Medical Surgical Intervention Sheehan S Syndrome
Diunggah oleh
irismgall0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
149 tayangan4 halamanJudul Asli
Medical surgical intervention sheehan;s syndrome
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
149 tayangan4 halamanMedical Surgical Intervention Sheehan S Syndrome
Diunggah oleh
irismgallHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
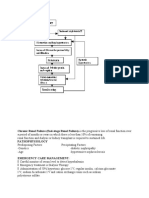
Medical Surgical Interventions
I. Pharmacologic Treatment
Treatment for Sheehan's syndrome is lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
One or more of the following medications are recommended:
• Corticosteroids. These drugs, such as hydrocortisone or prednisone,
replace the adrenal hormones that aren't being produced because of
an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency. Medications are
needed to be adjusted if the patient become seriously ill or experience
major physical stress.
Ex. Hydrocortisone 100 mg q6h IVTT
• Levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid, others). This medication
boosts deficient thyroid hormone levels caused by low or deficient
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) production.
• Estrogen. These are a group of steroid compounds, named for their
importance in the estrous cycle, and functioning as the primary female
sex hormone.
• Growth hormone. Some studies have shown that replacing growth
hormone in women with Sheehan's syndrome — as well as in people
with other forms of hypopituitarism — can help normalize weight,
lower cholesterol levels and improve overall quality of life.
Other medications taken by the client:
• Piperecillin Tazobactam 4.5g IVTT q8h
• Arithromycin 500mg OD
• KCl tab 1 tab TID
• Salbutamol + Ipratropium ½ tab + .5 cc PNSS q6h
• Clonidine 75mg/tab 1tab OD
I. Diagnostic Tests
• Radiology. Branch of medicine that uses ionizing and nonionizing
radiation for the diagnosis and treatment of disease.
Sella Turcica – usually the target of the radiology, a bony box in
the middle of the head where the pituitary gland sits.
Potential risk of the procedure is radiation.
• Cranial CT Scan. A cranial computed tomography (CT) scan is an
imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of
the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
Nursing considerations:
1. Nothing per orem 4-6 hours prior to procedure.
2. Assess for hypersensitivity if dye is to be used. Client will feel a
slight burning sensation in the arm and a metallic taste but will
disappear after a few seconds.
3. No metals as it may obscure the images.
4. Client should lay still during the procedure.
• MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). Magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) is a noninvasive way to take pictures of the body. It uses
powerful magnets and radio waves.
Nursing considerations:
1. Nothing per orem 4-6 hours prior to procedure.
2. Assess for hypersensitivity if dye is to be used.
3. No metals and clients who have metals within the body such as
artificial pacemakers are contraindicated to the procedure.
4. Claustrophobic clients may be given sedatives as ordered by
physician to decrease anxiety.
5. Client should lay still during the entire procedure.
• Radioimmunoassay. Used to measure hormone levels, and both
trophic pituitary and target hormones must be assessed.
Assays quantitative or qualitative tests of a substance to determine its
components; and to determine the presence or concentration of
infectious agents or antibodies etc.
• Urinalysis. The physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of
urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various
compounds that pass through the urine.
• Hematology. The diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of
the blood and bone marrow as well as of the immunologic, hemostatic
(blood clotting) and vascular systems.
• Blood Chemistry. Routine blood work to check the chemical
composition of the blood. The levels of various substances in the blood
can provide clues to a patient's condition, ranging from the presence of
a liver disorder to a pregnancy.
I. IV Therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the giving of liquid substances
directly into a vein. It is the fastest way to deliver fluids and medications
throughout the body.
• D5NSS 1L x KVO + D5W 2 vials
• D5W 500cc + 2 amps Apresoline + 2 amps Clonidine x 20
gtts/min
Restores acid-base balance replenished blood volume provide faster
administration route for meds, maintain body stores @ H2O electrolytes,
vitamins, proteins, minerals and calories in patient who cannot adequate
intake by mouth.
I. Special Orders
• Monitor vital signs hourly
• Monitor neurologic vital signs
• Turn to sides every 2 hours
• Don’t resuscitate
• Moderate to high back rest
• For CVP insertion
• Encourage to compliance of meds
• Titrate AC drip if BP is more than 160/80 mmHg
I. Diet and Activities of Daily Living
• NGT
Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a
plastic tube (nasogastric tube, NG tube) through the nose, past the throat,
and down into the stomach. The main use of a nasogastric tube is for feeding
and for administering drugs and other oral agents.
800 kcal divide by 6 feedings = 133 kcal/feeding
• When on Diet as Tolerated (DAT)
No special diet is necessary unless dictated by an underlying disease
process. Salt (NaCl) use in adrenal insufficiency may be liberalized in
special circumstances (e.g. diaphoresis).
• Activities of Daily Living (ADL)
No restrictions are necessary unless dictated by underlying disease
process.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- 2828100368063500002Dokumen4 halaman2828100368063500002sangama a0% (1)
- Sheehan's Syndrome PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanSheehan's Syndrome PathophysiologyirismgallBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Laboratory Tests for Hemostasis EvaluationDokumen5 halamanLaboratory Tests for Hemostasis EvaluationCMLBelum ada peringkat
- Vet Tech ExamDokumen39 halamanVet Tech Examransingh100% (1)
- What is migraine and how can it be managedDokumen6 halamanWhat is migraine and how can it be managedEliza SitinjakBelum ada peringkat
- Robotic Surgery A Current Perspective: ObjectiveDokumen7 halamanRobotic Surgery A Current Perspective: ObjectiveirismgallBelum ada peringkat
- GUILLIAN - BARRÉ SyndromeDokumen11 halamanGUILLIAN - BARRÉ SyndromeirismgallBelum ada peringkat
- Delay Cord Clamping Benefits Newborns Says ExpertDokumen2 halamanDelay Cord Clamping Benefits Newborns Says ExpertirismgallBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Renal FailureDokumen3 halamanChronic Renal FailureirismgallBelum ada peringkat
- MacroMinerals: Calcium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and MagnesiumDokumen9 halamanMacroMinerals: Calcium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and MagnesiumDerek AtienzaBelum ada peringkat
- Dengue AccomplishmentDokumen4 halamanDengue AccomplishmentKylie GolindangBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Inflammatory and Antiarrhythmic Effects of Beta Blocker in A Rat Model of Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen14 halamanAnti-Inflammatory and Antiarrhythmic Effects of Beta Blocker in A Rat Model of Rheumatoid ArthritisKndratBelum ada peringkat
- Pulp CappingDokumen3 halamanPulp CappingMeta Anjany FirmansyahBelum ada peringkat
- - - - - شاهينDokumen101 halaman- - - - شاهينDdsa FaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Roy TheoryDokumen32 halamanApplication of Roy TheoryAnusha VergheseBelum ada peringkat
- Bhs Inggris - Health and Nursing Related Vocabulary-1Dokumen9 halamanBhs Inggris - Health and Nursing Related Vocabulary-1septynovitaBelum ada peringkat
- Tumor Detection Through Mri Brain Images: Rohit Arya 20MCS1009Dokumen25 halamanTumor Detection Through Mri Brain Images: Rohit Arya 20MCS1009Rohit AryaBelum ada peringkat
- 13 Levels of AssessmentDokumen11 halaman13 Levels of AssessmentCatherine Cayda dela Cruz-BenjaminBelum ada peringkat
- JKNKLKLDokumen10 halamanJKNKLKLCyntia AndrinaBelum ada peringkat
- Health and Social Care Inequalities: The Impact of COVID-19 On People Experiencing Homelessness in BrazilDokumen13 halamanHealth and Social Care Inequalities: The Impact of COVID-19 On People Experiencing Homelessness in BrazilcinacchiBelum ada peringkat
- 10 DOH Approved Herbal Medicine: Prepared By: Washington, Luis D. Student Nurse BSN 2H-DDokumen11 halaman10 DOH Approved Herbal Medicine: Prepared By: Washington, Luis D. Student Nurse BSN 2H-DLuis WashingtonBelum ada peringkat
- Part I سنه القمله 2016Dokumen20 halamanPart I سنه القمله 2016Aloah122346Belum ada peringkat
- Dehorning DisbuddingDokumen4 halamanDehorning DisbuddingAnca AnghelescuBelum ada peringkat
- Karthik Covid Report 1295Dokumen1 halamanKarthik Covid Report 1295Karthikeya PuttaguntaBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Downer Cow and HypoMgDokumen13 halaman2-Downer Cow and HypoMgY.rajuBelum ada peringkat
- Chest Rub Ointment ExperimentDokumen2 halamanChest Rub Ointment ExperimentIsabel PeraltaBelum ada peringkat
- CucumberDokumen25 halamanCucumberDa Nie LBelum ada peringkat
- Cultivos de Clima CalidoDokumen14 halamanCultivos de Clima CalidoZayri Mile CasanovaBelum ada peringkat
- How To Measure Frailty in Your PatientsDokumen1 halamanHow To Measure Frailty in Your PatientsZahra'a Al-AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Single Best Answer Question-Writing Tips For Clinicians: J L Walsh, B H L Harris, P E SmithDokumen6 halamanSingle Best Answer Question-Writing Tips For Clinicians: J L Walsh, B H L Harris, P E SmithSandro ToninBelum ada peringkat
- Headache - 2001 - Jacome - Transitional Interpersonality Thunderclap HeadacheDokumen4 halamanHeadache - 2001 - Jacome - Transitional Interpersonality Thunderclap HeadacheactualashBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Fatigue During PregnancyDokumen2 halamanManaging Fatigue During PregnancyBlanz Irybelle KindomBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6 Cardiovascular: Vascular System - The HemodynamicsDokumen61 halamanLecture 6 Cardiovascular: Vascular System - The HemodynamicsAndreea ŞtefănescuBelum ada peringkat
- Elderly Hip FractureDokumen9 halamanElderly Hip FractureIlyes FerenczBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation of Nurses To Disaster ManagementDokumen10 halamanPreparation of Nurses To Disaster Managementai nisa hasnasariBelum ada peringkat