Chemistry Module Form 4
Diunggah oleh
mohd faisolJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chemistry Module Form 4
Diunggah oleh
mohd faisolHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
CHAPTER 8
SALTS
A salt is an ionic
substance produced
when the hydrogen
ion of the acid is
replaced by metal
ion or an ammonium
ion.
The salt consists of two
parts, cation from base
and anion from acid.
NaCl
NaOH
(Base)
HCl
(Acid)
148
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Table of Salts
Complete the table below.
Metal ion
Sulphate salt
(SO42-)
Chloride salt
(Cl-)
Nitrate salt
(NO3-)
Carbonate salt
(CO32-)
K+
K2SO4
KCl
KNO3
K2CO3
Na+
Ca2+
Mg2+
Al3+
Zn2+
Fe2+
Sn2+
Pb2+
Cu2+
Ag+
NH4+
Ba2+
Based on the table above, mark the insoluble salt.
149
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
SOLUBLE & INSOLUBLE SALTS
SALT
SOLUBLE
INSOLUBLE
K+ , Na+ , NH4+
All soluble
none
Nitrate salts
(NO3- )
All nitrate salts
none
Chloride salts
(Cl-)
Sulphate salts
(SO42-)
Carbonate
salts
(CO32-)
Oxide salts
(O2-)
All chloride salts
Lead (II) chloride,
PbCl2
Silver chloride, AgCl
Mercury chloride,
HgCl
All sulphate salts
Lead (II) sulphate
Calcium sulphate
Barium sulphate
Sodium carbonate,
Na2CO3
Potassium carbonate,
K2CO3
Ammonium carbonate,
(NH4)2CO3
Sodium oxide, Na2O
Potassium oxide, K2O
Calcium oxide, CaO
All others carbonate
salts
All oxide salts
(slightly soluble)
Hydroxide salts
(OH-)
Sodium hydroxide, NaOH
Potassium hydroxide, KOH
Calcium hydroxide,
Ca(OH)2
All hydroxide salts
(slightly soluble)
150
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Preparation and Purification of Soluble Salts
Soluble salt can be prepared by the following ways:
1. Reaction between acid and alkali - preparation for
sodium, potassium and ammonium salts only.
Eg: HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq)
NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
[write the step of preparation of the salts on the diagram]
Buret
HCl solution
NaOH solution
151
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Preparation and Purification of Soluble Salts
Soluble salt can be prepared by the following ways:
1. Reaction between acid and metal oxide
Eg: HNO3(aq) + MgO(s)
Mg(NO3)2 (aq) + H2O(l)
2. Reaction between acid and metal
Eg: H2SO4(aq) + Zn (s)
ZnSO4(aq) + H2 (g)
3. Reaction between acid and metal carbonate
Eg: HCl(aq) + CaCO3(s)
CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
[write the step of preparation of the salts on the diagram]
152
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Crystallization
is a process to crystallize
the soluble salts.
Recrystallization
process will carried out in
order to get pure and
more defined crystal
Physical characteristic of
crystals
Fixed geometrical shapes
such as a cuboids,
rhombic or prism
Flat surface, straight edges
and sharp angles.
Same shapes for same
substance but differ in
sizes
Fixes angle between two
neighbouring surfaces.
153
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Preparation of insoluble salts
An insoluble salt is prepared through precipitation method.
Aqueous solution of two soluble salts are mixed to form
insoluble and soluble salt:
[write the general equation of preparation insoluble salt]
The reaction is called double decomposition.
Two solutions contain ions that make up the insoluble salts.
Eg: Preparation of lead(II) iodide salt by using lead(II)
nitrate solution and potassium iodide solution.
[write the balance chemical equation]
Double Decomposition
154
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
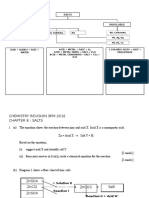
Chemical and Ionic Equation
Chemical and ionic equation can be written for all reaction
That used to prepare salts.
Example: Formation of precipitate Barium Sulphate, BaSO4.
1. Chemical Equation:
BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq)
BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl (aq)
2. Ionic Equation:
Ionic equation shows the ions take part in the reaction.
Exercise
1. Change each of the following word equations to a balanced
chemical equation.
a) Sulphuric acid + zinc
zinc sulphate + hydrogen gas.
b) Silver nitrate + potassium iodide
c) Nitric acid + chromium(III) hydroxide
silver iodide + potassium
nitrate
chromium(III) nitrate
+ water
155
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
2. Complete the following equations.
a) HCl (aq) +
NiO (s)
b) HNO3 (aq) + Ca(OH)2 (aq)
c) H2SO4 (aq) + MgCO3 (s)
3. Write an ionic equation for each reaction between the following
pairs of substances.
a) Sulphuric acid, H2SO4 and barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2 solution
b) Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl solution and silver nitrate, AgNO3
solution.
c) Lead(II) nitrate, Pb(NO3)2 solution and copper(II) sulphate,
CuSO4 solution.
d) Iron(III) oxide, Fe2O3 and hydrochloric acid, HCl.
156
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Constructing Ionic Equation using the Continuous Variation Method
Continuous variation method can be used to construct ionic
equation for the formation of insoluble salts.
Fixed volume of a reactant A is react with varying volumes
of a reactant B to determine the mole ratio of reactant A
that react completely with reactant B.
If x mol of reactant A with y mole of reactant B, than the
empirical formula for insoluble salt is A x B y.
Example:
2Fe3+ (aq) + 3CO32- (aq)
Fe2(CO3)3 (s)
157
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
158
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Example
1.
6.0 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3 Xn+ solution reacts completely with 4.0
cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 Ym- solution to form a salt XmYn. Write the
ionic equation and hence determine the empirical formula of
the salt reaction.
2.
18.0 cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 solution of Px+ ions reacts completely
with 9.0 cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 solution of Qy- ions to form a salt
PxQy. Write the ionic equation and hence determine the
empirical formula of the salt in this reaction.
159
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Solving Problem Involving Calculation of Quantities of Reactants or
Product in Stoichiometric Reactions
Since the quantities of chemicals involved in a reaction are in term
of moles, the quantities of chemicals (volume, mass and number of
particles) must be converted to moles in calculation regarding
quantities of reactant and products.
Exercise
1. Calculate the number of moles of aluminium sulphate
produced by the reaction of 0.2 mole of sulphuric acid with
excess aluminium oxide.
[0.067 mole]
2. 2.0 g of sodium hydroxide reacts with excess sulphuric acid.
What is the mass of sodium sulphate produces
[RAM: H,1 ; O,16 ; Na,23 ; S,32]
[ 3.55 g]
160
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
3. What the volume of carbon dioxide gas evolved at s.t.p when
2.1 g of magnesium carbonate reacts with excess nitric acid.
[ RAM: C,12;O,16;Mg,24; s.t.p = 22.4 dm3]
[ 560 cm3]
4. What is the mass of magnesium required to react with 20 cm3 of
2.0 mol dm3 hydrochloric acid to produce 120 cm3 of hydrogen
at temperature? [RAM: Mg,24 ; 1 mol = 24 dm3 at room temp.]
[ 0.12 g]
161
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Qualitative Analysis of Salts
Colour & Solubility of the Salt
GREEN
PALE GREEN
Iron(II) Sulphate, FeSO4
Iron(II) Nitrate, Fe(NO3)2
Iron(II) Chloride, FeCl2
REDDISH-BROWN
Iron(III) Sulphate, Fe2(SO4)3
Iron(III) Nitrate, Fe(NO3)3
Iron(III) Chloride, FeCl3
GREEN
INSOLUBLE
Copper(II) Carbonate, CuCO3
BLUE
Copper(II) Sulphate, CuSO4
Copper(II) Nitrate, Cu(NO3)2
Copper(II) Chloride, CuCl2
YELLOW/BROWN
[depend on concentration]
INSOLUBLE
Iron(III) Oxide, Fe2O3
BLUE
BROWN
BLACK
INSOLUBLE
Copper(II) Oxide, CuO
162
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Colour & Solubility of the Salt
WHITE
COLOURLESS
Potassium Oxide, K2O
Sodium Oxide, Na2O
Calcium Oxide, CaO
WHITE [cold]
WHITE
Magnesium Oxide, MgO
Aluminium Oxide, Al2O3
YELLOW [cold]
INSOLUBLE
YELLOW [hot]
INSOLUBLE
Zinc Oxide, ZnO
INSOLUBLE
BROWN [hot]
Lead(II) Oxide, PbO
163
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Gas test
Oxygen gas
hydrogen gas
Wooden splinter
Hydrogen gas, H2
Oxygen gas, O2
Carbon dioxide gas
sulphur dioxide gas
Carbon dioxide
HCl acid
Sulphur dioxide
HCl acid
Sodium Sulphite, Na2SO3
Sodium Carbonate,
Na2CO3
chlorine gas
ammonia gas
Red litmus paper
Glass rod dipped into
concentrated HCl acid
White fumes
Chlorine gas, Cl2
Ammonia gas, NH3
164
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
EFFECT OF HEAT ON SALTS
Carbonate salts
Sodium carbonate & potassium carbonate are very stable. They do
not decompose on heating.
Carbonate Salt
Heating
Metal Oxide +
Carbon dioxide
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ white ]
residue
[ white ]
Salts
1.
Calcium carbonate
2.
Magnesium carbonate
3.
Aluminium carbonate
Chemical Equation
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ white ]
Salts
1.
residue
[ yellow hot ]
[ white cold ]
Chemical Equation
Zinc carbonate
165
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Carbonate Salt
Heating
Metal Oxide +
Carbon dioxide
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ brown ]
residue
[ brown ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Iron(III) carbonate
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ green ]
residue
[ black ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Copper(II) carbonate
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ white ]
Salts
1.
residue
[ brown hot ]
[ yellow cold ]
Chemical Equation
Lead(II) carbonate
166
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Carbonate Salt
Heating
Metal + Carbon dioxide + Oxygen gas
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ white ]
residue
[ grey ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Mercury(II) carbonate
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ white ]
residue
[ shiny grey ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Silver carbonate
Heating
Carbonate salts
[ white ]
Salts
1.
residue
[ golden yellow ]
Chemical Equation
Aurum(II) carbonate
167
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
nitrate salts
Nitrate Salt
Heating
Metal Oxide + Oxygen gas + Nitrogen dioxide
Heating
nitrate salts
[ white ]
residue
[ white ]
Salts
1.
Calcium nitrate
2.
Magnesium nitrate
3.
Aluminium nitrate
Chemical Equation
Heating
nitrate salts
[ white ]
Salts
1.
residue
[ yellow hot ]
[ white cold ]
Chemical Equation
Zinc nitrate
168
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Nitrate Salt
Heating
Metal Oxide + Oxygen gas + Nitrogen dioxide
Heating
nitrate salts
[ brown ]
residue
[ brown ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Iron(III) nitrate
Heating
nitrate salts
[ blue ]
residue
[ black ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Copper(II) nitrate
Heating
nitrate salts
[ white ]
Salts
1.
residue
[ brown hot ]
[ yellow cold ]
Chemical Equation
Lead(II) nitrate
169
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Nitrate Salt
Heating
Metal + Nitrogen dioxide + Oxygen gas
Heating
nitrate salts
[ white ]
residue
[ grey ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Mercury(II) nitrate
Heating
nitrate salts
[ white ]
residue
[ shiny grey ]
Salts
1.
Chemical Equation
Silver nitrate
Nitrate Salt
Heating
Metal nitrite + Oxygen gas
Heating
nitrate salts
[ white ]
Salts
1.
Potassium nitrate
2.
Sodium nitrate
residue
[ white ]
Chemical Equation
170
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
TEST FOR ANIONS
Unknown aqueous salt solution
Salt needed to be
dissolved into water
first to produce
aqueous salt
solution.
[ state the procedure ]
[ state the procedure ]
[ state the procedure ]
OBSERVATION
[ state the procedure ]
[ label the diagram ]
OBSERVATION
OBSERVATION
[ label the diagram ]
[ label the diagram ]
[ label the diagram ]
CONCLUSION
CONCLUSION
CONCLUSION
CONCLUSION
[ state the anion ]
[ state the anion ]
[ state the anion ]
OBSERVATION
[ state the anion ]
171
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
TEST FOR CATIONS
Unknown aqueous salt solution
Salt needed to be
dissolved into water
(soluble salts) or in
dilute acid then
filtered (insoluble
salts) first to produce
aqueous salt solution.
Add NaOH drop by drop
No precipitate
White precipitate
Coloured precipitate
Green
Add NaOH drop by drop until excess
Dissolve in excess NaOH
Brown
Insoluble in excess NaOH
Blue
* All coloured ions insoluble in excess NaOH
172
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
TEST FOR CATIONS
Unknown aqueous salt solution
Salt needed to be
dissolved into water
(soluble salts) or in
dilute acid then
filtered (insoluble
salts) first to produce
aqueous salt solution.
Add NH3 drop by drop
No precipitate
White precipitate
Coloured precipitate
Green
Add NH3 drop by drop until excess
Dissolve in excess NH3
Brown
Insoluble in excess NH3
Blue
Dissolved in excess NH3
Dark blue solution
* Fe2+ & Fe3+ ions insoluble in excess NH3
173
mohd faisol mansor/chemistry form 4/chapter 8
Confirmatory Test for Cation
Cation
Procedure
Observation
Fe 2+
Fe 3+
Pb 2+
NH4 +
Exercise
1.
Identify the aqueous solutions based on the test and observation given.
Type
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
Observation
Potassium thiocyanate,
KSCN, solution is added.
Potassium iodide, KI, solution
is added.
Ammonia solution, NH3, is
added until excess.
A little hydrochloric acid is
added.
A sulphuric acid, iron(II)
sulphate solution and
concentrated sulphuric acid
is added.
Ammonia solution is added
until excess.
K2 CO3
ZnCl2
PbCl2
Answer
Blood red solution formed.
Yellow precipitate is
formed.
Blue precipitate dissolve to
form dark blue solution.
Effervescene occur and
lime water turn into chalky.
Brown ring formed.
White precipitate
dissolved.
CuSO4
NaNO3
FeCl3
174
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Preparation Of Soluble And Insoluble SaltsDokumen34 halamanPreparation Of Soluble And Insoluble Saltscar_yii100% (1)
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen18 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- SPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFDokumen12 halamanSPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFNurulBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionDokumen22 halamanSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiBelum ada peringkat
- Topical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramDokumen7 halamanTopical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramManiArasiChandranBelum ada peringkat
- Lukis Struktur AtomDokumen4 halamanLukis Struktur Atomu3kiBelum ada peringkat
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (BL)Dokumen12 halamanIT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (BL)Wong CrystalBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Dokumen2 halamanChemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Daniel Wong Sai Meng100% (1)
- 3 Oxidation and ReductionDokumen25 halaman3 Oxidation and ReductiondonutBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationDokumen43 halaman3 Chemical Formulae and EquationmawarhanifBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionDokumen32 halamanElectrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarBelum ada peringkat
- IT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Dokumen14 halamanIT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarBelum ada peringkat
- Solaf Chemistry SPM 2014: Chapter 1 Form 5: Rate of ReactionDokumen18 halamanSolaf Chemistry SPM 2014: Chapter 1 Form 5: Rate of ReactionNik Diana Hartika Nik Husain100% (1)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Dokumen8 halamanIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Skor A+ StudentDokumen21 halamanSeminar Skor A+ StudentSora HikaruBelum ada peringkat
- A CidDokumen3 halamanA CidJerry Pui Chaw MinBelum ada peringkat
- IT Chem F4 Topical Test 2 (BL)Dokumen8 halamanIT Chem F4 Topical Test 2 (BL)NORAZIAH AHMAD ZULKIPLIBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen30 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- Chap 8 Part 2Dokumen3 halamanChap 8 Part 2Naguib ZakariaBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Dokumen11 halamanAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433Belum ada peringkat
- Topical Test 6: Electrochemistry: Ujian Topikal 6: ElektrokimiaDokumen8 halamanTopical Test 6: Electrochemistry: Ujian Topikal 6: ElektrokimiaManiArasiChandranBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Dokumen15 halamanChemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Helene_mbbt100% (9)
- 2 Heat of PrecipitationDokumen9 halaman2 Heat of PrecipitationPew LingBelum ada peringkat
- Continuous Variation MethodDokumen1 halamanContinuous Variation Methoddalilac100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersDokumen12 halamanChemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersOrkid Fazz89% (9)
- Form 4 Chapter 8Dokumen60 halamanForm 4 Chapter 8Rabbi 08Belum ada peringkat
- SPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDokumen80 halamanSPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsManisha Sekaran MuniandyBelum ada peringkat
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Dokumen6 halamanIT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Titim MohdBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry SPMDokumen20 halamanChemistry SPMJacob ChowBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry SPM 2016 SaltDokumen2 halamanChemistry SPM 2016 SaltAzie Nurul AkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical ProcessDokumen60 halamanChemical ProcessThung LingBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Chemical Bonds AnswerDokumen12 halamanChapter 5 Chemical Bonds AnswerIvan Hoo Chean YiengBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 4 KSSM Definition GuideDokumen4 halamanChemistry Form 4 KSSM Definition Guideprebasubah100% (1)
- Form 4 Revision QuizDokumen80 halamanForm 4 Revision QuizEnvira LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 NoteDokumen19 halamanChemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 NoteshashababygewlBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Dokumen5 halamanChemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Azsyerrah Jahini67% (3)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Dokumen24 halamanChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9dinda syi100% (18)
- IT Bio F5 Final Year Examination (BL)Dokumen13 halamanIT Bio F5 Final Year Examination (BL)Rossliza YaacobBelum ada peringkat
- SPM State Trial Papers Form 5 Chapter 2: Carbon CompoundsDokumen16 halamanSPM State Trial Papers Form 5 Chapter 2: Carbon CompoundsLaw Jin YaoBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen17 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol67% (3)
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (BL)Dokumen9 halamanIT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (BL)Titim MohdBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen21 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol50% (4)
- Chapter 1 Rate of Reaction (Form 4 Chameistry)Dokumen12 halamanChapter 1 Rate of Reaction (Form 4 Chameistry)siowling0922Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 SchemeDokumen41 halamanChemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 Schemespm_victim2010100% (5)
- 2 Effect of Heat On SaltDokumen3 halaman2 Effect of Heat On SaltJacelynBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 Chemistry Perak (Gerak Gempur)Dokumen67 halaman2010 Chemistry Perak (Gerak Gempur)qalanisBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 1 Chemistry F4 Chapter3 Chemical Equation AnswerDokumen2 halamanWorksheet 1 Chemistry F4 Chapter3 Chemical Equation AnswerIpul Catur0% (1)
- Rate of ReactionDokumen20 halamanRate of ReactionQueen BlehBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Exercise - Chap 3Dokumen2 halamanChemistry Exercise - Chap 3eddielawBelum ada peringkat
- INDUSTRIAL METALS & ALLOYSDokumen3 halamanINDUSTRIAL METALS & ALLOYSChloeBelum ada peringkat
- KimDokumen104 halamanKimBayby SiZzle'zBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 5Dokumen51 halamanChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 5Yuzamrah Awang Noh100% (1)
- 8A Salts - AnswerDokumen14 halaman8A Salts - AnswerFrankieNgBelum ada peringkat
- 8.1 Definitions of SaltsDokumen5 halaman8.1 Definitions of Saltsscta94Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Dokumen29 halamanChemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Novah GurulooBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Chapter 8 SaltsDokumen32 halamanChemistry Chapter 8 SaltsnorlieyBelum ada peringkat
- GCSE Chemistry Notes: The Chemical Reactions of Common Mineral AcidsDokumen10 halamanGCSE Chemistry Notes: The Chemical Reactions of Common Mineral AcidsHanaa AbouziedBelum ada peringkat
- Salts - Solubilities: E.G. E.GDokumen10 halamanSalts - Solubilities: E.G. E.GTraci Yan Yan ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Notes Salts (Chemistry)Dokumen32 halamanNotes Salts (Chemistry)Darishana100% (1)
- Partition Fail KKDokumen19 halamanPartition Fail KKmohd faisolBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Chapter 3 Term 1Dokumen3 halamanQuiz Chapter 3 Term 1mohd faisolBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Chapter 2 Term 1 PDFDokumen4 halamanQuiz Chapter 2 Term 1 PDFmohd faisolBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen30 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- Quiz Chapter 2 Term 1Dokumen4 halamanQuiz Chapter 2 Term 1mohd faisolBelum ada peringkat
- Reducing Vehicle EmissionsDokumen4 halamanReducing Vehicle Emissionsmohd faisolBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen25 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (2)
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen21 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol50% (4)
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen32 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (3)
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokumen17 halamanChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol67% (3)
- Chapter 1 ChemistryDokumen4 halamanChapter 1 ChemistryHamidah Jaafar100% (1)
- (D') Three Major Classes of Chemical ReactionsDokumen31 halaman(D') Three Major Classes of Chemical ReactionsJoe NasalitaBelum ada peringkat
- 17bufferkspap 100308200536 Phpapp01Dokumen235 halaman17bufferkspap 100308200536 Phpapp01Isabelle AbadBelum ada peringkat
- SNC2D Chemical Reactions Types & PracticeDokumen3 halamanSNC2D Chemical Reactions Types & Practice1234567eer890Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - NOTESDokumen5 halamanChemical Reactions and Equations - NOTESIshanBelum ada peringkat
- Classify Reactions by TypeDokumen2 halamanClassify Reactions by TypeAvaricioElPecado100% (1)
- Chapter 428 Reactionsin Aqueous Equilibria 29Dokumen99 halamanChapter 428 Reactionsin Aqueous Equilibria 29Kent NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Chemical Reactions ExplainedDokumen28 halamanTypes of Chemical Reactions ExplainedIvan PrasetyaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 4 ConclusionDokumen2 halamanLab 4 ConclusionKiko Salinas80% (10)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 March 29 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDokumen9 halamanNCERT Solutions For Class 10 March 29 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsMohd Abuzar HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Pages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch9Dokumen36 halamanPages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch9api-261034721Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDokumen45 halamanChemical Reactions and EquationsSaloni ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Equations2Dokumen28 halamanChemical Equations2Saleem BashaBelum ada peringkat
- Introductory Chemistry An Active Learning Approach 6th Edition Cracolice Test BankDokumen15 halamanIntroductory Chemistry An Active Learning Approach 6th Edition Cracolice Test Bankduongvalerie9rkb3100% (25)
- Single and Double Displacement ReactionsDokumen4 halamanSingle and Double Displacement Reactionsسمير العطارBelum ada peringkat
- Science Minimum Level Learning Material Class X 2022-23Dokumen230 halamanScience Minimum Level Learning Material Class X 2022-23RAAGAV V MBelum ada peringkat
- 1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradDokumen12 halaman1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradKshitiz sharma100% (1)
- Experiment 1: Chemical Reactions: Prelab ReportDokumen6 halamanExperiment 1: Chemical Reactions: Prelab ReportNhật Tân Võ VươngBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3 CHM 420Dokumen8 halamanExperiment 3 CHM 420bellaamin100% (2)
- Double Displacement ReactionDokumen7 halamanDouble Displacement Reactionlheanne manzulBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Reactions Notes for Boards ExamDokumen21 halamanChemical Reactions Notes for Boards ExamBhaskar 8287Belum ada peringkat
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988058Dokumen9 halamanCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988058abiniveshofficial4708Belum ada peringkat
- TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONSDokumen12 halamanTYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONSNur Faizatul AtiqahBelum ada peringkat
- Movie: Types of Chemical Reactions: HTTP://WWW - Youtube.Co M/Watch?V I-Hhvx1Vc - 8Dokumen27 halamanMovie: Types of Chemical Reactions: HTTP://WWW - Youtube.Co M/Watch?V I-Hhvx1Vc - 8JeffreyBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 3 - Copper CycleDokumen10 halamanExp 3 - Copper CycleEmily YangBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM1LDokumen3 halamanCHEM1LAndrew DonaireBelum ada peringkat
- Expt 5 - Reactions and SolubilityDokumen15 halamanExpt 5 - Reactions and SolubilitySangeeth George0% (2)
- Shayma Chem II Lab Manual.... Petrochemical Engineering DepartmentDokumen55 halamanShayma Chem II Lab Manual.... Petrochemical Engineering DepartmentMUHAMMAD AKRAM100% (1)
- Types of Inorganic Chemical ReactionsDokumen8 halamanTypes of Inorganic Chemical Reactionsal sigmanovaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 2Dokumen6 halamanExperiment No. 2mayankroy9431Belum ada peringkat
- Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDokumen14 halamanClass 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsManwinder Singh GillBelum ada peringkat