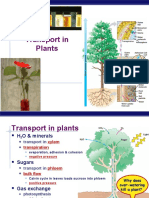
Biology Cell Unit Outline, 2010
Diunggah oleh
julie rainesDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biology Cell Unit Outline, 2010
Diunggah oleh
julie rainesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biology Cell Theory
Purpose:
1. Become familiar with cell structures and functions, including
cellular transport mechanisms.
2. To compare and contrast the main types of cells.
3. To study unicellular organisms in the Protista Kingdom.
4. To develop skills in using microscopes
5. To develop observational skills.
Essential Concepts/Knowledge:
1. How cell structure relates to function.
2. How various cell types compare and contrast in structure and
function.
3. Understands the basics of the cell theory.
4. How materials are transported to and from cells (ie. diffusion, osmosis, active transport,
endocytosis).
5. All living organisms have shared characteristics and how this applies to the protists.
6. Apply the theme of unity within diversity with cells in general and within the protists.
ASSIGNMENTS
A. Tools and techniques of Cytology Chap 7
1. Introduction to the Microscope Sec.7.1 p.211:#1-9
a. parts and function Sec.7.2 p. 169: Data lab; p.190: #5
b. types p. 211-12: #11-15,17
c. Specimen preparation Sec.7.3 p. 212: #21-28,32
(1) centrifuge and microtome Sec.7.4 p.212: #33-37,39,41-42
(2) differential staining worksheets/diagrams
2. Care and Use of the Microscope BONUS: p.212: 44 &45
a. diagramming technique
b. focusing sequence
B. Basic Unit of Life
1. History and scientists
2. Cell Theory-the 3 points
C. Cellular Organization Cell Labs
1. Structure vs. function Diagrams
a. The bilipid layer-the fluid mosiac model Online quizzes
b. Lipids-a key organic molecule
2. Specialization
3. Comparison of cell types
a. identification of basic organelles
b. prokaryote vs. eukaryote
D. Cellular transport & homeostasis Rate of Diffusion lab
1. Semipermeable-a fluid mosaic model Online quizzes
*Factors effecting permeability
2. Diffusions/osmosis & concentration gradient
3. Tonicity and turgor pressure
4. Active transport and solvent sieve theory
5. Endocytosis, exocytosis, and receptor mediated
6. Stomata, septa and plasmodesmata
7. Cytoplasmic streaming
You should now be able to:
___1. Identify the structures of a typical animal, plant, bacterial and fungal cell as well as viruses.
___2. Describe the functions of the cell structures.
___3. State the basic ideas of the cell theory.
___4. Compare and contrast the 4 major cell types.
___5. Explain how materials are transported through a membrane.
___6 Match the important scientists to their contribution
___7. Focus a microscope properly
___8. Make a wet mount slide and find the required cells without assistance.
___9. Draw and label a diagram of microscopic cells.
__10. Estimate the size of an object with a microscope.
__11. Use a digital microscope to record and label cells and calculate rates of motion.
__12. Explain the basic advantages and disadvantages of the different types of microscopes.
__13. Discuss the various methods of cell study (centrifuge, microtome, differential staining, etc.)
__14. Calculate rate of diffusion using experimental data and graphs.
__15. Apply concepts of tonicity and concentration gradients to determine direction/rate of diffusion.
_ 16. Apply the theme of unity within diversity to cells and their structures.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ecology Part 1-The Basics, 2014Dokumen34 halamanEcology Part 1-The Basics, 2014julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Notes 2014Dokumen36 halamanDNA Notes 2014julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology Part 2a AdaptationsDokumen16 halamanEcology Part 2a Adaptationsjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology, Part3-Biodiversity and PollutionDokumen51 halamanEcology, Part3-Biodiversity and Pollutionjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Replication: AP BiologyDokumen35 halamanDNA Replication: AP BiologyFatemeh HalabizBelum ada peringkat
- Change in Organisms Over Time: EvolutionDokumen23 halamanChange in Organisms Over Time: Evolutionjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular TransportDokumen45 halamanCellular Transportjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Life Unit 2013-14Dokumen78 halamanLife Unit 2013-14julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology 2b Succession and Carrying CapacityDokumen30 halamanEcology 2b Succession and Carrying Capacityjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemical CyclesDokumen13 halamanBiochemical Cyclesjulie raines100% (1)
- CH 17 Transcription TranslationDokumen46 halamanCH 17 Transcription TranslationLauren FletcherBelum ada peringkat
- DNA The Genetic Material: AP BiologyDokumen28 halamanDNA The Genetic Material: AP Biologyjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology 1,2012Dokumen33 halamanEcology 1,2012julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Mutations (KFogler)Dokumen9 halamanMutations (KFogler)julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Cancer: From DNA To Cell Cycle To TumorDokumen17 halamanUnderstanding Cancer: From DNA To Cell Cycle To Tumorjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Cells Part 3 Movement, 2011 12Dokumen7 halamanCells Part 3 Movement, 2011 12julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Biology Lab ReviewDokumen72 halamanAP Biology Lab ReviewPaweenwat ThongprasopBelum ada peringkat
- Cells: The Basic Unit of Life!!Dokumen35 halamanCells: The Basic Unit of Life!!julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Cells-Part 2 Eukaryote Vs Prokaryote, 2011-12Dokumen30 halamanCells-Part 2 Eukaryote Vs Prokaryote, 2011-12julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Visuals: Topics in Key Plant FunctionsDokumen2 halamanVisuals: Topics in Key Plant Functionsjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Digestion System (Kfogler)Dokumen34 halamanAP Bio Digestion System (Kfogler)julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Regulating The Internal Environment: AP BiologyDokumen45 halamanRegulating The Internal Environment: AP Biologyjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Plant Anatomy (KFogler)Dokumen26 halamanAP Bio Plant Anatomy (KFogler)julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Gas Exchange/respiratory System (KFogler)Dokumen28 halamanAP Bio Gas Exchange/respiratory System (KFogler)julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Plants (KFogler)Dokumen37 halamanAP Bio Plants (KFogler)julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Lab CorrectionsDokumen19 halamanCell Lab Correctionsjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Plant Transport (KFogler)Dokumen17 halamanAP Bio Plant Transport (KFogler)julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio PlantSecondaryGrowth& Hormones (KFolgler)Dokumen20 halamanAP Bio PlantSecondaryGrowth& Hormones (KFolgler)julie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- The Origin of Species: Mom, Dad There's Something You Need To KnowDokumen24 halamanThe Origin of Species: Mom, Dad There's Something You Need To Knowjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System: AP BiologyDokumen30 halamanNervous System: AP Biologyjulie rainesBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Service Manual: Fm/Am ReceiverDokumen6 halamanService Manual: Fm/Am ReceiverVeronicaGonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Corporates: Third Party InspectionDokumen1 halamanManaging Corporates: Third Party Inspectionrajaguru20003Belum ada peringkat
- Black BoxDokumen62 halamanBlack BoxRobertoBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Stock Report for Hose and FittingsDokumen36 halamanDaily Stock Report for Hose and FittingsAgus Dwi MechanicalBelum ada peringkat
- Traveling Like Royalty: The Palace on Wheels Train Tour of RajasthanDokumen10 halamanTraveling Like Royalty: The Palace on Wheels Train Tour of RajasthanSaahil Ledwani100% (1)
- Deviation StatementDokumen16 halamanDeviation StatementGyanendu DasBelum ada peringkat
- Camper Van ConversionDokumen198 halamanCamper Van ConversionGarrettPro100% (5)
- Land - and Aircraft Carrier-Based F-35C Jet Blast Deflector Noise Testing - Anthony R. Pilon, Lockheed Martin Aeronautics CompanyDokumen12 halamanLand - and Aircraft Carrier-Based F-35C Jet Blast Deflector Noise Testing - Anthony R. Pilon, Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Companybring it onBelum ada peringkat
- TFBRK We 0871 PDFDokumen202 halamanTFBRK We 0871 PDFabd alkader100% (1)
- Committee Meeting Minutes Apr. 08, 2019Dokumen2 halamanCommittee Meeting Minutes Apr. 08, 2019RyoBelum ada peringkat
- Stability Control of Submarine AppendageDokumen81 halamanStability Control of Submarine AppendageSamBelum ada peringkat
- Boarding PassDokumen2 halamanBoarding PassVidit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Bus Companies in The PhilippinesDokumen6 halamanBus Companies in The PhilippinesRonie SapadBelum ada peringkat
- RLF SETRA GB WebDokumen158 halamanRLF SETRA GB WebGustavo VydraBelum ada peringkat
- Travel and Tourism AssignmentDokumen102 halamanTravel and Tourism AssignmentMyBelum ada peringkat
- IBT Port Information 2009Dokumen46 halamanIBT Port Information 2009Rusli DainBelum ada peringkat
- DFMEA Worshop FinalDokumen18 halamanDFMEA Worshop FinalRishi KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Workbook Answer Key: Unit 9Dokumen1 halamanWorkbook Answer Key: Unit 9Управление ПерсоналомBelum ada peringkat
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDokumen23 halamanSupercharging and TurbochargingTrain Placement CellBelum ada peringkat
- Globalization FINAL 1Dokumen23 halamanGlobalization FINAL 1Namrah AroojBelum ada peringkat
- 2005 Campagnolo Spare Parts Catalog PDFDokumen150 halaman2005 Campagnolo Spare Parts Catalog PDFCBelum ada peringkat
- Use and Maintenance Manual: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDokumen122 halamanUse and Maintenance Manual: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineNicolas TurnerBelum ada peringkat
- Interlinking Urban Space GROUP 3 To Be EditDokumen18 halamanInterlinking Urban Space GROUP 3 To Be EditFrog JumpyBelum ada peringkat
- Georgia Department of Public Safety Pursuit PolicyDokumen11 halamanGeorgia Department of Public Safety Pursuit PolicyMatt ThielkeBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Electrical and InstrumentsDokumen19 halaman10 Electrical and InstrumentsAlberto BuonamiciBelum ada peringkat
- List of Supported Travel Websites and Agencies PDFDokumen3 halamanList of Supported Travel Websites and Agencies PDFNica Manuel100% (1)
- Volume - IIDokumen585 halamanVolume - IIRaji VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Car WarsDokumen68 halamanCar WarsTom Pickwell90% (10)
- Installation Operation Maintenance: ManualDokumen21 halamanInstallation Operation Maintenance: ManualFrancisBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Development of Mangalore - Key Factors and ChallengesDokumen8 halamanIndustrial Development of Mangalore - Key Factors and ChallengesUday Kumar IrvathurBelum ada peringkat