Pregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - Pathophysiology
Diunggah oleh
Cyrus De AsisJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - Pathophysiology
Diunggah oleh
Cyrus De AsisHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
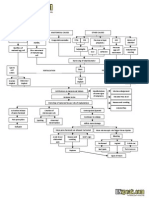
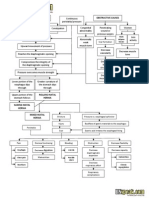
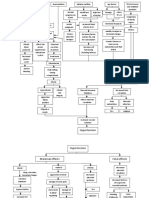
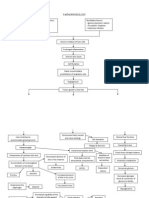
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Hormonal
changes
Renal problem
Normal
progesterone
Decreased
platelet
count
Risk for
bleeding
Insufficient
insulin
Rejection
of insulin
Teenage
Above
35 y/o
action
Insulin
antagonist
Fluid deficit
Alteration in the functioning of
the kidney
Altered
blood
productio
n
Polyhydramnios
Age factors
and multifetal
gestation
Alteration on the
bodys equilibruim
Malnutrition
Diabetes mellitus
Affects the
renninangiotensionaldosterone
system
Human
placental
lactogen
Abnormal
excretion
of protein
Increased blood
glucose level
Decrease glucose
reaches the cells
for consumption
Decrease cell
functioning
(including kidneys)
Hormonal incapacity
Congestion
of nearby
organs
Kidneys
Inability to adjust to
hormonal changes
Greater chances or
more severe
malnutrition and fluid
deficit
Proteinuria
Albuminemia
Increased intrauterine pressure
Fluid shifting
among
compartments
Congestion of the placenta
Edema
Hypovolemia
Aggravates
kidney
problem
Altered
skin
integrity
Decreased placental perfusion
Placental hormone
imbalance
Affects maternal
circulation
Oliguria or
anuria
Increased vascular
reistance
Hypertension
Decreased fetal
circulation
Fetal
malnutrition
Placental
infarction
SGA
Stillbirth
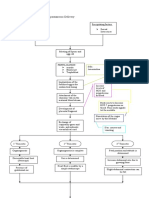
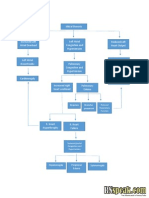
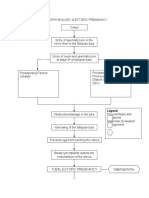
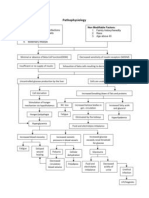
Hypertension
Maternal effects
KIDNEYS
BRAIN
Along with other
hormonal chnages
Damage of some parts
Hyperexcitation
More insult
to blood
regulating
system
Increased ICP
Congestion of
nerves
Convulsions
Coma
Visual
disturbances
Blurred
Halo
Dim
Blind spot
Disorientation
Severe headache
Irritability
Hyperreflexia
UTERUS
Aggravation of insult
Chemical
imbalance
Hyperirritability
Fetal effects
Damage of
Decreased
placental
perfusion
Decreased
osmolarity
Increased
edema
Decreased delivery
of oxygen and
essential nutrients
SGA
membrame
Increased
protein
excretion
Decreased
placental
circulation
oligohydr
amnios
Abruption
placentae
Shrinking
of placenta
Fetal
malnutrition
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Giving BirthDokumen1 halamanSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Giving BirthKristel Jane Lasaca50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of PreeclampsiaDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of PreeclampsiaKristine Alejandro100% (14)
- Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanDokumen4 halamanCerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis67% (12)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDokumen4 halamanCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis89% (9)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanEctopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDokumen2 halamanPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis87% (119)
- Anaphylactic Shock PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanAnaphylactic Shock PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia Schematic DiagramDokumen2 halamanIron Deficiency Anemia Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis83% (12)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanGestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealCyrus De Asis67% (6)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis93% (14)
- Preeclampsia PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanPreeclampsia PathophysiologyIrene Zuñiga100% (4)
- Neonatal Sepsis PathophysiologyDokumen4 halamanNeonatal Sepsis PathophysiologyAlex Marie100% (4)
- High Risk Pregnancy Review QuestionsDokumen59 halamanHigh Risk Pregnancy Review Questionsmitted100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioBelum ada peringkat
- 10th Aug. 2011 Structural Calculation (For Sub.) - 03Dokumen29 halaman10th Aug. 2011 Structural Calculation (For Sub.) - 03Nguyễn Tiến Việt100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDokumen5 halamanEctopic Pregnancy Pathophysiologyjoyrena ochondraBelum ada peringkat
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDokumen7 halamanPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorCarrie A100% (2)
- Diagram, PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanDiagram, PathophysiologyJennifer C. Sumadsad50% (4)
- Weaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaDokumen5 halamanWeaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaEwert Hesketh Nillama PaquinganBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology R2Dokumen1 halamanPathophysiology R2Sydelle GravadorBelum ada peringkat
- Schizophrenia Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanSchizophrenia Schematic DiagramCyrus De AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanLiver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Cancer Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanCancer Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Hyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanHyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis67% (9)
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Alzheimer's Disease Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanAlzheimer's Disease Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis76% (17)
- Congestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanCongestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Physical FitnessDokumen7 halamanFactors Affecting Physical FitnessMary Joy Escanillas Gallardo100% (2)
- Meet The Profesor 2021Dokumen398 halamanMeet The Profesor 2021Raúl AssadBelum ada peringkat
- SSCNC Turning Tutorial ModDokumen18 halamanSSCNC Turning Tutorial ModYudho Parwoto Hadi100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDareRaymondBelum ada peringkat
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaDokumen1 halamanPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaPearl IbisateBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanPregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyCamille Grace100% (1)
- Preeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanPreeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis80% (10)
- Pathophysiology of Gestational DMDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Gestational DMAnonymous GtR96jCBelum ada peringkat
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanGestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyAntonette CedroBelum ada peringkat
- Gestational HypertensionDokumen6 halamanGestational HypertensionDimitrisSoulisBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology PreeclampsiaPATHOSHOPPEBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology PP FinalDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology PP FinalLouie Kem Anthony Babaran0% (1)
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDokumen3 halamanPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study (Preeclampsia)Dokumen6 halamanCase Study (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (1)
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDokumen35 halamanNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryJohn Edward EscoteBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Gestational DiabetesDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Gestational DiabetesKM Onda100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyLiza MinonaBelum ada peringkat
- I. Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing (MCN) Focusing On At-Risk, High Risk, and Sick ClientsDokumen5 halamanI. Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing (MCN) Focusing On At-Risk, High Risk, and Sick ClientsSophia Loraine Dorone Jesura100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDokumen2 halamanPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYrye100% (1)
- Large For Gestational Age (LGA)Dokumen4 halamanLarge For Gestational Age (LGA)Aira AlaroBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Pre-EclampsiaDokumen51 halamanCase Study Pre-EclampsiaRomelle Jane M. VelascoBelum ada peringkat
- CPD PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanCPD PathophysiologyTeanne Bathan100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDokumen4 halamanAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge Planning FinalDokumen5 halamanDischarge Planning FinalRose AnnBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDokumen5 halamanPathophysiology EclampsiaYael EzraBelum ada peringkat
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Giving BirthDokumen2 halamanSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Giving BirtharianeBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology NSD FinalDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology NSD FinalDaniel Tan Galindez80% (5)
- Patho PhysiologyDokumen3 halamanPatho PhysiologyKeith MadarangBelum ada peringkat
- H-Mole NCPsDokumen7 halamanH-Mole NCPsJoevence Gazo CuaresmaBelum ada peringkat
- HypertensionDokumen3 halamanHypertensionCheryl Lim SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationRalph Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of NSVDDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of NSVDLenjun83% (6)
- NCP TEACHING PLAN (Postpartum)Dokumen2 halamanNCP TEACHING PLAN (Postpartum)teuuuuBelum ada peringkat
- FNCP FinalDokumen4 halamanFNCP FinalHector BalnegBelum ada peringkat
- Pcap PathoDokumen2 halamanPcap PathoDiana Jean Abad Dacumos69% (13)
- Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENADokumen2 halamanUrinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENASheena Arnoco ToraynoBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive System: Central Nervous System Hypothalamus Pituitary Ovaries Uterus, Breasts, Skin, VaginaDokumen44 halamanFemale Reproductive System: Central Nervous System Hypothalamus Pituitary Ovaries Uterus, Breasts, Skin, VaginayeandunBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDokumen5 halamanPathophysiology EclampsiaChristine Karen Ang SuarezBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysio PreeclampsiaDokumen2 halamanPathophysio PreeclampsiaMarlowe Czar Catalan SoriñoBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersDokumen72 halamanPediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersMarie Angelique Cruz CrestaniBelum ada peringkat
- My PCOSDokumen54 halamanMy PCOSanees_aneessBelum ada peringkat
- Complications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5Dokumen93 halamanComplications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5klyde_evangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanPathophysiologykristel_nicole18yahoBelum ada peringkat
- Hiperglukagon InggrisDokumen3 halamanHiperglukagon InggrisSyukron FadillahBelum ada peringkat
- Aging and Endocrine DisordersDokumen23 halamanAging and Endocrine DisordersadystiBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology DMDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology DMMJ AmarilloBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetic Cooking for One and TwoDari EverandDiabetic Cooking for One and TwoPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Cpdprogram Nursing 81718Dokumen301 halamanCpdprogram Nursing 81718PRC BoardBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma Pathophysiology and DiagramDokumen1 halamanAsthma Pathophysiology and DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Cpdprovider Nursing 81718Dokumen25 halamanCpdprovider Nursing 81718PRC BoardBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Assessment Tool An Application of Core - Care and Cure ModelDokumen1 halamanGeriatric Assessment Tool An Application of Core - Care and Cure ModelCyrus De AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyDokumen1 halamanPregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyCyrus De AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Major Effects Hormones Pregnant MotherDokumen1 halamanMajor Effects Hormones Pregnant MotherCyrus De AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDokumen2 halamanBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Burns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionDokumen1 halamanBurns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionCyrus De AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Preeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanPreeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis80% (10)
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrocephalus PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanHydrocephalus PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisDokumen2 halamanSchematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisCyrus De Asis0% (1)
- Full Download Short Term Financial Management 3rd Edition Maness Test BankDokumen35 halamanFull Download Short Term Financial Management 3rd Edition Maness Test Bankcimanfavoriw100% (31)
- Bahir Dar University BIT: Faculity of Mechanical and Industrial EngineeringDokumen13 halamanBahir Dar University BIT: Faculity of Mechanical and Industrial Engineeringfraol girmaBelum ada peringkat
- ChipmunkDokumen19 halamanChipmunkema.nemec13Belum ada peringkat
- Lc420euf Sda1 LGDokumen41 halamanLc420euf Sda1 LGjavierBelum ada peringkat
- Texto CuritibaDokumen1 halamanTexto CuritibaMargarida GuimaraesBelum ada peringkat
- PEDokumen12 halamanPEMae Ann Base RicafortBelum ada peringkat
- History of Flash Part - 2Dokumen7 halamanHistory of Flash Part - 2YOGESHWER NATH SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- JHS 182Dokumen137 halamanJHS 182harbhajan singhBelum ada peringkat
- Bhagwati School Strap Report AnalysisDokumen60 halamanBhagwati School Strap Report AnalysisReverse Minded100% (1)
- Sci NB Mod 2 LSN 3Dokumen4 halamanSci NB Mod 2 LSN 3Ramses octavio Rodriguez ocanasBelum ada peringkat
- Class 12 Maths Project On Prime NumbersDokumen13 halamanClass 12 Maths Project On Prime Numbersanon_3835245630% (1)
- Microbiology Part 3Dokumen74 halamanMicrobiology Part 3Authentic IdiotBelum ada peringkat
- Tsel Manual ThermoselDokumen25 halamanTsel Manual ThermoselPedro AlvelaisBelum ada peringkat
- Serial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Dokumen34 halamanSerial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Rohit PhalakBelum ada peringkat
- QuantAssay Software Manual 11-Mar-2019Dokumen51 halamanQuantAssay Software Manual 11-Mar-2019LykasBelum ada peringkat
- Final TestDokumen10 halamanFinal TestbennyBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDokumen16 halamanCell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDJ ISAACSBelum ada peringkat
- 7 +Royal+Court+Affairs,+Sultanate+of+OmanDokumen12 halaman7 +Royal+Court+Affairs,+Sultanate+of+OmanElencheliyan PandeeyanBelum ada peringkat
- Angewandte: ChemieDokumen13 halamanAngewandte: ChemiemilicaBelum ada peringkat
- SR6 Core Rulebook Errata Feb 2020Dokumen6 halamanSR6 Core Rulebook Errata Feb 2020yrtalienBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Power System Device Function NumberDokumen2 halamanElectrical Power System Device Function Numberdan_teegardenBelum ada peringkat
- Frontinus - Water Management of RomeDokumen68 halamanFrontinus - Water Management of RomezElfmanBelum ada peringkat
- YellowstoneDokumen1 halamanYellowstoneOana GalbenuBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 - Presentations (Image, Impact and Making An Impression) 2Dokumen25 halamanUnit 2 - Presentations (Image, Impact and Making An Impression) 2LK Chiarra Panaligan100% (1)
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDokumen6 halamanCell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsRPh Krishna Chandra JagritBelum ada peringkat