamanPhysics Unit Iii: Worksheet 2A: Clock Starts The Instant You See The Hazardcmejdi jBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Terminal VelocityDokumen2 halaman3 - Terminal VelocityFirdausJaafarBelum ada peringkat
- General Physics Lab Reports 1-12 (Online)Dokumen42 halamanGeneral Physics Lab Reports 1-12 (Online)Rama JarrarBelum ada peringkat
- Kedy Jan Cuanan Cengr 3140 LR1 1Dokumen8 halamanKedy Jan Cuanan Cengr 3140 LR1 1EULLYZEN RABANALBelum ada peringkat
- Acceleration On An Air TrackDokumen7 halamanAcceleration On An Air TrackSandra SaviromoBelum ada peringkat
- Week 6 Activity: Projectile Motion IIDokumen3 halamanWeek 6 Activity: Projectile Motion IIJ-heart Basabas MalpalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - KinematicsDokumen8 halamanChapter 1 - KinematicsREXTERYXBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment Projectile Motion: ObjectivesDokumen8 halamanExperiment Projectile Motion: ObjectivesMerryBelum ada peringkat
- Triangledigger ArticleDokumen9 halamanTriangledigger ArticleHugo D. AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics Lab ExperimentsDokumen56 halamanMechanics Lab ExperimentsAnonymous AOJRl09aBelum ada peringkat
- TutLab Week7Dokumen3 halamanTutLab Week7Muhammad NiaziBelum ada peringkat
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDokumen12 halamanCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate Xaminationfrank mutaleBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics PracticalsDokumen17 halamanKinematics PracticalsJennifer MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Projectile PhET Fis1Dokumen2 halamanProjectile PhET Fis1Roberto Javier Vázquez MenchacaBelum ada peringkat
- Ikmal Hakim Lab Fizik 2Dokumen6 halamanIkmal Hakim Lab Fizik 2MUHAMMAD IKMAL HAKIM ABDULLAHBelum ada peringkat
- L3 Group 8Dokumen15 halamanL3 Group 8Badulla M. TwaahaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample LabDokumen7 halamanSample LabJake BaltazarBelum ada peringkat
- GraphsDokumen16 halamanGraphsNoel CunninghamBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDokumen24 halamanAdvanced Structural Analysisbhkedar0% (1)
- PID Vs LQ Control Techniques Applied To An Indoor Micro QuadrotorDokumen6 halamanPID Vs LQ Control Techniques Applied To An Indoor Micro QuadrotorAlexandreSidantBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Homework 1Dokumen7 halaman1 Homework 1Alexis DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 S3Dokumen6 halamanUnit 1 S3cyumadripBelum ada peringkat
- Rockets Away: Quadratics and Newton's Third Law of Motion: BackgroundDokumen7 halamanRockets Away: Quadratics and Newton's Third Law of Motion: BackgroundPatrick WoessnerBelum ada peringkat
- DC Motor Modeling (Student)Dokumen6 halamanDC Motor Modeling (Student)Rafi KarimBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics and Dynamics WorksheetsDokumen49 halamanKinematics and Dynamics Worksheetsknoxphysics100% (1)
- D) AirDokumen9 halamanD) AirKanokporn LeerungnavaratBelum ada peringkat
- Bernoulli's EquationDokumen12 halamanBernoulli's EquationKing Everest100% (1)
- Lab Group 1Dokumen1 halamanLab Group 1xbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- EEL 3514 Communication SystemsDokumen3 halamanEEL 3514 Communication Systemsxbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Midterm Review 2014-1Dokumen2 halamanMidterm Review 2014-1xbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Lab 6 GraphDokumen1 halamanLab 6 Graphxbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Projectile InvestigationDokumen5 halamanProjectile Investigationxbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Exp.3 - Data - Sheet 1Dokumen1 halamanExp.3 - Data - Sheet 1xbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Titration HomeworkDokumen1 halamanTitration Homeworkxbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- EEL3160 LinksDokumen1 halamanEEL3160 Linksxbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter Practice QuestionsDokumen12 halamanChapter Practice QuestionsNoranisza MahmudBelum ada peringkat
- E C Assignment 1 2013 SU 15Dokumen1 halamanE C Assignment 1 2013 SU 15xbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Conclusion 7Dokumen1 halamanConclusion 7xbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Exp.3 - Data - Sheet 1Dokumen1 halamanExp.3 - Data - Sheet 1xbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Lab 6 GraphDokumen1 halamanLab 6 Graphxbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter16 PracticeQuestionsDokumen7 halamanChapter16 PracticeQuestionsxbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- How Many Atoms of O Enter Your Lungs When You Inhale 5Dokumen1 halamanHow Many Atoms of O Enter Your Lungs When You Inhale 5xbox4life007Belum ada peringkat
- SHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Dokumen15 halamanSHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Romeo Espinosa Carmona JrBelum ada peringkat
- Subeeka Akbar Advance NutritionDokumen11 halamanSubeeka Akbar Advance NutritionSubeeka AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- PDF BrochureDokumen50 halamanPDF BrochureAnees RanaBelum ada peringkat
- Joomag 2020 06 12 27485398153Dokumen2 halamanJoomag 2020 06 12 27485398153Vincent Deodath Bang'araBelum ada peringkat
- Previews 1633186 PreDokumen11 halamanPreviews 1633186 PreDavid MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- Abas Drug Study Nicu PDFDokumen4 halamanAbas Drug Study Nicu PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasBelum ada peringkat
- Agenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Dokumen13 halamanAgenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Tanvir AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Case ColorscopeDokumen7 halamanCase ColorscopeRatin MathurBelum ada peringkat
- (Problem Books in Mathematics) Antonio Caminha Muniz Neto - An Excursion Through Elementary Mathematics, Volume III - Discrete Mathematics and Polynomial Algebra (2018, Springer)Dokumen647 halaman(Problem Books in Mathematics) Antonio Caminha Muniz Neto - An Excursion Through Elementary Mathematics, Volume III - Discrete Mathematics and Polynomial Algebra (2018, Springer)Anonymous iH6noeaX7100% (2)
- MEMORANDUM OF AGREEMENT DraftsDokumen3 halamanMEMORANDUM OF AGREEMENT DraftsRichard Colunga80% (5)
- Pyromet Examples Self StudyDokumen2 halamanPyromet Examples Self StudyTessa BeeBelum ada peringkat
- 5045.CHUYÊN ĐỀDokumen8 halaman5045.CHUYÊN ĐỀThanh HuyềnBelum ada peringkat
- Physiol Toric Calculator: With Abulafia-Koch Regression FormulaDokumen1 halamanPhysiol Toric Calculator: With Abulafia-Koch Regression FormuladeliBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Dokumen16 halaman2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Tuhin DeyBelum ada peringkat
- How To Change Front Suspension Strut On Citroen Xsara Coupe n0 Replacement GuideDokumen25 halamanHow To Change Front Suspension Strut On Citroen Xsara Coupe n0 Replacement Guidematej89Belum ada peringkat
- Glossary of Blasting TermsDokumen13 halamanGlossary of Blasting TermsNitesh JainBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDokumen41 halamanAcute Suppurative Otitis Mediarani suwadjiBelum ada peringkat
- Painters Rates PDFDokumen86 halamanPainters Rates PDFmanthoexBelum ada peringkat
- Caroline Coady: EducationDokumen3 halamanCaroline Coady: Educationapi-491896852Belum ada peringkat
- BSNL BillDokumen3 halamanBSNL BillKaushik GurunathanBelum ada peringkat
- Standard BMW PDFDokumen19 halamanStandard BMW PDFIna IoanaBelum ada peringkat
- Legrand Price List-01 ST April-2014Dokumen144 halamanLegrand Price List-01 ST April-2014Umesh SutharBelum ada peringkat
- Dist - Propor.danfoss PVG32Dokumen136 halamanDist - Propor.danfoss PVG32Michal BujaraBelum ada peringkat
- Corelink Mmu600ae TRM 101412 0100 00 enDokumen194 halamanCorelink Mmu600ae TRM 101412 0100 00 enLv DanielBelum ada peringkat
- Work Sample 2 - Eoc and CrucibleDokumen35 halamanWork Sample 2 - Eoc and Crucibleapi-259791703Belum ada peringkat
- What Is The PCB Shelf Life Extending The Life of PCBsDokumen9 halamanWhat Is The PCB Shelf Life Extending The Life of PCBsjackBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing Apical PulseDokumen5 halamanAssessing Apical PulseMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- Index: © Christopher Pitt 2018 C. Pitt, The Definitive Guide To AdonisjsDokumen5 halamanIndex: © Christopher Pitt 2018 C. Pitt, The Definitive Guide To AdonisjsZidi BoyBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 Information ExchangeDokumen15 halaman2010 Information ExchangeAnastasia RotareanuBelum ada peringkat
- DL Manual - Com Vs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualDokumen124 halamanDL Manual - Com Vs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualThiago Teixeira PiresBelum ada peringkat