Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind Map
Diunggah oleh
Caryn Yeap0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
500 tayangan1 halamanBiology Form 4 Chapter 4
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniBiology Form 4 Chapter 4
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
500 tayangan1 halamanChapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind Map
Diunggah oleh
Caryn YeapBiology Form 4 Chapter 4
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
www.sureshkumarbio.wordpress.
com
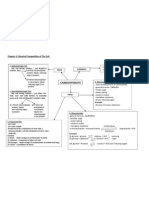
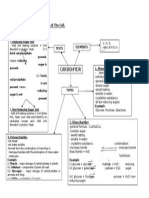
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of The Cell.
1. Reducing Sugar Test
- Add 2ml testing solution + 2ml Benedicts
solution. Heat.
(i) if brick red precipitate
present, means reducing
sugar is present.
TESTS
(ii) if brick red precipitate
is not present, means
reducing sugar is not
present.
1. Non-Reducing Sugar Test
- Add 2ml testing solution + 1ml dilute HCL.
Heat. Cool. Add solid NaHCO to neutralize
excess acid. Add 2ml Benedicts solution. Heat.
(i) ) if brick red precipitate (ii) if brick red
present, means
precipitate is
non-reducing sugar
not present,
is present.
means nonreducing sugar
is not present.
3. Polysaccharides
-not sweet
-not water soluble.
-formed from the combination of more than 2
monosaccharides with the elimination of more water
molecules.
Example
(i) Starch - major storage of carbohydrates in plants.
(ii) Cellulose component of plant cell wall.
(iii) Glycogen - major storage of carbohydrates in animals and fungi.
(iv) Chitin exoskeleton of insects.
- C, H, O.
- ratio of H:O is 2:1
ELEMENTS
CARBOHYDRATE
TYPES
1. Monosaccharides
- basic building blocks of carbohydrate.
-general formula : C6H12O6
-simple sugar.
-sweet tasting.
-soluble in water.
-crystalline substance.
-all are reducing sugars.
Example
-Glucose, Fructose, Galactose.
2. Disaccharides
-general formula : C12H22O11
-complex sugar.
- sweet tasting.
- soluble in water.
- crystalline substance.
-monosaccharide + monosaccharide
Example
(i) glucose + glucose
(ii) glucose + galactose
(iii) glucose + fructose
condensation
disaccharide + H 2O
hydrolysis
maltose + H 2O
Lactose + H 2O
reducing
sugar
sucrose + H 2O (non-reducing sugar)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hassiman, Riyadznalin, EDokumen3 halamanHassiman, Riyadznalin, ERiyadz100% (1)
- Values Education 10: The Maquiling School, IncDokumen6 halamanValues Education 10: The Maquiling School, IncMonria Fernando100% (1)
- BASIC CALCULUS Grade 11 Possible TopicDokumen4 halamanBASIC CALCULUS Grade 11 Possible TopicKingJames Lindo BarrogaBelum ada peringkat
- Philosophy Summative Test 3rd 2020 2021Dokumen2 halamanPhilosophy Summative Test 3rd 2020 2021Mariel VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- ESP CL Module 3 3-4 AnsweredDokumen15 halamanESP CL Module 3 3-4 AnsweredLymberth BenallaBelum ada peringkat
- Arts 10: 4 Quarter Week 3Dokumen10 halamanArts 10: 4 Quarter Week 3Neil John ArmstrongBelum ada peringkat
- Session 2 SH Enhancing Self AwarenessDokumen25 halamanSession 2 SH Enhancing Self AwarenesssharlynsuminguitBelum ada peringkat
- 5.3 (A) Covalent Bond MeaningDokumen33 halaman5.3 (A) Covalent Bond MeaningFidree AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Literary DevicesDokumen1 halamanLiterary Devicesapi-349405312100% (1)
- Module 1 15Dokumen78 halamanModule 1 15Andrew MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Politics and SportsDokumen2 halamanPhilippine Politics and SportsNoel IV T. BorromeoBelum ada peringkat
- Your Answer in Minimum of Twenty Sentences by Giving The Author's Background and Clarity in The Context of Description (20 Points)Dokumen4 halamanYour Answer in Minimum of Twenty Sentences by Giving The Author's Background and Clarity in The Context of Description (20 Points)Mau AcusaBelum ada peringkat
- In or CloutDokumen29 halamanIn or CloutKen De PaulaBelum ada peringkat
- PE10-Q4 4b For UploadDokumen19 halamanPE10-Q4 4b For UploadgeefaulksBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic TheoryDokumen42 halamanAtomic TheoryMarvin RoselBelum ada peringkat
- Health10 - q2 - Mod1 - Reproductive Health Laws - Version3 2.1Dokumen20 halamanHealth10 - q2 - Mod1 - Reproductive Health Laws - Version3 2.1Rosemarie Kwang-sunBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Comm - W4 - Answer SheetDokumen3 halamanOral Comm - W4 - Answer SheetKrista. meters100% (1)
- Esen Module 1 Packet 1 To 4Dokumen74 halamanEsen Module 1 Packet 1 To 4Marianne ArmasBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Respiration Notes 2012Dokumen18 halamanCellular Respiration Notes 2012Sean SolemBelum ada peringkat
- Filipino 10 Module4Dokumen22 halamanFilipino 10 Module4Shiela Mea BlancheBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1.1 What Have I Learned From Others?Dokumen6 halamanActivity 1.1 What Have I Learned From Others?Jonrheym RemegiaBelum ada peringkat
- Embodied Spirit by Jose CalasanzDokumen9 halamanEmbodied Spirit by Jose CalasanzJJ ArabiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ens140 Quiz2Dokumen9 halamanEns140 Quiz2Cristy Mae U. VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Legislative BranchDokumen19 halamanPhilippine Legislative BranchElton John Santos CapiliBelum ada peringkat
- Q2 Science 10 - Module 5Dokumen27 halamanQ2 Science 10 - Module 5Renzo Yunxi Asuncion50% (2)
- Rizal Park: Come and VisitDokumen2 halamanRizal Park: Come and VisitJeremy Dane JacintoBelum ada peringkat
- Knowledge, Wisdom and OpinionDokumen50 halamanKnowledge, Wisdom and OpinionAllen KateBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 - Testing For Sugars and StarchDokumen3 halamanLaboratory Activity No. 1 - Testing For Sugars and StarchRudolf Godwin FabeBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 Biodiversity Unit PlanDokumen3 halamanScience 10 Biodiversity Unit PlanSean MitchellBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 4 The CellDokumen13 halamanAssignment 4 The CellTinBelum ada peringkat
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDokumen30 halamanPlate Tectonic TheoryJEFFYLINEBelum ada peringkat
- Piaget's Cognitive Development TheoryDokumen30 halamanPiaget's Cognitive Development TheorySristi NandaBelum ada peringkat
- CONCEPT MAP of HISTORY of ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - JHON DAVE SURBANO - BSED-SCIENCE 2ADokumen1 halamanCONCEPT MAP of HISTORY of ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - JHON DAVE SURBANO - BSED-SCIENCE 2AJhon dave SurbanoBelum ada peringkat
- Ucsp Q2 LP Sy 2019 2020Dokumen22 halamanUcsp Q2 LP Sy 2019 2020Bernadette ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Eapp Performance Task: Julia May Loria CurieDokumen2 halamanEapp Performance Task: Julia May Loria CurieXander Christian RaymundoBelum ada peringkat
- The Cell and Its BeginningDokumen64 halamanThe Cell and Its BeginningbrettBelum ada peringkat
- John Philip B. Marcelino Ii-Cfm Activity 1Dokumen4 halamanJohn Philip B. Marcelino Ii-Cfm Activity 1Andrea Gwyneth VinoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 Intro To PhiloDokumen51 halamanLesson 1 Intro To PhiloRovie Perps Nopre AndesBelum ada peringkat
- ScienceDokumen17 halamanScienceTambong HailyBelum ada peringkat
- HealthDokumen19 halamanHealthDanna Jenessa Rubina Sune100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - First Law of Thermodynamics and CalorimetryDokumen4 halamanLesson 1 - First Law of Thermodynamics and CalorimetryJeff ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- PVM QpsDokumen1 halamanPVM QpsvanvanBelum ada peringkat
- AP ProjectDokumen5 halamanAP ProjectMark Clement AposagaBelum ada peringkat
- Regional Team Jane C. BasulDokumen9 halamanRegional Team Jane C. Basulshane yvaineBelum ada peringkat
- English 10 Week 4 Module Answer KeyDokumen21 halamanEnglish 10 Week 4 Module Answer KeyMarry Rose AfroilanBelum ada peringkat
- BSIT Jan 2006 QPDokumen43 halamanBSIT Jan 2006 QPAditya_Kumar_995Belum ada peringkat
- Worksheet No.3: Grade 8Dokumen5 halamanWorksheet No.3: Grade 8MICHELLE GUMANGANBelum ada peringkat
- Eng 10-Q3m1Dokumen28 halamanEng 10-Q3m1Lee AnBelum ada peringkat
- A Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDokumen6 halamanA Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerJenielyn SadoBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 7-Drama, Music and FilmDokumen22 halamanLesson 7-Drama, Music and FilmInoXentexo PopBelum ada peringkat
- Alex Lacson LifelineDokumen2 halamanAlex Lacson Lifelinehelloman14Belum ada peringkat
- Khan Academy Cell Theory QuestionsDokumen3 halamanKhan Academy Cell Theory QuestionsLora100% (1)
- Grade 10Dokumen48 halamanGrade 10PEDRO MARISCAL NHSBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 4Dokumen4 halamanActivity 4Misael Camposano100% (1)
- UCSP Quarter 1 Module 2Dokumen18 halamanUCSP Quarter 1 Module 2Lee Arne BarayugaBelum ada peringkat
- Objectives: Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDokumen38 halamanObjectives: Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonRoderick QuiniquitoBelum ada peringkat
- My Life Journey Through . . . with God: Reality and Facts of Life!Dari EverandMy Life Journey Through . . . with God: Reality and Facts of Life!Belum ada peringkat
- Bio Chapter 4 SPMDokumen1 halamanBio Chapter 4 SPMNavindran ChandranBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapDokumen1 halamanChapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapNg YieviaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapDokumen1 halamanChapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind Maphuileng_wongBelum ada peringkat
- Romeo and Juliet Drama ScriptjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhDokumen4 halamanRomeo and Juliet Drama ScriptjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhNurul AqilahBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Carboxilic Acid and EsterDokumen27 halaman6 Carboxilic Acid and EsterKamalasrinny RadhakrisnnanBelum ada peringkat
- Derived QuantitiesDokumen2 halamanDerived QuantitiesNurul AqilahBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Glossary For SPMDokumen20 halamanBiology Glossary For SPMNurul AqilahBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Biology Essays CollectionDokumen31 halamanSPM Biology Essays CollectionYvonne Choo Shuen Lann100% (49)