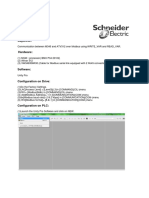
RTN 950 Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Diunggah oleh
Taha TounsiJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
RTN 950 Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Diunggah oleh
Taha TounsiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
V100R003C03
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue
01
Date
2011-10-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2011. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or representations
of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address:
Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website:
http://www.huawei.com
Email:
support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
About This Document
About This Document
Related Versions
The following table lists the product versions related to this document.
Product Name
Version
OptiX RTN 950
V100R003C03
iManager U2000
V100R006C00
Intended Audience
This document provides the guidelines to maintaining the OptiX RTN 950. It also describes the
alarms and performance events that are required for troubleshooting during the maintenance.
This document is intended for:
l
Network planning engineer
Data configuration engineer
System maintenance engineer
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol
Description
Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk,
which if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a hazard with a medium or low level
of risk, which if not avoided, could result in
minor or moderate injury.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
About This Document
Symbol
Description
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation,
which if not avoided, could result in
equipment damage, data loss, performance
degradation, or unexpected results.
Indicates a tip that may help you solve a
problem or save time.
Provides additional information to emphasize
or supplement important points of the main
text.
General Conventions
The general conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention
Description
Times New Roman
Normal paragraphs are in Times New Roman.
Boldface
Names of files, directories, folders, and users are in
boldface. For example, log in as user root.
Italic
Book titles are in italics.
Courier New
Examples of information displayed on the screen are in
Courier New.
Command Conventions
The command conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Convention
Description
Boldface
The keywords of a command line are in boldface.
Italic
Command arguments are in italics.
[]
Items (keywords or arguments) in brackets [ ] are optional.
{ x | y | ... }
Optional items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. One item is selected.
[ x | y | ... ]
Optional items are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars. One item is selected or no item is selected.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
About This Document
Convention
Description
{ x | y | ... }*
Optional items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. A minimum of one item or a maximum of all
items can be selected.
[ x | y | ... ]*
Optional items are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars. Several items or no item can be selected.
GUI Conventions
The GUI conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention
Description
Boldface
Buttons, menus, parameters, tabs, window, and dialog titles
are in boldface. For example, click OK.
>
Multi-level menus are in boldface and separated by the ">"
signs. For example, choose File > Create > Folder.
Change History
Updates between document issues are cumulative. Therefore, the latest document issue contains
all updates made in previous issues.
Updates in Issue 01 (2011-10-30) Based on Product Version V100R003C03
This document is the first issue of the V100R003C03 product version.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
Contents
About This Document.....................................................................................................................ii
1 Safety Precautions.........................................................................................................................1
1.1 General Safety Precautions.................................................................................................................................2
1.2 Warning and Safety Symbols.............................................................................................................................3
1.3 Electrical Safety..................................................................................................................................................4
1.4 Environment of Flammable Gas.........................................................................................................................7
1.5 Storage Batteries.................................................................................................................................................7
1.6 Radiation.............................................................................................................................................................9
1.6.1 Safe Usage of Optical Fibers.....................................................................................................................9
1.6.2 Electromagnetic Exposure.......................................................................................................................11
1.6.3 Forbidden Areas......................................................................................................................................11
1.6.4 Laser........................................................................................................................................................11
1.6.5 Microwave...............................................................................................................................................12
1.7 Working at Heights...........................................................................................................................................13
1.7.1 Hoisting Heavy Objects...........................................................................................................................13
1.7.2 Using Ladders..........................................................................................................................................14
1.8 Mechanical Safety............................................................................................................................................16
1.9 Other Precautions.............................................................................................................................................17
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations...........................................................................................19
2.1 Operation Guide for the Toggle Lever Switch.................................................................................................20
2.2 Operation Guide for the IF Jumper...................................................................................................................22
2.3 Operation Guide for the IF Cable.....................................................................................................................23
2.4 Operation Guide for the IF Board.....................................................................................................................24
3 Routine Maintenance..................................................................................................................26
4 Emergency Maintenance............................................................................................................28
4.1 Definition of Emergency..................................................................................................................................29
4.2 Purposes of Emergency Maintenance...............................................................................................................29
4.3 Procedure for Emergency Maintenance............................................................................................................29
5 Troubleshooting..........................................................................................................................36
5.1 General Troubleshooting Procedure.................................................................................................................38
5.2 Troubleshooting Service Interruptions.............................................................................................................40
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.......................................................................................................................46
5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services..................................................................................................54
5.5 Troubleshooting Pointer Justifications.............................................................................................................60
5.6 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with SDH Equipment............................................................................64
5.7 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with PDH Equipment............................................................................67
5.8 Troubleshooting Native Ethernet Service Faults..............................................................................................71
5.9 Troubleshooting Ethernet Service on the EoS/EoPDH Plane..........................................................................77
5.10 Troubleshooting MPLS Tunnels....................................................................................................................83
5.11 Troubleshooting CES Services.......................................................................................................................87
5.12 Troubleshooting ATM Services.....................................................................................................................92
5.13 Troubleshooting Ethernet Services Carried by PWs......................................................................................96
5.14 Troubleshooting Orderwire Faults................................................................................................................100
6 Part Replacement.......................................................................................................................103
6.1 Removing a Board..........................................................................................................................................105
6.2 Inserting a Board............................................................................................................................................108
6.3 Replacing the SDH Optical Interface Board..................................................................................................110
6.4 Replacing the PDH Interface Board...............................................................................................................111
6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.......................................................................................................................112
6.6 Replacing the Ethernet Interface Board..........................................................................................................113
6.7 Replacing the IF Board...................................................................................................................................114
6.8 Replacing the CF Card...................................................................................................................................116
6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board.............................................................................117
6.10 Replacing the Auxiliary Board.....................................................................................................................119
6.11 Replacing the Fan Board..............................................................................................................................120
6.12 Replacing the Power Board..........................................................................................................................122
6.13 Replacing the SFP........................................................................................................................................123
6.14 Replacing the ODU......................................................................................................................................125
6.15 Replacing the IF Cable.................................................................................................................................126
7 Database Backup and Restoration.........................................................................................128
7.1 NE Database...................................................................................................................................................129
7.2 Backing Up the Database Manually...............................................................................................................129
7.3 Setting the Database Backup Policy...............................................................................................................130
7.3.1 Setting the User-Defined Backup Policy...............................................................................................130
7.3.2 Enable the Backup Policy of the Device...............................................................................................131
7.3.3 Disable the Backup Policy of the Device..............................................................................................132
7.4 Restoring the Database...................................................................................................................................132
8 Supporting Task........................................................................................................................134
8.1 Hardware Loopback.......................................................................................................................................136
8.2 Cleaning Fiber Connectors and Adapters.......................................................................................................136
8.2.1 Cleaning Fiber Connectors by Using Cartridge Cleaners.....................................................................136
8.2.2 Cleaning Fiber Connectors by Using Lens Tissue................................................................................138
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vi
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
8.2.3 Cleaning Fiber Adapters by Using Optical Cleaning Sticks.................................................................139
8.3 Browsing Alarms, Abnormal Events, and Performance Events.....................................................................140
8.3.1 Checking the NE Status.........................................................................................................................140
8.3.2 Checking the Board Status....................................................................................................................141
8.3.3 Browsing Current Alarms......................................................................................................................141
8.3.4 Browsing Abnormal Events...................................................................................................................143
8.3.5 Browsing Current Performance Events.................................................................................................144
8.3.6 Browsing History Alarms......................................................................................................................144
8.3.7 Browsing History Performance Events.................................................................................................145
8.3.8 Browsing the Performance Event Threshold-Crossing Records...........................................................146
8.3.9 Browsing UAT Events...........................................................................................................................146
8.3.10 Configuring the Performance Monitoring Status of NEs....................................................................147
8.3.11 Setting Severity and Auto Reporting Status of Alarms.......................................................................148
8.3.12 Suppressing Alarms for Monitored Objects........................................................................................148
8.3.13 Suppressing Alarms for NEs...............................................................................................................149
8.3.14 Reversing Alarms for Service Ports....................................................................................................149
8.3.15 Setting Trigger Conditions of AIS Insertion.......................................................................................150
8.3.16 Setting Trigger Conditions of UNEQ Insertion...................................................................................151
8.3.17 Setting Bit Error Thresholds for Service Ports....................................................................................151
8.3.18 Setting Monitoring and Auto-Report Status of Performance Events..................................................152
8.3.19 Setting Performance Thresholds..........................................................................................................152
8.3.20 Resetting Performance Registers.........................................................................................................153
8.4 Querying a Report..........................................................................................................................................153
8.4.1 Querying the Board Information Report ..............................................................................................153
8.4.2 Querying the Board Manufacturing Information Report ......................................................................154
8.4.3 Querying the Microwave Link Information Report...............................................................................154
8.4.4 Querying the Network-wide License Report.........................................................................................155
8.5 Software Loopback.........................................................................................................................................156
8.5.1 Setting Loopback for the SDH Optical Interface Board........................................................................156
8.5.2 Setting Loopback for the Tributary Board............................................................................................158
8.5.3 Setting a Loopback for the Smart E1 Processing Board.......................................................................159
8.5.4 Setting a Loopback for the Packet-plane Ethernet Interface Board......................................................161
8.5.5 Setting Loopbacks for the EOS/EoPDH-Plane Ethernet Interface Board.............................................162
8.5.6 Setting Loopback for the IF Board........................................................................................................165
8.5.7 Locating a Fault by Performing Loopback Operations.........................................................................167
8.6 Reset...............................................................................................................................................................169
8.6.1 Cold Reset..............................................................................................................................................169
8.6.2 Warm Reset...........................................................................................................................................169
8.7 PRBS Test.......................................................................................................................................................170
8.7.1 Performing a PRBS Test for the Tributary Board.................................................................................170
8.7.2 Performing a PRBS Test for the IF Board.............................................................................................172
8.8 Querying the License Capacity.......................................................................................................................174
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
8.9 Setting the On/Off State of the Laser.............................................................................................................174
8.10 Setting the ALS Function.............................................................................................................................175
8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function......................................................................................................175
8.12 Querying Power Consumption of Boards.....................................................................................................176
8.13 Querying the Impedance of an E1 Channel..................................................................................................177
8.14 Monitoring Ethernet Packets Through Port Mirroring.................................................................................177
8.15 Querying the Attributes of an Ethernet Port.................................................................................................178
8.16 Setting Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization of Ethernet Ports.......................................179
8.17 Querying Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization of Ethernet Ports...................................180
8.18 Setting the Threshold of Received Traffic Flow on an Ethernet Port..........................................................181
8.19 Using the Ethernet Test Frames....................................................................................................................182
8.20 Switching the System Control Unit and the Cross-Connect Unit................................................................183
A Alarm Reference.......................................................................................................................185
A.1 Alarm List (in Alphabetical Order)...............................................................................................................186
A.2 Alarm List (Classified by Logical Boards)....................................................................................................206
A.2.1 CST.......................................................................................................................................................206
A.2.2 CSH.......................................................................................................................................................207
A.2.3 IF1.........................................................................................................................................................208
A.2.4 IFU2......................................................................................................................................................209
A.2.5 IFX2......................................................................................................................................................210
A.2.6 SL1D/SL1DA.......................................................................................................................................210
A.2.7 EM6T....................................................................................................................................................211
A.2.8 EM6TA.................................................................................................................................................211
A.2.9 EM6F....................................................................................................................................................211
A.2.10 EM6FA...............................................................................................................................................212
A.2.11 EFP8...................................................................................................................................................212
A.2.12 EMS6..................................................................................................................................................213
A.2.13 SP3S/SP3D.........................................................................................................................................214
A.2.14 AUX....................................................................................................................................................214
A.2.15 PIU......................................................................................................................................................214
A.2.16 FAN....................................................................................................................................................215
A.2.17 ISU2....................................................................................................................................................215
A.2.18 ISX2....................................................................................................................................................216
A.2.19 ML1/MD1...........................................................................................................................................216
A.2.20 ODU....................................................................................................................................................217
A.2.21 PMU....................................................................................................................................................217
A.2.22 TCU....................................................................................................................................................218
A.3 Alarms and Handling Procedures..................................................................................................................218
A.3.1 A_LOC.................................................................................................................................................218
A.3.2 ALM_E1RAI........................................................................................................................................219
A.3.3 ALM_GFP_dCSF.................................................................................................................................219
A.3.4 ALM_GFP_dLFD.................................................................................................................................220
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
viii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.5 ALM_IMA_LIF....................................................................................................................................222
A.3.6 ALM_IMA_LODS...............................................................................................................................223
A.3.7 ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE......................................................................................................224
A.3.8 ALM_IMA_RE_TX_UNUSABLE......................................................................................................226
A.3.9 ALM_IMA_RFI...................................................................................................................................227
A.3.10 AM_DOWNSHIFT............................................................................................................................229
A.3.11 APS_FAIL..........................................................................................................................................230
A.3.12 APS_INDI...........................................................................................................................................231
A.3.13 APS_MANUAL_STOP......................................................................................................................232
A.3.14 ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELL_EXC..................................................................................................233
A.3.15 AU_AIS..............................................................................................................................................234
A.3.16 AU_LOP.............................................................................................................................................235
A.3.17 B1_EXC..............................................................................................................................................236
A.3.18 B1_SD.................................................................................................................................................238
A.3.19 B2_EXC..............................................................................................................................................241
A.3.20 B2_SD.................................................................................................................................................243
A.3.21 B3_EXC..............................................................................................................................................245
A.3.22 B3_EXC_VC3....................................................................................................................................247
A.3.23 B3_SD.................................................................................................................................................249
A.3.24 B3_SD_VC3.......................................................................................................................................251
A.3.25 BAT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL...........................................................................................................254
A.3.26 BAT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL...........................................................................................................255
A.3.27 BD_NOT_INSTALLED.....................................................................................................................256
A.3.28 BD_STATUS......................................................................................................................................257
A.3.29 BDTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL................................................................................................................259
A.3.30 BIOS_STATUS..................................................................................................................................260
A.3.31 BIP_EXC............................................................................................................................................261
A.3.32 BIP_SD...............................................................................................................................................263
A.3.33 BOOTROM_BAD..............................................................................................................................264
A.3.34 BUS_ERR...........................................................................................................................................266
A.3.35 CES_ACR_LOCK_ABN...................................................................................................................267
A.3.36 CES_JTROVR_EXC..........................................................................................................................268
A.3.37 CES_JTRUDR_EXC..........................................................................................................................269
A.3.38 CES_LOSPKT_EXC..........................................................................................................................270
A.3.39 CES_MALPKT_EXC.........................................................................................................................271
A.3.40 CES_MISORDERPKT_EXC.............................................................................................................272
A.3.41 CES_RDI............................................................................................................................................273
A.3.42 CES_STRAYPKT_EXC....................................................................................................................274
A.3.43 CESPW_OPPOSITE_ACFAULT......................................................................................................275
A.3.44 CESPW_OPPOSITE_RAI.................................................................................................................275
A.3.45 CFCARD_FAILED............................................................................................................................276
A.3.46 CFCARD_OFFLINE..........................................................................................................................277
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ix
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.47 CHCS..................................................................................................................................................279
A.3.48 CLK_NO_TRACE_MODE................................................................................................................280
A.3.49 COMMUN_FAIL...............................................................................................................................281
A.3.50 CONFIG_NOSUPPORT....................................................................................................................283
A.3.51 DBMS_ABNORMAL........................................................................................................................285
A.3.52 DBMS_ERROR..................................................................................................................................286
A.3.53 DBMS_PROTECT_MODE...............................................................................................................287
A.3.54 DCNSIZE_OVER...............................................................................................................................288
A.3.55 DDN_LFA..........................................................................................................................................289
A.3.56 DOWN_E1_AIS.................................................................................................................................290
A.3.57 DROPRATIO_OVER.........................................................................................................................291
A.3.58 E1_LOC..............................................................................................................................................292
A.3.59 E1_LOS..............................................................................................................................................293
A.3.60 ENVHUM_SENSOR_FAIL...............................................................................................................294
A.3.61 ENVTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL.............................................................................................................295
A.3.62 ENVTEMP1_SENSOR_FAIL...........................................................................................................297
A.3.63 ENVTEMP2_SENSOR_FAIL...........................................................................................................298
A.3.64 ETH_APS_LOST...............................................................................................................................299
A.3.65 ETH_APS_PATH_MISMATCH.......................................................................................................300
A.3.66 ETH_APS_SWITCH_FAIL...............................................................................................................301
A.3.67 ETH_APS_TYPE_MISMATCH........................................................................................................302
A.3.68 ETH_CFM_LOC................................................................................................................................303
A.3.69 ETH_CFM_MISMERGE...................................................................................................................306
A.3.70 ETH_CFM_RDI.................................................................................................................................309
A.3.71 ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI....................................................................................................................311
A.3.72 ETH_EFM_DF...................................................................................................................................314
A.3.73 ETH_EFM_EVENT...........................................................................................................................315
A.3.74 ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK...................................................................................................................316
A.3.75 ETH_EFM_REMFAULT...................................................................................................................318
A.3.76 ETH_LOS...........................................................................................................................................319
A.3.77 ETH_NO_FLOW...............................................................................................................................320
A.3.78 ETHOAM_DISCOVER_FAIL..........................................................................................................322
A.3.79 ETHOAM_RMT_CRIT_FAULT.......................................................................................................323
A.3.80 ETHOAM_RMT_LOOP....................................................................................................................325
A.3.81 ETHOAM_RMT_SD.........................................................................................................................326
A.3.82 ETHOAM_SELF_LOOP...................................................................................................................328
A.3.83 ETHOAM_VCG_SELF_LOOP.........................................................................................................329
A.3.84 EX_ETHOAM_CC_LOS...................................................................................................................331
A.3.85 EX_ETHOAM_MPID_CNFLCT.......................................................................................................332
A.3.86 EXT_SYNC_LOS..............................................................................................................................334
A.3.87 FAN_AGING.....................................................................................................................................335
A.3.88 FAN_FAIL.........................................................................................................................................335
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.89 FCS_ERR...........................................................................................................................................337
A.3.90 FLOW_OVER....................................................................................................................................338
A.3.91 HARD_BAD.......................................................................................................................................339
A.3.92 HP_CROSSTR...................................................................................................................................341
A.3.93 HP_LOM............................................................................................................................................342
A.3.94 HP_RDI..............................................................................................................................................343
A.3.95 HP_REI...............................................................................................................................................344
A.3.96 HP_SLM.............................................................................................................................................345
A.3.97 HP_TIM..............................................................................................................................................346
A.3.98 HP_UNEQ..........................................................................................................................................347
A.3.99 HPAD_CROSSTR..............................................................................................................................348
A.3.100 IF_CABLE_OPEN...........................................................................................................................349
A.3.101 IF_INPWR_ABN.............................................................................................................................350
A.3.102 IF_MODE_UNSUPPORTED..........................................................................................................352
A.3.103 IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN..............................................................................................................353
A.3.104 IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN.............................................................................................................354
A.3.105 IMA_TXCLK_MISMATCH............................................................................................................355
A.3.106 IN_PWR_ABN.................................................................................................................................356
A.3.107 IN_PWR_HIGH...............................................................................................................................358
A.3.108 IN_PWR_LOW................................................................................................................................359
A.3.109 INTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL...............................................................................................................361
A.3.110 J0_MM..............................................................................................................................................362
A.3.111 K1_K2_M.........................................................................................................................................363
A.3.112 K2_M................................................................................................................................................364
A.3.113 LAG_BWMM...................................................................................................................................366
A.3.114 LAG_DOWN....................................................................................................................................367
A.3.115 LAG_MEMBER_DOWN................................................................................................................367
A.3.116 LAG_PORT_FAIL...........................................................................................................................369
A.3.117 LAG_VC_PORT_FAIL...................................................................................................................371
A.3.118 LAN_LOC........................................................................................................................................373
A.3.119 LASER_CLOSED............................................................................................................................374
A.3.120 LASER_MOD_ERR.........................................................................................................................375
A.3.121 LASER_MOD_ERR_EX.................................................................................................................376
A.3.122 LASER_SHUT.................................................................................................................................378
A.3.123 LCAS_FOPR....................................................................................................................................379
A.3.124 LCAS_FOPT....................................................................................................................................380
A.3.125 LCAS_PLCR....................................................................................................................................382
A.3.126 LCAS_PLCT....................................................................................................................................383
A.3.127 LCAS_TLCR....................................................................................................................................385
A.3.128 LCAS_TLCT....................................................................................................................................386
A.3.129 LCD..................................................................................................................................................388
A.3.130 LCS_LIMITED.................................................................................................................................389
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xi
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.131 LFA...................................................................................................................................................391
A.3.132 LICENSE_DIFF...............................................................................................................................392
A.3.133 LICENSE_LOST..............................................................................................................................396
A.3.134 LINK_ERR.......................................................................................................................................397
A.3.135 LMFA...............................................................................................................................................398
A.3.136 LOOP_ALM.....................................................................................................................................399
A.3.137 LP_CROSSTR..................................................................................................................................401
A.3.138 LP_R_FIFO......................................................................................................................................402
A.3.139 LP_RDI.............................................................................................................................................403
A.3.140 LP_RDI_VC12.................................................................................................................................404
A.3.141 LP_RDI_VC3...................................................................................................................................405
A.3.142 LP_REI.............................................................................................................................................406
A.3.143 LP_REI_VC12..................................................................................................................................407
A.3.144 LP_REI_VC3....................................................................................................................................408
A.3.145 LP_RFI.............................................................................................................................................409
A.3.146 LP_SLM...........................................................................................................................................410
A.3.147 LP_SLM_VC12................................................................................................................................410
A.3.148 LP_SLM_VC3..................................................................................................................................411
A.3.149 LP_T_FIFO.......................................................................................................................................412
A.3.150 LP_TIM............................................................................................................................................413
A.3.151 LP_TIM_VC12.................................................................................................................................414
A.3.152 LP_TIM_VC3...................................................................................................................................415
A.3.153 LP_UNEQ.........................................................................................................................................417
A.3.154 LP_UNEQ_VC12.............................................................................................................................418
A.3.155 LP_UNEQ_VC3...............................................................................................................................419
A.3.156 LPS_UNI_BI_M...............................................................................................................................420
A.3.157 LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT.................................................................................................................421
A.3.158 LPT_INEFFECT...............................................................................................................................422
A.3.159 LPT_RFI...........................................................................................................................................424
A.3.160 LSR_NO_FITED..............................................................................................................................425
A.3.161 LTI....................................................................................................................................................426
A.3.162 MAC_EXT_EXC.............................................................................................................................428
A.3.163 MAC_FCS_EXC..............................................................................................................................429
A.3.164 MOD_COM_FAIL...........................................................................................................................430
A.3.165 MOD_TYPE_MISMATCH.............................................................................................................431
A.3.166 MPLS_PW_BDI...............................................................................................................................433
A.3.167 MPLS_PW_Excess...........................................................................................................................433
A.3.168 MPLS_PW_LOCV...........................................................................................................................434
A.3.169 MPLS_PW_MISMATCH................................................................................................................436
A.3.170 MPLS_PW_MISMERGE.................................................................................................................437
A.3.171 MPLS_PW_SD.................................................................................................................................438
A.3.172 MPLS_PW_SF.................................................................................................................................439
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.173 MPLS_PW_UNKNOWN.................................................................................................................440
A.3.174 MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI.....................................................................................................................441
A.3.175 MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess.................................................................................................................441
A.3.176 MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI.....................................................................................................................442
A.3.177 MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV.................................................................................................................443
A.3.178 MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH......................................................................................................445
A.3.179 MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE.......................................................................................................446
A.3.180 MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL..........................................................................................................446
A.3.181 MPLS_TUNNEL_SD.......................................................................................................................448
A.3.182 MPLS_TUNNEL_SF.......................................................................................................................449
A.3.183 MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN.......................................................................................................450
A.3.184 MS_AIS............................................................................................................................................450
A.3.185 MS_CROSSTR.................................................................................................................................452
A.3.186 MS_RDI............................................................................................................................................453
A.3.187 MS_REI............................................................................................................................................454
A.3.188 MSAD_CROSSTR...........................................................................................................................455
A.3.189 MULTI_RPL_OWNER....................................................................................................................456
A.3.190 MW_AM_TEST...............................................................................................................................457
A.3.191 MW_BER_EXC...............................................................................................................................458
A.3.192 MW_BER_SD..................................................................................................................................462
A.3.193 MW_CFG_MISMATCH..................................................................................................................466
A.3.194 MW_CONT_WAVE........................................................................................................................467
A.3.195 MW_E1_LOST.................................................................................................................................468
A.3.196 MW_FEC_UNCOR..........................................................................................................................469
A.3.197 MW_LIM..........................................................................................................................................473
A.3.198 MW_LOF.........................................................................................................................................475
A.3.199 MW_RDI..........................................................................................................................................480
A.3.200 NESF_LOST.....................................................................................................................................481
A.3.201 NESOFT_MM..................................................................................................................................483
A.3.202 NESTATE_INSTALL......................................................................................................................486
A.3.203 NO_BD_SOFT.................................................................................................................................487
A.3.204 NP1_MANUAL_STOP....................................................................................................................488
A.3.205 NP1_SW_FAIL................................................................................................................................489
A.3.206 NP1_SW_INDI.................................................................................................................................490
A.3.207 NTP_SYNC_FAIL...........................................................................................................................491
A.3.208 OCD..................................................................................................................................................492
A.3.209 ODC_BATTERY_CURRENT_ABN..............................................................................................493
A.3.210 ODC_BATTERY_PWRDOWN......................................................................................................494
A.3.211 ODC_DOOR_OPEN........................................................................................................................497
A.3.212 ODC_FAN_FAILED........................................................................................................................498
A.3.213 ODC_HUMI_ABN...........................................................................................................................499
A.3.214 ODC_LOAD_PWRDOWN..............................................................................................................501
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xiii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.215 ODC_MDL_ABN.............................................................................................................................504
A.3.216 ODC_POWER_FAIL.......................................................................................................................505
A.3.217 ODC_SMOKE_OVER.....................................................................................................................508
A.3.218 ODC_SURGE_PROTECTION_FAIL.............................................................................................509
A.3.219 ODC_TEC_ALM.............................................................................................................................511
A.3.220 ODC_TEMP_ABN...........................................................................................................................512
A.3.221 ODC_WATER_ALM.......................................................................................................................514
A.3.222 OUT_PWR_ABN.............................................................................................................................515
A.3.223 OUT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL.........................................................................................................516
A.3.224 OUT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL.........................................................................................................518
A.3.225 PATCH_ACT_TIMEOUT...............................................................................................................519
A.3.226 PATCH_DEACT_TIMEOUT..........................................................................................................520
A.3.227 PATCH_PKGERR...........................................................................................................................520
A.3.228 PG_LINK_FAIL...............................................................................................................................521
A.3.229 PG_PRT_DEGRADED....................................................................................................................522
A.3.230 PLA_CFG_MISMATCH.................................................................................................................523
A.3.231 PORTMODE_MISMATCH.............................................................................................................524
A.3.232 PORT_EXC_TRAFFIC....................................................................................................................525
A.3.233 PORT_MODULE_OFFLINE...........................................................................................................527
A.3.234 POWER_ABNORMAL...................................................................................................................528
A.3.235 POWER_ALM.................................................................................................................................529
A.3.236 PW_DROPPKT_EXC......................................................................................................................531
A.3.237 PWAPS_LOST.................................................................................................................................532
A.3.238 PWAPS_PATH_MISMATCH.........................................................................................................532
A.3.239 PWAPS_SWITCH_FAIL.................................................................................................................533
A.3.240 PWAPS_TYPE_MISMATCH.........................................................................................................534
A.3.241 R_F_RST..........................................................................................................................................535
A.3.242 R_LOC..............................................................................................................................................536
A.3.243 R_LOF..............................................................................................................................................537
A.3.244 R_LOS..............................................................................................................................................539
A.3.245 R_S_ERR..........................................................................................................................................541
A.3.246 RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF...........................................................................................542
A.3.247 RADIO_MUTE................................................................................................................................543
A.3.248 RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH............................................................................................................544
A.3.249 RADIO_RSL_HIGH........................................................................................................................545
A.3.250 RADIO_RSL_LOW.........................................................................................................................546
A.3.251 RADIO_TSL_HIGH.........................................................................................................................548
A.3.252 RADIO_TSL_LOW.........................................................................................................................549
A.3.253 RELAY_ALARM_CRITICAL........................................................................................................549
A.3.254 RELAY_ALARM_IGNORE...........................................................................................................550
A.3.255 RELAY_ALARM_MAJOR.............................................................................................................551
A.3.256 RELAY_ALARM_MINOR.............................................................................................................552
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xiv
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.257 RMFA...............................................................................................................................................553
A.3.258 RPS_INDI.........................................................................................................................................553
A.3.259 RS_CROSSTR..................................................................................................................................556
A.3.260 RTC_FAIL........................................................................................................................................557
A.3.261 S1_SYN_CHANGE.........................................................................................................................558
A.3.262 SCCDATA_BACKUP_FAIL...........................................................................................................559
A.3.263 SEC_RADIUS_FAIL.......................................................................................................................561
A.3.264 SECU_ALM.....................................................................................................................................562
A.3.265 SRV_SHUTDOWN_LD..................................................................................................................563
A.3.266 SWDL_ACTIVATED_TIMEOUT..................................................................................................563
A.3.267 SWDL_AUTOMATCH_INH..........................................................................................................564
A.3.268 SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH.....................................................................................................565
A.3.269 SWDL_COMMIT_FAIL..................................................................................................................566
A.3.270 SWDL_INPROCESS.......................................................................................................................567
A.3.271 SWDL_NEPKGCHECK..................................................................................................................567
A.3.272 SWDL_PKG_NOBDSOFT..............................................................................................................568
A.3.273 SWDL_PKGVER_MM....................................................................................................................569
A.3.274 SWDL_ROLLBACK_FAIL.............................................................................................................570
A.3.275 SYN_BAD........................................................................................................................................571
A.3.276 SYNC_C_LOS.................................................................................................................................572
A.3.277 T_ALOS...........................................................................................................................................573
A.3.278 T_F_RST..........................................................................................................................................574
A.3.279 T_LOC..............................................................................................................................................575
A.3.280 TEMP_ALARM...............................................................................................................................576
A.3.281 THUNDERALM..............................................................................................................................577
A.3.282 TR_LOC...........................................................................................................................................578
A.3.283 TU_AIS.............................................................................................................................................579
A.3.284 TU_AIS_VC12.................................................................................................................................581
A.3.285 TU_AIS_VC3...................................................................................................................................583
A.3.286 TU_LOP...........................................................................................................................................585
A.3.287 TU_LOP_VC12................................................................................................................................586
A.3.288 TU_LOP_VC3..................................................................................................................................587
A.3.289 TUNNEL_APS_DEGRADED.........................................................................................................589
A.3.290 UHCS................................................................................................................................................590
A.3.291 UP_E1_AIS......................................................................................................................................591
A.3.292 VC_AIS............................................................................................................................................592
A.3.293 VC_LOC...........................................................................................................................................594
A.3.294 VC_RDI............................................................................................................................................595
A.3.295 VCAT_LOA.....................................................................................................................................597
A.3.296 VCAT_LOM_VC12.........................................................................................................................598
A.3.297 VCAT_LOM_VC3...........................................................................................................................600
A.3.298 VCAT_SQM_VC12.........................................................................................................................601
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xv
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
A.3.299 VCAT_SQM_VC3...........................................................................................................................603
A.3.300 VOLT_LOS......................................................................................................................................604
A.3.301 VP_AIS.............................................................................................................................................605
A.3.302 VP_LOC...........................................................................................................................................607
A.3.303 VP_RDI............................................................................................................................................609
A.3.304 W_R_FAIL.......................................................................................................................................611
A.3.305 WRG_BD_TYPE.............................................................................................................................612
A.3.306 XPIC_LOS........................................................................................................................................613
B Abnormal Event Reference.....................................................................................................615
B.1 Major Abnormal Performance Event List......................................................................................................616
B.2 Abnormal Performance Events and Handling Procedures.............................................................................616
B.2.1 IF 1+1 Protection Switching.................................................................................................................616
B.2.2 N+1 Protection Switching.....................................................................................................................618
B.2.3 SNCP Switching...................................................................................................................................620
B.2.4 Linear MSP Switching..........................................................................................................................622
B.2.5 Status Change of an APS Protection Group.........................................................................................624
B.2.6 Reporting of PW APS Switching Events..............................................................................................626
B.2.7 System Control Board Switching..........................................................................................................627
B.2.8 RMON Performance Value Below the Lower Limit............................................................................629
B.2.9 RMON Performance Value Above the Upper Limit............................................................................630
C Performance Event Reference................................................................................................631
C.1 Performance Events (by Event Type)............................................................................................................632
C.1.1 SDH/PDH Performance Event List......................................................................................................632
C.1.2 Radio Performance Events....................................................................................................................635
C.1.3 Other Performance Events....................................................................................................................638
C.2 Performance Events (by Logical Board)........................................................................................................639
C.2.1 CST/CSH..............................................................................................................................................639
C.2.2 IF1.........................................................................................................................................................640
C.2.3 IFU2/ISU2.............................................................................................................................................642
C.2.4 IFX2/ISX2.............................................................................................................................................646
C.2.5 SL1D/SL1DA.......................................................................................................................................650
C.2.6 EM6T....................................................................................................................................................652
C.2.7 EM6TA.................................................................................................................................................652
C.2.8 EM6F....................................................................................................................................................652
C.2.9 EM6FA.................................................................................................................................................653
C.2.10 EFP8....................................................................................................................................................654
C.2.11 EMS6..................................................................................................................................................655
C.2.12 SP3S/SP3D.........................................................................................................................................656
C.2.13 ML1/MD1...........................................................................................................................................657
C.2.14 ODU....................................................................................................................................................658
C.3 Performance Events and Handling Procedures..............................................................................................659
C.3.1 AUPJCHIGH, AUPJCLOW, and AUPJCNEW...................................................................................660
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xvi
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
C.3.2 TUPJCHIGH, TUPJCLOW, and TUPJCNEW....................................................................................661
C.3.3 RSBBE, RSES, RSSES, RSCSES, and RSUAS..................................................................................662
C.3.4 RSOOF and RSOFS..............................................................................................................................663
C.3.5 MSBBE, MSES, MSSES, MSCSES, and MSUAS..............................................................................664
C.3.6 MSFEBBE, MSFEES, MSFESES, MSFECSES, and MSFEUAS.......................................................665
C.3.7 HPBBE, HPES, HPSES, HPCSES, and HPUAS.................................................................................666
C.3.8 HPFEBBE, HPFEES, HPFESES, HPFECSES, and HPFEUAS..........................................................668
C.3.9 IF_BBE, IF_ES, IF_SES, IF_CSES, and IF_UAS...............................................................................669
C.3.10 LPBBE, LPES, LPSES, LPCSES, and LPUAS..................................................................................670
C.3.11 LPFEBBE, LPFEES, LPFESES, LPFECSES, and LPFEUAS..........................................................671
C.3.12 E1_LCV_SDH, E1_LLOSS_SDH, E1_LES_SDH, and E1_LSES_SDH.........................................672
C.3.13 TSL_MAX, TSL_MIN, TSL_CUR, and TSL_AVG.........................................................................673
C.3.14 RSL_MAX, RSL_MIN, RSL_CUR, and RSL_AVG........................................................................674
C.3.15 FEC_BEF_COR_ER, FEC_COR_BYTE_CNT and FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT........................674
C.3.16 QPSKWS, QAMWS16, QAMWS32, QAMWS64, QAMWS128, and QAMWS256.......................675
C.3.17 ATPC_P_ADJUST and ATPC_N_ADJUST.....................................................................................676
C.3.18 FB_AMDCNT and FB_AMUCNT....................................................................................................677
C.3.19 RLHTT, RLLTT, TLHTT, TLLTT....................................................................................................678
C.3.20 TPLMAX, TPLMIN, and TPLCUR...................................................................................................678
C.3.21 RPLMAX, RPLMIN, and RPLCUR..................................................................................................679
C.3.22 BDTEMPMAX, BDTEMPMIN, and BDTEMPCUR........................................................................679
C.3.23 XPIC_XPD_VALUE..........................................................................................................................680
C.3.24 PG_IF_BBE, PG_IF_ES, PG_IF_SES, PG_IF_CSES, and PG_IF_UAS..........................................681
C.3.25 E1_BBE, E1_ES, E1_SES, E1_CSES, and E1_UAS.........................................................................682
C.3.26 IF_SNR_MAX, IF_SNR_MIN, and IF_SNR_AVG..........................................................................684
C.3.27 OSPITMPMAX, OSPITMPMIN, and OSPITMPCUR......................................................................684
D RMON Event Reference..........................................................................................................686
D.1 List of RMON Alarm Entries........................................................................................................................687
D.2 List of RMON Performance Entries on the Packet-Plane.............................................................................688
D.3 List of RMON Performance Entries on the EoS/EoPDH Plane....................................................................699
D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures......................................................................................................702
D.4.1 ETHDROP............................................................................................................................................702
D.4.2 ETHEXCCOL.......................................................................................................................................703
D.4.3 ETHLATECOL....................................................................................................................................704
D.4.4 RXBBAD..............................................................................................................................................705
D.4.5 TXDEFFRM.........................................................................................................................................706
D.4.6 ETHUNDER.........................................................................................................................................707
D.4.7 ETHOVER............................................................................................................................................708
D.4.8 ETHFRG...............................................................................................................................................708
D.4.9 ETHJAB...............................................................................................................................................709
D.4.10 ETHCOL.............................................................................................................................................710
D.4.11 ETHFCS.............................................................................................................................................711
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xvii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Contents
D.4.12 ATMPW_LOSPKTS..........................................................................................................................712
D.4.13 ATMPW_MISORDERPKTS.............................................................................................................712
D.4.14 ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELLS..........................................................................................................713
D.4.15 ATM_CORRECTED_HCSERR........................................................................................................714
D.4.16 ATM_UNCORRECTED_HCSERR..................................................................................................714
D.4.17 CES_MISORDERPKTS.....................................................................................................................715
D.4.18 CES_STRAYPKTS............................................................................................................................716
D.4.19 CES_MALPKTS................................................................................................................................716
D.4.20 CES_JTRUDR....................................................................................................................................717
D.4.21 CES_JTROVR....................................................................................................................................718
D.4.22 CES_LOSPKTS..................................................................................................................................718
E Alarm Management..................................................................................................................720
E.1 NE Alarm Management.................................................................................................................................721
E.2 Board Alarm Management.............................................................................................................................721
E.2.1 Setting the Alarm Severity....................................................................................................................721
E.2.2 Alarm Suppression................................................................................................................................721
E.2.3 Alarm Auto-Report...............................................................................................................................721
E.2.4 Alarm Reversion...................................................................................................................................722
E.2.5 Setting of the Bit Error Alarm Threshold.............................................................................................722
E.2.6 AIS Insertion.........................................................................................................................................723
E.2.7 UNEQ Insertion....................................................................................................................................724
F Performance Event Management...........................................................................................725
F.1 NE Performance Event Management.............................................................................................................726
F.2 Board Performance Event Management.........................................................................................................726
G Alarm Suppression Relationship..........................................................................................727
H Indicators of Boards.................................................................................................................731
I Glossary.......................................................................................................................................748
I.1 0-9....................................................................................................................................................................749
I.2 A-E..................................................................................................................................................................749
I.3 F-J....................................................................................................................................................................758
I.4 K-O..................................................................................................................................................................763
I.5 P-T...................................................................................................................................................................769
I.6 U-Z..................................................................................................................................................................778
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xviii
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Safety Precautions
About This Chapter
This topic describes the safety precautions that you must follow when installing, operating, and
maintaining Huawei devices.
1.1 General Safety Precautions
This topic describes essential safety precautions that instruct you in the selection of measuring
and testing instruments when you install, operate, and maintain Huawei devices.
1.2 Warning and Safety Symbols
Before using the equipment, note the following warning and safety symbols on the equipment.
1.3 Electrical Safety
This topic describes safety precautions for high voltage, lightning strikes, high leakage current,
power cables, fuses, and ESD.
1.4 Environment of Flammable Gas
This topic describes safety precautions for the operating environment of a device.
1.5 Storage Batteries
This topic describes safety precautions for operations of storage batteries.
1.6 Radiation
This topic describes safety precautions for electromagnetic exposure and lasers.
1.7 Working at Heights
This topic describes safety precautions for working at heights.
1.8 Mechanical Safety
This topic describes safety precautions for drilling holes, handling sharp objects, operating fans,
and carrying heavy objects.
1.9 Other Precautions
This topic describes safety precautions for removing and inserting boards, binding signal cables,
and routing cables.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
1.1 General Safety Precautions
This topic describes essential safety precautions that instruct you in the selection of measuring
and testing instruments when you install, operate, and maintain Huawei devices.
All Safety Precautions
To ensure the safety of humans and a device, follow the marks on the device and all the safety
precautions in this document when installing, operating, and maintaining a device.
The "CAUTION", "WARNING", and "DANGER" marks in this document do not cover all the
safety precautions that must be followed. They are supplements to the safety precautions.
Local Laws and Regulations
When operating a device, always comply with the local laws and regulations. The safety
precautions provided in the documents are in addition/supplementary to the local laws and
regulations.
Basic Installation Requirements
The installation and maintenance personnel of Huawei devices must receive strict training and
be familiar with the proper operation methods and safety precautions before any operation.
l
Only trained and qualified personnel are permitted to install, operate, and maintain a device.
Only certified professionals are permitted to remove the safety facilities, and to troubleshoot
and maintain the device.
Only the personnel authenticated or authorized by Huawei are permitted to replace or
change the device or parts of the device (including software).
The operating personnel must immediately report the faults or errors that may cause safety
problems to the person in charge.
Grounding Requirements
The grounding requirements are applicable to the device that needs to be grounded.
l
When installing the device, always connect the grounding facilities first. When removing
the device, always disconnect the grounding facilities last.
Ensure that the grounding conductor is intact.
Do not operate the device in the absence of a suitably installed grounding conductor.
The device must be connected to the PGND permanently. Before operating the device,
check the electrical connections of the device, and ensure that the device is properly
grounded.
Human Safety
l
When there is a risk of a lightning strike, do not operate the fixed terminal or touch the
cables.
When there is risk of a lightning strike, unplug the AC power connector. Do not use the
fixed terminal or touch the terminal or antenna connector.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
NOTE
The preceding requirements apply to wireless fixed station terminals.
To avoid electric shocks, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to
telephone-network voltage (TNV) circuits.
Do not look into optical ports without eye protection. Otherwise, human eyes may be hurt
by laser beams.
Before operating the device, wear an ESD protective coat, ESD gloves, and an ESD wrist
strap. In addition, you need to get off the conductive objects, such as jewelry and watches,
to prevent electric shock and burn.
In case of fire, escape from the building or site where the device is located and press the
fire alarm bell or dial the telephone number for fire alarms. Do not enter the burning building
again in any situation.
Before any operation, install the device firmly on the ground or other rigid objects, such as
on a wall or in a rack.
When the system is working, ensure that the ventilation hole is not blocked.
When installing the front panel, use a tool to tighten the screws firmly, if required.
After installing the device, clean up the packing materials.
Device Safety
1.2 Warning and Safety Symbols
Before using the equipment, note the following warning and safety symbols on the equipment.
Table 1-1 lists the warning and safety symbols of the OptiX RTN 950 and their meanings.
Table 1-1 Warning and safety symbols of the OptiX RTN 950
Symbol
Indication
This symbol is for ESD protection.
A notice with this symbol indicates that you should wear
an ES wrist strap or glove when you touch a board.
Otherwise, you may cause damage to the board.
This symbol is for the laser class.
CLASS 1
LASER
PRODUCT
A notice with this symbol indicates the class of the laser.
Avoid direct exposure to the laser beams. Otherwise, it may
damage you eyes or skin.
LASER
RADIATION
DO NOT VIEW DIRECTLY
WITH OPTICAL
INSTRUMENTS
CLASS 1M LASER
PRODUCT
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Symbol
1 Safety Precautions
Indication
A notice with this symbol indicates where the subrack is
grounded.
ATTENTION
A notice with this symbol indicates that the air filter should
be cleaned periodically.
CLEAN PERIODICALLY
DON'T TOUCH THE
FAN LEAVES BEFORE
THEY SLOW DOWN !
This symbol is for fan safety.
A notice with this symbol indicates that the fan leaves
should not be touched when the fan is rotating.
1.3 Electrical Safety
This topic describes safety precautions for high voltage, lightning strikes, high leakage current,
power cables, fuses, and ESD.
High Voltage
DANGER
l A high-voltage power supply provides power for device operations. Direct human contact
with the high voltage power supply or human contact through damp objects can be fatal.
l Unspecified or unauthorized high voltage operations could result in fire or electric shock, or
both.
Thunderstorm
The requirements apply only to wireless base stations or devices with antennas and feeders.
DANGER
Do not perform operations on high voltage, AC power, towers, or backstays in stormy weather
conditions.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
High Leakage Current
WARNING
Before powering on a device, ground the device. Otherwise, the safety of humans and the device
cannot be ensured.
If a high leakage current mark is labeled near the power connector of the device, you must
connect the PGND terminal on the shell to the ground before connecting the device to an A/C
input power supply. This is to prevent the electric shock caused by leakage current of the device.
Power Cables
DANGER
Do not install or remove the power cable with a live line. Transient contact between the core of
the power cable and the conductor may generate electric arc or spark, which may cause fire or
eye injury.
l
Before installing or removing power cables, you must power off the device.
Before connecting a power cable, you must ensure that the label on the power cable is
correct.
Device with Power On
DANGER
Installing or removing a device is prohibited if the device is on.
DANGER
Do not install or remove the power cables of the equipment when it is powered on.
Short Circuits
When installing and maintaining devices, place and use the associated tools and instruments in
accordance with regulations to avoid short-circuits caused by metal objects.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
CAUTION
To avoid short-circuits when using a tool (such as a screwdriver), do not place the tool on the
ventilation plate of the subrack.
CAUTION
Prevent any screws from dropping into the subrack or chassis to avoid short-circuits.
Fuse
WARNING
If the fuse on a device blows, replace the fuse with a fuse of the same type and specifications to
ensure safe operation of the device.
Electrostatic Discharge
CAUTION
The static electricity generated by the human body may damage the electrostatic sensitive
components on the board, such as the large-scale integrated circuit (LSI).
l
The human body can generate static electromagnetic fields in the following situations:
physical movement, clothing friction, friction between shoes and the ground, plastics in
the hand. Such static electromagnetic effects can remain for an appreciable time.
Before operating a device, circuit boards, or ASICs, wear an ESD wrist strap that is properly
grounded. The ESD wrist strap can prevent the electrostatic-sensitive components from
being damaged by the static electricity in the human body.
Figure 1-1 shows the method of wearing an ESD wrist strap.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Figure 1-1 Wearing an ESD wrist strap
1.4 Environment of Flammable Gas
This topic describes safety precautions for the operating environment of a device.
DANGER
Do not place or operate devices in an environment of flammable or explosive air or gas.
Operating an electronic device in an environment of flammable gas causes a severe hazard.
1.5 Storage Batteries
This topic describes safety precautions for operations of storage batteries.
DANGER
Before operating a storage battery, you must read the safety precautions carefully and be familiar
with the method of connecting a storage battery.
l
Incorrect operations of storage batteries cause hazards. During operation, prevent any shortcircuit, and prevent the electrolyte from overflowing or leakage.
If the electrolyte overflows, it causes potential hazards to the device. The electrolyte may
corrode metal parts and the circuit boards, and ultimately damage the circuit boards.
A storage battery contains a great deal of energy. Misoperations may cause a short-circuit,
which leads to human injuries.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Basic Precautions
To ensure safety, note the following points before installing or maintaining the storage battery:
l
Use special insulation tools.
Wear an eye protector and take effective protection measures.
Wear rubber gloves and a protection coat to prevent the hazard caused by the overflowing
electrolyte.
When handling the storage battery, ensure that its electrodes are upward. Leaning or
reversing the storage battery is prohibited.
Before installing or maintaining the storage battery, ensure that the storage battery is
disconnected from the power supply that charges the storage battery.
Short-Circuit
DANGER
A battery short-circuit may cause human injuries. Although the voltage of an ordinary battery
is low, the instantaneous high current caused by a short-circuit emits a great deal of energy.
Avoid any short-circuit of batteries caused by metal objects. If possible, disconnect the working
battery before performing other operations.
Hazardous Gas
CAUTION
Do not use any unsealed lead-acid storage battery. Lay a storage battery horizontally and fix it
properly to prevent the battery from emitting flammable gas, which may cause fire or device
erosion.
Working lead-acid storage batteries emit flammable gas. Therefore, ventilation and fireproofing
measures must be taken at the sites where lead-acid storage batteries are placed.
Battery Temperature
CAUTION
If a battery overheats, the battery may be deformed or damaged, and the electrolyte may
overflow.
When the temperature of the battery is higher than 60C, you need to check whether the
electrolyte overflows. If the electrolyte overflows, take appropriate measures immediately.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Battery Leakage
CAUTION
In the event of acid overflow or spillage, neutralize the acid and clean it up appropriately.
When handling a leaky battery, protect against the possible damage caused by the acid. When
you find the electrolyte leaks, you can use the following substances to counteract and absorb the
leaking electrolyte:
l
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
In the event of acid overflow or spillage, neutralize the acid and clean it up as recommended by
the battery manufacturer and any local regulations for acid disposal.
If a person contacts battery electrolyte, clean the skin that contacts the battery electrolyte
immediately by using water. In case of a severe situation, the person must be sent to a hospital
immediately.
1.6 Radiation
This topic describes safety precautions for electromagnetic exposure and lasers.
1.6.1 Safe Usage of Optical Fibers
The laser beam can cause damage to your eyes. Hence, you must exercise caution when using
optical fibers.
DANGER
When installing or maintaining an optical interface board or optical fibers, avoid direct eye
exposure to the laser beams launched from the optical interface board or fiber connectors. The
laser beam can cause damage to your eyes.
Cleaning Fiber Connectors and Optical Interfaces
CAUTION
If fiber connectors or flanges are contaminated, optical power commissioning is seriously
affected. Therefore, the two endfaces and flange of every external fiber must be cleaned before
the fiber is led into the equipment through the ODF for being inserted into an optical interface
on the equipment.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
The fiber connectors and optical interfaces of the lasers must be cleaned with the following
special cleaning tools and materials:
l
Special cleaning solvent: It is preferred to use isoamylol. Propyl alcohol, however, can also
be used. It is prohibited that you use alcohol and formalin.
Non-woven lens tissue
Special compressed gas
Cotton stick (medical cotton or long fiber cotton)
Special cleaning roll, used with the recommended cleaning solvent
Special magnifier for fiber connectors
For cleaning steps, see Task Collection "Cleaning Fiber Connectors and Adapters" in the OptiX
RTN 950 Radio Transmission System Maintenance and Troubleshooting.
Replacing Optical Fibers
When replacing an optical fiber, cover the fiber connector of the unused optical fiber with a
protective cap.
Connecting Optical Fibers
l
Use an attenuator if the optical power is excessively high. A high received optical power
damages the optical interface.
Directly connect an attenuator to a slanting optical interface. Install the attenuator on the
IN port instead of the OUT port.
Do not directly connect an attenuator to the level optical interface. Use the optical
distribution frame (ODF) to connect an attenuator to a level optical interface.
Figure 1-2 shows a slanting optical interface, and Figure 1-3 shows a level optical interface.
Figure 1-2 Slanting optical interface
Slanting optical
interface
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Figure 1-3 Level optical interface
Level optical
interface
1.6.2 Electromagnetic Exposure
This topic describes safety precautions for electromagnetic exposure.
If multiple transmit antennas are installed on a tower or backstay, keep away from the transmit
directions of the antennas when you install or maintain an antenna locally.
CAUTION
Ensure that all personnel are beyond the transmit direction of a working antenna.
1.6.3 Forbidden Areas
The topic describes requirements for a forbidden area.
l
Before entering an area where the electromagnetic radiation is beyond the specified range,
the associated personnel must shut down the electromagnetic radiator or stay at least 10
meters away from the electromagnetic radiator, if in the transmit direction.
A physical barrier and an eye-catching warning flag should be available in each forbidden
area.
1.6.4 Laser
This topic describes safety precautions for lasers.
WARNING
When handling optical fibers, do not stand close to, or look into the optical fiber outlet directly
without eye protection.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Laser transceivers are used in the optical transmission system and associated test tools. The laser
transmitted through the bare optical fiber produces a small beam of light, and therefore it has
very high power density and is invisible to human eyes. When a beam of light enters eyes, the
eyes may be damaged.
In normal cases, viewing an un-terminated optical fiber or a damaged optical fiber without eye
protection at a distance greater than 150 mm does not cause eye injury. Eye injury may occur,
however, if an optical tool such as a microscope, magnifying glass, or eye loupe is used to view
an un-terminated optical fiber.
Safety Instructions Regarding Lasers
To avoid laser radiation, obey the following instructions:
l
All operations should be performed by authorized personnel who have completed the
required training courses.
Wear a pair of eye-protective glasses when you are handling lasers or fibers.
Ensure that the optical source is switched off before disconnecting optical fiber connectors.
Do not look into the end of an exposed fiber or an open connector when you are not sure
whether the optical source is switched off.
Use an optical power meter to measure the optical power and ensure that the optical source
is switched off.
Before opening the front door of an optical transmission device, ensure that you are not
exposed to laser radiation.
Do not use an optical tool such as a microscope, a magnifying glass, or an eye loupe to
view the optical connector or fiber that is transmitting optical signals.
Instructions Regarding Fiber Handling
Read and abide by the following instructions before handling fibers:
l
Only trained personnel are permitted to cut and splice fibers.
Before cutting or splicing a fiber, ensure that the fiber is disconnected from the optical
source. After disconnecting the fiber, cap to the fiber connectors.
1.6.5 Microwave
When installing and maintaining the equipment of Huawei, follow the safety precautions of
microwave to ensure the safety of the human body and the equipment.
WARNING
Strong radio frequency can harm the human body.
When installing or maintaining an aerial on the tower or mast that is installed with multiple
aerials, switch off the transmitter in advance.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
1.7 Working at Heights
This topic describes safety precautions for working at heights.
WARNING
When working at heights, be cautious to prevent objects from falling down.
The requirements for working at heights are as follows:
l
The personnel who work at heights must be trained.
Carry and handle the operating machines and tools with caution to prevent them from falling
down.
Safety measures, such as wearing a helmet and a safety belt, must be taken.
Wear cold-proof clothes when working at heights in cold areas.
Check all lifting appliances thoroughly before starting the work, and ensure that they are
intact.
1.7.1 Hoisting Heavy Objects
This topic describes the safety precautions for hoisting heavy objects that you must follow when
installing, operating, and maintaining Huawei devices.
WARNING
When heavy objects are being hoisted, do not walk below the cantilever or hoisted objects.
l
Only trained and qualified personnel can perform hoisting operations.
Before hoisting heavy objects, check that the hoisting tools are complete and in good
condition.
Before hoisting heavy objects, ensure that the hoisting tools are fixed to a secure object or
wall with good weight-bearing capacity.
Issue orders with short and explicit words to ensure correct operations.
Ensure that the angle between the two cables is less than or equal to 90 degrees during the
lifting, as shown in Figure 1-4.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Figure 1-4 Hoisting heavy objects
1.7.2 Using Ladders
This topic describes safety precautions for using ladders.
Checking Ladders
l
Before using a ladder, check whether the ladder is damaged. After checking that the ladder
is in good condition, you can use the ladder.
Before using a ladder, you should know the maximum weight capacity of the ladder. Avoid
overweighing the ladder.
Placing Ladders
The proper slant angle of the ladder is 75 degrees. You can measure the slant angle of the ladder
with an angle square or your arms, as shown in Figure 1-5. When using a ladder, to prevent the
ladder from sliding, ensure that the wider feet of the ladder are downward, or take protection
measures for the ladder feet. Ensure that the ladder is placed securely.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
Figure 1-5 Slanting a ladder
Climbing Up a Ladder
When climbing up a ladder, pay attention to the following points:
l
Ensure that the center of gravity of your body does not deviate from the edges of the two
long sides.
Before operations, ensure that your body is stable to reduce risks.
Do not climb higher than the fourth rung of the ladder (counted from up to down).
If you want to climb up a roof, ensure that the ladder top is at least one meter higher than the
roof, as shown in Figure 1-6.
Figure 1-6 Ladder top being one meter higher than the roof
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
1.8 Mechanical Safety
This topic describes safety precautions for drilling holes, handling sharp objects, operating fans,
and carrying heavy objects.
Drilling Holes
WARNING
Do not drill holes on the cabinet without prior permission. Drilling holes without complying
with the requirements affects the electromagnetic shielding performance of the cabinet and
damages the cables inside the cabinet. In addition, if the scraps caused by drilling enter the
cabinet, the printed circuit boards (PCBs) may be short-circuited.
l
Before drilling a hole on the cabinet, remove the cables inside the cabinet.
Wear an eye protector when drilling holes. This is to prevent eyes from being injured by
the splashing metal scraps.
Wear protection gloves when drilling holes.
Take measures to prevent the metallic scraps from falling into the cabinet. After the drilling,
clean up the metallic scraps.
Sharp Objects
WARNING
Wear protection gloves when carrying the device. This is to prevent hands from being injured
by the sharp edges of the device.
Fans
l
When replacing parts, place the objects such as the parts, screws, and tools properly. This
is to prevent them from falling into the operating fans, which damages the fans or device.
When replacing the parts near fans, keep your fingers or boards from touching operating
fans before the fans are powered off and stop running. Otherwise, the hands or the boards
are damaged.
Carrying Heavy Objects
Wear protection gloves when carrying heavy objects. This is to prevent hands from being hurt.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
WARNING
l The carrier must be prepared for load bearing before carrying heavy objects. This is to prevent
the carrier from being strained or pressed by the heavy objects.
l When you pull a chassis out of the cabinet, pay attention to the unstable or heavy objects on
the cabinet. This is to prevent the heavy objects on the cabinet top from falling down, which
may hurt you.
l
Generally, two persons are needed to carry a chassis. It is prohibited that only one person
carries a heavy chassis. When carrying a chassis, the carriers should stretch their backs and
move stably to avoid being strained.
When moving or lifting a chassis, hold the handles or bottom of the chassis. Do not hold
the handles of the modules installed in the chassis, such as the power modules, fan modules,
and boards.
1.9 Other Precautions
This topic describes safety precautions for removing and inserting boards, binding signal cables,
and routing cables.
Removing and Inserting a Board
CAUTION
When inserting a board, wear an ESD wrist strap or ESD gloves, and handle the board gently to
avoid distorting pins on the backplane.
l
Slide the board along the guide rails.
Do not contact one board with another to avoid short-circuits or damage.
When holding a board in hand, do not touch the board circuits, components, connectors,
or connection slots of the board to prevent damage caused by ESD of the human body to
the electrostatic-sensitive components.
Binding Signal Cables
CAUTION
Bind the signal cables separately from the high-current or high-voltage cables.
Routing Cables
In the case of extremely low temperature, heavy shock or vibration may damage the plastic skin
of the cables. To ensure the construction safety, comply with the following requirements:
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1 Safety Precautions
When installing cables, ensure that the environment temperature is above 0C.
If the cables are stored in a place where the ambient temperature is below 0C, transfer
them to a place at room temperature and store the cables for more than 24 hours before
installation.
Handle the cables gently, especially in a low-temperature environment. Do not perform
any improper operations, for example, pushing the cables down directly from a truck.
High Temperature
WARNING
If the ambient temperature exceeds 55C, the temperature of the front panel surface marked the
flag may exceed 70C. When touching the front panel of the board in such an environment,
you must wear the protection gloves.
IF Cables
WARNING
Before installing or removing an IF cable, you must turn off the power switch of the IF board.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations
Notices for High-Risk Operations
About This Chapter
This chapter provides notices for the operations that may cause bodily injury or equipment
damage if they are not performed properly during the commissioning and maintenance of
microwave equipment.
2.1 Operation Guide for the Toggle Lever Switch
The ODU-PWR switch on the IF board is a toggle lever switch which must be turned on and off
as per the following instructions to avoid damaging the IF board.
2.2 Operation Guide for the IF Jumper
Before removing or installing an IF jumper, turn off the ODU-PWR switch to avoid bodily injury
or damage to the IF board and ODU.
2.3 Operation Guide for the IF Cable
Before removing or installing an IF cable, turn off the ODU-PWR switch to avoid bodily injury
or damage to the IF board and ODU.
2.4 Operation Guide for the IF Board
Before removing or installing an IF board, turn off the ODU-PWR switch to avoid bodily injury
or damage to the IF board and ODU.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
19
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations
2.1 Operation Guide for the Toggle Lever Switch
The ODU-PWR switch on the IF board is a toggle lever switch which must be turned on and off
as per the following instructions to avoid damaging the IF board.
Position and Description of the Toggle Lever Switch
The toggle lever switch is located on the IF board and controls the power that is fed to the ODU,
as shown in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1 Toggle lever switch
O: OFF
I : ON
Turning On the Toggle Lever Switch
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Gently pull on the toggle lever switch out.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
Turn it to the left.
3.
Release the toggle lever switch.
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations
Turning Off the Toggle Lever Switch
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Gently pull on the toggle lever switch.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
21
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
Turn it to the right.
3.
Release the toggle lever switch.
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations
2.2 Operation Guide for the IF Jumper
Before removing or installing an IF jumper, turn off the ODU-PWR switch to avoid bodily injury
or damage to the IF board and ODU.
Procedure
Step 1 Turn off the ODU-PWR switch on the IF board. For details, see 2.1 Operation Guide for the
Toggle Lever Switch.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
22
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations
DANGER
Ensure that the ODU is completely powered off before removing or installing the IF jumper.
Step 2 Remove or install the IF jumper.
----End
2.3 Operation Guide for the IF Cable
Before removing or installing an IF cable, turn off the ODU-PWR switch to avoid bodily injury
or damage to the IF board and ODU.
Procedure
Step 1 Turn off the ODU power switch on the IF board. For details, see 2.1 Operation Guide for the
Toggle Lever Switch.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
23
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations
DANGER
Ensure that the ODU is completely powered off before removing or installing the IF cable.
Step 2 Install or remove the IF cable.
----End
2.4 Operation Guide for the IF Board
Before removing or installing an IF board, turn off the ODU-PWR switch to avoid bodily injury
or damage to the IF board and ODU.
Procedure
Step 1 Turn off the ODU-PWR switch on the IF board. For details, see 2.1 Operation Guide for the
Toggle Lever Switch.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
24
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2 Notices for High-Risk Operations
DANGER
Ensure that the ODU is completely powered off before removing or installing the IF board.
Step 2 Disconnect the IF jumper or IF cable.
Step 3 Remove or install the IF board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
25
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3 Routine Maintenance
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance operations are performed to detect and rectify hidden faults before the
hidden faults cause damage to equipment and affect services. Routine maintenance operations
are preventive measures.
For the OptiX RTN 950, routine maintenance items are classified into routine maintenance items
carried out on the network management system (NMS), field maintenance items for indoor
equipment, and field maintenance items for outdoor equipment.
Routine Maintenance Items Carried Out on the NMS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Maintenance Item
Recomm
ended
Mainten
ance
Cycle
Remarks
Checking the NE Status
Every day
Browsing Current Alarms
Every day
Browsing History Alarms
Every
week
Browsing Abnormal Events
Every
week
Browsing Current Performance Events
Every
week
Browsing History Performance Events
Every
week
Browsing History Transmit Power and
Receive Power
Every
week
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
26
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3 Routine Maintenance
Maintenance Item
Recomm
ended
Mainten
ance
Cycle
Remarks
Testing IF 1+1 Switching
Half a
year
Applies only to the equipment that is
configured in 1+1 protection mode.
During the 1+1 protection switching,
the protected services are interrupted.
Hence, it is recommended that you
perform the 1+1 protection switching
when the traffic is light.
Testing the IF N+1 Switching
Half a
year
Applies only to the equipment that is
configured with N+1 protection.
Field Maintenance Items for Indoor Equipment
Maintenance Item
Recommended
Maintenance Cycle
Remarks
Checking the
Telecommunications Room
Every two months
Maintaining the
Environment of Outdoor
Cabinets
Half a year
Field Maintenance Items for Outdoor Equipment
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Maintenance Item
Recommended
Maintenance
Cycle
Remarks
Checking the ODU
Half a year
Checking the Hybrid Coupler
Half a year
Checking the Antenna
Half a year
Checking the IF Cable
Half a year
Checking the LOS Condition
Half a year
Carry out a
complete check
after a level-8 or
higher hurricane,
an earthquake, or
other exceptional
circumstances.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
27
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4 Emergency Maintenance
Emergency Maintenance
About This Chapter
Emergency maintenance operations are performed in the case of emergencies or natural factors
that may result in emergencies during the operation of the equipment.
4.1 Definition of Emergency
For microwave equipment, an emergency refers to interruption of microwave services.
4.2 Purposes of Emergency Maintenance
Emergency maintenance operations are performed to restore the services quickly. This is
different from troubleshooting, whose purposes are to locate and rectify the faults.
4.3 Procedure for Emergency Maintenance
The procedure for emergency maintenance consists of a main procedure and a sub-procedure
for field troubleshooting.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
28
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4 Emergency Maintenance
4.1 Definition of Emergency
For microwave equipment, an emergency refers to interruption of microwave services.
4.2 Purposes of Emergency Maintenance
Emergency maintenance operations are performed to restore the services quickly. This is
different from troubleshooting, whose purposes are to locate and rectify the faults.
4.3 Procedure for Emergency Maintenance
The procedure for emergency maintenance consists of a main procedure and a sub-procedure
for field troubleshooting.
NOTE
In the case of emergency events, the customers in China can contact the 24-hour technical support center of
Huawei at 400-830-2118, and the customers in areas outside China can contact the local Huawei offices.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
29
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4 Emergency Maintenance
Main Procedure for Emergency Maintenance
Figure 4-1 Main procedure for emergency maintenance
Start
Is there an incorrect
operation?
Yes
Cancel the operation
No
2
Service interruoted by
external causes?
Yes
Contact tealted departments
to handle the problem
No
Query NE status and
alarms by using the NMS
NE access successful and
alaarms cleared?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
Proceed with the next step
Rectify the fault on site
No
Is the service
restored?
Yes
Is the service restored?
No
Contact Huawei engineers
Yes
5
Check the troubleshooting result
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
30
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4 Emergency Maintenance
Table 4-1 Description of the main procedure for emergency maintenance
Comment
No.
Description
The common incorrect operations are as follows:
l Modifying data configuration
l Performing loopback operations
l Shutting down the laser
l Muting the ODU
l Replacing boards/cables
l Loading the software
Faults owing to external factors, including the power supply, cables,
environment, and terminal equipment (such as switch devices)
The procedure is as follows:
1. Check the NE status.
2. If the NE is unreachable to the NMS, perform field troubleshooting
according to Figure 4-2. If alarms are reported on the NE, browse the
current alarms.
Generally, the following alarms can be cleared on the NMS:
APS_MANUAL_STOP, APS_FAIL, BD_NOT_INSTALLED,
DBMS_ERROR, ETH_APS_LOST, ETH_APS_SWITCH_FAIL,
ETH_APS_TYPE_MISMATCH, HP_TIM, HP_UNEQ,
IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN, IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN, J0_MM,
LOOP_ALM, LPS_UNI_BI_M, LP_SLM, LP_TIM, LP_UNEQ,
NESOFT_MM, NESF_LOST, RADIO_MUTE, WRG_BD_TYPE,
ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI, ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK,
MW_CFG_MISMATCH.
After the fault is rectified, proceed as follows:
1. Check the alarms, and ensure that the system is running properly.
2. Assign personnel to monitor the operation of the system during the peak
service hour, ensuring that subsequent faults can be handled in time.
3. Fill in the field maintenance operation sheet, record the fault symptoms
and troubleshooting results, and then send them to Huawei. Table 4-2
shows the field maintenance operation sheet.
Table 4-2 Field maintenance operation sheet
Maintained on
Actual Step
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Maintained by
Step in the Entire
Procedure
Troubleshooting
Result
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Remarks
31
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4 Emergency Maintenance
Maintained on
Actual Step
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Maintained by
Step in the Entire
Procedure
Troubleshooting
Result
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Remarks
32
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4 Emergency Maintenance
Field Troubleshooting Sub-Procedure
Figure 4-2 Field troubleshooting sub-procedure
Start
Obvious equipment Yes
damage?
Repair or replace
the equipment
No
Is the PWR indicator
on the PIU on?
No
Troubleshoot the
power input
Yes
Browse alarms
locally by using the
LCT
Yes
Equipment
alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
4
Yes
Radio link
alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
5
Yes
High order
path alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
6
Yes
Low order
path alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
Faulty interconnection with
SDH/PDH equipment?
Yes
7 Troubleshoot the
inter-connection
faulty
No
Packet service
fault?
Yes
Troubleshoot the
packet service fault
No
Locate the fault by
performing loopback
operations section by
section
Proceed to the next
step
No
Is the service
restored?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
33
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4 Emergency Maintenance
Table 4-3 Description of the field troubleshooting sub-procedure
Comment
No.
Description
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Check whether the circuit breaker for the input power is off. If the circuit
breaker is automatically turned off, find the cause (such as short circuits
or insufficient fuse capacity), and rectify the fault accordingly.
2. Check the power cables, especially the connectors of the power cables. If
the power cables or connectors of the power cables are incorrect, replace
the power cables or re-prepare the connectors of the power cables.
3. Check the voltage and polarization of the input power. If the voltage or
polarization of the input power does not meet the requirements, contact
power engineers for troubleshooting.
NOTE
The fuse capacity can be no less than 20A. The standard voltage of the input power is
-48 V/-60 V and the permitted voltage ranges from -38.4 V to -72.0 V.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Connecting the Web LCT to the IDU.
2. Creating NEs by Using the Search Method.
3. Logging In to an NE.
4. Checking Alarms.
NOTE
If you fail to log in to the created NE, ensure that the operations you performed are
correct, and then locate and rectify the fault according to the indicators of the system
control, switching, and timing board. For details about the indicators, see the OptiX RTN
950 IDU Hardware Description.
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l HARD_BAD
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l BD_STATUS
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l IF_CABLE_OPEN
l VOLT_LOS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
34
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
4 Emergency Maintenance
l PG_LINK_FAIL
l PG_PRT_DEGRADED
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l R_LOS
l R_LOF
l R_LOC
l MS_AIS
l AU_AIS
l AU_LOP
l B1_EXC
l B2_EXC
l MW_BER_EXC
5
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l HP_LOM
l B3_EXC
l HP_UNEQ
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l TU_AIS
l TU_LOP
l BIP_EXC
l LP_UNEQ
l T_ALOS
l E1_LOC
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
See 5.6 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with SDH Equipment or 5.7
Troubleshooting the Interconnection with PDH Equipment.
See 5.8 Troubleshooting Native Ethernet Service Faults, 5.9
Troubleshooting Ethernet Service on the EoS/EoPDH Plane, 5.11
Troubleshooting CES Services, 5.12 Troubleshooting ATM Services, and
5.13 Troubleshooting Ethernet Services Carried by PWs.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
35
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
About This Chapter
This guide describes the general troubleshooting procedure and the methods of rectifying the
common faults.
5.1 General Troubleshooting Procedure
When handling a fault, make a detailed record of the fault phenomena. The customers in China
can contact our 24-hour technical support center at 400-830-2118, and the customers in areas
outside China can contact the local Huawei offices.
5.2 Troubleshooting Service Interruptions
The service interruption fault indicates the service transmission failure due to an equipment fault
or a link fault.
5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link
When an NE reports MW_LOF, MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD or MW_FEC_UNCOR due
to failure or performance deterioration of a radio link, there is a radio link fault.
5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services
When an NE reports an alarm or a performance event on the IF board, regenerator section (RS),
multiplex section (MS), higher order path (HP), or lower order path (LP), there are bit errors in
services.
5.5 Troubleshooting Pointer Justifications
When an NE reports a large number of justification events about the administrative unit (AU)
pointer or the tributary unit (TU) pointer, there are pointer justification faults.
5.6 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with SDH Equipment
An interconnection fault occurs when the NE fails in transmitting SDH services with other SDH
equipment.
5.7 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with PDH Equipment
An interconnection fault occurs when the NE fails in transmitting PDH services with other PDH
equipment.
5.8 Troubleshooting Native Ethernet Service Faults
An Ethernet service fault may be the Ethernet service interruption or Ethernet service
deterioration.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
36
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
5.9 Troubleshooting Ethernet Service on the EoS/EoPDH Plane
The Ethernet services transmitted on the EoS/EoPDH plane can be transmitted over a TDM
network. The faults of the EoS/EoPDH-plane Ethernet services include service interruption and
service degradation.
5.10 Troubleshooting MPLS Tunnels
This section describes how to troubleshoot MPLS tunnels by using the MPLS OAM function or
MPLS Ping/Traceroute function.
5.11 Troubleshooting CES Services
This section describes how to troubleshoot CES services that are interrupted or degraded.
5.12 Troubleshooting ATM Services
This section describes how to troubleshoot ATM services that are interrupted or degraded.
5.13 Troubleshooting Ethernet Services Carried by PWs
This section describes how to troubleshoot Ethernet services that are carried by PWs and
transmitted in the PSN. These Ethernet services are considered faulty when they are interrupted
or deteriorate.
5.14 Troubleshooting Orderwire Faults
If orderwire calls cannot get through when services are normal, there is an orderwire fault.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
37
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
5.1 General Troubleshooting Procedure
When handling a fault, make a detailed record of the fault phenomena. The customers in China
can contact our 24-hour technical support center at 400-830-2118, and the customers in areas
outside China can contact the local Huawei offices.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
38
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-1 General troubleshooting procedure
Start
1
Record the fault phenomena
Caused by external factors?
Yes
Other troubleshooting
procedures
No
Analyze fault causes and locate
the fault
Is the fault
rectified?
4
Yes
No
Report to Huawei
Make a solution together
Attempt to rectify the fault
No
Is the service restored?
Yes
Observe the operation
No
Is the fault
rectified?
Yes
Fill in the troubleshooting
report
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
39
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-1 General troubleshooting procedure
Comment
No.
Description
When recording the fault phenomena, make a true and detailed record of the
entire process of the fault. Record the exact time when the fault occurs and
the operations performed before and after the fault occurs. Save the alarms,
performance events, and other important information.
You can use the click-to-collect function on the U2000 to collect data.
Faults owing to external factors, including the power supply, cables,
environment, and terminal equipment (such as switch devices)
If the fault is caused by the equipment, see 5.2 Troubleshooting Service
Interruptions.
To provide feedbacks or obtain technical support, customers in China can
contact the 24-hour technical support center at 400-830-2118, and the
customers in areas outside China can contact the local Huawei offices.
5.2 Troubleshooting Service Interruptions
The service interruption fault indicates the service transmission failure due to an equipment fault
or a link fault.
Fault Causes
l
The operation is improper.
The configuration data changes, the loopback is performed, the cable is replaced, or the
board is replaced.
The transmission NE or link is faulty.
The interconnection is improper.
If the transmission equipment functions normally and the connection is normal, check
whether the interconnection between the transmission equipment is proper and whether the
switch equipment is faulty.
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Check the operations before the service interruption to determine whether the service
interruption results from an incorrect operation.
2.
Query alarms on the centralized NMS or the NMS that is used on the site, and then locate
the fault based on the alarm analysis.
If multiple NEs report alarms, analyze the alarms in the following order: equipment alarm,
line alarm, higher order path alarm, and lower order path alarm.
3.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If the fault cannot be located through the alarm analysis method, locate the fault by
performing loopback section by section or replacing the corresponding parts.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
40
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
CAUTION
If the fault cannot be rectified immediately, restore the services quickly by adjusting the service
route or performing a forced switching.
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-2 General procedure for troubleshooting the service interruption
Start
Incorrect
operation?
Yes
Cancel the operation
No
Service interrupted
by external causes?
Yes
Contact related
departments to solve
the problem
No
Query NE status and alarms
by using the centralized NMS
NE access successful
and alarms cleared?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
Rectify the fault on site
Proceed with the
next step
No
Service restored?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
41
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-2 Description of the general procedure for troubleshooting the service interruption
Comment
No.
Description
The common incorrect operations are as follows:
l Modifying the data configuration
l Loopback
l Shutting down the laser
l Muting the ODU
l Replacing the board or cable
l Loading the software
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Faults owing to external factors, including the power supply, cables,
environment, and terminal equipment (such as switch devices)
For details, see 8.3.1 Checking the NE Status and 8.3.3 Browsing Current
Alarms.
Generally, the following alarms can be cleared on the NMS:
APS_MANUAL_STOP, APS_FAIL, BD_NOT_INSTALLED,
DBMS_ERROR, HP_TIM, HP_UNEQ, J0_MM, LOOP_ALM,
LPS_UNI_BI_M, LP_SLM, LP_TIM, LP_UNEQ, NESOFT_MM,
NESF_LOST, NESTATE_INSTALL, MW_CFG_MISMATCH,
RADIO_MUTE, and WRG_BD_TYPE.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
42
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-3 Field troubleshooting sub-procedure
Start
Obvious equipment Yes
damage?
Repair or replace
the equipment
No
Is the PWR indicator
on the PIU on?
No
Troubleshoot the
power input
Yes
Browse alarms
locally by using the
LCT
Yes
Equipment
alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
4
Yes
Radio link
alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
5
Yes
High order
path alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
6
Yes
Low order
path alarm?
Clear the alarm
No
Faulty interconnection with
SDH/PDH equipment?
Yes
7 Troubleshoot the
inter-connection
faulty
No
Packet service
fault?
Yes
Troubleshoot the
packet service fault
No
Locate the fault by
performing loopback
operations section by
section
Proceed to the next
step
No
Is the service
restored?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
43
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-3 Description of the field troubleshooting sub-procedure
Comment
No.
Description
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Check whether the circuit breaker for the input power is off. If the circuit
breaker is automatically turned off, find the cause (such as short circuits
or insufficient fuse capacity), and rectify the fault accordingly.
2. Check the power cables, especially the connectors of the power cables. If
the power cables or connectors of the power cables are incorrect, replace
the power cables or re-prepare the connectors of the power cables.
3. Check the voltage and polarization of the input power. If the voltage or
polarization of the input power does not meet the requirements, contact
power engineers for troubleshooting.
NOTE
The fuse capacity can be no less than 20A. The standard voltage of the input power is
-48 V/-60 V and the permitted voltage ranges from -38.4 V to -72.0 V.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Connecting the Web LCT to the IDU.
2. Creating NEs by Using the Search Method.
3. Logging In to an NE.
4. Checking Alarms.
NOTE
If you fail to log in to the created NE, ensure that the operations you performed are
correct, and then locate and rectify the fault according to the indicators of the system
control, switching, and timing board. For details about the indicators, see the OptiX RTN
950 IDU Hardware Description.
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l HARD_BAD
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l BD_STATUS
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l IF_CABLE_OPEN
l VOLT_LOS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
44
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
5 Troubleshooting
l PG_LINK_FAIL
l PG_PRT_DEGRADED
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l R_LOS
l R_LOF
l R_LOC
l MS_AIS
l AU_AIS
l AU_LOP
l B1_EXC
l B2_EXC
l MW_BER_EXC
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l HP_LOM
l B3_EXC
l HP_UNEQ
6
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l TU_AIS
l TU_LOP
l BIP_EXC
l LP_UNEQ
l T_ALOS
l E1_LOC
See 5.6 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with SDH Equipment or 5.7
Troubleshooting the Interconnection with PDH Equipment.
See 5.8 Troubleshooting Native Ethernet Service Faults, 5.9
Troubleshooting Ethernet Service on the EoS/EoPDH Plane, 5.11
Troubleshooting CES Services, 5.12 Troubleshooting ATM Services, and
5.13 Troubleshooting Ethernet Services Carried by PWs.
Experience and Summary
The maintenance personnel need to perform the routine maintenance operations periodically, to
detect and rectify faults before the faults affect the services and thus to reduce the equipment
fault rate.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
45
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link
When an NE reports MW_LOF, MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD or MW_FEC_UNCOR due
to failure or performance deterioration of a radio link, there is a radio link fault.
Context
The key to locating a radio link fault is to check whether the transmit power and the receive
power are normal and whether there is an external interference.
In the following two cases, the transmit power is abnormal. The first case is that the transmit
power exceeds the range that the ODU supports. The second case is that the difference between
the actual transmit power and the preset value is more than 2 dB when the ATPC is disabled.
The relevant alarms and performance events are as follows:
l
RADIO_TSL_HIGH
RADIO_TSL_LOW
TSL_CUR
TSL_MAX
TSL_MIN
TSL_AVG
NOTE
For the range of the transmit power, see the OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System Product
Description.
In the following two cases, the receive power is abnormal. In the first case, the receive power
is lower than the normal value (Normal value = Planned value - 3 dB). In the second case, the
receive power is lower than the receiver sensitivity or higher than the free space receive power
due to fading. The relevant alarms and performance events are as follows:
l
RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF
RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH
RADIO_RSL_HIGH
RADIO_RSL_LOW
RSL_CUR
RSL_MAX
RSL_MIN
RSL_AVG
NOTE
In the case of the radio link whose AM function is enabled, the receiver sensitivity is the specific receiver
sensitivity at the guaranteed capacity.
For details on the receiver sensitivity, see the OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System Product
Description.
Generally, external interference is classified into co-channel interference and adjacent channel
interference.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
46
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Co-channel interference refers to crosstalk from two different radio transmitters that use
the same frequency channel. Hence, the entire spectrum may be affected.
Adjacent channel interference refers to signal impairment to one frequency, due to presence
of another signal on a nearby frequency. Hence, a part of the spectrum is affected.
Interference is closely related to the frequency. Hence, the radio link may be faulty in one
direction if interference exists on the radio link.
Fault Causes
Table 5-4 Causes of radio link faults
Fault
Common Fault Cause
The transmit power is abnormal.
The ODU is faulty.
The receive power is always lower than the
normal value.
l The antenna direction is not adjusted
properly.
l The antennas have different polarization
directions.
l There is a mountain or building in the
transmit direction.
l The antenna is faulty or the connection
between the antenna and the ODU is
abnormal (for example, the waveguide
interface of the ODU is wet or the flexible
waveguide is not connected properly).
l The ODU is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
The receive power is abnormal due to slow
down fading.
The fading margin is insufficient.
The receive power is abnormal due to fast
fading.
The multipath fading is fast.
The receive power is normal or slow up
fading occurs, but the signal-noise ratio
(SNR) is abnormal.
There is external interference.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
47
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
NOTE
Based on the RSL, fading is classified into up fading and down fading.
l Up fading
The RSL is higher than the RSL in the free space. The difference can be 10-odd decibels.
l Down fading
The RSL is lower than the RSL after free space fading. The difference can be tens of decibels.
Based on the fading time, fading is classified into fast fading and slow fading.
l Fast fading
The fading lasts from several milliseconds to tens of seconds.
Generally, fast fading is caused by multipath fading. It occurs periodically. To be specific, fast fading
occurs in the period from 18:00 to 20:00 of a day or in a certain season of a year.
l Slow fading
The fading lasts from tens of seconds to several hours.
Generally, slow up fading is caused by interference. Slow down fading is caused by rain, and therefore
is also called rain fading. Rain fading occurs on links working at a frequency of 10 GHz or in areas
where heavy rain occurs.
Generally, slow down fading and fast fading are caused by factors related to the transmission link. Hence,
the radio link may be faulty in both directions in the case of slow down fading or fast fading.
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Check whether the ODU is muted, powered off, or looped back. Check whether the data
configuration is correct.
2.
Check whether the ODU and the IF board are faulty.
3.
If the transmit power is abnormal, replace the ODU.
4.
If the receive power is abnormal, analyze and locate the causes according to the fading
type.
5.
If the receive power is normal but the SNR is abnormal, check whether there is interference
before you proceed.
6.
If the preceding methods cannot locate faults, perform loopback operations.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
48
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-4 Procedure for troubleshooting the radio link
Start
Incorrect operation?
Yes
Cancel the
operation
No
2
ODU or IF related
alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
3
Query the
receive/transmit power
and SNR
No
Transmit power
normal?
Rectify the fault
Yes
RSL always lower
than the normal
value?
Yes
5
Rectify the fault
No
Slow down fading
causes abnormal
RSL?
Yes
6
Rectify the fault
No
Fast fading
causes abnormal
RSL?
Yes
7
Rectify the fault
No
Radio link
faulty in one
direction?
No
9
Perform loopback
operations
Yes
8
Rectify the fault
Proceed to
the next step
No
Is the fault
rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
49
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-5 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting the radio link
Comment No.
Description
1 Rectify
incorrect
operations.
Check the following points:
l Check whether the ODU is powered off.
l Check whether the ODU is muted.
l Check whether the IF board is looped back.
l Check whether the data configuration at the transmit end is the same
as the data configuration at the receive end.
l Check whether the data configuration matches the types of the ODU
and the hybrid coupler.
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
2 Rectify
equipment faults. l VOLT_LOS
l CONFIG_NOSUPPORT
l HARD_BAD
l TEMP_ALARM
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l RADIO_MUTE
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l IF_CABLE_OPEN
l MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
3 Query the
receive/transmit
power, and the
SNR
Query the receive/transmit power, and the SNR in the latest one week.
For details, refer to Querying the Historical Transmit Power and Receive
Power and Querying the SNR Values of a Radio Link.
4 Troubleshoot
the anomaly of
the transmit
power.
Replace the ODU.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
50
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Comment No.
Description
5 Troubleshoot
the anomaly that
the receive power
is lower than the
normal value.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. If the receive power decreases sharply and does not recover, check the
installation of the antenna. Ensure that the azimuth angle of the
antenna meets the requirement.
Check whether the antenna is aligned properly. Check whether the
received signal is from the main lobe.
If the antenna direction is not aligned properly, adjust the antenna in
a wide range.
2. If the difference between the receive power of the main ODU and
standby ODU at one end of the 1+1 HSB radio link is beyond the range
from 0 dB to 9 dB (in the case of an unbalanced hybrid coupler) or
beyond the range from 0 dB to 5 dB (in the case of a balanced hybrid
coupler), perform 1+1 HSB switching or replace the ODUs and hybrid
coupler to narrow down the fault to a specific part.
3. If the difference between the RSL at the receive end and transmit end
is larger than 10 dB, replace the ODUs to check whether the main or
standby ODU is faulty.
4. Check whether the setting of the polarization direction of the antenna
is correct. Rectify the wrong polarization direction.
5. Check whether the cable connector is made in accordance with
specifications. If any cable connectors do not comply with the
specifications, see the Installation Reference and remake cable
connectors.
6. Check whether the IF cable is soggy, broken, or pressed. If yes,
replace the IF cable.
7. Check whether there is a mountain or building in the transmit
direction. If the line of sight (LOS) is unavailable, adjust the height or
position of the antenna.
8. Replace the ODUs and hybrid coupler to narrow down the fault to a
specific part.
9. Check whether the gains of the antennas at the receive and transmit
ends comply with the specifications. Replace the antenna whose gain
does not comply with the specifications.
6 Troubleshoot
slow down
fading.
Contact the network planning department to make the following changes:
l Increase the fade margin on links.
l Use low-frequency ODUs.
l Use vertical polarization instead of horizontal polarization.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
51
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Comment No.
Description
7 Troubleshoot
fast fading.
Contact the network planning department to make the following changes:
l Adjust the position of the antenna to reduce the multipath fading.
1. Adjust the height of the antennas at both ends to increase the height
difference between the antennas.
2. In the case of strong reflection surfaces such as water surfaces,
plains, and smooth mountaintops, adjust the antenna to remove
reflection points. Alternatively, use the actual terrain to mask
surface reflection.
3. Lower the antenna height to reduce the path margin with LOS
conditions guaranteed.
l Adjust the RF configuration to change the radio link to the 1+1 SD
mode.
l In the case of a 1+1 SD radio link, adjust the height difference between
two antennas to ensure that the receive power of one antenna is higher
than the receive power of the other antenna.
l Increase the fading margin, by replacing the original antennas with
antennas of a larger diameter or increasing the transmit power of the
original antennas.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
52
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Comment No.
Description
8 Troubleshoot
interference.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. There is co-channel interference.
1. Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
2. Check the RSL at the local end. If the RSL exceeds -90 dBm, it
indicates that there is co-channel interference that may affect the
long-term availability and performance of the system.
2. There is adjacent channel interference.
1. Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
2. Adjust the microwave working mode at the local end and use the
minimum channel spacing.
3. Decrease the receive frequency at the local end by a half of the
channel spacing.
4. Test and record the RSL.
5. Increase the receive frequency at the local end, with a step of 0.5
MHz or 1 MHz. Record the RSL accordingly until the receive
frequency is equal to the original receive frequency plus a half of
the channel spacing.
6. Compare the recorded RSL values, and check whether the RSL in
a certain spectrum is abnormal if the received frequency is within
the permitted range.
3. Use Huawei frequency scanning scripts or a spectrum analyzer to
analyze the interference source.
4. Contact the network planning department to modify the networking
planning and design.
1. Plan Tx high sites and Tx low sites correctly to avoid using them
at the same time.
2. Plan frequencies or polarization modes correctly to avoid the same
polarization direction for microwave signals and interference
signals. Plan routes correctly.
5. Contact the spectrum management department to clear the
interference spectrum.
9 Perform
loopback
operations to
locate the fault.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Perform an inloop at the IF port.
If the fault persists after the inloop is performed, replace the IF
board.
2. Replace the ODU.
If the fault is rectified after the ODU is replaced, it indicates that the
ODU is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
53
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Experience and Summary
l
During the commissioning, ensure that the antenna is aligned properly, to prevent possible
incipient faults.
Periodically collect and analyze the data about the changes in the transmit power and receive
power so that you can detect and then rectify the incipient faults accordingly in time.
5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services
When an NE reports an alarm or a performance event on the IF board, regenerator section (RS),
multiplex section (MS), higher order path (HP), or lower order path (LP), there are bit errors in
services.
Fault Phenomena
The IF bit errors refer to the bit errors that the IF board detects through the self-defined overhead
byte in the microwave frame. The related alarms and performance events are as follows:
l
MW_BER_EXC
MW_BER_SD
MW_CFG_MISMATCH
MW_LOF
IF_BBE
IF_ES
IF_SES
IF_CSES
IF_UAS
The RS bit errors refer to the bit errors that the line processing unit or the IF board that works
in SDH mode through the B1 overhead byte in the RS overhead. The related alarms and
performance events are as follows:
l
B1_EXC
B1_SD
RS_CROSSTR
RSBBE
RSES
RSSES
RSCSES
RSUAS
NOTE
The IF board that works in PDH mode may also detect the previous RS bit error alarms and performance
events. In this case, the IF board detects bit error alarms and performance events in the PDH microwave
frame through the self-defined B1 byte.
The MS bit errors refer to the bit errors that the line board detects through the B2 byte in the MS
overhead. The related alarms and performance events are as follows:
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
54
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B2_EXC
B2_SD
MS_CROSSTR
MSBBE
MSES
MSSES
MSCSES
MSUAS
5 Troubleshooting
The HP bit errors refer to the bit errors that the line processing unit or the IF board that works
in SDH mode through the B3 byte in the HP overhead. The related alarms and performance
events are as follows:
l
B3_EXC
B3_SD
HP_CROSSTR
HPBBE
HPES
HPSES
HPCSES
HPUAS
The LP bit errors refer to the bit errors that the tributary board or IF board detects through the
V5 byte in the VC-12 overhead. The related alarms and performance events are as follows:
l
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
LP_CROSSTR
LPBBE
LPES
LPSES
LPCSES
LPUAS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
55
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Fault Causes
Table 5-6 Causes of bit errors
Fault
Common Fault Cause
There are IF bit errors.
l The radio link is faulty.
Check whether the MW_BER_EXC,
MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR,
MW_LOF or RPS_INDI alarm is
reported. If yes, the radio link is faulty.
l The services are incorrectly configured.
Check whether the
MW_CFG_MISMATCH alarm is
reported. If yes, the number of E1 services
is inconsistent on both ends of the radio
link.
l The IF board at the local end or opposite
end is faulty.
There are RS bit errors.
l The line is faulty.
The common causes for bit errors on
the optical line are as follows: the
optical fiber line, the optical power is
abnormal, the fiber performance
deteriorates, or the fiber connector is
not clean.
In the case of bit errors on the radio
link, check whether the
MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD,
MW_FEC_UNCOR or RPS_INDI
alarm is reported. If yes, the radio link
is faulty.
l The line processing unit or IF board is
faulty.
l The clock unit is faulty.
l The quality of the clock over the network
declines.
When the quality of the clock over the
network declines, a pointer justification
event occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
56
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Fault
Common Fault Cause
There are not any RS bit errors but there are
MS bit errors or HP bit errors.
l The line processing unit or IF board is
faulty.
l The quality of the clock over the network
declines.
When the quality of the clock over the
network declines, a pointer justification
event occurs.
l The working temperature of the line
processing unit or IF board is excessively
high.
There are only LP bit errors.
l The tributary board is faulty.
l The cross-connect unit is faulty.
l The working temperature of the board is
excessively high.
l The working temperature of the crossconnect unit is excessively high.
l There is a power surge or an external
interference source, or the equipment is
not properly grounded. (This cause does
not need to be considered during the
troubleshooting of an IF board.)
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Analyze the equipment alarms and performance events that are related to service
configuration errors and bit errors.
2.
When there are many types of alarms and performance events on a service path, first analyze
RS bit errors, then MS bit errors, HP bit errors, and finally LP bit errors.
3.
When multiple paths have bit errors, first check whether the overlapping part of the service
paths is faulty.
4.
If you fail to locate the fault by analyzing the alarms and performance events, perform
loopback operations section by section.
5.
Replace the parts whose performance may deteriorate with new ones.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
57
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-5 Procedure for troubleshooting bit errors
Start
2
Is there an
equipment alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
3
Is there a pointer
justification event?
Yes
SDH optical
interface board
No
Is there an
RS bit error alarm or a
performance
event?
Yes
No
Is there an
MS/ HP alarm or
performance
event?
Troubleshoot the pointer
justification
Troubleshoot RS bit errors
on the SDH optical interface
board
If the
alarming
board is
IF board
4
Troubleshoot RS bit errors
on the IF board
5
Yes
Troubleshoot MS/HP bit
errors
No
6
Is there an LP
alarm?
No
Locate the fault by performing
loopback operations section
by section
Yes
Troubleshoot LP bit
errors
Proceed with the next step
No
Is the fault
rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
58
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-7 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting bit errors
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l TEMP_ALARM
l HARD_BAD
l MW_CFG_MISMATCH
See 5.5 Troubleshooting Pointer Justifications.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Check whether the line board reports the B1_EXC, B1_SD, or
RS_CROSSTR alarm.
2. Interchange the Tx fiber core and the Rx fiber core at both ends of the
service path. If bit errors change after the exchange, it indicates that the
fiber is faulty. Otherwise, the equipment at both ends of the service path
is faulty.
3. In the case of a fiber fault, check whether the fiber between the equipment
and the ODF and the section of the fiber that is led out of the
telecommunications room are pressed. In addition, check whether the fiber
connectors are clean.
4. In the case of faults at both ends of the service path, use a fiber jumper to
loop back the optical ports. If the fault persists after the loopback, the line
board may be faulty.
5. In the case of faults at both ends of the service path, you can also replace
the board where the line unit is located or interchange between the board
and another board of the same type that is working normally. If the alarm
changes after the exchange, it indicates that the board is faulty.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Check whether the IF board reports the MW_BER_EXC,
MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR, MW_LOF, RPS_INDI,
B1_EXC, B1_SD, or RS_CROSSTR alarm.
2. If any of the alarms are reported, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio
Link and rectify the fault.
3. If none of the alarms occurs, replace the IF board.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Perform a loopback on the line board that reports the alarm.
If the fault persists after the loopback, replace the line board.
If the fault is rectified after the loopback, replace the line board at the
transmit end.
2. If you fail to rectify the fault by replacing the line board, check whether
there is a power surge or an external interference source or whether the
equipment is not properly grounded.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
59
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
5 Troubleshooting
1. Replace the board where the services are configured based on how the
service paths that have bit errors overlap each other.
2. If you fail to rectify the fault by replacing the board, check whether there
is a power surge or an external interference source or whether the
equipment is not properly grounded.
Experience and Summary
NOTE
The TDM services mentioned refer to Native TDM services.
The handling procedure applies when the STM-1e port. is faulty
During the routine maintenance, check bit error performance events periodically and handle
them in time.
To locate a fault, prefer the method of analyzing alarms and performance events to the
method of performing loopback operations and the method of replacing the parts.
5.5 Troubleshooting Pointer Justifications
When an NE reports a large number of justification events about the administrative unit (AU)
pointer or the tributary unit (TU) pointer, there are pointer justification faults.
Fault Phenomena
When the position of the first byte of the VC-4 in the AU-4 payload changes, the AU pointer
makes a justification accordingly. The performance events related to the AU pointer justification
are as follows:
l
AUPJCHIGH
AUPJCLOW
AUPJCNEW
NOTE
The AU pointer justification is made at an upstream NE but is detected and reported at a downstream NE.
When the service is configured to be at the VC-12 level, apply the reframing process to terminate
the AU pointer justification. The terminating method is to transform the AU pointer justification
into the TU pointer justification. The performance events related to the TU pointer justification
are as follows:
l
TUPJCHIGH
TUPJCLOW
TUPJCNEW
NOTE
The TU pointer justification is made at the NE where the AU pointer is transformed into the TU pointer,
but is detected and reported by the tributary board of the NE where services are terminated.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
60
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Fault Causes
l
The clock sources or the clock source levels are configured incorrectly. As a result, there
are two clock sources on the same network or a timing loop occurs.
The fiber connections are incorrect. As a result, a timing loop occurs.
The quality of the clock source declines, the clock unit is faulty, or there are other clockrelated faults.
The tributary board is faulty (only for the TU pointer justification).
Fault Locating Methods
When there are both AU pointer justifications and TU pointer justifications on a service path,
first handle the AU pointer justifications and then the TU pointer justifications.
Fault
Fault Locating Method
AU pointer justification
1. Analyze and clear clock alarms.
2. Rectify the incorrect data configuration
and incorrect fiber connections.
3. Change the clock configuration to locate
the station whose clock is asynchronous
with the entire network.
4. Replace the parts whose performance may
deteriorate with new ones.
TU pointer justification
1. Analyze and clear clock alarms.
2. Rectify the incorrect data configuration
and incorrect fiber connections.
3. Change the clock and service
configuration to locate the station whose
clock is asynchronous with the entire
network.
4. Replace the parts whose performance may
deteriorate with new ones.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
61
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-6 Procedure for troubleshooting pointer justifications
Start
Is there a clock-related
alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
Check the clock
configuration
Incorrect
configuration?
Yes
Modify the data
configuration
No
Check the fiber
connection
Incorrect fiber
connection?
Yes
Reconnect the fibers
No
4
An AU pointer
justification event?
Yes Locate the NE whose clock
is out of synchronization
Locate the faulty board
No
6
A TU pointer
justification event?
No
Yes Locate the NE whose clock
is out of synchronization
Locate the faulty board
Proceed with the
next step
No
Is the fault rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
62
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-8 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting pointer justifications
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l TEMP_ALARM
l HARD_BAD
l LTI
l SYNC_C_LOS
l S1_SYN_CHANGE
l EXT_SYNC_LOS
Check the following points:
l Check whether there are two clock reference sources on the entire network.
l Check whether a timing loop is generated.
Query ECC routes to check whether the fibers are connected correctly. Check
the fiber connections in the east and west directions of the NE that reports the
pointer justification event.
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
1. Locate a VC-4 channel that reports an AU pointer justification event.
2. Along the service source direction of the VC-4 channel, locate the source
NE of the entire VC-4 service (not the source NE of a timeslot in the VC-4).
3. Set the clock of the source NE to the free-run mode. Set the other NEs to
trace the clock of the source NE along the direction of the VC-4 service.
4. Along the clock tracing direction, locate the line board that is the first to
report the AU pointer justification of the VC-4 path.
The clock of the remote NE to which the line board is connected is
asynchronous with the reference clock. Hence, the line board on the remote
NE that receives the clock signal, the line board that sends the clock signal
to the remote NE, and the clock unit of the remote NE, may be faulty.
5. Set the clock of the sink NE to the free-run mode. Set the other NEs to
trace the clock of the sink NE along the direction of the VC-4 service.
6. Along the clock tracing direction, locate the line board that is the first to
report the AU pointer justification of the VC-4 path.
The clock of the remote NE to which the line board is connected is
asynchronous with the reference clock. Hence, the line board on the NE
that receives the clock signal, the line board that sends the clock signal to
the NE, and the clock unit of the NE, may be faulty.
7. Compare the results and find out the common points.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the possibly faulty boards.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
63
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
5 Troubleshooting
1. Modify the service configuration to ensure that the NE where the clock
reference source functions as the central NE and that the other NEs have
the E1 services of the central NE.
2. Along the clock tracing direction, locate the NE that is the first to report
the TU pointer justification event.
The clock of the NE is asynchronous with the reference clock. Hence, the
line board on the NE that receives the clock signal, the line board that sends
the clock signal to the NE, and the clock unit of the NE, may be faulty.
3. Modify the configuration data to ensure that all the NEs trace the clock
along the other direction.
4. Along the clock tracing direction, locate the NE that is the first to report
the TU pointer justification event.
The clock of the NE is asynchronous with the reference clock. Hence, the
line board on the NE that receives the clock signal, the line board that sends
the clock signal to the NE, and the clock unit of the NE, may be faulty.
5. Compare the results and find out the common points.
NOTE
This method is also applicable to locating an AU pointer justification event.
Replace the possibly faulty boards. In the case of a TU pointer justification
event, check whether the line board, the clock board, and the tributary board
are faulty.
Experience and Summary
On a properly synchronized network, there are few pointer justifications (less than six per day
on each port). Hence, monitoring the pointer of an SDH transmission system is an effective way
to check the synchronization status of the system.
5.6 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with SDH
Equipment
An interconnection fault occurs when the NE fails in transmitting SDH services with other SDH
equipment.
Fault Causes
l
The VC-12 numbering method of the OptiX equipment is different from the numbering
method of the equipment of certain vendors.
The OptiX equipment applies the timeslot numbering method. The numbering formula is:
VC-12 number = TUG-3 number + (TUG-2 number - 1) x 3 + (TU-12 number - 1) x 21.
This method is also called as the method of numbering by order.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
64
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Certain equipment applies the line numbering method. The numbering formula is: VC-12
number = (TUG-3 number - 1) x 21 + (TUG-2 number - 1) x 3 + TU-12 number. This
method is also called as the interleaved method.
l
The overhead bytes at both ends are inconsistent.
The indexes of the SDH interfaces do not meet the requirements.
NOTE
In the case of interconnection with ATM or Ethernet equipment, the common cause for an interconnection
failure is that the service is not set to the VC-4 pass-through service and thus the overheads are processed
in the terminating mode instead of the pass-through mode.
Fault Locating Methods
Analyze the fault phenomena and alarms that are generated on the equipment. Check the possible
fault causes one after another.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
65
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-7 Procedure for troubleshooting the interconnection with SDH equipment
Start
Is the
interconnected equipment Yes
the ATM/IP equipment?
Set the interconnection
service to be the VC-4 passthrough service
No
Query the VC-12 numbering
method of the interconnected
equipment
Is the
numbering mode the
line numbering?
Yes
Modify the data configuration.
Use the line numbering
method to set the VC-12
No
1
Is there an overhead
setting related alarm?
Yes
No
Is the interface the
STM-1 electrical
interface?
3
Handle the alarm
2
Yes
Check the grounding
No
Test the indexes of interfaces
Do the interfaces meet
relevant standards?
Yes
No
Handle the faults of the
interconnected equipment
Go to the next
step
Handle the faults of the local
equipment
No
Is the fault cleared?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
66
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-9 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting the interconnection with SDH
equipment
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l J0_MM
l HP_TIM
l LP_TIM
l HP_SLM
l LP_SLM
Check the following points:
l Check whether all the equipment and the DDF in the equipment room are
jointly grounded.
l Check whether the shielding layer of the coaxial cable connector on the
DDF is connected to the protection ground.
l Check whether the shielding layers of coaxial cables are grounded in the
same way.
NOTE
Disconnect all the signal cables between the interconnecting equipment. Use a
multimeter to measure the level between the shielding layers of the coaxial cables at the
receive and transmit ends of the SDH equipment. In addition, measure the level between
the shielding layers of the coaxial cables at the receive and transmit ends of the opposite
equipment. If the potential difference is large (about 0.5 V), the fault may be caused by
the grounding.
Common indexes of the optical interfaces are as follows:
l Mean launched optical power
l Receiver sensitivity
l Overload optical power
l Permitted frequency deviation of the input interface
Common indexes of the electrical interfaces:
l Permitted frequency deviation of the input interface
l Allowed attenuation of the input interface
Experience and Summary
To rectify an interconnection fault, you must be familiar with the characteristics of the interfaces
on the interconnected equipment.
5.7 Troubleshooting the Interconnection with PDH
Equipment
An interconnection fault occurs when the NE fails in transmitting PDH services with other PDH
equipment.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
67
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Fault Causes
l
There is an impedance mismatch between interfaces.
The equipment is not grounded properly.
The cable performance deteriorates.
The indexes of the PDH interfaces do not meet the requirements.
Fault Locating Methods
Analyze the fault phenomena and alarms that are generated on the equipment. Check the possible
fault causes one after another.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
68
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-8 Procedure for troubleshooting the interconnection with PDH equipment
Start
1
Check the impedance of
the interfaces
Is there an
Yes
impedance mismatch?
Replace the cable or the
tributary board
No
2
Is the cable a
coaxial cable?
Yes
Check the grounding
No
3
Check the cables
Is in good conditions?
No
Adjust the cables
Yes
Test the indexes of
interfaces
Do the interfaces
meet standards?
No
Troubleshoot the faults on
the interconnected
equipment
Yes
Troubleshoot the faults
on the local equipment
Proceed with the next step
No
Is the fault rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
69
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-10 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting the interconnection with PDH
equipment
Comment
No.
Description
Check the impedance of the E1 path. Ensure that the impedance of the E1
path is consistent with the cable type.
Check the following points:
l Check whether all the equipment and the DDF in the telecommunications
room are jointly grounded.
l Check whether the shielding layers of the coaxial cable connectors on the
DDF are connected to the protection ground.
l Check whether the shielding layers of coaxial cables are grounded in the
same manner.
NOTE
Disconnect all the signal cables between the interconnecting equipment sets. Use a
multimeter to measure the level between the shielding layers of the coaxial cables at the
receive and transmit ends of the PDH equipment and the level between the shielding
layers of the coaxial cables at the receive and transmit ends of the equipment at the
opposite end. If the potential difference is large (about 0.5 V), the fault may be caused
due to the improper grounding.
Check the following points:
l Check whether the wires of the cable are correctly connected.
l Check whether the cable is broken or pressed.
l Check whether the cable signal is interfered (for example, when the trunk
cable is bound with the power cable, the cable signal is interfered by the
power signal).
NOTE
Checking the cables involves checking the cables from the DDF to the client side
and checking the cables from the DDF to the transmission equipment side.
Check the following indexes:
l Input jitter tolerance
l Permitted frequency deviation of the input interface
l Output jitter
l Output frequency deviation
Experience and Summary
NOTE
The PDH services mentioned refer to Native E1 services.
In the case of interconnection with PDH equipment, improper grounding is the most common
cause for an interconnection failure.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
70
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
5.8 Troubleshooting Native Ethernet Service Faults
An Ethernet service fault may be the Ethernet service interruption or Ethernet service
deterioration.
Prerequisite
The Ethernet service interruption indicates that the Ethernet service is completely interrupted.
The Ethernet service deterioration indicates that the Ethernet service is abnormal. For example,
the network access speed is low, the equipment delay is long, the packet loss occurs, or incorrect
packets exist in the received or transmitted data.
Fault Phenomena
The Ethernet service interruption indicates that the Ethernet service is completely interrupted.
The Ethernet service deterioration indicates that the Ethernet service is abnormal. For example,
the network access speed is low, the equipment delay is long, the packet loss occurs, or incorrect
packets exist in the received or transmitted data.
Table 5-11 Common faults of Ethernet services
Symptom
Alarm
Board
Ethernet services are
interrupted.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
WRG_BD_TYPE, or
BD_STATUS
EM6TA, EM6FA, EM6F,
EM6T
COMMUN_FAIL,
LAG_DOWN
ETH_LOS,
ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK,
or LOOP_ALM
Ethernet services are
degraded.
LASER_MOD_ERR
EM6F
HARD_BAD or
TEMP_ALARM
EM6TA, EM6FA, EM6F or
EM6T
FLOW_OVER or
LAG_MEMBER_DOWN
EM6TA, EM6FA, EM6F or
EM6T
AM_DOWNSHIFT
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2 or IFX2
Fault Causes
l
The possible human factors are as follows:
An Ethernet board loopback or a transmission line loopback occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
71
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
The parameter settings of the Ethernet ports, such as the port enabled state, working
mode, and flow control, are different from the parameter settings of the Ethernet ports
on the interconnected equipment.
The service configuration is incorrect.
l
The equipment at the local end is faulty.
The line board is faulty or has bit errors.
When the AM function is enabled, the Ethernet service bandwidth decreases due to the
downward AM switch.
The interconnected equipment is faulty.
The network cable is faulty.
The external electromagnetic interference is severe.
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Rectify the human-caused faults such as a loopback and a data configuration error.
2.
Locate the fault cause according to the equipment alarms.
3.
Locate the fault cause according to the RMON performance events and alarms.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
72
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-9 Procedure for troubleshooting Ethernet service faults
Start
Incorrect operation?
Yes
Cancel this operation
No
2
An equipment
alarm or alarm on
the radio link?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
3
An Ethernet alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
4
A loop formed by
the E-LAN service
trails?
No
Yes
Any abnormal
RMON performance
events?
Yes
5
Query the port and service
traffic and analyze the fault
causes
No
6
No
Troubleshoot equipment
faults by performing
loopbacks section by
section or replacing boards
Release the loop
Troubleshoot the fault
according to the flow of
handling RMON
performance events
Proceed
with the
next step
No
Is the fault
rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
73
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-12 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting Ethernet service faults
Comment
No.
Description
Check the following points:
l Whether a loopback is set for the Ethernet port
l Whether a loopback is set for the transmission line
l Whether the parameter settings of the Ethernet port, such as the port
enabled state, working mode, and flow control, are the same as the
parameter settings of the Ethernet port on the interconnected equipment
l Check whether the Ethernet protocol and the Ethernet service
configuration (especially the attributes of the Ethernet port) are correct.
Pay special attention to the following equipment alarms:
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l HARD_BAD
l BD_STATUS
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l AM_DOWNSHIFT
Pay special attention to the following line alarms:
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l MW_BER_EXC
l MW_BER_SD
l MW_RDI
l MW_FEC_UNCOR
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l ETH_LOS
l ETH_NO_FLOW
l LAG_DOWN
l LAG_MEMBER_DOWN
l FLOW_OVER
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Follow instructions in Detecting E-LAN Service Loops to check whether ELAN services are looped back. Release the loops if any are formed.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
74
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Comment
No.
Description
Query the rate of an Ethernet port and locate faults based on the analysis
of Ethernet port rates.
l If the Ethernet port connecting the peer equipment has a too high or too
low receive rate, the peer equipment is faulty.
l If the rate of the Integrated IP radio port approaches or reaches the license
capacity of the IF port, the license capacity is too low and you need to
apply for a license allowing for a higher capacity.
l If the transmit rate of the Integrated IP radio port approaches or reaches
the maximum Ethernet bandwidth of the IF port, the bandwidth of the IF
port is too low and needs to be increased by the network planning
personnel.
l If the transmit rate of the Integrated IP radio port is much lower than the
receive rate of the Ethernet port, or if the receive rate of the Integrated IP
radio port is much higher than the transmit rate of the Ethernet port, the
local end is faulty. Locate the fault as follows:
Check the Ethernet service configuration and QoS configuration.
By querying QoS packet loss data in RMON events on the NMS, check
whether QoS settings are correct according to the packet loss data.
Check the Ethernet interface board, IF board, and system control,
switching and timing board by means of board replacement.
If the transmitted traffic is equal to the received traffic, query the traffic on
the same port in each VLAN to check whether bandwidth preemption occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
For RMON performance events, see the D RMON Event Reference.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
75
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-10 Procedure for troubleshooting an RMON performance event
Start
1
View the statistics group
performance on an Ethernet port
Is there any FCS error?
Yes
Rectify the fault of line bit
errors
No
Yes
Is there any collision
or fragment?
Check the working mode
of the port
No
Are broadcast packets
excessive?
Yes
Handle the problem on
excessive broadcast
packets
No
Use a meter to perform the test
Is the test passed?
Yes
Rectify the fault of the
interconnected equipment
No
5
Is it a MTU setting
problem?
Yes
Modify the MTU
value
No
Rectify the equipment fault by
loopback section by section or
replacing the board
Proceed with
the next step
No
Is the fault
rectified?
Yes
End
Table 5-13 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting an RMON performance event
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Comment
No.
Description
8.17 Querying Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization of
Ethernet Ports to obtain the real-time performance statistics data of the
Ethernet port.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
76
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
5 Troubleshooting
l Check the Ethernet cable. If the Ethernet cable is not qualified, replace it
with a new one.
l Change the Ethernet port that accesses the services on the Ethernet board.
If the new port does not have the RMON performance of an FCS error, it
indicates that the hardware of the original port is faulty. Otherwise, the
hardware of the Ethernet port on the equipment at the opposite end is
faulty.
Check the following points:
l Whether the port operating rates on the equipment at both ends are the
same
l Whether the working modes (full duplex or half duplex) of the Ethernet
port on the equipment at both ends are the same
l Whether the Ethernet port is set to auto-negotiation mode at one end and
the Ethernet port is set to full duplex mode at the opposite end (When the
Ethernet port is set to auto-negotiation mode at one end, the Ethernet port
must not be set to full duplex mode at the opposite end.)
4
Check for the cause for excessive broadcast packets (for example, you have
set the loopback for the Ethernet interface board or set the VB filtering
table incorrectly) and solve the problem. If the problem is caused on the
equipment at the opposite end, set the threshold of broadcast packet
suppression for an Ethernet port to reduce broadcast packets.
Test the MTU of the network by using a test meter. The maximum frame
length that is set for a port should be longer than the MTU of the network.
Experience and Summary
To troubleshoot an Ethernet service fault, you must be familiar with the characteristics, working
mode, and configured protocols of interfaces on the Ethernet equipment.
5.9 Troubleshooting Ethernet Service on the EoS/EoPDH
Plane
The Ethernet services transmitted on the EoS/EoPDH plane can be transmitted over a TDM
network. The faults of the EoS/EoPDH-plane Ethernet services include service interruption and
service degradation.
Fault Phenomena
The Ethernet service interruption indicates that the Ethernet service is completely interrupted.
The Ethernet service deterioration indicates that the Ethernet service is abnormal. For example,
the network access speed is low, the equipment delay is long, the packet loss occurs, or incorrect
packets exist in the received or transmitted data.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
77
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-14 Common faults of Ethernet services
Symptom
Alarm
Board
Ethernet services are
interrupted.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
WRG_BD_TYPE, or
BD_STATUS
EMS6/EFP8
ALM_GFP_dLFD or
ALM_GFP_dCSF
ETH_LOS or LOOP_ALM
LAG_PORT_FAIL,
LAG_VC_PORT_FAIL,
LCAS_TLCT, or
LCAS_TLCR
Ethernet services are
abnormal.
HARD_BAD or
TEMP_ALARM
FLOW_OVER
LCAS_FOPT,
LCAS_FOPR,
LCAS_PLCT, or
LCAS_PLCR
Fault Causes
l
The possible human factors are as follows:
An Ethernet board loopback or a transmission line loopback occurs.
The parameter settings of the Ethernet ports, such as the port enabled state, working
mode, and flow control, are different from the parameter settings of the Ethernet ports
on the interconnected equipment.
The configuration of the encapsulation/mapping protocol or the LCAS protocol is
inconsistent on both ends of the link.
The timeslot binding of VCTRUNKs is inconsistent on both ends of the link
The service configuration is incorrect.
The equipment at the local end is faulty.
The line board is faulty or has bit errors.
The interconnected equipment is faulty.
The network cable is faulty.
The external electromagnetic interference is severe.
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Rectify the human-caused faults such as a loopback and a data configuration error.
2.
Locate the fault cause according to the equipment alarms.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
78
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3.
5 Troubleshooting
Locate the fault cause according to the RMON performance events and alarms.
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-11 Procedure for troubleshooting Ethernet service faults
Start
11
Incorrect operation?
Yes
Cancel this operation
No
2 An equipment alarm Yes
or alarm on the radio
link?
No
3
An Ethernet
alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
Clear the alarm
Query the port and service
traffic and analyze the fault
causes
No
4 A loop formed by the Yes
E-LAN service trails?
Release the loop
No
5
Any abnormal
RMON performance
events?
Yes
Troubleshoot the fault according
to the flow of handling RMON
performance events
No
Fault on the
opposite
equipment?
Yes
Troubleshoot faults on the
opposite equipment
No
Troubleshoot equipment
faults by performing
loopbacks section by
section or replacing boards
Proceed
with the
next step
No
Is the fault
rectified?
Yes
En
d
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
79
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-15 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting Ethernet service faults
Comment
No.
Description
Check the following points:
l Whether a loopback is set for the Ethernet port
l Whether a loopback is set for the transmission line
l Whether the parameter settings of the Ethernet port, such as the port
enabled state, working mode, and flow control, are the same as the
parameter settings of the Ethernet port on the interconnected equipment
l The configuration of the encapsulation/mapping protocol or the LCAS
protocol is inconsistent on both ends of the link.
l The timeslot binding of VCTRUNKs is inconsistent on both ends of the
link.
l Check whether the Ethernet protocol and the Ethernet service
configuration (especially the attributes of the Ethernet port) are correct.
Pay special attention to the following equipment alarms:
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l HARD_BAD
l BD_STATUS
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
Pay special attention to the following line alarms:
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l R_LOS
l R_LOF
l MS_AIS
l AU_AIS
l AU_LOP
l B1_EXC
l B2_EXC
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
80
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
5 Troubleshooting
l ETH_LOS
l FLOW_OVER
l ALM_GFP_dCSF
l ALM_GFP_dLFD
l FCS_ERR
l LCAS_PLCT
l LCAS_TLCT
l LCAS_PLCR
l LCAS_TLCR
l LCAS_FOPT
l LCAS_FOPR
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If the LOOP_ALM alarm is reported after the configuring the Advanced
Attributes of Ethernet Interfaces operation is performed, it indicates that the
network to which Ethernet ports are connected has loops.
For RMON performance events, see C Performance Event Reference.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
81
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-12 Procedure for troubleshooting an RMON performance event
Start
1
View the statistics group
performance on an Ethernet port
Is there any FCS error?
Yes
Rectify the fault of line bit
errors
No
Yes
Is there any collision
or fragment?
No
Check the working mode
of the port
4
Handle the flow control
problem or increase the
bandwidth
Yes
Is there any
PAUSE frame?
No
Are broadcast packets
excessive?
Yes
Handle the problem on
excessive broadcast
packets
No
Use a meter to perform the test
Is the test passed?
Yes
Rectify the fault of the
interconnected equipment
No
6
Is it a MTU setting
problem?
Yes
Modify the MTU value
No
Rectify the equipment fault by
loopback section by section or
replacing the board
Proceed with
the next step
No
Is the fault
rectified?
Yes
End
Table 5-16 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting an RMON performance event
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Comment
No.
Description
View the statistics group performance on an Ethernet port to obtain the realtime performance statistics data of the Ethernet port.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
82
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
The troubleshooting procedure is as follows:
5 Troubleshooting
l Check the Ethernet cable. If the Ethernet cable is not qualified, replace it
with a new one.
l Change the Ethernet port that accesses the services on the Ethernet board.
If the new port does not have the RMON performance of an FCS error, it
indicates that the hardware of the original port is faulty. Otherwise, the
hardware of the Ethernet port on the equipment at the opposite end is
faulty.
Check the following points:
l Whether the port operating rates on the equipment at both ends are the
same
l Whether the working modes (full duplex or half duplex) of the Ethernet
port on the equipment at both ends are the same
l Whether the Ethernet port is set to auto-negotiation mode at one end and
the Ethernet port is set to full duplex mode at the opposite end (When the
Ethernet port is set to auto-negotiation mode at one end, the Ethernet port
must not be set to full duplex mode at the opposite end.)
Check the following points:
l Whether the flow control method is the same.
l Whether the Ethernet service traffic exceeds the bandwidth of the
VCTRUNK.
5
Check for the cause for excessive broadcast packets (for example, you have
set the loopback for the Ethernet interface board or set the VB filtering
table incorrectly) and solve the problem. If the problem is caused on the
equipment at the opposite end, set the threshold of broadcast packet
suppression for an Ethernet port to reduce broadcast packets.
Test the MTU of the network by using a test meter. The maximum frame
length that is set for a port should be longer than the MTU of the network.
Experience and Summary
To troubleshoot an Ethernet service fault, you must be familiar with the characteristics, working
mode, and configured protocols of interfaces on the Ethernet equipment.
5.10 Troubleshooting MPLS Tunnels
This section describes how to troubleshoot MPLS tunnels by using the MPLS OAM function or
MPLS Ping/Traceroute function.
Fault Phenomena
Common faults of MPLS tunnels are as follows.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
83
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
MPLS tunnels fail to be created, and services are unavailable.
MPLS tunnels are faulty, and services are interrupted.
MPLS APS switching fails, services are interrupted, and packet loss or bit errors occur.
Table 5-17 Common faults of MPLS tunnels
Symptom
Alarm
Board
MPLS tunnels are faulty.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
WRG_BD_TYPE,
BUS_ERR, BD_STATUS,
MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL,
MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV,
MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess,
MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH,
MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE,
MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN,
MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI,
MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI,
MPLS_TUNNEL_SD,
MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
CSH
AM_DOWNSHIFT
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2, or IFX2
MW_CFG_MISMATCH
MW_LIM
MW_LOF
Fault Causes
l
Incorrect operations are performed.
The transmission link is looped back.
Service configuration data is inconsistent between the local end and the opposite end.
Service configuration is incorrect.
The local NE is faulty.
The transmission link is faulty or has bit errors.
Service bandwidth decreases due to an AM downshift.
The opposite NE is faulty.
External electromagnetic interference is severe.
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the data is modified, whether the line is looped back, and whether any boards
are replaced.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
84
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
2.
Handle the link alarms on the MPLS server trail.
3.
Locate the faulty section by using the LSP Traceroute function.
4.
Locate the fault by replacing boards.
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-13 Procedure for troubleshooting MPLS tunnels
Start
Any incorrect
operation?
Yes
Cancel the operation
No
2
Any equipment- or
link-related alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
Yes
3
Any alarm related to MPLS
tunnel ?
Clear the alarm
No
Any fault of
interconnection
equipment
Yes
Handle the fault
No
Troubleshoot equipment faults by
performing loopbacks on sections
or replacing boards
Contact Huawei
technical engineers
No
Faults are rectified?
Yes
End
Table 5-18 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting MPLS tunnels
Comment
No.
Description
Check the following points:
l Whether a loopback is set for E1 ports
l Whether a loopback is set for the transmission link
l Whether the parameter settings such as the working mode of Ethernet ports
match those of the opposite NE
l Whether the parameter settings such as frame format and frame mode at
E1 ports match those of the opposite NE
l Whether MPLS service configuration is correct, especially whether tunnel
attributes are set correctly
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
85
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following equipment alarms:
5 Troubleshooting
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l HARD_BAD
l BD_STATUS
l BUS_ERR
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l AM_DOWNSHIFT
l MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Pay special attention to the following line alarms:
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l MW_BER_EXC
l MW_BER_SD
l MW_RDI
l MW_FEC_UNCOR
3
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI
l MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess
l MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI
l MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
l MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH
l MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE
l MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL
l MPLS_TUNNEL_SD
l MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
l MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN
Experience and Summary
Learn about the working principle and protocol configuration of MPLS tunnels before
troubleshooting MPLS tunnels.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
86
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
5.11 Troubleshooting CES Services
This section describes how to troubleshoot CES services that are interrupted or degraded.
Fault Phenomena
CES services are interrupted if they are completely unavailable. CES services are degraded if
they have packet loss or incorrect packets.
Table 5-19 Common faults of CES services
Symptom
Alarm
Board
CES services are interrupted.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
WRG_BD_TYPE,
BUS_ERR, BD_STATUS,
CES_LOSPKT_EXC
CSH, ML1, MD1
AM_DOWNSHIFT
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2, or IFX2
MW_CFG_MISMATCH
CES services are degraded.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
CES_JTROVR_EXC,
CES_JTRUDR_EXC,
CES_MALPKT_EXC,
CES_MISORDERPKT_EX
C, CES_STRAYPKT_EXC
CSH, ML1, MD1
AM_DOWNSHIFT
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2, or IFX2
MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Fault Causes
l
Incorrect operations are performed.
The transmission link is looped back.
Service configuration data is inconsistent between the local end and the opposite end.
Service configuration is incorrect.
The clock source is asynchronous.
Jitters and delays on the network are too great.
The local NE is faulty.
The transmission link is faulty or has bit errors.
Service bandwidth decreases due to an AM downshift.
The opposite NE is faulty.
External electromagnetic interference is severe.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
87
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Check whether the data is modified, whether the line is looped back, and whether any boards
are replaced.
2.
Check whether the PW works properly by using the PW ping function. If the PW is faulty,
check whether the MPLS tunnel works properly by using the LSP ping function. If the
MPLS tunnel works properly, check whether the PW has the same configuration at both
ends. If the configuration is the same, replace the board on the NNI side.
3.
If the PW works properly, check whether the PE data configured at both ends is the same.
If the PE data is different, change the PE data to the same.
4.
Check whether UNI-side data and CE-side data are consistent.
5.
Analyze the RMON performance events of CES services.
6.
Check whether there is impedance mismatch on channels and whether any electrical cables
are connected incorrectly.
7.
Replace Smart E1 processing boards.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
88
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-14 Procedure for troubleshooting CES services
Start
Any incorrect
operation?
Yes
Cancel the operation
No
2
Any equipment- or
link-related alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
Yes
3
Any alarm related to
tunnels/PWs?
Clear the alarm
No
4
Any alarm related to
CES services?
Any alarm on E1
ports?
Yes
Clear the alarm
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
6
Any RMON
performance event?
Yes
Handle the performance event
No
7
Any fault of
interconnection with
PDH equipment
Yes
Handle the fault
No
Troubleshoot equipment faults by
performing loopbacks on sections
or replacing boards
Contact Huawei
technical engineers
No
Faults are rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
89
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-20 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting CES services
Commen
t No.
Description
Check the following points:
l Whether a loopback is set for the E1 port
l Whether a loopback is set for the transmission link
l Check whether the parameter settings of CES services, PWs, and tunnels are
consistent at the source end and sink end.
l Check whether the parameter settings of physical ports (including frame
format, code, electrical port impedance, and overhead byte), are consistent.
l Check whether the network bandwidth is sufficient for the service traffic.
Pay special attention to the following equipment alarms:
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l HARD_BAD
l BD_STATUS
l BUS_ERR
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l AM_DOWNSHIFT
l MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Pay special attention to the following line alarms:
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l MW_BER_EXC
l MW_BER_SD
l MW_RDI
l MW_FEC_UNCOR
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
90
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Commen
t No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
5 Troubleshooting
l MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI
l MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess
l MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI
l MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
l MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH
l MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE
l MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL
l MPLS_TUNNEL_SD
l MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
l MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN
4
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l CES_JTROVR_EXC
l CES_JTRUDR_EXC
l CES_LOSPKT_EXC
l CES_MALPKT_EXC
l CES_MISORDERPKT_EXC
l CES_STRAYPKT_EXC
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l T_ALOS
l UP_E1_AIS
l LFA
l LMFA
l DOWN_E1_AIS
l ALM_E1RAI
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l CES_MISORDERPKT
l CES_LOSPKT
l CES_MALPKT
l CES_JTRUDR
l CES_JTROVR
l CES_STRAYPKT
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Troubleshoot the interconnection with the PDH equipment.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
91
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Experience and Summary
Learn about the working principle and protocol configuration of CES services before
troubleshooting CES services.
5.12 Troubleshooting ATM Services
This section describes how to troubleshoot ATM services that are interrupted or degraded.
Fault Phenomena
ATM services are interrupted if they are completely unavailable. ATM services are degraded if
they have packet loss or incorrect packets.
Table 5-21 Common faults of ATM services
Symptom
Alarm
Board
ATM services are
interrupted.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
WRG_BD_TYPE,
BUS_ERR, BD_STATUS,
ALM_IMA_LIF,
ALM_IMA_LODS,
ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE,
ALM_IMA_RE_TX_UNUSABLE,
IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN,
IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN,
LCD
CSH, ML1, MD1
AM_DOWNSHIFT
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2, or IFX2
MW_CFG_MISMATCH
ATM services are degraded.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
ALM_IMA_LIF,
ALM_IMA_LODS,
ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE,
ALM_IMA_RE_TX_UNUSABLE, OCD
CSH, ML1, MD1
AM_DOWNSHIFT
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2, or IFX2
MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Fault Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Incorrect operations are performed.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
92
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
The transmission link is looped back.
Service configuration data is inconsistent between the local end and the opposite end.
Service configuration is incorrect.
l
The local NE is faulty.
The transmission link is faulty or has bit errors.
Service bandwidth decreases due to an AM downshift.
The opposite NE is faulty.
External electromagnetic interference is severe.
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Check whether the data is modified, whether the link is looped back, and whether any
boards are replaced.
2.
Check whether the PW works properly by using the PW ping function. If the PW is faulty,
check whether the MPLS tunnel works properly by using the LSP ping function. If the
MPLS tunnel works properly, check whether the PW has the same configuration at both
ends. If the configuration is the same, replace the board on the NNI side.
3.
If the PW works properly, check whether the PE data configured at both ends is the same.
If the PE data is different, change the PE data to the same.
4.
Check whether UNI-side data and CE-side data are consistent.
5.
Analyze the RMON performance events of ATM services.
6.
Check whether there is impedance mismatch on channels and whether any electrical cables
are connected incorrectly.
7.
Replace Smart E1 processing boards.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
93
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-15 Procedure for troubleshooting ATM services
Start
Any incorrect
operation?
Yes
Cancel the operation
No
2
Any equipment- or
link-related alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
Yes
Any alarm related to ATM
services?
Clear the alarm
No
4
Any alarm at the E1
port?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
5
Any RMON
performance event?
Yes
Handle the performance event
No
6
Any fault of
interconnection with
PDH equipment
Yes
Handle the fault
No
Troubleshoot equipment faults by
performing loopbacks on sections
or replacing boards
Contact Huawei
technical engineers
No
Faults are rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
94
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-22 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting ATM services
Comment
No.
Description
Check the following points:
l Whether a loopback is set for the E1 port
l Whether a loopback is set for the transmission link
l Whether the parameter settings of ATM VPI/VCI, PWE3 CW, PW, and
Tunnel are consistent between the source end and the sink end.
l Whether the parameter settings of interconnected ports are consistent
Whether E1 frame format, coding, overhead bytes, and E1 timeslot
mode (30/31) are correctly configured
Whether IMA parameters (including protocol version, clock mode,
frame length, and maximum differential delay) are correctly
configured
l Check whether the network bandwidth is sufficient for the service traffic.
Pay special attention to the following equipment alarms:
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l HARD_BAD
l BD_STATUS
l BUS_ERR
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l AM_DOWNSHIFT
l MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Pay special attention to the following line alarms:
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l MW_BER_EXC
l MW_BER_SD
l MW_RDI
l MW_FEC_UNCOR
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
95
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
5 Troubleshooting
l ALM_IMA_LIF
l ALM_IMA_LODS
l ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE
l ALM_IMA_RE_TX_UNUSABLE
l IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN
l IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN
l OCD
l LCD
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l T_ALOS
l UP_E1_AIS
l LFA
l LMFA
l DOWN_E1_AIS
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELLS
l ATM_UNCORRECTED_HCSERR
6
Troubleshoot the interconnection with the PDH equipment.
Experience and Summary
Learn about the working principle and protocol configuration of ATM services before
troubleshooting ATM services.
5.13 Troubleshooting Ethernet Services Carried by PWs
This section describes how to troubleshoot Ethernet services that are carried by PWs and
transmitted in the PSN. These Ethernet services are considered faulty when they are interrupted
or deteriorate.
Fault Symptoms
Ethernet services are interrupted if they are completely unavailable. Ethernet services deteriorate
if they have great delays, packet loss, or incorrect packets.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
96
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-23 Common faults of Ethernet services
Symptom
Alarm
Board
Ethernet services are
interrupted.
HARD_BAD,
TEMP_ALARM,
WRG_BD_TYPE,
BUS_ERR, BD_STATUS
EM6TA, EM6FA, EM6F or
EM6T
COMMUN_FAIL,
LAG_DOWN
ETH_LOS,
ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK,
or LOOP_ALM
Ethernet services deteriorate.
LASER_MOD_ERR
EM6FA, EM6F
HARD_BAD or
TEMP_ALARM
EM6TA, EM6FA, EM6F or
EM6T
FLOW_OVER or
LAG_MEMBER_DOWN
EM6TA, EM6FA, EM6F or
EM6T
AM_DOWNSHIFT
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2 or IFX2
Fault Causes
l
Incorrect operations are performed.
The transmission link is looped back.
Service configuration data is inconsistent between the local end and the opposite end.
Service configuration is incorrect.
The local NE is faulty.
The transmission link is faulty or has bit errors.
Service bandwidth decreases due to an AM downshift.
The opposite NE is faulty.
External electromagnetic interference is severe.
Fault Locating Methods
1.
Check whether the data is modified, whether the link is looped back, and whether any
boards are replaced.
2.
Check whether the PW works properly by using the PW ping function. If the PW is faulty,
check whether the MPLS tunnel works properly by using the LSP ping function. If the
MPLS tunnel works properly, check whether the PW has the same configuration at both
ends. If the configuration is the same, replace the board on the NNI side.
3.
If the PW works properly, check whether the PE data configured at both ends is the same.
If the PE data is different, change the PE data to the same.
4.
Check whether UNI-side data and CE-side data are consistent.
5.
Analyze the RMON performance events of Ethernet services.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
97
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
6.
Check whether there is impedance mismatch on channels and whether any electrical cables
are connected incorrectly.
7.
Replace Ethernet interface boards.
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-16 Procedure for troubleshooting Ethernet services carried by PWs
Start
Any incorrect
operation?
Yes
Cancel the operation
No
2
Any equipment- or
link-related alarm?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
Yes
Any alarm related to tunnels/PWs
that carry services?
Clear the alarm
No
4
Any alarm on the
UNI side?
Yes
Clear the alarm
No
5
Any RMON
performance event?
Yes
Handle the performance event
No
6
Any fault of
interconnection with
PDH equipment
Yes
Handle the fault
No
Troubleshoot equipment faults by
performing loopbacks on sections
or replacing boards
Contact Huawei
technical engineers
No
Faults are rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
98
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-24 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting Ethernet services carried by PWs
Comment
No.
Description
Check the following points:
l Whether a loopback is set for the E1 port
l Whether a loopback is set for the transmission link
l Whether the parameter settings of ATM VPI/VCI, PWE3 CW, PW, and
tunnel are consistent between the source end and the sink end
l Whether the parameter settings of interconnected ports are consistent
Whether E1 frame format, coding, overhead bytes, and E1 timeslot
mode (30/31) are correctly configured
Whether IMA parameters (including protocol version, clock mode,
frame length, and maximum differential delay) are correctly
configured
l Check whether the network bandwidth is sufficient for the service traffic.
Pay special attention to the following equipment alarms:
l POWER_ALM
l FAN_FAIL
l HARD_BAD
l BD_STATUS
l BUS_ERR
l NESF_LOST
l TEMP_ALARM
l RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l IF_INPWR_ABN
l AM_DOWNSHIFT
l MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Pay special attention to the following line alarms:
l MW_LIM
l MW_LOF
l MW_BER_EXC
l MW_BER_SD
l MW_RDI
l MW_FEC_UNCOR
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
99
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Comment
No.
Description
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
5 Troubleshooting
l MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI
l MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess
l MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI
l MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
l MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH
l MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE
l MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL
l MPLS_TUNNEL_SD
l MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
l MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN
Check the following points:
l Whether the UNI-side performance of the faulty service is normal
l Whether the working mode and tag attribute of the UNI are the same as
those of its interconnected port
Pay special attention to the following alarms:
l ETH_LOS
l ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI
5
For RMON performance events, see D RMON Event Reference.
Troubleshoot the interconnection with the PDH equipment.
Experience and Summary
Learn about the working principle and protocol configuration of Ethernet services carried by
PWs before troubleshooting these services.
5.14 Troubleshooting Orderwire Faults
If orderwire calls cannot get through when services are normal, there is an orderwire fault.
Fault Causes
l
The phone set is set incorrectly.
The phone line is connected incorrectly.
The orderwire is configured incorrectly.
The orderwire unit is faulty.
The system control unit is faulty.
The line unit or radio link is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
100
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Fault Locating Methods
l
Check whether the phone set is set correctly, whether the phone line is connected correctly,
and whether the orderwire is configured correctly.
Replace the possibly faulty board to locate the fault.
Troubleshooting Procedure
Figure 5-17 Procedure for troubleshooting orderwire faults
Start
Check the phone setting
Is the phone
correctly set?
No
Modify the phone setting
Yes
Is the phone line
correctly connected?
No
Reconnect the phone line
Yes
2
Check the orderwire
configuration
Is the configuration
correct?
No
Modify the configuration
Yes
Replace the possibly faulty
board
No
Proceed with the next step
Is the fault rectified?
Yes
End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
101
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
5 Troubleshooting
Table 5-25 Description of the procedure for troubleshooting orderwire faults
Comment
No.
Description
Check the following points:
l Check whether the ring current switch "RING" on the phone set is set to
"ON".
l Check whether the dialing mode switch is set to "T", namely, the dual tone
multi-frequency mode.
l An orderwire phone set should be in on-hook state when it is not in
communication, and the upper-right red indicator in the front view of the
orderwire phone set should be off.
If the red indicator is on, it indicates that the phone set is in off-hook state.
Press the "TALK" button in the front of phone set to hook it up. In certain
occasions, the maintenance personnel press the "TALK" button is pressed
by mistake. As a result, the phone set stay in off-hook state all the time
and the orderwire call from the other NEs cannot get through.
Check the following points:
l Whether all orderwire phone numbers on a subnet are of the same length
l Whether all orderwire phone numbers on a subnet are unique
l Whether the overhead bytes of all the NEs on a subnet are the same
l Whether the orderwire port is set correctly
Replace the boards where the orderwire unit, system control unit, and
line unit are located to locate the fault.
Experience and Summary
To troubleshoot orderwire faults, you must check the orderwire phone periodically.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
102
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Part Replacement
About This Chapter
Part replacement is a method frequently used to locate faults. The replacement operation varies
according to the specific part type.
Background Information
Table 6-1 Part replacement description
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Part Name
Operation
Tool
SL1D, SL1DA
6.3 Replacing the SDH Optical
Interface Board
EM6T, EM6F,
EMS6,
EM6TA,
EM6FA, and
EFP8
6.6 Replacing the Ethernet
Interface Board
l
l
l
l
CF card
6.8 Replacing the CF Card
CST and CSH
6.9 Replacing the System Control,
Switch and Timing Board
AUX
6.10 Replacing the Auxiliary
Board
SP3D and SP3S
6.4 Replacing the PDH Interface
Board
IF1, IFU2,
ISX2, ISU2,
and IFX2
6.7 Replacing the IF Board
PIU
6.12 Replacing the Power Board
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Fiber remover
l ESD wrist strap
l Screwdriver
l U2000
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
103
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Part Name
Operation
ML1 and MD1
6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board
FAN
6.11 Replacing the Fan Board
6 Part Replacement
Tool
l ESD wrist strap
l U2000
ODU
6.14 Replacing the ODU
l Ejector lever (torque wrench)
l U2000
l Silicon
l Waterproof adhesive tape
IF cable
6.15 Replacing the IF Cable
l Multimeter
l Ejector lever
l Electro-technical knife
l File
l Installation parts and
accessories of the connector
l IF cable
l Waterproof adhesive tape
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
104
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
6.1 Removing a Board
Removing a board is a basic operation for replacing a board.
Procedure
Step 1 Insert one end of the ESD wrist strap into the ESD connector on the cabinet. Wear the ESD wrist
strap.
Figure 6-1 Wear the ESD wrist strap
Step 2 Optional: If cables are connected to the board, make labels for the cables and then remove the
cables.
NOTE
Use fiber removers to remove fibers or network cables.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
105
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Figure 6-2 Tweezer fiber remover
Step 3 Remove the board.
1.
Loosen the screws on the panel of the board.
Figure 6-3 Removing a board (1)
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Hold the left and right ejector levers with hands. Push them outwards to disengage the board
from the backplane.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
106
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Figure 6-4 Removing a board (2)
NOTE
As shown in Figure 6-5, there is a latch on each ejector lever of the System control Switch&Timing
board. To remove the System control Switch&Timing board, you need to push the latches when
pulling the ejector levers outward.
Figure 6-5 Removing the System control Switch&Timing board
3.
Pull out the board gently along the slot guide rail.
Figure 6-6 Removing a board (3)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
107
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
CAUTION
Remove the board slowly to prevent the components on the boards from colliding.
Step 4 Put the removed board into the antistatic box or bag.
----End
6.2 Inserting a Board
Inserting a board is a basic operation for replacing a board.
Procedure
Step 1 Insert one end of the ESD wrist strap into the ESD connector on the cabinet. Wear the ESD wrist
strap.
Figure 6-7 Wear the ESD wrist strap
Step 2 Insert the board.
1.
Hold the ejector levers on the panel with both hands. Push them outwards so that the angle
between the ejector lever and the panel is about 45 degrees.
2.
Push the board gently along the slot guide rail until the board cannot slide further.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
108
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Figure 6-8 Inserting a board (1)
CAUTION
Insert the board slowly to prevent the components on the boards from colliding.
3.
Press the two ejector levers inward with force.
Figure 6-9 Inserting a board (2)
4.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Tighten screws on the panel.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
109
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Figure 6-10 Inserting a board (3)
Step 3 Optional: If cables are connected to the board, recover the original cable connections according
to the labels that are made previously.
----End
6.3 Replacing the SDH Optical Interface Board
When the SDH optical interface board is replaced, the unprotected services on the board are
interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
You must know the service protection and protection channels of the board to be replaced.
The spare SDH optical interface board must be available, and the version and type of the
spare board must be the same as the version and type of the board to be replaced. You can
query the board manufacturing information to obtain the version of the board to be
replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Fiber remover
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Optional: If the services on the board are configured with SNCP, ensure that the services are
already switched to the protection channel.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Query the SNCP protection group.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
110
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
6 Part Replacement
Perform the forced switching, if the port on the board functions as the current working
channel, the current protection channel is not on the board, and the state of the current
protection channel is normal or SD.
Step 3 Optional: If the services on the board are configured with linear MSP, ensure that the services
are already switched to the protection channel.
1.
Query the linear MSP group.
2.
Perform the forced switching, if the port on the board functions as the current working
channel, the current protection channel is not on the board, and the state of the current
protection channel is normal or SD.
Step 4 Remove the board.
Step 5 Check whether the version and SFP type of the spare board are the same as the version and SFP
type of the board to be replaced.
Step 6 Insert the board.
Step 7 After the board starts to work, check the STAT indicator on the board. The STAT indicator
should be on and green.
Step 8 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms on the board.
Step 9 Optional: If the forced switching has been performed on the board, release the forced switching.
Step 10 Optional: If the linear MSP switching has been performed for the services, release the forced
switching.
----End
6.4 Replacing the PDH Interface Board
When the PDH interface board is replaced, the services on the board are interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
You must know the service protection and protection channels of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be made available, and the version and type of the spare board must
be the same as those of the board to be replaced. You can query the board manufacturing
information to obtain the version of the board to be replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
111
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Step 2 Remove the board.
Step 3 Check and ensure that the version and type of the spare board are the same as the version and
type of the board to be replaced.
Step 4 Insert the board.
Step 5 After the board starts to work, check the indicators on the board. The STAT indicator should be
on and green.
Step 6 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms on the board.
----End
6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board
When the Smart E1 board is replaced, the services on the board are interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
You must know the service protection and protection channels of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be available, and the version and type of the spare board must be the
same as the version and type of the board to be replaced. You can query the board
manufacturing information to obtain the version of the board to be replaced.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board to be replaced.
Step 2 Remove the board.
Step 3 Verify that the spare board has the same board version and board type as the board to be replaced.
Step 4 Insert the spare board.
Step 5 After the substitute board starts to work, check the indicators on the board. The STAT indicator
is on and green.
NOTE
Smart E1 boards are hot-swappable. After the spare board is installed, it enters initialization state and starts to
work 2 minutes later.
Step 6 Query the current alarms of the substitute board.
There is no new alarm on the board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
112
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
6.6 Replacing the Ethernet Interface Board
When the Ethernet interface board is replaced, the unprotected services on the board are
interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
You must know the service protection and protection channels of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be made available, and the version and type of the spare board must
be the same as those of the board to be replaced. You can query the board manufacturing
information to obtain the version of the board to be replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Fiber remover
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Optional: If the services are configured with MPLS APS, ensure that the services are already
switched to the protection tunnel.
1.
Querying MPLS APS Status.
2.
If the board functions as the current working board, perform the forced switching.
Step 3 Optional: If the services are configured with PW APS, ensure that the services are already
switched to the protection PW.
1.
Querying PW APS Status.
2.
If the board functions as the current working board, perform the forced switching.
Step 4 Remove the board.
Step 5 Check and ensure that the board version and the model of the SFP module on the spare board
are the same as the board version and the model of the SFP module on the board to be replaced.
Step 6 Insert the board.
NOTE
Ethernet interface boards are hot-swappable. After the substitute board is installed, it enters initialization state
and starts working two minutes later.
If dynamic ARP is disabled on the NE at the opposite end of an MPLS tunnel, you need to change the static
ARP table entries of the opposite NE.
Step 7 After the board starts to work, check the indicators on the board. The STAT indicator should be
on and green.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
113
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Step 8 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms on the board.
Step 9 Optional: If the forced switching has been performed for the services, release the forced
switching.
----End
6.7 Replacing the IF Board
When the IF board is replaced, the unprotected services on the board are interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
You must know the service protection and protection channels of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be available, and the version and type of the spare board must be the
same as the version and type of the board to be replaced. You can query the board
manufacturing information to obtain the version of the board to be replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Optional: If the services on the board are configured with SNCP, ensure that the services are
already switched to the protection channel.
1.
Query the SNCP protection group.
2.
If the port on the board functions as the current working channel, the current protection
channel is not on the board, perform the forced switching.
Step 3 Optional: If the services on the radio link are configured with 1+1 protection, switch the service
to the protection IF board.
1.
Query the IF 1+1 protection group.
2.
If the board functions as the current working board, perform the forced switching.
Step 4 Optional: If the services on the radio link are configured with N+1 protection, ensure that the
services are already switched to the protection IF board.
1.
Query the IF N+1 protection group.
2.
If the board functions as the current working board, perform the forced switching.
Step 5 Optional: If the services are configured with MPLS APS, ensure that the services are already
switched to the protection tunnel.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Querying MPLS APS Status.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
114
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
6 Part Replacement
If the board functions as the current working board, perform the forced switching.
Step 6 Optional: If the services are configured with PW APS, ensure that the services are already
switched to the protection PW.
1.
Querying PW APS Status.
2.
If the board functions as the current working board, perform the forced switching.
Step 7 Optional: If the IF board is configured with the XPIC function, see Setting the ODU Transmitter
State and mute the ODU at the opposite end.
Step 8 Turn off the ODU-PWR switch on the front panel of the IF board to be replaced.
CAUTION
To turn off the ODU-PWR switch, you need to pull the switch lever outwards slightly and then
set the switch to the "O" position.
Step 9 Remove the board.
Step 10 Check and ensure that the version and type of the spare board are the same as the version and
type of the board to be replaced.
Step 11 Ensure that the ODU-PWR switch on the front panel of the spare IF board is turned off.
Step 12 Insert the board.
Step 13 After the board starts to work, check the indicators on the board. The STAT indicator should be
on and green.
Step 14 Turn on the ODU-PWR switch on the front panel of the IF board.
CAUTION
To turn on the ODU-PWR switch, you need to pull the switch lever outwards slightly and then
set the switch to the "I" position.
IF boards are hot-swappable. After the substitute board is installed, it enters initialization state
and starts working two minutes later.
If dynamic ARP is disabled on the NE at the opposite end of an MPLS tunnel, you need to change
the static ARP table entries of the opposite NE.
Step 15 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms on the board.
Step 16 Optional: If the forced switching has been performed for the services, release the forced
switching.
Step 17 Optional: If the forced protection switching has been performed for the radio link, release the
forced switching.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
115
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Step 18 If the IF board is configured with the XPIC function, see Setting the ODU Transmitter State and
unmute the ODU at the opposite end.
----End
6.8 Replacing the CF Card
If the NE is configured with only one System control Switch&Timing board, all the services are
interrupted during the replacement of the CF card.
Prerequisite
l
You must be aware of the impact of CF card replacement.
You must know the specific position of the CF card to be replaced.
You must be a user with "NE maintainer" authority or higher.
You must obtain a spare CF card that has the same capacity as the CF card to be replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
U2000
Fiber remover
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Optional: If the board is configured with 1+1 protection, ensure that the services are switched
from the current working board to the protection board.
1.
See 8.20 Switching the System Control Unit and the Cross-Connect Unit, and ensure
that the current working board functions as the protection board.
2.
If the board functions as the current working board, perform the manual switching.
Step 3 Remove the board.
Step 4 Remove the CF card according to the illustration in the following figure.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
116
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Step 5 Check the spare CF card.
Step 6 Install the spare CF card according to the illustration in the following figure.
Step 7 Insert the board.
Step 8 After the board starts to work, observe the indicators on the board. The STAT indicator should
be on and green.
Step 9 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms.
Step 10 Optional: If the manual switching has been performed on the board, release the manual
switching.
----End
6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board
All the services are interrupted during the period of replacing the system control switch and
timing board, if the NE is configured with only one system control switch and timing board.
Prerequisite
l
You must be aware of the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
You must know the service protection and protection channels of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be made available, and the version and type of the spare board must
be the same as those of the board to be replaced. You can query the board manufacturing
information to learn about the version of the board to be replaced.
Impact on System
If no protection board is available, the replacement of the System Control Switch and Timing
board results in service interruption.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Fiber remover
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
117
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Context
NOTE
After the NE database is restored successfully, a cold reset is automatically performed on the NE.
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Replace the System control Switch&Timing board.
If...
Then...
One System control Switch and Timing
board is configured
1. Notify the onsite maintenance personnel to
remove the board.
2. Check and ensure that the version and type of
the spare board (including the patch version)
are correct.
NOTE
If the spare board and the board to be replaced have
different patch versions, contact Huawei
engineers for loading correct patches.
3. Remove the CF card from the original board
and then install the CF card to the spare board.
For details about how to install the CF card,
see 6.8 Replacing the CF Card.
4. Insert the spare board into the chassis.
5. Press and hold the CF RCV button on the
board for 8 seconds so that the board
automatically restores the NE databases,
system parameters, software packages, and
NE logs from the CF card.
NOTE
l In the process of restoring the NE database, the
PROG indicator on the board blinks green for
about 20 minutes.
l If the database restoration is successful, the
NE resets automatically. After the NE resets
successfully, the STAT and PROG indicator
is on and green.
l If the database restoration fails, the NE does
not reset, and the PROG is red. In this case,
contact Huawei technical support engineers
for rectifying the fault.
NOTE
After the NE starts up normally, the STAT and PROG
indicator on the board is green.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
118
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
If...
Then...
Two System control Switch and Timing
boards are configured
1. Before replacing the main system control
board, switch the main system control board
to the protection board. For details, see 8.20
Switching the System Control Unit and the
Cross-Connect Unit.
NOTE
Replacing the standby system control board does
not need to switch the system control board to the
protection board.
2. Remove the board to be replaced.
3. Check whether the version and type of the
spare board are the same as the version and
type of the board to be replaced.
4. Insert the spare board.
5. Wait for about 10 minutes to complete the
backup of the data on the main and standby
system control units.
NOTE
After the NE starts up normally, the STAT and PROG
indicator on the board is green.
Step 3 Query the current alarms of the board. There should be no new alarms.
----End
6.10 Replacing the Auxiliary Board
When the auxiliary board is replaced, the services on the auxiliary board are interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be made available, and the version and type of the spare board must
be the same as those of the board to be replaced. You can query the board manufacturing
information to obtain the version of the board to be replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Fiber remover
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
119
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Step 2 Remove the board.
Step 3 Check and ensure that the version and type of the spare board are the same as the version and
type of the board to be replaced.
Step 4 Insert the spare board.
Step 5 After the board starts to work, check the indicators on the board. The STAT indicator should be
on and green.
Step 6 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms on the auxiliary board.
----End
6.11 Replacing the Fan Board
The IDU cannot perform air cooling in the process of replacing the fan board. Therefore, you
need to replace the fan board quickly.
Prerequisite
l
You must be aware of the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be made available, and the version and type of the spare board must
be the same as those of the board to be replaced. You can query the board manufacturing
information to learn about the version of the board to be replaced.
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
U2000
Precautions
WARNING
Do not touch the blades until the fan has stopped rotating.
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Move the cables away from the front panel of the fan board assembly.
Step 3 Remove the fan board.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
120
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Step 4 Check and ensure that the version and type of the spare board are the same as the version and
type of the board to be replaced.
Step 5 Insert the standby fan board.
2
Step 6 After the board starts to work, observe the indicators on the board. The FAN indicator should
be on and green.
Step 7 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
121
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
6.12 Replacing the Power Board
If another power board works normally during the replacement period, the services at the IDU
are not affected.
Prerequisite
l
You must be aware of the impact of board replacement.
You must know the specific position of the board to be replaced.
The spare board must be made available, and the version and type of the spare board must
be the same as those of the board to be replaced. You can query the board manufacturing
information to obtain the version of the board to be replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Precautions
WARNING
Before replacing the board, you must turn off the power switch of the PDU. Do not connect the
interface to the power plug. After inserting the PIU properly, insert the power plug, and then
turn on the power switch of the PDU.
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Notify the onsite maintenance personnel to turn off the output power switch on the power supply
equipment.
Step 3 Remove the cables connected to the board.
NOTE
When removing the power cable, press the former section of the red button and pull the red button.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
122
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
1
2
1
2
1
Press
Press the front of the red latch.
Properly move the red latch outwards.
Step 4 Remove the power board gently and horizontally along the guide rail.
Step 5 Check and ensure that the version and type of the spare board are the same as the version and
type of the board to be replaced.
Step 6 Insert the spare board steadily along the guide rail.
Step 7 Reconnect the cables between the board and the power supply equipment.
Step 8 Notify the onsite maintenance personnel to turn on the output power switch on the equipment.
Step 9 After the board starts to work, observe the indicators on the board. The PWR indicator should
be on and green.
----End
6.13 Replacing the SFP
When the small form pluggable (SFP) is replaced, the unprotected services on the optical/
electrical port are interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of SFP replacement.
You must know the specific position of the SFP to be replaced.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
123
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
You must know the service protection and protection channels of the SFP to be replaced.
The spare SFP must be available, and the version and type of the spare SFP must be the
same as the version and type of the SFP to be replaced. You can query the board
manufacturing information to obtain the version of the SFP to be replaced.
Context
NOTE
The SL1D can be equipped with the SFP to provide 2xSTM-1 optical or 2xSTM-1 electrical interfaces. The
EM6F can be equipped with the SFP to provide 2xGE optical interfaces or 2xGE electrical interfaces.
Tools, Equipment and Materials
l
ESD wrist strap
Screwdriver
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms of the board.
Step 2 Optional: If SNCP is configured for services at the optical interface, ensure that the services
are already switched to the protection channel.
1.
Query the status of the SNCP group.
2.
If the port on the local board functions as the working channel, the protection channel does
not involve the local board, and the protection channel is in the normal or SD state, perform
forced switching.
Step 3 Optional: If linear MSP is configured for services at the optical interface, ensure that the services
are already switched to the protection channel.
1.
Query the status of the linear MSP group.
2.
If the port on the local board functions as the working channel, the protection channel does
not involve the local board, and the protection channel is in the normal or SD state, perform
forced switching.
Step 4 Record the cable connections of the SFP, and then disconnect cables.
Step 5 Check the types of the spare SFP and the SFP to be replaced, and remove the SFP module.
NOTE
When removing the SFP electrical module, press the blcak button first.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
124
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
1
2
Press the unclocking button.
Remove the SFP electical module.
Step 6 Insert the standby SFP module and reconnect cables based on the record.
Step 7 Query the current alarms of the board.
There should be no new alarms on the board.
Step 8 Optional: If the forced switching has been performed on the board, release the forced switching.
Step 9 Optional: If the linear MSP switching has been performed for the services, release the forced
switching.
----End
6.14 Replacing the ODU
When the ODU is replaced, the unprotected services on the ODU are interrupted.
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of ODU replacement.
You must know the specific positions of the ODU to be replaced and the IF board connected
to the ODU.
The spare ODU must be at hand, whose type must be the same as the type of the ODU to
be replaced.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
Ejector lever (torque spanner)
U2000
Silicon
Waterproof adhesive tape
Precautions
Before you replace an ODU that is installed on the coupler, power off the ODU to be replaced,
but do not power off or mute the other ODU. Otherwise, the services may be affected. The
interface of the coupler ejects little RF radiation, thus meeting the safety standards for microwave
radiation.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
125
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
If the XPIC work group is configured for the IF board that is connected to the ODU to be replaced,
the ODU at the opposite end of the XPIC work group needs to be muted.
Procedure
Step 1 Query the current alarms on the ODU and then record the results.
Step 2 Turn off the ODU-PWR switch on the front panel of the IF board.
Step 3 Remove the IF cable and the PGND cable from the ODU.
Step 4 Remove the ODU.
Option
Description
If...
Then...
You need to remove the ODU with a
waveguide interface
Loosen the four latches of the ODU and
disconnect the ODU from the antenna, the
hybrid coupler, or ODU adapter.
You need to remove the ODU with a
coaxial interface
Remove the ODU from the post.
You need to remove the RTN XMC ODU Loosen the captive screws on the ODU and
disconnect the ODU from the antenna, the
hybrid coupler, or ODU adapter.
Step 5 Ensure the type of the spare ODU is the same as the type of the ODU to be replaced.
Step 6 Install the ODU.
Option
Description
If...
Then...
You need to install a new ODU with a
waveguide interface
See the RTN 600 ODU Quick Installation
Guide.
You need to install a new ODU with a
coaxial interface
See the RTN 600 ODU Quick Installation
Guide.
You need to install a new RTN XMC ODU See the RTN XMC ODU Installation Guide.
Step 7 Connect the PGND cable and the IF cable to the ODU.
Step 8 Waterproof the IF interface on the ODU.
Step 9 Turn on the ODU-PWR switch on the front panel of the IF board.
Step 10 After the ODU starts to work, check the ODU indicator and LINK indicator on the IF board.
The ODU indicator and LINK indicator should be on and green.
Step 11 Query the current alarms of the ODU. There should be no new alarms on the ODU.
----End
6.15 Replacing the IF Cable
When the IF cable is replaced, the unprotected services on the IF cable are interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
126
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
6 Part Replacement
Prerequisite
l
You must know the impact of IF cable replacement.
You must know the specific positions of the IF cable to be replaced and the IF board
connected to the IF jumper.
In the case of the RG-8U IF cable or the 1/2-inch IF cable, an IF jumper is required to
connect the IF cable to the IDU and both ends of the IF cable should be terminated with
type-N connectors. In the case of the 5D IF cable, the IF cable is connected directly to the
IDU and the cable end connecting to the IDU should be terminated with the TNC connector
and the cable end connecting to the ODU should be terminated with the type-N connector.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
Multimeter
Ejector lever
Electro-technical knife
File
Installation parts and accessories of the connector
IF cable
Waterproof adhesive tape
Procedure
Step 1 Query and record the current alarm of the IDU.
Step 2 Turn off the ODU-PWR switch on the front panel of the IF board.
Step 3 Disconnect the IF cable from the IF jumper and from the ODU.
Step 4 Use a multimeter to test the connectivity of the IF cable to determine whether you need to make
new connectors for the IF cable or replace the IF cable with a new one.
If...
Then...
You need to make new connectors for the
IF cable
See the Installation Reference and make new
connectors for the IF cable.
You need to replace the IF cable with a new Replace the IF cable with a new one.
one
Step 5 Connect the IF cable to the IF jumper and to the ODU.
Step 6 Waterproof the connectors at the two ends of the IF cable with the waterproof adhesive tape.
Step 7 Turn on the ODU-PWR switch on the front panel of the IF board.
Step 8 After the ODU starts to work, check the ODU and LINK indicators on the IF board.
The ODU indicator and LINK indicator should be on and green.
Step 9 Query the current alarms of the IDU.
There should be no new alarms on the IDU.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
127
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
7 Database Backup and Restoration
Database Backup and Restoration
About This Chapter
The OptiX RTN 950 supports database backup and restoration through the NMS.
7.1 NE Database
An NE database stores the communication data, security data, alarm data, performance data, and
configuration data of an NE in a certain structure to facilitate the relevant query and modification,
hence ensuring that the data can be restored after the NE is reset.
7.2 Backing Up the Database Manually
The NE configuration data is stored in the database of an NE. To prevent the database from
being damaged due to certain risky operations such as replacing a faulty system control, crossconnect, and timing board or upgrading the software, you need to manually back up the database
on a regular basis and before performing any risk operation.
7.3 Setting the Database Backup Policy
You can set the policy of backing up a database to realize the function of periodically backing
up the database.
7.4 Restoring the Database
If the database is damaged, you can restore the NE database by using the database files that are
saved previously.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
128
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
7 Database Backup and Restoration
7.1 NE Database
An NE database stores the communication data, security data, alarm data, performance data, and
configuration data of an NE in a certain structure to facilitate the relevant query and modification,
hence ensuring that the data can be restored after the NE is reset.
An NE database includes the following types:
l
Memory database (MDB)
The data in the MDB varies according to the configuration and is lost when the system
control unit is reset or when the NE is powered off.
Dynamic random database (DRDB)
The DRDB automatically stores the data that is checked successfully. The DRDB is resident
in the reserved memory. Hence, the data in the DRDB is not lost when a warm reset is
performed on the system control unit. The data, however, is lost when a cold reset is
performed on the system control unit or when the NE is powered off.
Flash database (FDB)
The FDB includes FDB0 and FDB1. The FDB is resident in the flash memory on the board.
Hence, the data in the FDB is permanently stored.
After being delivered to the system control unit, the NE configuration data is stored in the MDB.
After checking the NE configuration data successfully, the system control unit automatically
copies the data from the MDB to the DRDB and delivers the board configuration data generated
after successful check to the relevant board.
The NE backs up the DRDB database into the FDB0 and FDB1 databases of the flash memory
at an interval of 30 minutes.
After the NE is restarted because of power-off, the system control unit checks whether the
configuration data in the DRDB is available. If yes, the system control unit restores the data. If
the configuration data in the DRDB is damaged, the system control unit restores the data from
FDB0 or FDB1.
On the CF card, NE databases, system parameters (including NE-IP, NE-ID, and subnet mask),
software packages, and NE logs are stored. After the CRV button on the system control,
switching and timing board is pressed and held for 8 seconds, the data stored on the CF card is
loaded to the board. To synchronize the data on the CF card with the NE databases, system
parameters, and NE logs on the system control, switching and timing board, the regular backup
function needs to be enabled. By default, the data is backed up every 24 hours.
NOTE
The software packages on the CF card are updated with those on the system control, switching and timing board
during package diffusion. Therefore, no automatic or manual operation is performed to synchronize the software
packages.
The system control, switching and timing board and the CF card must have same software packages. If they
have different software packages, the SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH alarm is reported.
7.2 Backing Up the Database Manually
The NE configuration data is stored in the database of an NE. To prevent the database from
being damaged due to certain risky operations such as replacing a faulty system control, crossIssue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
129
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
7 Database Backup and Restoration
connect, and timing board or upgrading the software, you need to manually back up the database
on a regular basis and before performing any risk operation.
Prerequisite
l
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
You must log in to the NE.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 On the NMS, choose Administration > NE Software Management > NE Data Backup/
Restoration from the Main Menu.
Step 2 In NE View, click Find.
Step 3 In the Find NE dialog box, set the search conditions and search for the NE that requires database
backup.
Step 4 Click OK.
Step 5 Click Backup.
NOTE
Press and hold the Ctrl button on the keyboard, you can select multiple NEs to back up the data at one time.
Step 6 Set the data backup path to NMS Server or NMS Client according to the requirements.
Step 7 Click Start to start backing up the NE data. In NE View, Operation Status indicates the progress
of backing up the data. After the data backup is successful, Operation Status displays a message,
indicating that the operation is successful.
----End
7.3 Setting the Database Backup Policy
You can set the policy of backing up a database to realize the function of periodically backing
up the database.
7.3.1 Setting the User-Defined Backup Policy
Through this task, you can set the backup policy for a specific NE.
Prerequisite
l
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
You must log in to the NE.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
130
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
7 Database Backup and Restoration
Background Information
Each NE has a default data backup policy.
l
Database packages are backed up once at 2:00.
The default backup policy is disabled by default.
A maximum of five database packages can be backed up at a time.
Data changes do not trigger any backup operations.
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Administration > NE Software Management > NE Backup Policy Management
from the Main Menu.
Then, the NE Backup Policy Management dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 In Auto Backup Policy window, set NE type.
The version, name, and IP address of the selected NE are displayed.
Step 3 Click New Policy.
Step 4 Optional: Click
to import the information of the NEs.
Step 5 Optional: Click
to export the information of the NEs.
The information of the selected NEs is stored in the specified location.
Step 6 In NE Table, select one or more NEs.
Step 7 Click Next.
Then, the Setting Policy dialog box is displayed.
Step 8 Set Policy Name, Period Backup Policy, and Period Save Policy.
NOTE
l If The Added NE's Policy Status is set to Enable, the NMS performs the backup operation within
the specified period, day, and time.
l If The Added NE's Policy Status is set to Disable, the backup policy is still in the Disable state
although the policy period reaches the specified period, day, and time.
Step 9 Click Advanced Settings, and set Backup Type, Max Backup Num, and Configuration
Change Backup for a certain type of NEs.
Step 10 Click OK.
Step 11 Click OK.
----End
7.3.2 Enable the Backup Policy of the Device
Through this task, you can set the backup policy of a device to the running state.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
131
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
7 Database Backup and Restoration
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Administration > NE Software Management > NE Backup Policy Management
from the Main Menu.
Then, the NE Backup Policy Management dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 In Auto Backup Policy window, set NE type.
The version, name, and IP address of the selected NE are displayed.
Step 3 Right click the selected NE, Click Enable Backup Policy.
----End
7.3.3 Disable the Backup Policy of the Device
Through this task, you can set the backup policy of a device to the suspended state.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Administration > NE Software Management > NE Backup Policy Management
from the Main Menu.
Then, the NE Backup Policy Management dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 In Auto Backup Policy window, set NE type.
The version, name, and IP address of the selected NE are displayed.
Step 3 Right click the selected NE, Click Disable Backup Policy.
----End
7.4 Restoring the Database
If the database is damaged, you can restore the NE database by using the database files that are
saved previously.
Prerequisite
l
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
The data to be restored must be backed up.
You must log in to the NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
132
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
7 Database Backup and Restoration
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 On the NMS, choose Administration > NE Software Management > NE Data Backup/
Restoration from the Main Menu.
The NE Data Backup/Restoration window is displayed.
Step 2 In NE View, click Find.
Then, the Find NE dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 In the Find NE dialog box, set the search conditions to search for the NEs that need to restore
databases.
Step 4 Click OK.
Step 5 Select the NE whose data needs to be recovered, and click Recover.
NOTE
You can select multiple NEs to recover the data at one time.
Then, the Recover dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 Select Browse in File Name.
Then, the Select File dialog box is displayed.
Step 7 Select files from NMS Server or NMS Client, and then choose the files to be recovered. Click
OK.
Step 8 In the Recover dialog box, click Start.
Step 9 Click Yes in the prompt dialog box.
The system starts recovering the selected data files on the specified NE.
In the NE list of NE View, Operation Status indicates the progress of recovering the data.
After the data is recovered, Operation Status displays a message, indicating that the operation
is successful.
Step 10 In NE View, right-click the NE and choose Active Database from the shortcut menu.
The Active Database dialog box is displayed.
Step 11 Click Start to start activating the database.
NOTE
If the NE transmits data services, select Deliver to Board.
Services are interrupted during the activation of databases.
In NE View, Operation Status indicates the progress of activating the database. After the
database is activated, Operation Status indicates that the operation is successful.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
133
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Supporting Task
About This Chapter
This chapter describes the common maintenance operations.
8.1 Hardware Loopback
Hardware loopback refers to the loopback operation performed by changing the physical
connection.
8.2 Cleaning Fiber Connectors and Adapters
The optical connectors are easily contaminated in the maintenance process. The minute dust
particles that can be seen only in the microscope can also affect the quality of optical signals. In
this case, the system performance deteriorates. Hence, the fiber connectors or adapters that are
terminated need to be cleaned in time.
8.3 Browsing Alarms, Abnormal Events, and Performance Events
The U2000 is used to browse alarms, abnormal events, and performance events at the network
layer.
8.4 Querying a Report
You can obtain the version, manufacture, and microwave link information of all the boards by
querying the corresponding report.
8.5 Software Loopback
Software loopback refers to the loopback operation that is implemented by using the NMS.
During software loopback, you need not visit the engineering site. Hence, software loopback is
used more widely than hardware loopback.
8.6 Reset
Reset is an important method of troubleshooting software faults. Reset is classified into cold
reset, warm reset.
8.7 PRBS Test
The pseudorandom binary sequence (PRBS) test is an important method of network maintenance
and self-check.
8.8 Querying the License Capacity
You can check whether the loaded license file meets the requirements by querying the license
capacity.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
134
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.9 Setting the On/Off State of the Laser
When performing operations such as testing a fiber cut, you can set the on/off state of the laser
rather than removing and re-inserting the optical fiber on site.
8.10 Setting the ALS Function
The SDH optical interface board supports the automatic laser shutdown (ALS) function. This
function enables the board to turn off a laser when the board does not transmit services, the
optical fiber is faulty, or the received optical signals are lost.
8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function
To protect the communication between the NMS and NE against improper operations, an NE
supports the automatic release of the ODU muting, software loopback, and other operations that
require you to exercise caution. The automatic release time is five minutes by default. You can
set whether to enable the automatic release function and the automatic release time through the
NMS.
8.12 Querying Power Consumption of Boards
This section describes how to query power consumption of the ODU and each board.
8.13 Querying the Impedance of an E1 Channel
The impedance of an E1 channel is 75 ohms or 120 ohms.
8.14 Monitoring Ethernet Packets Through Port Mirroring
To monitor and analyze the Ethernet packets at a port, you can enable the port mirroring function
so that the received or transmitted packets on the port are duplicated to another Ethernet port to
which the Ethernet tester is connected. Then, you can monitor and analyze the packets. This
function is supported by the EFP8/EMS6 board of the OptiX RTN 950.
8.15 Querying the Attributes of an Ethernet Port
Through the operation, you can learn about the attributes of an Ethernet port, such as rate.
8.16 Setting Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization of Ethernet Ports
To query the traffic, physical bandwidth, or bandwidth utilization of Ethernet ports within a
certain period, you need to enable the monitoring for the object before that period starts. The
FE/GE ports and Integrated IP radio ports on the packet plane support this operation.
8.17 Querying Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization of Ethernet Ports
This section describes how to query the change curve of the traffic, physical bandwidth, or
bandwidth utilization of Ethernet ports within a certain period. The FE/GE ports and Integrated
IP radio ports on the packet plane support this operation.
8.18 Setting the Threshold of Received Traffic Flow on an Ethernet Port
The FLOW_OVER alarm is reported when the traffic flow received on an Ethernet port exceeds
the specified threshold. Only the FE port on the EFP8 board supports this operation.
8.19 Using the Ethernet Test Frames
By using the Ethernet test frames, you can check the connectivity of VCTRUNKs. Only the
EFP8 board supports this operation.
8.20 Switching the System Control Unit and the Cross-Connect Unit
When the OptiX RTN 950 is configured with two system control, cross-connect, and timing
boards, you can manually switch the system control unit and the cross-connect unit as required.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
135
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.1 Hardware Loopback
Hardware loopback refers to the loopback operation performed by changing the physical
connection.
Background Information
Hardware loopback is classified into optical cable loopback, PDH cable loopback, and Ethernet
port loopback.
l
Optical cable loopback indicates that the receive and transmit optical fibers are connected
through a fiber jumper on the ODF. In certain occasions, an optical attenuator is added
based on the actual situation, to prevent the optical board from being damaged by the
excessive receive optical power.
PDH cable loopback indicates that the receive and transmit PDH cables are connected
through a short-circuiting cable or connector on the DDF.
Ethernet port loopback indicates that the receive and transmit service signals on one
Ethernet port are looped back through a special loopback Ethernet cable.
8.2 Cleaning Fiber Connectors and Adapters
The optical connectors are easily contaminated in the maintenance process. The minute dust
particles that can be seen only in the microscope can also affect the quality of optical signals. In
this case, the system performance deteriorates. Hence, the fiber connectors or adapters that are
terminated need to be cleaned in time.
8.2.1 Cleaning Fiber Connectors by Using Cartridge Cleaners
When there are special cartridge cleaners (such as the CLETOP cassette cleaner), use them for
cleaning the fiber connectors.
Prerequisite
l
Disconnect both ends of the fiber. Ensure that there is no laser light on the fiber connectors.
Inspect the fiber connector with a fiber microscope to ensure that the fiber connectors are
contaminated.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
Cartridge cleaner
Procedure
Step 1 Press down and hold the lever. Then, the shutter slides back and exposes a new cleaning area.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
136
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Figure 8-1 Using the CLETOP cassette cleaner
Step 2 Position the fiber tip slightly against the cleaning area and drag the fiber tip slightly in the
downward direction.
Figure 8-2 Dragging the fiber tip slightly on one cleaning area
Step 3 Repeat the same in the other cleaning area in the same direction as Step 2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
137
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Figure 8-3 Dragging the fiber tip slightly on the other cleaning area
Step 4 Release the lever to close the cleaning area.
----End
8.2.2 Cleaning Fiber Connectors by Using Lens Tissue
When there is no cartridge cleaners, use the lens tissue for cleaning fiber connectors.
Prerequisite
l
Disconnect both ends of the fiber. ensure that there is no laser light on the fiber connectors.
Inspect the fiber connector with a fiber microscope to ensure that the fiber connectors are
contaminated.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
Clean solvent
Non-woven lens tissue
Special compressed gas
NOTE
l The isoamylol is preferred as the clean solvent, and the propyl can also be used as the clean solvent.
Do not use alcohol or formalin.
l The fiber cleaning tissue or lint-free wipes can substitute the non-woven lens tissue.
l The special cleaning roll can substitute the special compressed gas.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
138
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Procedure
Step 1 Place a small amount of cleaning solvent on the lens tissue.
Step 2 Drag the fiber tip slightly on the lens tissue.
Figure 8-4 Cleaning the fiber with the lens tissue
Step 3 Repeat Step 2 several times on the areas of the lens tissue that have not been used.
Step 4 Use the compressed gas to blow the fiber tip.
When using compressed gas, note the following points:
l First spray it into the air because the initial spray of condensation may contain certain
sediment.
l Ensure that the injector nozzle is as close as possible to (but does not touch) the connector
surface.
----End
8.2.3 Cleaning Fiber Adapters by Using Optical Cleaning Sticks
The fiber adapters need to be cleaned with optical cleaning sticks. This section describes the
method of cleaning fiber adapters on the optical interface board. The same method can be used
to clean fiber adapters on the optical attenuators and flanges.
Prerequisite
l
Before you clean the fiber adapter, remove the optical fiber and shut down the laser. For
details about how to shut down a laser, see 8.9 Setting the On/Off State of the Laser.
Inspect the fiber adapter with a fiber microscope to ensure that the fiber adapter is
contaminated.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
139
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
l
Optical cleaning sticks
Clean solvent
Special compressed gas
NOTE
l In the case of the SC and FC optical interface, use the cleaning stick with a diameter of 2.5 mm. In the
case of the LC optical interface, use the cleaning stick with a diameter of 1.25 mm.
l The medical cotton or long fiber cotton can substitute the optical cleaning stick.
l The isoamylol is preferred as the clean solvent, and the propyl can also be used as the clean solvent.
Do not use alcohol or formalin.
l The special cleaning roll can substitute the special compressed gas.
Procedure
Step 1 Apply a small amount of cleaning solvent on the optical cleaning stick.
Step 2 Touch the adapter gently with the optical cleaning stick and turn the stick clockwise four to five
times.
Ensure that there is direct contact between the stick tip and fiber tip so that the solvent can clean
the adapter tip.
Step 3 Use the compressed gas to blow the fiber adapter.
When using compressed gas, note the following points:
l First spray the compressed gas into the air because the initial spray of condensation gas may
contain some sediment.
l Ensure that the injector nozzle is as close as possible to (but does not touch) the inner surface
of the connector.
----End
8.3 Browsing Alarms, Abnormal Events, and Performance
Events
The U2000 is used to browse alarms, abnormal events, and performance events at the network
layer.
8.3.1 Checking the NE Status
You can learn about the basic information such as whether the NE fails to communicate with
the NMS and whether any alarms are reported by checking the NE status.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
140
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Precautions
NOTE
By default, the color of the NE icon on the NMS indicates the NE status.
Procedure
Step 1 In Main Topology, select the required NE.
Step 2 In Main Topology, click
Step 3 Click the Attribute tab.
Step 4 View the NE status and alarm status.
TIP
You can also determine the NE status based on the comparison between the NE icon and the description
at the Legend tab.
----End
8.3.2 Checking the Board Status
You can learn about the board status in a visual manner by checking the slot diagram.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 On the Main Topology, double-click the desired NE. The NE Panel is displayed. The NE is in
Running Status.
Step 2 Click the
icon. The legend description is displayed.
Step 3 Check the running status of the boards based on the legend description. If a board is running
normally, the board icon is green.
----End
8.3.3 Browsing Current Alarms
You can find the faults that occur on the equipment by browsing current alarms.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
141
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Fault > Browse Current Alarm from the Main Menu.
Step 2 Optional: In the Filter dialog box, click the Basic Settings tab.
1.
In Severity, select the alarm severity to be queried.
2.
In Status, select the alarm status to be queried.
3.
In Type, select the alarm type.
4.
In Last Occurrence Time Segment, specify the alarm generation time.
5.
In Clearance Time Segment, specify the alarm clearance time.
Step 3 In the Filter dialog box, click the Alarm Source tab.
Step 4 Select the object to be queried.
Option
Description
Browse all alarms on the NE.
Select All Objects.
Browse certain alarms on the NE. 1. Select Custom.
2. Choose Add > Object below NE.
3. Select the required NE in the left pane of Object
below NE, and click
4. Click OK.
Alarm Source displays Selected Alarm Source.
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 Browse the displayed alarms.
Step 7 Select the newly generated alarms, record the details of the alarms, and click Acknowledge.
The Confirm dialog box is displayed.
Step 8 Click Yes.
Step 9 Notify the troubleshooting personnel to clear the alarms in time.
For the details, see A.3 Alarms and Handling Procedures.
----End
Related Information
A current alarm refers to an alarm that is not cleared.
You can browse the network-wide alarms based on the alarm severity by clicking the alarm
indicators in the upper right corner.
l
You can click
(red) to browse the network-wide critical alarms.
You can click
(orange) to browse the network-wide major alarms.
You can click
(yellow) to browse the network-wide minor alarms.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
142
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
You can click
8 Supporting Task
(light-blue) to browse the network-wide warning alarms.
NOTE
By default, the number shown by each indicator indicates the number of current network-wide alarms, which
are not cleared, of the specific severity.
8.3.4 Browsing Abnormal Events
You can find the faults that occur on the equipment in a specific time by browsing abnormal
events. An abnormal event refers to an exception that occurs on the system at a particular time
rather than an exception that persists for a certain time of period.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Fault > Browse Event Logs from the Main Menu.
Step 2 In the Filter dialog box, click the Event Source tab.
Step 3 Select the object to be queried.
Option
Description
Browse all performance events on the NE. Select All Objects.
Browse certain performance events on the 1. Select Custom.
NE.
2. Choose Add > Object below NE.
3. Select the required NE in the left pane of
Object below NE, and click
4. Click OK.
Event Source displays Selected Event
Source.
Step 4 Click OK.
Step 5 Browse the abnormal events.
For details on how to handle an abnormal event, see B.2 Abnormal Performance Events and
Handling Procedures.
----End
Related Information
Being different from an alarm that has both the occurrence time and the clearance time, an
abnormal event has only the occurrence time.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
143
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.3.5 Browsing Current Performance Events
You can know the running status of the equipment by browsing current SDH/PDH performance
events. The counter of current performance events measures all the performance events that arise
between the start time of the monitoring period and the current time.
Prerequisite
l
The performance monitoring function must be enabled. For details about how to enable the
performance monitoring function, see 8.3.10 Configuring the Performance Monitoring
Status of NEs.
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Performance > Browse SDH Performance from the Main Menu, and then click the
Current Performance Data tab.
Step 2 Select one or more NEs from the left pane, and click
Step 3 Select All in Monitored Object Filter Condition.
Step 4 Select 15-Minute in the Monitor Period field.
Step 5 Click the Count tab, and then select Display Continuous Severely Errored Seconds.
Step 6 Click Query to browse the current performance events.
In normal cases, no bit error performance events should be displayed, and the number of pointer
justification events should be less than six per day.
Step 7 Click the Gauge tab, select All for the performance event type, and then select Display Current
Value and Display Maximum and Minimum Values in the right pane.
Step 8 Click Query to browse the displayed performance events.
In normal cases, compared with the history records, the gauge indicators, such as the board
temperature, do not change drastically.
Step 9 Re-define the time span by setting Monitor Period to 24-Hour.
Step 10 Repeat Step 5 through Step 8 to query the current performance events in a period of 24 hours.
----End
8.3.6 Browsing History Alarms
You can know the faults that occur on the equipment in a past period of time by browsing history
alarms. A history alarm refers to an alarm that is already cleared.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
144
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Fault > Browse History Alarm from the Main Menu.
Step 2 Optional: In the Filter dialog box, click the Basic Settings tab.
1.
In Severity, select the alarm severity to be queried.
2.
In Type, select the alarm type.
3.
In Occurrence Time Segment, specify the alarm generation time.
4.
In Clearance Time Segment, specify the alarm clearance time.
The time span starts from the time when the last history alarm browsing operation was
performed to the current time.
Step 3 In the Filter dialog box, click the Alarm Source tab.
Step 4 Select the object to be queried.
Option
Description
Browse all alarms on the NE.
Select All Objects.
Browse certain alarms on the NE. 1. Select Custom.
2. Choose Add > Object below NE.
3. Select the required NE in the left pane of Object
below NE, and click
4. Click OK.
Alarm Source displays Selected Alarm Source.
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 Browse the displayed history alarms.
----End
8.3.7 Browsing History Performance Events
You can know the faults that occur on the equipment in a past period of time by browsing history
performance events.
Prerequisite
l
The performance monitoring function must be enabled. For details about how to enable the
performance monitoring function, see 8.3.10 Configuring the Performance Monitoring
Status of NEs.
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
145
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Performance > Browse SDH Performance from the main menu, and then click the
History Performance Data tab.
Step 2 Select one or more NEs from the left pane, and click
Step 3 Set the parameters, such as Monitored Object Filter Condition, Monitor Period, Data
Source.
Step 4 Click the Gauge tab, and set Performance Event Type.
Step 5 Click the Count tab, and set Performance Event Type.
Step 6 Click Query.
----End
8.3.8 Browsing the Performance Event Threshold-Crossing Records
You can learn about the threshold-crossing information of the performance events of an NE by
browsing the performance event threshold-crossing records.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Browse the performance event threshold-crossing records that are displayed.
Step 2 Choose Performance > Browse SDH Performance from the Main Menu.
Step 3 Click the Performance Threshold-Crossing Record tab.
Step 4 Select an NE from the Object Tree in the NE Explorer. Click
Step 5 Set the parameters such as Monitored Object Filter Condition, Monitor Period, and
Performance Event Type.
Step 6 Click Query.
----End
8.3.9 Browsing UAT Events
Learn about the severe abnormalities on the transmission line by browsing UAT events.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
146
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Context
UAT refers to a period of 10 consecutive seconds during which the bit error ratio per second of
the digital signal in either of the transmission directions of a transmission system is inferior to
10-3. These 10 seconds are considered to be part of the unavailable time.
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 2 Choose Performance > UAT Event from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set Monitored Object Filter Condition, From, To, and Data Source.
Step 4 Set Function Block Type and Display Options.
Step 5 Click Query.
Step 6 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.3.10 Configuring the Performance Monitoring Status of NEs
By performing this operation task, you can manually enable or disable performance monitoring
for NEs, or set the performance monitoring period.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the NE from the Object Tree, and then choose Performance > NE
Performance Monitoring Time from the Function Tree.
Step 2 Configure the performance monitoring parameters of the NEs.
1.
Select 15-Minute or 24-Hour.
2.
Select Enabled or Disabled in Set 15-Minute Monitoring or Set 24-Hour Monitoring.
3.
Set the start time and end time of the performance monitoring of NEs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
147
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
NOTE
l Generally, both Set 15-Minute Monitoring and Set 24-Hour Monitoring are enabled.
l You can specify the start time of the performance monitoring function, only after selecting Enabled
in the Set 15-Minute Monitoring or Set 24-Hour Monitoring area.
l You can specify the end time of the performance monitoring function, only after selecting Enabled
and then selecting To in the Set 15-Minute Monitoring or Set 24-Hour Monitoring area.
4.
Click Apply. Close the displayed dialog box.
----End
8.3.11 Setting Severity and Auto Reporting Status of Alarms
This section describes how to set the severity and auto reporting status of specific alarms.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired object.
Step 2 Choose Alarm > Alarm Severity and Auto Reporting from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select any items in the column Event and set Severity and Auto Reporting Status for them.
Step 4 Click Apply to save the settings.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.3.12 Suppressing Alarms for Monitored Objects
This section describes how to suppress specific alarms for a specific monitored object.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
148
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 2 Choose Alarm > Alarm Suppression from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set Monitored Object and click Query.
Step 4 Set Status in Alarm Suppression.
Step 5 Click Apply.
Step 6 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.3.13 Suppressing Alarms for NEs
This section describes how to suppress certain alarms for NEs.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired NE.
Step 2 Choose Alarm > NE Alarm Suppression from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set Status in Alarm Suppression.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.3.14 Reversing Alarms for Service Ports
This section describes how to reverse alarms for service ports.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
149
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired NE.
Step 2 Choose Alarm > NE Alarm Attribute from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set Reversion Mode to Manual Restoration.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
Step 6 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 7 Choose Alarm > Alarm Reversion from the Function Tree.
Step 8 Set Reversion Status for the required port.
Step 9 Click Apply.
Step 10 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.3.15 Setting Trigger Conditions of AIS Insertion
This section describes how to set the trigger conditions of AIS insertion for specific monitored
objects.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board. Choose Alarm > QoS Alarm > AIS Insertion
from the Function Tree.
Step 2 Set the trigger conditions of AIS insertion. If you select Enabled under an alarm, the AIS signal
is inserted when this alarm occurs; otherwise, the AIS signal is not inserted when this alarm
occurs.
Step 3 Click Apply.
Step 4 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
150
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.3.16 Setting Trigger Conditions of UNEQ Insertion
This section describes how to set the trigger conditions of UNEQ insertion for service ports.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 2 Choose Alarm > QoS Alarm > UNEQ Insertion Switch from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set the trigger conditions of UNEQ insertion. If you select Enabled under an alarm, the UNEQ
signal (all 0s) is inserted when this alarm occurs; otherwise, the UNEQ signal is not inserted
when this alarm occurs.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.3.17 Setting Bit Error Thresholds for Service Ports
This section describes how to set bit error thresholds for service ports.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 2 Choose Alarm > QoS Alarm > Bit Error Alarm Threshold from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set bit error thresholds.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
151
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.3.18 Setting Monitoring and Auto-Report Status of Performance
Events
This section describes how to set monitoring and auto-report status of specific performance
events for monitored objects.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 2 Choose Performance > Performance Monitor Status from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set the following parameters: Monitor Status, 15-Minute Auto-Report, and 24-Hour AutoReport.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.3.19 Setting Performance Thresholds
This section describes how to set the thresholds of specific performance events for monitored
objects.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 2 Choose Performance > Performance Threshold from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set Threshold Value.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
152
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.3.20 Resetting Performance Registers
This section describes how to reset performance registers. After performance registers are reset,
their counts are cleared and they immediately start a new counting period.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In the NE Explorer, select the desired board.
Step 2 Choose Performance > Reset Board Performance Register from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Set Monitored Object and register types.
Step 4 Click Reset.
Step 5 In the Hint dialog box that is displayed, click Yes.
Step 6 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.4 Querying a Report
You can obtain the version, manufacture, and microwave link information of all the boards by
querying the corresponding report.
8.4.1 Querying the Board Information Report
You can obtain the logic version, and software version of each board by querying the board
information report.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Inventory > Physical Inventory from the Main Menu.
Step 2 Select Board from Physical Inventory Type in the Physical Inventory window.
Step 3 In Physical Inventory, click the Board List tab.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
153
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Step 4 Click Filter.
In Filter window, set the board or board attributes that need to be queried. Click OK.
Step 5 The board information displayed in the Board List.
Step 6 Optional: Click Save As.
Set the parameters in Saving Options.
Step 7 Click OK. Then, you can save and archive the board information as a text file.
Step 8 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.4.2 Querying the Board Manufacturing Information Report
You can obtain the manufacturing information about each board and the SFP module by querying
the board manufacturing information report.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Inventory > Project Document > Board Manufacturer Information from the Main
Menu.
Step 2 In Board Manufacturer Information, click the Board Manufacturer Information tab.
Step 3 Select one or multiple NEs from the left pane, and click
Step 4 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
Step 5 Click Query.
The Query processing bar is displayed.
Step 6 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
Step 7 Optional: Click Save As.
Step 8 Set the parameters in Saving Options.
Step 9 Click OK. Then, you can save and archive the board manufacturing information as a text file.
----End
8.4.3 Querying the Microwave Link Information Report
You can obtain the current and recent transmit/receive power of microwave links by querying
the microwave link information report.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
154
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 In Main Menu, choose Inventory > Microwave Report > Microwave Link Report.
Step 2 In the left pane of the Microwave Link Report tab page, choose one or more NEs, and click
.
Step 3 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
Step 4 Optional: Click Save As.
Step 5 Set the parameters in Saving Options.
Step 6 Click OK. Then, you can save and archive the microwave link information as a text file.
----End
8.4.4 Querying the Network-wide License Report
By querying the network-wide license report, you can check the license information of each NE.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Inventory > Microwave Report > Microwave License Capacity Report from the
Main Menu.
Step 2 Select one or more NEs in the left pane, and click
Step 3 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
Step 4 Optional: Click Save As. Save the license report as a file and archive the file properly.
Step 5 Set the parameters in Saving Options.
Step 6 Click OK. Then, the license report is saved and archived as a file.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
155
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.5 Software Loopback
Software loopback refers to the loopback operation that is implemented by using the NMS.
During software loopback, you need not visit the engineering site. Hence, software loopback is
used more widely than hardware loopback.
8.5.1 Setting Loopback for the SDH Optical Interface Board
The SDH optical interface board supports the optical/electrical interface inloop/outloop and the
VC-4 path inloop/outloop.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The optical/electrical interface inloop is a process wherein the signals over an SDH port are
looped back at the overhead processing unit towards the backplane.
Figure 8-5 Optical/electrical interface inloop
Backplane
SDH optical
interface board
SDH
The optical/electrical interface outloop is a process wherein the signals over an SDH port are
looped back at the overhead processing unit towards the remote equipment.
Figure 8-6 Optical/electrical interface outloop
Backplane
SDH optical
interface board
SDH
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
156
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
The VC-4 path outloop is a process wherein the signals on a VC-4 path are looped back at the
logic processing unit towards the remote equipment.
Figure 8-7 VC-4 path outloop
SDH optical
interface board
Backplane
VC-4
The VC-4 path inloop is a process wherein the signals on a VC-4 path are looped back at the
logic processing unit towards the backplane.
Figure 8-8 VC-4 path inloop
Backplane
SDH optical
board
VC-4
Precautions
CAUTION
l The services may be interrupted at the port or on the path where the loopback is performed.
l A software loopback may be released automatically after a certain period (five minutes, by
defaults). For details, see 8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function.
Procedure
Step 1 Select the SDH optical interface board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > SDH Interface from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select By Function, and select the loopback mode from the drop-down list.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
157
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
To Perform...
Choose...
Optical/electrical interface loopback
Optical(Electrical) Interface Loopback
VC-4 path loopback
VC4 Loopback
Step 4 Set the loopback status of the port or path based on the requirements.
Step 5 Click Apply.
Then, the Confirm dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 Click OK.
Step 7 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.5.2 Setting Loopback for the Tributary Board
The tributary board supports the tributary inloop and outloop.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The tributary inloop is a process wherein the signals over a PDH port are looped back at the
coding/decoding unit towards the backplane.
Figure 8-9 Tributary inloop
Backplane
PDH interface board
PDH
The tributary outloop is a process wherein the signals on a tributary path are looped back at the
PDH interface board of the local IDU towards the remote equipment.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
158
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Figure 8-10 Tributary outloop
Backplane PDH interface board
PDH
Precautions
CAUTION
The services may be interrupted on the port or on the path where the loopback is performed.
Procedure
Step 1 Select the PDH interface board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > PDH Interface from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select By Function, and select Tributary Loopback from the drop-down list.
Step 4 Set the loopback status of the path based on the requirements.
Step 5 Click Apply.
Then, the Confirm dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 Click OK.
Step 7 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.5.3 Setting a Loopback for the Smart E1 Processing Board
A Smart E1 processing board supports inloops and outloops on E1 ports.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
159
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Context
The E1 inloop is a process wherein the signals over an E1 port are looped back from the coding/
decoding unit to the backplane.
Figure 8-11 E1 inloop
Backplane
Smart E1
Processing Board
E1
The E1 outloop is a process wherein the signals over an E1 port are looped back from the Smart
E1 processing board of the local IDU to the remote equipment.
Figure 8-12 E1 outloop
Smart E1
Backplane Processing Boards
E1
Precautions
CAUTION
l The services may be interrupted at the port or on the path where the loopback is performed.
l A software loopback may be released automatically within a period (5 minutes, by default).
For details, see 8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function.
Procedure
Step 1 Select the Smart E1 processing board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > Interface Management > PDH Interface from the Function Tree.
Step 3 In the Advanced Attributes tab, select the required port.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
160
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Step 4 Set the loopback status of the port as required.
Step 5 Click Apply.
The system displays a prompt dialog box for confirmation.
Step 6 Click OK.
Step 7 Close the dialog box.
----End
8.5.4 Setting a Loopback for the Packet-plane Ethernet Interface
Board
The Packet-plane Ethernet interface board supports the Ethernet port inloop (at the MAC layer
and PHY layer).
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The Ethernet port MAC inloop is a process wherein the Ethernet physical signals are looped
back at the service processing module of the board at the MAC layer towards the backplane.
The Ethernet port PHY inloop is a process wherein the Ethernet frame signals are looped back
at the interface module of the board at the PHY layer towards the backplane.
Figure 8-13 Ethernet port inloop
Backplane
Ethernet service
processing board
MAC
PHY
Precautions
NOTE
PORT 10 on the EFP8 board can not be configured with loops.
PORT 8 on the EMS6 board can not be configured with loops.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
161
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
CAUTION
l A loopback operation results in service interruption.
l A software loopback may be released automatically after a certain period (five minutes, by
defaults). For details, see 8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function.
CAUTION
When Port Mode of an Ethernet port is set to Layer 3, do not perform any loopback on the port.
In this case, LSP Traceroute is recommended for locating faults.
Procedure
Step 1 Select an Ethernet processing board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Select the corresponding function options from the Function Tree based on the loopback type.
To Perform...
Choose...
PHY loopback 1. Choose Configuration > Interface Management > Ethernet
Interface from the Function Tree.
2. Click the Advanced Attributes tab.
MAC loopback 1. Choose Configuration > Interface Management > Ethernet
Interface from the Function Tree.
2. Click the Advanced Attributes tab.
Step 3 Set the loopback status of the port based on the requirements.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Then, the Confirm dialog box is displayed.
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.5.5 Setting Loopbacks for the EOS/EoPDH-Plane Ethernet
Interface Board
EPF8 board supports the inloop at Ethernet ports (at the MAC layer and PHY layer) and the
inloop in VC-12 paths. EMS6 board supports the inloop at Ethernet ports (at the MAC layer and
PHY layer) and the inloop in VC-3 paths.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
162
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Context
A MAC layer inloop is an inloop where the service processing module loops back the Ethernet
physical signals towards the backplane through the MAC layer. A PHY layer inloop is an inloop
where the interface module loops back the Ethernet frame signals towards the backplane through
the PHY layer.
NOTE
PORT 9 in the EFP8 board only supports inloop at the MAC layer.
PORT 7 in the EMS6 board only supports inloop at the MAC layer.
Figure 8-14 Ethernet port inloop
Backplane
Ethernet service
processing board
MAC
PHY
An inloop in a VC-12 path is an inloop where the logic processing unit of a board loops back
the signals in a specific VC-12 path towards the backplane.
Figure 8-15 VC-12 path inloop
Backplane
EFP8
EOPDH
An inloop in a VC-3 path is an inloop where the logic processing unit of a board loops back the
signals in a specific VC-3 path towards the backplane.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
163
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Figure 8-16 VC-3 path inloop
Backplane
EMS6
EOS
Precautions
CAUTION
l A loopback operation may interrupt the services on the port where the loopback is performed.
l A software loopback may be automatically released within a period (five minutes by default).
For details, see 8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function.
NOTE
A VC-3 loopback can be performed only after the EMS6 is configured with services.
Procedure
Step 1 In NE Explorer, select the required board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Select the corresponding function options from the Function Tree according to the loopback
type.
To Perform...
Choose...
PHY loopback
1. Choose Configuration > Ethernet Interface Management >
Ethernet Interface from the Function Tree.
2. Select External Port.
3. Click the Basic Attributes tab.
MAC loopback
1. Choose Configuration > Ethernet Interface Management >
Ethernet Interface from the Function Tree.
2. Select External Port.
3. Click the Basic Attributes tab.
VC-12 path inloop 1. Choose Configuration > SDH Interface from the Function Tree.
2. Select By Function.
3. Select the required VC-12 path.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
164
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
To Perform...
Choose...
VC-3 path inloop
1. Choose Configuration > SDH Interface from the Function Tree.
2. Select By Board/Port(Channel).
3. Select the required VC-3 path.
Step 3 Set the loopback status of the port as required.
Step 4 Click Apply.
The confirmation dialog box is displayed.
Step 5 Click OK.
The prompt dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 Click OK.
Step 7 Close the prompt dialog box.
----End
8.5.6 Setting Loopback for the IF Board
Loopbacks on the IF board are classified into IF port loopback, composite port loopback, and
Integrated IP radio port MAC loopback. The IF1 board supports the IF port inloop, IF port
outloop, composite port inloop, and composite port outloop. The IFU2/IFX2 board supports the
IF port inloop, IF port outloop, composite port inloop, composite port outloop, and Integrated
IP radio port MAC inloop. The ISU2/ISX2 board supports the IF port inloop, IF port outloop,
composite port inloop, and composite port outloop.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The IF port inloop is a process wherein the IF signals are looped back at the modem unit towards
the backplane.
Figure 8-17 IF port inloop
Backplane
IF board
IF signal
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
165
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
The IF port outloop is a process wherein the IF signals are looped back at the modem unit of the
board towards the remote equipment.
Figure 8-18 IF port outloop
Backplane
IF board
IF signal
The composite port inloop is a process wherein the microwave baseband signal is looped back
at the MUX/DEMUX unit of the board towards the backplane.
Figure 8-19 Composite port inloop
Backplane
IF board
Microwave
baseband signal
The composite outloop is a process wherein the microwave baseband signal is looped back at
the MUX/DEMUX unit of the board towards the remote equipment.
Figure 8-20 Composite port outloop
Backplane
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
IF board
Microwave
baseband
signal
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
166
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Precautions
CAUTION
l The services may be interrupted at the port or on the path where the loopback is performed.
l A software loopback may be released automatically after a certain period (five minutes, by
defaults). For details, see 8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function.
l To perform the software loopback on the standby IF board of the 1+1 HSB/FD/SD protection
group, switch the standby IF board to the working state forcedly. Otherwise, the operation
may fail.
l Before performing the loopback operation for the IFU2/IFX2 board, disable the AM function
at both ends of the radio link.
CAUTION
When Port Mode of an Integrated IP radio port is set to Layer 3, do not perform any loopback
on the port. In this case, LSP Traceroute is recommended for locating faults.
Procedure
Step 1 Select the corresponding IF board from the Object Tree in the NE explorer.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > Interface Management > Microwave Interface from the Function
Tree.
Step 3 Select Loopback Attributes.
Step 4 Select the port where the loopback needs to be performed and set loopback type.
Step 5 Click Apply.
Then, the Confirm dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 Click OK to close the dialog box.
Then, a dialog box is displayed.
Step 7 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.5.7 Locating a Fault by Performing Loopback Operations
Loopback is a common method of locating the fault.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
167
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Service Trail
Figure 8-21 shows how to locate a fault by performing a loopback operation.
Figure 8-21 Service trail
PDH
tributary
board
Cross-connect
IF
board
board
ODU
ODU
NE1
PDH
Cross-connect
tributary
board
board
SDH
IF
Cross-connect
tributary
board
board
board
NE2
IF
board
ODU
ODU
NE4
IF Cross-connect
board
board
SDH
tributary
board
NE3
Optical cable
Precautions
The LSP Traceroute method, instead of sectional loopbacks, is recommended for locating the
faults of PWE3 services.
Procedure
Step 1 If the services are available on the radio links, perform the inter-station loopbacks to narrow
down the fault to a specific hop.
1.
Set the outloops for the SDH optical interface boards on NE2 and NE3, and then perform
the inter-station loopbacks to locate the fault.
Step 2 After the fault is located on the specific radio link, perform the intra-station loopbacks to narrow
down the fault to a specific NE or board.
1.
Set inloop for the IF board on the NEs at both ends of the radio link where the fault occurs,
to check whether the service receiver or the radio link is faulty.
2.
If the fault is located in the service receiver, set outloop for the PDH tributary board to
check whether the interface board or switch unit is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
168
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3.
8 Supporting Task
If the radio link is faulty, replace the IF board and ODU to check whether the IF board or
ODU is faulty.
----End
8.6 Reset
Reset is an important method of troubleshooting software faults. Reset is classified into cold
reset, warm reset.
8.6.1 Cold Reset
Cold reset is a process wherein the board software is reset and the board is re-initiated. The
software of each board runs as a software module in the CPU on the system control, switching,
and timing board. During the board initialization, the FPGA, if any, is re-loaded.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Precautions
CAUTION
Cold reset causes service interruption because it is similar to the procedure of removing and
inserting a board.
Procedure
Step 1 In NE Panel, right-click the board where the cold reset needs to be performed.
Step 2 Choose Cold Reset from the shortcut menu.
Then, the Warning dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click OK.
Step 4 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.6.2 Warm Reset
Warm reset is a process wherein the board software is reset but the board is not re-initiated. The
software of each board runs as a software module in the CPU on the integrated board of the
system control unit, cross-connect unit, and timing unit.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
169
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Precautions
During warm reset, the board software is reset but the services are not interrupted.
Procedure
Step 1 In NE Panel, right-click the board where the warm reset needs to be performed.
Step 2 Choose Warm Reset from the shortcut menu.
Then, the Warning dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click OK.
Step 4 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.7 PRBS Test
The pseudorandom binary sequence (PRBS) test is an important method of network maintenance
and self-check.
8.7.1 Performing a PRBS Test for the Tributary Board
If a special test tool is unavailable, you can perform the PRBS test by using the embedded test
system on the tributary board.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The OptiX RTN 950 supports the PRBS test in the tributary direction and in the cross-connect
direction.
The PRBS test in the tributary direction can be performed to check the connection between the
tributary board and the DDF, as shown in Figure 8-22.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
170
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Figure 8-22 PRBS test in the tributary direction
DDF frame
PDH interface board
PRBS
Transmitter
1
PRBS
Recevicer
1
Loopback at the DDF frame
The PRBS test in the cross-connect direction can be performed to check the connection between
the tributary board and the remote NE, as shown in Figure 8-23.
Figure 8-23 PRBS test in the cross-connect direction
a) IF board working as the line board
PDH interface
board
Cross-connect
board
IF board
IF board
OUT
PRBS
transmitter
2
PRBS
receiver
IN
NE at the local end
1
VC-4 inloop or
composite port inloop
IF port inloop
NE at the opposite end
3
IF port outloop
b) Line board working as the SDH optical interface board
PDH interface board
SDH optical
interface board
Cross-connect board
OUT
PRBS
transmitter
1
PRBS
receiver
IN
NE at the opposite end
NE at the local end
1 VC-4 inloop
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
2 Port inloop
3 Port outloop
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
171
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Precautions
CAUTION
l During the PRBS test, the services in the tested path are interrupted.
l The PRBS test can be performed only in one path and in one direction at one time.
Procedure
Step 1 Set the loopback at the proper location. For details, see Figure 8-22 and Figure 8-23.
Step 2 Select the E1 interface board from the Object Tree.
Step 3 Choose Configuration > PRBS Test from the Function Tree.
Step 4 Select the port to be tested.
Step 5 Set Duration and Measured in Time.
NOTE
l The PRBS test supports three time units: one second, 10 minutes, and one hour.
l A maximum of 255 test cycles is permissible for the PRBS test.
Step 6 Optional: Select Accumulating Mode.
Step 7 Click Start to Test.
A prompt is displayed.
Step 8 Click OK.
Step 9 When Process is displayed as 100%, click Query to check the test result.
NOTE
The result of a PRBS test can be normal, error, or invalid.
l Invalid: indicates that no bit is received. In this case, the curve is yellow.
l Normal: indicates that the path is in normal state. In this case, the number of PRBSs is zero, and the
curve is green.
l Error: indicates that the path has errors. In this case, the number of total PRBSs is a non-zero number,
and the curve is red.
----End
8.7.2 Performing a PRBS Test for the IF Board
If a special test tool is unavailable, you can perform the PRBS test by using the embedded test
system on the IF board.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
172
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Precautions
Figure 8-24 PRBS test of the IF board
IF board
ODU
ODU
IF board
PRBS
transmitter
1
PRBS
transmitter
NE at the local end
NE at the opposite end
1 IF port outloop
CAUTION
l During the PRBS test, the services in the tested path are interrupted.
l The PRBS test can be performed only in one path and in one direction at one time.
l The standby IF unit does not support the PRBS test. Before you perform the PRBS test for
the standby IF board of a 1+1 HSB/FD/SD protection group, you must switch the standby
IF board to the working state.
Procedure
Step 1 Perform an outloop on the opposite IF board. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting Loopback for the
IF Board.
Step 2 Select the IF board from the Object Tree.
Step 3 Choose Configuration > PRBS Test from the Function Tree.
Step 4 Select the port to be tested.
Step 5 Set Duration and Measured in Time.
NOTE
l The time unit of the PRBS test can be one second, 10 minutes, or one hour.
l A maximum of 255 test cycles is permissible for the PRBS test.
Step 6 Optional: Select Accumulating Mode.
Step 7 Click Start to Test.
A prompt is displayed.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
173
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Step 8 Click OK.
Step 9 When Process is displayed as 100%, click Query to check the test result.
NOTE
The result of a PRBS test can be normal, error, or invalid.
l Invalid: indicates that no bit is received. In this case, the curve is yellow.
l Normal: indicates that the path is in normal state. In this case, the number of PRBSs is zero, and the
curve is green.
l Error: indicates that the path has errors. In this case, the number of total PRBSs is a non-zero number,
and the curve is red.
----End
8.8 Querying the License Capacity
You can check whether the loaded license file meets the requirements by querying the license
capacity.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Select the NE from the Object Tree in the NE Explorer.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > License Management.
Step 3 Click Query, browse the license capacity of the NE.
----End
8.9 Setting the On/Off State of the Laser
When performing operations such as testing a fiber cut, you can set the on/off state of the laser
rather than removing and re-inserting the optical fiber on site.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
174
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Procedure
Step 1 Select the desired SDH optical interface board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > SDH Interface from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select By Function.
Step 4 Select Laser Switch from the drop-down list.
Step 5 Select a port, and then set Laser Switch.
Step 6 Click Apply.
A confirmation dialog box is displayed.
Step 7 Click OK.
A prompt is displayed.
Step 8 Click OK.
----End
8.10 Setting the ALS Function
The SDH optical interface board supports the automatic laser shutdown (ALS) function. This
function enables the board to turn off a laser when the board does not transmit services, the
optical fiber is faulty, or the received optical signals are lost.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Select the desired SDH optical interface board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > Automatic Laser Shutdown from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select a port, and then set Automatic Shutdown to Enabled.
Step 4 Click Apply to save the settings.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
----End
8.11 Setting the Automatic Release Function
To protect the communication between the NMS and NE against improper operations, an NE
supports the automatic release of the ODU muting, software loopback, and other operations that
require you to exercise caution. The automatic release time is five minutes by default. You can
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
175
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
set whether to enable the automatic release function and the automatic release time through the
NMS.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Configuration > NE Batch Configuration > Automatic Disabling of NE Function
from the Main Menu.
Step 2 Select the desired NE from the Object Tree. Click
Step 3 In Automatic Disabling of NE Function, set Auto Disabling and Auto Disabling Time
(min).
Step 4 Click Apply to complete the settings for the automatic release function.
----End
8.12 Querying Power Consumption of Boards
This section describes how to query power consumption of the ODU and each board.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE monitor authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Configuration > NE Batch Configuration > Power Management from the Main
Menu.
Step 2 In the NE Power dialog box, select the Board Power tab.
Step 3 Select the required NE or board from the object tree, and then click
Step 4 Click Query.
The Query progress bar is displayed.
Step 5 Close the dialog box that is displayed.
Step 6 On the Board Power tab page, browse Nominal Power Consumption and Current Power
Consumption of the selected board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
176
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.13 Querying the Impedance of an E1 Channel
The impedance of an E1 channel is 75 ohms or 120 ohms.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Select a PDH tributary board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > PDH Interface from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select By Board/Port(Channel).
Step 4 Select Port in the list.
Step 5 Select a port, and check Port Impedance.
----End
8.14 Monitoring Ethernet Packets Through Port Mirroring
To monitor and analyze the Ethernet packets at a port, you can enable the port mirroring function
so that the received or transmitted packets on the port are duplicated to another Ethernet port to
which the Ethernet tester is connected. Then, you can monitor and analyze the packets. This
function is supported by the EFP8/EMS6 board of the OptiX RTN 950.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Context
The OptiX RTN 950 supports the mirroring, monitoring, and analyzing of the Ethernet packets
that are received or transmitted on the port.
Figure 8-25 Schematic diagram of Ethernet port mirroring
Ethernet processing unit
Mirroring
port
Ethernet
equipment
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Monitoring
port
Duplication
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Ethernet tester
177
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
To monitor the data in different directions, port mirroring can be performed in the ingress
direction and in the egress direction. For the ports on EFP8/EMS6 board:
l
In the ingress direction
Also in the upstream direction. The equipment duplicates the packets received from the
mirroring port to the observing port, and then transmits the packets from the observing port
to the Ethernet tester.
In the egress direction
Also in the downstream direction. The equipment duplicates the packets transmitted by the
mirroring port to the observing port, and then transmits the packets from the observing port
to the Ethernet tester.
In the ingress direction, the ports mirror the data transmitted from the VCTRUNK to the TDM
side. In the egress direction, the ports mirror the data transmitted from the TDM side to the
VCTRUNK.
Procedure
Step 1 In NE Explorer, select the EFP8or EMS6 board.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > Ethernet Interface Management > Port Mirroring from the
Function Tree.
Step 3 Click New, and set Mirror Listener Port, Uplink Listened Port, and Downlink Listened
Port.
Step 4 Click OK.
----End
8.15 Querying the Attributes of an Ethernet Port
Through the operation, you can learn about the attributes of an Ethernet port, such as rate.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
178
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Procedure
Step 1 Optional: Query the attributes of the FE or GE port on the packet plane.
1.
In NE Explorer, select the required NE from the Object Tree.
2.
Choose Configuration > Interface Management > Ethernet Interface from the Function
Tree.
3.
Click the Advanced Attributes tab.
4.
Check the parameters such as Port Physical Parameters, Transmitting Rate, and
Receiving Rate.
Step 2 Optional: Querying the attributes of the Integrated IP radio port.
1.
In NE Explorer, select the required NE from the Object Tree.
2.
Choose Configuration > Interface Management > Microwave Interface from the
Function Tree.
3.
Click the Advanced Attributes tab.
4.
Check the parameters such as Transmitting Rate and Receiving Rate.
Step 3 Optional: Query the attributes of the external port on the EFP8 board.
1.
In NE Explorer, select the EFP8 board from the Object Tree.
2.
Choose Configuration > Ethernet Interface Management > Ethernet Interface from
the Function Tree.
3.
Select External Port.
4.
Click the Advanced Attributes tab.
5.
Check the parameters such as Transmitting Rate and Receiving Rate.
NOTE
By performing this operation, you can query the attributes of the external ports on the EFP8 board (PORT1 to
PORT8) and the attributes of the bridging port on the EFP8 board (PORT9).
----End
8.16 Setting Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth
Utilization of Ethernet Ports
To query the traffic, physical bandwidth, or bandwidth utilization of Ethernet ports within a
certain period, you need to enable the monitoring for the object before that period starts. The
FE/GE ports and Integrated IP radio ports on the packet plane support this operation.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
The flow monitoring function is enabled on the Ethernet port. To enable the flow monitoring
function on a port, see 8.16 Setting Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization
of Ethernet Ports.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
179
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Background Information
After the flow monitoring function is enabled, the system saves the statistics about the received
traffic and transmitted traffic with an interval of 15 minutes. In normal cases, the system stores
the statistics that are collected in the last 30 days. In the system, every measurement entry shows
the average transmit rate and average receive rate within a period of 15 minutes. You can query
the statistics in the last 30 days.
Procedure
Step 1 Select a board from the Object Tree in the NE Explorer.
Step 2 Choose Performance > Ethernet Port Flow Monitoring from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select the Set Monitoring tab. Set Flow Monitoring, Physical Bandwidth Monitoring,
Bandwidth Usage Monitoring to Enabled for the Ethernet port.
Step 4 Click Apply.
Step 5 Close the displayed Result dialog box.
----End
8.17 Querying Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth
Utilization of Ethernet Ports
This section describes how to query the change curve of the traffic, physical bandwidth, or
bandwidth utilization of Ethernet ports within a certain period. The FE/GE ports and Integrated
IP radio ports on the packet plane support this operation.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
The flow monitoring function is enabled on the Ethernet port. To enable the flow monitoring
function on a port, see 8.16 Setting Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization
of Ethernet Ports.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Background Information
After the flow monitoring function is enabled, the system saves the statistics about the received
traffic and transmitted traffic with an interval of 15 minutes. In normal cases, the system stores
the statistics that are collected in the last 30 days. In the system, every measurement entry shows
the average transmit rate and average receive rate within a period of 15 minutes. You can query
the statistics in the last 30 days.
Procedure
Step 1 Select a board from the Object Tree in the NE Explorer.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
180
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Step 2 Choose Performance > Ethernet Port Flow Monitoring from the Function Tree.
Step 3 Select the Query Flow tab.
Step 4 Set the Monitored Object, Monitored Indicator, Start Time, End Time, and Display
Mode.
Step 5 Click Query.
The system displays the query result in a table or in a graph.
Step 6 Close the displayed Result dialog box.
----End
8.18 Setting the Threshold of Received Traffic Flow on an
Ethernet Port
The FLOW_OVER alarm is reported when the traffic flow received on an Ethernet port exceeds
the specified threshold. Only the FE port on the EFP8 board supports this operation.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Precautions
NOTE
The receive traffic threshold cannot be set for the Ethernet ports on the packet domain.
Procedure
Step 1 In NE Explorer, select an Ethernet processing board from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > Ethernet Interface Management > Ethernet Interface from the
Function Tree.
Step 3 Select External Port.
Step 4 Select the Advanced Attributes tab.
Step 5 Select an Ethernet port and set Traffic Threshold and Port Traffic Threshold Time
Window.
Step 6 Click Apply.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
181
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
8.19 Using the Ethernet Test Frames
By using the Ethernet test frames, you can check the connectivity of VCTRUNKs. Only the
EFP8 board supports this operation.
Prerequisite
l
You must be an NM user with NE maintainer authority or higher.
The service traffic is encapsulated or mapped by using the GFP method.
Tools, Instruments, and Materials
U2000
Background Information
The Ethernet board uses the specific GFP management frame or Ethernet frame as the test frame.
One frame is transmitted to the opposite Ethernet board per second. After receiving the test
frame, the Ethernet board returns the response frame. Upon receiving the response frame, the
Ethernet service processing board at the local end can judge the connectivity of the VCTRUNK
in between.
Figure 8-26 Ethernet test frames between Ethernet boards
Test frame
Local
Ethernet
board
Response frame
Remote
Ethernet
board
Precautions
CAUTION
Do not use the test frames when the network traffic is heavy.
Procedure
Step 1 In NE Explorer, select the EFP8 board.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > Ethernet Maintenance > Ethernet Test from the Function Tree.
Then, the Ethernet Test dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Select the test port and click Clear Counters. Select Clear All Counters .
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
182
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Step 4 Set Send Mode and Frames to Send.
NOTE
It is recommended that you choose "Burst mode", and a maximum of 10 frames can be transmitted each
time.
Step 5 Click Apply.
The system starts transmitting and receiving test frames.
Step 6 After Status displays Finished Sending, click Query.
Step 7 Check Counter of Frames Sent and Counter of Received Response of Test Frame.
Test frames are used to check the network connectivity. If some of the test frames are lost but
no alarm is reported on the SDH side, you can infer that the network is normal. If all the test
frames are lost, you can infer that the network is faulty.
----End
Related Information
If you choose the continue mode, the local port transmits test frames continuously until the test
is disabled.
8.20 Switching the System Control Unit and the CrossConnect Unit
When the OptiX RTN 950 is configured with two system control, cross-connect, and timing
boards, you can manually switch the system control unit and the cross-connect unit as required.
Prerequisite
You must be an NM user with NE operator authority or higher.
Tools, Equipment, and Materials
U2000
Procedure
Step 1 Select the desired NE from the Object Tree.
Step 2 Choose Configuration > Board 1+1 Protection from the Function Tree.
Step 3 In 1+1 Protection List, select Cross-Connect Protection Pair.
Step 4 Perform the 1+1 protection switching on the board.
If...
Then...
Active Board is set to Working Board
Click Working/Protection Switching.
Active Board is set to Protection Board
Click Restore Working/Protection.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
183
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
8 Supporting Task
Step 5 In the prompt that is displayed, click OK.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
184
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Reference
Alarms are important indicators when abnormalities occur on the equipment. This chapter
describes all the possible alarms on the OptiX RTN 950 and how to handle these alarms.
A.1 Alarm List (in Alphabetical Order)
The following table lists all the possible alarms generated by the OptiX RTN 950 in alphabetical
order.
A.2 Alarm List (Classified by Logical Boards)
This part lists the alarms that are reported by each board.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
185
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.1 Alarm List (in Alphabetical Order)
The following table lists all the possible alarms generated by the OptiX RTN 950 in alphabetical
order.
Table A-1 Alarm list
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
A_LOC
Loss of clock in the
upstream bus
Major
ALM_E1RAI
E1 link remote alarm
indication
Minor
ALM_GFP_dCSF
Loss of GFP client
signals
Critical
ALM_GFP_dLFD
Out of frame state of
generic framing
procedure (GFP)
frames
Major
ALM_IMA_LIF
Frame delimitation is
out-of-frame at the
local end of the IMA
link.
Major
ALM_IMA_LODS
Differential delay of
the IMA link crosses
the threshold.
Major
ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE
The IMA link on the
opposite NE fails in
the receive direction.
Minor
ALM_IMA_RE_TX_UNUSABLE
The IMA link on the
opposite NE fails in
the transmit
direction.
Minor
ALM_IMA_RFI
Frame delimitation is
out-of-frame at the
remote end of the
IMA link.
Major
AM_DOWNSHIFT
Downshift of AM
modes
Major
APS_FAIL
Failure indication of
MS protection
switching
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
186
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
APS_INDI
Indication of the APS
protection switching
Major
APS_MANUAL_STOP
MS protocol stopped
manually
Minor
ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELL_EXC
The number of
unknown ATM cells
exceeds the specified
threshold in a time
unit.
Major
AU_AIS
AU alarm indication
Major
AU_LOP
Loss of AU pointers
Major
B1_EXC
Excessive
regenerator section
errors (B1)
Minor
B1_SD
Signal degradation
due to excessive
regenerator section
errors (B1)
Minor
B2_EXC
Excessive multiplex
section errors (B2)
Major
B2_SD
Signal degradation
due to excessive
multiplex section
errors (B2)
Minor
B3_EXC
Excessive higher
order path bit errors
(B3)
Major
B3_EXC_VC3
Excessive B3 bit
errors in a VC-3 path
Major
B3_SD
Signal degradation
due to excessive
higher order path bit
errors (B3)
Minor
B3_SD_VC3
Signal degradation
due to excessive
VC-3 path (B3) bit
errors
Minor
BAT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
The temperature
sensor of battery
group 1 fails.
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
187
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
BAT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
The temperature
sensor of battery
group 2 fails.
Major
BD_NOT_INSTALLED
The logical board is
not added on the
NMS.
Minor
BD_STATUS
The board is out-ofposition.
Major
BDTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
The board
temperature sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Major
BIOS_STATUS
The board is in BIOS
state.
Major
BIP_EXC
Excessive BIP errors
Minor
BIP_SD
Signal degradation
due to excessive BIP
errors
Minor
BOOTROM_BAD
BOOTROM data
check fails.
Major
BUS_ERR
Bus errors
Critical
CES_ACR_LOCK_ABN
The locking function
of CES ACR service
clock is abnormal.
Minor
CES_JTROVR_EXC
The number of jitter
buffer overflows
crosses the specified
threshold.
Major
CES_JTRUDR_EXC
The number of jitter
buffer underflows
crosses the specified
threshold.
Major
CES_LOSPKT_EXC
The number of lost
packets crosses the
specified threshold in
a time unit.
Major
CES_MALPKT_EXC
The number of
deformed packets
crosses the specified
threshold in a time
unit.
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
188
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
CES_MISORDERPKT_EXC
The number of lost
disordered packets
crosses the specified
threshold in a time
unit.
Major
CES_RDI
Remote defect
indication
Minor
CES_STRAYPKT_EXC
The number of
errored packets
crosses the specified
threshold in a time
unit.
Major
CESPW_OPPOSITE_ACFAULT
The AC circuit on the
opposite NE is faulty.
Major
CESPW_OPPOSITE_RAI
Remote alarm
indication
Major
CFCARD_FAILED
The operation on the
CF card fails.
Major
CFCARD_OFFLINE
The CF card is offline.
Major
CHCS
Correctable cell
errors
Minor
CLK_NO_TRACE_MODE
The clock source is
not in locked mode.
Minor
COMMUN_FAIL
Inter-board
communication fails.
Major
CONFIG_NOSUPPORT
Configuration is not
supported.
Major
DBMS_ABNORMAL
The status of
databases is
abnormal.
Major
DBMS_ERROR
Errors in the
processing of system
databases
Major
DBMS_PROTECT_MODE
System databases in
protection mode
Critical
DCNSIZE_OVER
Over-sized DCN
network
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
189
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
DDN_LFA
The frame alignment
signal of framed E1
services is lost.
Major
DOWN_E1_AIS
Alarm indication of 2
Mbit/s downstream
signals
Minor
DROPRATIO_OVER
The number of lost
packets due to port
congestion crosses
the threshold.
Minor
E1_LOC
Loss of 2M clock in
upstream signals
Major
E1_LOS
Loss of 2 Mbit/s line
signals
Minor
ENVHUM_SENSOR_FAIL
The ambient
humidity sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Major
ENVTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
The ambient
temperature sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Major
ENVTEMP1_SENSOR_FAIL
The ambient
temperature sensor 1
of the cabinet fails.
Major
ENVTEMP2_SENSOR_FAIL
The ambient
temperature sensor 2
of the cabinet fails.
Major
ETH_APS_LOST
Loss of APS frames
Minor
ETH_APS_PATH_MISMATCH
The working and
protection paths of
the APS protection
group differ between
the two ends.
Major
ETH_APS_SWITCH_FAIL
Protection switching
failure
Major
ETH_APS_TYPE_MISMATCH
Protection scheme
mismatch
Major
ETH_CFM_LOC
Loss of connectivity
Critical
ETH_CFM_MISMERGE
Misconnection
Critical
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
190
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
ETH_CFM_RDI
The maintenance
association end point
(MEP) fails to
receive CCM
packets.
Minor
ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI
Errored frames
Minor
ETH_EFM_DF
Discovery failure
Major
ETH_EFM_EVENT
Performance events
at the opposite end
Major
ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK
A loopback occurs.
Major
ETH_EFM_REMFAULT
Faults occur at the
opposite end.
Critical
ETH_LOS
Loss of Ethernet port
connection
Critical
ETH_NO_FLOW
No flow on the
Ethernet port
Major
ETHOAM_DISCOVER_FAIL
Discovery failure is
detected by point-topoint Ethernet OAM.
Minor
ETHOAM_RMT_LOOP
A remote loopback is
detected by point-topoint Ethernet OAM.
Minor
ETHOAM_RMT_SD
Remote Ethernet
performance
degradation is
detected by point-topoint Ethernet OAM.
Minor
ETHOAM_RMT_CRIT_FAULT
Severe faults are
detected by point-topoint Ethernet OAM
at the remote end.
Minor
ETHOAM_SELF_LOOP
An MAC port
loopback is detected
by point-to-point
Ethernet OAM.
Major
ETHOAM_VCG_SELF_LOOP
A VCTRUNK port
loopback is detected
by point-to-point
Ethernet OAM.
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
191
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
EX_ETHOAM_CC_LOS
Loss of periodical
connectivity check
packets
Critical
EX_ETHOAM_MPID_CNFLCT
Conflict of
maintenance point
IDs
Major
EXT_SYNC_LOS
Loss of external
clock sources
Critical
FAN_AGING
Aged fans
Minor
FAN_FAIL
Failure of fan boards
Major
FCS_ERR
Frame check
sequence (FCS)
errors
Critical
FLOW_OVER
Excessive data traffic
received by Ethernet
ports
Minor
HARD_BAD
Hardware faults
Critical
HP_CROSSTR
Threshold-crossing
performance event of
the higher order path
Minor
HP_LOM
Loss of multiframes
in the higher order
path
Major
HP_RDI
Higher order path
remote defect
indication
Minor
HP_REI
Higher order path
remote error
indication
Warning
HP_SLM
Higher order path
signal label
mismatch
Minor
HP_TIM
High order path trace
identifier mismatch
Minor
HP_UNEQ
Unequipped higher
order path
Minor
HPAD_CROSSTR
Adaptation
performance
threshold-crossing of
the higher order path
Minor
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
192
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
IF_CABLE_OPEN
IF cables are
disconnected.
Major
IF_INPWR_ABN
The power supplied
by an IF board to an
ODU is abnormal.
Major
IF_MODE_UNSUPPORTED
Preset IF working
mode is not
supported.
Major
IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN
The IMA group at the
local end fails.
Major
IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN
The IMA group at the
remote end fails.
Major
IMA_TXCLK_MISMATCH
The transmit clock
modes at the two ends
of the IMA group are
different.
Minor
IN_PWR_ABN
Abnormal input
optical power
Major
IN_PWR_HIGH
Over high input
optical power
Critical
IN_PWR_LOW
Over low input
optical power
Critical
INTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
The air inlet
temperature sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Major
J0_MM
Trace identifier
mismatch
Minor
K1_K2_M
K1 and K2 mismatch
Minor
K2_M
K2 mismatch
Minor
LAG_BWMM
Bandwidth
inconsistency in the
LAG group
Major
LAG_DOWN
The LAG is
unavailable.
Major
LAG_MEMBER_DOWN
A member port of a
link aggregation
group (LAG) is
unavailable.
Minor
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
193
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
LAG_PORT_FAIL
A member port of a
LAG fails.
Minor
LAG_VC_PORT_FAIL
A VCG port of an
LAG fails.
Minor
LAN_LOC
Ethernet
communication
failure
Major
LASER_CLOSED
The laser is shut
down.
Major
LASER_MOD_ERR
The type of the
pluggable optical
module on the board
does not match the
type of the optical
interface.
Major
LASER_MOD_ERR_EX
The type of the
pluggable optical
module on the board
does not match the
type of the optical
interface.
Major
LASER_SHUT
The laser is shut
down.
Major
LCAS_FOPR
LCAS protocol fails
in the receive
direction.
Major
LCAS_FOPT
LCAS protocol fails
in the transmit
direction.
Major
LCAS_PLCR
Loss of partial
bandwidth in the
LCAS receive
direction
Minor
LCAS_PLCT
Loss of partial
bandwidth in the
LCAS transmit
direction
Minor
LCAS_TLCR
Loss of total
bandwidth in the
LCAS receive
direction
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
194
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
LCAS_TLCT
Loss of total
bandwidth in the
LCAS transmit
direction
Major
LCD
Loss of cell
delimitation
Major
LCS_LIMITED
The capacity of the
configured services
exceeds the range
permitted by the
license file.
Major
LFA
Out of frame state of
E1 frames
Major
LICENSE_DIFF
The license file on the
IF board is different
from the backup file
on the system control
board.
Warning
LICENSE_LOST
The NE fails to detect
any license file.
Major
LINK_ERR
Faults occur in a data
link.
Critical
LMFA
Out of frame state of
E1 multiframes
Major
LOOP_ALM
A loopback occurs.
Minor
LP_CROSSTR
Performance
threshold-crossing of
the lower order path
Minor
LP_R_FIFO
FIFO overflow on the
receive side of the
lower order path
Minor
LP_RDI
Lower order path
remote defect
indication
Minor
LP_RDI_VC12
VC-12 path remote
defect indication
Minor
LP_RDI_VC3
VC-3 path remote
defect indication
Minor
LP_REI
Lower order path
remote error
indication
Minor
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
195
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
LP_REI_VC12
VC-12 path remote
error indication
Minor
LP_REI_VC3
VC-3 path remote bit
error indication
Minor
LP_RFI
Lower order path
remote failure
indication
Minor
LP_SLM
Lower order path
signal label
mismatch
Minor
LP_SLM_VC12
VC-12 path signal
label mismatch
Minor
LP_SLM_VC3
VC-3 path signal
label mismatch
Minor
LP_T_FIFO
FIFO overflow on the
transmit side of the
lower order path
Minor
LP_TIM
Lower order path
trace identifier
mismatch
Minor
LP_TIM_VC12
VC-12 path trace
identifier mismatch
Minor
LP_TIM_VC3
VC-3 path tracking
identification
mismatch
Minor
LP_UNEQ
Unequipped lower
order paths
Minor
LP_UNEQ_VC12
Unequipped VC-12
paths
Minor
LP_UNEQ_VC3
VC-3 path
unequipped
Minor
LPS_UNI_BI_M
The switching mode
is single-ended at one
end and dual-ended at
the other end.
Minor
LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT
The LPT closes the
access port of the
local NE.
Major
LPT_INEFFECT
LPT function failed
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
196
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
LPT_RFI
Link state passthrough function fails
at the remote end.
Critical
LSR_NO_FITED
Laser not installed
Critical
LTI
Loss of clock
synchronization
source
Major
MAC_EXT_EXC
The number of bit
errors at the MAC
layer crosses the
threshold.
Major
MAC_FCS_EXC
The software detects
that the number of bit
errors at the MAC
layer crosses the
threshold.
Major
MOD_COM_FAIL
Module
communication
failure
Major
MOD_TYPE_MISMATCH
Port module type
mismatch
Critical
MPLS_PW_BDI
PW backward defect
indication
Minor
MPLS_PW_Excess
Excessive trail
termination source
identifiers (TTSIs)
are received on the
PW.
Minor
MPLS_PW_LOCV
Loss of PW
connectivity
Critical
MPLS_PW_MISMATCH
The trail termination
source identifiers
(TTSIs) on the PW do
not match with the
specified one.
Critical
MPLS_PW_MISMERGE
The trail termination
source identifiers
(TTSIs) are
mismerged on the
PW.
Major
MPLS_PW_SD
Signal degradation
on the PW
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
197
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
MPLS_PW_SF
Signal failure on the
PW
Major
MPLS_PW_UNKNOWN
Unknown defects on
the PW
Major
MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI
Tunnel backward
defect indication
Minor
MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess
Excessive trail
termination source
identifiers (TTSIs)
are received on the
tunnel.
Minor
MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI
Tunnel forward
defect indication
Major
MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
Loss of tunnel
connectivity
Critical
MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH
The trail termination
source identifiers
(TTSIs) on the tunnel
do not match with the
specified one.
Critical
MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE
The trail termination
source identifiers
(TTSIs) are
mismerged on the
tunnel.
Major
MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL
The OAM protocol
negotiation between
the two ends of the
tunnel fails.
Minor
MPLS_TUNNEL_SD
Signal degradation
on the tunnel
Major
MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
Signal failure on the
tunnel
Major
MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN
Unknown defects on
the tunnel
Major
MS_AIS
Multiplex section
alarm indication
Major
MS_CROSSTR
Multiplex section
performance
threshold-crossing
Minor
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
198
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
MS_RDI
Multiplex section
remote defect
indication
Minor
MS_REI
Multiplex section
remote error
indication
Warning
MSAD_CROSSTR
Multiplex section
adaptation
performance
threshold-crossing
Minor
MULTI_RPL_OWNER
The ring network has
multiple
RPL_OWNER
nodes.
Minor
MW_AM_TEST
The IF port is in the
AM testing state.
Minor
MW_BER_EXC
Excessive errors on
radio links
Minor
MW_BER_SD
Signal degradation
due to excessive
errors on radio links
Minor
MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Configuration
mismatch on radio
links
Critical
MW_CONT_WAVE
Continuous wave
Minor
MW_E1_LOST
Loss of E1 signals
Major
MW_FEC_UNCOR
Microwave frames
have the errors that
cannot be corrected
by using the forward
error correction
(FEC) technology.
Minor
MW_LIM
Label mismatch on
radio links
Major
MW_LOF
Loss of microwave
frames
Critical
MW_RDI
Remote defect
indication on radio
links
Minor
NESF_LOST
The NE software is
lost.
Critical
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
199
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
NESOFT_MM
The software in the
main area is different
from that in the
standby area.
Major
NESTATE_INSTALL
The NE is in the
installation state.
Critical
NO_BD_SOFT
The board software is
lost.
Critical
NP1_MANUAL_STOP
The N+1 protection
protocol is stopped
manually.
Minor
NP1_SW_FAIL
The N+1 protection
switching fails.
Major
NP1_SW_INDI
N+1 protection
switching indication
Major
NTP_SYNC_FAIL
Synchronization with
the NTP time fails.
Minor
OCD
Out of cell
delimitation
Major
ODC_BATTERY_CURRENT_ABN
Abnormal current of
the storage battery
Major
ODC_BATTERY_PWRDOWN
The storage battery
fails to supply power
for the equipment.
Major
ODC_DOOR_OPEN
The door of an
outdoor cabinet is
open.
Critical
ODC_FAN_FAILED
Fan failure
Major
ODC_HUMI_ABN
The relative humidity
in the cabinet
environment crosses
the specified
threshold.
Minor
ODC_LOAD_PWRDOWN
The secondary load is
powered off.
Major
ODC_MDL_ABN
The power module is
abnormal.
Major
ODC_POWER_FAIL
Exceptions occur in
the AC input power
voltage.
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
200
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
ODC_SMOKE_OVER
Smoke occurs in an
outdoor cabinet.
Critical
ODC_SURGE_PROTECTION_FAIL
The surge protection
function of the
outdoor cabinet fails.
Critical
ODC_TEC_ALM
The TEC air
conditioning module
in the cabinet fails.
Major
ODC_TEMP_ABN
The ambient
temperature of the
cabinet or the
temperature of the
storage battery is
inappropriate.
Minor
ODC_WATER_ALM
Water in the outdoor
cabinet
Critical
OUT_PWR_ABN
Abnormal output
optical power
Critical
OUT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
The air outlet
temperature sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Major
OUT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
The external
recycling outlet
temperature sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Major
PATCH_ACT_TIMEOUT
Activating patch
packages times out.
Minor
PATCH_DEACT_TIMEOUT
Deactivating patch
packages times out.
Minor
PATCH_PKGERR
Abnormal patch
package
Minor
PG_LINK_FAIL
Links of the 1+1
protection group fail.
Critical
PG_PRT_DEGRADED
The working link or
protection link of the
1+1 protection group
is faulty.
Major
PLA_CFG_MISMATCH
Inconsistent PLA
configurations
Critical
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
201
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
PORT_EXC_TRAFFIC
The traffic is higher
than the port
bandwidth threshold.
Warning
PORT_MODULE_OFFLINE
Port not in position
Major
PORTMODE_MISMATCH
The working mode of
the remote FE port
does not match that of
the local FE port.
Minor
POWER_ABNORMAL
Power input alarm
Major
POWER_ALM
Power module alarm
Major
PW_DROPPKT_EXC
The number of lost
packets in a PW
crosses the threshold.
Warning
PWAPS_LOST
Loss of APS frames
Minor
PWAPS_PATH_MISMATCH
The working and
protection paths of
the APS protection
group differ between
the two ends.
Major
PWAPS_SWITCH_FAIL
Protection switching
failure
Major
PWAPS_TYPE_MISMATCH
Protection scheme
mismatch
Major
R_F_RST
Reset of the receive
FIFO
Minor
R_LOC
Loss of clock on the
receive line side
Critical
R_LOF
Loss of frame on the
receive line side
Critical
R_LOS
Loss of signal or loss
of microwave frame
on the receive line
side
Critical
R_S_ERR
Errors in the received
signal
Critical
RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF
Radio fading margin
is insufficient.
Minor
RADIO_MUTE
The radio transmitter
is muted.
Warning
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
202
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH
Antennas are not
aligned.
Minor
RADIO_RSL_HIGH
Over high radio
receive signal level
Critical
RADIO_RSL_LOW
Over low radio
receive signal level
Critical
RADIO_TSL_HIGH
Over high radio
transmit signal level
Critical
RADIO_TSL_LOW
Over low radio
transmit signal level
Critical
RELAY_ALARM_CRITICAL
There are critical
alarm inputs.
Critical
RELAY_ALARM_IGNORE
There are warning
inputs.
Warning
RELAY_ALARM_MAJOR
There are major
alarm inputs.
Major
RELAY_ALARM_MINOR
There are minor
alarm inputs.
Minor
RMFA
Loss of multiframe
alignment at the
remote end
Minor
RPS_INDI
Radio protection
switching indication
Major
RS_CROSSTR
Regenerator section
performance
threshold-crossing
Minor
RTC_FAIL
The real-time clock
(RTC) of the system
control board fails.
Major
S1_SYN_CHANGE
Clock source
switching in S1 mode
Major
SEC_RADIUS_FAIL
RADIUS
authentication fails.
Major
SECU_ALM
Security alarm
Major
SRV_SHUTDOWN_LD
Ethernet services are
interrupted.
Warning
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
203
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
SWDL_ACTIVATED_TIMEOUT
The commit
operation is not
performed during
software package
loading.
Critical
SWDL_AUTOMATCH_INH
The automatic match
function is disabled.
Minor
SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH
The board software
version and the
version of the
running software are
inconsistent.
Critical
SWDL_COMMIT_FAIL
The submit operation
fails.
Minor
SWDL_INPROCESS
The package
diffusion is being
performed on the NE.
Warning
SWDL_NEPKGCHECK
Certain files in the
package stored in
flash memory are
lost.
Critical
SWDL_PKG_NOBDSOFT
The software
package does not
contain any board
software.
Minor
SWDL_PKGVER_MM
Software package
version consistency
check fails.
Minor
SWDL_ROLLBACK_FAIL
The version rollback
on an NE fails.
Minor
SYN_BAD
Synchronous source
degradation
Minor
SYNC_C_LOS
Loss of
synchronization
clock sources
Warning
A.3.262 SCCDATA_BACKUP_FAIL
Batch backup of SCC
boards fails.
Minor
T_ALOS
Loss of analog
signals at 2 Mbit/s
interfaces
Major
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
204
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
T_F_RST
Reset of the transmit
FIFO
Minor
T_LOC
Loss of clock on the
transmit line side
Major
TEMP_ALARM
Excessive board
temperature
Minor
THUNDERALM
Surge protection
fails.
Minor
TR_LOC
Clock failure
Major
TU_AIS
TU alarm indication
Major
TU_AIS_VC12
VC-12 path TU alarm
indication
Major
TU_AIS_VC3
TU of VC-3 level
alarm indication
Major
TU_LOP
Loss of TU pointers
Major
TU_LOP_VC12
Loss of TU pointers
in VC-12 paths
Major
TU_LOP_VC3
TU of VC-3 level loss
of pointer
Major
TUNNEL_APS_DEGRADED
The tunnel protection
group degrades.
Major
UP_E1_AIS
Alarm indication of 2
Mbit/s upstream
signals
Minor
UHCS
Uncorrectable cell
errors
Minor
VC_AIS
Alarm indication
signal of the VC
connection
Critical
VC_LOC
Loss of VC
connectivity check
Major
VC_RDI
Remote defect
indication of the VC
connection
Major
VCAT_LOA
Excessive virtual
concatenation delay
Critical
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
205
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Name
Description
Alarm Severity
VCAT_LOM_VC12
Loss of multiframe of
VC-12 path virtual
concatenation
Major
VCAT_LOM_VC3
The virtually
concatenated
multiframes in a
VC-3 path are lost.
Major
VCAT_SQM_VC12
SQ mismatch of
VC-12 path virtual
concatenation
Major
VCAT_SQM_VC3
SQ mismatch of
VC-3 path virtual
concatenation
Major
VOLT_LOS
Loss of voltage
Major
VP_AIS
Alarm indication
signal of the VP
connection
Critical
VP_LOC
Loss of VP
connectivity check
Major
VP_RDI
Remote defect
indication of the VP
connection
Major
W_R_FAIL
Failure in reading and
writing chip registers
Major
WRG_BD_TYPE
Errored board types
Major
XPIC_LOS
Loss of XPIC
compensation signals
Critical
A.2 Alarm List (Classified by Logical Boards)
This part lists the alarms that are reported by each board.
NOTE
The NE software consider a physical board as one or more logical boards when managing the physical board.
The NMS also considers a physical board as one or more logical boards when managing the physical board.
For OptiX RTN 950, all physical boards correspond to logical boards of the same names.
A.2.1 CST
APS_FAIL
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
APS_INDI
APS_MANUAL_ST
OP
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
BD_NOT_INSTAL
LED
206
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
BD_STATUS
BIOS_STATUS
BOOTROM_BAD
CFCARD_FAILED
CFCARD_OFFLIN
E
CLK_NO_TRACE_
MODE
DBMS_ABNORM
AL
DBMS_ERROR
DBMS_PROTECT_
MODE
DCNSIZE_OVER
EXT_SYNC_LOS
HARD_BAD
K1_K2_M
K2_M
LAN_LOC
LCS_LIMITED
LICENSE_LOST
LPS_UNI_BI_M
LTI
NESF_LOST
NESOFT_MM
NESTATE_INSTA
LL
NP1_MANUAL_ST
OP
NP1_SW_FAIL
NP1_SW_INDI
NTP_SYNC_FAIL
PATCH_ACT_TIM
EOUT
PATCH_DEACT_T
IMEOUT
PATCH_PKGERR
PG_LINK_FAIL
PG_PRT_DEGRAD
ED
PLA_CFG_MISMA
TCH
POWER_ALM
RPS_INDI
RTC_FAIL
S1_SYN_CHANGE
SCCDATA_BACK
UP_FAIL
SEC_RADIUS_FAI
L
SECU_ALM
SWDL_ACTIVATE
D_TIMEOUT
SWDL_AUTOMAT
CH_INH
SWDL_CHGMNG_
NOMATCH
SWDL_COMMIT_
FAIL
SWDL_INPROCES
S
SWDL_NEPKGCH
ECK
SWDL_PKG_NOB
DSOFT
SWDL_PKGVER_
MM
SWDL_ROLLBAC
K_FAIL
SYN_BAD
SYNC_C_LOS
TEMP_ALARM
WRG_BD_TYPE
APS_FAIL
APS_INDI
APS_MANUAL_ST
OP
BD_NOT_INSTAL
LED
BD_STATUS
BIOS_STATUS
BOOTROM_BAD
CFCARD_FAILED
CFCARD_OFFLIN
E
CLK_NO_TRACE_
MODE
DBMS_ABNORM
AL
DBMS_ERROR
DBMS_PROTECT_
MODE
DCNSIZE_OVER
ETH_APS_LOST
ETH_APS_PATH_
MISMATCH
ETH_APS_SWITC
H_FAIL
ETH_APS_TYPE_
MISMATCH
EXT_SYNC_LOS
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
K1_K2_M
K2_M
LAG_BWMM
LAN_LOC
LCS_LIMITED
LICENSE_LOST
LPS_UNI_BI_M
A.2.2 CSH
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
207
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT
LTI
MOD_COM_FAIL
MPLS_PW_BDI
MPLS_PW_Excess
MPLS_PW_LOCV
MPLS_PW_MISM
ATCH
MPLS_PW_MISME
RGE
MPLS_PW_SD
MPLS_PW_SF
MPLS_PW_UNKN
OWN
MPLS_TUNNEL_B
DI
MPLS_TUNNEL_E
xcess
MPLS_TUNNEL_F
DI
MPLS_TUNNEL_L
OCV
MPLS_TUNNEL_
MISMATCH
MPLS_TUNNEL_
MISMERGE
MPLS_TUNNEL_O
AMFAIL
MPLS_TUNNEL_S
D
MPLS_TUNNEL_S
F
MPLS_TUNNEL_U
NKNOWN
NESF_LOST
NESOFT_MM
NESTATE_INSTA
LL
NP1_MANUAL_ST
OP
NP1_SW_FAIL
NP1_SW_INDI
NTP_SYNC_FAIL
PATCH_ACT_TIM
EOUT
PATCH_DEACT_T
IMEOUT
PATCH_ERR
PATCH_PKGERR
PG_LINK_FAIL
PG_PRT_DEGRAD
ED
PLA_CFG_MISMA
TCH
POWER_ALM
PW_DROPPKT_EX
C
PWAPS_LOST
PWAPS_PATH_MI
SMATCH
PWAPS_SWITCH_
FAIL
PWAPS_TYPE_MI
SMATCH
RPS_INDI
RTC_FAIL
S1_SYN_CHANGE
SCCDATA_BACK
UP_FAIL
SEC_RADIUS_FAI
L
SECU_ALM
SRV_SHUTDOWN
_LD
SWDL_ACTIVATE
D_TIMEOUT
SWDL_AUTOMAT
CH_INH
SWDL_CHGMNG_
NOMATCH
SWDL_COMMIT_
FAIL
SWDL_INPROCES
S
SWDL_NEPKGCH
ECK
SWDL_PKG_NOB
DSOFT
SWDL_PKGVER_
MM
SWDL_ROLLBAC
K_FAIL
SYN_BAD
SYNC_C_LOS
TEMP_ALARM
TUNNEL_APS_DE
GRADED
WRG_BD_TYPE
AU_AIS
AU_LOP
B1_EXC
B1_SD
B2_EXC
B2_SD
B3_EXC
B3_SD
BD_STATUS
HARD_BAD
HP_CROSSTR
HP_LOM
A.2.3 IF1
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
208
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
HP_RDI
HP_REI
HP_SLM
HP_TIM
HP_UNEQ
IF_CABLE_OPEN
IF_MODE_UNSUP
PORTED
LCS_LIMITED
LICENSE_DIFF
LICENSE_LOST
LOOP_ALM
MS_AIS
MS_CROSSTR
MS_RDI
MS_REI
MSAD_CROSSTR
MW_CONT_WAV
E
MW_FEC_UNCOR
MW_LIM
MW_LOF
MW_RDI
R_LOC
R_LOF
R_LOS
RS_CROSSTR
T_LOC
TEMP_ALARM
VOLT_LOS
WRG_BD_TYPE
AM_DOWNSHIFT
BD_STATUS
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
BUS_ERR
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
IF_CABLE_OPEN
LAG_BWMM
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LCS_LIMITED
LICENSE_DIFF
LICENSE_LOST
LOOP_ALM
LP_RDI
LP_REI
LP_UNEQ
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
MW_BER_EXC
MW_BER_SD
MW_CFG_MISMA
TCH
MW_CONT_WAV
E
MW_E1_LOST
MW_FEC_UNCOR
MW_LIM
MW_LOF
MW_RDI
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
R_LOC
R_LOF
TEMP_ALARM
TU_AIS
TU_LOP
VOLT_LOS
WRG_BD_TYPE
A.2.4 IFU2
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
209
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.2.5 IFX2
AM_DOWNSHIFT
BD_STATUS
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
BUS_ERR
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
IF_CABLE_OPEN
LAG_BWMM
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LCS_LIMITED
LICENSE_DIFF
LICENSE_LOST
LOOP_ALM
LP_RDI
LP_REI
LP_UNEQ
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
MW_BER_EXC
MW_BER_SD
MW_CFG_MISMA
TCH
MW_CONT_WAV
E
MW_E1_LOST
MW_FEC_UNCOR
MW_LIM
MW_LOF
MW_RDI
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
R_LOC
R_LOF
TEMP_ALARM
TU_AIS
TU_LOP
VOLT_LOS
WRG_BD_TYPE
XPIC_LOS
AU_AIS
AU_LOP
B1_EXC
B1_SD
B2_EXC
B2_SD
B3_EXC
B3_SD
BD_STATUS
HARD_BAD
HP_CROSSTR
HP_LOM
HP_RDI
HP_REI
HP_SLM
HP_TIM
HP_UNEQ
IN_PWR_HIGH
IN_PWR_LOW
J0_MM
LASER_CLOSED
LASER_MOD_ER
R_EX
LOOP_ALM
LSR_NO_FITED
MS_AIS
MS_CROSSTR
MS_RDI
MS_REI
MSAD_CROSSTR
R_LOC
R_LOF
R_LOS
RS_CROSSTR
T_LOC
WRG_BD_TYPE
A.2.6 SL1D/SL1DA
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
210
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.2.7 EM6T
BD_STATUS
BUS_ERR
COMMUN_FAIL
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_EVENT
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETH_LOS
ETH_NO_FLOW
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LOOP_ALM
LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
PORTMODE_MISMATCH
TEMP_ALARM
WRG_BD_TYPE
BD_STATUS
BUS_ERR
COMMUN_FAIL
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_EVENT
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETH_LOS
ETH_NO_FLOW
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LOOP_ALM
LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
PORTMODE_MISMATCH
TEMP_ALARM
WRG_BD_TYPE
BD_STATUS
BUS_ERR
COMMUN_FAIL
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
A.2.8 EM6TA
A.2.9 EM6F
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
211
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_EVENT
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETH_LOS
ETH_NO_FLOW
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
IN_PWR_ABN
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LASER_MOD_ER
R
LASER_SHUT
LOOP_ALM
LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT
LSR_NO_FITED
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
PORTMODE_MISMATCH
TEMP_ALARM
WRG_BD_TYPE
BD_STATUS
BUS_ERR
COMMUN_FAIL
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_EVENT
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETH_LOS
ETH_NO_FLOW
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
IN_PWR_ABN
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LASER_MOD_ER
R
LASER_SHUT
LOOP_ALM
LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT
LSR_NO_FITED
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
PORTMODE_MISMATCH
TEMP_ALARM
WRG_BD_TYPE
ALM_GFP_dCSF
ALM_GFP_dLFD
BD_STATUS
BIP_EXC
A.2.10 EM6FA
A.2.11 EFP8
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
212
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
BIP_SD
COMMUN_FAIL
DOWN_E1_AIS
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_LOS
ETHOAM_DISCO
VER_FAIL
ETHOAM_RMT_C
RIT_FAULT
ETHOAM_RMT_L
OOP
ETHOAM_RMT_S
D
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
ETHOAM_VCG_S
ELF_LOOP
EX_ETHOAM_CC
_LOS
EX_ETHOAM_MPI
D_CNFLCT
FCS_ERR
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
LAG_PORT_FAIL
LAG_VC_PORT_F
AIL
LCAS_FOPR
LCAS_FOPT
LCAS_PLCR
LCAS_PLCT
LCAS_TLCR
LCAS_TLCT
LFA
LMFA
LOOP_ALM
LP_RDI_VC12
LP_REI_VC12
LP_SLM_VC12
LP_TIM_VC12
LP_UNEQ_VC12
LPT_RFI
NO_BD_SOFT
RMFA
TEMP_ALARM
TU_AIS_VC12
TU_LOP_VC12
VCAT_LOA
VCAT_LOM_VC12
VCAT_SQM_VC12
W_R_FAIL
WRG_BD_TYPE
ALM_GFP_dCSF
ALM_GFP_dLFD
B3_EXC_VC3
B3_SD_VC3
BD_STATUS
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
BUS_ERR
COMMUN_FAIL
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_LOS
ETHOAM_DISCO
VER_FAIL
ETHOAM_RMT_C
RIT_FAULT
ETHOAM_RMT_L
OOP
ETHOAM_RMT_S
D
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
EX_ETHOAM_CC
_LOS
EX_ETHOAM_MPI
D_CNFLCT
FCS_ERR
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
IN_PWR_ABN
LAG_PORT_FAIL
LAG_VC_PORT_F
AIL
LCAS_FOPR
LCAS_FOPT
LCAS_PLCR
LCAS_PLCT
LCAS_TLCR
LCAS_TLCT
LINK_ERR
LOOP_ALM
LP_RDI_VC12
LP_RDI_VC3
LP_REI_VC12
LP_REI_VC3
LP_SLM_VC12
LP_SLM_VC3
LP_TIM_VC12
LP_TIM_VC3
LP_UNEQ_VC12
A.2.12 EMS6
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
213
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
LP_UNEQ_VC3
LPT_INEFFECT
LPT_RFI
MOD_TYPE_MISMATCH
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
NO_BD_SOFT
OUT_PWR_ABN
PORT_MODULE_
OFFLINE
TEMP_ALARM
TU_AIS_VC12
TU_AIS_VC3
TU_LOP_VC12
TU_LOP_VC3
VCAT_LOA
VCAT_LOM_VC12
VCAT_LOM_VC3
VCAT_SQM_VC12
VCAT_SQM_VC3
WRG_BD_TYPE
A_LOC
BD_STATUS
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
DOWN_E1_AIS
E1_LOC
E1_LOS
HARD_BAD
HPAD_CROSSTR
LOOP_ALM
LP_CROSSTR
LP_R_FIFO
LP_RDI
LP_REI
LP_RFI
LP_SLM
LP_T_FIFO
LP_TIM
LP_UNEQ
R_F_RST
R_S_ERR
WRG_BD_TYPE
T_ALOS
T_F_RST
TU_AIS
TU_LOP
UP_E1_AIS
DDN_LFA
BD_STATUS
HARD_BAD
RELAY_ALARM_
CRITICAL
RELAY_ALARM_I
GNORE
RELAY_ALARM_
MAJOR
RELAY_ALARM_
MINOR
WRG_BD_TYPE
BD_STATUS
HARD_BAD
POWER_ABNORM
AL
THUNDERALM
WRG_BD_TYPE
A.2.13 SP3S/SP3D
A.2.14 AUX
A.2.15 PIU
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
214
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.2.16 FAN
BD_STATUS
FAN_AGING
FAN_FAIL
POWER_ALM
WRG_BD_TYPE
AM_DOWNSHIFT
AU_AIS
AU_LOP
B1_EXC
B1_SD
B2_EXC
B2_SD
B3_EXC
B3_SD
BD_STATUS
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
BUS_ERR
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
HP_CROSSTR
HP_LOM
HP_RDI
HP_REI
HP_SLM
HP_TIM
HP_UNEQ
IF_CABLE_OPEN
LAG_BWMM
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LCS_LIMITED
LICENSE_DIFF
LICENSE_LOST
LOOP_ALM
LP_RDI
LP_REI
LP_UNEQ
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MS_AIS
MS_CROSSTR
MS_RDI
MS_REI
MSAD_CROSSTR
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
MW_AM_TEST
MW_BER_EXC
MW_BER_SD
MW_CFG_MISMA
TCH
MW_CONT_WAV
E
MW_E1_LOST
MW_FEC_UNCOR
MW_LIM
MW_LOF
MW_RDI
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
R_LOC
R_LOF
RS_CROSSTR
T_LOC
TEMP_ALARM
TU_AIS
TU_LOP
VOLT_LOS
WRG_BD_TYPE
A.2.17 ISU2
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
215
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.2.18 ISX2
AM_DOWNSHIFT
AU_AIS
AU_LOP
B1_EXC
B1_SD
B2_EXC
B2_SD
B3_EXC
B3_SD
BD_STATUS
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
BUS_ERR
DROPRATIO_OVE
R
ETH_CFM_LOC
ETH_CFM_MISME
RGE
ETH_CFM_RDI
ETH_CFM_UNEXP
ERI
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_LOOPB
ACK
ETH_EFM_REMF
AULT
ETHOAM_SELF_L
OOP
FLOW_OVER
HARD_BAD
HP_CROSSTR
HP_LOM
HP_RDI
HP_REI
HP_SLM
HP_TIM
HP_UNEQ
IF_CABLE_OPEN
LAG_BWMM
LAG_DOWN
LAG_MEMBER_D
OWN
LCS_LIMITED
LICENSE_DIFF
LICENSE_LOST
LOOP_ALM
LP_RDI
LP_REI
LP_UNEQ
MAC_EXT_EXC
MAC_FCS_EXC
MS_AIS
MS_CROSSTR
MS_RDI
MS_REI
MSAD_CROSSTR
MULTI_RPL_OWN
ER
MW_AM_TEST
MW_BER_EXC
MW_BER_SD
MW_CFG_MISMA
TCH
MW_CONT_WAV
E
MW_E1_LOST
MW_FEC_UNCOR
MW_LIM
MW_LOF
MW_RDI
PORT_EXC_TRAF
FIC
R_LOC
R_LOF
RS_CROSSTR
T_LOC
TEMP_ALARM
TU_AIS
TU_LOP
VOLT_LOS
WRG_BD_TYPE
XPIC_LOS
ALM_E1RAI
ALM_IMA_LIF
ALM_IMA_LODS
ALM_IMA_RE_RX
_UNUSABLE
ALM_IMA_RE_TX
_UNUSABLE
ALM_IMA_RFI
ATMPW_UNKNO
WNCELL_EXC
BD_STATUS
CES_ACR_LOCK_
ABN
CES_JTROVR_EX
C
CES_JTRUDR_EX
C
CES_LOSPKT_EX
C
A.2.19 ML1/MD1
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
216
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
CES_MALPKT_EX
C
CES_MISORDERP
KT_EXC
CES_RDI
CES_STRAYPKT_
EXC
CESPW_OPPOSIT
E_ACFAULT
CESPW_OPPOSIT
E_RAI
CHCS
WRG_BD_TYPE
HARD_BAD
IMA_GROUP_LE_
DOWN
IMA_GROUP_RE_
DOWN
IMA_TXCLK_MISMATCH
LCD
LFA
LMFA
LOOP_ALM
OCD
POWER_ABNORM
AL
T_ALOS
TEMP_ALARM
TR_LOC
UHCS
UP_E1_AIS
VC_AIS
VC_LOC
VC_RDI
VP_AIS
VP_LOC
VP_RDI
BUS_ERR
BD_STATUS
CONFIG_NOSUPP
ORT
HARD_BAD
IF_INPWR_ABN
LOOP_ALM
POWER_ALM
RADIO_FADING_
MARGIN_INSUFF
RADIO_MUTE
RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH
RADIO_RSL_HIG
H
RADIO_RSL_LOW
RADIO_TSL_HIG
H
RADIO_TSL_LOW
TEMP_ALARM
WRG_BD_TYPE
BAT1TEMP_SENS
OR_FAIL
BAT2TEMP_SENS
OR_FAIL
BD_STATUS
ENVHUM_SENSO
R_FAIL
ENVTEMP1_SENS
OR_FAIL
ENVTEMP2_SENS
OR_FAIL
HARD_BAD
ODC_BATTERY_C
URRENT_ABN
ODC_BATTERY_P
WRDOWN
ODC_DOOR_OPE
N
ODC_HUMI_ABN
ODC_LOAD_PWR
DOWN
ODC_MDL_ABN
ODC_POWER_FAI
L
ODC_SMOKE_OV
ER
ODC_SURGE_PRO
TECTION_FAIL
ODC_TEMP_ABN
ODC_WATER_AL
M
WRG_BD_TYPE
A.2.20 ODU
A.2.21 PMU
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
217
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.2.22 TCU
BD_STATUS
BDTEMP_SENSOR
_FAIL
ENVTEMP_SENSO
R_FAIL
HARD_BAD
INTEMP_SENSOR
_FAIL
ODC_DOOR_OPE
N
ODC_FAN_FAILE
D
ODC_SMOKE_OV
ER
ODC_SURGE_PRO
TECTION_FAIL
ODC_TEC_ALM
ODC_TEMP_ABN
ODC_WATER_AL
M
OUT1TEMP_SENS
OR_FAIL
OUT2TEMP_SENS
OR_FAIL
WRG_BD_TYPE
A.3 Alarms and Handling Procedures
This chapter describes all the alarms on the OptiX RTN 950 in alphabetical order and how to
handle these alarms.
A.3.1 A_LOC
Description
The A_LOC is an alarm indicating that a clock signal is lost in the uplink bus.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the A_LOC alarm occurs, the services carried by the board are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the board where the alarmed tributary unit is located.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
218
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.2 ALM_E1RAI
Description
The ALM_E1RAI is an alarm indicating that the E1 link on the opposite NE reports alarms. This
alarm is reported on the local NE when the T_ALOS, UP_E1_AIS, DOWN_E1_AIS, LFA, or
LMFA alarm is reported on the opposite NE.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the services on the local NE in the downstream direction are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The E1 link on the opposite NE reports the T_ALOS, LFA, LMFA, UP_E1_AIS,
or DOWN_E1_AIS alarm.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The E1 link on the opposite NE reports the T_ALOS, LFA, LMFA, UP_E1_AIS, or
DOWN_E1_AIS alarm.
Step 2 Handle these alarms first.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.3 ALM_GFP_dCSF
Description
The ALM_GFP_dCSF is an alarm indicating that the generic framing procedure (GFP) customer
signal is lost. When the source end fails to receive the GFP customer signal, it sends the
management frame to the sink end. The ALM_GFP_dCSF alarm is reported when the sink end
receives the management frame.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
219
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00 0x01
indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUNK 1.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Timeslot binding is different at the source and sink VCTRUNKs.
Cause 2: The radio link performance degrades.
Cause 3: The alarmed board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Timeslot binding is different at the source and sink VCTRUNKs.
1.
Reconfigure the timeslot binding at the source and sink VCTRUNKs.
Step 2 Cause 2: The radio link performance degrades.
1.
Troubleshoot the radio link.
Step 3 Cause 3: The alarmed board is faulty.
1.
Replace the faulty board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.4 ALM_GFP_dLFD
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
220
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The ALM_GFP_dLFD is an alarm indicating that the GFP frame is out of frame. This alarm
occurs when a board detects that the GFP frame is out of frame.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the logical port, and the value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00 0x01
indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUNK 1.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Bit errors occur on certain links or certain links are faulty.
Cause 2: When the LCAS is disabled, the source and the sink VCTRUNKs are configured
with different timeslots or different numbers of paths.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Bit errors occur on certain links or certain links are faulty.
1.
Check whether the links where the service travels have errors or become faulty.
If...
Then...
The links are faulty
Rectify the fault.
The links are normal
Replace the alarmed board.
Step 2 Cause 2: When the LCAS is disabled, the source and the sink VCTRUNKs are configured with
different timeslots or different numbers of paths.
1.
Correct the configuration data. For details, see Configuring VCTRUNKs on an Ethernet
Board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
221
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.5 ALM_IMA_LIF
Description
The ALM_IMA_LIF is an alarm indicating that the IMA link is out of frame in the receive
direction. This alarm occurs when the frame alignment is lost on the IMA link in the receive
direction.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the ATM Trunk ID.
Impact on the System
l
When this alarm occurs, the alarmed IMA link is unavailable. Therefore, the number of
available links in the IMA group decreases. If the bandwidth of the services configured for
the IMA group exceeds the total bandwidth of available IMA links, congestion occurs on
the IMA port, causing loss of cells.
After this alarm is cleared, the affected IMA link becomes available.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
222
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The path reports any SDH alarm
Handle the relevant alarms first.
The path does not report any SDH alarm
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
1.
Disable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
2.
Check the IMA group configuration at the two ends and ensure that the configuration is
consistent.
3.
Enable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
4.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
1.
Replace the board. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
Loss of frame alignment
A frame alignment word, provided at the physical layer, occupies the initial position of a frame
and defines the start of information field. An Out Of Frame (OOF) defect is declared when the
position of frame alignment word cannot be determined in the input bit stream.
A.3.6 ALM_IMA_LODS
Description
The ALM_IMA_LODS is an alarm indicating the differential delay on the IMA link crosses the
threshold. This alarm occurs when the maximum differential delay on the IMA link exceeds the
preset value.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
223
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the ATM Trunk ID.
Impact on the System
The IMA links are unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The maximum differential delay is configured incorrectly.
Cause 2: Within one IMA group, the transmission distances of member links have too large
gaps.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The maximum differential delay is configured incorrectly.
1.
Change the maximum differential delay to a greater value. For details, see Modifying CES
Service Parameters.
Step 2 Cause 2: Within one IMA group, the transmission distances of member links have too large
gaps.
1.
Use the meter to measure the transmission time on E1 links. If the transmission time on
different links has a gap larger than 25 ms (default value), adjust the IMA links or delete
the member link with over long transmission time from the IMA group.
----End
Related Information
Differential delay
Differential delay refers to the service delay difference between E1 links.
A.3.7 ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE
Description
The ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE is an alarm indicating that the IMA link on the opposite
NE fails in the receive direction.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
224
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the ATM Trunk ID.
Impact on the System
l
When this alarm occurs, the alarmed IMA link is unavailable. Therefore, the number of
available links in the IMA group decreases. If the bandwidth of the services configured for
the IMA group exceeds the total bandwidth of available IMA links, congestion occurs on
the IMA port, causing loss of cells.
After this alarm is cleared, the affected IMA link becomes available.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
If...
Then...
The path reports any SDH alarm
Handle the relevant alarms first.
The path does not report any SDH alarm
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
1.
Disable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
2.
Check the IMA group configuration at the two ends and ensure that the configuration is
consistent.
3.
Enable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
4.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
1.
Replace the board. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
225
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.8 ALM_IMA_RE_TX_UNUSABLE
Description
The ALM_IMA_RE_TX_UNUSABLE is an alarm indicating that the IMA link on the opposite
NE fails in the transmit direction.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the ATM Trunk ID.
Impact on the System
l
When this alarm occurs, the alarmed IMA link is unavailable. Therefore, the number of
available links in the IMA group decreases. If the bandwidth of the services configured for
the IMA group exceeds the total bandwidth of available IMA links, congestion occurs on
the IMA port, causing loss of cells.
After this alarm is cleared, the affected IMA link becomes available.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
226
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The path reports any SDH alarm
Handle the relevant alarms first.
The path does not report any SDH alarm
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
1.
Disable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
2.
Check the IMA group configuration at the two ends and ensure that the configuration is
consistent.
3.
Enable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
4.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
1.
Replace the board. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.9 ALM_IMA_RFI
Description
The ALM_IMA_RFI is an alarm indicating that the IMA link on the opposite NE is out of frame
(OOF) in the receive direction. This alarm occurs when the frame alignment is lost on the IMA
link of the opposite NE and the opposite NE notifies the local NE of its OOF state.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
227
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the ATM Trunk ID.
Impact on the System
l
When this alarm occurs, the alarmed IMA link is unavailable. Therefore, the number of
available links in the IMA group decreases. If the bandwidth of the services configured for
the IMA group exceeds the total bandwidth of available IMA links, congestion occurs on
the IMA port, causing loss of cells.
After this alarm is cleared, the affected IMA link becomes available.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The path that carries the IMA link reports the SDH alarms, such as R_LOS,
R_LOF, and MS_AIS.
If...
Then...
The path reports any SDH alarm
Handle the relevant alarms first.
The path does not report any SDH alarm
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The IMA protocol negotiation fails between the two ends.
1.
Disable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
2.
Check the IMA group configuration at the two ends and ensure that the configuration is
consistent.
3.
Enable the IMA protocol at the two ends.
4.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The IMA link is faulty.
1.
Replace the board. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
Frame alignment loss
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
228
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A frame alignment word, provided at the physical layer, occupies the initial position of a frame
and defines the start of information field. An Out Of Frame (OOF) defect is declared when the
position of frame alignment word cannot be determined in the input bit stream.
A.3.10 AM_DOWNSHIFT
Description
The AM_DOWNSHIFT is an alarm indicating the downshift of the AM scheme. This alarm
occurs when the AM scheme is downshifted from the highest-efficiency scheme to the lowerefficiency scheme. When the AM scheme is upshifted from the lower-efficiency scheme to the
highest-efficiency scheme, this alarm is cleared.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the AM_DOWNSHIFT alarm occurs, the transmission capacity is reduced.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The external factors (for example, the climate) cause the degradation of the
working channels.
Cause 2: There are interferences around the working channels.
Cause 3: The ODU at the transmit end has abnormal transmit power.
Cause 4: The ODU at the receive end has abnormal receive power.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The external factors (for example, the climate) cause the degradation of the working
channels.
1.
When the external factors (for example, the climate) cause the degradation of the working
channels, the downshift of the AM scheme is normal. Hence, no measures should be taken
to handle the alarm.
Step 2 Cause 2: There are interferences around the working channels.
1.
Eliminate the interferences around the working channels.
Step 3 Cause 3: The ODU at the transmit end has abnormal transmit power.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
229
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Use the NMS to check whether the transmit power of the ODU at the transmit end is normal.
For details on troubleshooting at the transmit end, see Troubleshooting Microwave
Links.
Step 4 Cause 4: The ODU at the receive end has abnormal receive power.
1.
Use the NMS to check whether the receive power of the ODU at the receive end is normal.
For details on troubleshooting at the receive end, see Troubleshooting Microwave
Links.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.11 APS_FAIL
Description
The APS_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the MS protection switching fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the type of the protection group.
l 0x01: linear MS protection
Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
When the APS_FAIL alarm occurs, the services cannot be switched. If the current paths are
unavailable, the services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: The parameters of the MSP protocol are set incorrectly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
230
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The parameters of the MSP protocol are lost.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The parameters of the MSP protocol are set incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the parameters of the MSP protocol are set correctly.
If...
Then...
The parameters are set incorrectly
Set the parameters correctly.
The parameters are set correctly
Go to the next step.
Step 2 Cause 2: The parameters of the MSP protocol are lost.
1.
Check whether the MSP protocol is normal on the network.
2.
Check whether the MSP protocol is normal on the network. For details, see Enabling/
Disabling the linear MSP protocol.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the protocol is End the alarm handling.
restarted
The alarm persists after the protocol is
restarted
Contact Huawei engineers to handle the
alarm.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.12 APS_INDI
Description
The APS_INDI is an alarm indicating that the MS protection switching occurs.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
231
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the type of the protection group.
l 0x01: linear MS protection.
Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
During the switching ( 50 ms), the service is interrupted. After the switching is complete, the
services are restored to normal. In the case of 1:N MS protection, after the switching starts and
before the switching is complete, the extra services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The MS protection switching occurs.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The MS protection switching occurs.
1.
Query the linear MSP group.
2.
Check whether the MSP protocol is in the manual switching state, forced switching state,
or locked switching state. If yes, release the switching and check whether the alarm is
cleared.
3.
Check whether the MSP protocol is in the automatic switching state. Do as follows:
a.
Handle the R_LOS, R_LOF, MS_AIS, B2_EXC, or B2_SD alarm that the equipment
reports. After the alarms are cleared, wait until the MSP protocol is changed from the
automatic switching state to the normal state. Then, check whether the APS_INDI
alarm is cleared.
b.
Check whether the service board configured with the MSP protocol is faulty. If yes,
replace the faulty board and then check whether the APS_INDI alarm is cleared.
c.
Check whether the currently working system control and cross-connect board is faulty.
If the currently working system control and cross-connect board is faulty and a
protection system control and cross-connect board is available, switch the service to
the protection system control and cross-connect board and replace the faulty system
control and cross-connect board. Then, check whether the APS_INDI alarm is
cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.13 APS_MANUAL_STOP
Description
The APS_MANUAL_STOP is an alarm indicating that the MSP protocol is stopped manually.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
232
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the type of the protection group.
l 0x01: linear MS protection.
Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
When the APS_MANUAL_STOP alarm occurs, the MSP protocol may fail and therefore the
protection switching may fail.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The MSP protocol is stopped manually.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The MSP protocol is stopped manually.
1.
Enable/Disable the linear MSP protocol.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.14 ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELL_EXC
Description
The ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELL_EXC is an alarm indicating that the number of unknown
cells exceeds the specified threshold in a time unit. This alarm occurs when the board detects
that, within a period (2.5s), the number of unknown cells crosses the specified threshold.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
233
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
An unknown cell is discarded once it is detected. As a result, the packet loss rate increases and
services are affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: PW control words mismatch.
Cause 2: PW types mismatch.
Cause 3: Fragments are received on the network side.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the configuration at the two ends of the PW is consistent. If not, modify the
configuration.
Step 2 Check whether connections are correct. If not, reconnect fibers or reconfigure connections.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.15 AU_AIS
Description
The AU_AIS is an alarm indicating the administrative unit (AU). This alarm occurs when the
board detects the AU pointer of all 1s for three consecutive frames.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
234
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When the AU_AIS alarm occurs, the service in the alarmed AU-4 path is interrupted. If the
services are configured with protection, protection switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The opposite NE inserts the AU_AIS alarm.
Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite NE is faulty.
Cause 3: The receive unit of the local NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The opposite NE inserts the AU_AIS alarm.
If...
Then...
The alarm that triggers the AU_AIS insertion occurs
Clear the alarm immediately.
No such alarms that trigger the AU_AIS insertion occur
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite NE is faulty.
1.
2.
Replace the board where the line unit is located or the IF board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to the next step.
Replace the system control board on the opposite NE.
Step 3 Cause 3: The receive unit of the local NE is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.16 AU_LOP
Description
The AU_LOP is an alarm indicating the loss of the AU pointer. This alarm occurs when a board
detects the AU pointer of invalid values or with the NDF for eight consecutive frames.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
235
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the AU_LOP alarm occurs, the service in the alarmed AU-4 path is interrupted. If the
services are configured with protection, protection switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The transmit unit of the opposite NE is faulty.
Cause 2: The receive unit of the local NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The transmit unit of the opposite NE is faulty.
1.
2.
Replace the board where the line unit is located on the opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to the next step.
Replace the system control board on the opposite NE.
Step 2 Cause 2: The receive unit of the local NE is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.17 B1_EXC
Description
The B1_EXC is an alarm indicating that the B1 errors (in the regenerator section) exceed the
threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects that the B1 errors exceed the preset B1_EXC
alarm threshold (10-3 by default).
An IF board that works in PDH mode may also report this alarm. This alarm is detected by using
the self-defined overhead byte B1 in PDH microwave frames.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
236
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the B1_EXC alarm occurs, the services on the port are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
1.
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite end and the receive power at the local
end meet the specifications of the optical interfaces. For details, see 8.3.5 Browsing
Current Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power of the opposite NE is Replace the board where the SDH
over low
optical interface unit is located on the
opposite NE.
The transmit power of the opposite NE is The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power of the local
NE is close to the value (for example,
within 3 dB) of the receiver sensitivity.
2.
Exchange the core fibers of the optical cables in the receive and transmit directions of a
channel.
If...
Then...
The errors vary with the change of the fiber The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
The errors do not vary with the change of the Ensure that the board is normal.
fiber.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
237
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3.
A Alarm Reference
If the fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out of the equipment room are pressed,
and whether the fiber connector is dirty. If yes, replace the fiber jumper or fiber connector.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Check whether the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR or
RPS_INDI alarm is reported. If yes, clear the alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
1.
Check the network clock status of the alarmed NE.
If...
Then...
The clock source of the local NE is
different from the clock source of the
opposite NE
The clock may become asynchronous and B1
errors may occur. Reconfigure the clock
source, and ensure that the clock is
synchronized on the local NE and opposite
NE.
The clock of the local NE and the clock This may cause errors and even service
of the opposite NE form a timing loop interruption. In this case, reconfigure the clock
source and release the timing loop.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
1.
The board of the SDH line unit on the local NE is faulty. Loop back the optical interfaces
of the NE by using a fiber jumper to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the optical Replace the board where the alarmed
interfaces are looped back
line unit is located on the local NE.
The fault is rectified after the optical
interfaces are looped back
Replace the board where the line unit is
located on the opposite NE.
Step 5 Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Perform an inloop for the multiplexing interface of the IF board on the local NE.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
multiplexing interface is looped back
Replace the alarmed IF board on the
local NE.
The fault is rectified after the multiplexing Replace the alarmed IF board on the
interface is looped back
opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
Handle the errors of TDM services.
A.3.18 B1_SD
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
238
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The B1_SD is an alarm indicating that the signal degrades due to the excessive B1 errors (in the
regenerator section). This alarm occurs when the board detects that the B1 errors exceed the
preset B1_SD alarm threshold (10-6 by default) but do not reach the preset B1_EXC alarm
threshold (10-3 by default).
An IF board that works in PDH mode may also report this alarm. This alarm is detected by using
the self-defined overhead byte B1 in PDH microwave frames.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the B1_SD alarm occurs, the service performance on the port degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
1.
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite end and the receive power at the local
end meet the specifications of the optical interfaces. For details, see 8.3.5 Browsing
Current Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power of the opposite NE is Replace the board where the SDH
over low
optical interface unit is located on the
opposite NE.
The transmit power of the opposite NE is The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power of the local
NE is close to the value (for example,
within 3 dB) of the receiver sensitivity
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
239
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
Exchange the core fibers of the optical cables in the receive and transmit directions of a
channel.
If...
Then...
The errors vary with the change of the fiber The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
The errors do not vary with the change of the Ensure that the board is normal.
fiber
3.
If the fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out of the equipment room are pressed,
and whether the fiber connector is dirty. If yes, replace the fiber jumper or fiber connector.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Check whether the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is
generated. If yes, clear the alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
1.
Check the network clock status of the alarmed NE.
If...
Then...
The clock source of the local NE is
different from the clock source of the
opposite NE
The clock may become asynchronous and
errors may occur. Reconfigure the clock
source, and ensure that the clock is
synchronized on the local NE and opposite
NE.
The clock of the local NE and the clock This may cause errors and even service
of the opposite NE form a timing loop interruption. In this case, reconfigure the clock
source and release the timing loop.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
1.
The SDH optical line board of the local NE is faulty. Loop back the optical interfaces of
the NE by using a fiber jumper to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the optical Replace the board where the alarmed
interfaces are looped back
line unit is located on the local NE.
The fault is rectified after the optical
interfaces are looped back
Replace the board where the line unit is
located on the opposite NE.
Step 5 Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Perform an inloop for the multiplexing interface of the IF board on the local NE.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
multiplexing interface is looped back
Replace the alarmed IF board on the
local NE.
The fault is rectified after the multiplexing Replace the alarmed IF board on the
interface is looped back
opposite NE.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
240
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
Handle the errors of TDM services.
A.3.19 B2_EXC
Description
The B2_EXC is an alarm indicating that the B2 errors (in the multiplex section) exceed the
threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects that the number of B2 errors exceeds the
preset B2_EXC alarm threshold (10-3 by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services on the port are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
1.
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite end and the receive power at the local
end meet the specifications of the optical interfaces. For details, see 8.3.5 Browsing
Current Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power of the opposite NE is Replace the board where the SDH
over low
optical interface unit is located on the
opposite NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
241
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
If...
A Alarm Reference
Then...
The transmit power of the opposite NE is The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power of the local
NE is close to the value (for example,
within 3 dB) of the receiver sensitivity
2.
Exchange the core fibers of the optical cables in the receive and transmit directions of a
channel to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The errors vary with the change of the fiber The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
The errors do not vary with the change of the Ensure that the board is normal.
fiber
3.
If the fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out of the equipment room are pressed,
and whether the fiber connector is dirty. If yes, replace the fiber jumper or fiber connector.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Check whether the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR or
RPS_INDI alarm is reported. If yes, clear the alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
1.
Check the network clock status of the alarmed NE.
If...
Then...
The clock source of the local NE is
different from the clock source of the
opposite NE
The clock may become asynchronous and
errors may occur. Reconfigure the clock
source, and ensure that the clock is
synchronized on the local NE and opposite
NE.
The clock of the local NE and the clock This may cause errors and even service
of the opposite NE form a timing loop interruption. In this case, reconfigure the clock
source and release the timing loop.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
1.
The board of the SDH line unit on the local NE is faulty. Loop back the optical interfaces
of the NE by using a fiber jumper to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the optical Replace the board where the alarmed
interfaces are looped back
line unit is located on the local NE.
The fault is rectified after the optical
interfaces are looped back
Replace the board where the line unit is
located on the opposite NE.
Step 5 Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Perform an inloop for the multiplexing interface of the IF board on the local NE.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
242
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
multiplexing interface is looped back
Replace the alarmed IF board on the
local NE.
The fault is rectified after the multiplexing Replace the alarmed IF board on the
interface is looped back
opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
Handle the errors of TDM services.
A.3.20 B2_SD
Description
The B2_SD is an alarm indicating that the signal degrades due to the excessive B2 errors (in the
multiplex section). This alarm occurs when the board detects that the number of B2 errors is
higher than the preset B2_SD alarm threshold (10-6 by default) and lower than the preset
B2_EXC alarm threshold (10-3 by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service performance on the port degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
243
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite end and the receive power at the local
end meet the specifications of the optical interfaces. For details, see 8.3.5 Browsing
Current Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power of the opposite NE is Replace the board where the SDH
over low
optical interface unit is located on the
opposite NE.
The transmit power of the opposite NE is The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power of the local
NE is close to the value (for example,
within 3 dB) of the receiver sensitivity
2.
Exchange the core fibers of the optical cables in the receive and transmit directions of a
channel to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The errors vary with the change of the fiber The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
The errors do not vary with the change of the Ensure that the board is normal.
fiber
3.
If the fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out of the equipment room are pressed,
and whether the fiber connector is dirty. If yes, replace the fiber jumper or fiber connector.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Check whether the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is
generated. If yes, clear the alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
1.
Check the network clock status of the alarmed NE.
If...
Then...
The clock source of the local NE is
different from the clock source of the
opposite NE
The clock may become asynchronous and
errors may occur. Reconfigure the clock
source, and ensure that the clock is
synchronized on the local NE and opposite
NE.
The clock of the local NE and the clock This may cause errors and even service
of the opposite NE form a timing loop interruption. In this case, reconfigure the clock
source and release the timing loop.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
1.
The SDH optical/electrical line board of the local NE is faulty. Loop back the optical
interfaces of the station by using a fiber jumper to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the optical Replace the board where the alarmed
interfaces are looped back
line unit is located on the local NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
244
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The fault is rectified after the optical
interfaces are looped back
Replace the board where the line unit is
located on the opposite NE.
Step 5 Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Perform an inloop for the multiplexing interface of the IF board on the local NE.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
multiplexing interface is looped back
Replace the alarmed IF board on the
local NE.
The fault is rectified after the multiplexing Replace the alarmed IF board on the
interface is looped back
opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
Handle the errors of TDM services.
A.3.21 B3_EXC
Description
The B3_EXC is an alarm indicating that the B3 errors (in the higher order path) exceed the
threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects that the number of B3 errors exceeds the
preset B3_EXC alarm threshold (10-3 by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the B3_EXC alarm occurs, the service on the alarmed path is interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
245
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
1.
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite end and the receive power at the local
end meet the specifications of the optical interfaces. For details, see 8.3.5 Browsing
Current Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power of the opposite NE is Replace the board where the SDH
over low
optical interface unit is located on the
opposite NE.
The transmit power of the opposite NE is The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power of the local
NE is close to the value (for example,
within 3 dB) of the receiver sensitivity
2.
Exchange the core fibers of the optical cables in the receive and transmit directions of a
channel to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The errors vary with the change of the fiber The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
The errors do not vary with the change of the Ensure that the board is normal.
fiber
3.
If the fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out of the equipment room are pressed,
and whether the fiber connector is dirty. If yes, replace the fiber jumper or fiber connector.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Check whether the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR or
RPS_INDI alarm is reported. If yes, clear the alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
1.
Check the network clock status of the alarmed NE.
If...
Then...
The clock source of the local NE is
different from the clock source of the
opposite NE
In this case, the clock may become
asynchronous and errors may occur.
Reconfigure the clock source, and ensure that
the clock is synchronized on the local NE and
opposite NE.
The clock of the local NE and the clock This may cause errors and even service
of the opposite NE form a timing loop interruption. In this case, reconfigure the clock
source and release the timing loop.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
246
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
The board of the SDH line unit on the local NE is faulty. Loop back the optical interfaces
of the NE by using a fiber jumper to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the optical Replace the board where the alarmed
interfaces are looped back
line unit is located on the local NE.
The fault is rectified after the optical
interfaces are looped back
Replace the board where the line unit is
located on the opposite NE.
Step 5 Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Perform an inloop for the multiplexing interface of the IF board on the local NE.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
multiplexing interface is looped back
Replace the alarmed IF board on the
local NE.
The fault is rectified after the multiplexing Replace the alarmed IF board on the
interface is looped back
opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
Handle the errors of TDM services.
A.3.22 B3_EXC_VC3
Description
The B3_EXC_VC3 alarm indicates that the number of B3 bit errors in a VC-3 path crosses the
threshold. A board reports this alarm when detecting that the number of B3 bit errors crosses
the B3_EXC_VC3 alarm threshold (10-3, by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
247
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
The services in the alarmed path have a large number of bit errors.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Higher-level bit error alarms occur in the system.
Cause 2: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet optical
port).
Cause 3: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet electrical
port).
Cause 4: A board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Higher-level bit error alarms occur in the system.
1.
Check whether the local or upstream site detects B1_EXC, B1_SD, B2_EXC, B2_SD,
B3_EXC, or B3_SD alarms. If yes, clear the higher-level alarms.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2 or Cause 3.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet optical port).
1.
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite site and the receive power at the local
site meet the specifications of the optical ports. For details, see Browsing Current
Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power at the opposite site is Replace the optical module at the
too low
opposite site.
The transmit power at the opposite site is A fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power at the local
site is close to the receiver sensitivity (for
example, a difference within 3 dB)
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Exchange the optical fibers in the receive and transmit directions of an optical path segment.
If...
Then...
The number of bit errors changes
Go to the next step.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
248
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3.
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The number of bit errors does not change
Go to Cause 4.
If a fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out from the equipment room are pressed,
and whether any fiber connector is dirty or damaged. If yes, clean or replace the fiber
connector, or replace the fiber jumper. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 4.
Step 3 Cause 3: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet electrical port).
1.
Check whether the cable grounding, cable connectors, and cables are damaged. If yes,
replace the faulty cables.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: A board is faulty.
1.
Perform an inloop at the Ethernet port that connects to the alarmed VC-3 path.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
Ethernet port is looped back
Replace the alarmed Ethernet processing
board at the local site.
The fault is rectified after the Ethernet Replace the Ethernet processing board at
port is looped back
the opposite site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.23 B3_SD
Description
The B3_SD is an alarm indicating that the signal degrades due to the excessive B3 errors (in the
higher order path). This alarm occurs when the board detects that the number of B3 errors is
higher than the preset B3_SD alarm threshold (10-6 by default) and lower than the preset
B3_EXC alarm threshold (10-3 by default).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
249
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service performance on the port degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
1.
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite end and the receive power at the local
end meet the specifications of the optical interfaces. For details, see 8.3.5 Browsing
Current Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power of the opposite NE is Replace the board where the SDH
over low
optical interface unit is located on the
opposite NE.
The transmit power of the opposite NE is The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power of the local
NE is close to the value (for example,
within 3 dB) of the receiver sensitivity
2.
Exchange the core fibers of the optical cables in the receive and transmit directions of a
channel to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The errors vary with the change of the fiber The fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
The errors do not vary with the change of the Ensure that the board is normal.
fiber
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
250
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3.
A Alarm Reference
If the fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out of the equipment room are pressed,
and whether the fiber connector is dirty. If yes, replace the fiber jumper or fiber connector.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Check whether the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is
generated. If yes, clear the alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: The network clock quality degrades.
1.
Check the network clock status of the alarmed NE.
If...
Then...
The clock source of the local NE is
different from the clock source of the
opposite NE
In this case, the clock may become
asynchronous and errors may occur.
Reconfigure the clock source, and ensure that
the clock is synchronized on the local NE and
opposite NE.
The clock of the local NE and the clock This may cause errors and even service
of the opposite NE form a timing loop interruption. In this case, reconfigure the clock
source and release the timing loop.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface board).
1.
The SDH optical/electrical line board of the local NE is faulty. Loop back the optical
interfaces of the station by using a fiber jumper to locate the fault.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the optical Replace the board where the alarmed
interfaces are looped back
line unit is located on the local NE.
The fault is rectified after the optical
interfaces are looped back
Replace the board where the line unit is
located on the opposite NE.
Step 5 Cause 5: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
Perform an inloop for the multiplexing interface of the IF board on the local NE.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
multiplexing interface is looped back
Replace the alarmed IF board on the
local NE.
The fault is rectified after the multiplexing Replace the alarmed IF board on the
interface is looped back
opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
Handle the errors of TDM services.
A.3.24 B3_SD_VC3
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
251
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The B3_SD_VC3 alarm indicates a signal degrade (SD) condition caused by excessive B3 bit
errors in VC-3 paths. A board reports this alarm when detecting that the number of B3 bit errors
crosses the B3_SD_VC3 alarm threshold (10-6, by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the path that reports the alarm. For example, 0x00
0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
When the B3_SD_VC3 alarm occurs, the services in the alarmed path deteriorate.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Higher-level bit error alarms occur in the system.
Cause 2: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet optical
port).
Cause 3: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet electrical
port).
Cause 4: A board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Higher-level bit error alarms occur in the system.
1.
Check whether the local or upstream site detects B1_EXC, B1_SD, B2_EXC, B2_SD,
B3_EXC, or B3_SD alarms. If yes, clear the higher-level alarms.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2 or Cause 3.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
252
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet optical port).
1.
Check whether the transmit power at the opposite site and the receive power at the local
site meet the specifications of the optical ports. For details, see Browsing Current
Performance Events.
If...
Then...
The transmit power at the opposite site is Replace the optical module at the
too low
opposite site.
The transmit power at the opposite site is A fiber is faulty. Go to the next step.
normal, but the receive power at the local
site is close to the receiver sensitivity (for
example, a difference within 3 dB)
2.
3.
Exchange the optical fibers in the receive and transmit directions of an optical path segment.
If...
Then...
The number of bit errors changes
Go to the next step.
The number of bit errors does not change
Go to Cause 4.
If a fiber is faulty, check whether the fiber jumper from the equipment to the optical
distribution frame (ODF) and the fiber that is led out from the equipment room are pressed,
and whether any fiber connector is dirty or damaged. If yes, clean or replace the fiber
connector, or replace the fiber jumper. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 4.
Step 3 Cause 3: The line performance deteriorates (the alarm is reported by an Ethernet electrical port).
1.
Check whether the cable grounding, cable connectors, and cables are damaged. If yes,
replace the faulty cables.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: A board is faulty.
1.
Perform an inloop at the Ethernet port that connects to the alarmed VC-3 path.
If...
Then...
The fault is not rectified after the
Ethernet port is looped back
Replace the alarmed Ethernet processing
board at the local site.
The fault is rectified after the Ethernet Replace the Ethernet processing board at
port is looped back
the opposite site.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
253
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.25 BAT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The BAT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the temperature sensor of battery
group 1 fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The temperature data of battery group 1 cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The temperature sensor of battery group 1 is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The temperature sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The temperature sensor of battery group 1 is faulty.
1.
Replace the temperature sensor of battery group 1.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
254
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: The temperature sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the temperature sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.26 BAT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The BAT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the temperature sensor of battery
group 2 fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The temperature data of battery group 2 cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The temperature sensor of battery group 2 is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The temperature sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The temperature sensor of battery group 2 is faulty.
1.
Replace the temperature sensor of battery group 2.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
255
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: The temperature sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the board temperature sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.27 BD_NOT_INSTALLED
Description
The BD_NOT_INSTALLED is an alarm indicating that the physical board is installed in a
certain slot, but the logical board is not added.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
256
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicates the ID of the slot.
Impact on the System
When the BD_NOT_INSTALLED alarm occurs, the physical board in this slot cannot work.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The logical board is not added in the corresponding logical slot.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The logical board is not added in the corresponding logical slot.
1.
Configure the logical board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.28 BD_STATUS
Description
The BD_STATUS is an alarm indicating that the board is not in position.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the BD_STATUS alarm occurs, the alarmed board fails to work.
Possible Causes
If the alarm is reported by a board of the IDU, the possible causes are as follows:
l
Cause 1 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: The board is installed in an incorrect
slot.
Cause 2 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: The board and the backplane are not
connected properly.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
257
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 3 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: The slot is faulty.
Cause 4 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: A certain board is faulty.
If the alarm is reported by the ODU, the possible causes are as follows:
l
Cause 1 of the alarm reported by the ODU: The other alarms are generated.
Cause 2 of the alarm reported by the ODU: The ODU is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: The board is installed in an incorrect slot.
1.
Check whether the logical slot and physical slot of the alarmed board are consistent. For
details, see 8.3.2 Checking the Board Status.
If...
Then...
The alarmed board is installed in an
incorrect slot
Install the board in a correct slot.
The alarmed board is installed in a
correct slot
Ensure that the board and the backplane
are connected properly.
Step 2 Cause 2 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: The board and the backplane are not
connected properly.
1.
Remove and insert the alarmed board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
removed and inserted
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
removed and inserted
Ensure that the board is normal.
Step 3 Cause 3 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: The slot is faulty.
1.
Contact Huawei engineers to handle the fault of the slot.
TIP
Generally, the slot becomes faulty due to the broken pin or bent pin. Remove the board, and use a
torch to observe whether there is any broken pin or bent pin.
2.
If a vacant slot is available, insert the board in the vacant slot and add the board again.
Then, the board can work normally.
Step 4 Cause 4 of the alarm reported by a board of the IDU: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Ensure that the slot is normal.
Step 5 Cause 1 of the alarm reported by the ODU: The other alarms are generated.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Query whether the IF board reports the HARD_BAD, BD_STATUS,
IF_CABLE_OPEN, BD_NOT_INSTALLED or VOLT_LOS alarm.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
258
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The IF board reports any of the preceding alarms
Clear the alarm immediately.
The IF board does not report any of the preceding
alarms
Replace the alarmed ODU.
Step 6 Cause 2 of the alarm reported by the ODU: The ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed ODU.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.29 BDTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The BDTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the board temperature sensor of the
cabinet fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The board temperature data of the TCU cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The board temperature sensor is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The board temperature sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The board temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the board temperature sensor.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
259
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board temperature sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the board temperature sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.30 BIOS_STATUS
Description
The BIOS_STATUS is an alarm indicating that the board is in BIOS state.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Processing alarm
Parameters
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the slot ID of the board that is in BIOS state.
Impact on the System
The services on the alarmed board are interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
260
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The board software is lost.
Cause 2: The board software becomes abnormal.
Procedure
Step 1 Perform a cold reset on the alarmed standby system control, switching, and timing board, and
then check whether the alarm is cleared.
Step 2 If the alarm persists, remove the standby system control, switching, and timing board, and
then reseat the board.
Step 3 If the alarm persists, replace the board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.31 BIP_EXC
Description
The BIP_EXC is an alarm indicating that the BIP errors exceed the threshold. This alarm occurs
when the board detects that the number of BIP-2 errors (in byte V5) exceeds the preset BIP_EXC
alarm threshold (10-3 by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the BIP_EXC alarm occurs, the service on the alarmed path is interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
Cause 3: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
261
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
1.
Check whether the performance degradation alarm occurs on the STM-1 path or radio link
along which the E1 service signal travels. If yes, clear the alarm immediately.
The common line performance degradation alarms are as follows:
B1_EXC, B1_SD, B2_EXC, B2_SD, B3_EXC, B3_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR,
RPS_INDI, MW_BER_EXC, and MW_BER_SD.
If...
Then...
There is any of the preceding alarms
Clear the alarm immediately.
No such alarms occur
Ensure that the board is normal.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
1.
Check whether any alarm occurs on the tributary board or IF board that transmits the service
signal. If yes, clear the alarm immediately.
Step 3 Cause 3: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
1.
Replace the board where the E1 service unit is located. Then, check whether the alarm
is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the system control and cross-connect board.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
1.
Replace the Hybrid IF board. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the system control and cross-connect board.
----End
Related Information
Handle the errors of TDM services.
The alarm parameters have the meanings listed in Table A-2 when EMS6 board report the alarm.
Table A-2 Alarm Parameters of EMS6
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the ID of the path that reports the
alarm. For example, 0x00 0x01 indicate that
the alarm is reported in path 1.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
262
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.32 BIP_SD
Description
The BIP_SD is an alarm indicating that the signal degrades due to the BIP errors. This alarm
occurs when the board detects that the number of BIP-2 errors (in byte V5) is higher than the
preset BIP_SD alarm threshold (10-6 by default) and lower than the preset BIP_EXC alarm
threshold (10-3 by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the BIP_SD alarm occurs, the service on the alarmed path degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
Cause 3: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
1.
Check whether the performance degradation alarm occurs on the STM-1 path or radio link
along which the E1 service signal travels. If yes, clear the alarm immediately.
The common line performance degradation alarms are as follows:
B1_EXC, B1_SD, B2_EXC, B2_SD, B3_EXC, B3_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR,
RPS_INDI, MW_BER_EXC, and MW_BER_SD.
If...
Then...
There is any of the preceding alarms
Clear the alarm immediately.
No such alarms occur
Ensure that the board is normal.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
263
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether any alarm occurs on the tributary board or IF board that transmits the service
signal.
If...
Then...
An alarm occurs
Clear the alarm immediately.
No alarm occurs
Ensure that the board is normal.
Step 3 Cause 3: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by an E1 service board).
1.
Replace the board where the E1 service unit is located. Then, check whether the alarm
is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the system control and cross-connect board.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board is faulty (if the alarm is reported by a Hybrid IF board).
1.
Replace the Hybrid IF board. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the system control and cross-connect board.
----End
Related Information
Handle the errors of TDM services.
The alarm parameters have the meanings listed in Table A-3 when EMS6 board report the alarm.
Table A-3 Alarm Parameters of EMS6
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the ID of the path that reports the
alarm. For example, 0x00 0x01 indicate that
the alarm is reported in path 1.
A.3.33 BOOTROM_BAD
Description
The BOOTROM_BAD is an alarm indicating that the BOOTROM data consistency check fails.
This alarm occurs when the BOOTROM data is damaged during a periodical check by the
system.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
264
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicates the type of the BOOTROM damage.
l 0x00, 0x01: damage of the basic BIOS
l 0x00, 0x02: damage of the extended BIOS
Parameter 4, Parameter 5
The values are always 0xff 0xff.
Impact on the System
When the BOOTROM_BAD alarm occurs, it indicates that errors occur in the system database
processing. The system configuration may be lost. As a result, the failure indication is returned
for certain query and setting commands, and certain system functions cannot work.
l
When the NE is already started, the BOOTROM_BAD alarm does not affect the system
and services.
If the BOOTROM_BAD alarm occurs and a hard reset is performed on a board, the board
fails to load the BIOS and cannot be started.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The basic BIOS is damaged.
Cause 2: The extended BIOS is damaged.
Cause 3: The BOOTROM database is damaged.
Cause 4: The system control switch and timing board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
265
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.34 BUS_ERR
Description
The BUS_ERR alarm indicates bus errors. This alarm occurs when the bus becomes abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicates the ID of the board that has errors.
Impact on the System
When the BUS_ERR alarm occurs, the services that travel along the faulty bus are interrupted
or have errors.
Possible Causes
The possible causes of the BUS_ERR alarm are as follows:
l
Cause 1: The board is not properly inserted.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The board is not properly inserted.
1.
Remove and insert the board.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the alarmed board. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
266
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
The alarm parameters have the meanings listed in Table A-4 when EMS6 board report the alarm.
Table A-4 Alarm parameters of EMS6
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the bus error type.
0x10: The Serdes bus of the GE bridge is
faulty.
A.3.35 CES_ACR_LOCK_ABN
Description
The CES_ACR_LOCK_ABN is an alarm indicating that the locking function of CES ACR
service clock is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4 Indicate the index of PW that carries the services associated with
the ACR clock source.
Parameter 5
Indicates clock mode.
l 0x01: tracing mode.
l 0x02: holdover mode.
l 0x03: free-run mode.
Parameter 6
Indicates whether the clock is locked.
l 0x00: unlocked.
l 0x01: locked.
Impact on the System
Service quality is affected.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: CES ACR services are unavailable or have alarms.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
267
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The network is unstable.
Cause 3: NEs on the service path are abnormal.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: CES ACR services are unavailable or have alarms.
1.
Query the CES services associated with the ACR clock source. For details, see Configuring
the Primary Clock for an ACR Clock Domain.
2.
Check whether these services have alarms. For details, see 8.3.3 Browsing Current
Alarms.
Step 2 Cause 2: The network is unstable.
1.
Check for jitters and delays on the network. Query service performance statistics. For
details, see 8.3.5 Browsing Current Performance Events.
2.
Analyze service performance statistics. If the network is unstable, rectify the faults on the
network, or switch the affected services to a stable network.
Step 3 Cause 3: NEs on the service path are abnormal.
1.
Query alarms reported by the NEs on the service path. For details, see 8.3.3 Browsing
Current Alarms.
2.
Handle the alarms. For details, see A.3 Alarms and Handling Procedures.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.36 CES_JTROVR_EXC
Description
The CES_JTROVR_EXC is an alarm indicating that the number of jitter buffer overflows
crosses the specified threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects that, the number of
jitter buffer overflows per second crosses the specified threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The buffer area does not have sufficient space for the received frames. As a result, packets are
discarded.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
268
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The size of buffer area is set to a low value.
Cause 2: The PSN network clocks used for the transmission of CES services are not
synchronized.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The size of buffer area is set to a low value.
1.
Query the size of buffer area. For details, see Querying CES Service Information.
2.
Determine whether the size can be increased according to network planning. If yes, change
the size to a greater value. For details, see Managing CES Services.
Step 2 Cause 2: The PSN network clocks used for the transmission of CES services are not
synchronized.
1.
Synchronize the PSN network clock by setting clock synchronization, reducing
transmission nodes, and optimizing transmission routes.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.37 CES_JTRUDR_EXC
Description
The CES_JTRUDR_EXC is an alarm indicating that the number of jitter buffer underflows
crosses the specified threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects that, within a period
(10s), the number of jitter buffer underflows per second crosses the specified threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, no packets are available in the buffer area for transmission. As a result,
underflows occur in the buffer area.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
269
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The PSN network clocks used for the transmission of CES services are not
synchronized.
Cause 3: The link is looped.
Cause 4: The link is congested.
Cause 5: The size of buffer area is set to a low value.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
1.
Troubleshoot the link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Cause 2: The PSN network clocks used for the transmission of CES services are not
synchronized.
1.
Synchronize the PSN network clock by setting clock synchronization, reducing
transmission nodes, and optimizing transmission routes.
Step 3 Cause 3: The link is looped.
1.
Release the loop.
Step 4 Cause 4: The link is congested.
1.
Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
Step 5 Cause 5: The size of buffer area is set to a low value.
1.
Query the size of buffer area. For details, see Querying CES Service Information.
2.
Determine whether the size can be increased according to network planning. If yes, change
the size to a greater value. For details, see Managing CES Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.38 CES_LOSPKT_EXC
Description
The CES_LOSPKT_EXC is an alarm indicating that the number of lost packets of CES services
crosses the threshold in a time unit. This alarm occurs when the board detects that, within a
period (10s), the number of lost packets per second crosses the specified threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
270
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, all 1s are inserted and services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
Cause 2: The link is looped.
Cause 3: The link is congested.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
1.
Troubleshoot the link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Cause 2: The link is looped.
1.
Release the loop.
Step 3 Cause 3: The link is congested.
1.
Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
Packets are lost when the sequence numbers of received packets are greater than expected.
A.3.39 CES_MALPKT_EXC
Description
The CES_MALPKT_EXC is an alarm indicating that, in a time unit, the number of deformed
frames in CES services crosses the threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects that,
within a period (10s), the number of deformed frames in CES services crosses the specified
threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
A deformed frame is discarded once it is detected. As a result, the packet loss rate increases and
services are affected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
271
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The RTP head enabling status is different between the two ends of the PW.
Cause 2: Bit errors occur on the link.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The RTP head enabling status is different between the two ends of the PW.
1.
Set the RTP head enabling status to the same on the two ends of the PW. For details, see
Modifying CES Service Parameters.
Step 2 Cause 2: Bit errors occur on the link.
1.
Troubleshoot the link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
----End
Related Information
If a CESoPSN frame contains valid TDM data and does not contain any error indication, but the
size of the CESoPSN frame is not consistent with the specified size, a deformed CESoPSN frame
is generated.
A.3.40 CES_MISORDERPKT_EXC
Description
The CES_MISORDERPKT_EXC is an alarm indicating that, in a unit time, the number of lost
disordered packets crosses the specified threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects
that, within a period (10s), the number of lost disordered packets per second crosses the specified
threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The packets are disordered. As a result, the packet loss rate increases and services are affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
Cause 2: The link is looped.
Cause 3: The link is congested.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
272
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
1.
See 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Cause 2: The link is looped.
1.
Release the loop.
Step 3 Cause 3: The link is congested.
1.
Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
Packets are disordered when the sequence numbers of received packets are smaller than
expected.
A.3.41 CES_RDI
Description
The CES_RDI is an alarm of remote defect indication. When the CES_LOSPKT_EXC alarm is
reported at the remote end, the remote end sets the R bit in control word to 1. Upon receiving a
packet in which the R bit is 1, the local end reports the CES_RDI alarm.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The packet loss rate at the remote end crosses the specified threshold.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
Cause 2: The link is looped.
Cause 3: The link is congested.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Signals degrade on the link.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
See 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
273
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 2 Cause 2: The link is looped.
1.
Release the loop.
Step 3 Cause 3: The link is congested.
1.
Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.42 CES_STRAYPKT_EXC
Description
The CES_STRAYPKT_EXC is an alarm indicating that, in a time unit, the number of errored
packets in CES services crosses the threshold. This alarm occurs when the board detects that,
within a period (10s), the number of errored packets in CES services per second crosses the
specified threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
An errored packet is discarded once it is detected. As a result, the packet loss rate increases and
services are affected.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: Links are misconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Links are misconnected.
1.
Check the link configuration and rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
Incorrect packets are received when the tracing source field in the RTP head is different from
expected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
274
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.43 CESPW_OPPOSITE_ACFAULT
Description
The CESPW_OPPOSITE_ACFAULT is an alarm indicating that the AC circuit on the remote
NE is faulty. On detection of an AC circuit fault, the remote NE sets the L bit in the control word
to 1. When receiving a packet in which the L bit is 1, the local NE reports the
CESPW_OPPOSITE_ACFAULT alarm.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The remote NE reports the T_ALOS, UP_E1_AIS, LFA, LMFA, R_LOS, R_LOF, or
MS_AIS alarm.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the remote NE reports the T_ALOS, UP_E1_AIS, LFA, LMFA, R_LOS,
R_LOF, or MS_AIS alarm.
1.
If yes, handle these alarms.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.44 CESPW_OPPOSITE_RAI
Description
The CESPW_OPPOSITE_RAI is a remote alarm indication. On detection of the RAI alarm, the
remote NE sets the L bit of the control word to 0 and the M field of the control word to 10. When
receiving the packet in which the L bit is 0 and the M field is 10, the local NE reports the
CESPW_OPPOSITE_RAI alarm.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
275
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services in the downstream direction of the remote NE are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The remote NE detects the RAI alarm.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The remote NE detects the RAI alarm.
1.
Clear the ALM_E1RAI alarm on the remote NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.45 CFCARD_FAILED
Description
The CFCARD_FAILED is an alarm indicating that the operation on the CF card fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the CFCARD_FAILED alarm occurs, the database cannot be backed up to the CF card
or be restored from the CF card. This alarm may cause rollback of the package loading upgrade.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
276
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The CF card fails to be initialized.
Cause 2: The file system of the CF card does not match.
Cause 3: The system control and communication board is faulty, and the file system of the
CF card fails to be created.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The CF card fails to be initialized.
Cause 2: The file system of the CF card does not match.
1.
Replace the CF card and check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
Yes
End the alarm handling.
No
Go to Cause 3.
Step 2 Cause 3: The system control and communication board is faulty, and the file system of the CF
card fails to be created.
1.
Check whether the HARD_BAD alarm occurs on the system control and communication
board.
2.
If yes, perform a cold reset on the system control and communication board. Then, check
whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
Yes
End the alarm handling.
No
Replace the system control and communication board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.46 CFCARD_OFFLINE
Description
The CFCARD_OFFLINE is an alarm indicating that the CF card is out of service.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
277
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When the CFCARD_OFFLINE alarm occurs, the database cannot be backed up to the CF card
or be restored from the CF card. This alarm may cause rollback of the package loading upgrade.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The CF card is not inserted.
Cause 2: The CF card is in poor contact with the system control and communication board.
Cause 3: The CF card is faulty.
Cause 4: The system control and communication board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The CF card is not inserted.
1.
Check whether the CF card is installed on the system control and communication board.
If...
Then...
No
Install the CF card.
Yes
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The CF card is in poor contact with the system control and communication board.
1.
Check whether the CF card is loosened. If yes, re-insert the CF card.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
Yes
End the alarm handling.
No
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The CF card is faulty.
1.
Replace the CF card.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
Yes
End the alarm handling.
No
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The system control and communication board is faulty.
1.
Check whether the HARD_BAD alarm occurs on the system control and communication
board.
2.
If yes, perform a cold reset on the system control and communication board. Then, check
whether the alarm is cleared.
3.
If the alarm persists, replace the system control and communication board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
278
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.47 CHCS
Description
The CHCS is an alarm indicating the correctable cell error. When a correctable bit error is
detected in the cell header, the CHCS alarm occurs.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the CHCS alarm occurs, the services are not affected. The alarm only indicates that some
cells with a bit error are detected during cell delimitation at the ATM port.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A few bit errors occur in the receive tunnel corresponding to the alarmed ATM
port.
Cause 2: The ATM physical-layer processing chip of the board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A few bit errors occur in the receive tunnel corresponding to the alarmed ATM port.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the receive tunnel reports any alarms about excessive bit errors,
such as B1_SD, B2_SD, and B3_SD.
2.
On the NMS, check whether the service is looped.
3.
If yes, modify the service configuration to release the loop, and then check whether the
alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The ATM physical-layer processing chip of the board is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the board that reports the CHCS alarm and check whether the alarm
is cleared. For details, see 8.6.1 Cold Reset.
2.
Optional: If the CHCS alarm persists after the cold reset, replace the alarmed board and
check whether the alarm is cleared. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.
NOTE
Board replacement is not recommended because the alarm does not affect the services.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
279
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.48 CLK_NO_TRACE_MODE
Description
The CLK_NO_TRACE_MODE alarm indicates that a clock source is not in locked mode. This
alarm is reported when the current clock does not trace any clock sources.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the clock mode.
l 0x01: holdover
l 0x02: free-run
Impact on the System
When the clock source is not in the locked mode, the system clock is not of high quality. Services
may have bit errors when the clocks of the NEs are not synchronized. Pointer justification may
occur in TDM services. If a base station traces a clock that is carried by an Ethernet service, an
alarm indicating a large clock frequency deviation may occur.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The system clock source priority table is not configured.
Cause 2: All the clock sources in the clock source priority table fail.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The system clock source priority table is not configured.
1.
Configure the system clock source priority table. For details, see Configuring the Clock
Sources.
Step 2 Cause 2: All the clock sources in the clock source priority table fail.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
280
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Troubleshoot the synchronization sources that are listed in the clock source priority table.
If...
Then...
The synchronization source is an
external clock
Handle the EXT_SYNC_LOS alarm.
The synchronization source is a line
clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the line
board.
The synchronization source is an IF
clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the IF board.
The synchronization source is a
tributary clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the tributary
board.
The synchronization source is an
Ethernet clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the Ethernet
board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.49 COMMUN_FAIL
Description
The COMMUN_FAIL is an alarm indicating the inter-board communication failure. This alarm
is reported when the communication between a board and the SCC board is interrupted.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the port. The value is always 0x01.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
281
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicates the ID of the path on which the alarm is generated.
Parameter 2 is always 0x00. Parameter 3 has the following
meanings:
l 0x03: inter-board Ethernet communication
Parameter 4, Parameter 5 Parameters 4 and 5 are reserved, and their values are always 0xFF.
Impact on the System
The NE configuration cannot be delivered to the board or the board cannot work. Consequently,
the services cannot be configured or the protection switching function is unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A certain board is reset.
Cause 2: A board and the backplane are connected improperly.
Cause 3: The alarmed board is faulty.
Cause 4: A slot is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A certain board is reset.
1.
After you reset the board, the alarm disappears automatically.
Step 2 Cause 2: A board and the backplane are connected improperly.
1.
Remove and insert the alarmed board. For details, see 6.1 Removing a Board and 6.2
Inserting a Board. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm disappears after the board is
removed and inserted
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced.
Clear the alarm according to the solution
for the alarm that is generated when a
board is faulty.
Step 3 Cause 3: The alarmed board is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the alarmed board, and then check whether the alarm is cleared. For details, see 6
Part Replacement.
If...
Then...
The alarm disappears after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Clear the alarm according to the solution
for the alarm that is generated when a
slot is faulty.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
282
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 4 Cause 3: A slot is faulty.
1.
Contact Huawei engineers to handle the faulty slot.
TIP
The slot becomes faulty due to broken pins or bent pins. Remove the board, and use a torch to check
whether any pins are broken or bent.
2.
If a vacant slot is available, insert the board in the vacant slot, and then update the data
on the NMS so that the board can work normally.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.50 CONFIG_NOSUPPORT
Description
The CONFIG_NOSUPPORT is an alarm indicating that the configuration is not supported. This
alarm is reported if the ODU detects that the specified parameters do not meet the requirements
of the ODU.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates that the configuration data does not meet the requirements.
l 0x01: The frequency is set incorrectly.
l 0x02: The T/R spacing is set incorrectly.
l 0x03: The transmit power is set incorrectly.
l 0x04: The ATPC threshold is set incorrectly.
l 0x05: The bandwidth is set incorrectly.
l 0x06: The modulation mode is set incorrectly.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
283
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When the CONFIG_NOSUPPORT alarm occurs, the ODU fails to work normally. If the
equipment is configured with the 1+1 FD protection, the active ODU generates the
CONFIG_NOSUPPORT alarm. In this case, the IF 1+1 protection switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The type and configuration parameters of the ODU do not match the requirements.
Cause 2: The AM parameters are incorrectly changed. (This cause can be verified only
when Parameter 1 is 0x03.)
NOTE
Perform the handling procedure of Cause 2 if the following conditions are met: The AM function is enabled
on the radio link; the transmit power configured for the ODU is lower than the maximum rated power in
AM guaranteed capacity mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The type and configuration parameters of the ODU do not match the requirements.
1.
Determine the parameter that does not meet the requirement according to the alarm
parameter. Then, handle the fault accordingly.
If...
Then...
The alarm parameter takes a value from Perform the operation described in Step
0x01 to 0x03
1.2.
The alarm parameter takes a value from Perform the operation described in Step
0x04 to 0x06
1.3.
2.
3.
Check whether the parameters of the ODU interface meet the requirements of network
planning. For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
If...
Then...
The parameters meet the requirements of
network planning
Use the ODU of the proper model.
The parameters do not meet the
requirements of network planning
Modify the ODU interface parameters.
Check whether the parameters of the IF interface meet the requirements of network
planning. For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
If...
Then...
The parameters meet the requirements of Replace the IF board.
network planning
The parameters do not meet the
requirements of network planning
Modify the IF interface parameters. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU
Information of a Radio Link.
Step 2 Cause 2: The AM parameters are incorrectly changed. (This cause can be verified only when
Parameter 1 is 0x03.)
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Verify that the alarm is caused by incorrect change of AM parameters.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
284
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Perform the handling procedure of Cause 2 if the following conditions are met:
l The AM function is enabled on the radio link.
l The transmit power configured for the ODU is lower than the maximum rated power in
AM guaranteed capacity mode
If...
Then...
The conditions are met and the transmit Perform a cold reset for the alarmed
power needs to be changed
ODU.
The conditions are met but the transmit Change the parameters of ODU interfaces
power does not need to be changed
to recover the original value of transmit
power.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.51 DBMS_ABNORMAL
Description
The DBMS_ABNORMAL is an alarm indicating that the database status is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the cause of the alarm.
l 0x01: NVRAM is faulty.
l 0x02: Space is insufficient.
l 0x03: Transaction commit times out.
l 0x04: A database is deleted.
Impact on the System
If data changes are made after this alarm occurs, data changes cannot take effect.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
285
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: NVRAM is faulty.
Cause 2: Space is insufficient.
Cause 3: Transaction commit times out.
Cause 4: A database is deleted.
Procedure
Step 1 Reset the alarmed board.
Step 2 Check whether the alarm is cleared. If the alarm persists, replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.52 DBMS_ERROR
Description
The DBMS_ERROR is an alarm indicating that errors occur in the processing of the system
database.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the DBMS_ERROR alarm occurs, it indicates that errors occur in the system database
processing. The system configuration may be lost. As a result, the failure indication is returned
for certain query and setting commands, and certain system functions cannot work.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The database processing fails or the database is damaged.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The database processing fails or the database is damaged.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Reset the system control board.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
286
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
reset
End the fault handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
reset
Ensure that the system control board is
normal.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.53 DBMS_PROTECT_MODE
Description
The DBMS_PROTECT_MODE is an alarm indicating that the system database is in protection
mode.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, it indicates that errors occur in the system database processing and the
system configuration may be lost. As a result, the failure indication is returned for some query
and setting commands, and some system functions are unavailable.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The database enters the protection mode due to frequent resets of the NE software.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The database enters the protection mode due to frequent resets of the NE software.
1.
6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
287
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.54 DCNSIZE_OVER
Description
The DCNSIZE_OVER is an alarm indicating an over-sized DCN network.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the size of the DCN network.
Impact on the System
l
Some NEs become unreachable to the NMS because DCN packets cannot be forwarded
timely due to insufficient CPU resources.
The DCN network is prone to route flapping and storms.
Possible Causes
Cause: The size of the DCN network crosses the preset threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The size of the DCN network crosses the preset threshold.
1.
Replan the DCN network based on actual networking conditions.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
288
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.55 DDN_LFA
Description
The DDN_LFA is an alarm indicating loss of basic frame alignment for framed E1 services.
This alarm occurs when DDN side fails to receive the basic frame alignment signal for framed
E1 services.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
E1 services on the alarmed board are unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The interconnected user equipment is faulty.
Cause 2: The service frame format is configured incorrectly.
Cause 3: The alarmed board has hardware faults.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The interconnected user equipment is faulty.
1.
Troubleshoot the interconnected user equipment.
Step 2 Cause 2: The service frame format is configured incorrectly.
1.
Set the E1 frame format of the local port to the same as that of the opposite port.
Step 3 Cause 3: The alarmed board has hardware faults.
1.
Check whether the alarmed board also reports any hardware alarms, such as
HARD_BAD.
2.
If yes, perform a cold reset on the alarmed board and check whether the DDN_LFA alarm
is cleared.
CAUTION
If the service on the board is not protected, a cold reset on the board causes service
interruptions.
3.
If the alarm persists, replace the board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
289
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
Basic frame
As defined in ITU-T G.704, a basic frame is an even frame with frame alignment sequence (FAS)
or an odd frame with non frame alignment sequence (NFAS).
A.3.56 DOWN_E1_AIS
Description
The DOWN_E1_AIS is an alarm of the 2 Mbit/s downlink signal. This alarm occurs when the
tributary board detects the 2 Mbit/s downlink signal of all 1s.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the DOWN_E1_AIS alarm occurs, the E1 signal in the alarmed path is unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The opposite NE transmits the E1_AIS alarm.
Cause 2: On the local NE, the receive unit of the tributary board or the system control and
cross-connect board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The opposite NE transmits the E1_AIS alarm.
1.
Check whether the opposite NE reports the UP_E1_AIS or T_ALOS alarm.
If...
Then...
The opposite NE reports the UP_E1_AIS Clear the alarm immediately.
or T_ALOS alarm
The opposite NE does not report the
UP_E1_AIS or T_ALOS alarm
Ensure that the board on the local NE is
normal.
Step 2 Cause 2: On the local NE, the receive unit of the tributary board or the system control and crossconnect board is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the board where the alarmed tributary unit is located. Then, check whether
the alarm is cleared.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
290
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
If...
A Alarm Reference
Then...
The alarm is cleared The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the system control and cross-connect board on the
local NE.
----End
Related Information
If EFP8 reports the alarm, the alarm parameters have the meanings listed inTable A-5.
Table A-5 Alarm Parameters of EFP8
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
0x01, indicates optical interface number.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicates the number of the path.
A.3.57 DROPRATIO_OVER
Description
The DROPRATIO_OVER alarm indicates that the number of lost packets crosses the threshold
when queue congestion occurs at a port. This alarm is reported when the ratio of lost packets on
an object under performance monitoring is higher than the expected ratio.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the direction in which traffic crosses the threshold.
l 0x00: Traffic crosses the threshold in the receive direction.
l 0x01: Traffic crosses the threshold in the transmit direction.
Impact on the System
Service packet loss occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
291
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Service configuration is incorrect.
Cause 2: Actual traffic exceeds the configured port bandwidth or committed information
rate (CIR).
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Service configuration is incorrect.
1.
Check and reconfigure services according to the network plan.
Step 2 Cause 2: Actual traffic exceeds the configured port bandwidth or CIR.
1.
8.17 Querying Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth Utilization of Ethernet
Ports. If traffic is large, check whether a network storm has occurred, and eliminate the
source that illegally sends a large amount of data.
2.
If the port bandwidth is too low, follow instructions in Modifying Port Policies to increase
port bandwidth or expand the network.
----End
Related Information
If packet loss is indicated in the receive direction, check the method of handling red packets in
the traffic classification configuration. If the method of handling red packets is non-discard,
packets may not be actually lost in the receive direction.
A.3.58 E1_LOC
Description
The E1_LOC is an alarm indicating that the uplink 2M clock is lost. This alarm occurs when
the tributary board fails to extract the clock from the E1 signal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the E1_LOC occurs, the service is not affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The opposite NE is faulty.
Cause 2: The wiring sequence of the cable is incorrect.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
292
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 3: The receive unit of the tributary board on the local NE is faulty.
Cause 4: The input E1 signal has an abnormal waveform.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The opposite NE is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault on the opposite NE.
Step 2 Cause 2: The wiring sequence of the cable is incorrect.
1.
Redo the cable.
Step 3 Cause 3: The receive unit of the tributary board on the local NE is faulty.
1.
Replace the board where the line unit is located.
Step 4 Cause 4: The input E1 signal has an abnormal waveform.
1.
Check whether any external interference causes the abnormal waveform of the E1 signal.
If...
Then...
There is the external interference
The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
There is no external interference
Contact Huawei engineers.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.59 E1_LOS
Description
The E1_LOS is an alarm indicating the loss of the E1 signal. This alarm occurs when the tributary
board detects the uplink E1 signal of all 0s.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the E1_LOS alarm occurs, the E1 service is interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
293
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The cable is not connected or the cable is faulty.
Cause 2: The opposite NE is faulty.
Cause 3: The tributary board on the local NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The cable is not connected or the cable is faulty.
1.
Check whether the cable is connected properly.
If...
Then...
The cable is not connected properly
Connect the cable properly.
The cable is prepared incorrectly
Redo the cable.
Step 2 Cause 2: The opposite NE is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault on the opposite NE.
Step 3 Cause 3: The tributary board on the local NE is faulty.
1.
Replace the board where the tributary unit is located.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.60 ENVHUM_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The ENVHUM_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the ambient humidity sensor of the
cabinet fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The ambient humidity data of the PMU cannot be collected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
294
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The ambient humidity sensor is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The ambient humidity sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The ambient humidity sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the ambient humidity sensor.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: The ambient humidity sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the ambient humidity sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.61 ENVTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The ENVTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the ambient temperature sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
295
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The ambient temperature data of the TCU cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The ambient temperature sensor is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The ambient temperature sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The ambient temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the ambient temperature sensor.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: The ambient temperature sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the ambient temperature sensor.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
296
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.62 ENVTEMP1_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The ENVTEMP1_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that ambient temperature sensor 1 of
the cabinet fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Ambient temperature data 1 of the PMU cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Ambient temperature sensor 1 is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: Ambient temperature sensor 1 is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Ambient temperature sensor 1 is faulty.
1.
Replace ambient temperature sensor 1.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
297
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: Ambient temperature sensor 1 is not installed.
1.
Install ambient temperature sensor 1.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.63 ENVTEMP2_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The ENVTEMP2_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that ambient temperature sensor 2 of
the cabinet fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Ambient temperature data 2 of the PMU cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Ambient temperature sensor 2 is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: Ambient temperature sensor 2 is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Ambient temperature sensor 2 is faulty.
1.
Replace ambient temperature sensor 2.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
298
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: Ambient temperature sensor 2 is not installed.
1.
Install ambient temperature sensor 2.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.64 ETH_APS_LOST
Description
The ETH_APS_LOST is an alarm indicating that the APS frame is lost. This alarm occurs when
no APS frame is received from the protection channel.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the APS protection may fail.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: The opposite NE is not configured with the APS protection.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
299
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The APS protection group is deactivated.
Cause 3: The settings of the APS protection group differ between the two ends.
Cause 4: The service on the protection channel is interrupted.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The opposite NE is not configured with the APS protection.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the opposite NE is configured with the APS protection. For
details, see Querying MPLS APS Status.
If...
Then...
The opposite NE is not configured with the APS protection
Go to the next step.
The opposite NE is configured with the APS protection
Go to Cause 2.
2.
Create a matching APS protection group on the opposite NE, and activate the APS protocol.
Check whether the alarm clears.
3.
If the alarm persists, proceed to cause 4.
Step 2 Cause 2: The APS protection group is deactivated.
1.
2.
Check whether the APS protocol is activated at both ends.
If...
Then...
The APS protocol is deactivated at one end
Activate the APS protocol at the end.
The APS protocol is activated at both ends
Go to Cause 3.
Check whether the alarm clears. If the alarm persists, go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The settings of the APS protection group differ between the two ends.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the settings of the APS protection group are the same at the
two ends. If the settings differ between the two ends, change them to the same. Then,
deactivate and activate the APS protection group at the two ends.
2.
Check whether the alarm clears. If the alarm persists, go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The service on the protection channel is interrupted.
1.
Check whether the protection channel reports an alarm related to signal loss or signal
degrade, such as ETH_LOS. If yes, clear the alarm immediately.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.65 ETH_APS_PATH_MISMATCH
Description
The ETH_APS_PATH_MISMATCH is an alarm indicating that the working and protection
paths of the APS protection group differ between the two ends. This alarm is reported when the
working and protection paths of one APS protection group at one end are different from those
at the other end.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
300
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, service protection fails.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The configured working and protection paths differ between the two ends.
Cause 2: The physical link is connected incorrectly.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The configured working and protection paths differ between the two ends.
1.
Check whether the APS settings at the two ends are the same. For details, see Querying
MPLS APS Status.
2.
If the APS settings are different, change the settings to the same. Then, deactivate and
activate the APS protection group at the two ends. Then, check whether the alarm clears.
3.
If the alarm persists, go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The physical link is connected incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the fiber or cable is correctly connected between the two ends. If not,
connect the fiber or cable properly.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.66 ETH_APS_SWITCH_FAIL
Description
The ETH_APS_SWITCH_FAIL is an alarm of a protection switching failure. This alarm is
reported when the request signal in the transmitted Automatic Protection Switching (APS) frame
is different from the bridge signal in the received APS frame and this symptom lasts for 50 ms.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
301
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, service protection fails.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The settings of the APS protection group differ between the two ends.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The settings of the APS protection group differ between the two ends.
1.
Change the settings to the same. For details, see Creating an MPLS APS Protection Group.
Then, deactivate and activate the APS protection group at the two ends.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.67 ETH_APS_TYPE_MISMATCH
Description
The ETH_APS_TYPE_MISMATCH is an alarm of protection scheme mismatch. This alarm is
reported when the information in the received Automatic Protection Switching (APS) frame is
different from the APS settings at the local end.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
302
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the specific difference.
l 0x01: Indicates that the switching type is different.
l 0x02: Indicates that the switching direction is different.
l 0x03: Indicates that the revertive mode is different.
Impact on the System
This alarm may cause the APS protection failure, and therefore the service protection fails.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The switching type is different.
Cause 2: The switching direction is different.
Cause 3: The revertive mode is different.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the possible cause of the alarm according to the alarm parameters.
1.
Change the settings of the APS protection group to the same at the two ends. For details,
see Querying MPLS APS Status. Then, deactivate and activate the APS protection group
at the two ends.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.68 ETH_CFM_LOC
Description
The ETH_CFM_LOC is an alarm indicating the loss of connectivity. This alarm occurs when
the system fails to receive the CCM packet from the remote MEP in 3.5 connectivity check (CC)
periods successively.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
303
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2, Parameter 3,
Parameter 4 (Port)
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 5, Parameter 6 (VLAN ID)
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Parameter 7 (Direction)
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Parameter 8 (Level)
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low)
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium)
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high)
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low)
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high)
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low)
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium)
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high)
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates the
supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
Parameter 9, Parameter 10 (RMEPID)
Indicates the ID of the remote MEP.
Impact on the System
l
When the ETH_CFM_LOC alarm occurs, the LB and LT detection functions of Ethernet
service OAM are unavailable.
The service between the relevant standard MEPs may be interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line between the local standard MEP and the remote standard MEP is
interrupted.
Cause 2: The Ethernet service in the maintenance association (MA) to which the local MEP
belongs is faulty.
Cause 3: Serious congestion occurs on the network.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line between the local standard MEP and the remote standard MEP is interrupted.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the physical links (such as network cables and fibers) between the standard
MEPs are connected properly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
304
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The physical links are connected improperly
Connect the physical links properly.
The physical links are connected properly
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The Ethernet service in the maintenance association (MA) to which the local MEP
belongs is faulty.
1.
Check whether Ethernet service in the maintenance association (MA) to which the local
MEP belongs is configured correctly.
If...
Then...
The service is configured incorrectly Modify the configuration of the service to ensure
consistency at two ends.
The service is configured correctly
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Serious congestion occurs on the network.
1.
Check the utilization of bandwidth. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth
or eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
The Table A-6 describes the meanings of the parameters in the ETH_CFM_LOC alarm reported
by the EoS/EoPDH plane.
Table A-6 Alarm Parameters
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4
MD
Parameter 5 to Parameter 8
MA
Parameter 9, Parameter 10
MEP ID
Parameter 11 to Parameter 14
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
When these parameters indicate the
VCTRUNK ID, parameter values = (0x01 0x10) + 0x80.
Parameter 15, Parameter 16
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Parameter 17
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
305
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 18
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low)
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium)
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high)
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low)
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high)
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low)
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium)
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high)
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates
the supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
Parameter 19, Parameter 20
Indicates the ID of the remote MEP.
NOTE
If the alarmed port is a VCTRUNK, these
parameters are not supported.
A.3.69 ETH_CFM_MISMERGE
Description
The ETH_CFM_MISMERGE is an alarm indicating an incorrect connection. This alarm occurs
when the system receives the CCM packet whose MA mismatches or whose priority is lower.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2, Parameter 3,
Parameter 4 (Port)
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 5, Parameter 6 (VLAN ID)
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
306
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 7 (Direction)
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Parameter 8 (Level)
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low)
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium)
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high)
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low)
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high)
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low)
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium)
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high)
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates the
supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
Impact on the System
When the ETH_CFM_MISMERGE alarm occurs, the service between the relevant standard
MEPs may be interrupted, and the data flow may be routed incorrectly.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The names of the maintenance domain and the maintenance alliance that the
standard MEPs correspond to are inconsistent.
Cause 2: The levels of the maintenance domains that the standard MEPs correspond to are
different.
Cause 3: The physical connection is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The names of the maintenance domain and the maintenance alliance that the standard
MEPs correspond to are inconsistent.
1.
Check whether the names of the maintenance domain and the maintenance alliance that the
standard MEPs correspond to are consistent.
If...
Then...
The names are inconsistent Set the other names of maintenance domain and
maintenance alliance to ensure consistency at both ends.
The names are consistent
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The levels of the maintenance domains that the standard MEPs correspond to are
different.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
307
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether the MD levels of the standard MEPs are the same.
If...
Then...
The levels are different Set the MD levels again to ensure consistency at both ends.
The levels are the same Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The physical connection is incorrect.
1.
Check the physical connection of the Ethernet service route and rectify the fault of the
physical connection if any.
----End
Related Information
The Table A-7 describes the meanings of the parameters in the ETH_CFM_LOC alarm reported
by the EoS/EoPDH plane.
Table A-7 Alarm Parameters
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4
MD
Parameter 5 to Parameter 8
MA
Parameter 9, Parameter 10
MEP ID
Parameter 11 to Parameter 14
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
When these parameters indicate the
VCTRUNK ID, parameter values = (0x01 0x10) + 0x80.
Parameter 15, Parameter 16
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Parameter 17
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
308
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 18
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low)
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium)
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high)
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low)
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high)
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low)
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium)
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high)
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates
the supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
A.3.70 ETH_CFM_RDI
Description
The ETH_CFM_RDI is an alarm indicating the CCM packet with RDI received from the remote
MEP. This alarm occurs when the system receives the CCM packet with RDI from the remote
maintenance end point (MEP).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2, Parameter 3,
Parameter 4 (Port)
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 5, Parameter 6 (VLAN ID)
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
309
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 7 (Direction)
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Parameter 8 (Level)
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low).
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium).
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high).
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low).
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high).
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low).
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium).
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high).
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates the
supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
Parameter 9, Parameter 10 (RMEPID)
Indicates the ID of the remote MEP.
Impact on the System
l
When the ETH_CFM_RDI alarm occurs, the loopback (LB) and link trace (LT) detection
functions of Ethernet service OAM are unavailable.
The service between the relevant standard MEPs may be interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The remote MEP fails to receive the correct CCM packet.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The remote MEP fails to receive the correct CCM packet.
1.
Determine the alarmed port according to the alarm parameter.
2.
Check whether the remote MEP that is connected to the port reports the
ETH_CFM_MISMERGE, ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI, or ETH_CFM_LOC alarm.
----End
Related Information
The Table A-8 describes the meanings of the parameters in the ETH_CFM_LOC alarm reported
by the EoS/EoPDH plane.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
310
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Table A-8 Alarm Parameters
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4
MD
Parameter 5 to Parameter 8
MA
Parameter 9, Parameter 10
MEP ID
Parameter 11 to Parameter 14
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
When these parameters indicate the
VCTRUNK ID, parameter values = (0x01 0x10) + 0x80.
Parameter 15, Parameter 16
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Parameter 17
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Parameter 18
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low)
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium)
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high)
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low)
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high)
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low)
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium)
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high)
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates
the supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
Parameter 19, Parameter 20
Indicates the ID of the remote MEP.
NOTE
If the alarmed port is a VCTRUNK, these
parameters are not supported.
A.3.71 ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI
Description
The ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI is an alarm indicating the errored frame. This alarm occurs when
the system receives invalid CCM packets.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
311
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2, Parameter 3,
Parameter 4 (Port)
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 5, Parameter 6 (VLAN ID)
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Parameter 7 (Direction)
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Parameter 8 (Level)
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low)
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium)
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high)
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low)
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high)
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low)
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium)
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high)
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates the
supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
Impact on the System
l
When the ETH_CFM_UNEXPERI alarm occurs, the LB and LT detection functions of
Ethernet service OAM are unavailable.
The service may become abnormal due to the loop.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: No remote MEP is configured.
Cause 2: The configuration of the MEPs at both ends is inconsistent. For example, the
connectivity check (CC) periods are different, and the IDs of the MEPs are in conflict.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
312
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 3: The service is looped back and the looped packet is received.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: No remote MEP is configured.
1.
Check whether the remote MEP is configured. If not, configure the remote MEP first.
Step 2 Cause 2: The configuration of the MEPs at both ends is inconsistent. For example, the
connectivity check (CC) periods are different, and the IDs of the MEPs are in conflict.
1.
Check whether the CC periods set at the MEPs are the same.
If...
Then...
The CC periods are different Change the CC periods to ensure consistency at both
ends.
The CC periods are the same Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the IDs of the MEPs in the maintenance domain are in conflict.
If...
Then...
The IDs are in conflict
Change the conflicting IDs.
The IDs are not in conflict
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The service is looped back and the looped packet is received.
1.
Check whether any loop exists at each IP port of the service trail. If yes, release the loop
and clear the alarm.
----End
Related Information
The Table A-9 describes the meanings of the parameters in the ETH_CFM_LOC alarm reported
by the EoS/EoPDH plane.
Table A-9 Alarm Parameters
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4
MD
Parameter 5 to Parameter 8
MA
Parameter 9, Parameter 10
MEP ID
Parameter 11 to Parameter 14
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
When these parameters indicate the
VCTRUNK ID, parameter values = (0x01 0x10) + 0x80.
Parameter 15, Parameter 16
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
313
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 17
Indicates the direction of the local MEP.
l 0x00: The port is direction insensitive.
l 0x01: The port is in the ingress direction.
l 0x02: The port is in the egress direction.
Parameter 18
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
l 0x00: consumer MEP level (low)
l 0x01: consumer MEP level (medium)
l 0x02: consumer MEP level (high)
l 0x03: provider MEP level (low)
l 0x04: provider MEP level (high)
l 0x05: operator MEP level (low)
l 0x06: operator MEP level (medium)
l 0x07: operator MEP level (high)
NOTE
Consumer indicates the user, provider indicates
the supplier, and operator indicates the carrier.
A.3.72 ETH_EFM_DF
Description
The ETH_EFM_DF is an alarm indicating negotiation failure. This alarm occurs when the pointto-point OAM protocol negotiation fails at the Ethernet port.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
314
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the reason why the negotiation fails.
l 0x01: The local link is faulty.
l 0x02: The local end fails to receive any OAM packets in a specified period.
l 0x03: The OAM settings of the opposite end do not meet the requirements of
the local end.
l 0x04: The OAM settings of the local end do not meet the requirements of the
opposite end.
Impact on the System
When the ETH_EFM_DF alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed port may be interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The physical port of the local end is faulty.
Cause 2: The point to point OAM protocol is not enabled at the opposite end.
Cause 3: The OAM configuration at both ends is inconsistent.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The physical port of the local end is faulty.
1.
Check whether the physical port is faulty. If yes, replace the board where the Ethernet
port is located.
Step 2 Cause 2: The point to point OAM protocol is not enabled at the opposite end.
1.
Enable the point to point OAM protocol at the opposite end.
Step 3 Cause 3: The OAM configuration at both ends is inconsistent.
1.
Reconfigure the point to point OAM protocol and ensure the consistency at both ends.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.73 ETH_EFM_EVENT
Description
The ETH_EFM_EVENT is an alarm indicating the performance event reported on the opposite
NE. This alarm occurs when the local end receives the link error indication packet (OAMPDUM)
from the opposite end.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
315
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the type of the link event.
l 0x01: errored symbol period.
l 0x02: errored frame.
l 0x03: errored frame period.
l 0x04: errored frame seconds summary.
Impact on the System
When the ETH_EFM_EVENT alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed port may be interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The physical port at the local end is faulty.
Cause 2: The equipment at the opposite end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The physical port at the local end is faulty.
1.
Check whether the physical port is faulty. If yes, replace the board where the Ethernet
port is located.
Step 2 Cause 2: The equipment at the opposite end is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the equipment at the opposite end.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.74 ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
316
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK is an alarm indicating the loopback. This alarm occurs when the
local end initiates a loopback or responds to a loopback request from the opposite end.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the state of the loopback.
l 0x01: The local end initiates a loopback.
l 0x02: The local end responds to a loop request from the opposite end.
Impact on the System
When the ETH_EFM_LOOPBACK alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed port is looped back.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The local end initiates a loopback.
Cause 2: The opposite end initiates a loopback.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local end initiates a loopback.
1.
According to the alarm parameter, it is determined that the local end initiates a loopback.
Determine the causes of the loopback initiated at the local end and release the loopback as
soon as possible.
Step 2 Cause 2: The opposite end initiates a loopback.
1.
According to the alarm parameter, it is determined that the opposite end initiates a loopback.
Determine the causes of the loopback initiated at the opposite port and release the loopback
as soon as possible.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
317
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.75 ETH_EFM_REMFAULT
Description
The ETH_EFM_REMFAULT is an alarm indicating the fault on the opposite NE. This alarm
occurs when the local end receives the fault indication packet (OAMPDUM) from the opposite
end.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the fault type at the opposite end.
l 0x01: link fault.
l 0x02: dying gasp.
l 0x03: critical event.
Impact on the System
When the ETH_EFM_REMFAULT alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed port may be
interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The opposite NE is reset.
Cause 2: The opposite NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The opposite NE is reset.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the opposite NE is reset frequently.
If...
Then...
The opposite NE is reset frequently
Rectify the fault on the opposite NE.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
318
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
If...
A Alarm Reference
Then...
The opposite NE is not reset frequently Reset the opposite NE, and the alarm is
cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The opposite NE is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault on the opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.76 ETH_LOS
Description
The ETH_LOS is an alarm indicating the loss of Ethernet port connection.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the ETH_LOS alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed port is interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The negotiation fails because the transmit port and receive port work in different
modes.
Cause 2: The cable or fiber is faulty.
Cause 3: The local NE is faulty.
Cause 4: The opposite NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The negotiation fails because the transmit port and receive port work in different modes.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the transmit port and receive port work in the same mode.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
319
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The transmit port and receive port work Correctly set the working modes of the
in different modes
transmit port and receive port.
The transmit port and receive port work Go to Cause 2.
in the same mode
Step 2 Cause 2: The cable or fiber is faulty.
1.
Check the network cable or fiber jumper connected to the alarmed port.
If...
Then...
The network cable is loose or damaged
Connect the network cable properly or
replace the damaged network cable.
The connector of the fiber jumper is dirty Clean the connector.
The connector or fiber is damaged
Insert the connector properly or replace the
damaged fiber jumper.
The connection is normal
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The local NE is faulty.
1.
Check whether any fault occurs on the alarmed port.
If...
Then...
The equipment is faulty
Replace the alarmed board on the local NE.
The equipment is normal
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The opposite NE is faulty.
1.
Check whether any fault occurs on the equipment interconnected with the alarmed port.
2.
Rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.77 ETH_NO_FLOW
Description
The ETH_NO_FLOW is an alarm indicating that the Ethernet port has no flow. This alarm is
reported when an enabled Ethernet port is in link up state but has no flow.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
320
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the MAC port number.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the path ID.
Parameter 2 indicates the most significant bits and the value is
always 0x00. Parameter 3 indicates the least significant bits and the
value is always 0x01.
Parameter 4
Indicates the direction in which the flow is unavailable.
l 0x00: Rx direction.
l 0x01: Tx direction.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, it indicates that the alarmed port has no flow.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The port is enabled and in link up state, but is configured with no service.
Cause 2: The port is enabled and in link up state, but does not transmit any packet due to
the service fault at the local end.
Cause 3: The port is enabled and in link up state, but does not receive any packet due to
the service fault at the remote end.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the MAC port number, alarmed board, and cause according to the parameters.
Step 2 Cause 1: No services are configured.
1.
Configure the Ethernet service.
Step 3 Cause 2: No services are available.
If...
Then...
No services are available in the transmit
direction
Check whether the service is normal at the
local end.
No services are available in the receive
direction
Check whether the service is normal at the
remote end.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
321
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.78 ETHOAM_DISCOVER_FAIL
Description
The ETHOAM_DISCOVER_FAIL alarm indicates a discovery failure when the point-to-point
ETH-OAM function is enabled. This alarm occurs when the OAM function is enabled at a port
of a board and the negotiation between the port and the opposite equipment fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 The values are always 0x00 0x01.
Parameter 4
Indicates the reason why the negotiation fails.
l 0x01: A fault occurs at the local receive link.
l 0x02: The local end fails to transmit OAM packets.
l 0x03: The OAM packets from the opposite end are not received.
l 0x04: The OAM configuration of the opposite end does not meet
the requirements of the local end.
l 0x05: The OAM configuration of the local end does not meet
the requirements of the opposite end.
l 0x06-0xff: other unknown reasons.
Impact on the System
The OAM function based on IEEE 802.3ah is unavailable.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
322
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The physical port of the local end is faulty.
Cause 2: The P2P OAM protocol is not enabled at the opposite end.
Cause 3: The OAM configuration at both ends is inconsistent.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The physical port of the local end is faulty.
1.
Check whether the physical port is faulty. If yes, replace the alarmed board.
Step 2 Cause 2: The P2P OAM protocol is not enabled at the opposite end.
1.
Enable the P2P OAM protocol at the opposite end. For details, see Enabling the OAM
Auto-Discovery Function.
Step 3 Cause 3: The OAM configuration at both ends is inconsistent.
1.
Reconfigure the P2P OAM protocol and ensure the consistency at both ends. For details,
see Enabling the OAM Auto-Discovery Function.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.79 ETHOAM_RMT_CRIT_FAULT
Description
The ETHOAM_RMT_CRIT_FAULT is an alarm indicating that the point-to-point Ethernet
OAM detects a critical fault at the remote end. This alarm occurs when a port with the OAM
function enabled receives the OAM packets that contain critical fault information from the
opposite end.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
323
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 The values are always 0x00 0x01.
Parameter 4
Indicates the type of the fault.
l 0x01: A link fault occurs at the port of the opposite end.
l 0x02: Irrecoverable problems such as the power failure occur at
the opposite end.
l 0x03-0xff: other faults.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the services on the link may be interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A link fault occurs at the remote MEP.
Cause 2: Irrecoverable problems such as power failure occur at the remote MEP.
Cause 3: Other faults occur at the remote MEP.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the fault type according to Parameter 4.
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x01
Go to Cause 1.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x02
Go to Cause 2.
Parameter 4 is a value from 0x03 to 0xff.
Go to Cause 3.
Step 2 Cause 1: A link fault occurs at the remote MEP.
1.
Handle the ETH_LOS alarm at the remote port.
Step 3 Cause 2: Irrecoverable problems such as power failure occur at the remote MEP.
1.
Handle the problems such as power failure at the remote MEP, and recover the power supply
to the remote MEP.
Step 4 Cause 3: Other faults occur at the remote MEP.
1.
Contact Huawei technical support engineers.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
324
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.80 ETHOAM_RMT_LOOP
Description
The ETHOAM_RMT_LOOP is an alarm indicating that a remote loopback is initiated when the
point-to-point Ethernet OAM function is enabled. This alarm occurs when the local equipment
initiates a remote loopback or responds to the remote loopback initiated by the opposite
equipment.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
The values are always 0x00 0x01.
Parameter 4
l 0x01: The loopback is initiated.
l 0x02: The loopback is responded.
Impact on the System
The services are looped back between the local equipment and the opposite equipment. The
services and other protocol packets are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The local end issues a loopback command and the opposite end responds to the
command.
Cause 2: The opposite end issues a loopback command and the local end responds to the
command.
Procedure
Step 1 Check the alarm on the NMS and determine the type of loopback according to the alarm
parameters.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
325
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x01
Go to Cause 1.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x02
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 1: The local end issues a loopback command and the opposite end responds to the
command.
1.
Determine the causes of the loopback at the local end and release the loopback.
Step 3 Cause 2: The opposite end issues a loopback command and the local end responds to the
command.
1.
Determine the causes of the loopback at the opposite end and release the loopback.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.81 ETHOAM_RMT_SD
Description
The ETHOAM_RMT_SD alarm indicates that the point-to-point Ethernet-OAM detects the
degradation of remote Ethernet performance. This alarm occurs when a port with the OAM
function enabled receives link event notification packets from the opposite end.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
The values are always 0x00 0x01.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
326
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 4
Indicates the type of the received link event.
l 0x01: errored frame event
l 0x02: errored frame period event
l 0x03: errored frame second event
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the performance of services degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The link event notification function is enabled at the opposite end.
Cause 2: The link performance thresholds of the opposite end are inappropriate.
Cause 3: The link performance deteriorates.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The link event notification function is enabled at the opposite end.
1.
Check whether the link event notification function is enabled at the opposite end.
If...
Then...
If yes
Disable the link event notification function at the opposite end.
If not
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The link performance thresholds of the opposite end are inappropriate.
1.
Check whether the link performance thresholds of the opposite end are appropriate.
If...
Then...
If not
Set the thresholds to appropriate values.
If yes
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The link performance deteriorates.
1.
Improve the link performance at the opposite end so that the opposite end does not send
any link event notification packet to the local end. Then, the alarm at the local end is cleared
automatically.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
327
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.82 ETHOAM_SELF_LOOP
Description
The ETHOAM_SELF_LOOP is an alarm indicating the loopback of the MAC port that runs the
point-to-point OAM protocol. This alarm occurs when the MAC port of a board receives the
OAM protocol packet sent by the port itself or the board after the loop detection function is
enabled.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Environmental alarms
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the loopback type.
l 0x01: selfloop of the port.
l 0x02: selfloop of the board.
Impact on the System
When the ETHOAM_SELF_LOOP alarm occurs, a network storm may occur due to the
loopback.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The cable connected to the port is self-looped, or the port is connected to a LAN
that has a loopback, or the PHY/MAC loopback is manually configured at the port.
Cause 2: Two ports of the board are connected through cables or two ports of the board are
connected to the same LAN.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the loopback type according to Parameter 1, and then handle the loopback
accordingly.
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 1 is 0x01
Go to Cause 1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
328
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 1 is 0x02
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 1: The cable connected to the port is self-looped, or the port is connected to a LAN that
has a loopback, or the PHY/MAC loopback is manually configured at the port.
If...
Then...
The PHY/MAC loopback is manually
configured at the port
Manually release the PHY/MAC loopback (or
wait five minutes for the automatic release by
the NE if the automatic loopback release
function is enabled on the NE). Then, the
selfloop is released.
The cable connected to the port is selflooped
Connect the cable properly to release the
selfloop.
The port is connected to a LAN that has a
loopback
Release the loopback on the LAN, or break the
connection between the port and the LAN, to
release the selfloop.
Step 3 Cause 2: Two ports of the board are connected through cables or two ports of the board are
connected to the same LAN.
1.
Check whether two ports of the board are connected through cables or whether two ports
of the board are connected to the same LAN.
If...
Then...
The two ports are connected through
cables
Disconnect the cables to release the
selfloop.
The two ports are connected to the same Break the connection between a port and the
network
LAN to release the selfloop.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.83 ETHOAM_VCG_SELF_LOOP
Description
The ETHOAM_VCG_SELF_LOOP alarm indicates that a VCTRUNK port is looped back when
the point-to-point Ethernet OAM function is enabled. This alarm occurs when the loopback
detection function is enabled and the VCTRUNK port receives the OAM protocol packets
transmitted by the port itself or the board where the VCTRUNK port resides.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
329
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Environment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the loopback type.
l 0x01: The port is self-looped.
l 0x02: The board is self-looped.
l 0x03-0xff: unknown types.
Impact on the System
If the function of automatic shutdown in the case of a selfloop is enabled at the alarmed port,
the services at the alarmed port are interrupted. Otherwise, a network storm may occur.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A loopback occurs on the lines connected to one VCTRUNK.
Cause 2: The lines connected to two VCTRUNKs on the same board are interconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Check the alarm on the NMS and determine the type of loopback according to the alarm
parameters.
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x01
Go to Cause 1.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x02
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 1: The port is self-looped.
1.
Release the loopback at the port.
2.
Reconfigure the lines connected to the VCTRUNK port and ensure that the port is not selflooped.
Step 3 Cause 2: The board is self-looped.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
330
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Reconfigure the lines connected to the VCTRUNK ports and ensure that the lines connected
to any two VCTRUNK ports on the same board are not interconnected.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.84 EX_ETHOAM_CC_LOS
Description
The EX_ETHOAM_CC_LOS is an alarm indicating the loss of periodic connectivity check
(CC) packets. This alarm occurs when the sink MEP fails to receive CC packets from the same
source MEP in a period (3.5 transmission periods of CC packets at the source MEP).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4
Indicates the ID of the remote MEP.
Parameter 5 to Parameter 8
Indicates the ID of the local MEP.
Parameter 9, Parameter 10
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
l PORT number, Parameter 9 is 0x00.
l VCTRUNK number, Parameter 9 is 0x80.
Parameter 11, Parameter 12
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Parameter 13
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
Parameter 14 to Parameter 17
Indicates the ID of the remote MEP.
Parameter 18 - Parameter 21
Indicates the ID of the local MEP.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
331
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
A unidirectional connectivity failure occurs in the Ethernet service between two MEPs.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line between two MEPs is interrupted.
Cause 2: The Ethernet services in the MA to which the alarmed MEP belongs are faulty.
Cause 3: The services between two MEPs are congested or interrupted.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line between two MEPs is interrupted.
1.
Check whether the physical links (such as network cables or optical fibers) that carry
services between the two MEPs are correctly connected.
If...
Then...
If not
Re-connect the cables to rectify the faults on physical links.
If yes
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The Ethernet services in the MA to which the alarmed MEP belongs are faulty.
1.
Check whether the Ethernet services in the MA to which the alarmed MEP belongs are
configured correctly.
If...
Then...
If not
Modify the configuration to ensure consistency at both ends.
If yes
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The services between two MEPs are congested or interrupted.
1.
Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.85 EX_ETHOAM_MPID_CNFLCT
Description
The EX_ETHOAM_MPID_CNFLCT is an alarm indicating the conflict of MPIDs. This alarm
occurs when two MEPs in one MD have the same maintenance point identity (MPID) and one
MEP receives the packets from the other MEP.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
332
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Environment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4
Indicates the ID of the local MEP.
Parameter 5, Parameter 6
Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
l PORT number, Parameter 9 is 0x00.
l VCTRUNK number, Parameter 9 is 0x80.
Parameter 7, Parameter 8
Indicates the VLAN ID of the MEP.
Parameter 9
Indicates the MD level of the local MEP.
Parameter 10 to Parameter 13
Indicates the ID of the local MEP.
Impact on the System
MPIDs must be unique on a network. When this alarm occurs, the LB and LT functions are
abnormal and OAM packets are received incorrectly.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: At least two MEPs in an MD have the same MPID.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: At least two MEPs in an MD have the same MPID.
1.
Check the alarm on the NMS and determine the associated MP ID according to the alarm
parameters.
2.
Query the information about the MEP. Delete the incorrect MEPs and create MEPs with
unique MP IDs.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
333
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.86 EXT_SYNC_LOS
Description
The EXT_SYNC_LOS is an alarm of the loss of the external clock source.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
l
When the EXT_SYNC_LOS alarm occurs, if only the external clock source and internal
clock source are configured in the clock source priority list, the NE traces the internal clock
source after the external clock source is lost and enters the free-run state 24 hours later.
If another valid clock source of higher priority and good quality is configured in the clock
source priority list, however, the clock protection switching occurs.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The external clock source is configured in the clock source priority list, but the external
clock source cannot be detected or become invalid.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The external clock source is configured in the clock source priority list, but the external
clock source cannot be detected or become invalid.
1.
2.
Check whether the equipment that provides the external clock source is faulty.
If...
Then...
The equipment is faulty
Rectify the fault.
The equipment is normal
Go to the next step.
Check whether the cable that connects the external clock source is normal.
If...
Then...
The cable is abnormal
Replace the cable.
The cable is normal
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
334
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.87 FAN_AGING
Description
The FAN_AGING is an alarm of the aged fan. This alarm occurs when the fan rotates at a speed
lower than eighty percent of the nominal speed.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the number of the alarmed fan.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the temperature of the NE is too high and impacts the long-term
operation of the NE.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The fan is aged.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The fan is aged.
1.
Replace the fan.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.88 FAN_FAIL
Description
The FAN_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the fan is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
335
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the number of the fan.
Impact on the System
When the FAN_FAIL alarm occurs, the heat dissipation of the system is affected.
After an alarm is reported, clear it immediately. Otherwise, services may be interrupted or
equipment may be damaged.
When a fan is faulty, perform the following operations:
l
Replace the faulty fan with one that works properly within a period of 96 hours if the
ambient temperature ranges from 0C to 40C .
Replace the faulty fan with one that works properly within a period of 24 hours if the
ambient temperature is higher than 40C .
When multiple fans are faulty, replace them immediately.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The board and the backplane are connected improperly.
Cause 2: Fan failure occurs.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The board and the backplane are connected improperly.
1.
Remove the fan board. Clean the dust on the fan and reinsert the fan board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
removed and inserted
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
removed and inserted
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: Fan failure occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
336
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Replace the alarmed fan board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.89 FCS_ERR
Description
The FCS_ERR is an alarm indicating the errors of frame check sequence (FCS). This alarm
occurs when a board detects FCS errors in the received frames.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the VCTRUNK number where the alarm occurs.
Impact on the System
When the FCS_ERR alarm occurs, if the encapsulation protocols or encapsulation parameters
are inconsistent at both ends of Ethernet services, the services may have errors and even become
interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The encapsulation protocols or encapsulation parameters are inconsistent at both
ends of services.
Cause 2: Service channels have errors.
Cause 3: The alarmed board is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
337
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The encapsulation protocols or encapsulation parameters are inconsistent at both ends
of services.
1.
2.
Check whether the encapsulation protocols or encapsulation parameters are consistent at
both ends of services.
If...
Then...
The protocols are inconsistent
Correct the configuration data.
The protocols are consistent
Go to the next step.
Check whether the encapsulation parameters are consistent at both ends of services.
If...
Then...
The parameters are inconsistent
Correct the configuration data.
The parameters are consistent
Go to the next step.
Step 2 Cause 2: Service channels have errors.
1.
Check whether any error alarm or performance event occurs on the line board that carries
the services.
If...
Then...
Yes
Handle the alarm or performance event.
No
Go to the next step.
Step 3 Cause 3: The alarmed board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.90 FLOW_OVER
Description
The FLOW_OVER is an alarm indicating that the data flow received by the Ethernet port exceeds
the threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
338
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the receive or transmit direction in which traffic crosses the specified
threshold.
l 0x00: the receive direction
l 0x01: the transmit direction
Impact on the System
When the FLOW_OVER alarm occurs, the extra data may be discarded by the port.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The traffic threshold of the local port is very low.
Cause 2: The opposite end transmits excessive data flow.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The traffic threshold of the local port is very low.
1.
Increase the traffic threshold of the local port to a value that is lower than the rate of the
local port.
Step 2 Cause 2: The opposite end transmits excessive data flow.
1.
Configure the QoS policies at the opposite end to reduce the data flow that the opposite
end transmits.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.91 HARD_BAD
Description
The HARD_BAD is an alarm indicating hardware errors.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
339
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 3
Indicate the internal faults detected by the board.
Impact on the System
The alarmed board fails to work. If the board is configured with the 1+1 protection, protection
switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The board and the backplane are connected improperly.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Cause 3: The slot is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The board and backplane are connected improperly.
1.
Remove and insert the alarmed board. For details, see 6.1 Removing a Board and 6.2
Inserting a Board. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
removed and inserted
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
removed and inserted
Ensure that the board is normal.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the alarmed board, and then check whether the alarm is cleared. For details, see 6
Part Replacement.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
340
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Ensure that the slot is normal.
Step 3 Cause 3: The slot is faulty.
1.
Contact Huawei engineers to handle the faulty slot.
TIP
Generally, the slot becomes faulty due to the broken pin or bent pin. Remove the board, and use a
torch to observe whether there is any broken pin or bent pin.
2.
If a vacant slot is available, insert the board in the vacant slot and add the board again.
Then, the board can work normally.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.92 HP_CROSSTR
Description
The HP_CROSSTR is an alarm indicating that the higher order path error crosses the threshold.
This alarm occurs when the board detects that the performance event that the higher order path
error crosses the preset threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the performance monitoring period:
l 0x01: 15 minutes
l 0x02: 24 hours
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
341
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the ID of a performance event that causes the alarm.
l 0x30: HPBBE
l 0x31: HPES
l 0x32: HPSES
l 0x33: HPFEBBE
l 0x34: HPFEES
l 0x35: HPFESES
l 0x36: HPUAS
l 0x37: HPCSES
l 0x38: HPFECSES
l 0x4c: HPFEUAS
Impact on the System
When the HP_CROSSTR alarm occurs, a large number of errors occur in the service, and the
service may be interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The higher order path error crosses the preset threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The higher order path error crosses the preset threshold.
1.
Check the threshold crossing records to find out the performance event that the higher order
path error crosses the preset threshold. For details, see 8.3.8 Browsing the Performance
Event Threshold-Crossing Records.
2.
Handle the threshold-crossing performance event.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.93 HP_LOM
Description
The HP_LOM is an alarm indicating the loss of the higher order path multiframe. This alarm
occurs when the board detects that byte H4 is inconsistent with the expected multiframe
sequence.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
342
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the HP_LOM alarm occurs, the service on the alarmed path is interrupted. If the services
are configured with protection, protection switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The transmit unit of the opposite NE is faulty.
Cause 2: The receive unit of the local NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The transmit unit of the opposite NE is faulty.
1.
Replace the board where the line unit is located on the opposite NE. Then, check
whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the system control, cross-connect, and timing board
on the opposite NE.
Step 2 Cause 2: The receive unit of the local NE is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.94 HP_RDI
Description
The HP_RDI is an alarm indicating the higher order path remote receive failure. This alarm
occurs when the board detects that bit 5 of byte G1 is 1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
343
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the HP_RDI alarm occurs, the service on the local NE is not affected. The service received
by the opposite NE, however, is interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
higher order path remote receive failure.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
higher order path remote receive failure.
1.
Clear the alarms such as HP_LOM and B3_EXC that the AU-4 path reports on the opposite
NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.95 HP_REI
Description
The HP_REI is an alarm indicating the higher order path remote error. This alarm occurs when
the board detects that bits 1-4 of G1 take a value from 1 to 8.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
344
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The service on the local site is not affected. The service received by the opposite station, however,
has errors.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
higher order path remote errors.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
higher order path remote receive failure.
1.
Handle the HP_BBE performance event that the AU-4 path reports on the opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.96 HP_SLM
Description
The HP_SLM is an alarm indicating the lower order path label mismatch. This alarm occurs
when the board detects the C2 byte mismatch.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The C2 byte received by the local NE does not match with the C2 byte transmitted
by the remote NE.
Cause 2: Configuration data is incorrect.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
345
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The C2 byte received by the local NE does not match with the C2 byte transmitted by
the remote NE.
1.
Configure the same service type at the source and sink of the AU-4 path. For details, see
Configuring Overhead Bytes.
Step 2 Cause 2: Configuration data is incorrect.
1.
If the alarmed port is the SDH port that is interconnected with the ATM/Ethernet equipment,
configure the service as VC-4 pass-through service. For details, see Creating CrossConnections of SNCP Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.97 HP_TIM
Description
The HP_TIM is an alarm indicating the higher order path trace identifier mismatch. This alarm
occurs when the board detects the J1 byte mismatch.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If the service is configured with the protection that considers the HP_TIM alarm as a trigger
condition, the protection switching is triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The receivable J1 byte on the local NE does not match with the J1 byte transmitted
on the opposite NE.
Cause 2: Configuration data is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The receivable J1 byte on the local NE does not match with the J1 byte transmitted on
the opposite NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
346
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Disable the receivable J1 byte on the local NE or set the receivable J1 byte on the local NE
to the same as the transmitted J1 byte on the opposite NE. For details, see Configuring
VC-4 POHs.
Step 2 Cause 2: Configuration data is incorrect.
1.
If the alarmed port is the SDH port that is interconnected with the ATM/Ethernet equipment,
configure the service as VC-4 pass-through service. For details, see Creating CrossConnections of SNCP Services or Creating the Cross-Connections of Point-to-Point
Services.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the configuration The fault is rectified. End the alarm
is changed
handling.
The alarm persists after the configuration
is changed
2.
Go to the next step.
Check whether the cross-connections are configured correctly at the intermediate nodes
where the service travels. If not, reconfigure the cross-connections. For details, see Creating
Cross-Connections of SNCP Services or Creating the Cross-Connections of Point-to-Point
Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.98 HP_UNEQ
Description
The HP_UNEQ is an alarm indicating the unequipped higher order path. This alarm occurs when
the board detects that the C2 byte is 0.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the HP_UNEQ alarm occurs, the service in the alarmed AU-4 path is unavailable. If the
service is configured with the protection that considers the alarm as a trigger condition, the
protection switching is triggered.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
347
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The line port at the local NE is configured with services, but the corresponding
line port at the opposite NE is not configured with services.
Cause 2: Byte C2 is set to 0 at the opposite NE.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The line port at the local NE is configured with services, but the corresponding line
port at the opposite NE is not configured with services.
1.
Configure line services on the opposite NE. For details, see Creating Cross-Connections
of SNCP Services or Creating the Cross-Connections of Point-to-Point Services.
Step 2 Cause 2: Byte C2 is set to 0 at the opposite NE.
1.
Change the setting of byte C2. For details, see Configuring VC-4 POHs.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.99 HPAD_CROSSTR
Description
The HPAD_CROSSTR is an alarm indicating that the higher order path adaptation performance
crosses the threshold. This alarm occurs when a board detects that the performance event of TU
pointer justification crosses the preset threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the performance monitoring period:
l 0x01: 15 minutes
l 0x02: 24 hours
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
348
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the ID of a performance event that causes the alarm.
l 0xaa: TUPJCHIGH
l 0xab: TUPJCLOW
l 0xac: TUPJCNEW
Impact on the System
When the HPAD_CROSSTR alarm occurs, bit errors may occur in the service.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The performance event of TU pointer justification crosses the preset threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The performance event of TU pointer justification crosses the preset threshold.
1.
Check the threshold crossing records to find out the performance event of TU pointer
justification that crosses the preset threshold. For details, see 8.3.8 Browsing the
Performance Event Threshold-Crossing Records.
2.
Handle the threshold-crossing performance event.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.100 IF_CABLE_OPEN
Description
The IF_CABLE_OPEN is an alarm indicating that the IF cable is open.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the IF_CABLE_OPEN alarm occurs, the service on the alarmed IF port is interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
349
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The IF cable is loose or faulty.
Cause 2: The IF port on the IF board is damaged.
Cause 3: The power module of the ODU is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The IF cable is loose or faulty.
1.
Check whether the connector of the IF cable is loose or whether the connector is made
properly.
The connectors to be checked include the connector between the IF fiber jumper and the
IF board, the connector between the IF fiber jumper and the IF cable, and the connector
between the IF cable and the ODU.
If...
Then...
The connector is loose
Connect the connector tightly.
The connector is made improperly See the Installation Reference and make new
connectors for the IF cable.
None of the above
2.
Go to the next step.
Check whether the surface of the IF fiber jumper and the IF cable is damaged.
If...
Then...
The cable does not meet the requirement
Replace the cable with a qualified one.
The cable meets the requirement
Go to Cause 2 or Cause 3.
Step 2 Cause 2: The IF port on the IF board is damaged.
1.
Replace the alarmed IF board.
Step 3 Cause 3: The power module of the ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the ODU connected to the alarmed IF board.
----End
Related Information
NOTE
When rectifying the faults of the IF cable, IF port, and ODU, you must turn off the ODU before the
operation. You can turn on the ODU only after the operation is complete.
A.3.101 IF_INPWR_ABN
Description
The IF_INPWR_ABN is an alarm indicating that the power supplied by an IF board to an ODU
is abnormal.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
350
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
l 0x01: Indicates that the input power of the ODU is too high.
l 0x02: Indicates that the input power of the ODU is too low.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the services on the ODU are interrupted. If 1+1 protection is configured,
this alarm also triggers 1+1 HSB switching.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The IF board is faulty.
Cause 2: The IF cable is faulty.
Cause 3: The ODU is faulty.
Cause 4: The IF fiber jumper and the IF board are connected incorrectly.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The IF board is faulty.
1.
Replace the IF board connected to the alarmed ODU.
Step 2 Cause 2: The IF cable is faulty.
1.
Check whether the connectors of the IF cable are loose or prepared incorrectly.
The connectors to be checked include the connector between the IF fiber jumper and the
IF board, the connector between the IF fiber jumper and the IF cable, and the connector
between the IF cable and the ODU.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If...
Then...
Any of the connectors is loose
Connect the connector tightly.
Any of the connectors is prepared
incorrectly
See the Installation Reference and make
new connectors for the IF cable.
All connectors are normal
Go to the next step.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
351
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether the surface of the IF fiber jumper and the IF cable is damaged or deformed,
and test the connectivity between the IF fiber jumper and the IF cable. For details, see
Testing the Connectivity of the IF Cable.
If...
Then...
The IF cable is below standard
Replace the IF cable.
The IF cable is up to standard
The IF board or ODU may be faulty.
Step 3 Cause 3: The ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed ODU.
Step 4 Cause 4: The IF fiber jumper and the IF board are connected incorrectly.
1.
Connect the IF fiber jumper and the IF board correctly.
----End
Related Information
The logical slot ID of the ODU is obtained by adding 20 to the slot ID of the IF board connected
to the ODU.
A.3.102 IF_MODE_UNSUPPORTED
Description
The IF_MODE_UNSUPPORTED is an alarm indicating that the configured IF working mode
is not supported. This alarm occurs if the board is not loaded with the FPGA file that supports
the configured IF working mode.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
352
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the FPGA file that is loaded to the board.
l 0x01 indicates that FPGA file 250 is loaded.
l 0x02 indicates that FPGA file 002 is loaded.
Impact on the System
When the IF_MODE_UNSUPPORTED alarm occurs, the service on the alarmed IF port is
interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The board is not loaded with the FPGA file that supports the configured IF working
mode, or the FPGA file that supports the configured IF working mode is damaged.
Procedure
l
Cause 1: The board is not loaded with the FPGA file that supports the configured IF working
mode, or the FPGA file that supports the configured IF working mode is damaged.
1.
Contact Huawei engineers to upgrade the software and the FPGA file.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.103 IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN
Description
The IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN is an alarm indicating that the IMA group at the local end fails.
This alarm occurs when the IMA group is in non-Active state on the local NE or when the
activated links of the IMA group on the local NE are less than the minimum number.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, all links of the alarmed IMA group are unavailable.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
353
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The IMA links on the local NE are faulty.
Cause 2: The activated links of the IMA group on the local NE are less than the minimum
number.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The IMA links on the local NE are faulty.
1.
Check whether the T_ALOS alarm is reported at the E1 port. If yes, clear this alarm.
2.
Check whether the IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN alarm is cleared. If the alarm persists,
configure the related services at other ports or replace the related board.
Step 2 Cause 2: The activated links of the IMA group on the local NE are less than the minimum number.
If...
Then...
The ALM_IMA_LIF alarm occurs Clear the ALM_IMA_LIF alarm immediately.
Activate the links of the IMA group on the local NE.
No other alarm occurs
Reconfigure the links of the IMA group on the local
NE.
When the number of activated links of the IMA group reaches the minimum number, the alarm
clears automatically.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.104 IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN
Description
The IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN is an alarm indicating that the IMA group at the remote end
fails. This alarm occurs when the IMA group is in non-Active state on the remote NE or when
the activated links of the IMA group on the remote NE are less than the minimum number.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the ports of the IMA group are congested and services have bit errors.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
354
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The IMA links on the remote NE are faulty.
Cause 2: The activated links of the IMA group on the remote NE are less than the minimum
number.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The IMA links on the remote NE are faulty.
1.
Check whether the T_ALOS alarm is reported at the E1 port. If yes, clear this alarm.
2.
Check whether the IMA_GROUP_RE_DOWN alarm is cleared. If the alarm persists,
configure the related services at other ports or replace the related board.
Step 2 Cause 2: The activated links of the IMA group on the remote NE are less than the minimum
number.
If...
Then...
The ALM_IMA_LIF alarm occurs Clear the ALM_IMA_LIF alarm immediately.
Activate the links of the IMA group on the opposite NE.
No other alarm occurs
Reconfigure the links of the IMA group on the remote
NE.
When the number of activated links of the IMA group reaches the minimum number, the alarm
clears automatically.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.105 IMA_TXCLK_MISMATCH
Description
The IMA_TXCLK_MISMATCH is an alarm indicating that the transmit clock modes of an IMA
group are inconsistent at the two ends.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
355
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The IMA_TXCLK_MISMATCH alarm may cause loss of ATM cells.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The transmit clock modes of an IMA group are inconsistent at the two ends.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The transmit clock modes of an IMA group are inconsistent at the two ends.
1.
Check the alarm information and determine the NE, board, and ATM trunk related to the
alarm.
2.
Modify the Clock Mode parameter of the alarmed ATM trunk to the same value as that of
the opposite end. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
----End
Related Information
The Clock Mode parameter can be set to two modes.
l
CTC mode: Common transmit clock mode. In CTC mode, all transmit clocks of the links
in an IMA group are from the same clock source.
ITC mode: Independent transmit clock mode. In ITC mode, the transmit clocks of the links
in an IMA group are from different clock sources. When the IMA group is set to the line
clock mode, the ITC mode is recommended.
A.3.106 IN_PWR_ABN
Description
The IN_PWR_ABN is an alarm indicating that the input optical power is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the IN_PWR_ABN alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed optical interface has errors
and even becomes unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: The transmit power of the opposite NE is over high or over low.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
356
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The model of the selected optical module is incorrect.
Cause 3: The optical module at the receive end is faulty.
Cause 4: The fiber performance degrades.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The transmit power of the opposite NE is over high or over low.
1.
Browse current performance events, and query the performance event of the transmit
optical power on the opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The transmit optical power does not meet Replace the optical module.
the requirement
The transmit optical power is over high
Add a proper attenuator to reduce the
receive optical power.
Step 2 Cause 2: The model of the selected optical module is incorrect.
1.
Query the board manufacturing information report, and check whether the models of
the SFP optical modules used at both ends are correct.
If...
Then...
The models are incorrect
Replace the optical module.
The models are correct
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The optical module at the receive end is faulty.
1.
Use the optical power meter to test the receive optical power, and check whether the receive
optical power meets the requirement. If yes, contact Huawei engineers to replace the optical
module.
Step 4 Cause 4: The fiber performance degrades.
If...
Then...
The connector of the fiber jumper is dirty Clean fiber connectors.
The connector or fiber is damaged
Insert the connector properly or replace the
damaged fiber jumper.
----End
Related Information
The following table describes the meanings of the parameters in the IN_PWR_ABN alarm
reported by the EMS6.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the port number.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
357
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
The value of Parameter 2 is always 0x00, and
the value of Parameter 3 is always 0x01. The
two parameters indicate the path ID.
Parameter 4, Parameter 5
Reserved. The values are always 0xFF.
A.3.107 IN_PWR_HIGH
Description
The IN_PWR_HIGH is an alarm indicating that the input optical power is over high.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the IN_PWR_HIGH alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed optical interface has errors.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The transmit power of the opposite NE is over high.
Cause 2: The model of the selected optical module is incorrect.
Cause 3: The optical module at the receive end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The transmit power of the opposite site is over high.
1.
Browse current performance events, and query the performance event of the transmit
optical power on the opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The transmit optical power does not meet Contact Huawei engineers to replace the
the requirement
optical module.
The transmit optical power meets the
requirement
Add a proper attenuator to reduce the
receive optical power.
Step 2 Cause 2: The model of the selected optical module is incorrect.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
358
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Query the board manufacturing information report, and check whether the models of
the SFP optical modules used at both ends are correct.
If...
Then...
The models are incorrect
Contact Huawei engineers to replace the optical module.
The models are correct
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The optical module at the receive end is faulty.
1.
Use the optical power meter to test the receive optical power, and check whether the receive
optical power meets the requirement. If yes, contact Huawei engineers to replace the optical
module.
----End
Related Information
The optical power threshold set for the IN_PWR_HIGH alarm is lower than the overload point.
SDH Interface Performance.
A.3.108 IN_PWR_LOW
Description
The IN_PWR_LOW is an alarm indicating that the input optical power is over low.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the IN_PWR_LOW alarm occurs, the service at the alarmed optical interface has errors.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The transmit power of the opposite NE is over low.
Cause 2: The model of the selected optical module is incorrect.
Cause 3: The optical module at the receive end is faulty.
Cause 4: The fiber performance degrades.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The transmit power of the opposite NE is over low.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
359
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Browse current performance events, and query the performance event of the transmit
optical power on the opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The transmit optical power does not meet Contact Huawei engineers to replace the
the requirement
optical module.
The transmit optical power meets the
requirement
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The model of the selected optical module is incorrect.
1.
Query the board manufacturing information report, and check whether the models of
the SFP optical modules used at both ends are correct.
If...
Then...
The models are incorrect
Contact Huawei engineers to replace the optical module.
The models are correct
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The optical module at the receive end is faulty.
1.
Use the optical power meter to test the receive optical power, and check whether the receive
optical power meets the requirement.
If...
Then...
The receive optical power meets the
requirement
Contact Huawei engineers to replace the
optical module.
The receive optical power does not meet the Go to Cause 4.
requirement
Step 4 Cause 4: The fiber performance degrades.
1.
Clean fiber connectors and adapters.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the connector is
cleaned
The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists after the connector is
cleaned
Replace the fiber.
----End
Related Information
The optical power threshold set for the IN_PWR_LOW alarm is higher than the sensitivity point.
SDH Interface Performance.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
360
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.109 INTEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The INTEMP_SENSOR_FAILL is an alarm indicating that the air inlet temperature sensor of
the cabinet fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The air inlet temperature data of the TCU cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The air inlet temperature sensor is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The air inlet temperature sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The air inlet temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the air inlet temperature sensor.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
361
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
A Alarm Reference
Step 4 Cause 4: The air inlet temperature sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the air inlet temperature sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.110 J0_MM
Description
The J0_MM is an alarm indicating the trace identifier mismatch. This alarm occurs when the
board detects the J0 byte mismatch.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The receivable J0 byte on the local NE does not match the transmitted J0 byte on the
opposite NE.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The receivable J0 byte on the local NE does not match the transmitted J0 byte on the
opposite NE.
1.
Disable the receivable J0 byte on the local NE. For details, see Configuring RSOHs.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
362
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.111 K1_K2_M
Description
The K1_K2_M is an alarm indicating the K1/K2 byte mismatch. This alarm occurs when the
board detects inconsistent channel numbers that the transmitted K1 byte (bits 5-8) and the
received K2 byte (bits 1-4) indicate.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the protection group type.
l 0x01: linear MS protection.
l 0x02: ring MS protection.
Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
When the K1_K2_M alarm occurs, the MSP protocol may fail and therefore the protection
switching may fail.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The switching modes configured at both ends are single-ended switching and dualended switching separately.
Cause 2: The fiber connection is incorrect.
Cause 3: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The switching modes configured at both ends are single-ended switching and dualended switching separately.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the switching modes at both ends are the same.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
363
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The switching modes are different
Configure the switching modes as the same.
The switching modes are the same
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The fiber connection is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the fiber connection is correct. For example, the fiber at the receive or
transmit port may be incorrectly connected, or disconnected.
If...
Then...
The fiber connection is incorrect
Connect the fiber properly.
The connection is correct
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the board where the line unit is located on the opposite NE. Then, check
whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.112 K2_M
Description
The K2_M is an alarm indicating the K2 byte mismatch. This alarm occurs when the board
detects that the protection mode indicated by the received K2 (bit 5) is different from the
protection mode of the NE.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
364
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the protection group type.
l 0x01: linear MS protection.
l 0x02: ring MS protection.
Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
When the K2_M alarm occurs, the MSP protocol may fail and therefore the protection switching
may fail.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Two NEs of the linear MSP group are configured with different protection modes
(1+1 or 1:N).
Cause 2: The MSP protocol is stopped when the protection switching occurs.
Cause 3: The fiber connection is incorrect.
Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Two NEs of the linear MSP group are configured with different protection modes (1
+1 or 1:N).
1.
Query the status of the linear MSP, and check whether two NEs of the linear MSP group
are configured with different protection modes (1+1 or 1:N).
If...
Then...
The protection modes are different
Configure the protection modes as the same.
The protection modes are the same
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The MSP protocol is stopped when the protection switching occurs.
1.
Query the status of the linear MSP, and check whether the MSP protocol is stopped on the
opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The protocol is stopped Restart the MSP protocol on the opposite NE. For details, see
Starting/Stopping the Linear MSP Protocol.
The protocol is running Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The fiber connection is incorrect.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the fiber connection is correct. For example, the fiber at the receive or
transmit port may be incorrectly connected, or disconnected.
If...
Then...
The connection is incorrect
Connect the fiber properly
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
365
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The connection is correct
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the board where the line unit is located on the opposite NE. Then, check
whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.113 LAG_BWMM
Description
LAG_BWMM is an alarm indicating the bandwidth inconsistency in the LAG group.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
For a LAG group in load-sharing mode, data services may be lost.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: In the LAG group, the license capacities of the ports differ from each other.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: In the LAG group, the license capacities of the ports differ from each other.
1.
Query the license capacities of the ports of the LAG group by using the NMS.
2.
If the license capacities of the ports differ from each other, reload a license file of an
appropriate capacity.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
366
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.114 LAG_DOWN
Description
The LAG_DOWN is an alarm indicating that the link aggregation group (LAG) is unavailable.
This alarm occurs when the LAG does not have activated members.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the LAG_DOWN alarm occurs, the service at the member port of the LAG is interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: All the member ports of the aggregation group are invalid for the same causes as the
LAG_MEMBER_DOWN alarm.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: All the member ports of the LAG are invalid for the same causes as the
LAG_MEMBER_DOWN alarm.
1.
Determine the alarmed port according to the alarm parameter.
2.
Rectify the fault at each member port according to the description of
LAG_MEMBER_DOWN.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.115 LAG_MEMBER_DOWN
Description
The LAG_MEMBER_DOWN is an alarm indicating that a member port of a link aggregation
group (LAG) is unavailable. This alarm occurs when a member port of an LAG can neither be
activated nor function as a protection port.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
367
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2 Indicates the slot ID of the alarmed board.
Parameter 3
Indicates the ID of the alarmed subboard. The value is always 0xff.
Parameter 4, Parameter 5 Indicates the ID of the alarmed port.
Parameter 6
Indicates the cause that makes the port unavailable.
l 0x01: The port link is faulty or disabled.
l 0x02: The port fails to receive the LACP packets.
l 0x03: The port works in half-duplex mode.
l 0x04: The port is self-looped.
Impact on the System
The port in the LAG cannot share the service load, and the port does not transmit or receive any
services.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The port link is faulty or disabled.
Cause 2: The port receives no LACP packets.
Cause 3: The port works in half-duplex mode or not in Auto-Negotiation mode.
Cause 4: The port is self-looped.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the alarmed port and the cause of the alarm according to the alarm parameters.
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x01
Perform the operations described in step Step 2.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x02
Perform the operations described in step Step 3.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x03
Perform the operations described in step Step 4.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x04
Perform the operations described in step Step 5.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
368
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 2 Cause 1: The port link is faulty or disabled.
1.
2.
On the NMS, check whether the port in the LAG is enabled. For details, see Querying the
Protocol Information of the LAG.
If...
Then...
The port is not enabled
Enable the port in the LAG.
The port is enabled
Go to the next step.
Check the link status of all ports and check whether the ETH_LOS alarm is reported.
If...
Then...
The alarm is reported
Clear the ETH_LOS alarm immediately and rectify the
fault of the port link.
The alarm is not reported Go to Cause 2.
Step 3 Cause 2: The port receives no LACP packets.
1.
Check whether the local port and the remote port transmit the LACP packets. For details,
see Querying the Protocol Information of the LAG. If the LACP packets are not transmitted,
configure the ports at two ends to ensure that the packets can be normally transmitted.
Step 4 Cause 3: The port works in half-duplex mode or not in Auto-Negotiation mode.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the port in the LAG works in half-duplex mode. For details,
see Querying the Protocol Information of the LAG. If the port works in half-duplex mode,
change the working mode of the port into full-duplex.
2.
On the NMS, change the working mode of the port into full-duplex and Auto-Negotiation.
Step 5 Cause 4: The port is self-looped.
1.
Check whether the port is self-looped. For details, see 8.15 Querying the Attributes of
an Ethernet Port. If the port is self-looped, release the selfloop. For details, see 8.5.4
Setting a Loopback for the Packet-plane Ethernet Interface Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.116 LAG_PORT_FAIL
Description
The LAG_PORT_FAIL is an alarm indicating that a port in the LAG fails. When a port in the
LAG is unavailable, the LAG_PORT_FAIL alarm is reported.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
369
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the number of the IP port.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
The values are always 0x00 0x01.
Parameter 4
Indicates the cause of the protection failure.
l 0x01: The link of the port is faulty or fails.
l 0x02: The port is in half-duplex mode.
l 0x03: The port fails to receive the LACP packets.
l 0x04: The port detects the selfloop.
l 0x05: Other unknown reasons.
Parameter 5
The value is always 0xff.
Impact on the System
The port in the LAG cannot share the service load, and the port does not transmit or receive any
services.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The port is disabled or the link is faulty.
Cause 2: The port is in the half-duplex mode.
Cause 3: The port fails to receive the LCAP packets.
Cause 4: The port detects a selfloop.
Cause 5: other unknown reasons
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the port where the alarm occurs and the alarm cause according to the alarm parameter.
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x01
Go to Cause 1.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x02
Go to Cause 2.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x03
Go to Cause 3.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x04
Go to Cause 4.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
370
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x05
Go to Cause 5.
Step 2 Cause 1: The port is disabled or the link is faulty.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the port in the LAG is enabled. For details, see Setting the
General Attributes of Ethernet Ports.
If...
Then...
The port is not enabled Enable the port in the LAG group.
The port is enabled
Check the link state of each port. If any link is faulty, rectify
the fault.
Step 3 Cause 2: The port is in the half-duplex mode.
1.
On the NMS, check the working mode of the port in the LAG group. If the port is in halfduplex mode, change the working mode of the port into full-duplex. For details, see Setting
the General Attributes of Ethernet Ports.
Step 4 Cause 3: The port fails to receive the LCAP packets.
1.
2.
On the NMS, check whether the LAG group is properly configured on the opposite end.
For details, see Querying the Protocol Information of the LAG.
If...
Then...
The LAG group is not properly configured
Reconfigure the LAG group.
The LAG group is properly configured
Go to the next step.
Check whether the local port and the remote port transmit the LACP packets. If the LACP
packets are not transmitted, configure the ports at both ends to ensure that the packets can
be normally transmitted. For details, see Querying the Protocol Information of the LAG.
Step 5 Cause 4: The port detects a selfloop.
1.
Release the selfloop of the port with reference to Enabling Self-Loop Detection.
Step 6 Cause 5: other unknown reasons
1.
Contact Huawei engineers.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.117 LAG_VC_PORT_FAIL
Description
The LAG_VC_PORT_FAIL is an alarm indicating that a VCG port in the LAG fails. When the
VCTRUNK is unavailable, the alarm is reported.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
371
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the number of the faulty VCG port in the LAG. Parameter
2 indicates the most significant bits and Parameter 3 indicates the
least significant bits.
Parameter 4
Indicates the cause of the protection failure.
l 0x01: The link of the port is faulty or fails.
l 0x03: The port fails to receive the LACP packets.
l 0x04: The link of the port is configured into a loop.
l 0x05: other unknown reasons.
Parameter 5
The value is always 0xff.
Impact on the System
The port in the LAG cannot share the service load, and the port does not transmit or receive any
services.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The link of the port is faulty or fails.
Cause 2: The port fails to receive the LCAP packets.
Cause 3: The port detects a selfloop.
Cause 4: other unknown reasons
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the port where the alarm occurs and the alarm cause according to the alarm parameter.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
372
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x01
Go to Cause 1.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x03
Go to Cause 2.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x04
Go to Cause 3.
The value of Parameter 4 is 0x05
Go to Cause 4.
Step 2 Cause 1: The port is disabled or the link is faulty.
1.
Check the link state of each VCG port. If any link is faulty, rectify the fault.
Step 3 Cause 2: The port fails to receive the LCAP packets.
1.
2.
On the NMS, check whether the LAG group is properly configured on the opposite end.
If...
Then...
The LAG group is not properly configured
Reconfigure the LAG group.
The LAG group is properly configured
Go to the next step.
Check whether the local port and the remote port transmit the LACP packets. If the LACP
packets are not transmitted, configure the ports at both ends to ensure that the packets can
be normally transmitted.
Step 4 Cause 3: The port detects a selfloop.
1.
Release the selfloop of the port.
Step 5 Cause 4: other unknown reasons
1.
Contact Huawei engineers.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.118 LAN_LOC
Description
The LAN_LOC is an alarm indicating the Ethernet communication failure.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
373
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the network port ID. For example, 0x01 indicates network
port 1 and 0x02 indicates network port 2.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicates the number of the path on which the alarm is reported.
Parameter 2 indicates the most significant bits and the value is
always 0x00. Parameter 3 indicates the least significant bits and the
value is always 0x01.
Impact on the System
When the alarm is reported, the communication of the network port is interrupted. As a result,
the NE is out of control. The existing services of the NE, however, are not affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The cable is not connected to the network port, or the cable is faulty.
Cause 2: The network port is faulty.
Cause 3: The system control, switching, and timing board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 View the alarm on the NMS. Determine the network port ID according to the alarm parameter
1.
Step 2 Cause 1: The cable is not connected to the network port, or the cable is faulty.
1.
Check whether the cable of the network port is loose or no cable is connected. Properly
connect the NMS to the network port. The LINK indicator is in green.
Step 3 Cause 2: The network port is faulty.
1.
Replace the faulty board. For details, see 6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and
Timing Board.
Step 4 Cause 3: The system control, switching, and timing board is faulty.
1.
Replace the system control, switching, and timing board. For details, see 6.9 Replacing
the System Control, Switch and Timing Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.119 LASER_CLOSED
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
374
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The LASER_CLOSED is an alarm indicating that the laser is shut down. This alarm occurs when
the laser is shut down by using the NMS.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the LASER_CLOSED alarm occurs, the optical interface fails to carry services.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The laser on the local NE is shut down by using the NMS.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The laser on the local NE is shut down by using the NMS.
1.
Find out the cause of shutting down the laser and start up the laser as soon as possible.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.120 LASER_MOD_ERR
Description
The LASER_MOD_ERR is an alarm indicating that the type of the pluggable optical module
on the board does not match the type of the optical interface.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
375
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When the LASER_MOD_ERR alarm occurs, the performance of the optical interface degrades
and serious degradation even causes service interruption.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The optical module installed at the optical interface does not match the rate of the
optical interface.
Cause 2: The small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module does not match the interface type.
Cause 3: The optical module is faulty.
Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The optical module installed at the optical interface does not match the rate of the
optical interface.
1.
Check whether the optical module installed at the optical interface matches the rate of the
optical interface. For details, see 8.4.2 Querying the Board Manufacturing Information
Report .
If...
Then...
The optical module does not match the
rate of the optical interface
Contact Huawei engineers to replace the
optical module with one that matches the
rate of the optical interface.
The optical module matches the rate of
the optical interface
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The SFP module does not match the interface type.
1.
Replace the existing SFP module with a proper SFP module.
Step 3 Cause 3: The optical module is faulty.
1.
Replace the faulty optical module.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the optical module is replaced
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists after the optical module is replaced
Go to Cause 3.
Step 4 Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.121 LASER_MOD_ERR_EX
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
376
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The LASER_MOD_ERR is an alarm indicating that the type of the pluggable optical module
on the board does not match the type of the optical interface.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the LASER_MOD_ERR_EX alarm occurs, the performance of the optical interface
degrades and serious degradation even causes service interruption.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The optical module installed at the optical interface does not match the rate of the
optical interface.
Cause 2: The small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module does not match the interface type.
Cause 3: The optical module is faulty.
Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The optical module installed at the optical interface does not match the rate of the
optical interface.
1.
Check whether the optical module installed at the optical interface matches the rate of the
optical interface. For details, see 8.4.2 Querying the Board Manufacturing Information
Report .
If...
Then...
The optical module does not match the
rate of the optical interface
Contact Huawei engineers to replace the
optical module with one that matches the
rate of the optical interface.
The optical module matches the rate of
the optical interface
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The SFP module does not match the interface type.
1.
Replace the existing SFP module with a proper SFP module.
Step 3 Cause 3: The optical module is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the faulty optical module.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
377
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the optical module is replaced
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists after the optical module is replaced
Go to Cause 3.
Step 4 Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.122 LASER_SHUT
Description
The LASER_SHUT is an alarm indicating that the laser is shut down. This alarm occurs when
the laser is shut down by using the NMS.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the laser_shut alarm occurs, the optical interface fails to carry services.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The laser on the local NE is shut down by using the NMS.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The laser on the local NE is shut down by using the NMS.
1.
Find out the cause of shutting down the laser and start up the laser as soon as possible.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
378
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.123 LCAS_FOPR
Description
The LCAS_FOPR is an alarm indicating that the LCAS protocol in the receive direction fails.
This alarm occurs if the receive unit of the LCAS module of a board detects an abnormal state
in which the LCAS might fail to negotiate or cannot negotiate correctly.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00 0x01
indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUNK 1.
Impact on the System
The Ethernet service is not normal.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Configuration data of the LCAS protocol is incorrect.
Cause 2: The link is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Configuration data of the LCAS protocol is incorrect.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the LCAS enabling state and the LCAS parameters are the same at both
ends of the link.
If...
Then...
The settings of the LCAS protocols are
not consistent
Properly enable the LCAS protocols at both
ends.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
379
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The settings of the LCAS protocols at
both ends are consistent
Go to Cause 2.
Check whether configurations of the local and opposite NEs are correct. For example, check
whether a VCG on one NE is connected to multiple VCGs on the opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The configurations of the local and opposite NEs are Correct the configuration data.
incorrect
The configurations of the local and opposite NEs are Go to Cause 2.
correct
Step 2 Cause 2: The link is faulty.
1.
2.
Check whether the link where the service travels has errors or becomes faulty.
If...
Then...
The link is faulty
Rectify the fault.
The link is normal
Go to the next step.
Restart the LCAS protocols at both ends. Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.124 LCAS_FOPT
Description
The LCAS_FOPT is an alarm indicating that the LCAS protocol in the transmit direction fails.
This alarm occurs if the transmit unit of the LCAS module of a board detects an abnormal state
in which the LCAS might fail to negotiate or cannot negotiate correctly.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
380
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00 0x01
indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUNK 1.
Impact on the System
The Ethernet service is not normal.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Configuration data of the LCAS protocol is incorrect.
Cause 2: The link is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Configuration data of the LCAS protocol is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the LCAS enabling state and the LCAS parameters are the same at both
ends of the link.
If...
Then...
The settings of the LCAS protocols are
not consistent
Properly enable the LCAS protocols at both
ends.
The settings of the LCAS protocol at both Go to Cause 2.
ends are consistent
2.
Check whether configurations of the local and opposite NEs are correct. For example, check
whether a VCG on one NE is connected to multiple VCGs on the opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The configurations of the local and opposite NEs are Correct the configuration data.
incorrect
The configurations of the local and opposite NEs are Go to Cause 2.
correct
Step 2 Cause 2: The link is faulty.
1.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the link where the service travels has errors or becomes faulty.
If...
Then...
The link is faulty
Rectify the fault.
The link is normal
Go to the next step.
Restart the LCAS protocols at both ends. Then, check whether the alarm clears.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
381
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.125 LCAS_PLCR
Description
The LCAS_PLCR is an alarm indicating that a part of the LCAS bandwidth in the receive
direction is lost. This alarm occurs when a board detects that the number of paths that carry the
overloads in the receive direction of the VCTRUNK with the LCAS function enabled is less
than the preset number but is not zero.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00 0x01
indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUNK 1.
Impact on the System
The available Ethernet service bandwidth is smaller than the configured bandwidth.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the
remote site is different from that at the local site.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
382
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: Some paths in the transmit direction of the remote site are faulty.
Cause 3: Some paths in the receive direction of the local site are faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the remote
site is different from that at the local site.
1.
Check whether the VCTRUNKs at the transmit and the receive directions at the local site
are configured with the same number of physical paths and timeslots.
If...
Then...
The sink and source VCTRUNKs are
Correct the configuration data. For details,
bound with different number of physical see Dynamically Increasing/Decreasing the
paths or bound with different timeslots VCTRUNK Bandwidth.
If yes
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: Some paths in the transmit direction of the remote site are faulty.
1.
Check whether any path alarm exists in the transmit direction of the remote site.
If...
Then...
Any of the preceding alarms occurs
Clear the alarm immediately.
No alarm occurs
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Some paths in the receive direction of the local site are faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.126 LCAS_PLCT
Description
The LCAS_PLCT is an alarm indicating that part of the LCAS bandwidth in the transmit
direction is lost. This alarm occurs when a board detects that the number of paths that carry the
overloads in the transmit direction of the VCTRUNK with the LCAS function enabled is less
than the preset number but is not zero.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
383
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00 0x01
indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUN 1.
Impact on the System
The available transmit bandwidth of Ethernet services is less than the preset bandwidth. When
the transmitted services are more than the available transmit bandwidth, packet loss occurs.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the
remote site is different from that at the local site.
Cause 2: Some paths in the receive direction of the remote site are faulty.
Cause 3: Some paths in the transmit direction of the local site are faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the remote
site is different from that at the local site.
1.
Check whether the sink and source VCTRUNKs are bound with the same number of
physical paths or the same timeslots.
If...
Then...
The sink and source VCTRUNKs are
Correct the configuration data. For details,
bound with different number of physical see Dynamically Increasing/Decreasing the
paths or different timeslots
VCTRUNK Bandwidth.
The sink and source VCTRUNKs are
Go to Cause 2.
bound with the same number of physical
paths or the same timeslots
Step 2 Cause 2: Some paths in the receive direction of the remote site are faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether any path alarm exists in the receive direction of the remote site.
If...
Then...
Any of the preceding alarms occurs
Clear the alarm immediately.
No alarm occurs
Go to the next step.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
384
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 3 Cause 3: Some paths in the transmit direction of the local site are faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.127 LCAS_TLCR
Description
The LCAS_TLCR is an alarm indicating that all the LCAS bandwidth in the receive direction
is lost. This alarm occurs when no path in the receive direction of the VCTRUNK with LCAS
enabled carries the overload but paths are configured to carry the overload.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicates the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00
0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUN 1.
Impact on the System
There is no available bandwidth in the receive direction, and the Ethernet services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the
remote site is different from that at the local site.
Cause 2: Some paths in the transmit direction of the remote site are faulty.
Cause 3: Some paths in the receive direction of the local site are faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
385
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the remote
site is different from that at the local site.
1.
Check whether the VCTRUNKs at the transmit and the receive directions at the local site
are configured with the same number of physical paths and timeslots.
If...
Then...
The sink and source VCTRUNKs are
Correct the configuration data. For details,
bound with different number of physical see Dynamically Increasing/Decreasing the
paths or bound with different timeslots VCTRUNK Bandwidth.
The sink and source VCTRUNKs are
Go to Cause 2.
bound with the same number of physical
paths or the same timeslots
Step 2 Cause 2: Some paths in the transmit direction of the remote site are faulty.
1.
Check whether any path alarm exists in the transmit direction of the remote site.
If...
Then...
Any of the preceding alarms occurs
Clear the alarm immediately.
No alarm occurs
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Some paths in the receive direction of the local site are faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.128 LCAS_TLCT
Description
The LCAS_TLCT is an alarm indicating that all the LCAS bandwidth in the transmit direction
is lost. This alarm occurs when no path in the transmit direction of the VCTRUNK with LCAS
enabled carries the overload but paths are configured to carry the overload.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
386
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK. For example, 0x00 0x01
indicate that the alarm is reported in VCTRUNK 1.
Impact on the System
There is no available bandwidth in the transmit direction, and the Ethernet services are
interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the
remote site is different from that at the local site.
Cause 2: Some paths in the receive direction of the remote site are faulty.
Cause 3: Some paths in the transmit direction of the local site are faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The number of paths or timeslots that are configured for the VCTRUNK at the remote
site is different from that at the local site.
1.
Check whether the sink and source VCTRUNKs are bound with the same number of
physical paths or the same timeslots.
If...
Then...
The sink and source VCTRUNKs are
Correct the configuration data. For details,
bound with different number of physical see Dynamically Increasing/Decreasing the
paths or bound with different timeslots VCTRUNK Bandwidth.
The sink and source VCTRUNKs are
Go to Cause 2.
bound with the same number of physical
paths or bound with the same timeslots
Step 2 Cause 2: Some paths in the receive direction of the remote site are faulty.
1.
Check whether any path alarm exists in the receive direction of the remote site.
If...
Then...
Any of the preceding alarms occurs
Clear the alarm immediately.
No alarm occurs
Go to the next step.
Step 3 Cause 3: Some paths in the transmit direction of the local site are faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
387
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.129 LCD
Description
The LCD is an alarm indicating loss of cell delimitation. This alarm occurs when the OCD alarm
continuously occurs within the transmission period of N cells. The letter "N" indicates the LCD
alarm threshold value. For different ports, the threshold value is different.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
l
When the LCD alarm occurs, all the services in the receive direction of the port are
interrupted and all the connections at the port insert segment or end AIS cells to the
downstream.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The path connected to the ATM port receives signals in an incorrect manner. For
example, the MS_AIS, AU_AIS or AU_LOP alarm occurs.
Cause 2: A great number of bit errors occur in the receive path. The receive path reports
alarms indicating excessive bit errors, such as B1_EXC, B2_EXC, and B3_EXC.
Cause 3: The ATM processing chip of the board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The path connected to the ATM port receives signals in an incorrect manner. For
example, the MS_AIS, AU_AIS or AU_LOP alarm occurs.
1.
Check whether the MS_AIS, AU_AIS, or AU_LOP alarm occurs in the path connected
to the ATM port.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms first, and then check whether the LCD alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: A great number of bit errors occur in the receive path. The receive path reports alarms
indicating excessive bit errors, such as B1_EXC, B2_EXC, and B3_EXC.
1.
Check whether the B1_EXC, B2_EXC, or B3_EXC alarm occurs in the receive path.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms first, and then check whether the LCD alarm is cleared.
Step 3 Cause 3: The ATM processing chip of the board is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
388
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
1.
Perform a cold reset on the board that reports the LCD alarm. For details, see 8.6.1 Cold
Reset.
2.
If the LCD alarm persists, replace the alarmed board. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the
Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
End and segment
The end point, used to monitor the entire virtual connection, is set at the end of the chain network.
The segment point is used to monitor a segment of the entire link.
Thresholds of generating the LCD alarm at different ports
l
For the external ATM port, the threshold of generating the LCD alarm is seven cells.
For a VC-4 VCTRUNK port, the threshold of generating the LCD alarm is 360 cells.
For a VC-12 VCTRUNK port, the threshold of generating the ALM_IMA_LINK_LCD
alarm in the bound E1 link is 104 cells. If only one E1 link is bound with the VCTRUNK,
the LCD alarm is reported when the ALM_IMA_LINK_LCD alarm occurs. If the
VCTRUNK is bound with multiple E1 links in the IMA group, and if the number of E1
links in which the ALM_IMA_LINK_LCD alarm occurs is greater than the value derived
from the total number of bound E1 links subtracted by the minimum number of activated
links in the receive direction of the IMA group, the LCD alarm is reported at the VCTRUNK
port. Otherwise, the LCD alarm is not reported.
A.3.130 LCS_LIMITED
Description
The LCS_LIMITED alarm indicates that the configuration capacity of an NE exceeds the
capacity authorized by the license file.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
389
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the alarm cause.
l 0x01: The E1 service capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by the license
file.
l 0x02: The AM license file is not loaded.
l 0x03: For IF protection, the bandwidth at the standby port authorized by the
license file is lower than the bandwidth at the main port authorized by the
license file.
l 0x05: The ATM/IMA capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by the license
file.
l 0x06: The air port LAG capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by the
license file.
l 0x07: The E1 priority capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by the license
file.
l 0x08: The synchronous Ethernet capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by
the license file.
l 0x09: The air port compression capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by
the license file
l 0x10: The MPLS service license capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by
the license file.
l 0x11: The PLA license capacity exceeds the capacity authorized by the
license file.
l 0x12: The total service bandwidth (TDM service bandwidth and data service
bandwidth) exceeds the bandwidth allowed by the Ethernet license file for
the working and protection links.
Impact on the System
When the LCS_LIMITED alarm occurs, the change of radio service capacity cannot take effect
on the NE.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The AM configuration on the NE exceeds the capacity authorized by the license
file.
Cause 2: For IF protection, the bandwidth at the standby port authorized by the license file
is lower than the bandwidth at the main port authorized by the license file.
Cause 3: The services configured on the NE exceed the capacity authorized by the license
file.
Procedure
Step 1 Query the capacity of the license by using the NMS.
Step 2 Cause 1: The AM configuration on the NE exceeds the capacity authorized by the license file.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
390
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Check the AM enabling status. If the license does not allow the AM to be enabled, set the
AM function to disabled.
Step 3 Cause 2: For IF protection, the bandwidth at the standby port authorized by the license file is
lower than the bandwidth at the main port authorized by the license file.
1.
Check whether the capacities that are authorized by the license files for the main and
standby IF boards in an IF protection group are consistent with the capacities specified in
the contract. If not, contact Huawei technical support engineers to reload correct license
files.
Step 4 Cause 3: The services configured on the NE exceed the capacity authorized by the license file.
1.
when the alarm parameter is 0x01, check whether the radio service configuration exceeds
the capacity authorized by the license file. For details, see Setting the Hybrid/AM
Attributes. If yes, reduce the number of E1 services.
2.
Purchase and load the corresponding service license.
----End
Related Information
For TDM services, radio service capacities of NEs are calculated based on the service crossconnections on IF boards.
A.3.131 LFA
Description
The LFA is an alarm indicating that the E1 frame alignment at the local end of the inverse
multiplexing for ATM (IMA) link in the receive direction is lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicates the path ID.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
391
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
l
When this alarm occurs, the alarmed E1 link is unavailable, and the available links in the
IMA group are reduced.
If the VCTRUNK link binds only one member, the service is interrupted when the LFA
alarm occurs.
After this alarm clears, the E1 link in the IMA group will be recovered automatically.
Possible Causes
The possible causes of the LFA alarm are as follows:
l
Cause 1: The demultiplexing module of the E1 frame cannot perform the frame alignment
function, and therefore the frame alignment loss alarms are reported. These alarms include
TU_LOP, TU_AIS, and alarm indicating that the cross-connection is not configured.
Cause 2: The alarmed board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Check for the TU_LOP and TU_AIS alarms on the NMS. If these alarms occur, handle
these alarms first.
Step 2 Cause 2: The alarmed board is faulty.
1.
Check whether the HARD_BAD alarm occurs on the board.
2.
If the alarm occurs, perform a cold reset on the board that reports the hardware failure
alarm, and check whether the alarm clears.
CAUTION
If the service on the board is not protected, a cold reset on the board causes service
interruptions.
3.
If the alarm persists, replace the board. For details, see 6.6 Replacing the Ethernet
Interface Board or 6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
Basic frame
As defined in ITU-T G.704, a basic frame is an even frame with frame alignment sequence (FAS)
or an odd frame with non frame alignment sequence (NFAS).
A.3.132 LICENSE_DIFF
Description
The LICENSE_DIFF is an alarm indicating that the license file on the IF board is different from
the backup file on the system control board. After the IF board or system control board is
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
392
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
replaced, the license file on the IF board may be different from the backup file on the system
control board.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the type of the license file.
l 0x01: AM license.
l 0x02: Hybrid license.
l 0x03: TDM license.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
393
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 2 Indicates the capacity of the license file on the IF board.
When the value of Parameter 1 is 0x01:
l 0x01: The AM function is disabled.
l 0x02: The AM function is enabled.
When the value of Parameter 1 is 0x02:
l 0x01: The hybrid capacity is 10 Mbit/s.
l 0x02: The hybrid capacity is 20 Mbit/s.
l 0x03: The hybrid capacity is 50 Mbit/s.
l 0x04: The hybrid capacity is 100 Mbit/s.
l 0x05: The hybrid capacity is 150 Mbit/s.
l 0x06: The hybrid capacity is 200 Mbit/s.
l 0x07: The hybrid capacity is 300 Mbit/s.
l 0x08: The hybrid capacity is 400 Mbit/s.
l 0x09: The hybrid capacity is beyond the control of licenses.
When the value of Parameter 1 is 0x03:
l 0x01: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 8xE1.
l 0x02: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 16xE1.
l 0x03: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 32xE1.
l 0x04: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 48xE1.
l 0x05: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 64xE1.
l 0x06: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 128xE1.
l 0x07: The TDM radio transmission capacity is beyond the control of licenses.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
394
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 3 Indicates the capacity of the license file on the system control board.
When the value of Parameter 1 is 0x01:
l 0x01: The AM function is disabled.
l 0x02: The AM function is enabled.
When the value of Parameter 1 is 0x02:
l 0x01: The hybrid capacity is 10 Mbit/s.
l 0x02: The hybrid capacity is 20 Mbit/s.
l 0x03: The hybrid capacity is 50 Mbit/s.
l 0x04: The hybrid capacity is 100 Mbit/s.
l 0x05: The hybrid capacity is 150 Mbit/s.
l 0x06: The hybrid capacity is 200 Mbit/s.
l 0x07: The hybrid capacity is 300 Mbit/s.
l 0x08: The hybrid capacity is 400 Mbit/s.
l 0x09: The hybrid capacity is beyond the control of licenses.
When the value of Parameter 1 is 0x03:
l 0x01: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 8xE1.
l 0x02: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 16xE1.
l 0x03: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 32xE1.
l 0x04: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 48xE1.
l 0x05: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 64xE1.
l 0x06: The TDM radio transmission capacity is 128xE1.
l 0x07: The TDM radio transmission capacity is beyond the control of licenses.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: After the IF board or system control board is replaced, the license file on the IF
board may be different from the backup file on the system control board.
Procedure
Step 1 This alarm only warns the user of the different license capacities on the IF board and the system
control board. No handling is required. Software patrol is performed automatically 48 hours later
and synchronizes the license capacities. Then, the alarm clears.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
395
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.133 LICENSE_LOST
Description
The LICENSE_LOST is an alarm indicating that the NE fails to detect the license file.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the type of the license file.
l 0x02: Hybrid license
l 0x03: TDM license
l 0x05: ATM/IMA license
l 0x06: NE license
Impact on the System
When the LICENSE_LOST alarm occurs, the functions authorized by the license file cannot
take effect.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The license file is lost or is not loaded.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The license file is lost or is not loaded.
1.
Contact Huawei engineers to reload the license file to the NE.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
396
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.134 LINK_ERR
Description
The LINK_ERR alarm indicates that a data link is faulty.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical port. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by optical port 1.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the path that reports the alarm. For example, 0x00
0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported by path 1.
Impact on the System
Services in the alarmed path are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The optical fiber connected to the Ethernet optical port is faulty.
Cause 2: The working modes of the ports at the local and opposite ends are different.
Cause 3: The equipment at the local or opposite end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The optical fiber connected to the Ethernet optical port is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the optical fiber connected to the Ethernet optical port is faulty.
If...
Then...
The optical fiber is faulty
Replace the fiber.
The optical fiber is not faulty
Go to Cause 2.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
397
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 2 Cause 2: The working modes of the ports at the local and opposite ends are different.
1.
Check whether the working modes of the ports at the local and opposite ends are different.
If...
Then...
The working modes of the ports at the
local and opposite ends are different
Set the working modes of the ports to the
same.
The working modes of the ports at the
local and opposite ends are the same
Go to the next step.
Step 3 Cause 3: The equipment at the local or opposite end is faulty.
1.
Use an optical fiber to perform a loopback at the the alarmed port. For details, see 8.1
Hardware Loopback.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
Replace the Ethernet board at the opposite end.
The alarm persists
Replace the Ethernet board at the local end.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.135 LMFA
Description
The LMFA is an alarm indicating the E1 multiframe alignment is lost when the E1 frame is a
CRC-4 multiframe.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicates the path ID.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
398
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the alarmed E1 links become unavailable. As a result, fewer links of
the IMA group are available. If the IMA group is comprised of only one link, services will be
interrupted.
Possible Causes
The possible cause of the LMFA alarm is as follows:
l
Cause 1: The alarmed board is faulty.
Cause 2: The frame format is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The alarmed board is faulty.
1.
Check whether the HARD_BAD alarm occurs on the board.
2.
If the alarm occurs, perform a cold reset on the board that reports the hardware failure
alarm, and check whether the alarm clears.
CAUTION
If the service on the board is not protected, a cold reset on the board causes service
interruptions.
3.
If the alarm persists, replace the board.
Step 2 Cause 2: The frame format is incorrect.
1.
Check the frame format of the opposite port. For details, see Setting Advanced Attributes
of Smart E1 Ports.
2.
Set the frame format to CRC-4 Multiframe if it is incorrect.
----End
Related Information
Basic frame
As defined in ITU-T G.704, a basic frame is an even frame with frame alignment sequence (FAS)
or an odd frame with non frame alignment sequence (NFAS).
Multiframe
A multiframe is composed of sixteen PCM frames, and can implement cyclic redundancy check
(CRC).
A.3.136 LOOP_ALM
Description
The LOOP_ALM is an alarm indicating that a loop occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
399
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the type of loopback.
l 0x00: optical/electrical port inloop.
l 0x01: optical/electrical port outloop.
l 0x02: path inloop.
l 0x03: path outloop.
l 0x04: loopback on the user side.
l 0x05: loopback on the multiplexing side.
l 0x08: ATM layer inloop.
l 0x09: ATM layer outloop.
l 0x0A: PHY layer inloop.
l 0x0B: PHY layer outloop.
l 0x0C: MAC layer inloop.
l 0x0D: MAC layer outloop.
l 0x0E: VC-4 timeslot inloop.
l 0x0F: VC-4 timeslot outloop.
l 0x10: VC-3 timeslot inloop.
l 0x11: VC-3 timeslot outloop.
l 0x12: VC-12 timeslot inloop.
l 0x13: VC-12 timeslot outloop.
l 0x14: IF outloop.
l 0x15: IF inloop.
l 0x16: RF inloop.
l 0xFF: any of the preceding loopback modes.
Impact on the System
When the LOOP_ALM alarm occurs, the looped port or path cannot carry services.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
400
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
Cause 1: A loop is performed on the local NE.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A loop is performed on the local NE.
1.
Determine the type of loopback according to the alarm parameter.
2.
Find out the cause of the loopback, and set the loopback status of the alarmed port to NonLoopback.
For details, see 8.5 Software Loopback.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.137 LP_CROSSTR
Description
The LP_CROSSTR is an alarm indicating that the lower order path error crosses the threshold.
This alarm occurs when the board detects that the performance event that the lower order path
error crosses the preset threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the performance monitoring period:
l 0x01: 15 minutes
l 0x02: 24 hours
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
401
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the ID of a performance event that causes the alarm.
l 0x90: LPBBE
l 0x91: LPES
l 0x92: LPSES
l 0x93: LPFEBBE
l 0x94: LPFEES
l 0x95: LPFESES
l 0x96: LPUAS
l 0x8e: LPFEUAS
l 0x97: LPCSES
l 0x98: LPFECSES
Impact on the System
When the LP_CROSSTR alarm occurs, a large number of errors occur in the service, and the
service may even be interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The lower order path error crosses the preset threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The lower order path error crosses the preset threshold.
1.
Check the threshold crossing records to find out the performance event that the lower order
path error crosses the preset threshold.
2.
Handle the threshold-crossing performance event.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.138 LP_R_FIFO
Description
The LP_R_FIFO is an alarm indicating that the FIFO overflows on the transmit side of the lower
order path.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
402
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the LP_R_FIFO alarm occurs, the service has errors.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The clock of the local NE is not synchronized with the clock of the opposite NE.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The clock of the local NE is not synchronized with the clock of the opposite NE.
1.
Browse current performance events, and check whether the performance event of TU
pointer justification occurs on the local NE and the opposite NE.
If...
Then...
The TU pointer justification occurs
Handle the performance event. For details,
see C.3.2 TUPJCHIGH, TUPJCLOW,
and TUPJCNEW.
The TU pointer justification does not
occur
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.139 LP_RDI
Description
The LP_RDI is an alarm indicating the lower order path remote receive failure. This alarm occurs
when the board detects that bit 8 of byte V5 is 1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
403
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the LP_RDI alarm occurs, the service on the local NE is not affected. The service received
by the opposite NE, however, is interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
lower order path remote receive failure.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
lower order path remote receive failure.
1.
Handle the lower order path alarm on the opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.140 LP_RDI_VC12
Description
The LP_RDI_VC12 is an alarm indicating that data reception fails at the remote end of VC-12
lower order path. This alarm occurs when the board detects that bit 8 of byte V5 is 1.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
404
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the service on the local NE is not affected. The service received by the
opposite NE, however, is interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the remote site, and the message says that data
reception fails at the remote end of a lower order path.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the remote site, and the message says that data
reception fails at the remote end of a lower order path.
1.
Handle the alarm of the lower order path on the remote site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.141 LP_RDI_VC3
Description
The LP_RDI_VC3 alarm indicates that data reception at the remote end of a lower order (VC-3)
path fails. A board reports this alarm when detecting that bit 5 in byte G1 is 1.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
405
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
When the LP_RDI_VC3 alarm occurs, the services at the local site are not affected, but the
opposite site cannot receive services.
Possible Causes
The local site receives a message from the opposite site, and the message says that data reception
fails at the remote end of a lower order (VC-3) path.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The local site receives a message from the opposite site, and the message says that data
reception fails at the remote end of a lower order (VC-3) path.
1.
Handle the alarm in the lower order (VC-3) path at the opposite site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.142 LP_REI
Description
The LP_REI is an alarm indicating the lower order path remote error. This alarm occurs when
the board detects that bit 3 of V5 is 1.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the LP_REI alarm occurs, the service on the local NE is not affected. The service received
by the opposite NE, however, has errors.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
406
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
lower order path remote errors.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
lower order path remote errors.
1.
Handle the LP_BBE performance event on the opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.143 LP_REI_VC12
Description
The LP_REI_VC12 is an alarm indicating that there are bit errors at the remote end of a VC-12
lower order path. This alarm occurs when the board detects that bit 3 of byte V5 is 1.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
Bit errors exist in the service in the receive direction of the remote site.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the remote site, and the message says that there
are bit errors in the lower order path.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
407
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the remote site, and the message says that there
are bit errors in the lower order path.
1.
Handle the LPBBE performance event of the remote site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.144 LP_REI_VC3
Description
The LP_REI_VC3 alarm indicates that there are bit errors at the remote end of a lower order
(VC-3) path. A board reports this alarm when detecting that any one of bits 1 to 4 in byte G1 is
1.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
Bit errors exist in received services at the opposite site.
Possible Causes
The local site receives a message from the opposite site, and the message says that there are bit
errors at the remote end of a lower order (VC-3) path.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
408
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The local site receives a message from the opposite site, and the message says that there
are bit errors at the remote end of a lower order (VC-3) path.
1.
Handle the alarm in the lower order (VC-3) path at the opposite site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.145 LP_RFI
Description
The LP_RFI is an alarm indicating the lower order path remote failure. This alarm occurs when
the board detects that bit 4 of V5 is 1.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the LP_RFI alarm occurs, the service on the local NE is not affected. The alarm only
indicates that the lower order paths on the opposite NE cannot carry services.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
lower order path remote failure.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local NE detects the message that is returned by the opposite NE and indicates the
lower order path remote failure.
1.
Handle the lower order path alarm on the opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
409
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.146 LP_SLM
Description
The LP_SLM is an alarm indicating that a mismatched signal label is detected in the lower order
path. This alarm is reported when the board detects a signal label mismatch between the V5
bytes.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services in the lower order path are unavailable.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The signal label contained in the V5 byte that is received by the local site does not
match with the signal label contained in the V5 byte that is transmitted by the remote site.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The signal label contained in the V5 byte that is received by the local site does not
match with the signal label contained in the V5 byte that is transmitted by the remote site.
1.
Modify the signal label contained in the V5 byte that is to be received by the local site or
is to be transmitted by the remote site. Ensure that the signal labels at both ends match with
each other. For details, see Configuring VC-12 POHs.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.147 LP_SLM_VC12
Description
The LP_SLM_VC12 is an alarm indicating that a mismatched signal label is detected in the
lower order path. This alarm is reported when the board detects a signal label mismatch between
the V5 bytes.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
410
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
The service in this lower order path is unavailable.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The signal label contained in the V5 byte that is received by the local site does not
match with the signal label contained in the V5 byte that is transmitted by the remote site.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The signal label contained in the V5 byte that is received by the local site does not
match with the signal label contained in the V5 byte that is transmitted by the remote site.
1.
Modify the signal label contained in the V5 byte that is to be received by the local site or
is to be transmitted by the remote site. Ensure that the signal labels at both ends match with
each other. For details, see Configuring VC-12 POHs.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.148 LP_SLM_VC3
Description
The LP_SLM_VC3 alarm indicates that a mismatched signal label is detected in a lower order
(VC-3) path. A board reports this alarm when detecting a mismatched signal label in byte C2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
411
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
The services in the lower order (VC-3) path are unavailable.
Possible Causes
The signal label in byte C2 that is received at the local site does not match with the signal label
in byte C2 that is transmitted at the opposite site.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The signal label in byte C2 that is received at the local site does not match with the
signal label in byte C2 that is transmitted at the opposite site.
1.
Reset the signal label in byte C2 that is received at the local site or the signal label in byte
C2 that is transmitted at the local site. Ensure that the signal labels are the same at both
sites. For details, see Configuring VC-4 POHs.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.149 LP_T_FIFO
Description
The LP_T_FIFO is an alarm indicating that the FIFO overflows on the transmit side of the lower
order path.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
412
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Bit errors occur in the services.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The frequency offset of the input signal is very large.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The frequency offset of the input signal is very large.
1.
Use an SDH analyzer to check whether the frequency offset of the input signal is within
50 ppm.
If...
Then...
The frequency offset is very large
Troubleshoot the remote site.
The frequency offset is within 50 ppm
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.150 LP_TIM
Description
The LP_TIM is an alarm indicating a mismatched trace identifier is detected in the lower order
path. This alarm is reported when the board detects a mismatch between the J2 bytes at both
ends.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
413
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The J2 byte to be received by the local site does not match with the J2 byte to be
transmitted by the remote site.
Cause 2: The data configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The J2 byte to be received by the local site does not match with the J2 byte to be
transmitted by the remote site.
1.
Set the byte mode of the J2 byte to be received by the local site to the disable mode.
Alternatively, set the J2 byte to be received by the local site to match with the J2 byte to
be transmitted by the remote site. For details, see Configuring VC-12 POHs.
Step 2 Cause 2: The data configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the cross-connections of the intermediate nodes where the service travels
are configured correctly. If not, reconfigure the cross-connections. For details, see Querying
TDM Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.151 LP_TIM_VC12
Description
The LP_TIM_VC12 is an alarm indicating a mismatched trace identifier is detected in the lower
order path. This alarm is reported when the board detects a mismatch between the J2 bytes at
both ends.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
414
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The J2 byte to be received by the local site does not match with the J2 byte to be
transmitted by the remote site.
Cause 2: The data configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The J2 byte to be received by the local site does not match with the J2 byte to be
transmitted by the remote site.
1.
Set the byte mode of the J2 byte to be received by the local site to the disable mode.
Alternatively, set the J2 byte to be received by the local site to match with the J2 byte to
be transmitted by the remote site. For details, see Configuring VC-12 POHs.
Step 2 Cause 2: The data configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the cross-connections of the intermediate nodes where the service travels
are configured correctly. If not, reconfigure the cross-connections. For details, see Querying
TDM Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.152 LP_TIM_VC3
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
415
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The LP_TIM_VC3 alarm indicates that a mismatched trace identifier is detected in a lower order
(VC-3) path. A board reports this alarm when detecting a mismatched trace identifier in byte J1.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Byte J1 to be received at the local site does not match with byte J1 to be transmitted
at the opposite site.
Cause 2: The data configuration at intermediate sites is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Byte J1 to be received at the local site does not match with byte J1 to be transmitted at
the opposite site.
1.
Set byte J1 to be received at the local site to the disable mode or the same as byte J1 to be
transmitted at the opposite site. For details, see Configuring VC-4 POHs.
Step 2 Cause 2: The data configuration at intermediate sites is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the cross-connections of intermediate sites where the services travel are
configured correctly. If not, reconfigure the cross-connections. For details, see Querying
TDM Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
416
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.153 LP_UNEQ
Description
The LP_UNEQ is an alarm indicating that the lower order path is unequipped. This alarm is
reported when the board detects that the V5 byte signal label is 0.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services in the path are unavailable. If the services are configured with protection, protection
switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
The data configuration is incorrect.
l
Cause 1: The tributary path at the local site is configured with services, but the tributary
path at the remote site is not configured with services.
Cause 2: The cross-connection configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The tributary path at the local site is configured with services, but the tributary path at
the remote site is not configured with services.
1.
Check whether the tributary path at the remote site is configured with services. For details,
see Querying TDM Services.
If...
Then...
The tributary path at the remote site is not Configure services for the tributary path at
configured with services
the remote site.
The tributary path at the remote site is
configured with services
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The cross-connection configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the cross-connection configuration at the intermediate nodes is correct. If
not, reconfigure the cross-connections. For details, see Querying TDM Services.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
417
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.154 LP_UNEQ_VC12
Description
The LP_UNEQ_VC12 is an alarm indicating that the VC-12 path is unequipped. This alarm
occurs when the board detects that the V5 byte signal label is 0.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
If the alarm is generated due to incorrect service configurations, the services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
The data configuration is incorrect.
l
Cause 1: The tributary path at the local site is configured with services, but the tributary
path at the remote site is not configured with services.
Cause 2: The cross-connection configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The tributary path at the local site is configured with services, but the tributary path at
the remote site is not configured with services.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the tributary path at the remote site is configured with services. For details,
see Querying TDM Services.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
418
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The tributary path at the remote site is not configured with
services
Configure services.
The tributary path at the remote site is configured with services Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The cross-connection configuration at the intermediate nodes is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the cross-connection configuration at the intermediate nodes is correct. If
not, reconfigure the cross-connections. For details, see Querying TDM Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.155 LP_UNEQ_VC3
Description
The LP_UNEQ_VC3 alarm indicates that a lower order (VC-3) path is unequipped. A board
reports this alarm when detecting that the C2 byte signal label is 0.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
The services in the path are unavailable. If the services are configured with protection, protection
switching is triggered.
Possible Causes
The data configuration is incorrect.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
419
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 1: The tributary path at the local site is configured with services, but the tributary
path at the opposite site is not.
Cause 2: The cross-connection configuration at the intermediate sites is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The tributary path at the local site is configured with services, but the tributary path at
the opposite site is not.
1.
Check whether the tributary path at the opposite site is configured with services. For details,
see Querying TDM Services.
If...
Then...
The tributary path at the opposite site is not configured with
services
Configure services.
The tributary path at the opposite site is configured with
services
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The cross-connection configuration at the intermediate sites is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the cross-connection configuration at the intermediate sites is correct. If
not, reconfigure the cross-connections. For details, see Querying TDM Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.156 LPS_UNI_BI_M
Description
The LPS_UNI_BI_M is an alarm indicating that switching modes (single-ended or dual-ended)
at both ends of the linear MSP do not match with each other.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
420
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the type of the protection group.
0x01: linear MS protection.
Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
The system performs protection switching in single-ended mode.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The linear MSP is configured incorrectly.
The LPS_UNI_BI_M alarm is generated only when the following conditions are met:
l
The switching modes (single-ended or dual-ended) at the local and remote sites are
different.
The last three bits of the K2 byte are set to the indicated mode.
The type of the protocol is set to a restructure protocol.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The linear MSP is configured incorrectly.
1.
Change the MSP switching modes at both ends, and ensure that they are the same. For
details, see Querying the Status of the Linear MSP.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.157 LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT
Description
The LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT is an alarm indicating that the LPT closes the access port of the
local NE. Upon detecting that the convergence port of the local NE or the access port of the
remote NE is faulty, the LPT automatically closes the access port of the local NE. Then, the
LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT alarm is reported.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
421
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicates the board ID.
Parameter 3
Indicates the ID of the sub-board.
Parameter 4, Parameter 5
Indicate the port ID.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services are switched to the backup network and the LPT closes the
access port of the remote NE at the same time.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The convergence port of the local NE or the access port of the remote NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The convergence port of the local NE or the access port of the remote NE is faulty.
1.
Check whether the convergence port of the local NE, the access port and the convergence
port of the remote NE report the ETH_LOS alarm or other alarms related to boards and
optical modules.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms. Then, check whether the LPT_CFG_CLOSEPORT alarm is
cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.158 LPT_INEFFECT
Description
The LPT_INEFFECT is an alarm indicating that the LPT function fails. If the user configures
the LPT function but the board does not support the LPT function, the LPT_INEFFECT alarm
is reported.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
422
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the IP port.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the port ID.
The values are always 0x00 0x01.
Parameter 4, Parameter 5
The values are always 0xff 0xff.
Impact on the System
When the alarm is generated, the services are not affected. If the board hardware is of a very
early version, the board software automatically prevents the LPT protocol state machine from
running, but reserves the LPT configuration.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The board hardware is of a very early version, and the user configures the LPT function.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The board hardware is of a very early version, and the user configures the LPT function.
1.
Check whether the LPT function is required.
If...
Then...
The LPT function is required
Replace the board with a board of the proper
version. For details, see 6 Part Replacement.
The LPT function is not required Delete the configuration of the LPT. For details, see
LPT Configuration.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
423
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.159 LPT_RFI
Description
The LPT_RFI is a remote failure indication of the link path through (LPT) function. This alarm
occurs when the LPT function detects the failure of the remote port or the LPT service network.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the IP port.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the optical interface. The values are always 0x00
0x01.
Parameter 4
The value is always 0xff.
Impact on the System
During the data transmission, the links are unavailable and the services are interrupted when the
LPT function detects the failure of the remote port or the service network. At the same time, the
backup links are enabled. If the backup links are available, the services can be restored on the
backup links.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The remote port fails due to the alarms such as ETH_LOS and
LSR_NO_FITED, or the remote port is disabled.
Cause 2: The LPT service network is faulty.
The communication link is interrupted.
There are the bit error threshold-crossing alarms BIP_EXC and B3_EXC.
There are the alarms such as TU_LOP, TU_AIS, VCAT_LOA,
VCAT_LOM_VC12, and LP_UNEQ_VC12.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
424
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Check the alarms on the NMS, determine the board that reports the LPT_RFI alarm, and then
determine the ID of the alarmed port on the board according to Parameter 1.
Step 2 Cause 1: The remote port fails due to the alarms such as ETH_LOS and LSR_NO_FITED, or
the remote port is disabled.
1.
2.
Check whether the corresponding opposite port is enabled.
If...
Then...
The opposite port is disabled
Enable the opposite port.
The opposite port is enabled
Go to the next step.
Check whether any link fault alarm occurs on the line board.
If...
Then...
Any link fault alarm occurs Handle the link fault alarms. Focus on the R_LOS and
MW_LOF alarms and handle them first.
No link fault alarm occurs
Go to Cause 2.
Step 3 Cause 2: The LPT service network is faulty.
1.
Check whether the following alarms occur on the Ethernet boards of the MEPs at both ends.
Then, handle the alarms.
l ETH_LOS
l LSR_NO_FITED
l BIP_EXC and B3_EXC
l TU_LOP, TU_AIS, VCAT_LOA, VCAT_LOM_VC12, and LP_UNEQ_VC12
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.160 LSR_NO_FITED
Description
The LSR_NO_FITED is an alarm indicating that the SFP optical module is not installed.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
425
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The optical interface fails to carry services.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The laser of the local site is not installed.
Cause 2: The optical module is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The SFP optical module of the local site is not installed.
1.
Find out why the SFP optical module is not installed, and contact Huawei technical support
engineers for the installation.
Step 2 Cause 2: The optical module is faulty.
1.
6.13 Replacing the SFP.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.161 LTI
Description
The LTI is an alarm indicating that the synchronization sources are lost. This alarm is reported
when all the synchronization sources for the NE are lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
0x01: system priority list
0x02: external clock priority list
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
426
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The clock enters the free-run mode and loses synchronization with other NE clocks.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The clock configuration is incorrect.
Cause 2: All the clock sources in the clock source priority table fail.
Cause 3: A fiber cut or a cable cut occurs.
Cause 4: The synchronization source is set to the manual reversion mode.
Cause 5: No input is available from the external clock source.
Cause 6: The board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The clock configuration is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the data in the clock source priority table meets the network planning
requirement. For details, see Querying the Clock Synchronization Status.
If...
Then...
The configuration is incorrect
Correct the configuration.
The configuration is correct
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: All the clock sources in the clock source priority table fail.
1.
Troubleshoot the synchronization sources based on the clock source priority table.
If...
Then...
The synchronization source is an
external clock
Handle the EXT_SYNC_LOS alarm.
The synchronization source is a line
clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the line
board.
The synchronization source is an IF
clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the IF board.
The synchronization source is a
tributary clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the tributary
board.
The synchronization source is an
Ethernet clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the Ethernet
board.
Step 3 Cause 3: A fiber cut or a cable cut occurs.
1.
Connect the fiber or cable properly.
Step 4 Cause 4: The synchronization source is set to the manual reversion mode.
1.
See Modifying the Recovery Parameter of the Clock Source, and set the clock source to
the automatic reversion mode.
Step 5 Cause 5: No input is available from the external clock source.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
See Configuring Clock Sources for External Clock Output, and configure the clock source
that provides external clock signals.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
427
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 6 Cause 6: The board is faulty.
1.
Replace the board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.162 MAC_EXT_EXC
Description
The MAC_EXT_EXC alarm indicates that the number of bit errors at the MAC layer crosses
the threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the threshold crossing type.
l 0x01: ETHDROP threshold crossing
l 0x02: ETHEXCCOL threshold crossing
l 0x03: RXBBAD threshold crossing
Impact on the System
When the MAC_EXT_EXC alarm occurs, the performance of services degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: ETHDROP threshold crossing. The number of packet loss events crosses the upper
threshold.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
428
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: ETHEXCCOL threshold crossing. The number of frames unsuccessfully
transmitted after successive collisions crosses the upper threshold.
Cause 3: RXBBAD threshold crossing. The number of bytes in received bad packets crosses
the upper threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the working modes of the ports at the transmit and receive ends are the same.
1.
On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports at the transmit and receive ends.
If...
Then...
The ports at the transmit and receive
Set the working modes of the ports at the
ends work in different modes or in half- transmit and receive ends to full-duplex or
duplex mode
auto-negotiation. Ensure that the working
modes of the ports at the transmit and receive
ends are the same. For details, see Setting the
General Attributes of Ethernet Ports.
The ports at the transmit and receive
Go to the next step.
ends work in the same mode and neither
port works in half-duplex mode.
Step 2 Handle the problem that the opposite site transmits packets abnormally.
Step 3 Handle the quality problem with the transmission line.
Check whether the local end reports alarms such as ETH_LOS as the external line is damaged
or over attenuated. If yes, see the related handling method to clear the alarms.
Step 4 Replace the faulty board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.163 MAC_FCS_EXC
Description
The MAC_FCS_EXC alarm indicates that the software detects that the number of bit errors at
the MAC layer crosses the threshold. The software periodically detects the number of bytes
received by the MAC chip and the number of bytes that have bit errors. The MAC_FCS_EXC
alarm is reported when the number of bit errors crosses the threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
429
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the MAC_FCS_EXC alarm occurs, the performance of services degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The performance of the line signals degrades.
Cause 2: The input optical power is abnormal.
Cause 3: A fiber connector is dirty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The performance of the line signals degrades.
1.
On the NMS, check for a LOOP_ALM alarm. If there is any, clear it. For details, see 8.5
Software Loopback.
2.
If the LOOP_ALM alarm persists, check whether the NMS is under a denial-of-service
(DOS) attack. If yes, eliminate the source that transmits a large amount of invalid data, and
then check whether the LOOP_ALM alarm is cleared.
3.
If the LOOP_ALM alarm persists, check whether a cable or fiber is faulty. Replace the
faulty cable or fiber, and then check whether the LOOP_ALM alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The input optical power is abnormal.
1.
Check whether the alarmed port reports an IN_PWR_ABN alarm as well.
2.
If there is any, clear the IN_PWR_ABN alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: A fiber connector is dirty.
1.
Clean the fiber connector and the optical receive port. For details, see 8.2 Cleaning Fiber
Connectors and Adapters.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.164 MOD_COM_FAIL
Description
The MOD_COM_FAIL is an alarm indicating that Module communicates abnormally.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
430
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 0x11 indicates that the communication between the system control unit and
packet switching unit is failed.
Impact on the System
The related operations cannot be performed by using the NMS and the performance information
of each module cannot be queried.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The software processing of the related modules of the board is faulty.
Cause 2: The board hardware is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The software processing of the related modules of the board is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the faulty board by using the NMS. For details, refer to 8.6.1 Cold
Reset.
2.
remove the faulty board and insert it again.
Step 2 Cause 2: The board hardware is faulty.
1.
Replace the faulty board. For details, refer to 6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch
and Timing Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.165 MOD_TYPE_MISMATCH
Description
The MOD_TYPE_MISMATCH alarm indicates that a mismatched port module is detected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
431
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Maloperation
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the ID of the port that reports the alarm. For example, 0x01 indicates
that the alarm is reported by port 1.
Impact on the System
The services at the alarmed port are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The preset type of the SFP module is different from the actual type of the SFP module.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The preset type of the SFP module is different from the actual type of the SFP module.
1.
Find out the port that reports the alarm according to the alarm parameters.
2.
Check whether the preset type of the SFP module is the same as the actual type of the SFP
module.
If...
Then...
The preset type of the SFP module is the Replace the optical/electrical SFP
same as the actual type of the SFP module module. Ensure that the new SFP module is
of the correct type.
The preset type of the SFP module is
Reset the type of the SFP module.
different from the actual type of the SFP
module
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
432
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.166 MPLS_PW_BDI
Description
The MPLS_PW_BDI is an alarm of PW backward defect indication. This alarm occurs when
the local NE receives the BDI packet, notifying that the remote NE detects that the PW is faulty.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services on the transmit side of the local NE are faulty.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The remote NE detects that the PW is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The remote NE detects that the PW is faulty.
If...
Then...
A board on the remote NE is reset or faulty
Rectify the fault on the remote NE.
The physical link between the local NE and the
remote NE is faulty
Rectify the fault on the physical link.
The bandwidth allocated to the PW is fully
occupied.
Increase the bandwidth of the PW.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.167 MPLS_PW_Excess
Description
The MPLS_PW_Excess is an alarm indicating that excessive trail termination source identifiers
(TTSIs) are received on the PW. This alarm occurs when five or more correct CV/FFD packets
are received within three consecutive CV/FFD periods.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
433
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Services may be interrupted if excessive redundant packets are received.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Multiple PWs are configured with the same label and PW ID.
Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Multiple PWs are configured with the same label and PW ID.
1.
Check whether multiple PWs are configured with the same label and PW ID.
2.
If yes, delete the redundant PWs or change the PW ID and label of each PW to unique
values.
3.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
1.
Check whether any fiber or cable is misconnected.
2.
If yes, rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.168 MPLS_PW_LOCV
Description
The MPLS_PW_LOCV is an alarm of PW connectivity loss. This alarm occurs when no
expected CV/FFD packets are received within three consecutive CV/FFD periods.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
434
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The remote NE of the PW stops transmitting CV/FFD packets.
Cause 2: The OAM is different between the ends of the PW.
Cause 3: The PW that carries services is faulty.
Cause 4: The remote NE of the PW is faulty.
Cause 5: The service interface is configured incorrectly.
Cause 6: Serious congestion occurs on the network.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The remote NE of the PW stops transmitting CV/FFD packets.
1.
Check whether the remote NE of the PW stops transmitting CV/FFD packets.
If...
Then...
The remote NE of the PW stops
transmitting CV/FFD packets
Enable the CV/FFD detection and then
check whether the alarm clears.
The remote NE of the PW keeps
transmitting CV/FFD packets
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The OAM is different between the ends of the PW.
1.
Check whether the OAM is different between the ends of the PW. If no, Setting PW OAM
Parameters according to the plan. If yes, go to cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The PW that carries services is faulty.
1.
Check whether the local NE and remote NE of the PW report any alarm related to boards.
If yes, clear the alarm. Then, check whether the MPLS_PW_LOCV alarm is cleared.
2.
Check whether any link-related alarm is reported. If yes, clear the alarm. Then, check
whether the MPLS_PW_LOCV alarm is cleared.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 4.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
435
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 4 Cause 4: The remote NE of the PW is faulty.
1.
Check whether the interconnected board of the remote NE reports the COMMUN_FAIL
alarm. If yes, the board is being reset. Clear the COMMUN_FAIL alarm and then check
whether the MPLS_PW_LOCV alarm is cleared.
2.
If the interconnected board of the remote NE reports other alarms, clear these alarms. Then,
check whether the MPLS_PW_LOCV alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 5.
Step 5 Cause 5: The service interface is configured incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the service interface is configured correctly according to service planning.
2.
If not, reconfigure the service interface. Then, check whether the MPLS_PW_LOCV alarm
is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 6.
Step 6 Cause 6: Serious congestion occurs on the network.
1.
Check whether the bandwidth allocated to the faulty tunnel is fully occupied.
2.
If yes, increase the bandwidth of the PW or eliminate the sources that transmit a large
amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.169 MPLS_PW_MISMATCH
Description
The MPLS_PW_MISMATCH is an alarm indicating that the trail termination source identifiers
(TTSIs) on the PW do not match with the specified one. This alarm occurs when only the packets
with wrong TTSIs are received within three consecutive CV/FFD periods.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
436
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
Services are interrupted or the packets from other PWs are received.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The ingress node or egress node of the faulty PW is configured incorrectly.
Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The ingress node or egress node of the faulty PW is configured incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the ingress node and egress node of the faulty PW are configured correctly
according to NE planning.
2.
If the ingress node or egress node is configured incorrectly, correct the configuration and
then check whether the alarm clears.
Step 2 Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
1.
Check whether any fiber or cable is misconnected.
2.
If yes, rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.170 MPLS_PW_MISMERGE
Description
The MPLS_PW_MISMERGE is an alarm indicating that the trail termination source identifiers
(TTSIs) are mismerged on the PW. This alarm is reported if the CV/FFD packets with correct
TTSIs and those with wrong TTSIs are received in three consecutive CV/FFD periods.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Services are interrupted or the packets from other PWs are received.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
437
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The PW is configured incorrectly.
Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The PW is configured incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the PW are configured correctly according to NE planning.
2.
If the PW is configured incorrectly, correct the configuration and then check whether the
alarm clears.
Step 2 Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
1.
Check whether any fiber or cable is misconnected.
2.
If yes, rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.171 MPLS_PW_SD
Description
The MPLS_PW_SD is an alarm of signal degrade on the PW. This alarm is reported when the
packet loss rate of the connectivity check (CC) crosses the SD threshold but is lower than the
SF threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Services degrade and moderate packet loss occurs.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The bandwidth of the PW is fully occupied.
Cause 2: The physical port has bit errors or packet loss.
Cause 3: The fiber connector or the optical module is dirty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
438
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The bandwidth of the PW is fully occupied.
1.
Check whether the bandwidth allocated to the faulty PW is fully occupied.
2.
If yes, increase the bandwidth of the PW or eliminate the sources that transmit a large
amount of invalid data. Then, check whether the MPLS_PW_SD alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The physical port has bit errors or packet loss.
1.
Check whether the fiber connector is loose. If yes, insert the fiber connector securely.
Step 3 Cause 3: The fiber connector or the optical module is dirty.
1.
Clean the fiber connector or the optical module. For details, see Checking and cleaning
fiber connectors.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.172 MPLS_PW_SF
Description
The MPLS_PW_SF is an alarm of signal failure on the PW. This alarm occurs when the number
of received connectivity check (CC) packets is less than the signal failure (SF) threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Services fail and severe packet loss occurs.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The bandwidth of the PW is fully occupied.
Cause 2: The physical port has bit errors or packet loss.
Cause 3: The fiber connector or the optical module is dirty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The bandwidth of the PW is fully occupied.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
439
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
1.
Check whether the bandwidth allocated to the faulty PW is fully occupied.
2.
If yes, increase the bandwidth of the PW or eliminate the sources that transmit a large
amount of invalid data. Then, check whether the MPLS_PW_SF alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The physical port has bit errors or packet loss.
1.
Check whether the fiber connector is loose. If yes, insert the fiber connector securely.
Step 3 Cause 3: The fiber connector or the optical module is dirty.
1.
Clean the fiber connector or the optical module. For details, see Checking and cleaning
fiber connectors.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.173 MPLS_PW_UNKNOWN
Description
The MPLS_PW_UNKNOWN is an alarm of unknown defects on the PW. This alarm occurs
when the connectivity check (CC) packets of unexpected types, periods, and values are received
within three consecutive periods.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
PW OAM fails.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The PW OAM configuration at the two ends is different.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The PW OAM configuration at the two ends is different.
1.
Change the PW OAM configuration to the same at the two ends.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
440
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.174 MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI is an alarm of tunnel backward defect indication. This alarm occurs
when the port of the local NE receives the backward defect indication (BDI) packet, notifying
that the opposite NE detects that the tunnel is faulty.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the services on the local NE is normal.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The opposite NE detects MPLS alarms.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The opposite NE detects MPLS alarms.
1.
Clear the MPLS alarms reported on the opposite NE.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.175 MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess is an alarm indicating that excessive trail termination source
identifiers (TTSIs) are received in the tunnel. This alarm occurs when the Ethernet port of the
local NE receives five or more correct CV/FFD packets within three consecutive CV/FFD
periods.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
441
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Services may be interrupted if excessive redundant packets are received.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Physical links are misconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Physical links are misconnected.
1.
Check whether any fiber or cable is misconnected between the two ends. If yes, reconnect
the fiber or cable.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.176 MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI is an alarm of tunnel forward defect indication. This alarm is
reported when the local NE receives the forward defect indication (FDI) packet, notifying that
the upstream tunnel at the physical layer is faulty.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services may be interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
442
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The upstream NE detects that the physical link that carries the tunnel is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The upstream NE detects that the physical link that carries the tunnel is faulty.
If...
Then...
The link-related alarms, such as MW_BER_EXC,
MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR and MW_LOF, are
reported
Clear these alarms first.
The transmit board of the local NE reports hardware-related
alarms (alarms on the optical modules or boards), such as
HARD_BAD and LSR_NO_FITED
Clear these alarms first.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.177 MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV is an alarm of tunnel connectivity loss. This alarm occurs when
the port of the local NE fails to receive expected CV/FFD packets within three CV/FFD periods.
(The expected CV/FFD packets must carry correct TTSIs and have the correct type, period, and
value.)
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the services that the faulty tunnel carries are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: In detection mode of manual, the MPLS OAM settings, such as detection packet
type and detection packet period, differ at the two ends.
Cause 2: Severe congestion occurs on the network.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
443
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 3: A certain board is faulty.
Cause 4: The physical link between the two ends is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: In detection mode of manual, the MPLS OAM settings, such as detection packet type
and detection packet period, differ at the two ends.
1.
Check whether the MPLS OAM settings are the same at the two ends.
2.
If the MPLS OAM settings are different at the two ends, change them to the same.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: Severe congestion occurs on the network.
1.
If the alarm persists, check whether the bandwidth allocated to the faulty tunnel is fully
used. If the bandwidth of the faulty tunnel is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or eliminate
the sources that transmit a large amount of invalid data.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Check whether the remote NE reports the COMMUN_FAIL alarm. If yes, you can infer
that the remote NE is being reset. Wait until the COMMUN_FAIL alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the local NE and the remote NE report alarms related to optical modules or
boards, such as HARD_BAD and LSR_NO_FITED. If yes, clear these alarms first.
3.
Then, check whether the MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The physical link between the two ends is faulty.
1.
Check whether any fiber or cable is damaged. If yes, replace the damaged fiber or cable.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
444
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.178 MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH is an alarm indicating that the trail termination source
identifiers (TTSIs) on the tunnel do not match with the specified one. This alarm is reported if
no CV/FFD packets with correct TTSIs are received in three consecutive CV/FFD periods.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services are interrupted or packets from other tunnels are received.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The tunnel settings are incorrect. For example, the LSR IDs or tunnel IDs differ
at the two ends of the tunnel.
Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The tunnel settings are incorrect. For example, the LSR IDs or tunnel IDs differ at the
two ends of the tunnel.
1.
Check whether the tunnel settings are the same at the two ends.
l If the source NE is an ingress node, Sink Node is the LSR ID of the sink NE. If the sink
NE is an egress node, Source Node is the LSR ID of the source NE.
l Tunnel IDs of the source NE and sink NE of a tunnel must be set to the same.
2.
If the tunnel IDs are different, change them to the same.
Step 2 Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
1.
Check whether any fiber or cable is misconnected between the two ends. If yes, connect
the fiber or cable properly.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
445
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.179 MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE is an alarm indicating that the trail termination source
identifiers (TTSIs) are mismerged in the tunnel. This alarm is reported if the CV/FFD packets
with correct TTSIs and those with wrong TTSIs are received in three consecutive CV/FFD
periods.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the packets from other tunnels are received.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Multiple tunnels are configured with the same label.
Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Multiple tunnels are configured with the same label.
1.
Check whether multiple tunnels are configured with the same label.
2.
If multiple tunnels are configured with the same label, delete the redundant labels or change
the label of each tunnel to a unique value.
Step 2 Cause 2: Physical links are misconnected.
1.
Check whether any fiber or cable is misconnected between the two ends. If yes, connect
the fiber or cable properly.
----End
Related Information
On the NE, the label of each MPLS tunnel is unique.
A.3.180 MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
446
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL is an alarm indicating that the OAM protocol negotiation
between the two ends of the tunnel fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, services are switched to the backup network and the LPT closes the
access port of the remote NE at the same time.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The OAM function is enabled and the detection mode is auto-sensing on one end
and is disabled on the other end.
Cause 2: The tunnel is unavailable when the OAM function is enabled and the detection
mode is auto-sensing.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The OAM function is enabled and the detection mode is auto-sensing on one end and
is disabled on the other end.
1.
Enable the OAM function.
Step 2 Cause 2: The tunnel is unavailable when the OAM function is enabled and the detection mode
is auto-sensing.
1.
Check whether the sink node of the alarmed tunnel reports the HARD_BAD,
ETH_LOS, or R_LOS alarm.
2.
If yes, clear the alarm. After the OAM protocol negotiation succeeds, the
MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL alarm clears.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
447
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.181 MPLS_TUNNEL_SD
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_SD is an alarm of signal degrade on the tunnel. This alarm is reported
when the packet loss rate of the CV/FFD crosses the SD threshold but is lower than the SF
threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Services degrade and moderate packet loss occurs.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Excessive bit errors occur.
Cause 2: The bandwidth of the tunnel is fully used.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Excessive bit errors occur.
1.
Check whether the FCS_ERR alarm is reported. If yes, clear the FCS_ERR alarm and then
check whether the MPLS_TUNNEL_SD alarm is cleared.
2.
If the alarm persists, proceed to cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The bandwidth of the tunnel is fully used.
1.
Check whether the bandwidth allocated to the tunnel is fully used. If the bandwidth of the
faulty tunnel is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or eliminate the sources that transmit a
large amount of invalid data. Check whether the alarm clears.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
448
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.182 MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_SF is an alarm indicating that the tunnel signal degrades severely. This
alarm is reported if the loss ratio of the CV/FFD packets is higher than the SF threshold and CV/
FFD packets are received in three consecutive periods.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the quality of service degrades severely and a large number of packets
are lost.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Excessive bit errors occur.
Cause 2: The bandwidth of the tunnel is fully used.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Excessive bit errors occur.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the FCS_ERR alarm is reported. If yes, clear the
FCS_ERR, and then check whether the MPLS_TUNNEL_SF is cleared.
2.
If the MPLS_TUNNEL_SF persists, go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The bandwidth of the tunnel is fully used.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the bandwidth of the tunnel is fully used. If the bandwidth of
the tunnel is fully used, increase the bandwidth allocated to the tunnel or eliminate any
source that transmits a large amount of invalid data. Check whether the alarm is cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
449
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.183 MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN
Description
The MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN is an alarm indicating that certain unknown defects exist
on the tunnel. This alarm is reported when the port receives the CV packets and the FFD packets.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the OAM function is affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The OAM settings differ at the two ends.
Cause 2: The NE receives packets from an unknown source.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The OAM settings differ at the two ends.
1.
If the MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN alarm is reported transiently, check whether Tunnel
OAM configuration is changed on the local NE and the opposite NE.
2.
If the local NE and the opposite NE have different Tunnel OAM configuration, the
MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN alarm is reported transiently and then the
MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV alarm is reported. Ensure that both ends have the same Tunnel
OAM configuration. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The NE receives packets from an unknown source.
1.
Check whether there is any service configured between the NE and an unknown source, or
whether the NE is connected to an unknown source.
2.
If yes, modify the incorrect configuration or reconnect the fibers.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.184 MS_AIS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
450
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The MS_AIS is an alarm indicating multiplex section alarms. This alarm is reported when the
board detects that bits 6-8 of the K2 byte in the three consecutive frames are 111.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services on the line port are interrupted. If the services are configured with protection,
protection switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Cause 2: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
1.
2.
3.
Replace the line board at the opposite site based on the type of the alarmed board.
If...
Then...
The line board reports the alarm
Replace the line board at the opposite end.
The IF board reports the alarm
Replace the IF board at the opposite end.
Replace the board and then check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board replacement
End the fault handling.
The alarm persists after the board replacement
Go to the next step.
Replace the system control, cross-connect, and timing board at the opposite end.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board replacement
End the fault handling.
The alarm persists after the board replacement
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
451
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.185 MS_CROSSTR
Description
The MS_CROSSTR is an alarm indicating that a performance indicator of the multiplex section
crosses the threshold. This alarm is reported when the board detects that the MS BER
performance indicator crosses the preset threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the performance monitoring period:
l 0x01: 15 minutes
l 0x02: 24 hours
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Parameter 2 is always 0x00. Parameter 3 indicate the ID of a
performance event that causes the alarm and has the following
meanings:
l 0x10: MSBBE
l 0x11: MSES
l 0x12: MSSES
l 0x13: MSFEBBE
l 0x14: MSFEES
l 0x15: MSFESES
l 0x16: MSUAS
l 0x17: MSCSES
l 0x18: MSFECSES
l 0x21: MSFEUAS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
452
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
A large number of bit errors occur in the services, and the services may be interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Services are interrupted for a long time.
Cause 2: The MS BER performance indicator crosses the preset threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Services are interrupted for a long time.
NOTE
Handle the alarm as follows if the value of parameter 3 is 0x16:
1.
Check whether fibers are properly connected. If not, connect the fibers again according to
planning information.
2.
Check whether cross-connections are configured for service ports. If not, configure crossconnections again according to planning information.
Step 2 Cause 2: The MS BER performance indicator crosses the preset threshold.
1.
Check the threshold crossing records of MS BER performance events to find out the
performance event that crosses the preset threshold. For details, see 8.3.8 Browsing the
Performance Event Threshold-Crossing Records.
2.
Handle the performance event that crosses the threshold.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.186 MS_RDI
Description
The MS_RDI is an alarm indicating that data reception at the remote end of the multiplex section
fails. This alarm is reported when the board detects that bits 6-8 of the K2 byte are 110.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
453
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The services on the local site are not affected. The services received by the opposite station,
however, are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the opposite station, and the message indicates
that data reception at the remote end of the multiplex section fails.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the opposite station, and the message indicates
that data reception at the remote end of the multiplex section fails.
1.
Rectify the fault that occurs on the opposite station.
The possible alarms are as follows:
l MS_AIS
l R_LOS
l R_LOF
l B2_EXC
l B2_SD
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.187 MS_REI
Description
The MS_REI is an alarm indicating that bit errors occur on the remote end of the multiplex
section. This alarm is reported when the board detects that the M1 byte is non-zero.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services on the local site are not affected. The services received by the opposite station,
however, has bit errors.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
454
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the opposite station, and the message indicates
that bit errors occur on the remote end of the multiplex section.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local site receives a message from the opposite station, and the message indicates
that bit errors occur on the remote end of the multiplex section.
1.
Handle the MS_BBE performance event on the port of the opposite station.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.188 MSAD_CROSSTR
Description
The MSAD_CROSSTR is an alarm indicating that the adaptation performance indicator of the
multiplex section crosses the threshold. This alarm is reported when the board detects that an
AU pointer adaptation performance indicator crosses the preset threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the performance monitoring period:
l 0x01: 15 minutes
l 0x02: 24 hours
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the ID of a performance event that causes the alarm.
l 0x2a: AUPJCHIGH
l 0x2b: AUPJCLOW
l 0x2c: AUPJCNEW
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
455
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
Bit errors may occur in the services.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: An AU pointer adaptation performance indicator crosses the preset threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: An AU pointer adaptation performance indicator crosses the preset threshold.
1.
Check the threshold crossing records of the AU pointer adaptation performance events to
find out the performance event that crosses the preset threshold. For details, see 8.3.8
Browsing the Performance Event Threshold-Crossing Records.
2.
Handle the performance event that crosses the threshold.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.189 MULTI_RPL_OWNER
Description
The MULTI_RPL_OWNER is an alarm indicating that the ring network contains several
RPL_OWNER nodes.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the ID of the ERPS instance.
Impact on the System
The ERPS protection fails and the services configured on the Ethernet ring are interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
456
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The related data is configured incorrectly.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The related data is configured incorrectly.
1.
Reconfigure the ERPS protection. For details, see Creating Ethernet Ring Protection
Instances.
----End
Related Information
The following table describes the meanings of the parameters in the MULTI_RPL_OWNER
alarm reported by the EMS6.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 4
Indicates the port ID.
Parameter 5, Parameter 6
Indicate the ID of the ERPS instance.
A.3.190 MW_AM_TEST
Description
The MW_AM_TEST is an alarm indicating that the IF port is in the AM testing state.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Other alarms
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The transmission capacity is reduced during the AM test.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause: The AM testing is enabled.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
457
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The AM testing is enabled.
1.
After the AM testing ends, disable the AM testing.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.191 MW_BER_EXC
Description
The MW_BER_EXC is an alarm indicating that excessive bit errors occur on the radio link. This
alarm is reported when the bit errors on the radio link exceed the specified threshold (10-3 by
default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the MW_BER_EXC alarm occurs, the service on the port is interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Cause 3: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Cause 4: An interference event occurs.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
At the local end, check whether the receive power of the ODU is normal. If yes, determine
the abnormality and take proper measures. For details, see Querying the Historical Transmit
Power and Receive Power
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
458
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The RSL is lower than the receiver
sensitivity
Follow the steps:
1. Check the installation of the antenna to ensure
that the azimuth of the antenna meets the
requirement.
2. Check the antenna direction. Check whether
the received signal is from the main lobe.
If the antenna direction does not meet the
requirement, adjust the antenna in a wide
range.
3. Check whether the setting of the polarization
direction of the antenna is correct. Adjust the
incorrect polarization direction.
4. Check whether the antenna gain at both the
transmit and receive ends meets the
specifications. Replace the antennas that do
not meet the requirement.
5. Check whether any mountain or building
obstacle exists in the transmit direction.
If yes, contact the network planning
department for proper modification of the
planning design, hence preventing the block
of the mountain or building obstacle.
The RSL is higher than the specified
RSL of the network. The offset value is
tens of decibels. The duration is from
tens of seconds to several hours.
Slow up fading occurs. Follow the steps:
1. Check whether any co-channel interference
occurs.
a. Mute the ODU at the opposite end. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU
Information of a Radio Link.
b. Check the RSL at the local end. For details,
see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90
dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
interference that may affect the long-term
availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
2. Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the
interference source.
3. Contact the spectrum management
department to clear the interference spectrum
or change plans to minimize the interference.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
459
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The RSL is lower than the specified RSL
of the network. The offset value is tens of
decibels. The duration is from tens of
seconds to several hours.
Slow down fading occurs. Generally, the radio
link may be faulty in both directions, because
slow fading is imposed by the transmission path.
Contact the network planning department to make
the following changes:
l Increase the installation height of the antenna.
l Reduce the transmission distance.
l Increase the antenna gain.
l Increase the transmit power.
If the RSL is lower than or higher than Fast fading occurs. Contact the network planning
the specified RSL of the network and if department to make the following changes:
the duration is from several milliseconds
l Adjust the position of the antenna to block the
to tens of seconds.
reflected wave or make the reflection point fall
on the ground that has a small reflection
coefficient, therefore reducing the multipath
fading.
l Adjust the RF configuration to make the links
in the 1+1 SD configuration.
l If the links are configured with the 1+1 SD
protection, adjust the height offset between
two antennas to make the receive power of one
antenna stronger than the receive power of the
other antenna.
l Increase the fading margin.
Step 2 Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station and excluding the position one by one.
Follow the steps:
1.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the opposite end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting Loopback
for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified after the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any cable
connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
3.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not meet
the requirement.
4.
Then, check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified Replace the ODU at the opposite end.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
460
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
End the alarm handling.
Step 3 Cause 3: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station and excluding the position one by one.
Follow the steps:
1.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the local end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting Loopback
for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the local end is rectified after the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any cable
connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
3.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not meet
the requirement.
4.
Then, check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the ODU at the local end.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
End the alarm handling.
Step 4 Cause 4: An interference event occurs.
1.
2.
3.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether any co-channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Check the RSL at the local end. For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90 dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
interference that may affect the long-term availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
Check whether any adjacent channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Adjust the radio working mode at the local end and use the minimum channel spacing.
For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
c.
Decrease the received frequency at the local end by a half of the channel spacing. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
d.
Test and record the RSL.
e.
Increase the received frequency at the local end, with a step length of 0.5 MHz or 1
MHz, and record the RSL accordingly until the received frequency is equal to the
original received frequency plus a half of the channel spacing.
f.
Compare the recorded RSLs, and check whether the RSL in a certain spectrum is
abnormal if the received frequency is within the permitted range.
Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the interference source.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
461
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4.
A Alarm Reference
Contact the spectrum management department to clear the interference spectrum or change
plans to minimize the interference.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.192 MW_BER_SD
Description
The MW_BER_SD is an alarm indicating that signal deteriorates on the radio link. This alarm
is reported when the bit errors on the radio link exceed the specified threshold (10-6 by default)
but does not reach the MW_BER_EXC alarm threshold (10-3 by default).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service performance on the port deteriorates. If the equipment is configured with 1+1 FD/
SD protection, switching on the channel side may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Cause 3: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Cause 4: An interference event occurs.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
At the local end, check whether the receive power of the ODU is normal. If yes, determine
the abnormality and take proper measures. For details, see Querying the Historical Transmit
Power and Receive Power
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
462
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The RSL is lower than the receiver
sensitivity
Follow the steps:
1. Check the installation of the antenna to ensure
that the azimuth of the antenna meets the
requirement.
2. Check the antenna direction. Check whether
the received signal is from the main lobe.
If the antenna direction does not meet the
requirement, adjust the antenna in a wide
range.
3. Check whether the setting of the polarization
direction of the antenna is correct. Adjust the
incorrect polarization direction.
4. Check whether the antenna gain at both the
transmit and receive ends meets the
specifications. Replace the antennas that do
not meet the requirement.
5. Check whether any mountain or building
obstacle exists in the transmit direction.
If yes, contact the network planning
department for proper modification of the
planning design, hence preventing the block
of the mountain or building obstacle.
The RSL is higher than the specified
RSL of the network. The offset value is
tens of decibels. The duration is from
tens of seconds to several hours.
Slow up fading occurs. Follow the steps:
1. Check whether any co-channel interference
occurs.
a. Mute the ODU at the opposite end. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU
Information of a Radio Link.
b. Check the RSL at the local end. For details,
see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90
dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
interference that may affect the long-term
availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
2. Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the
interference source.
3. Contact the spectrum management
department to clear the interference spectrum
or change plans to minimize the interference.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
463
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The RSL is lower than the specified RSL
of the network. The offset value is tens of
decibels. The duration is from tens of
seconds to several hours.
Slow down fading occurs. Generally, the radio
link may be faulty in both directions, because
slow fading is imposed by the transmission path.
Contact the network planning department to make
the following changes:
l Increase the installation height of the antenna.
l Reduce the transmission distance.
l Increase the antenna gain.
l Increase the transmit power.
If the RSL is lower than or higher than Fast fading occurs. Contact the network planning
the specified RSL of the network and if department to make the following changes:
the duration is from several milliseconds
l Adjust the position of the antenna to block the
to tens of seconds.
reflected wave or make the reflection point fall
on the ground that has a small reflection
coefficient, therefore reducing the multipath
fading.
l Adjust the RF configuration to make the links
in the 1+1 SD configuration.
l If the links are configured with the 1+1 SD
protection, adjust the height offset between
two antennas to make the receive power of one
antenna stronger than the receive power of the
other antenna.
l Increase the fading margin.
Step 2 Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station and excluding the position one by one.
Follow the steps:
1.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the opposite end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting Loopback
for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified after the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any cable
connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
3.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not meet
the requirement.
4.
Then, check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified Replace the ODU at the opposite end.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
464
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
End the alarm handling.
Step 3 Cause 3: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station and excluding the position one by one.
Follow the steps:
1.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the local end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting Loopback
for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the local end is rectified after the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any cable
connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
3.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not meet
the requirement.
4.
Then, check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the ODU at the local end.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
End the alarm handling.
Step 4 Cause 4: An interference event occurs.
1.
2.
3.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether any co-channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Check the RSL at the local end. For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90 dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
interference that may affect the long-term availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
Check whether any adjacent channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Adjust the radio working mode at the local end and use the minimum channel spacing.
For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
c.
Decrease the received frequency at the local end by a half of the channel spacing. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
d.
Test and record the RSL.
e.
Increase the received frequency at the local end, with a step length of 0.5 MHz or 1
MHz, and record the RSL accordingly until the received frequency is equal to the
original received frequency plus a half of the channel spacing.
f.
Compare the recorded RSLs, and check whether the RSL in a certain spectrum is
abnormal if the received frequency is within the permitted range.
Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the interference source.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
465
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4.
A Alarm Reference
Contact the spectrum management department to clear the interference spectrum or change
plans to minimize the interference.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.193 MW_CFG_MISMATCH
Description
The MW_CFG_MISMATCH is an alarm of configuration mismatch on radio links. This alarm
occurs when an NE detects configuration mismatch on both ends of a radio link. For example,
the number of E1 signals, the number of STM-1 signals, AM enabling, 1588 overhead enabling,
modulation mode may be configured differently on both ends of a radio link.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the cause of the fault.
l 0x01: The number of E1 signals is different.
l 0x02: The AM enabling is different.
l 0x03: The 1588 overhead enabling is different.
l 0x04: The modulation mode is different.
l 0x05: The service mode is different.
l 0x06: The number of STM-1 signals is different.
l 0x09: The IP header compression enabling is different.
Parameter 2
When the value of Parameter 1 is 0x09:
l 0x01: The air interface compression at L2 is different.
l 0x02: The air interface compression at L3 is different.
When Parameter 1 takes another value, Parameter 2 is reserved.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
466
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the service configuration cannot take effect or services are interrupted.
After the NE is power cycled or reset, this alarm may still affect services.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The number of E1 signals is different on both ends of a radio link.
Cause 2: The AM enabling is different on both ends of a radio link.
Cause 3: The 1588 overhead enabling is different on both ends of a radio link.
Cause 4: The modulation mode is different on both ends of a radio link.
Cause 5: The service mode is different on both ends of a radio link.
Cause 6: The IP header compression is different on both ends of a radio link.
Cause 7: The air interface compression at L2 or L3 is different.
Cause 8: The number of STM-1 signals is different on both ends of a radio link.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the possible cause of the alarm according to the alarm parameters.
Step 2 Check the configuration on both ends of the radio link. Ensure that the configuration is the same
on both ends of the radio link. For details, see Managing Radio Links.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.194 MW_CONT_WAVE
Description
The MW_CONT_WAVE is an alarm of continuous wave. This alarm occurs if the continuous
wave function is enabled on the IF board and clears after the continuous wave function is
disabled.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If the continuous wave function is enabled, radio links cannot transmit services.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
467
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The continuous wave function is enabled.
Procedure
Step 1 Disable the continuous wave function.
1.
In NE Explorer, select the IF board.
2.
Choose Configuration > IF Interface from the Function Tree.
3.
Select the alarmed port from IF Attribution.
4.
Set 350MHz Consecutive Wave Status to Stop.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.195 MW_E1_LOST
Description
The MW_E1_LOST is an alarm indicating that E1 services are lost. This alarm occurs when the
AM downshifts the modulation scheme or E1 bandwidth decreases in the current modulation
scheme.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the timeslots of E1 services.
Impact on the System
Some E1 services are lost.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
468
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The AM downshifts the modulation scheme.
Cause 2: E1 bandwidth decreases in the current modulation scheme.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The AM downshifts the modulation scheme.
1.
Handle the alarm according to AM_DOWNSHIFT.
Step 2 Cause 2: E1 bandwidth decreases in the current modulation scheme.
1.
Check whether the decrease of E1 bandwidth is caused by incorrect operations. If yes,
restore E1 bandwidth to an appropriate value; if not, ignore the alarm.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.196 MW_FEC_UNCOR
Description
The MW_FEC_UNCOR is an alarm indicating that radio frames forward error correction (FEC)
encoding cannot be corrected.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Bit errors occur in the services. If the equipment is configured with 1+1 FD/SD protection, HSM
channel protection switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Cause 3: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Cause 4: An interference event occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
469
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
1.
At the local end, check whether the receive power of the ODU is normal. If yes, determine
the abnormality and take proper measures. For details, see Querying the Historical Transmit
Power and Receive Power
If...
Then...
The RSL is lower than the receiver
sensitivity
Follow the steps:
1. Check the installation of the antenna to ensure
that the azimuth of the antenna meets the
requirement.
2. Check the antenna direction. Check whether
the received signal is from the main lobe.
If the antenna direction does not meet the
requirement, adjust the antenna in a wide
range.
3. Check whether the setting of the polarization
direction of the antenna is correct. Adjust the
incorrect polarization direction.
4. Check whether the antenna gain at both the
transmit and receive ends meets the
specifications. Replace the antennas that do
not meet the requirement.
5. Check whether any mountain or building
obstacle exists in the transmit direction.
If yes, contact the network planning
department for proper modification of the
planning design, hence preventing the block
of the mountain or building obstacle.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
470
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The RSL is higher than the specified
RSL of the network. The offset value is
tens of decibels. The duration is from
tens of seconds to several hours.
Slow up fading occurs. Follow the steps:
1. Check whether any co-channel interference
occurs.
a. Mute the ODU at the opposite end. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU
Information of a Radio Link.
b. Check the RSL at the local end. For details,
see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90
dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
interference that may affect the long-term
availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
2. Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the
interference source.
3. Contact the spectrum management
department to clear the interference spectrum
or change plans to minimize the interference.
The RSL is lower than the specified RSL
of the network. The offset value is tens of
decibels. The duration is from tens of
seconds to several hours.
Slow down fading occurs. Generally, the radio
link may be faulty in both directions, because
slow fading is imposed by the transmission path.
Contact the network planning department to make
the following changes:
l Increase the installation height of the antenna.
l Reduce the transmission distance.
l Increase the antenna gain.
l Increase the transmit power.
If the RSL is lower than or higher than Fast fading occurs. Contact the network planning
the specified RSL of the network and if department to make the following changes:
the duration is from several milliseconds
l Adjust the position of the antenna to block the
to tens of seconds.
reflected wave or make the reflection point fall
on the ground that has a small reflection
coefficient, therefore reducing the multipath
fading.
l Adjust the RF configuration to make the links
in the 1+1 SD configuration.
l If the links are configured with the 1+1 SD
protection, adjust the height offset between
two antennas to make the receive power of one
antenna stronger than the receive power of the
other antenna.
l Increase the fading margin.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
471
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 2 Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station and excluding the position one by one.
Follow the steps:
1.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the opposite end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting Loopback
for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified after the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any cable
connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
3.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not meet
the requirement.
4.
Then, check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified Replace the ODU at the opposite end.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
End the alarm handling.
Step 3 Cause 3: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station and excluding the position one by one.
Follow the steps:
1.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the local end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting Loopback
for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the local end is rectified after the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
2.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any cable
connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
3.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not meet
the requirement.
4.
Then, check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the ODU at the local end.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
End the alarm handling.
Step 4 Cause 4: An interference event occurs.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether any co-channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Check the RSL at the local end. For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90 dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
472
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
interference that may affect the long-term availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
2.
Check whether any adjacent channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Adjust the radio working mode at the local end and use the minimum channel spacing.
For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
c.
Decrease the received frequency at the local end by a half of the channel spacing. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
d.
Test and record the RSL.
e.
Increase the received frequency at the local end, with a step length of 0.5 MHz or 1
MHz, and record the RSL accordingly until the received frequency is equal to the
original received frequency plus a half of the channel spacing.
f.
Compare the recorded RSLs, and check whether the RSL in a certain spectrum is
abnormal if the received frequency is within the permitted range.
3.
Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the interference source.
4.
Contact the spectrum management department to clear the interference spectrum or change
plans to minimize the interference.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.197 MW_LIM
Description
The MW_LIM is an alarm indicating that a mismatched radio link identifier is detected. This
alarm is reported if an IF board detects that the link ID in the radio frame overheads is inconsistent
with the specified link ID.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
After the IDU IF board reports the MW_LIM alarm, the IF board inserts the AIS alarm into the
received signal. Then, the services on the radio link are interrupted. If the services are configured
with SNCP, protection switching may be triggered.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
473
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The link ID of the local site does not match with the link ID of the opposite station.
Cause 2: The services on other radio links are received due to the incorrect configuration
of the radio link receive frequency at the local or opposite station.
Cause 3: The antenna receives the radio from the other stations, because the direction of
the antenna is set incorrectly.
Cause 4: The polarization direction of the XPIC is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The link ID of the local site does not match with the link ID of the opposite station.
1.
Check whether the link ID of the local site matches with the link ID of the opposite station.
For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link. If not, set the link
IDs of the two stations to the same value according to the requirements of the networking
planning.
Step 2 Cause 2: The services on other radio links are received due to the incorrect configuration of the
radio link receive frequency at the local or opposite station.
1.
Check whether the receive and transmit frequencies of the local site are consistent with the
receive and transmit frequencies of the opposite station. For details, see Configuring the
IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link. If not, set the receive and transmit frequencies of the
two stations again.
Step 3 Cause 3: The antenna receives radio signals from the other stations, because the direction of the
antenna is set incorrectly.
1.
Adjust the direction of the antenna and ensure that the antennas at both ends are aligned.
Step 4 Cause 4: The polarization direction of the XPIC is incorrect.
1.
If XPIC protection groups are configured, check whether the XPIC configuration is correct.
For details, see Creating an XPIC Workgroup.
a.
b.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the settings of XPIC IF board in polarization direction-V and
polarization direction-H meet the requirement of the planning.
If...
Then...
The polarization direction does not meet
the requirement of the planning
Delete the working XPIC group that is
configured incorrectly and create the
other working XPIC group again.
The polarization direction meets the
requirement of the planning
Go to the next step.
Check whether Link ID-V and Link ID-H meet the requirement of the planning.
If...
Then...
The link ID does not meet the
requirement of the planning
Reset the ID of the radio link of the XPIC
IF board according to the planning. For
details, see Creating an XPIC Working
Group.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
474
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The link ID meets the requirement of the
planning
Go to the next step.
Check and modify the XPIC IF board and ODU, and the mapping relationship between the
ODU and the feed bottom. Ensure that the XPIC IF boards in the polarization direction V
of the two ends are interconnected with each other through the radio link in the polarization
direction V, and the XPIC IF boards in the polarization direction H of the two ends are
interconnected with each other through the radio link in the polarization direction H.
----End
Related Information
The MW_LIM alarm is generated due to the inconsistency between the specified link ID and
the received link ID. When the MW_LOF alarm is generated on the link, the received link ID
is a random value. In this case, the link ID is invalid. The MW_LIM alarm is also suppressed
by the MW_LOF alarm.
A.3.198 MW_LOF
Description
The MW_LOF is an alarm indicating that the radio frame is lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services are interrupted. If the system is configured with protection, protection switching
may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The other alarms are generated.
Cause 2: In the case of TDM radio services, the IF working modes at the local site and the
opposite station are different. In the case of Integrated IP radio services, the channel
bandwidth and modulation modes at the local site and the opposite station are different.
Cause 3: The operating frequency of the ODU at the local site is inconsistent with the
operating frequency of the ODU at the opposite station.
Cause 4: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
475
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Cause 5: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Cause 6: The receive power of the ODU is abnormal.
Cause 7: An interference event occurs.
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The other alarms are generated.
1.
Check whether any alarms are generated in the equipment of the local site. If yes, take
priority to clear them.
The relevant alarms are as follows:
l HARD_BAD
l VOLT_LOS
l IF_CABLE_OPEN
l BD_STATUS
l RADIO_RSL_LOW
l CONFIG_NOSUPPORT
l TEMP_ALARM
Step 2 Cause 2: In the case of TDM radio services, the IF working modes at the local site and the
opposite station are different. In the case of Integrated IP radio services, the channel bandwidth
and modulation modes at the local site and the opposite station are different.
1.
In the case of TDM radio services, check whether the working mode of the IF board at the
local site is consistent with the working mode of the IF board at the opposite station. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link. If not, reset the working
mode of the IF board according to the network planning.
In the case of Hybrid radio services, check whether the channel bandwidth and modulation
modes are the same at both ends. If not, change the channel bandwidth and modulation
modes according to the network planning. For details, see Setting the Hybrid/AM
Attributes.
Step 3 Cause 3: The operating frequency of the ODU at the local site is inconsistent with the operating
frequency of the ODU at the opposite station.
1.
Ensure that the type of the ODU at the local site is consistent with the type of the ODU at
the opposite station.
2.
Reset the operating frequency of the ODU according to the network planning. For details,
see Setting ODU Transmit Frequency Attributes.
Set the transmit frequency of the local site to the same as the receive frequency of the
opposite station. Then, set the receive frequency of the local site to the same as the transmit
frequency of the opposite station.
Step 4 Cause 4: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
1.
Check whether any alarms are generated in the equipment of the local site. If yes, take
priority to clear them.
The relevant alarms are as follows:
l HARD_BAD
l BD_STATUS
l VOLT_LOS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
476
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
l IF_CABLE_OPEN
l RADIO_MUTE
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l TEMP_ALARM
2.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station.
Follow the steps:
a.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the opposite end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting
Loopback for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified
after the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
b.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any
cable connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
c.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not
meet the requirement.
d.
Then, check whether the fault at the opposite end is rectified.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not
rectified
Replace the ODU at the opposite end.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified End the alarm handling.
Step 5 Cause 5: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
1.
Locate the fault by looping back the opposite station.
Follow the steps:
a.
Perform an inloop on the IF port at the local end. For details, see 8.5.6 Setting
Loopback for the IF Board. Check whether the fault at the local end is rectified after
the loopback.
If...
Then...
The fault at the opposite end is not rectified
Replace the IF board.
The fault at the opposite end is rectified
Go to the next step.
b.
Check whether the cable connector is prepared according to the requirement. If any
cable connector does not meet the requirement, make a new connector.
c.
Check whether the IF cable is wet, broken, or pressed. Replace the cable that does not
meet the requirement.
d.
Check whether the fault at the local end is rectified.
Step 6 Cause 6: The receive power of the ODU is abnormal.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
477
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
At the local site, check whether the receive power of the ODU is abnormal. For details, see
Browse history performance events. If yes, determine the abnormality and take proper
measures.
If...
Then...
The RSL is lower than the receiver
sensitivity
Follow the steps:
1. Check the installation of the antenna to ensure
that the azimuth of the antenna meets the
requirement.
2. Check the antenna direction. Check whether
the received signal is from the main lobe.
If the antenna direction does not meet the
requirement, adjust the antenna in a wide
range.
3. Check whether the setting of the polarization
direction of the antenna is correct. Adjust the
incorrect polarization direction.
4. Check whether the antenna gain at both the
transmit and receive ends meets the
specifications. Replace the antennas that do
not meet the requirement.
5. Check whether any mountain or building
obstacle exists in the transmit direction.
If yes, contact the network planning
department for proper modification of the
planning design, hence preventing the block
of the mountain or building obstacle.
The RSL is higher than the specified
RSL of the network. The offset value is
tens of decibels. The duration is from
tens of seconds to several hours.
Slow up fading occurs. Follow the steps:
1. Check whether any co-channel interference
occurs.
a. Mute the ODU at the opposite end. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU
Information of a Radio Link.
b. Check the RSL at the local end. For details,
see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90
dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
interference that may affect the long-term
availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
2. Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the
interference source.
3. Contact the spectrum management
department to clear the interference spectrum
or change plans to minimize the interference.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
478
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The RSL is lower than the specified RSL
of the network. The offset value is tens of
decibels. The duration is from tens of
seconds to several hours.
Slow down fading occurs. Generally, the radio
link may be faulty in both directions, because
slow fading is imposed by the transmission path.
Contact the network planning department to make
the following changes:
l Increase the installation height of the antenna.
l Reduce the transmission distance.
l Increase the antenna gain.
l Increase the transmit power.
If the RSL is lower than or higher than Fast fading occurs. Contact the network planning
the specified RSL of the network and if department to make the following changes:
the duration is from several milliseconds
l Adjust the position of the antenna to block the
to tens of seconds.
reflected wave or make the reflection point fall
on the ground that has a small reflection
coefficient, therefore reducing the multipath
fading.
l Adjust the RF configuration to make the links
in the 1+1 SD configuration.
l If the links are configured with the 1+1 SD
protection, adjust the height offset between
two antennas to make the receive power of one
antenna stronger than the receive power of the
other antenna.
l Increase the fading margin.
Step 7 Cause 7: An interference event occurs.
Follow the steps:
1.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether any co-channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Check the RSL at the local end. For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information
of a Radio Link. If the RSL exceeds -90 dBm, it indicates that there is co-channel
interference that may affect the long-term availability and errored-second
performance of the system.
Check whether any adjacent channel interference occurs.
a.
Mute the ODU at the opposite end.
b.
Adjust the radio working mode at the local end and use the minimum channel spacing.
For details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
c.
Decrease the received frequency at the local end by a half of the channel spacing. For
details, see Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
d.
Test and record the RSL.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
479
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
e.
Increase the received frequency at the local end, with a step length of 0.5 MHz or 1
MHz, and record the RSL accordingly until the received frequency is equal to the
original received frequency plus a half of the channel spacing.
f.
Compare the recorded RSLs, and check whether the RSL in a certain spectrum is
abnormal if the received frequency is within the permitted range.
3.
Use a spectrum analyzer to analyze the interference source.
4.
Contact the spectrum management department to clear the interference spectrum or change
plans to minimize the interference.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.199 MW_RDI
Description
The MW_RDI is an alarm indicating that there are defects at the remote end of the radio link.
This alarm is reported when the IF board detects an RDI in the radio frame overheads.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If the local site is configured with the reverse switching function, the 1+1 switching is triggered
on the IF board when the working and protection IF boards receive the MW_RDI alarm at the
same time. This alarm also indicates that the services received by the opposite station are
interrupted.
Possible Causes
After detecting a service alarm that is caused by the fault in a radio link, the receive station
returns a radio link fault indication to the transmit station.
Procedure
Step 1 Clear the radio alarms that occur at the opposite station. The possible alarms are as follows:
l MW_LOF
l R_LOF
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
480
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
l R_LOC
l MW_FEC_UNCOR
l XPIC_LOS
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.200 NESF_LOST
Description
The NESF_LOST is an alarm indicating that the NE software is lost. This alarm is reported when
the system control, cross-connect, and timing board detects that the NE software is lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
481
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the routine inspection object.
l 0x01: FPGA of the system control board in ofs1
l 0x02: FPGA of the system control board in ofs2
l 0x03: ofs1/hwx/nesoft.hwx
l 0x04: ofs2/hwx/nesoft.hwx
l 0x05: ofs1/hwx/ne.ini
l 0x06: ofs2/hwx/ne.ini
l 0x07: ofs1/hwx/ocp.ini
l 0x08: ofs2/hwx/ocp.ini
l 0x09: ofs1/fpga/if1_002.pga
l 0x0a: ofs2/fpga/if1_002.pga
l 0x0b: ofs1/fpga/if1_250.pga
l 0x0c: ofs2/fpga/if1_250.pga
l 0x0d: ofs1/fpga/sl1d.pga
l 0x0e: ofs2/fpga/sl1d.pga
l 0x0f: ofs1/fpga/sl91ifu2.pga
l 0x10: ofs2/fpga/sl91ifu2.pga
l 0x11: ofs1/fpga/sl91ifx2.pga
l 0x12: ofs2/fpga/sl91ifx2.pga
l 0x13: ofs1/fpga/sl91aux.pga
l 0x14: ofs2/fpga/sl91aux.pga
l 0x15: ofs1/hwx/lusoft.hwx
l 0x16: ofs2/hwx/lusoft.hwx
l 0x17: ofs1/hwx/lusoft.ini
l 0x18: ofs2/hwx/lusoft.ini
l 0x19: ofs1/fpga/sl91em6t.pga
l 0x1a: ofs2/fpga/sl91em6t.pga
l 0x1b: ofs1/fpga/pvg610.pga
l 0x1c: ofs2/fpga/pvg610.pga
l 0x1d: ofs1/fpga/pvg610x.pga
l 0x1e: ofs2/fpga/pvg610x.pga
l 0x1f: ofs1/hwx/extbios.hwx
l 0x20: ofs2/hwx/extbios.hwx
l 0x21: ofs1/hwx/luexbios.hwx
l 0x22: ofs2/hwx/luexbios.hwx
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
482
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 4
Indicates the specific alarm cause when a different bit is 1.
l 0x01: If the first bit is 1, it indicates that the file does not exist.
l 0x02: If the second bit is 1, it indicates that verification of the
file fails.
Impact on the System
If the NE software does not exist in the active and standby areas, an NE cannot be restarted after
it is powered off or reset.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: No new NE software is loaded after the existing NE software is erased.
Cause 2: Loading the NE software is unsuccessful.
Cause 3: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: No new NE software is loaded after the existing NE software is erased.
Cause 2: Loading the NE software is unsuccessful.
1.
Check whether the alarm is caused by the loading operation.
If...
Then...
The alarm is caused by the loading
operation
Contact the Huawei technical support
engineers to reload the software.
The alarm is not caused by the loading
operation
Go to the next step.
Step 2 Cause 3: A certain board is faulty.
1.
For details, see 6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.201 NESOFT_MM
Description
The NESOFT_MM is an alarm indicating that the first software system is different from the
second software system. This alarm is reported when the NE detects that the first software system
and the second software system of the system control, cross-connect, and timing board mismatch
with each other.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
483
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the location of the file.
l 0x01: the files in the flash memory
l 0x02: the software that is currently running
l 0x03: the software in the CF card
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
484
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the IDs of the inconsistent files in the flash memory of the
system control board if the value of Parameter 1 is 0x01,
l 0x01: FPGA of the system control board in ofs1
l 0x02: FPGA of the system control board in ofs2
l 0x03: ofs1/hwx/nesoft.hwx
l 0x04: ofs2/hwx/nesoft.hwx
l 0x05: ofs1/hwx/ne.ini
l 0x06: ofs2/hwx/ne.ini
l 0x07: ofs1/hwx/ocp.ini
l 0x08: ofs2/hwx/ocp.ini
l 0x09: ofs1/fpga/if1_002.pga
l 0x0a: ofs2/fpga/if1_002.pga
l 0x0b: ofs1/fpga/if1_250.pga
l 0x0c: ofs2/fpga/if1_250.pga
l 0x0d: ofs1/fpga/sl1d.pga
l 0x0e: ofs2/fpga/sl1d.pga
l 0x0f: ofs1/fpga/sl91ifu2.pga
l 0x10: ofs2/fpga/sl91ifu2.pga
l 0x11: ofs1/fpga/sl91ifx2.pga
l 0x12: ofs2/fpga/sl91ifx2.pga
l 0x13: ofs1/fpga/sl91aux.pga
l 0x14: ofs2/fpga/sl91aux.pga
l 0x15: ofs1/hwx/lusoft.hwx
l 0x16: ofs2/hwx/lusoft.hwx
l 0x17: ofs1/hwx/lusoft.ini
l 0x18: ofs2/hwx/lusoft.ini
l 0x19: ofs1/fpga/sl91em6t.pga
l 0x1a: ofs2/fpga/sl91em6t.pga
l 0x1b: ofs1/fpga/pvg610.pga
l 0x1c: ofs2/fpga/pvg610.pga
l 0x1d: ofs1/fpga/pvg610x.pga
l 0x1e: ofs2/fpga/pvg610x.pga
l 0x1f: ofs1/hwx/luexbios.hwx
l 0x20: ofs2/hwx/luexbios.hwx
l 0x21: ofs1/fpga/plc034.pga
l 0x22: ofs2/fpga/plc034.pga
Indicate the IDs of the inconsistent files in the currently running
software if the value of Parameter 1 is 0x02.
l 0x01: NeSoft(D)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
485
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
l 0x02: Platform(D)
l 0x04: ExtBios
l 0x05: Logic
l 0x06: Dsp
Parameter 4
Indicate the cause of the alarm.
l 0x04: The file versions in the master and slave areas of a single
system control board are inconsistent.
l 0x08: The file versions in the active and standby system control
boards are inconsistent.
l 0x0c: The file versions in the master and slave areas of a single
system control board are inconsistent and the file versions on
the active and standby system control boards are also
inconsistent.
Impact on the System
l
This alarm affects active/standby switching of system control boards if the active and
standby system control boards have different NE software versions.
If no NE software exists in the flash memory, the system is unable to restart after poweroff or reset.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The software running on the active and standby SCC boards has different versions.
Cause 2: The software stored in the ofs1 and ofs2 areas of the active SCC board has different
versions.
Cause 3: The software stored in the mapping directories of active and standby SCC boards
has different versions.
Procedure
Step 1 Contact Huawei technical support engineers for reloading the software.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.202 NESTATE_INSTALL
Description
The NESTATE_INSTALL is an alarm indicating that the NE is in the install state.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
486
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The NE fails to work.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The NE database check fails.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The NE database check fails.
1.
Restore the data from the backup database on the CF card.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.203 NO_BD_SOFT
Description
The NO_BD_SOFT is an alarm indicating that the board software is lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
487
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicates the number of the lost file.
Impact on the System
l
If the board software is lost, the board fails to work normally.
If the FPGA is lost, the FPGA does not have a backup copy.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The software fails to be loaded.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The software fails to be loaded.
1.
Contact the Huawei technical support engineers to reload the software.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.204 NP1_MANUAL_STOP
Description
The NP1_MANUAL_STOP is an alarm indicating that the N+1 protection protocol is disabled
manually.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01
indicates that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
488
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The N+1 protection may fail, or the protection switching may fail.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The N+1 protection protocol is disabled manually.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The N+1 protection protocol is disabled manually.
1.
Start the N+1 protection protocol.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.205 NP1_SW_FAIL
Description
The NP1_SW_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the N+1 protection switching fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01
indicates that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
The services cannot be switched. If the current paths are unavailable, the services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: The parameters of the N+1 protection for the alarmed node are set incorrectly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
489
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The network-wide N+1 protection protocol runs abnormally.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The parameters of the N+1 protection for the alarmed node are set incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the parameters of the N+1 protection are set correctly according to the
planning. For details, see Creating an N+1 Protection Group.
If...
Then...
The parameters of the N+1 protection are Set the parameters of the N+1 protection
set incorrectly
correctly.
The parameters of the N+1 protection are Go to Cause 2.
set correctly
Step 2 Cause 2: The network-wide N+1 protection protocol runs abnormally.
1.
Stop and restart the protocol manually. For details, see Starting/Stopping the N+1
Protection Protocol.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the protocol is End the alarm handling.
restarted.
The alarm persists after the protocol is
restarted
Contact the Huawei technical support
engineers to handle the alarm.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.206 NP1_SW_INDI
Description
The NP1_SW_INDI is an alarm indicating that the N+1 protection switching is detected.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
490
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter1, Parameter 2 Indicates the ID of the alarmed protection group. For example, 0x01
indicates that the alarm is reported by protection group 1.
Impact on the System
During the N+1 protection switching, the services are interrupted. After the N+1 switching is
complete, the services are restored to normal. After the switching starts and before the switching
is complete, the extra services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The N+1 protection switching is performed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The N+1 protection switching is performed.
1.
Find out the cause of switching, and take appropriate measures.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.207 NTP_SYNC_FAIL
Description
The NTP_SYNC_FAIL is an alarm indicating that NTP time synchronization fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Time on the alarmed NE is different from time on the NTP server. The records on the NE, such
as performance events, alarms, and operations, cannot be kept with exact time.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The NTP server is not configured or is configured incorrectly.
Cause 2: The NTP server cannot communicate with the NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
491
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 3: The NTP server fails.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The NTP server is not configured or is configured incorrectly.
1.
Configure the NTP server correctly.
2.
Re-configure the NTP parameters for the NE.
Step 2 Cause 2: The NTP server cannot communicate with the NE.
1.
Check whether the cable connecting the gateway NE to the NTP server is normal. If not,
rectify the connection fault.
2.
Check whether the DCN communication between the NTP server and the NE is normal. If
not, configure the DCN communication correctly.
Step 3 Cause 3: The NTP server fails.
1.
Troubleshoot the NTP server.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.208 OCD
Description
The OCD is an alarm indicating out-of-cell delimitation. This alarm occurs when the cell
delimitation state machine is in the HUNT or PRESYN state.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the OCD alarm occurs, all the services in the receive direction of the alarmed ATM port
lose cells.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A great number of bit errors occur in the receive path. The receive path reports
the alarms indicating excessive bit errors, such as B1_EXC, B2_EXC, and B3_EXC.
Cause 2: The ATM processing chip of the board is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
492
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A great number of bit errors occur in the receive path. The receive path reports the
alarms indicating excessive bit errors, such as B1_EXC, B2_EXC, and B3_EXC.
1.
Check whether the B1_EXC, B2_EXC, or B3_EXC alarm occurs in the receive path.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms first, and then check whether the OCD alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The ATM processing chip of the board is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the board that reports the OCD alarm. For details, see 8.6.1 Cold
Reset.
2.
If the OCD alarm persists, replace the alarmed board. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the
Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.209 ODC_BATTERY_CURRENT_ABN
Description
The ODC_BATTERY_CURRENT_ABN is an alarm indicating that the current of the storage
battery is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the cause of the alarm.
l 0x01: The internal current loop of the storage battery is broken.
l 0x02: The recharge current of the storage battery is very high.
l 0x03: The storage battery is discharged unevenly.
Impact on the System
The equipment may fail to work normally, or event the equipment is damaged.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
493
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The circuit breaker or fuse of the storage battery in the cabinet is off.
Cause 2: The positive and negative polarities of the storage battery are connected inversely.
Cause 3: The power module frame is faulty.
Cause 4: The power monitoring module is faulty.
Cause 5: The power module is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The circuit breaker or fuse of the storage battery in the cabinet is off.
If...
Then...
The circuit breaker of the storage battery is open
Close the circuit breaker.
The fuse of the storage battery is broken
Replace the fuse.
Step 2 Cause 2: The positive and negative polarities of the storage battery are connected inversely.
1.
Connect the positive and negative polarities of the storage battery correctly.
Step 3 Cause 3: The power module frame is faulty.
1.
Check whether the power module frame is damaged. If the power module frame is damaged,
replace the power module frame.
Step 4 Cause 4: The power monitoring module is faulty.
1.
Replace the power monitoring module.
Step 5 Cause 5: The power module is faulty.
1.
Check whether the ODC_MDL_ABN alarm is reported.
If...
Then...
The ODC_MDL_ABN alarm is reported Rectify the fault by referring the solution
to the ODC_MDL_ABN alarm.
The ODC_MDL_ABN alarm is not
reported
Replace the power module.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.210 ODC_BATTERY_PWRDOWN
Description
The ODC_BATTERY_PWRDOWN is an alarm indicating that the storage battery fails to
provide power for the equipment.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
494
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the cause of the alarm.
l 0x01: power-off due to low voltage
l 0x02: power-off due to NMS control
l 0x03: power-off due to human interference
l 0x04: power-off due to high temperature
Impact on the System
The equipment does not have backup a power supply.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1 of power-off due to NMS control: The storage battery fails to provide power for
the equipment due to NMS control.
Cause 1 of power-off due to local human interference: The BAT button on the front panel
of the PMU is set to OFF.
Cause 1 of power-off due to low voltage: The AC input power is abnormal.
Cause 2 of power-off due to low voltage: The power module is faulty.
Cause 3 of power-off due to low voltage: The power monitoring module is faulty.
Cause 1 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature that results in power-off
of the storage battery due to high temperature is set to an inappropriate value.
Cause 2 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature of the storage battery is
very high.
Cause 3 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature sensor of the power module
is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the cause of the alarm according to the alarm parameters displayed on the NMS.
Step 2 Cause 1 of power-off due to NMS control: The storage battery fails to provide power for the
equipment due to NMS control.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
495
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Enable the battery to power on the equipment.
Step 3 Cause 1 of power-off due to local human interference: The BAT button on the front panel of the
PMU is set to OFF.
1.
On the front panel of the PMU, hold the BAT ON button for 5-10 seconds to turn on the
storage battery.
Step 4 Cause 1 of power-off due to low voltage: The AC input power is abnormal.
1.
2.
3.
Query the threshold that results in an alarm when the AC power voltage is abnormal. Then,
determine whether the threshold is appropriate according to the configuration and planning
information.
If...
Then...
The threshold is inappropriate
Set the threshold to an appropriate value.
The threshold is appropriate
Go to the next step.
Check whether the AC circuit breaker is closed.
If...
Then...
The AC circuit breaker is open
Close the AC circuit breaker.
The AC circuit breaker is closed
Go to the next step.
Check the connection of the AC power cable.
If...
Then...
The connection of the AC power cable is incorrect.
Connect the cable properly.
The AC power cable is deteriorated and damaged.
Replace the cable.
Step 5 Cause 2 of power-off due to low voltage: The power module is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the power module by referring to the solution to the
ODC_MDL_ABN alarm.
Step 6 Cause 3 of power-off due to low voltage: The power monitoring module is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the power monitoring module.
Step 7 Cause 1 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature that results in power-off of the
power module due to high temperature is set to an inappropriate value.
1.
Query the threshold that results in an alarm due to high temperature. Then, determine
whether the threshold is appropriate according to the configuration and planning
information.
If...
Then...
The threshold is inappropriate Set the threshold to an appropriate value.
The threshold is appropriate
Perform the operations required when the alarm is
generated by cause 2 of power-off due to high
temperature.
Step 8 Cause 2 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature of the storage battery is very
high.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the storage battery.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
496
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 9 Cause 3 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature sensor of the power module is
faulty.
1.
Replace the temperature sensor of the power module.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.211 ODC_DOOR_OPEN
Description
The ODC_DOOR_OPEN is an alarm indicating that the door of an outdoor cabinet is open.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If the cabinet door is open, the temperature, ambient humidity, and dust-proof measures of the
equipment are affected by the external environment.
In addition, the equipment may be damaged or stolen.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The door access alarm is set incorrectly.
Cause 2: The cabinet door is open.
Cause 3: The cable between the door sensor and the monitor device is connected incorrectly.
Cause 4: The door sensor is faulty.
Cause 5: The monitor device is faulty.
Cause 6: No door sensor is installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The door access alarm is set incorrectly.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the door access alarm is set correctly according to the configuration and
planning information.
If...
Then...
The door access alarm is set correctly
Go to Cause 2.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
497
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The door access alarm is set incorrectly
Set the door access alarm correctly.
Step 2 Cause 2: The cabinet door is open.
1.
Close the cabinet door.
Step 3 Cause 3: The cable between the door sensor and the monitor device is connected incorrectly.
1.
Check the cable between the door sensor and the monitor device.
If...
Then...
The cable is connected incorrectly or is loose
Connect the cable properly.
The cable is deteriorated or damaged
Replace the cable.
The connection is correct
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The door sensor is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the door sensor.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 5.
Step 5 Cause 5: The monitor device is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the monitor device.
Step 6 Cause 6: No door sensor is installed.
1.
Install a door sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.212 ODC_FAN_FAILED
Description
The ODC_FAN_FAILED is an alarm indicating that the fan is faulty.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
498
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the position of the fault.
l 0x01: The internal fan is faulty.
l 0x02: The external fan is faulty.
Impact on the System
The cabinet cannot dissipate heat properly. As a result, the equipment may be damaged and the
services may be affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The fan cable is connected incorrectly.
Cause 2: The fan is faulty.
Cause 3: The fan is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the faulty fan according to the alarm parameters displayed on the NMS.
Step 2 Cause 1: The fan cable is connected incorrectly.
1.
Connect the cable properly to the fan according to the specified regulations or rules.
Step 3 Cause 2: The fan is faulty.
1.
Replace the fan module.
Step 4 Cause 3: The fan is not installed.
1.
Install the TEC module that contains a fan.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.213 ODC_HUMI_ABN
Description
The ODC_HUMI_ABN is an alarm indicating that the relative humidity in the cabinet
environment exceeds the specified threshold.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
499
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Environment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the cause of the alarm.
l 0x01: The relative humidity is very high.
l 0x02: The relative humidity is very low.
Impact on the System
In the case of high relative humidity, the equipment may be damaged. In the case of low relative
humidity, the life of the equipment may be shortened.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The threshold that results in an alarm is set incorrectly.
Cause 2: The cable between the humidity sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
Cause 3: The humidity sensor is faulty.
Cause 4: The associated monitoring equipment is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The threshold that results in an alarm is set incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the humidity threshold is set correctly according to the configuration and
planning information.
If...
Then...
The humidity threshold is set correctly
Perform the operations required when
the alarm is generated due to cause 2.
The humidity threshold is set incorrectly Set the humidity threshold to an
appropriate value.
Step 2 Cause 2: The cable between the humidity sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
500
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The cable is connected incorrectly or is loose Connect the cable properly.
The cable is deteriorated and damaged
Handle the exceptions of the cable.
The cable is not deteriorated and damaged
Perform the operations required when the
alarm is generated due to cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The humidity sensor is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the sensor.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Perform the operations required when the alarm is generated
due to cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The monitoring equipment is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the monitoring equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.214 ODC_LOAD_PWRDOWN
Description
The ODC_LOAD_PWRDOWN is an alarm indicating that the secondary load is powered off.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
501
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the cause of the alarm.
l 0x01: power-off due to low voltage
l 0x02: power-off due to background control
l 0x03: power-off due to startup in the case of low temperature
l 0x04: power-off due to high temperature
Impact on the System
The services on the secondary load are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1 of power-off due to NMS control: The load is powered off due to NMS control.
Cause 1 of power-off due to low voltage: The AC input power is abnormal.
Cause 2 of power-off due to low voltage: The power module is faulty.
Cause 3 of power-off due to low voltage: The power monitoring module is faulty.
Cause 1 of power-off due to low temperature: The cabinet temperature is very low.
Cause 2 of power-off due to low temperature: The ambient temperature sensor is faulty.
Cause 1 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature that results in power-off
of the load due to high temperature is set to an inappropriate value.
Cause 2 of power-off due to high temperature: The cabinet temperature is very high.
Cause 3 of power-off due to high temperature: The ambient temperature sensor is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the cause of the alarm according to the alarm parameters displayed on the NMS.
Step 2 Cause 1 of power-off due to NMS control: The load is powered off due to NMS control.
1.
Turn on the storage battery for the equipment.
Step 3 Cause 1 of power-off due to low voltage: The AC input power is abnormal.
1.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Query the threshold that results in an alarm when the AC power voltage is abnormal. Then,
determine whether the threshold is appropriate according to the configuration and planning
information.
If...
Then...
The threshold is inappropriate
Set the threshold to an appropriate value.
The threshold is appropriate
Go to the next step.
Check whether the AC circuit breaker is closed.
If...
Then...
The AC circuit breaker is closed
Go to the next step.
The AC circuit breaker is open
Close the AC circuit breaker.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
502
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3.
A Alarm Reference
Check the connection of the AC power cable.
If...
Then...
The connection of the AC power cable is
incorrect.
Connect the cable properly.
The AC power cable is deteriorated and
damaged.
Handle the exceptions of the cable.
Step 4 Cause 2 of power-off due to low voltage: The power module is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the power module by referring to the solution to the
ODC_MDL_ABN alarm.
Step 5 Cause 3 of power-off due to low voltage: The power monitoring module is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the power monitoring module.
Step 6 Cause 1 of power-off due to low temperature: The cabinet temperature is very low.
1.
Check whether the heat exchanger works properly.
If...
Then...
The heat exchanger does not work
properly
Rectify the fault of the heat exchange.
The heat exchanger works properly
Perform the operations required when the
alarm is generated by cause 2 of power-off
due to low temperature.
Step 7 Cause 2 of power-off due to low temperature: The ambient temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the temperature sensor of the power module.
Step 8 Cause 1 of power-off due to high temperature: The temperature that results in power-off of the
load due to high temperature is set to an inappropriate value.
1.
Query the threshold that results in an alarm in the case of power-off due to high temperature
of the load. Then, determine whether the threshold is appropriate according to the
configuration and planning information.
If...
Then...
The threshold is inappropriate Set the threshold to an appropriate value.
The threshold is appropriate
Perform the operations required when the alarm is
generated by cause 2 of power-off due to high
temperature.
Step 9 Cause 2 of power-off due to high temperature: The cabinet temperature is very high.
1.
Check whether the ambient temperature is very high all the time.
2.
Check whether the heat exchanger works properly.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If...
Then...
The heat exchanger does not work
properly
Rectify the fault of the heat exchange.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
503
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The heat exchanger works properly
Perform the operations required when the
alarm is generated by cause 3 of power-off
due to high temperature.
Step 10 Cause 3 of power-off due to high temperature: The ambient temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the ambient temperature sensor.
----End
Related Information
The secondary load refers to the load that the DC power outlet of the cabinet corresponds to.
A.3.215 ODC_MDL_ABN
Description
The ODC_MDL_ABN is an alarm indicating that the power module is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the alarmed power module.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicates the cause of the alarm.
l 0x01: The power module is switched off.
l 0x02: The power module is faulty.
l 0x03: The power module stops self-protection.
l 0x04: The power module fails to communicate with the power
monitoring module, or the power module is not in position.
l 0x05: The outdoor cabinet is not installed with a power module,
and the logical slot for a power module is not set on the NMS.
l 0x06: The outdoor cabinet is installed with a power module, but
the logical slot for the power module is not set on the NMS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
504
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
If the power module is faulty, the loading capability of the power system is affected. As a result,
the storage battery may discharge, or even the entire power system of the equipment is powered
off.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The power module is not configured on the NMS.
Cause 2: The power module is not in position, or the power module is not inserted properly.
Cause 3: The power module is faulty.
Cause 4: The power monitoring unit is abnormal.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The power module is not configured on the NMS.
1.
Set the logical slot of the power module on the NMS.
Step 2 Cause 2: The power module is not in position, or the power module is not inserted properly.
If...
Then...
The power module is not in position
Install the power module.
The power module is not inserted securely
Install the power module properly.
Step 3 Cause 3: The power module is faulty.
1.
Replace the power module.
Step 4 Cause 4: The power monitoring unit is abnormal.
1.
Rectify the fault of the power monitoring unit.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.216 ODC_POWER_FAIL
Description
The ODC_POWER_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the AC input power voltage and DC output
power voltage of an outdoor cabinet are abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
505
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the type of the fault.
l 0x56: The AC input power is very high.
l 0x57: The AC input power is very low.
l 0x58: The DC output power is very high.
l 0x59: The DC output power is very low.
l 0x5b: No AC input power is available.
l 0x5c: The AC power voltage is abnormal.
Impact on the System
l
If the AC input power voltage is abnormal, the equipment is powered on by the storage
battery and cannot work for a long time.
If the DC output power voltage is abnormal, the services on the equipment are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The AC input power voltage is abnormal.
Cause 2: The DC output power voltage is abnormal.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The AC input power voltage is abnormal.
1.
2.
3.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
The threshold that results in an alarm due to the AC input power voltage is set incorrectly.
If...
Then...
The threshold is set incorrectly
Set the threshold to an appropriate value.
The threshold is set correctly
Go to the next step.
The AC circuit breaker is open.
If...
Then...
The AC circuit breaker is open
Close the AC circuit breaker.
The AC circuit breaker is closed
Go to the next step.
The AC power cable is connected incorrectly.
If...
Then...
The cable is connected incorrectly or is loose
Connect the cable properly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
506
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4.
5.
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The cable is deteriorated and damaged
Handle the exceptions of the cable.
The cable is connected correctly
Go to the next step.
The AC power grid distributes the power abnormally.
If...
Then...
The AC power grid distributes the power
abnormally
Rectify the fault of the power module
at the base station.
The AC power grid distributes the power
normally
Go to the next step.
The monitoring equipment is faulty.
If...
Then...
The monitoring equipment is faulty
Rectify the fault of the monitoring
equipment.
The monitoring equipment is not faulty Perform the operations required when the
alarm is generated due to cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The DC output power voltage is abnormal.
1.
2.
3.
The threshold that results in an alarm is set incorrectly.
If...
Then...
The threshold is set incorrectly
Set the threshold to an appropriate value.
The threshold is set correctly
Go to the next step.
The PSU module is faulty.
If...
Then...
The PSU module is faulty
Rectify the fault of the PSU module.
The PSU module is not faulty
Go to the next step.
The power of the storage battery is insufficient.
If...
Then...
The power of the storage battery is
insufficient
Recharge the storage battery.
The power of the storage battery is
sufficient
Rectify the fault of the monitoring
equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
507
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.217 ODC_SMOKE_OVER
Description
The ODC_SMOKE_OVER is an alarm indicating that smoke occurs in an outdoor cabinet.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Environment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The equipment may be burned.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The smoke alarm is set incorrectly.
Cause 2: A fire and heavy smoke occur at the equipment in the cabinet.
Cause 3: The cable between the smoke sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
Cause 4: The smoke sensor is faulty.
Cause 5: The associated monitoring equipment is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The smoke alarm is set incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the smoke alarm is set correctly according to the configuration and planning
information.
If...
Then...
The smoke alarm is set correctly
Perform the operations required when the
alarm is generated due to cause 2.
The smoke alarm is set incorrectly Set the smoke alarm correctly.
Step 2 Cause 2: A fire and heavy smoke occur at the equipment in the cabinet.
1.
Extinguish the fire in the cabinet.
Step 3 Cause 3: The cable between the smoke sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the cable between the sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
correctly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
508
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The cable is connected incorrectly or is
loose
Connect the cable properly.
The cable is deteriorated and damaged
Replace the cable.
The cable is not deteriorated and damaged Perform the operations required when
the alarm is generated due to cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The smoke sensor is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the sensor.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Perform the operations required when the alarm is generated
due to cause 5.
Step 5 Cause 5: The associated monitoring equipment is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the monitoring equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.218 ODC_SURGE_PROTECTION_FAIL
Description
The ODC_SURGE_PROTECTION_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the surge protection
function of the outdoor cabinet is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
509
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the type of the alarm.
l 0x01: AC surge protection alarm
l 0x02: DC surge protection alarm
Impact on the System
The AC surge protection function of the cabinet is disabled.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The alarm is set incorrectly.
Cause 2: The cable between the lightning sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
Cause 3: The lightning sensor is faulty.
Cause 3: The lightning arrestor is faulty.
Cause 5: The associated monitoring equipment is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The alarm is set incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the alarm is set correctly according to the configuration and planning
information.
If...
Then...
The alarm is set correctly
Perform the operations required when the alarm is
generated due to cause 2.
The alarm is set incorrectly Set the surge protection alarm correctly.
Step 2 Cause 2: The cable between the lightning sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
1.
Check the cable connection between the sensor and the monitoring equipment.
If...
Then...
The cable is connected incorrectly or is
loose
Connect the cable properly.
The cable is deteriorated and damaged
Replace the cable.
The cable is not deteriorated and damaged Perform the operations required when
the alarm is generated due to cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The lightning sensor is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the sensor.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
510
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
If...
A Alarm Reference
Then...
The alarm is cleared End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Perform the operations required when the alarm is generated
due to cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 3: The lightning arrestor is faulty.
1.
Check whether the alarm output end of the lightning arrestor works properly.
If...
Then...
The alarm output end of the lightning
arrestor works properly
Perform the operations required when the
alarm is generated due to cause 5.
The alarm output end of the lightning
arrestor does not work properly
Replace the lightning arrestor.
Step 5 Cause 5: The associated monitoring equipment is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the monitoring equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.219 ODC_TEC_ALM
Description
The ODC_TEC_ALM is an alarm indicating that the TEC air conditioning module in the cabinet
does not work properly.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If the TEC air conditioning module does not work properly, the storage battery may operate at
very high or low temperature and therefore the safety performance of the storage battery
degrades.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: The TEC cable is connected incorrectly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
511
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The TEC module is faulty.
Cause 3: The monitoring equipment is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The TEC cable is connected incorrectly.
1.
Connect the TEC cable correctly.
Step 2 Cause 2: The TEC module is faulty.
1.
Replace the TEC module.
Step 3 Cause 3: The monitoring equipment is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the monitoring equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.220 ODC_TEMP_ABN
Description
The ODC_TEMP_ABN is an alarm indicating that the ambient temperature of the cabinet or
the temperature of the storage battery is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Environment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the cause of the alarm.
l 0x01: The ambient temperature is higher than the upper threshold.
l 0x01: The ambient temperature is lower than the lower threshold.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
512
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
Meaning
Parameter 2
Indicates the temperature type.
A Alarm Reference
l 0x01: The temperature at the air outlet is very high or low.
l 0x0b: Ambient temperature 1 is very high or low.
l 0x0c: Ambient temperature 2 is very high or low.
l 0x0d: The temperature of the battery group is very high or low.
Impact on the System
If the temperature is abnormal, the equipment performance degrades and the life of the equipment
decreases.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The temperature threshold that results in an alarm is set incorrectly.
Cause 2: The cable between the temperature sensor and the monitoring equipment is
connected incorrectly.
Cause 3: The temperature sensor is faulty.
Cause 4: The associated monitoring equipment is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The temperature threshold that results in an alarm is set incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the temperature alarm is set correctly according to the configuration and
planning information.
If...
Then...
The temperature alarm is set correctly
Perform the operations required when
the alarm is generated due to cause 2.
The temperature alarm is set incorrectly Set the temperature alarm correctly.
Step 2 Cause 2: The cable between the temperature sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the cable between the sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
correctly.
If...
Then...
The cable is connected incorrectly or is
loose
Connect the cable properly.
The cable is deteriorated and damaged
Handle the exceptions of the cable.
The cable is not deteriorated and damaged Perform the operations required when
the alarm is generated due to cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Rectify the fault of the sensor.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
513
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether the alarm is cleared.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Perform the operations required when the alarm is generated
due to cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The monitoring equipment is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the monitoring equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.221 ODC_WATER_ALM
Description
The ODC_WATER_ALM is an alarm indicating that certain water enters the cabinet.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Environment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The moisture in the cabinet increases, and the equipment in the cabinet may be damaged.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The water alarm is set incorrectly.
Cause 2: Certain water enters the cabinet.
Cause 3: The cable between the water sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
incorrectly.
Cause 4: The water sensor is faulty.
Cause 5: The associated monitoring equipment is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The water alarm is set incorrectly.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the water alarm is set correctly according to the configuration and planning
information.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
514
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The water alarm is set correctly
Perform the operations required when the
alarm is generated due to cause 2.
The water alarm is set incorrectly Set the water alarm correctly.
Step 2 Cause 2: Certain water enters the cabinet.
1.
Dry the cabinet and take waterproof measures for the cabinet.
Step 3 Cause 3: The cable between the sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected incorrectly.
1.
Check whether the cable between the sensor and the monitoring equipment is connected
correctly.
If...
Then...
The cable is connected incorrectly or is
loose
Connect the cable properly.
The cable is deteriorated and damaged
Handle the exceptions of the cable.
The cable is not deteriorated and damaged Perform the operations required when
the alarm is generated due to cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The sensor is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the sensor.
Step 5 Cause 5: The monitoring equipment is faulty.
1.
Rectify the fault of the monitoring equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.222 OUT_PWR_ABN
Description
The OUT_PWR_ABN alarm indicates that the output optical power is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
515
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the port ID.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the path ID. The parameters have a fixed value of 0x00
0x01.
Parameter 4, Parameter 5 Are reserved. The value is always 0xFF.
Impact on the System
The OUT_PWR_ABN alarm affects the transmission performance of services, and may even
result in service interruption.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The output optical power is too high or low.
Cause 2: A board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The output optical power is too high or low.
1.
Browse optical power performance events.
If...
Then...
The output optical power does not meet the Replace the optical module.
requirement
The output optical power is too high
Add a proper attenuator to reduce the input
optical power.
Step 2 Cause 2: A board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.223 OUT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The OUT1TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the air outlet temperature sensor
of the cabinet fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
516
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The air outlet temperature data of the TCU cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The air outlet temperature sensor is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The air outlet temperature sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The air outlet temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the air outlet temperature sensor.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
Step 4 Cause 4: The air outlet temperature sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the air outlet temperature sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
517
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.224 OUT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL
Description
The OUT2TEMP_SENSOR_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the external cycling air outlet
temperature sensor of the cabinet fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The external cycling air outlet temperature data of the TCU cannot be collected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The external cycling air outlet temperature sensor is faulty.
Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Cause 4: The external cycling air outlet temperature sensor is not installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The external cycling air outlet temperature sensor is faulty.
1.
Replace the external cycling air outlet temperature sensor.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The control board of the cabinet is faulty.
1.
Replace the cabinet.
2.
Then, check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: Cables are misconnected or damaged.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
518
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
Replace damaged cables.
2.
Connect cables correctly.
A Alarm Reference
Step 4 Cause 4: The external cycling air outlet temperature sensor is not installed.
1.
Install the external cycling air outlet temperature sensor.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.225 PATCH_ACT_TIMEOUT
Description
The PATCH_ACT_TIMEOUT is an alarm indicating that activating the patch package times
out. This alarm occurs when the patch package is in the active state for a period longer than the
specified period of time. In this case, the user needs to process the patch package.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the PATCH_ACT_TIMEOUT alarm occurs, it does not affect services.
Possible Causes
Cause: The patch package is in the active state for a period longer than the specified period of
time.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The patch package is in the active state for a period longer than the specified period of
time.
1.
Check whether the activated patch package is normal.
2.
If yes, run the patch package to make the it valid. If not, delete the patch package. Then,
the alarm is cleared automatically.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
519
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.226 PATCH_DEACT_TIMEOUT
Description
The PATCH_DEACT_TIMEOUT is an alarm indicating that deactivating the patch package
times out. This alarm occurs when the patch package is in the inactive state for a period longer
than the specified period of time. In this case, the user needs to process the patch package.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the PATCH_DEACT_TIMEOUT alarm occurs, it does not affect services.
Possible Causes
Cause: The patch package is in the inactive state for a period longer than the specified period of
time.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The patch package is in the inactive state for a period longer than the specified period of
time.
1.
To make the patch package valid, activate the patch package.
2.
Otherwise, delete the patch package. Then, the alarm is cleared automatically.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.227 PATCH_PKGERR
Description
The PATCH_PKGERR alarm indicates that a patch package is incorrect or has been damaged
or deleted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
520
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor alarm
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If a patch package is incorrect or has been damaged or deleted, the patch package cannot be
successfully loaded, activated, or run.
NOTE
When this alarm is reported, services are not interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A patch package is incorrect.
Cause 2: A patch package has been damaged.
Cause 3: A patch package has been deleted.
Procedure
Step 1 Load a correct patch package.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.228 PG_LINK_FAIL
Description
The PG_LINK_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the links in a 1+1 protection group fail.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
521
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The services on the radio links are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause: Service alarms occur on the main and standby boards.
Procedure
Step 1 Set the Alarm Report Mode to Protection group and board alarms. For details, see Querying
the IF 1+1 Protection Status.
NOTE
When alarms with different priorities occur on a board at the same time, the board reports only the alarms
with the highest priority. Alarms can be arranged in descending order by priority: hardware alarms >
configuration alarms > service alarms.
Step 2 Handle the queried alarms.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.229 PG_PRT_DEGRADED
Description
The PG_PRT_DEGRADED is an alarm indicating that the main link or standby link in a 1+1
protection group is faulty.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the board ID.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
522
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The services at the NE are not affected, but radio link protection fails.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Service alarms occur on the main board.
Cause 2: Service alarms occur on the standby board.
Procedure
Step 1 Locate the faulty board according to the alarm parameter.
Step 2 Set the Alarm Report Mode to Protection group and board alarms. For details, see Querying
the IF 1+1 Protection Status.
NOTE
When service alarms with different priorities occur on a board at the same time, the board reports only the
alarms with the highest priority. Alarms can be arranged in descending order by priority: hardware alarms
> configuration alarms > service alarms.
Step 3 Handle the queried alarms.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.230 PLA_CFG_MISMATCH
Description
The PLA_CFG_MISMATCH alarm indicates that the PLA configuration data is inconsistent
between two ends of a radio link.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2 Indicate the ID of a PLA group.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
523
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 3, Parameter 4 Indicate the error type.
l 0x00: indicates that no PLA group is configured at the opposite
end of a radio link.
l 0x01: indicates that the enabled status of Layer 2 header
compression function at the local end of a radio link is different
from that at the opposite end.
Impact on the System
Services at both ends of a radio link are unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A PLA group is configured at the local end but no PLA group is configured at the
opposite end.
Cause 2: The enabled status of the Layer 2 header compression function at the local end of
a radio link is different from that at the opposite end.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A PLA group is configured at the local end but no PLA group is configured at the
opposite end.
1.
Follow instructions in Creating a PLA Group to configure a PLA group at the opposite end
of the radio link.
Step 2 Cause 2: The enabled status of the Layer 2 header compression function at the local end of a
radio link is different from that at the opposite end.
1.
Follow instructions in Querying the PLA Group Status to determine the ports whose
configuration data needs to be changed according to planning information.
2.
Follow instructions in Setting the Advanced Attributes of IF_ETH Ports to change the
enabled status of the Layer 2 header compression function for PLA member ports.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.231 PORTMODE_MISMATCH
Description
The PORTMODE_MISMATCH is an alarm indicating that the working mode of the remote FE
port does not match with that of the local FE port. This alarm is reported when the local FE port
works in auto-negotiation mode and the opposite FE port works in non-auto-negotiation mode.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
524
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1, Parameter 2
Indicate the working mode of the FE port.
Impact on the System
When the PORTMODE_MISMATCH alarm occurs, the service on the local NE is not affected. .
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The local FE port works in auto-negotiation mode and the opposite FE port works
in non-auto-negotiation mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local FE port works in auto-negotiation mode and the opposite FE port works in
non-auto-negotiation mode.
1.
Disable the opposite FE port. For details, refer to Setting the General Attributes of Ethernet
Ports.
2.
Enable the opposite FE port and set work mode of the port to auto-negotiation. For details,
refer to Setting the General Attributes of Ethernet Ports.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.232 PORT_EXC_TRAFFIC
Description
The PORT_EXC_TRAFFIC alarm indicates that the traffic over a port exceeds its threshold.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
525
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the traffic in the receive or transmit direction exceeds its threshold.
l 0x00: indicates the receive direction.
l 0x01: indicates the transmit direction.
Impact on the System
Services are congested.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The configured bandwidth limit is too low.
Cause 2: The port traffic is too high.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The configured bandwidth limit is too low.
1.
Follow instructions in Configuring Traffic Shaping for Egress Queues to check the
configured bandwidth limit.
2.
If the configured bandwidth limit is too low, follow instructions in Configuring Traffic
Shaping for Egress Queues to increase the bandwidth limit value or perform network
expansion.
Step 2 Cause 2: The configured port traffic is too high.
1.
Follow instruction in 8.17 Querying Traffic, Physical Bandwidth, or Bandwidth
Utilization of Ethernet Ports to query the bandwidth utilization over a port.
2.
If the port bandwidth utilization is higher than its threshold, check whether a network storm
occurs. If a network storm occurs, eliminate the source that transmits a large amount of
invalid data.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
526
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.233 PORT_MODULE_OFFLINE
Description
The PORT_MODULE_OFFLINE alarm indicates that a port is offline.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the port that reports the alarm.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Have a fixed value of 0x00 0x01.
Parameter 4, Parameter 5
Are reserved and have a fixed value of 0xff.
Impact on the System
The services over the alarmed port are interrupted.
Possible Causes
The alarmed port is enabled but house no SFP module.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The alarmed port is enabled but house no SFP module.
1.
Check whether the alarmed port needs to receive/transmit a service.
If...
Then...
The alarmed port needs to receive/
transmit a service
Go to the next step.
The alarm port does not need to receive/ Follow instructions in Setting the General
transmit a service
Attributes of Ethernet Ports to disable the
alarmed port.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the alarmed port houses an SFP module.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
527
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
3.
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarmed port houses no SFP
module
Follow instructions in Installing an SFP
Module to add an SFP module.
The alarmed port houses an SFP
module
Go to the next step.
Re-install the SFP module.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
No further action is required.
The alarm persists Follow instructions in Replacing an SFP Module to replace the
SFP module.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.234 POWER_ABNORMAL
Description
The POWER_ABNORMAL is an alarm indicating that the input power supply is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the number of the voltage channel.
l 0x01: the first channel of voltage
l 0x02: the second channel of voltage
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
528
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 2
Indicates the type of the alarm.
l 0x00: voltage loss
l 0x01: undervoltage
l 0x02: overvoltage
Impact on the System
When the POWER_ABNORMAL alarm occurs, the power supply is abnormal, and therefore
the board may fail to work normally.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The power cable is cut, damaged, or incorrectly connected.
Cause 2: The input power is abnormal.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The power cable is cut, damaged, or incorrectly connected.
1.
Check whether the power cable is cut, damaged, or incorrectly connected. If the power
cable is cut or damaged, replace it with a proper power cable. If the power cable is
incorrectly connected, reconnect the power cable.
Step 2 Cause 2: The input power is abnormal.
1.
Contact the engineers for power supply to rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.235 POWER_ALM
Description
The POWER_ALM is an alarm indicating that the power module is abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
529
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 If the POWER_ALM alarm is reported on a board on the IDU, this parameter
indicates the ID of the alarmed power module. For example, 0x01 indicates that
the alarm is reported by power module 1 of the board.
If the POWER_ALM is reported on the ODU, this parameter indicates the type
of the power fault.
l 0x01: The -5 V power supply is faulty.
l 0x02: The power supply for the power amplifier is faulty.
Parameter 2 l 0x01: under-voltage
l 0x02: over-voltage
Impact on the System
The power modules are configured with protection. If only one power module reports the
POWER_ALM alarm, the system is not affected.
Possible Causes
If the alarm is reported by a board of the IDU, the possible causes are as follows:
l
Cause 1: The input power or the PIU is abnormal.
Cause 2: The power module is abnormal.
If the alarm is reported on the ODU, the cause is as follows:
l
Cause 1: The power module of the ODU is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 (POWER_ALM reported by a board of the IDU) Cause 1: The input power or the PIU is
abnormal.
1.
Check whether alarms are reported on the PIU, If yes, clear these alarms immediately.
Step 2 (POWER_ALM reported by a board of the IDU) Cause 2: The power module is abnormal.
1.
Replace the alarmed board. For details, see 6 Part Replacement.
Step 3 (POWER_ALM reported on the ODU) Cause 1: The power module of the ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the ODU. For details, see 6.14 Replacing the ODU.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
530
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.236 PW_DROPPKT_EXC
Description
The PW_DROPPKT_EXC alarm indicates that the packet loss ratio on a PW exceeds its
threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Processing alarm
Parameters
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 Has a fixed value of 0x00, indicating that the traffic in the ingress or egress
direction crosses its threshold.
Impact on the System
A small number of packets are lost, affecting service real-time performance.
Possible Causes
Cause: A small number of packets are lost on the alarmed PW.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: A small number of packets are lost on the alarmed PW.
1.
Follow instructions in Querying Information and Running Status of PWs to check the
bandwidth utilization of the alarmed PW. If the PW bandwidth is exhausted, increase the
bandwidth or eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
531
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.237 PWAPS_LOST
Description
The PWAPS_LOST is an alarm indicating that the APS frame is lost. This alarm occurs when
no APS frame is received from the protection channel.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the service protection fails.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The remote NE of the PW is not configured with any protection group.
Cause 2: The service on the protection channel is interrupted.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The remote NE of the PW is not configured with any protection group.
1.
Check whether the remote NE of the PW is configured with a protection group. If yes,
ensure that the configuration is the same at the two ends.
Step 2 Cause 2: The service on the protection channel is interrupted.
1.
Check whether the protection channel is faulty. If yes, rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.238 PWAPS_PATH_MISMATCH
Description
The PWAPS_PATH_MISMATCH is an alarm indicating that the working and protection paths
of the APS protection group differ between the two ends. This alarm is reported when the
working and protection paths of one APS protection group at one end are different from those
at the other end.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
532
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the service protection fails.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The configured working and protection paths differ between the two ends.
Cause 2: Certain physical links are incorrectly connected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The configured working and protection paths differ between the two ends.
1.
Check whether the APS settings at the two ends are the same.
2.
If the APS settings are different, change the settings to the same.
Step 2 Cause 2: Certain physical links are incorrectly connected.
1.
Connect the fibers or cables properly.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.239 PWAPS_SWITCH_FAIL
Description
The PWAPS_SWITCH_FAIL is an alarm indicating a switching failure of the PW APS
protection group. This alarm is reported when the request signal in the transmitted Automatic
Protection Switching (APS) frame is different from the bridge signal in the received APS frame
and this symptom lasts for 50 ms.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
533
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the service protection fails.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The configured working and protection paths differ between the two ends.
Cause 2: Certain physical links are incorrectly connected.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The configured working and protection paths differ between the two ends.
1.
Check whether the APS settings at the two ends are the same.
2.
If the APS settings are different, change the settings to the same.
Step 2 Cause 2: Certain physical links are incorrectly connected.
1.
Connect the fibers or cables properly.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.240 PWAPS_TYPE_MISMATCH
Description
The PWAPS_TYPE_MISMATCH is an alarm indicating that the local NE and the opposite NE
are configured with different PW protection types. This alarm occurs when the information in
the received APS frames is inconsistent with the APS protection scheme configured at the local
end.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the service protection fails.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
534
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The configured protection modes (1+1 protection or 1:1 protection) differ at the
two ends of the PW.
Cause 2: The configured switching modes (single-ended or dual-ended) differ at the two
ends of the PW.
Cause 3: The configured revertive modes (revertive or non-revertive) differ at the two ends
of the PW.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the APS protection settings, such as protection mode, switching mode, and
revertive mode, are the same at the local and remote ends.
Step 2 If the APS protection settings are different, change the settings to the same.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.241 R_F_RST
Description
The R_F_RST is an alarm indicating that the receive FIFO is reset.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The clocks at both stations are not synchronous.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The clocks at both stations are not synchronous.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Query whether a TU pointer adaptation performance event is reported at both ends. For
details, see 8.3.5 Browsing Current Performance Events.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
535
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
If...
A Alarm Reference
Then...
An AU pointer adaptation performance Handle the performance event. For details,
event is reported
see C.3.2 TUPJCHIGH, TUPJCLOW,
and TUPJCNEW.
An AU pointer adaptation performance Go to Cause 2.
event is not reported
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.242 R_LOC
Description
The R_LOC is an alarm indicating that the clock is lost on the receive line side. This alarm is
reported when the line board fails to extract clock signal from the line signal or the IF board fails
to extract clock signal from the IF signal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services on the line port or the IF port are interrupted. If the system is configured with
protection, protection switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
At the local end, perform an inloop on the port of the alarmed board. For details, see 8.5
Software Loopback.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
536
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm persists after the loopback
Replace the alarmed local board.
The alarm is cleared after the loopback
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed opposite board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is The fault is rectified. End the alarm handling.
replaced
The alarm persists after the board is Replace the system control, switch&timing
replaced
board at the opposite end.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.243 R_LOF
Description
The R_LOF is an alarm indicating that frames are lost on the receive side. This alarm is reported
when the OOF state lasts for three milliseconds.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services are interrupted. If the system is configured with protection, protection switching
may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Certain alarms are generated (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
Cause 3: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Cause 4: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
537
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Certain high-level alarms are generated (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
2.
If the alarm is reported by the IF board, check whether the MW_BER_EXC,
MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is generated.
If...
Then...
The alarm is generated
Take priority to clear the
MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD,
MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm.
The alarm is not generated
Go to the next step.
Set the inloop on the alarmed IF port.
If...
Then...
The alarm persists after the inloop is
performed
Go to Cause 4.
The alarm is cleared after the inloop is
performed
Go to Cause 3.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH optical interface
board).
1.
If the alarm is reported by an optical interface board, exchange the transmit and receive
fiber jumpers at both ends.
If...
Then...
The alarm persists after the exchange
Go to Cause 3 or 4
The line port of the opposite station reports
the R_LOF alarm
Troubleshoot the optical fibers.
Step 3 Cause 3: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
1.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the opposite board where the line unit is or the opposite IF board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board
replacement
The fault is rectified, and the alarm
handling is complete.
The alarm persists after the board
replacement
Go to the next step.
Replace the system control and cross-connect board at the opposite end.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
538
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board
replacement
The fault is rectified, and the alarm
handling is complete.
The alarm persists after the board
replacement
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
A.3.244 R_LOS
Description
In the case of SDH boards, the R_LOS is an alarm indicating that the signals on the receive line
side are lost. In the case of IF boards, the R_LOS is an alarm indicating that the radio frames on
the receive line side are lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services are interrupted. If the system is configured with protection, protection switching
may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Certain alarms are generated (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH line board).
Cause 3: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
Cause 4: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
539
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Certain alarms are generated (if the alarm is reported by an IF board).
1.
2.
If the alarm is reported by the IF board, check whether the MW_BER_EXC,
MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is generated.
If...
Then...
The alarm is generated
Take priority to clear the
MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD,
MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm.
The alarm is not generated
Go to the next step.
Set the inloop on the alarmed IF port.
If...
Then...
The alarm persists after the inloop is
performed
Go to Cause 4.
The alarm is cleared after the inloop is
performed
Go to Cause 3.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line performance degrades (if the alarm is reported by an SDH line board).
1.
If the alarm is reported by an optical interface board, exchange the transmit and receive
fiber jumpers at both ends.
If...
Then...
The alarm persists after the exchange
Go to Cause 3 or 4
The line port of the opposite station reports
the R_LOF alarm
Troubleshoot the optical fibers.
Step 3 Cause 3: The transmit unit of the opposite station is faulty.
1.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the opposite board where the line unit is or the opposite IF board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board
replacement
The fault is rectified, and the alarm
handling is complete.
The alarm persists after the board
replacement
Proceed to the next step.
Replace the system control and cross-connect board at the opposite end.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
540
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board
replacement
The fault is rectified, and the alarm
handling is complete.
The alarm persists after the board
replacement
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The receive unit of the local site is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
The handling procedure applies when this alarm is reported by the STM-1e port.
A.3.245 R_S_ERR
Description
The R_S_ERR is an alarm indicating that the received signal has errors.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The frequency offset of the input signal is very large.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The frequency offset of the input signal is very large.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the tributary board supports the type of the input signal.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
541
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The tributary board does not support the Change the type of the output signal of the
type of the input signal.
remote site.
The tributary board supports the type of Go to the next step.
the input signal.
2.
Test the frequency offset of the input signal.
If...
Then...
The frequency offset is very large
Troubleshoot the remote site.
The frequency offset meets the requirement
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.246 RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF
Description
The RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF is an alarm indicating that the mean receive power
of the ODUs are lower than the threshold of the receive power (the threshold value is about the
receiver sensitivity + 14 dB).
When the receive power of the ODUs in consecutive six hours is lower than the threshold, the
system reports the alarm. When the mean receive power of the ODUs becomes normal and lasts
for three minutes after the alarm is reported, the alarm is cleared.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_LOF or MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is not
generated, the service is not affected.
Possible Causes
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Cause 1: The ODU fault of the transmit end causes the abnormal transmit power.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
542
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Cause 2: The direction of the antenna is deflected.
Cause 3: The transmission environment changes.
Cause 4: The fade margin in the case of rain and fog in the network planning is insufficient.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The ODU fault of the transmit end causes the abnormal transmit power.
1.
Check whether the ODU at the transmit end reports the RADIO_TSL_LOW alarm.
If...
Then...
The ODU at the transmit end reports the
RADIO_TSL_LOW alarm
Handle the RADIO_TSL_LOW alarm.
The ODU at the transmit end does not report the Go to Cause 2.
RADIO_TSL_LOW alarm
Step 2 Cause 2: The direction of the antenna is deflected.
1.
Check whether the direction of the antenna is deflected.
If...
Then...
The direction of the antenna is deflected
Adjust the direction of the antenna.
The direction of the antenna is not deflected
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The transmission environment changes.
1.
Check whether the transmission environment changes. For example, check whether any
building blocks the transmission and increases the link fading significantly.
If...
Then...
The transmission environment changes
Contact the network planning department for
re-planning the transmission trail.
The transmission environment does not
change
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The fade margin in the case of rain and fog in the network planning is insufficient.
1.
If the alarm is reported frequently, contact the network planning department to increase the
fade margin by re-planning the transmission trail.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.247 RADIO_MUTE
Description
The RADIO_MUTE is an alarm indicating that radio transmitter is muted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
543
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The transmitter does not transmit services.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The other alarms are generated.
Cause 2: The transmitter of the local site is muted manually.
Cause 3: The IF board is faulty, causing abnormal IF output.
Cause 4: The data output is abnormal because the ODU is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The other alarms are generated.
1.
Check whether the CONFIG_NOSUPPORT or IF_INPWR_ABN alarm is generated. If
yes, take priority to clear the alarm.
Step 2 Cause 2: The transmitter of the local site is muted manually.
1.
Check whether the transmitter of the ODU is muted. For details, see Configuring the IF/
ODU Information of a Radio Link. If yes, cancel the muting operation. Then, set the
transmitting status of the ODU to unmute.
Step 3 Cause 3: The IF board is faulty, causing abnormal IF output.
1.
Replace the IF board.
Step 4 Cause 4: The data output is abnormal because the ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the ODU.
----End
Related Information
The logical slot ID of the ODU is obtained by adding 20 to the slot ID of the IF board connected
to the ODU.
A.3.248 RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH
Description
The RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH is an alarm indicating that the antennas are not aligned. When
the receive power is set on the NE, the NE enables the antenna alignment indication function.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
544
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If the actual receive power of the ODU is lower than the power to be received 3 dB, the
RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH alarm is reported. Then, if the antennas are aligned for continuous
30 minutes, the antenna alignment indication function is disabled automatically. Afterwards, the
RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH alarm is reported only when the
RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF alarm is reported.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If the MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_LOF or MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is not
generated, the service is not affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Antennas are not aligned during the equipment commissioning.
Cause 2: The RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF is reported when the NE is running.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Antennas are not aligned during the equipment commissioning.
1.
Align the antennas, and ensure that the actual receive power is within the range of preset
receive power +/-3 dB.
Step 2 Cause 2: The RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF is reported when the NE is running.
1.
Handle the RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF alarm. When the
RADIO_FADING_MARGIN_INSUFF alarm is cleared, the RADIO_RSL_BEYONDTH
alarm is cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.249 RADIO_RSL_HIGH
Description
The RADIO_RSL_HIGH is an alarm indicating that the radio receive power is very high. This
alarm is reported if the detected receive power is equal to or higher than the upper threshold of
the ODU (-20 dBm).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
545
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service transmission is affected. If the system is configured with 1+1 protection, protection
switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The local ODU is faulty.
Cause 2: There is a strong interference source nearby.
Cause 3: The transmit power of the opposite ODU is very high.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local ODU is faulty.
1.
6.14 Replacing the ODU.
Step 2 Cause 2: There is a strong interference source nearby.
1.
Check whether any nearby signal source transmits signals whose frequency is close to the
specified range. If yes, check whether the signal source can be shut down or removed. If
not, contact the network planning department for replanning the frequency.
Step 3 Cause 3: The transmit power of the opposite ODU is very high
1.
Reset the transmit power of the ODU at the opposite end. For details, see Configuring the
IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.250 RADIO_RSL_LOW
Description
The RADIO_RSL_LOW is an alarm indicating that the radio receive power is very low. This
alarm is reported if the detected receive power is equal to or lower than the upper threshold of
the ODU (-90 dBm).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
546
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
If no MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_LOF or MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is
generated, the services are not affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Other alarms occur at the opposite station.
Cause 2: The transmit power of the opposite station is very low.
Cause 3: The local ODU is faulty.
Cause 4: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Other alarms occur at the opposite station.
Check whether any of the following alarms is generated in the equipment of the opposite station.
If yes, take priority to clear the alarm.
l RADIO_MUTE
l CONFIG_NOSUPPORT
l RADIO_TSL_LOW
l BD_STATUS
Step 2 Cause 2: The transmit power of the opposite station is very low.
1.
See Configuring the IF/ODU Information of a Radio Link. Check whether the transmit
power of the opposite station is normal. If not, replace the ODU of the opposite station.
Step 3 Cause 3: The local ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the ODU at the local end.
Step 4 Cause 4: Signal attenuation on the radio link is very heavy.
1.
Browse history alarms and check whether the alarm is generated continuously.
If the alarm is generated occasionally, contact the network planning department to change
the design to increase the anti-fading performance.
2.
Check whether the antennas at both ends are adjusted properly.
If not, align the antennas again.
3.
Check whether any mountain or building obstacle exists in the transmit direction.
If yes, contact the network planning department for proper modification of the planning
design, hence preventing the block of the mountain or building obstacle.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
547
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether the polarization direction of the antenna, ODU, and hybrid coupler is set
correctly.
If not, correct the polarization direction.
5.
Check whether the outdoor units such as antennas, combiner, ODU, and flexible waveguide
are wet, damp, or damaged.
If yes, replace the unit that is wet, damp, or damaged. For the operations, see 6 Part
Replacement
6.
Check whether the antenna gain at both the transmit and receive ends meets the requirement.
If not, replace the antenna.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.251 RADIO_TSL_HIGH
Description
The RADIO_TSL_HIGH is an alarm indicating that the radio transmit power is too high. This
alarm is reported when the detected transmit power is higher than the upper power threshold of
the ODU.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service transmission is affected. If the system is configured with 1+1 protection, protection
switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local ODU is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the ODU.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
548
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.252 RADIO_TSL_LOW
Description
The RADIO_TSL_LOW is an alarm indicating that the radio transmit power is very low. This
alarm is reported when the detected transmit power is less than the lower power threshold of the
ODU.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service transmission is affected. If the system is configured with 1+1 protection, protection
switching may be triggered.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The local ODU is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The local ODU is faulty.
1.
Replace the ODU.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.253 RELAY_ALARM_CRITICAL
Description
The RELAY_ALARM_CRITICAL is an alarm indicating the critical alarm inputs. This alarm
occurs when the user sets the severity of an available alarm input to critical and there is such an
alarm input.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
549
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the RELAY_ALARM_CRITICAL alarm occurs, it does not affect the operation of the
board or the services on the NE.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: There is a critical alarm input.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: There is a critical alarm input.
1.
Clear the alarms of the external equipment according to the defined meanings of the alarms.
Then, the RELAY_ALARM_CRITICAL alarm is cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.254 RELAY_ALARM_IGNORE
Description
The RELAY_ALARM_IGNORE is an alarm indicating the warning alarm inputs. This alarm
occurs when the user sets the severity of an available alarm input to warning and there is such
an alarm input.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
550
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
When the RELAY_ALARM_IGNORE alarm occurs, it does not affect the operation of the board
or the services on the NE.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: There is a warning alarm input.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: There is a warning alarm input.
1.
Clear the alarms of the external equipment according to the defined meanings of the alarms.
Then, the RELAY_ALARM_IGNORE alarm is cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.255 RELAY_ALARM_MAJOR
Description
The RELAY_ALARM_MAJOR is an alarm indicating the major alarm inputs. This alarm occurs
when the user sets the severity of an available alarm input to major and there is such an alarm
input.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the RELAY_ALARM_MAJOR alarm occurs, it does not affect the operation of the board
or the services on the NE.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: There is a major alarm input.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: There is a major alarm input.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
551
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Clear the alarms of the external equipment according to the defined meanings of the alarms.
Then, the RELAY_ALARM_MAJOR alarm is cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.256 RELAY_ALARM_MINOR
Description
The RELAY_ALARM_MINOR is an alarm indicating the minor alarm inputs. This alarm occurs
when the user sets the severity of an available alarm input to minor and there is such an alarm
input.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the RELAY_ALARM_MINOR alarm occurs, it does not affect the operation of the board
or the services on the NE.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: There is a minor alarm input.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: There is a minor alarm input.
1.
Clear the alarms of the external equipment according to the defined meanings of the alarms.
Then, the RELAY_ALARM_MINOR alarm is cleared.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
552
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.257 RMFA
Description
The RMFA is an alarm indicating the loss of multiframe alignment at the remote end. This alarm
occurs when the local end detects all 1s of the remote indication bits in Z consecutive CAS
multiframes (Z = 1-5) of the framed E1/T1 input.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the path ID.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the services at the local site are not affected. The alarm indicates that
the LMFA alarm occurs at the opposite end.
Possible Causes
The LMFA alarm occurs at the opposite end.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the opposite end of the alarmed path reports the LMFA alarm. If yes, clear the
LMFA alarm. Then, the RMFA alarm at the local end clears.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.258 RPS_INDI
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
553
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The RPS_INDI is an alarm indicating that the radio protection switching is detected.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the protection group.
Parameter 2
Indicates the type of protection switching.
0x01: HSB protection switching
0x02: HSM protection switching
Impact on the System
l
During the HSB protection switching, services are interrupted. After the HSB switching is
complete, the services are restored to normal.
During the HSM protection switching, no bit errors occur and the services are not affected.
Possible Causes
l
The possible causes of the HSB protection switching are as follows:
Cause 1: An external switching event occurs
Cause 2: An automatic switching event occurs.
Cause 3: A reverse switching event occurs.
The possible causes of HSM protection switching are as follows:
The quality of the main channel degrades.
In the case of Hybrid radio, the automatic switching condition of the HSM is that the
quality of the main channel degrades.
In the case of SDH/PDH radio, an alarm that triggers the HSM switching is reported on
the radio link.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the type of the protection switching based on the alarm parameters.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
554
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 2 Cause 1 of HSB switching: An external switching event occurs. That is, the NMS issues a
command to trigger the switching.
1.
Check whether the switching is the forced switching or manual switching. For details, see
Querying the IF 1+1 Protection Status.
If...
Then...
The switching is the forced switching or Find the cause and release the switching
manual switching
immediately.
The switching is not the forced
switching or manual switching
Go to Cause 2 of HSB switching.
Step 3 Cause 2 of HSB switching: An automatic switching event occurs. That is, the equipment is faulty,
or the service is defective.
1.
Check whether the following faults or alarms occur. If yes, rectify the faults or clear the
alarms.
l The hardware of the IF board or the ODU is faulty.
l VOLT_LOS
l RADIO_TSL_HIGH, RADIO_TSL_LOW, or RADIO_RSL_HIGH
l IF_INPWR_ABN or CONFIG_NOSUPPORT
l R_LOC, R_LOF, R_LOS, or MW_LOF
NOTE
l If the switching is non-revertive, the services are not automatically switched to the working path
when the working path is restored to normal, and the RPS_INDI alarm persists. In this case, you
need to manually switch the services from the protection path to the working path. The RPS_INDI
alarm is cleared only when the switching is successful.
l If the switching is revertive, the services are automatically switched to the working path only
when the specified wait-to-restore (WTR) time expires after the working path is restored to
normal. The RPS_INDI alarm is cleared only when the switching is successful.
Step 4 Cause 3 of HSB switching: A reverse switching event occurs.
1.
Query whether the active and standby IF boards report the MW_RDI alarm. If yes, take
priority to clear the MW_RDI alarm.
Step 5 Cause 1 of HSM switching: In the case of Hybrid radio, the quality of the main channel degrades.
1.
Check whether the AM_DOWNSHIFT alarm is reported by an IF board. If the alarm is
reported by an IF board, refer to AM_DOWNSHIFT to rectify the fault that causes the
quality of the main channel to degrade. If the alarm is not reported by an IF board, the
quality of the main channel degrades possibly due to the weather. In this case, you do not
need to handle the problem, because this is a normal situation.
Step 6 Cause 2 of HSM switching: In the case of SDH/PDH radio, an alarm that triggers the HSM
switching is reported on the radio link.
1.
Check whether any alarm that triggers the HSM switching is reported by an IF board of the
IF 1+1 protection group. If yes, take priority to clear the alarm.
HSM switching may be triggered by any of the following alarms:
l R_LOC, R_LOF, R_LOS, or MW_LOF
l MW_BER_EXC, MW_BER_SD, MW_FEC_UNCOR
l B1_SD or B2_SD
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
555
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.259 RS_CROSSTR
Description
The RS_CROSSTR is an alarm indicating that a regenerator section performance indicator
crosses the threshold. This alarm is reported if a board detects that a regenerator section bit error
performance event crosses the preset threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the performance monitoring period:
l 0x01: 15 minutes
l 0x02: 24 hours
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Parameter 2 is always 0x00. Parameter 3 indicate the ID of a
performance event that causes the alarm and has the following
meanings:
l 0x01: RSBBE
l 0x02: RSES
l 0x03: RSSES
l 0x04: RSOOF
l 0x05: RSOFS
l 0x06: RSUAS
l 0x07: RSCSES
Impact on the System
A large number of bit errors occur in the services, and the services may be interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
556
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Services are interrupted for a long time.
Cause 2: The regenerator section bit error performance indicator crosses the preset
threshold.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Services are interrupted for a long time.
NOTE
Handle the alarm as follows if the value of parameter 3 is 0x06:
1.
Check whether fibers are properly connected. If not, connect the fibers again according to
planning information.
2.
Check whether cross-connections are configured for service ports. If not, configure crossconnections again according to planning information.
Step 2 Cause 2: The regenerator section bit error performance indicator crosses the preset threshold.
1.
Find out the performance event that crosses the preset threshold. For details, see 8.3.8
Browsing the Performance Event Threshold-Crossing Records.
2.
Handle the performance event that crosses the threshold.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.260 RTC_FAIL
Description
The RTC_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the real-time clock (RTC) on the system control
board fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service is not affected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
557
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The RTC on the system control board is abnormal.
Cause 2: The board temperature is too high.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The RTC on the system control board is abnormal.
1.
Replace the system control, switching, and timing board.
Step 2 Cause 2: The board temperature is too high.
1.
8.3.3 Browsing Current Alarms, and if the board reports the TEMP_ALARM alarm,
clear this alarm first.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.261 S1_SYN_CHANGE
Description
The S1_SYN_CHANGE is an alarm indicating that the clock source is switched in S1 byte
mode.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
0x01: system priority list
0x02: external clock priority list
Impact on the System
If the new clock source has a lower quality, pointer justifications and bit errors are generated
after the switching of clock source. As a result, the quality of services is affected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
558
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
When the SSM protocol or extended SSM protocol is enabled.
l
Cause 1: The original clock source is lost.
Cause 2: The fiber is cut off.
Cause 3: The external BITS is interrupted.
Cause 4: The S1_SYN_CHANGE alarm occurs at the upstream station.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The original clock source is lost.
1.
Handle the SYNC_C_LOS alarm that is related to the original clock source.
Step 2 Cause 2: The fiber is cut off.
1.
Replace the faulty fiber.
Step 3 Cause 3: The external BITS is interrupted.
1.
Check whether the cable connect NE to BITS is normal. If not, replace the faulty cable.
Step 4 Cause 4: The S1_SYN_CHANGE alarm reported at the upstream station.
1.
Handle the S1_SYN_CHANGE alarm reported at the upstream station.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.262 SCCDATA_BACKUP_FAIL
Description
The SCCDATA_BACKUP_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the batch backup on SCC boards
fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
559
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
A Alarm Reference
Meaning
Parameter 1 Indicates the cause of the failure.
l 0x31: The database backup fails.
l 0x32: Software version verification fails on the main and standby SCC
boards.
l 0x33: Communication between the main and standby SCC boards fails.
l 0x34: The main and standby SCC boards have different data after an upgrade.
Impact on the System
Data synchronization between the main and standby SCC boards fails, and the switching between
the two boards is unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The main and standby SCC boards have different versions of software.
Cause 2: Communication between the main and standby SCC boards fails.
Cause 3: Databases on the main and standby SCC boards are damaged.
Cause 4: The main and standby SCC boards have different data after an upgrade.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The main and standby SCC boards have different versions of software.
1.
Query and record the software versions of the main and standby SCC boards according to
8.4.1 Querying the Board Information Report .
2.
If the software versions are different, determine the correct version based on the version
mapping table and replace the SCC board with an incorrect version. For details, see 6.9
Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board.
Step 2 Cause 2: Communication between the main and standby SCC boards fails.
1.
Check whether the system reports the COMMUN_FAIL alarm.
2.
If yes, clear the COMMUN_FAIL alarm. The system will start batch backup
automatically.
Step 3 Cause 3: Databases on the main and standby SCC boards are damaged.
1.
Check whether the system reports the DBMS_ERROR alarm. For details, see 8.3.3
Browsing Current Alarms.
2.
If yes, clear the DBMS_ERROR alarm. Then, check whether the SYNC_FAIL alarm is
cleared.
Step 4 Cause 4: The main and standby SCC boards have different data after an upgrade.
1.
Re-install the standby SCC board.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
560
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.263 SEC_RADIUS_FAIL
Description
The SEC_RADIUS_FAIL is an alarm indicating that RADIUS authentication fails overmany
times. This alarm is reported when the RADIUS authentication fails for five consecutive times.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1 to Parameter 5
Indicates the most significant five characters of username.
Impact on the System
A user cannot log in to an NE.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The active period of the account expires.
Cause 2: Configurations on the RADIUS server are incorrect, such as passwords and access
policies.
Cause 3: There are unauthenticated login attempts.
Cause 4: The shared key for the NE and the RADIUS server is configured incorrectly.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The active period of the account expires.
1.
Use an active account.
Step 2 Cause 2: Configurations on the RADIUS server are incorrect, such as passwords and access
policies.
1.
Enter the correct password.
2.
Set correct access policies.
Step 3 Cause 3: There are unauthenticated login attempts.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Eliminate the source that initiates the unauthenticated login attempts.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
561
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 4 Cause 4: The shared key for the NE and the RADIUS server is configured incorrectly.
1.
Set the shared key correctly.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.264 SECU_ALM
Description
The SECU_ALM is an alarm indicating that an illegal user fails to log in to the NE.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The SECU_ALM alarm is ended soon after it is reported, and the alarm does not affect the system
and services.
Possible Causes
An illegal user tries to log in to the NE.
Procedure
Step 1 An illegal user tries to log in to the NE.
1.
Query the NE log to check the user name that is used for the login.
----End
Related Information
After a user fails to log in to an NE for five consecutive times (if the interval between two logins
is less than 3 minutes, the two logins are consecutive logins), the SECU_ALM alarm is reported
upon each subsequent login failure and meanwhile the user is locked for 60 seconds. During the
60 seconds, the user cannot log in to the NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
562
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.265 SRV_SHUTDOWN_LD
Description
The SRV_SHUTDOWN_LD alarm indicates that an Ethernet service is deactivated. This alarm
is reported when an Ethernet service is deactivated due to a service loop. This alarm is cleared
after the Ethernet service is reactivated.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The loop of the alarmed Ethernet service is released, and the Ethernet service is restored.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: A loop occurs in an Ethernet service and therefore the Ethernet service is deactivated.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A loop occurs in an Ethernet service and therefore the Ethernet service is deactivated.
1.
Check whether a service is looped back on the path of the alarmed Ethernet service.
2.
Re-configure the preceding service based on the network plan.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.266 SWDL_ACTIVATED_TIMEOUT
Description
The SWDL_ACTIVATED_TIMEOUT is an alarm indicating the activation timeout of the
software package. During the package loading, the system reports the alarm if no data is
submitted within 30 minutes after activation of the NE software or board software.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
563
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The NE does not perform the submit operation. As a result, the software in the two areas of the
double-area boards on the NE is inconsistent.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The radio link is faulty. As a result, the NE involved in the package loading fails to
receive the submit command.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The radio link is faulty. As a result, the NE involved in the package loading fails to
receive the submit command.
1.
Check whether the radio link is faulty.
If...
Then...
The radio link is faulty
Troubleshoot the radio link to ensure that the link
between the nodes to be loaded is normal.
The radio link is normal Perform the package loading to the NE again.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.267 SWDL_AUTOMATCH_INH
Description
The SWDL_AUTOMATCH_INH is an alarm indicating that the automatic match function is
disabled. When the automatic match function of the board is disabled, the system reports the
alarm if the board cannot match the software from the system control board.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
564
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When a board whose version is not consistent with the software version of the NE is installed,
the software versions of the whole NE are not consistent if the board cannot automatically match
the software from the system control board. As a result, certain functions of the NE cannot run
normally.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The automatic match function is disabled.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The automatic match function is disabled.
1.
Contact the Huawei technical support engineers for troubleshooting.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.268 SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH
Description
The SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH is an alarm of software inconsistency. After an NE is
power recycled and the boards on the NE become online, if the system detects that the system
control board and the CF card are inconsistent in software packages, the system reports the
SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH alarm.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH alarm is reported, certain functions of the NE may
be affected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
565
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
Cause 1: After a system control board is replaced, the software package in the new system control
board is inconsistent with that in the CF card.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: After a system control board is replaced, the software package in the new system control
board is inconsistent with that in the CF card.
1.
Perform the package diffusion again on the NE where the SWDL_CHGMNG_NOMATCH
alarm is reported.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.269 SWDL_COMMIT_FAIL
Description
The SWDL_COMMIT_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the commission operation on the NE
fails. This alarm is reported when the commission operation fails in the package diffusion.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the SWDL_COMMIT_FAIL alarm occurs, the software versions in the two areas of the
double-area board are inconsistent.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: File backup fails.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: File backup fails.
1.
Check whether the loaded package is correct.
2.
Perform the package diffusion again on the NE where the alarm is reported.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
566
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.270 SWDL_INPROCESS
Description
The SWDL_INPROCESS is an alarm indicating that the package diffusion is in process on the
NE.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the SWDL_INPROCESS alarm is reported, the operations, such as modifying
configuration, uploading/downloading files, and backing up the database, are not allowed,
because the software package is being loaded to the NE.
Possible Causes
The package diffusion is being performed on the NE.
Procedure
Step 1 The SWDL_INPROCESS alarm is cleared automatically after the loading or rollback is
complete. Hence, this alarm can be neglected.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.271 SWDL_NEPKGCHECK
Description
The SWDL_NEPKGCHECK is an alarm of software inconsistency. This alarm is reported in
the following two situations: the CF card and flash memory are inconsistent in software package
and the flash memory has a software package; in a routine check (the check is not initiated by
issuing commands), the system detects that some files are missing from the software package
stored in the CF card or from the software package stored in the flash memory.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
567
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
l
If this alarm occurs during package loading, package loading fails.
If this alarm occurs in other conditions, automatic file matching fails.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: Certain files of the package are missing and cannot be recovered.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Certain files of the package are missing and cannot be recovered.
1.
Ensure that the loaded software package is correct. Perform the package diffusion again on
the NE where the SWDL_NEPKGCHECK alarm is reported.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.272 SWDL_PKG_NOBDSOFT
Description
The SWDL_PKG_NOBDSOFT is an alarm indicating that certain board software is missing
from the software package. This alarm is reported when the required software is missing from
the software package during the automatic match of the board.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
568
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Impact on the System
The board cannot perform automatic match, because the board software is missing from the
software package. Therefore, the board software version is inconsistent with the NE software
version, and certain functions of the NE may be affected.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: Certain board software is uninstalled during the software package loading.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Certain board software is uninstalled during the software package loading.
1.
Add the required board software to the software package. Alternatively, perform the
software package loading again.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.273 SWDL_PKGVER_MM
Description
The SWDL_PKGVER_MM is an alarm indicating that the consistency check on the software
package version fails. This alarm is reported when the consistency check on the software package
version fails.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The software version of the software package is inconsistent with the software version described
in the software package. As a result, certain functions of the NE may be affected.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The software version information in the description file of the software package is
inconsistent with the actual software version information.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
569
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The software version information in the description file of the software package is
inconsistent with the actual software version information.
1.
Ensure that the loaded software package is correct. Perform the package diffusion again on
the NE where the alarm is reported.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.274 SWDL_ROLLBACK_FAIL
Description
The SWDL_ROLLBACK_FAIL is an alarm indicating that the rollback on the NE fails. This
alarm is reported when the rollback fails for any board on the NE.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Processing alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The board software version and the NE software version may mismatch, and certain functions
of the NE may be affected.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: Certain board software is uninstalled during the software package loading.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Certain board software is uninstalled during the software package loading.
1.
Add the required board software to the software package. Alternatively, perform the
software package loading again.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
570
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
A.3.275 SYN_BAD
Description
The SYN_BAD is an alarm indicating that the quality of the synchronization source declines.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The NE clock fails to be locked.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The quality of the synchronization source declines.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The quality of the synchronization source declines.
1.
Take different measures based on the traced synchronization source.
If...
Then...
The traced synchronization source is an Perform Steps Step 1.2 to Step 1.4.
external clock
The traced synchronization source is a
line clock
2.
3.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the system control,
switching&timing board of the upstream
NE.
Check whether the configuration of the external clock is correct.
If...
Then...
The configuration is incorrect
Change the configuration data.
The configuration is correct
Go to the next step.
Check whether the opposite equipment that provides the clock source is faulty.
If...
Then...
The equipment is faulty
Rectify the fault.
The equipment functions normally
Go to the next step.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
571
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
4.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether the cable that is connected to the external clock source is in normal status.
If...
Then...
The cable is not in normal status
Replace the cable.
The cable is in normal status
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.276 SYNC_C_LOS
Description
The SYNC_C_LOS is an alarm indicating that the synchronization source is lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Warning
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The NE clock degrades or enters the free-run mode.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The clock source is lost.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The clock source is lost.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Troubleshoot the synchronization sources of the lost clock source based on the clock source
priority table.
If...
Then...
The synchronization source is an
external clock
Handle the EXT_SYNC_LOS alarm.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
572
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The synchronization source is an IF
clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the IF board.
The synchronization source is a line
clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the line
board.
The synchronization source is a
tributary clock
Handle the alarm that occurs on the tributary
board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.277 T_ALOS
Description
The T_ALOS is an alarm indicating that the 2 Mbit/s analog signal is lost at the specific port.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The 2Mbit/s services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: No 2 Mbit/s services are received on the port.
Cause 2: The opposite NE is faulty.
Cause 3: The IF cable is faulty.
Cause 4: The alarmed board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: No 2 Mbit/s services are received on the port.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the alarmed port receives the 2 Mbit/s service.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
573
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
If...
A Alarm Reference
Then...
The services are not received Transmit the services to the port or delete the
unnecessary service configuration.
The services are received
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The equipment at the opposite end is faulty.
1.
Check whether the equipment at the opposite end is faulty.
If...
Then...
The equipment is faulty
Rectify the fault.
The equipment is normal
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The IF cable is faulty.
1.
Check whether the IF cable is faulty.
If...
Then...
The IF cable is faulty
Rectify the fault.
The IF cable is not faulty
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 4: The alarmed board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.278 T_F_RST
Description
The T_F_RST is an alarm indicating that the transmit FIFO is reset.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services in the PDH path are interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
574
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The frequency offset of the input signal is very large.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The frequency offset of the input signal is very large.
1.
Measure the frequency offset of the input signal.
If...
Then...
The frequency offset is very large
Troubleshoot the remote site.
The frequency offset is within 50 ppm
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.279 T_LOC
Description
The T_LOC is an alarm indicating that the clock is lost on the transmit line side.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The services in the alarmed AU-4 path are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The cross-connect and timing board is faulty.
Cause 2: The line board is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
575
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The cross-connect and timing board is faulty.
1.
Replace the cross-connect and timing board at the local site.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line board is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.280 TEMP_ALARM
Description
The TEMP_ALARM is an alarm indicating that the board temperature crosses the threshold.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Environmental alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
l 0x01: The temperature crosses the upper threshold.
l 0x02: The temperature crosses the lower threshold.
Impact on the System
The board fails to work normally.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
576
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The board temperature crosses the threshold.
Cause 2: The temperature detection circuit of the board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The board temperature crosses the threshold.
1.
If the alarm is reported by the ODU, take appropriate measures (for example, installing a
sunshade) to control the temperature.
2.
If the alarm is reported by the board on the IDU, check whether the temperature control
devices, such as air-conditioners, work normally.
3.
If...
Then...
The temperature control devices work
abnormally
Adjust the temperature control devices.
The temperature control devices work
normally
Go to the next step.
Check whether the heat dissipation hole on the IDU is covered or blocked.
If...
Then...
The heat dissipation hole is covered or
blocked
Clear or remove the covering materials or
obstacles.
The heat dissipation hole is not covered or Go to Cause 2.
blocked
Step 2 Cause 2: The temperature detection circuit of the board is faulty.
1.
If the ambient temperature is normal and no other heat dissipation problems exist, replace
the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.281 THUNDERALM
Description
The THUNDERALM is an alarm indicating the surge protection failure. If the system detects
the surge protection circuit fails, the THUNDERALM occurs.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Environment alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
577
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the THUNDERALM occurs, the system operation and services are not affected, but the
surge protection function fails.
Possible Causes
The possible causes of the THUNDERALM alarm are as follows:
l
Cause 1: The fuse tube of the surge protection circuit is interrupted.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The fuse tube of the surge protection circuit is interrupted.
1.
Replace the fuse tube, and then check whether the alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Replace the board that reports the THUNDERALM alarm.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.282 TR_LOC
Description
The TR_LOC is an alarm indicating that the clock is faulty. This alarm is reported when a board
detects that the clock signal transmitted from the clock unit to the board is lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
578
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the slot ID of the board that loses the clock.
A Alarm Reference
l 0x01: board with a smaller slot ID.
l 0x02: board with a larger slot ID.
l 0x03: two boards.
Impact on the System
l
If the protection cross-connect board is faulty, the services are not affected.
If the working cross-connect board is faulty, the services are switched, therefore causing
transient service interruption.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: If one board reports this alarm, the board hardware is faulty.
Cause 2: If multiple boards report this alarm, the clock cable of the cross-connect board is
faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Locate the alarmed board according to the alarm parameter.
Step 2 Cause 1: If one board reports this alarm, the board hardware is faulty.
1.
Perform a warm reset on the alarmed board, and then check whether the alarm is cleared.
If the alarm persists, perform a cold reset on the alarmed board. For details, see Resetting
a Boards.
2.
If the alarm persists, remove the alarmed board and check whether certain pins on the
backplane are bent. Insert the board again, and then check whether the alarm is cleared.
3.
If the alarm persists, replace the alarmed board. For details, see Replacing a Board.
Step 3 Cause 2: If multiple boards report this alarm, the clock cable of the cross-connect board is faulty.
1.
If the working cross-connect board is faulty, perform 1+1 protection switching on the crossconnect board. For details, see Performing 1+1 Protection Switching.
2.
Perform a cold reset on the protection cross-connect board, and then check whether the
alarm is cleared.
3.
If the alarm persists, remove and insert the protection cross-connect board, and then check
whether the alarm is cleared.
4.
If the alarm persists, replace the protection cross-connect board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.283 TU_AIS
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
579
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Description
The AU_AIS is an alarm indicating that the TU has errors. This alarm is reported if a board
detects that the signal in the TU path is all 1s.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service in the alarmed TU path is interrupted. If the services are configured with protection,
protection switching is also triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
Cause 2: The line is faulty.
Cause 3: The board at the opposite end is faulty.
Cause 4: The board at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
1.
See Creating the Cross-Connections of Point-to-Point Services to check whether the SDH
service data is incorrect.
If...
Then...
The SDH service data is incorrect
Change the configuration data.
The SDH service data is correct
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line is faulty.
1.
Check whether a line alarm that causes AIS insertion is reported on the service trail.
NOTE
For details about the line alarms that cause AIS insertion, see E.2.6 AIS Insertion.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
If...
Then...
The line alarm is reported
Clear the line alarms that cause AIS insertion.
No line alarms are reported
Go to the next step.
See 8.5 Software Loopback to locate whether the board at the local end or at the opposite
end is faulty.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
580
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The board at the opposite end is faulty
Go to Cause 3.
The board at the local end is faulty
Go to Cause 4.
Step 3 Cause 3: The board at the opposite end is faulty.
1.
Replace the faulty board at the opposite end.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board at the local end is faulty.
1.
2.
3.
Replace the board where the local line unit resides.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to the next step.
Replace the system control, cross-connect, and timing board at the local end.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to the next step.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.284 TU_AIS_VC12
Description
The TU_AIS_VC12 is an indication of TU alarms at VC-12 level. This alarm occurs when a
board detects TU pointers of all 1s.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
581
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, the services in the alarmed VC-12 path are interrupted. If the services
are configured with protection, protection switching is also triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
Cause 2: The line is faulty.
Cause 3: The board at the opposite site is faulty.
Cause 4: The board at the local site is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the SDH service data is correct. For details, see Creating the CrossConnections of Point-to-Point Services.
If...
Then...
The SDH service data is incorrect
Change the configuration data.
The SDH service data is correct
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The line is faulty.
1.
Check whether a line alarm that causes AIS insertion is reported on the service trail.
NOTE
For details about the line alarms that cause AIS insertion, see E.2.6 AIS Insertion.
If...
Then...
The line alarm is reported
Change the configuration data.
No line alarms are reported
Go to Step 3.
Step 3 Check whether the fault occurs at the local site or at the opposite site. For details, see 8.5.5
Setting Loopbacks for the EOS/EoPDH-Plane Ethernet Interface Board.
If...
Then...
The board at the opposite site is faulty
Go to Cause 3.
The board at the local site is faulty
Go to Cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 3: The board at the opposite site is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
582
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Replace the faulty board at the opposite site.
Step 5 Cause 4: The board at the local site is faulty.
1.
2.
Replace the line board at the local site. For details, see 6.3 Replacing the SDH Optical
Interface Board.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to the next step.
Replace the alarmed board at the local site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.285 TU_AIS_VC3
Description
The TU_AIS_VC3 is a TU-3 alarm indication. The alarm is reported when a board detects TU
pointers of all "1"s.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
The services in the alarmed TU-3 paths are interrupted. If the services are configured with
protection, protection switching is triggered.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
583
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: SDH service configuration data is incorrect.
Cause 2: The service path is faulty.
Cause 3: The board at the opposite end is faulty.
Cause 4: The board at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: SDH service configuration data is incorrect.
1.
Follow instructions in Creating the Cross-Connections of Point-to-Point Services to check
whether the SDH service configuration data is incorrect.
If...
Then...
The SDH service configuration data is
incorrect
Rectify the SDH service configuration
data.
The SDH service configuration data is
correct
Go to cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The service path is faulty.
1.
Check whether a line alarm that will cause AIS insertion is reported on the service path.
NOTE
For the line alarms that will cause AIS insertion, see E.2.6 AIS Insertion.
If...
Then...
A line alarm that will cause AIS
insertion is reported
Rectify the SDH service configuration data.
No line alarm is reported
Go to step 3.
Step 3 Follow instructions in 8.5.4 Setting a Loopback for the Packet-plane Ethernet Interface
Board to identify whether the board at the local end or at the opposite end is faulty.
If...
Then...
The board at the opposite end is faulty
Go to cause 3.
The board at the local end is faulty
Go to cause 4.
Step 4 Cause 3: The board at the opposite end is faulty.
1.
Replace the faulty board at the opposite end.
Step 5 Cause 4: The board at the local end is faulty.
1.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Follow instructions in 6.3 Replacing the SDH Optical Interface Board to replace the line
board at the local end.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
No further action is required.
The alarm persists
Go to the next step.
Follow instructions in 6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board to
replace the system control, switching, and timing board.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
584
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
No further action is required.
The alarm persists Follow instructions in Replacing an Alarmed Board to replace the
board that reports the alarm.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.286 TU_LOP
Description
The TU_LOP is an alarm indicating that the TU pointer is lost. This alarm is reported if a board
detects that the TU-PTR value is an invalid pointer or NDF reversion in eight consecutive frames.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The service in the alarmed TU path is interrupted. If the services are configured with protection,
protection switching is also triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The system control, cross-connect, and timing board is faulty.
Cause 2: The tributary board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The system control, cross-connect, and timing board is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Replace the system control, cross-connect, and timing board at the local end.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to Cause 2.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
585
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Step 2 Cause 2: The tributary board is faulty.
1.
Replace the board where the tributary unit resides.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.287 TU_LOP_VC12
Description
The TU_LOP_VC12 is an alarm indicating that the VC-12 TU pointer is lost. This alarm is
reported when a board receives invalid pointers or new data flags (NDFs) in eight consecutive
VC-12 frames.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
Services in the alarmed TU path are interrupted. If the services are configured with protection,
protection switching is also triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
Cause 2: The board at the opposite site is faulty.
Cause 3: The board at the local site is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
586
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
1.
A Alarm Reference
Check whether the SDH service data is correct. For details, see Creating the CrossConnections of Point-to-Point Services.
If...
Then...
The SDH service data is incorrect
Change the configuration data.
The SDH service data is correct
Go to Step 2.
Step 2 Check whether the fault occurs at the local site or at the opposite site. For details, see 8.5.5
Setting Loopbacks for the EOS/EoPDH-Plane Ethernet Interface Board.
If...
Then...
The board at the opposite site is faulty
Go to Cause 2.
The board at the local site is faulty
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 2: The board at the opposite site is faulty.
1.
In this case, replace the faulty board at the opposite site.
Step 4 Cause 3: The board at the local site is faulty.
1.
2.
Replace the line board at the local site. For details, see 6.3 Replacing the SDH Optical
Interface Board.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears after the board is
replaced
The fault is rectified. End the alarm
handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to the next step.
Replace the alarmed board at the local site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.288 TU_LOP_VC3
Description
The TU_LOP_VC3 alarm indicates that a TU-3 pointer is lost. This alarm is reported if a board
detects that eight consecutive VC-3 TU-PTR values are invalid or the NDF field in eight
consecutive VC-3 TU-PTR values are reversed.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
587
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
The services in the alarmed TU-3 path are interrupted. If the services are configured with
protection, protection switching is triggered.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: SDH service configuration data is incorrect.
Cause 2: The board at the opposite end is faulty.
Cause 3: The board at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: SDH service configuration data is incorrect.
1.
Follow instructions in Creating the Cross-Connections of Point-to-Point Services to check
whether the SDH service configuration data is incorrect.
If...
Then...
The SDH service configuration data is
incorrect
Rectify the SDH service configuration
data.
The SDH service configuration data is
correct
Go to step 2.
Step 2 Follow instructions in 8.5.4 Setting a Loopback for the Packet-plane Ethernet Interface
Board to identify whether the board at the local end or at the opposite end is faulty.
If...
Then...
The board at the opposite end is faulty
Go to cause 2.
The board at the local end is faulty
Go to cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 2: The board at the opposite end is faulty.
1.
Replace the faulty board at the opposite end.
Step 4 Cause 3: The board at the local end is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Follow instructions in 6.3 Replacing the SDH Optical Interface Board to replace the line
board at the local end.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
588
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
3.
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
No further action is required.
The alarm persists
Go to the next step.
Follow instructions in 6.9 Replacing the System Control, Switch and Timing Board to
replace the system control, switching, and timing board.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
No further action is required.
The alarm persists
Go to the next step.
Follow instructions in Replacing an Alarmed Board to replace the board that reports the
alarm.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.289 TUNNEL_APS_DEGRADED
Description
The TUNNEL_APS_DEGRADED is an alarm indicating that a tunnel protection group
degrades.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Service alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The protection tunnel is faulty and the protection group fails.
Possible Causes
Cause: The protection tunnel in the tunnel protection group is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause: The protection tunnel in the tunnel protection group is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check the status of the tunnel protection group and confirm that the protection tunnel is
faulty.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
589
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
8.3.3 Browsing Current Alarms and clear the alarms in the protection tunnel.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.290 UHCS
Description
The UHCS is an alarm of uncorrected header check sequence. This alarm occurs when multiple
uncorrectable bit errors exist in the cell headers.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
When the UHCS alarm occurs, some cells with multiple bit errors are detected during cell
delimitation at the ATM port. Consequently, the user cells are lost.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: A few bit errors occur in the receive path related to the ATM port which reports
the UHCS alarm.
Cause 2: The ATM physical-layer processing chip of the board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: A few bit errors occur in the receive path connected to the ATM port which reports the
UHCS alarm.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the related receive path reports any alarms indicating excessive
bit errors, such as B1_SD, B2_SD, and B3_SD.
2.
On the NMS, check whether the service is looped.
3.
If yes, modify the service configuration to release the loop, and then check whether the
alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: The ATM physical-layer processing chip of the board is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Perform a cold reset on the board that reports the UHCS alarm and check whether the alarm
is cleared. For details, see 8.6.1 Cold Reset.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
590
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
Optional: If the UHCS alarm persists after the cold reset, replace the alarmed board and
check whether the alarm is cleared. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.291 UP_E1_AIS
Description
The UP_E1_AIS is an alarm indication of the 2 Mbit/s uplink signal. This alarm is reported
when the tributary board detects that the 2 Mbit/s uplink signal is all 1s.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Minor
Communication alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
E1 signals are unavailable.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The opposite equipment transmits the AIS signal.
Cause 2: The receive unit of the tributary board on the local equipment is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The opposite equipment transmits the AIS signal.
1.
Check whether the opposite equipment transmits the AIS signal.
If...
Then...
The opposite equipment transmits the
AIS signal
Rectify the fault on the opposite equipment.
The opposite equipment does not
transmit the AIS signal
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The receive unit of the tributary board on the local equipment is faulty.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
591
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.292 VC_AIS
Description
The VC_AIS is an alarm indication of the virtual channel (VC) connection. This alarm occurs
when the VC connection that is set with the segment end point attribute receives the AIS cells,
indicating that the upstream ATM services are abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the direction of ATM connection.
l 0x01: forward
l 0x02: backward
Parameter 2
Indicates the status of ATM connection.
l 0x01: working connection
l 0x00: protection connection
Parameter 3
Indicates the segment and end attribute of ATM connection.
l 0x01: segment
l 0x02: end
Impact on the System
l
If the continuity check (CC) sink is enabled on an upstream NE but the upstream NE does
not receive any CC cells, the local NE reports the VP_AIS. Then, the connection, though
not interrupted, is not loaded with any user service.
In other cases, when the local NE detects that the VC connection is interrupted, the AIS
cells are inserted in the downstream direction and the RDI cells are returned to the upstream
NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
592
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: An upstream NE reports the VC_LOC, and the AIS cells are inserted to the
downstream.
Cause 2: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is
abnormal in the receive direction and therefore inserts AIS cells to the downstream.
Cause 3: The board on the local NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: An upstream NE reports the VC_LOC, and the AIS cells are inserted to the downstream.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the VC_LOC occurs and the ATM connections that report the
VC_LOC have the same ID.
2.
If the VC_LOC occurs, clear the VC_LOC and then the AIS insertion stops.
Step 2 Cause 2: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is abnormal
in the receive direction and therefore inserts AIS cells to the downstream.
1.
Check whether any alarm, such as the R_LOS, R_LOF, MS_AIS, AU_AIS, AU_LOP,
TU_AIS or TU_LOP occurs in the upstream SDH path.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms and then the AIS insertion stops.
Step 3 Cause 3: The board on the local NE is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the alarmed board.
2.
If the alarm persists, replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
Unidirectional Connection
A complete bidirectional connection consists of two unidirectional connections: a forward
connection and a backward connection. The direction of the forward and backward connections
is based on the same node.
End and Segment
The end point refers to the termination point in the chain network, and it is used to monitor the
whole virtual connection.
The segment point is, generally, used to monitor a segment of the whole link.
Segment End Point
This is one of the segment end attributes. The segment end attributes include: segment point,
end point, segment and end point, non segment and end point.
l
If an NE is set with the segment end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are
generated at the segment and end.
If an NE is set with the segment point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated
at a segment.
If an NE is set with the end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated at
an end.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
593
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
If an NE is set with the non segment end point attribute, it fails to retrieve the alarms that
are generated at the segment and end.
A.3.293 VC_LOC
Description
The VC_LOC is an alarm indicating loss of connectivity on the virtual channel (VC). This alarm
is reported when the CC is enabled but no cell is received within 3.5s (0.5s).
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the direction of ATM connection.
l 0x01: forward
l 0x02: backward
Parameter 2
Indicates the status of ATM connection.
l 0x01: working connection
l 0x00: protection connection
Parameter 3
Indicates the segment and end attribute of ATM connection.
l 0x01: segment
l 0x02: end
l 0x03: segment and end
Impact on the System
l
If the CC sink is enabled on the local NE but the local NE does not receive any CC cells,
the service connection, though not interrupted, is not loaded with any user service.
In other cases, the service is interrupted when the alarm occurs.
When this alarm occurs, the system automatically inserts AIS cells to the downstream.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
594
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The CC sink is enabled on the local NE, but no CC source is enabled on the
upstream NE.
Cause 2: No bandwidth is available on the local NE.
Cause 3: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is
abnormal in the receive direction.
Cause 4: The board on the local NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The CC sink is enabled on the local NE, but no CC source is enabled on the upstream
NE.
1.
Check whether the CC function on the local NE is activated.
2.
If yes, Deactivate the CC function on the local NE. Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: No bandwidth is available on the local NE.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the bandwidth allocated to the tunnel is fully used.
2.
If yes, increase the bandwidth or eliminate the sources that transmit a large amount of
invalid data.
Step 3 Cause 3: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is abnormal
in the receive direction.
1.
Check whether any alarm, such as the R_LOS, R_LOF, MS_AIS, AU_AIS, AU_LOP,
TU_AIS or TU_LOP, occurs in an upstream SDH path.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms and check whether the VC_LOC is cleared.
Step 4 Cause 4: The board on the local NE is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the alarmed board.
2.
If the alarm persists, replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.294 VC_RDI
Description
The VC_RDI is an alarm indicating that defects occur at the remote end of the virtual channel
(VC) connection. This alarm occurs when a forward or backward VC connection that is set with
the segment end point attribute receives the RDI cells, indicating that the downstream services
are abnormal.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
595
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the direction of ATM connection.
l 0x01: forward
l 0x02: backward
Parameter 2
Indicates the status of ATM connection.
l 0x01: working connection
l 0x00: protection connection
Parameter 3
Indicates the segment and end attribute of ATM connection.
l 0x01: segment
l 0x02: end
Impact on the System
l
When this alarm occurs, it indicates that a segment end point at the remote end of the VC
connection receives AIS cells and returns RDI cells to the local end, but the services at the
local end are not affected.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The VC_AIS occurs in the receive direction of the downstream VC connection.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The VC_AIS occurs in the receive direction of the downstream VC connection.
1.
Check whether the VC_AIS occurs in the receive direction of the downstream VC
connection.
2.
If yes, clear the VC_AIS and then check whether the VC_RDI is cleared.
Step 2 Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Perform a cold reset on the alarmed board.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
596
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
If the alarm persists, replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
Unidirectional Connection
A complete bidirectional connection consists of two unidirectional connections: a forward
connection and a backward connection. The direction of the forward and backward connections
is based on the same node.
End and Segment
The end point refers to the termination point in the chain network, and it is used to monitor the
whole virtual connection.
The segment point is, generally, used to monitor a segment of the whole link.
Segment End Point
This is one of the segment end attributes. The segment end attributes include: segment point,
end point, segment and end point, non segment and end point.
l
If an NE is set with the segment end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are
generated at the segment and end.
If an NE is set with the segment point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated
at a segment.
If an NE is set with the end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated at
an end.
If an NE is set with the non segment end point attribute, it fails to retrieve the alarms that
are generated at the segment and end.
A.3.295 VCAT_LOA
Description
The VCAT_LOA is an alarm indicating alignment loss of virtual concatenations. This alarm is
reported if a board detects that the time delays between the timeslots bound to a VCTRUNK
exceed the permissible limit.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Service alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
597
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
Indicate the ID of the VCTRUNK path.
Impact on the System
The virtually concatenated services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The timeslots bound to a VCTRUNK travel through different physical links, so the
delays between the virtually concatenated links are long.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The timeslots bound to a VCTRUNK travel through different physical links, so the
delays between the virtually concatenated links are long.
1.
Determine the ID of the alarmed VCTRUNK path based on the alarm parameters.
2.
Check whether the transmission routes of the paths bound to a VCTRUNK are the same.
If not, adjust their routes to the same.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.296 VCAT_LOM_VC12
Description
The VCAT_LOM_VC12 is an alarm indicating the loss of virtual concatenation multiframes in
the VC-12 path. This alarm is reported if the board detects that the K4 byte of the VC-12 path
does not match the expected multiframe sequence.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
598
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
The alarmed path is unavailable. If the LCAS function is disabled, the services in the path are
interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Bit errors occur on the line.
Cause 2: The MFI field in the K4 byte sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
Cause 3: The delays between virtual concatenations are over long.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Bit errors occur on the line.
1.
Check whether any bit error alarm such as BIP_EXC and BIP_SD occurs.
If...
Then...
A bit error alarm occurs
Handle the alarm immediately.
No bit error alarm occurs
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The MFI field in the K4 byte sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
1.
Replace the board at the opposite site. For details, see 6.6 Replacing the Ethernet
Interface Board.
2.
Replace the board and then check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The delays between virtual concatenations are over long.
1.
Check whether the VCAT_LOA alarm is reported in this path.
If...
Then...
The VCAT_LOA alarm is reported
Handle the VCAT_LOA alarm immediately.
The VCAT_LOA alarm is not reported Go to Cause 2.
2.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check whether the VCAT_LOM_VC12 alarm clears after handling the VCAT_LOA
alarm.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
599
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
If...
A Alarm Reference
Then...
The alarm persists Replace the alarmed board at the local site. For details, see Replace
the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.297 VCAT_LOM_VC3
Description
The VCAT_LOM_VC3 alarm indicates the loss of virtually concatenated multiframes in a VC-3
path. A board reports this alarm when detecting that byte H4 in the VC-3 path does not match
the expected multiframe sequence.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
The path that reports the alarm is unavailable. If the LCAS function is disabled, services are
interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Bit errors occur in the line.
Cause 2: The MFI field in byte K4 sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
Cause 3: The delays between virtual concatenations are too long.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
600
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Bit errors occur in the line.
1.
Check for the bit error alarms such as BIP_EXC or BIP_SD.
If...
Then...
The bit error alarms exist
Handle the alarms immediately.
The bit error alarms do not exist
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The MFI field in byte K4 sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
1.
Follow instructions in 6.6 Replacing the Ethernet Interface Board to replace the board
at the opposite site.
2.
Replace the alarmed board and then check whether the alarm clears.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists
Go to Cause 3.
Step 3 Cause 3: The delays between virtual concatenations are too long.
1.
Check whether a VCAT_LOA alarm is reported in this path.
If...
Then...
A VCAT_LOA alarm is reported in this Handle the VCAT_LOA alarm
path
immediately.
No VCAT_LOA alarm is reported in this Go to Cause 2.
path
2.
Check whether the VCAT_LOM_VC3 alarm clears after handling the VCAT_LOA alarm.
If...
Then...
The VCAT_LOM_VC3 alarm clears
End the alarm handling.
The VCAT_LOM_VC3 alarm persists Follow instructions in 6.6 Replacing the
Ethernet Interface Board to replace the
alarmed board at the local site.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.298 VCAT_SQM_VC12
Description
The VCAT_SQM_VC12 is an alarm indicating the SQ number mismatch of a virtual
concatenation in the VC-12 path. This alarm is reported if the board detects that the SQ of a
virtual concatenation does not match the expected value.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
601
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the optical interface. The value is always 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-12 path.
Impact on the System
The alarmed path is unavailable. If the LCAS function is disabled, services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Bit errors occur on certain links or certain links are faulty.
Cause 2: The SQ number sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Bit errors occur on certain links or certain links are faulty.
1.
2.
Check whether bit errors or line alarms occur. Focus on the bit error alarm BIP_EXC or
BIP_SD.
If...
Then...
Bit errors or line alarms occur
Clear these alarms.
No bit errors or line alarms occur
Go to the next step.
Replace the alarmed board.
Step 2 Cause 2: The SQ number sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
1.
Replace the corresponding board at the opposite site.
If...
Then...
The alarm clears after the board is
replaced
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Contact Huawei technical support engineers
for handling the alarm.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
602
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.299 VCAT_SQM_VC3
Description
The VCAT_SQM_VC3 alarm indicates that the sequence (SQ) number mismatch of a virtual
concatenation in a VC-3 path. A board reports this alarm when detecting that the SQ of a virtual
concatenation does not match the expected value.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Has a fixed value of 0x01.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3 Indicate the ID of the VC-3 path that reports the alarm. For example,
0x00 0x01 indicate that the alarm is reported in VC-3 path 1.
Impact on the System
The path that reports the alarm is unavailable. If the LCAS function is disabled, services are
interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Bit errors occur on a link or a link is faulty.
Cause 2: The SQ number sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Bit errors occur on a link or a link is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check for bit error alarms or line alarms, especially BIP_EXC and BIP_SD.
If...
Then...
Bit error alarms or line alarms occur
Clear these alarms.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
603
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
If...
Then...
No bit error alarms or line alarms occur
Go to Cause 2.
Replace the alarmed board.
Step 2 Cause 2: The SQ number sent from the opposite site is incorrect.
1.
Replace the related board at the opposite site.
If...
Then...
The VCAT_SQM_VC3 alarm clears after the End the alarm handling.
board is replaced
The VCAT_SQM_VC3 alarm persists after
the board is replaced
Contact Huawei technical support
engineers.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.300 VOLT_LOS
Description
The VOLT_LOS is an alarm indicating that the power voltage is unavailable.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
The value is always 0x01.
Impact on the System
The ODU that is connected to the IF board that reports this alarm fails to work.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
604
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The output power is abnormal.
Cause 2: The input power is abnormal.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The output power is abnormal.
1.
2.
Check the power switch of the ODU.
If...
Then...
The power switch is turned off
Turn on the power switch.
The power switch is turned on
Go to the next step.
Use the multimeter to check the IF fiber jumper, IF cable, or ODU section by section for
a short circuit.
If...
Then...
A short circuit exists
Replace the short-circuited component,
and then replace the alarmed IF board.
No short circuits exist
Replace the alarmed IF board.
CAUTION
If the alarm is reported due to a short circuit, replace the short-circuited cable or ODU, and
then replace the IF board. Otherwise, the new IF board may be damaged again.
Step 2 Cause 2: The input power is abnormal.
1.
Replace the alarmed IF board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.301 VP_AIS
Description
The VP_AIS is an alarm indication of the virtual path (VP) connection. When a forward or
backward VP connection that is set with the segment end point attribute receives the AIS cells,
the alarm is reported, indicating that the upstream services are abnormal.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
605
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the direction of ATM connection.
l 0x01: forward
l 0x02: backward
Parameter 2
Indicates the status of ATM connection.
l 0x01: working connection
l 0x00: protection connection
Parameter 3
Indicates the segment and end attribute of ATM connection.
l 0x01: segment
l 0x02: end
Impact on the System
l
If the continuity check (CC) sink is enabled on an upstream NE but the upstream NE does
not receive any CC cells, the local NE reports the alarm. In this case, the connection, though
not interrupted, is not loaded with any user service.
In other cases, when the local NE detects that the VP connection is interrupted, the AIS
cells are inserted to the downstream and the RDI cells are returned to the upstream NE.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: An upstream NE reports the VP_LOC, and the AIS cells are inserted to the
downstream.
Cause 2: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is
abnormal in the receive direction and inserts AIS cells to the downstream.
Cause 3: The board on the local NE is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: An upstream NE reports the VP_LOC, and the AIS cells are inserted to the downstream.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
606
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
1.
On the NMS, check whether the VP_LOC occurs and the ATM connections that report the
VP_LOC have the same ID.
2.
If the VP_LOC occurs, clear the VP_LOC and then the AIS insertion stops.
Step 2 Cause 2: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is abnormal
in the receive direction and therefore inserts AIS cells to the downstream.
1.
Check whether any alarm, such as the R_LOS, R_LOF, MS_AIS, TU_AIS, TU_LOP,
AU_AIS or AU_LOP, occurs in an upstream SDH path.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms and then the AIS insertion stops.
Step 3 Cause 3: The board on the local NE is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the alarmed board.
2.
If the alarm persists, replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
Unidirectional Connection
A complete bidirectional connection consists of two unidirectional connections: a forward
connection and a backward connection. The direction of the forward and backward connections
is based on the same node.
End and Segment
The end point refers to the termination point in the chain network, and it is used to monitor the
whole virtual connection.
The segment point is, generally, used to monitor a segment of the whole link.
Segment End Point
This is one of the segment end attributes. The segment end attributes include: segment point,
end point, segment and end point, non segment and end point.
l
If an NE is set with the segment end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are
generated at the segment and end.
If an NE is set with the segment point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated
at a segment.
If an NE is set with the end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated at
an end.
If an NE is set with the non segment end point attribute, it fails to retrieve the alarms that
are generated at the segment and end.
A.3.302 VP_LOC
Description
The VP_LOC is an alarm indicating loss of connectivity on the virtual path (VP). This alarm is
reported when the CC is enabled but no cell is received within 3.5s (0.5s). When any cell is
received, the alarm is cleared automatically.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
607
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the direction of ATM connection.
l 0x01: forward
l 0x02: backward
Parameter 2
Indicates the status of ATM connection.
l 0x01: working connection
l 0x00: protection connection
Parameter 3
Indicates the segment and end attribute of ATM connection.
l 0x01: segment
l 0x02: end
l 0x03: segment and end
Impact on the System
l
If the CC sink is enabled on the local NE but the local NE does not receive any CC cells,
the service connection, though not interrupted, is not loaded with any user service.
In other cases, the service is interrupted when the alarm occurs.
When this alarm occurs, the system automatically inserts AIS cells to the downstream.
The VP_LOC is suppressed when the VP_AIS occurs.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The CC sink is enabled on the local NE, but no CC source is enabled on the
upstream NE.
Cause 2: No bandwidth is available on the local NE.
Cause 3: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is
abnormal in the receive direction.
Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
608
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The CC sink is enabled on the local NE, but no CC source is enabled on the upstream
NE.
1.
Deactivate the CC function on the local NE.
Step 2 Cause 2: No bandwidth is available on the local NE.
1.
On the NMS, check whether the bandwidth allocated to the tunnel is fully used.
2.
If yes, increase the bandwidth or eliminate the sources that transmit a large amount of
invalid data.
Step 3 Cause 3: On the local NE, the ATM port connected to a faulty upstream SDH path is abnormal
in the receive direction.
1.
Check whether any alarm, such as the R_LOS, R_LOF, MS_AIS, TU_AIS, TU_LOP,
AU_AIS or AU_LOP, occurs in an upstream SDH path.
2.
If yes, clear these alarms.
Step 4 Cause 4: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the alarmed board.
2.
Check whether the alarm is cleared. If not, replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.303 VP_RDI
Description
The VP_RDI is an alarm indicating that defects occur at the remote end of the virtual path (VP)
connection. This alarm occurs when a forward or backward VP connection that is set with the
segment end point attribute receives the RDI cells, indicating that the downstream services are
abnormal.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Communication alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
609
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the direction of ATM connection.
A Alarm Reference
l 0x01: forward
l 0x02: backward
Parameter 2
Indicates the status of ATM connection.
l 0x01: working connection
l 0x00: protection connection
Parameter 3
Indicates the segment and end attribute of ATM connection.
l 0x01: segment
l 0x02: end
Impact on the System
l
When this alarm occurs, the services are not affected. This alarm just indicates that the
services in the receive direction of the downstream VP connection are abnormal. The AIS
cells are received in a segment point of the connection, and the RDI cells are returned to
the upstream VP connection.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: The VP_AIS occurs in the receive direction of the downstream VP connection.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
Cause 1: The VP_AIS occurs in the receive direction of the downstream VP connection.
Procedure
1.
Check whether the VP_AIS occurs in the receive direction of the downstream VP
connection.
2.
If yes, clear the VP_AIS and then check whether the VP_RDI is cleared.
Cause 2: A certain board is faulty.
1.
Perform a cold reset on the alarmed board. For details, see 8.6.1 Cold Reset.
2.
If the alarm persists, replace the alarmed board. For details, see 6.5 Replacing the
Smart E1 Board.
----End
Related Information
Unidirectional Connection
A complete bidirectional connection consists of two unidirectional connections: a forward
connection and a backward connection. The direction of the forward and backward connections
is based on the same node.
End and Segment
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
610
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
The end point refers to the termination point in the chain network, and it is used to monitor the
whole virtual connection.
The segment point is, generally, used to monitor a segment of the whole link.
Segment End Point
This is one of the segment end attributes. The segment end attributes include: segment point,
end point, segment and end point, non segment and end point.
l
If an NE is set with the segment end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are
generated at the segment and end.
If an NE is set with the segment point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated
at a segment.
If an NE is set with the end point attribute, it can retrieve the alarms that are generated at
an end.
If an NE is set with the non segment end point attribute, it fails to retrieve the alarms that
are generated at the segment and end.
A.3.304 W_R_FAIL
Description
The W_R_FAIL is an alarm indicating a failure of reading or writing chip register.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
When you view an alarm on the network management system, select the alarm. In the Alarm
Details field display the related parameters of the alarm. The alarm parameters are in the
following format: Alarm Parameters (hex): parameter1 parameter2...parameterN, for example,
Alarm Parameters (hex): 0x01 0x08. For details about each parameter, refer to the following
table.
Name
Meaning
Parameter 1
Indicates the ID of the register.
Parameter 2, Parameter 3
The values are always 0x00 0x01.
Impact on the System
Services in the alarmed path are interrupted.
Possible Causes
Cause 1: The chip register is faulty or the read/write timing is incorrect.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
611
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: The chip register is faulty or the read/write timing is incorrect.
1.
Replace the alarmed board.
----End
Related Information
None.
A.3.305 WRG_BD_TYPE
Description
The WRG_BD_TYPE is an alarm indicating that the type of the board is incorrect.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Major
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
The board fails to work.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
Cause 2: The board of an incorrect type is installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
1.
See Configuring the Logical Board to check whether the board type complies with the
planning requirement.
If...
Then...
The board type does not meet the planning
requirement
Change the configuration data.
The board type meets the planning requirement
Go to Cause 2.
Step 2 Cause 2: The board of an incorrect type is installed.
1.
Replace the board of an incorrect type.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
612
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
A Alarm Reference
Related Information
None.
A.3.306 XPIC_LOS
Description
The XPIC_LOS is an alarm indicating that the XPIC compensation signals are lost.
Attribute
Alarm Severity
Alarm Type
Critical
Equipment alarm
Parameters
None.
Impact on the System
Bit errors may occur in the service at the port, and the service may even be interrupted.
Possible Causes
l
Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
Cause 2: The radio link is faulty.
Cause 3: The XPIC cable is faulty.
Cause 4: The IF board or ODU is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Cause 1: Configuration data is incorrect.
1.
Check whether the XPIC function needs to be enabled. If not, see Setting IF Attributes to
disable the XPIC function, and then perform a self-loop at the XPIC port on the board by
using the XPIC cable.
Step 2 Cause 2: The radio link is faulty.
1.
Check whether the paired board that is connected to the XPIC IF board through the XPIC
cable reports the MW_LOF alarm. If yes, first clear the MW_LOF alarm.
Step 3 Cause 3: The XPIC cable is faulty.
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Check the connection of the XPIC cable.
If...
Then...
The cable is improperly connected
Connect the XPIC cable properly.
The cable is properly connected
Go to the next step.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
613
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
A Alarm Reference
Test the make and break of the XPIC cable by using the multimeter. If the XPIC cable is
damaged, replace it.
Step 4 Cause 4: The IF board or ODU is faulty.
Locate the fault by replacing the IF board or ODU.
1.
Replace the paired board of the XPIC IF board.
The paired board of the XPIC IF board refers to the other XPIC IF board connected to the
alarmed XPIC IF board through the XPIC cable.
2.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the board is
replaced
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists after the board is
replaced
Go to the next step.
Replace the ODU that is connected to the paired XPIC IF board.
If...
Then...
The alarm is cleared after the ODU is
replaced
End the alarm handling.
The alarm persists after the ODU is
replaced
Replace the alarmed XPIC IF board.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
614
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Abnormal Event Reference
Abnormal events are important indicators when abnormalities occur on the equipment. This
chapter describes all the possible important abnormal events on the OptiX RTN 950 and how to
handle these events.
B.1 Major Abnormal Performance Event List
Abnormal events are important indicators when abnormalities occur on the equipment. This
chapter describes all the possible important abnormal events on the OptiX RTN 950 and how to
handle these events.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
615
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
B.1 Major Abnormal Performance Event List
Abnormal events are important indicators when abnormalities occur on the equipment. This
chapter describes all the possible important abnormal events on the OptiX RTN 950 and how to
handle these events.
Table B-1 Major performance event list
Event Name
Source
B.2.1 IF 1+1 Protection Switching
CST and CSH
B.2.2 N+1 Protection Switching
B.2.3 SNCP Switching
B.2.4 Linear MSP Switching
B.2.5 Status Change of an APS Protection
Group
B.2.6 Reporting of PW APS Switching
Events
B.2.7 System Control Board Switching
CST and CSH
B.2.8 RMON Performance Value Below
the Lower Limit
EM6FA, EM6TA, EFP8, EMS6, EM6F and
EM6T
B.2.9 RMON Performance Value Above
the Upper Limit
B.2 Abnormal Performance Events and Handling
Procedures
This chapter describes all the important abnormal performance events on the OptiX RTN 950
in an alphabetical order and how to handle these abnormal performance events.
B.2.1 IF 1+1 Protection Switching
Description
This abnormal event indicates that the 1+1 HSB/FD/SD switching occurs on the equipment.
Attribute
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Severity
Type
Major
Service
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
616
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Parameters
Name
Meaning
Protection Group ID
Indicates the ID of the protection group where
the IF 1+1 protection switching occurs.
Current Working Board Slot
Indicates the slot ID of the current working
board.
Current Working Board Sub Slot
Indicates the sub slot ID of the current
working board.
The value is always 0xff.
Current Working Port No.
Indicates the ID of the working port.
Current Active Board
Indicates the current working board.
l Active on working board
l Active on protection board
Active Board Status
Indicates the current state of the working
board.
l Normal
l Failed
l MW_RDI
l Unknown
Standby Board Status
Indicates the current status of the protection
board.
l Normal
l Failed
l MW_RDI
l Unknown
Switching Request
Indicates the type of an IF 1+1 protection
switching request.
l No request
l Automatic switching
l Manual switching
l Forced switching
l Lockout of switching
l Wait-to-restore
l RDI switching
NOTE
The parameter names and parameter values may vary with the version of the NMS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
617
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Impact on System
l
During the HSB protection switching, services are interrupted. After the HSB switching is
complete, the services are restored to normal.
During the HSM protection switching, no bit errors occur and the services are not affected.
Related Alarms
When the IF 1+1 protection switching occurs, the RPS_INDI alarm is reported.
Possible Causes
l
The possible causes of the HSB protection switching are as follows:
The hardware of the ODU or IF unit at the local end is faulty.
The working channel of the local end receives the MW_RDI alarm.
The external switching, which is triggered by the switching command issued from the
NMS software, occurs. The external switching includes lockout of switching, forced
switching, and manual switching.
The possible causes of the HSM protection switching are as follows:
The quality of the main channel degrades.
In the case of Hybrid radio, the quality of the main channel degrades.
In the case of SDH/PDH radio, an alarm that triggers the HSM switching is reported on
the radio link. These alarms include R_LOC, R_LOF, R_LOS, MW_LOF,
MW_FEC_UNCOR, B1_SD(IF1).
Procedure
Step 1 Rectify the fault according to the switching request type indicated by the parameter and the
description in RPS_INDI.
----End
B.2.2 N+1 Protection Switching
Description
This abnormal event indicates that the N+1 protection switching occurs on the equipment.
Attribute
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Severity
Type
Major
Service
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
618
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Parameters
Name
Meaning
Protection Group ID
Indicates the ID of the protection group where
the IF N+1 protection switching occurs.
Path Name ID
Indicates the ID of the path where the IF N+1
protection switching occurs.
Switching Request
Indicates the type of an IF N+1 protection
switching request.
l Lockout of protection channel
l Forced switching
l SF switching
l SD switching
l Manual switching
l Wait-to-restore
l Exercise
l Reverse request
l No request
Switching Status
Indicates the state of an N+1 protection
group.
l Protocol unstarted
l Idle status
l Switching status
l Protocol starting
Indicates the ID of the protected channel.
Protected Unit
The ID is 0xff if no switching is performed.
Switching Local/Remote End Indication
Indicates the local or remote switching.
l Local end
l Remote end
The switching status reason is changed
Indicates the cause of the IF N+1 protection
switching.
l Local request
l External command
l K-byte request
l Timer expiry
NOTE
The parameter names and parameter values may vary with the version of the NMS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
619
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Impact on System
During the N+1 protection switching (not more than 50 ms), the services are interrupted. After
the N+1 switching is complete, the services are restored to normal. After the switching starts
and before the switching is complete, the extra services are interrupted.
NOTE
If the IF N+1 protection switching is caused by exercise switching, service signals are not switched actually
because the exercise switching is used to check whether the NE can run the N+1 protocol normally.
Related Alarms
When the IF N+1 protection switching occurs, the NP1_SW_INDI alarm is reported.
Possible Causes
l
The external switching occurs.
Lockout of protection channel
Forced switching
Manual switching
An automatic switching occurs.
The hardware of the IDU or IF board is faulty. Focus on checking whether the
HARD_BAD or BD_STATUS alarm is reported.
The MW_LOF, R_LOC, R_LOF, R_LOS, MS_AIS, or B2_EXC alarm is reported
on the working path.
Procedure
Step 1 Rectify the fault according to the switching request type and the switching cause indicated by
the parameters.
If...
Then...
The switching is caused by the external
switching
Find the cause of the external switching, and
then release the external switching
immediately.
The switching is caused by the automatic Clear the alarm that triggers the automatic
switching
switching.
----End
B.2.3 SNCP Switching
Description
This abnormal event indicates that the SDH SNCP switching occurs in the service that is
configured with the SNCP.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
620
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Attribute
Severity
Type
Major
Service
Name
Meaning
Source
Indicates the service source of the SNCP
protection group.
Sink
Indicates the service sink of the SNCP
protection group.
Status
Indicates the current working path.
Parameters
l Working at protection channel
l Working at working channel
Switching Status
Indicates the switching status.
l Manual to standby
l Force to active
l Force to standby
l Lockout switching
l SF switching
l SD switching
l Wait-to-restore
l Idle
Working Channel Current Status
Indicates the current status of the SNCP
working path.
l Normal
l SD
l SF
Protection Channel Current Status
Indicates the current status of the SNCP
protection path.
l Normal
l SD
l SF
NOTE
The parameter names and parameter values may vary with the version of the NMS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
621
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Impact on System
When the SNCP switching occurs, you must find the cause. If the related link is faulty, recover
the link immediately. Ensure that the states of the SNCP working path and the SNCP protection
path are normal.
Possible Causes
l
The SDH SNCP switching is automatically triggered.
The hardware of the line board is faulty.
The R_LOS, R_LOF, R_LOC, MS_AIS, B2_EXC, AU_LOP, AU_AIS,
HP_LOM, MW_LOF (only when the IF board functions as the line board),
MW_LIM (only when the IF board functions as the line board), B3_EXC, B3_SD,
HP_TIM (in the case of VC-4 services), HP_UNEQ (in the case of VC-4 services),
TU_AIS (in the case of VC-12 services) or TU_LOP (in the case of VC-12 services),
LP_UNEQ (Optional condition), LP_TIM (Optional condition), BIP_SD (Optional
condition), BIP_EXC (Optional condition), or MW_BER_EXC.
The SDH SNCP switching is manually triggered.
Forced switching
Manual switching
Procedure
Step 1 On the NMS, query the type of the SDH SNCP switching request.
Step 2 Rectify the fault according to the switching request type.
If...
Then...
The SDH SNCP switching is automatically
triggered
Rectify the fault according to the related
alarm, and eliminate the conditions of the
automatic switching.
The SDH SNCP switching is manually
triggered
Find the cause of the manual switching, and
then release the manual switching
immediately.
----End
B.2.4 Linear MSP Switching
Abnormal Event Description
This abnormal event indicates that a linear MSP switching occurs in the service that is configured
with the MSP.
Abnormal Event Attributes
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Level
Type
Major
Service
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
622
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Abnormal Event Parameters
Parameter Name
Definition
Indicates the ID of the protection group.
Indicates the ID of the protection group where
a linear MSP switching occurs.
Current working path
Indicates the current working path of the
linear MSP group.
l Working unit
l Protection unit
Switching request type
Indicates the type of a linear MSP switching
request.
l Locked switching
l Forced switching
l SF switching
l SD switching
l Manual switching
l Wait-to-restore
l Exercise
l Reverse request
l Non-revertive request
l No request
Switching status
Indicates the switching status.
l Protocol not started
l Idle
l Switching
l Protocol being started
Remote/local end indication
Indicates the remote or local end.
l No remote/local end
l Local end
l Remote end
Cause of switching status change
Indicates the cause of switching status
change.
l Local request
l External command
l K-byte request
l Timer expiry
NOTE
The parameter names and parameter values may vary with the version of the NMS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
623
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Impact on System
l
During the switching time (not more than 50 ms), the services are interrupted. After the
switching is complete, the services are restored to normal. After the switching starts and
before the switching is complete, the extra services are interrupted.
Troubleshooting measures need to be taken immediately when an MSP switching occurs
because the possible causes are fiber cuts and failures of terminal nodes.
Relevant Alarms
When a linear MSP switching occurs, the APS_INDI alarm may be reported.
Possible Causes
l
An external switching command is issued to trigger manual, forced, or exercise switching.
An automatic switching occurs.
After the R_LOS, R_LOF, MS_AIS, B2_EXC, B2_SD, B3_EXC, B3_SD, HP_TIM (in
the case of VC-4 services), HP_UNEQ (in the case of VC-4 services), TU_AIS (in the
case of VC-12 services), or TU_LOP (in the case of VC-12 services) alarm is reported,
the MSP protection group changes to the switching status, and an automatic switching alarm
is reported.
The hardware or line is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 On the NMS, query the switching type and the protection group ID.
Step 2 Rectify the fault according to the switching request type.
If...
Then...
The switching is caused by external
switching
Find out the cause and clear the switching
immediately.
The switching is an automatic switching
Clear the relevant alarm, and rectify the
hardware or line fault first.
----End
B.2.5 Status Change of an APS Protection Group
Description
This abnormal event indicates that an APS protection group switches.
Attribute
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Severity
Type
Major
Service
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
624
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Parameters
Name
Meaning
Protection Group ID
ID of the protection group whose APS status
is changed
APS Protection Group Switching Status
Current working status of the APS protection
group
l Working path
l Protection path
APS Protection Group Protocol Status
APS protection group protocol status
Working Path Status of the APS Protection
Group
Working path status of the APS protection
group:
l Valid
l Invalid
Protection Path Status of the APS Protection
Group
Protection path status of the APS protection
group:
l Valid
l Invalid
NOTE
The parameter names and parameter values may vary according to the version of the NMS.
Impact on the System
During the switching, the services are interrupted. After the switching is complete, the services
are restored. After the switching starts and before the switching is complete, the extra services
are interrupted.
Related Alarms
None.
Possible Causes
l
An external switching command (for example, manual switching) is issued.
An automatic switching occurs.
When an MPLS link is faulty, the MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV, MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI,
MPLS_TUNNEL_SD, MPLS_TUNNEL_SF, MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMATCH,
MPLS_TUNNEL_MISMERGE, MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess, or
MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN alarm occurs on the working path.
Procedure
Step 1 On the NMS, query the switching type and the protection group ID.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
625
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Step 2 Rectify the fault according to the switching request type and the switching cause indicated by
the parameters.
If...
Then...
The switching is an external switching
Find the cause of the external switching, and then
clear manual switching immediately.
The switching is an automatic switching Handle the relevant alarms first.
----End
B.2.6 Reporting of PW APS Switching Events
Description
This abnormal event indicates that a PW APS protection group switches.
Attribute
Severity
Type
Major
Service
Name
Meaning
Protection Group ID
ID of the protection group whose APS status
is changed
APS Protection Group Switching Status
Current working status of the APS protection
group
Parameters
l Working path
l Protection path
APS Protection Group Protocol Status
APS protection group protocol status
Working Path Status of the APS Protection
Group
Working path status of the APS protection
group:
l Valid
l Invalid
Protection Path Status of the APS Protection
Group
Protection path status of the APS protection
group:
l Valid
l Invalid
NOTE
The parameter names and parameter values may vary according to the version of the NMS.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
626
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Impact on the System
During the switching, the services are interrupted. After the switching is complete, the services
are restored. After the switching starts and before the switching is complete, the extra services
are interrupted.
Related Alarms
None.
Possible Causes
l
An external switching command (for example, manual switching) is issued.
An automatic switching occurs.
When an MPLS link is faulty, the MPLS_PW_LOCV, MPLS_PW_MISMATCH,
MPLS_PW_SD, MPLS_PW_SF, MPLS_PW_MISMERGE, MPLS_PW_Excess, or
MPLS_PW_UNKNOWN alarm occurs on the working path.
Procedure
Step 1 On the NMS, query the switching type and the protection group ID.
Step 2 Rectify the fault according to the switching request type and the switching cause indicated by
the parameters.
If...
Then...
The switching is an external switching
Find the cause of the external switching, and then
clear manual switching immediately.
The switching is an automatic switching Handle the relevant alarms first.
----End
B.2.7 System Control Board Switching
Description
This abnormal event indicates that the system control boards are switched when the working
system control board on the equipment that is configured with the 1+1 protection becomes faulty.
Attribute
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Severity
Type
Major
Equipment
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
627
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
Parameters
Name
Meaning
Group ID
Indicates the group ID.
Protection Type
Cross-connect board protection.
Working Unit
Indicates the slot ID of the current working
board.
Protection Unit
Indicates the slot ID of the current protection
board.
Current Working Unit
Indicates the current status of the board.
l Work at protection unit
l Work at working unit
Switching Type
Indicates the switching type.
Manual Switching
NOTE
The parameter names and parameter values may vary with the version of the NMS.
Impact on System
If the system control boards are switched because the original working system control board is
faulty, rectify the fault on the original working system control board immediately. Otherwise,
the services are interrupted if the current working system control board becomes faulty.
Possible Causes
l
The switching is manually triggered.
The switching is automatically triggered.
Generally, the switching is automatically triggered when the hardware of the board becomes
faulty. Hence, focus on the following alarms reported on the original working system
control board: HARD_BAD.
Procedure
Step 1 On the NMS, check whether the manual switching operation is performed.
If...
Then...
The manual switching operation is
performed on the NMS
Find the cause of the manual switching, and
then release the manual switching immediately.
No manual switching operations are
performed on the NMS
Go to the next step.
Step 2 On the NMS, check whether any alarms indicating the board hardware fault are reported. If yes,
clear the alarms and rectify the fault.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
628
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
B.2.8 RMON Performance Value Below the Lower Limit
Description
This abnormal event indicates that the current RMON performance value is lower than the preset
lower limit.
Attribute
Severity
Type
Minor
Communication
Name
Meaning
Performance ID
Indicates the ID of the current RMON
performance event.
Current Performance Value
Indicates the value of the current RMON
performance event.
Lower Limit
Indicates the lower limit of the current
RMON performance event.
Parameters
Impact on System
Different abnormal performance events have different impacts on the system. For details, see
D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures.
Related Alarms
Different alarms are reported when different RMON performance values are lower than the
lower limits. For details, see D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures.
Possible Causes
The lower limit of a performance event is set to a non-zero value.
Procedure
Step 1 Set the lower limit of the performance event to 0.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
629
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
B Abnormal Event Reference
B.2.9 RMON Performance Value Above the Upper Limit
Description
This abnormal event indicates that the current RMON performance value is higher than the preset
upper limit.
Attribute
Severity
Type
Minor
Communication
Name
Meaning
Performance ID
Indicates the ID of the current RMON
performance event.
Current Performance Value
Indicates the value of the current RMON
performance event.
Upper Limit
Indicates the upper limit of the current
RMON performance event.
Parameters
Impact on System
Different abnormal performance events have different impacts on the system. For details, see
D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures.
Related Alarms
Different alarms are reported when different RMON performance values are higher than the
upper limits. For details, see D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures.
Possible Causes
When the performance values of different abnormal RMON performance events are higher than
the upper limits, the causes are different. For details, see D.4 RMON Events and Handling
Procedures.
Procedure
Step 1 See D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures to handle different abnormal performance
events.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
630
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Performance Event Reference
Performance events are important indicators when the equipment performance changes. This
chapter describes all the possible performance events on the OptiX RTN 950 and how to handle
these performance events.
C.1 Performance Events (by Event Type)
The list is categorized based on the performance event type, and includes all the events of the
OptiX RTN 950.
C.2 Performance Events (by Logical Board)
This part lists all the performance events that are reported by each board.
C.3 Performance Events and Handling Procedures
Based on the type of a performance event, this chapter describes all the performance events on
the OptiX RTN 950 and how to handle these performance events.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
631
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.1 Performance Events (by Event Type)
The list is categorized based on the performance event type, and includes all the events of the
OptiX RTN 950.
C.1.1 SDH/PDH Performance Event List
SDH/PDH performance events are classified into six categories: pointer justification,
regenerator section error, multiplex section error, higher order path error, lower order path error,
and E1 line side code violation.
Table C-1 Pointer Justification Performance Events
Event Name
Description
AUPJCHIGH
Indicates the count of positive AU pointer
justifications.
AUPJCLOW
Indicates the count of negative AU pointer
justifications.
AUPJCNEW
Indicates the count of new AU pointer
justifications.
TUPJCHIGH
Indicates the count of positive TU pointer
justifications.
TUPJCLOW
Indicates the count of negative TU pointer
justifications.
TUPJCNEW
Indicates the count of new TU pointer
justifications.
Table C-2 Regenerator Section Error Performance Events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
RSBBE
Indicates the regenerator section background
block error.
RSES
Indicates the regenerator section errored
second.
RSSES
Indicates the regenerator section severely
errored second.
RSUAS
Indicates the regenerator section unavailable
second.
RSCSES
Indicates the regenerator section consecutive
severely errored second.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
632
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
RSOFS
Indicates the regenerator section out-offrame second.
RSOOF
Indicates the count of regenerator section outof-frame events.
NOTE
In the case of PDH radio, regenerator section bit error performance events also exist and they are detected
according to the overheads used for detecting frame alignment and bit errors in the PDH microwave frames.
Table C-3 Multiplex Section Error Performance Events
Event Name
Description
MSBBE
Indicates the multiplex section background
block error.
MSES
Indicates the multiplex section errored
second.
MSSES
Indicates the multiplex section severely
errored second.
MSCSES
Indicates the multiplex section consecutive
severely errored second.
MSUAS
Indicates the multiplex section unavailable
second.
MSFEBBE
Indicates the multiplex section far end
background block error.
MSFEES
Indicates the multiplex section far end errored
second.
MSFESES
Indicates the multiplex section far end
severely errored second.
MSFECSES
Indicates the multiplex section far end
consecutive severely errored second.
MSFEUAS
Indicates the multiplex section far end
unavailable second.
Table C-4 Higher Order Path Error Performance Events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
HPBBE
Indicates the higher order path background
block error.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
633
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
HPES
Indicates the higher order path errored
second.
HPSES
Indicates the higher order path severely
errored second.
HPCSES
Indicates the higher order path consecutive
severely errored second.
HPUAS
Indicates the higher order path unavailable
second.
HPFEBBE
Indicates the higher order path far end
background block error.
HPFEES
Indicates the higher order path far end errored
second.
HPFESES
Indicates the higher order path far end
severely errored second.
HPFECSES
Indicates the higher order path far end
consecutive severely errored second.
HPFEUAS
Indicates the higher order path far end
unavailable second.
Table C-5 Lower Order Path Error Performance Events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
LPBBE
Indicates the lower order path background
block error.
LPES
Indicates the lower order path errored second.
LPSES
Indicates the lower order path severely
errored second.
LPCSES
Indicates the lower order path consecutive
severely errored second.
LPUAS
Indicates the lower order path unavailable
second.
LPFEBBE
Indicates the lower order path far end
background block error.
LPFEES
Indicates the lower order path far end errored
second.
LPFESES
Indicates the lower order path far end
severely errored second.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
634
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
LPFECSES
Indicates the lower order path far end
consecutive severely errored second.
LPFEUAS
Indicates the lower order far end unavailable
second.
Table C-6 E1 Line Side Code Violation Performance Events
Event Name
Description
E1_LCV_SDH
Indicates the count of E1 line side code
violations.
E1_LLOSS_SDH
Indicates the E1 line side loss-of-signal
second.
E1_LES_SDH
Indicates the E1 line side code violation
errored second.
E1_LSES_SDH
Indicates the E1 line side code violation
severely errored second.
Table C-7 E1 Error Performance Events
Event Name
Description
E1_BBE
Indicates the E1 background block error.
E1_ES
Indicates the E1 errored second.
E1_SES
Indicates the E1 severely errored second.
E1_CSES
Indicates the E1 consecutive severely errored
second.
E1_UAS
Indicates the E1 unavailable second.
C.1.2 Radio Performance Events
The radio performance events are performance events of the radio link bit errors, ATPC, AM,
and power.
Table C-8 Radio power performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
TSL_MAX
Maximum value of radio transmit signal level
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
635
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
TSL_MIN
Minimum value of radio transmit signal level
TSL_CUR
Current value of radio transmit signal level
TSL_AVG
Average value of radio transmit signal level
RSL_MAX
Maximum value of radio receive signal level
RSL_MIN
Minimum value of radio receive signal level
RSL_CUR
Current value of radio receive signal level
RSL_AVG
Average value of radio receive signal level
TLHTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a transit power higher than the upper
threshold
TLLTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a transit power higher than the lower
threshold
RLHTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a receive power lower than the upper
threshold
RLLTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a receive power lower than the lower
threshold
Table C-9 FEC performance events
Event Name
Description
FEC_BEF_COR_ER
FEC bit error rate before correction
FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT
FEC uncorrected block count
FEC_COR_BYTE_CNT
The number of bytes that are corrected
through the FEC
Table C-10 Radio link error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
IF_BBE
Radio link background block errors
IF_ES
Radio link errored seconds
IF_SES
Radio link severely errored seconds
IF_UAS
Radio link unavailable second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
636
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
IF_CSES
Radio link consecutive severely errored
seconds
Table C-11 ATPC performance events
Event Name
Description
ATPC_P_ADJUST
Positive ATPC adjustment
ATPC_N_ADJUST
Negative ATPC adjustment
Table C-12 AM performance events
Event Name
Description
QPSKWS
Working time of the QPSK mode
QAMWS16
Working time of the 16QAM mode
QAMWS32
Working time of the 32QAM mode
QAMWS64
Working time of the 64QAM mode
QAMWS128
Working time of the 128QAM mode
QAMWS256
Working time of the 256QAM mode
FB_AMDCNT
Count of the downshift of the AM scheme
FB_AMUCNT
Count of the upshift of the AM scheme
Table C-13 XPIC performance events
Event Name
Description
XPIC_XPD_VALUE
XPIC XPD value
Table C-14 IF 1+1 protection group error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
PG_IF_BBE
IF 1+1 protection group background block
errors
PG_IF_ES
IF 1+1 protection group errored seconds
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
637
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
PG_IF_SES
IF 1+1 protection group severely errored
seconds
PG_IF_UAS
IF 1+1 protection group unavailable second
PG_IF_CSES
IF 1+1 protection group consecutive severely
errored seconds
Table C-15 IF port error performance events
Event Name
Description
IF_SNR_MAX
Maximum signal to noise ratio
IF_SNR_MIN
Minimum signal to noise ratio
IF_SNR_AVG
Average signal to noise ratio
C.1.3 Other Performance Events
In addition to the SDH and radio performance events, the OptiX RTN 950 supports performance
events of the optical power and the temperature.
Table C-16 Optical power performance events
Event Name
Description
TPLMAX
Maximum value of transmit optical power
TPLMIN
Minimum value of transmit optical power
TPLCUR
Current value of transmit optical power
RPLMAX
Maximum value of receive optical power
RPLMIN
Minimum value of receive optical power
RPLCUR
Current value of receive optical power
Table C-17 Board temperature performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
638
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Table C-18 Laser temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
OSPITMPMAX
Maximum temperature of a laser core
OSPITMPMIN
Minimum temperature of a laser core
OSPITMPCUR
Current temperature of a laser core
C.2 Performance Events (by Logical Board)
This part lists all the performance events that are reported by each board.
NOTE
The NE software consider a physical board as one or more logical boards when managing the physical board.
The NMS also considers a physical board as one or more logical boards when managing the physical board.
For OptiX RTN 950, all physical boards correspond to logical boards of the same names.
C.2.1 CST/CSH
The CST/CSH board reports only the board temperature performance events and IF 1+1
protection group error performance events.
Table C-19 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
Table C-20 IF 1+1 protection group error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
PG_IF_BBE
IF 1+1 protection group background block
errors
PG_IF_ES
IF 1+1 protection group errored seconds
PG_IF_SES
IF 1+1 protection group severely errored
seconds
PG_IF_UAS
IF 1+1 protection group unavailable second
PG_IF_CSES
IF 1+1 protection group consecutive severely
errored seconds
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
639
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.2.2 IF1
The IF1 board reports three types of performance events: SDH/PDH performance events,
microwave performance events, and temperature performance events.
SDH/PDH Performance Events
Table C-21 Pointer justification performance events
Event Name
Description
AUPJCHIGH
Count of positive AU pointer justification
AUPJCLOW
Count of negative AU pointer justification
AUPJCNEW
Count of new AU pointer justifications
Table C-22 Regenerator section error performance events
Event Name
Description
RSBBE
Regenerator section block of background
error
RSES
Regenerator section errored second
RSSES
Regenerator section severely errored second
RSUAS
Regenerator section unavailable second
RSCSES
Regenerator section consecutive severely
errored second
RSOFS
Regenerator section out-of-frame second
RSOOF
Regenerator section out of frame
NOTE
The regenerator section error performance events also occur in the case of the PDH radio. The PDH radio
frame is detected through the overheads that are used for frame location and bit error detection.
Table C-23 Multiplex section error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
MSBBE
Multiplex section block of background error
MSES
Multiplex section errored second
MSSES
Multiplex section severely errored second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
640
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
MSCSES
Multiplex section consecutive severely
errored second
MSUAS
Multiplex section unavailable second
MSFEBBE
Multiplex section far end block of
background error
MSFEES
Multiplex section far end errored second
MSFESES
Multiplex section far end severely errored
second
MSFECSES
Multiplex section far end consecutive
severely errored second
MSFEUAS
Multiplex section far end unavailable second
Table C-24 Higher order path error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
HPBBE
Higher order path background block error
HPES
Higher order path errored second
HPSES
Higher order path severely errored second
HPCSES
Higher order path consecutive severely
errored second
HPUAS
Higher order path unavailable second
HPFEBBE
Higher order path far end background block
error
HPFEES
Higher order path far end errored second
HPFESES
Higher order path far end severely errored
second
HPFECSES
Higher order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
HPFEUAS
Higher order path far end unavailable second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
641
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Radio Performance Events
Table C-25 FEC performance events
Event Name
Description
FEC_BEF_COR_ER
FEC bit error rate before correction
FEC_COR_BYTE_CNT
Frame count incorrect by FEC
Table C-26 IF port error performance events
Event Name
Description
IF_SNR_MAX
Maximum signal to noise ratio
IF_SNR_MIN
Minimum signal to noise ratio
IF_SNR_AVG
Average signal to noise ratio
Other Performance Events
Table C-27 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
C.2.3 IFU2/ISU2
The IFU2/ISU2 board reports three types of performance events: PDH performance events, radio
performance events, and board temperature performance events.
SDH Performance Events (Only reported by ISU2)
Table C-28 Pointer justification performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
AUPJCHIGH
Count of positive AU pointer justification
AUPJCLOW
Count of negative AU pointer justification
AUPJCNEW
Count of new AU pointer justifications
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
642
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Table C-29 Regenerator section error performance events
Event Name
Description
RSBBE
Regenerator section block of background
error
RSES
Regenerator section errored second
RSSES
Regenerator section severely errored second
RSUAS
Regenerator section unavailable second
RSCSES
Regenerator section consecutive severely
errored second
RSOFS
Regenerator section out-of-frame second
RSOOF
Regenerator section out of frame
Table C-30 Multiplex section error performance events
Event Name
Description
MSBBE
Multiplex section block of background error
MSES
Multiplex section errored second
MSSES
Multiplex section severely errored second
MSCSES
Multiplex section consecutive severely
errored second
MSUAS
Multiplex section unavailable second
MSFEBBE
Multiplex section far end block of
background error
MSFEES
Multiplex section far end errored second
MSFESES
Multiplex section far end severely errored
second
MSFECSES
Multiplex section far end consecutive
severely errored second
MSFEUAS
Multiplex section far end unavailable second
Table C-31 Higher order path error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
HPBBE
Higher order path background errored block
HPES
Higher order path errored second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
643
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
HPSES
Higher order path severely errored second
HPCSES
Higher order path consecutive severely
errored second
HPUAS
Higher order path unavailable second
HPFEBBE
Higher order path far end background errored
block
HPFEES
Higher order path far end errored second
HPFESES
Higher order path far end severely errored
second
HPFECSES
Higher order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
HPFEUAS
Higher order path far end unavailable second
PDH Performance Events
Table C-32 Lower order path error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
LPBBE
Lower order path block of background error
LPES
Lower order path errored second
LPSES
Lower order path severely errored second
LPCSES
Lower order path continuous severe bit error
second
LPUAS
Lower order path unavailable second
LPFEBBE
Lower order path far end block of background
error
LPFEES
Lower order path far end errored second
LPFESES
Lower order path far end severely errored
second
LPFECSES
Lower order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
LPFEUAS
Lower order far end unavailable second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
644
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Radio Performance Events
Table C-33 FEC performance events
Event Name
Description
FEC_BEF_COR_ER
FEC bit error rate before correction
FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT
FEC uncorrected block count
Table C-34 Radio link error performance events
Event Name
Description
IF_BBE
Radio link background block errors
IF_ES
Radio link errored seconds
IF_SES
Radio link severely errored seconds
IF_UAS
Radio link unavailable second
IF_CSES
Radio link consecutive severely errored
seconds
Table C-35 AM performance events
Event Name
Description
QPSKWS
Working time of the QPSK mode
QAMWS16
Working time of the 16QAM mode
QAMWS32
Working time of the 32QAM mode
QAMWS64
Working time of the 64QAM mode
QAMWS128
Working time of the 128QAM mode
QAMWS256
Working time of the 256QAM mode
FB_AMDCNT
Count of the downshift of the AM scheme
FB_AMUCNT
Count of the upshift of the AM scheme
Table C-36 IF port error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
IF_SNR_MAX
Maximum signal to noise ratio
IF_SNR_MIN
Minimum signal to noise ratio
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
645
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
IF_SNR_AVG
Average signal to noise ratio
Other Performance Events
Table C-37 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
C.2.4 IFX2/ISX2
The IFX2/ISX2 board reports three types of performance events: PDH performance events,
radio performance events, and board temperature performance events.
SDH Performance Events (Only reported by ISX2)
Table C-38 Pointer justification performance events
Event Name
Description
AUPJCHIGH
Count of positive AU pointer justification
AUPJCLOW
Count of negative AU pointer justification
AUPJCNEW
Count of new AU pointer justifications
Table C-39 Regenerator section error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
RSBBE
Regenerator section block of background
error
RSES
Regenerator section errored second
RSSES
Regenerator section severely errored second
RSUAS
Regenerator section unavailable second
RSCSES
Regenerator section consecutive severely
errored second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
646
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
RSOFS
Regenerator section out-of-frame second
RSOOF
Regenerator section out of frame
Table C-40 Multiplex section error performance events
Event Name
Description
MSBBE
Multiplex section block of background error
MSES
Multiplex section errored second
MSSES
Multiplex section severely errored second
MSCSES
Multiplex section consecutive severely
errored second
MSUAS
Multiplex section unavailable second
MSFEBBE
Multiplex section far end block of
background error
MSFEES
Multiplex section far end errored second
MSFESES
Multiplex section far end severely errored
second
MSFECSES
Multiplex section far end consecutive
severely errored second
MSFEUAS
Multiplex section far end unavailable second
Table C-41 Higher order path error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
HPBBE
Higher order path background errored block
HPES
Higher order path errored second
HPSES
Higher order path severely errored second
HPCSES
Higher order path consecutive severely
errored second
HPUAS
Higher order path unavailable second
HPFEBBE
Higher order path far end background errored
block
HPFEES
Higher order path far end errored second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
647
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
HPFESES
Higher order path far end severely errored
second
HPFECSES
Higher order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
HPFEUAS
Higher order path far end unavailable second
PDH Performance Events
Table C-42 Lower order path error performance events
Event Name
Description
LPBBE
Lower order path block of background error
LPES
Lower order path errored second
LPSES
Lower order path severely errored second
LPCSES
Lower order path continuous severe bit error
second
LPUAS
Lower order path unavailable second
LPFEBBE
Lower order path far end block of background
error
LPFEES
Lower order path far end errored second
LPFESES
Lower order path far end severely errored
second
LPFECSES
Lower order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
LPFEUAS
Lower order far end unavailable second
Radio Performance Events
Table C-43 FEC performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
FEC_BEF_COR_ER
FEC bit error rate before correction
FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT
FEC uncorrected block count
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
648
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Table C-44 Radio link error performance events
Event Name
Description
IF_BBE
Radio link background block errors
IF_ES
Radio link errored seconds
IF_SES
Radio link severely errored seconds
IF_UAS
Radio link unavailable second
IF_CSES
Radio link consecutive severely errored
seconds
Table C-45 AM performance events
Event Name
Description
QPSKWS
Working time of the QPSK mode
QAMWS16
Working time of the 16QAM mode
QAMWS32
Working time of the 32QAM mode
QAMWS64
Working time of the 64QAM mode
QAMWS128
Working time of the 128QAM mode
QAMWS256
Working time of the 256QAM mode
FB_AMDCNT
Count of the downshift of the AM scheme
FB_AMUCNT
Count of the upshift of the AM scheme
Table C-46 IF port error performance events
Event Name
Description
IF_SNR_MAX
Maximum signal to noise ratio
IF_SNR_MIN
Minimum signal to noise ratio
IF_SNR_AVG
Average signal to noise ratio
Table C-47 XPIC performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
XPIC_XPD_VALUE
XPIC XPD value
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
649
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Other Performance Events
Table C-48 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
C.2.5 SL1D/SL1DA
The SL1D/SL1DA board reports three types of performance events: SDH performance events,
and optical power performance events.
SDH Performance Events
Table C-49 Pointer justification performance events
Event Name
Description
AUPJCHIGH
Count of positive AU pointer justification
AUPJCLOW
Count of negative AU pointer justification
AUPJCNEW
Count of new AU pointer justifications
Table C-50 Regenerator section error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
RSBBE
Regenerator section block of background
error
RSES
Regenerator section errored second
RSSES
Regenerator section severely errored second
RSUAS
Regenerator section unavailable second
RSCSES
Regenerator section consecutive severely
errored second
RSOFS
Regenerator section out-of-frame second
RSOOF
Regenerator section out of frame
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
650
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Table C-51 Multiplex section error performance events
Event Name
Description
MSBBE
Multiplex section block of background error
MSES
Multiplex section errored second
MSSES
Multiplex section severely errored second
MSCSES
Multiplex section consecutive severely
errored second
MSUAS
Multiplex section unavailable second
MSFEBBE
Multiplex section far end block of
background error
MSFEES
Multiplex section far end errored second
MSFESES
Multiplex section far end severely errored
second
MSFECSES
Multiplex section far end consecutive
severely errored second
MSFEUAS
Multiplex section far end unavailable second
Table C-52 Higher order path error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
HPBBE
Higher order path background errored block
HPES
Higher order path errored second
HPSES
Higher order path severely errored second
HPCSES
Higher order path consecutive severely
errored second
HPUAS
Higher order path unavailable second
HPFEBBE
Higher order path far end background errored
block
HPFEES
Higher order path far end errored second
HPFESES
Higher order path far end severely errored
second
HPFECSES
Higher order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
HPFEUAS
Higher order path far end unavailable second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
651
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Other Performance Events
Table C-53 Optical power performance events
Event Name
Description
TPLMAX
Maximum value of transmit optical power
TPLMIN
Minimum value of transmit optical power
TPLCUR
Current value of transmit optical power
RPLMAX
Maximum value of receive optical power
RPLMIN
Minimum value of receive optical power
RPLCUR
Current value of receive optical power
C.2.6 EM6T
The EM6T board reports only the board temperature performance events.
Table C-54 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
C.2.7 EM6TA
The EM6TA board reports only the board temperature performance events.
Table C-55 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
C.2.8 EM6F
The EM6F board reports optical power performance events and board temperature performance
events.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
652
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Table C-56 Optical power performance events
Event Name
Description
TPLMAX
Maximum value of transmit optical power
TPLMIN
Minimum value of transmit optical power
TPLCUR
Current value of transmit optical power
RPLMAX
Maximum value of receive optical power
RPLMIN
Minimum value of receive optical power
RPLCUR
Current value of receive optical power
Table C-57 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
C.2.9 EM6FA
The EM6FA board reports optical power performance events and board temperature
performance events.
Table C-58 Optical power performance events
Event Name
Description
TPLMAX
Maximum value of transmit optical power
TPLMIN
Minimum value of transmit optical power
TPLCUR
Current value of transmit optical power
RPLMAX
Maximum value of receive optical power
RPLMIN
Minimum value of receive optical power
RPLCUR
Current value of receive optical power
Table C-59 Board temperature performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
653
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
C.2.10 EFP8
The EFP8 board reports the temperature and PDH performance events.
Table C-60 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
Table C-61 Lower order path error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
LPBBE
Lower order path block of background error
LPES
Lower order path errored second
LPSES
Lower order path severely errored second
LPCSES
Lower order path continuous severe bit error
second
LPUAS
Lower order path unavailable second
LPFEBBE
Lower order path far end block of background
error
LPFEES
Lower order path far end errored second
LPFESES
Lower order path far end severely errored
second
LPFECSES
Lower order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
LPFEUAS
Lower order far end unavailable second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
654
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.2.11 EMS6
The EMS6 board reports the SDH performance events, board temperature performance events,
laser temperature performance events, and optical power performance events.
Table C-62 Lower order path error performance events
Event Name
Description
LPBBE
Lower order path block of background error
LPES
Lower order path errored second
LPSES
Lower order path severely errored second
LPCSES
Lower order path continuous severe bit error
second
LPUAS
Lower order path unavailable second
LPFEBBE
Lower order path far end block of background
error
LPFEES
Lower order path far end errored second
LPFESES
Lower order path far end severely errored
second
LPFECSES
Lower order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
Table C-63 Higher order path error performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
HPBBE
Higher order path background errored block
HPES
Higher order path errored second
HPSES
Higher order path severely errored second
HPCSES
Higher order path consecutive severely
errored second
HPUAS
Higher order path unavailable second
HPFEBBE
Higher order path far end background errored
block
HPFEES
Higher order path far end errored second
HPFESES
Higher order path far end severely errored
second
HPFECSES
Higher order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
655
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Table C-64 Board temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Maximum value of board temperature
BDTEMPMIN
Minimum value of board temperature
BDTEMPCUR
Current value of board temperature
Table C-65 Laser temperature performance events
Event Name
Description
OSPITMPMAX
Maximum temperature of a laser core
OSPITMPMIN
Minimum temperature of a laser core
OSPITMPCUR
Current temperature of a laser core
Table C-66 Optical power performance events
Event Name
Description
TPLMAX
Maximum value of transmit optical power
TPLMIN
Minimum value of transmit optical power
TPLCUR
Current value of transmit optical power
RPLMAX
Maximum value of receive optical power
RPLMIN
Minimum value of receive optical power
RPLCUR
Current value of receive optical power
C.2.12 SP3S/SP3D
The SP3S/SP3D board reports only the PDH performance events.
Table C-67 Pointer justification performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
TUPJCHIGH
Count of positive TU pointer justifications
TUPJCLOW
Count of negative TU pointer justifications
TUPJCNEW
Count of new TU pointer justifications
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
656
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Table C-68 Lower order path error performance events
Event Name
Description
LPBBE
Lower order path block of background error
LPES
Lower order path errored second
LPSES
Lower order path severely errored second
LPCSES
Lower order path continuous severe bit error
second
LPUAS
Lower order path unavailable second
LPFEBBE
Lower order path far end block of background
error
LPFEES
Lower order path far end errored second
LPFESES
Lower order path far end severely errored
second
LPFECSES
Lower order path far end consecutive
severely errored second
LPFEUAS
Lower order far end unavailable second
Table C-69 E1 Error Performance Events
Event Name
Description
E1_BBE
Indicates the E1 background block error.
E1_ES
Indicates the E1 errored second.
E1_SES
Indicates the E1 severely errored second.
E1_CSES
Indicates the E1 consecutive severely errored
second.
E1_UAS
Indicates the E1 unavailable second.
C.2.13 ML1/MD1
The ML1/MD1 board reports E1 performance events and board temperature performance events.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
657
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
E1 Performance Events
Table C-70 E1 Performance Event List
Event Name
Description
E1_LCV_SDH
Indicates the count of E1 line side code
violations.
E1_LLOSS_SDH
Indicates the E1 line side loss-of-signal
second.
E1_LES_SDH
Indicates the E1 line side code violation
errored second.
E1_LSES_SDH
Indicates the E1 line side code violation
severely errored second.
Other Performance Events
Table C-71 Board Temperature Performance Events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Indicates the maximum board
temperature.
BDTEMPMIN
Indicates the minimum board
temperature.
BDTEMPCUR
Indicates the current board temperature.
C.2.14 ODU
The ODU reports radio performance events and board temperature performance events.
Table C-72 Radio power performance events
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Event Name
Description
TSL_MAX
Maximum value of radio transmit signal level
TSL_MIN
Minimum value of radio transmit signal level
TSL_CUR
Current value of radio transmit signal level
TSL_AVG
Average value of radio transmit signal level
RSL_MAX
Maximum value of radio receive signal level
RSL_MIN
Minimum value of radio receive signal level
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
658
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Event Name
Description
RSL_CUR
Current value of radio receive signal level
RSL_AVG
Average value of radio receive signal level
TLHTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a transit power higher than the upper
threshold
TLLTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a transit power higher than the lower
threshold
RLHTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a receive power lower than the upper
threshold
RLLTT
The duration when the ODU at the local end
has a receive power lower than the lower
threshold
Table C-73 ATPC performance events
Event Name
Description
ATPC_P_ADJUST
Positive ATPC adjustment
ATPC_N_ADJUST
Negative ATPC adjustment
Table C-74 Board Temperature Performance Events
Event Name
Description
BDTEMPMAX
Indicates the maximum board
temperature.
BDTEMPMIN
Indicates the minimum board
temperature.
BDTEMPCUR
Indicates the current board temperature.
C.3 Performance Events and Handling Procedures
Based on the type of a performance event, this chapter describes all the performance events on
the OptiX RTN 950 and how to handle these performance events.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
659
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.3.1 AUPJCHIGH, AUPJCLOW, and AUPJCNEW
Description
l
AUPJCHIGH indicates the count of positive AU pointer justifications.
AUPJCLOW indicates the count of negative AU pointer justifications.
AUPJCNEW indicates the count of new AU pointer justifications.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
PPJE (AUPJCHIGH)
NPJE (AUPJCLOW)
NDF (AUPJCNEW)
Unit
Block
Impact on System
Less than six AUPJCHIGH and AUPJCLOW events do not affect the system. If the pointer is
justified for many times, or the AUPJCNEW event occurs, bit errors may occur in the service.
Related Alarms
When the AUPJCHIGH, AUPJCLOW, or AUPJCNEW performance event crosses the preset
threshold, the MSAD_CROSSTR alarm is reported.
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
AUPJCHIGH
1500
30000
AUPJCLOW
1500
30000
AUPJCNEW
1500
30000
Possible Causes
The NE clock is out-of-synchronization.
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.5 Troubleshooting Pointer Justifications for handling.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
660
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.3.2 TUPJCHIGH, TUPJCLOW, and TUPJCNEW
Description
l
TUPJCHIGH indicates the count of positive TU pointer justifications.
TUPJCLOW indicates the count of negative TU pointer justifications.
TUPJCNEW indicates the count of new TU pointer justifications.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
TUPPJE (TUPJCHIGH)
TUNPJE (TUPJCLOW)
TUNDF (TUPJCNEW)
Unit
Block
Impact on System
Less than six TUPJCHIGH and TUPJCLOW events on each port do not affect the system. If the
pointer is justified for many times, or the TUPJCNEW event occurs, bit errors may occur in the
service.
Related Alarms
When the TUPJCHIGH, TUPJCLOW, or TUPJCNEW performance event crosses the preset
threshold, the HPAD_CROSSTR alarm is reported.
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
TUPJCHIGH
1500
30000
TUPJCLOW
1500
30000
TUPJCNEW
1500
30000
Possible Causes
The NE clock is out-of-synchronization.
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.5 Troubleshooting Pointer Justifications for handling.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
661
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.3.3 RSBBE, RSES, RSSES, RSCSES, and RSUAS
Description
l
RSBBE indicates the regenerator section background block error.
Background block error (BBE) refers to the errored blocks excluding the errored blocks in
the unavailable and severely errored seconds.
RSES indicates the regenerator section errored second.
Errored second (ES) refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
RSSES indicates the regenerator section severely errored second.
Severely errored second (SES) refers to a second in which 30% or more than 30% errored
blocks exist or at least one severely disturbed period (SDP) exists. SDP is the period in
which the BER of all the consecutive blocks in a period of less than four consecutive blocks
or 1 ms (the longer period is applied) is equal to or higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
RSCSES indicates the regenerator section consecutive severely errored second.
Consecutive severely errored second (CSES) refers to a second in which the SES occurs
continuously for less than 10 seconds.
RSUAS indicates the regenerator section unavailable second.
The unavailable time begins at the onset of 10 consecutive SESs, with the 10 SESs included.
When SESs disappear for 10 consecutive seconds, the available time begins from the
eleventh second, with the previous 10 seconds included.
NOTE
When the IF board works in PDH mode, these performance events may also be reported. These events are
detected through the self-defined overhead byte B1 in the PDH radio frame.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
B1CNT
Unit
Block (RSBBE)
Second (RSES, RSSES, RSCSES, and
RSUAS)
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
When the RSBBE, RSES, RSSES, RSCSES, or RSUAS performance event crosses the preset
threshold, the RS_CROSSTR alarm is reported.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
662
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
RSBBE
1500
15000
RSES
50
100
RSSES
20
50
RSUAS
20
50
RSCSES
4 (number of consecutive SESs)
Possible Causes
The system detects the regenerator section bit errors through the B1 byte.
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services for handling.
Step 2 When an RSUAS performance event is reported, check whether cross-connections are
configured and whether fibers are properly connected at service ports. If cross-connections are
not configured, configure cross-connections again according to planning information; if fibers
are incorrectly connected, connect the fibers again according to planning information.
----End
C.3.4 RSOOF and RSOFS
Description
l
RSOOF indicates the regenerator section out of frame.
The out-of-frame (OOF) block refers to a data block in which incorrect A1 and A2 bytes
are detected.
RSOFS indicates the regenerator section out-of-frame second.
The out-of-frame second (OFS) refers to a second in which one or more OOF blocks are
detected.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
OOF
Unit
Block (RSOOF)
Second (RSOFS)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
663
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Impact on System
The system discards OOF data blocks. Therefore, an RSOOF event is equivalent to a big error
(if one RSOOF exists in a second, the BER is not less than 1.25 x 10-5).
Related Alarms
If RSOOF is received in five consecutive frames, the equipment changes to the OOF state. If
the OOF state lasts for 3 ms, the R_LOF alarm is reported and all the services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
The system detects incorrect A1 and A2 bytes.
Procedure
Step 1 If the R_LOF alarm, as well as the performance event, is reported, eliminate the errors according
to the alarm. Otherwise, see 5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services for handling.
----End
C.3.5 MSBBE, MSES, MSSES, MSCSES, and MSUAS
Description
l
MSBBE indicates the multiplex section background block error.
BBE refers to the errored blocks excluding the errored blocks in the unavailable and
severely errored seconds.
MSES indicates the multiplex section errored second.
ES refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
MSSES indicates the multiplex section severely errored second.
SES refers to a second in which 15% or more than 15% errored blocks exist or at least one
SDP exists. SDP is the period in which the BER of all the consecutive blocks in a period
of less than four consecutive blocks or 1 ms (the longer period is applied) is equal to or
higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
MSCSES indicates the multiplex section consecutive severely errored second.
CSES refers to a second in which the SES occurs continuously for less than 10 seconds.
MSUAS indicates the multiplex section unavailable second.
The unavailable time begins at the onset of 10 consecutive SESs, with the 10 SESs included.
When SESs disappear for 10 consecutive seconds, the available time begins from the
eleventh second, with the previous 10 seconds included.
Attribute
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
B2CNT
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
664
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Attribute
Description
Unit
Block (MSBBE)
Second (MSES, MSSES, MSCSES, and
MSUAS)
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
When the MSBBE, MSES, MSSES, MSCSES, or MSUAS performance event crosses the preset
threshold, the MS_CROSSTR alarm is reported.
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
MSBBE
1500
15000
MSES
50
100
MSES
20
50
MSUAS
20
50
MSCSES
4 (number of consecutive SESs)
Possible Causes
The system detects multiplex section bit errors through the B2 byte.
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services for handling.
Step 2 When an MSUAS performance event is reported, check whether cross-connections are
configured and whether fibers are properly connected at service ports. If cross-connections are
not configured, configure cross-connections again according to planning information; if fibers
are incorrectly connected, connect the fibers again according to planning information.
----End
C.3.6 MSFEBBE, MSFEES, MSFESES, MSFECSES, and MSFEUAS
Description
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
MSFEBBE indicates the multiplex section far end background block error.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
665
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Far end background block error (FEBBE) indicates that the BBE occurs at the opposite
end.
l
MSFEES indicates the multiplex section far end errored second.
Far end errored second (FEES) indicates that the ES occurs at the opposite end.
MSFESES indicates the multiplex section far end severely errored second.
Far end severely errored second (FESES) indicates that the SES occurs at the opposite end.
MSFECSES indicates the multiplex section far end consecutive severely errored second.
Far end consecutive severely errored second (FECSES) indicates that the CSES occurs at
the opposite end.
MSFEUAS indicates the multiplex section far end unavailable second.
Far end unavailable second (FEUAS) indicates that the UAS occurs at the opposite end.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
LFEBE
Unit
Block (MSFEBBE)
Second (MSFEES, MSFESES, MSFECSES,
and MSFEUAS)
Impact on the System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
The MS_REI alarm is reported at the local end.
Possible Causes
The system detects multiplex section far end bit errors through the M1 byte.
Procedure
Step 1 Clear the corresponding performance event at the opposite end.
----End
C.3.7 HPBBE, HPES, HPSES, HPCSES, and HPUAS
Description
l
HPBBE indicates the higher order path background block error.
BBE refers to the errored blocks excluding the errored blocks in the unavailable and
severely errored seconds.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
666
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
HPES indicates the higher order path errored second.
ES refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
HPSES indicates the higher order path severely errored second.
SES refers to a second in which 30% or more than 30% errored blocks exist or at least one
SDP exists. SDP is the period in which the BER of all the consecutive blocks in a period
of less than four consecutive blocks or 1 ms (the longer period is applied) is equal to or
higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
HPCSES indicates the higher order path consecutive severely errored second.
CSES refers to a second in which the SES occurs continuously for less than 10 seconds.
HPUAS indicates the higher order path unavailable second.
The unavailable time begins at the onset of 10 consecutive SESs, with the 10 SESs included.
When SESs disappear for 10 consecutive seconds, the available time begins from the
eleventh second, with the previous 10 seconds included.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
B3CNT
Unit
Block (HPBBE)
Second (HPES, HPSES, HPCSES, and
HPUAS)
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
When the HPBBE, HPES, HPSES, HPCSES, or HPUAS performance event crosses the preset
threshold, the HP_CROSSTR alarm is reported.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
HPBBE
1500
15000
HPES
50
100
HPSES
20
50
HPUAS
20
50
HPCSES
4 (number of consecutive SESs)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
667
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Possible Causes
The system detects higher order path bit errors through the B3 byte.
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services for handling.
----End
C.3.8 HPFEBBE, HPFEES, HPFESES, HPFECSES, and HPFEUAS
Description
l
HPFEBBE indicates the higher order path far end background block error.
Far end background block error (FEBBE) indicates that the BBE occurs at the opposite
end.
HPFEES indicates the higher order path far end errored second.
FEES indicates that the ES occurs at the opposite end.
HPFESES indicates the higher order path far end severely errored second.
FESES indicates that the SES occurs at the opposite end.
HPFECSES indicates the higher order path far end consecutive severely errored second.
FECSES indicates that the CSES occurs at the opposite end.
HPFEUAS indicates the higher order path far end unavailable second.
FEUAS indicates that the UAS occurs at the opposite end.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
PFEBE
Unit
Block (HPFEBBE)
Second (HPFEES, HPFESES, HPFECSES,
and HPFEUAS)
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
The HP_REI alarm is reported at the local end.
Possible Causes
The system detects the higher order path far end bit errors through bits 1 to 4 in the G1 byte.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
668
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Clear the corresponding performance event at the opposite end.
----End
C.3.9 IF_BBE, IF_ES, IF_SES, IF_CSES, and IF_UAS
Description
l
IF_BBE indicates the radio link background block error.
BBE refers to the errored blocks excluding the errored blocks in the unavailable and
severely errored seconds.
IF_ES indicates the radio link errored second.
ES refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
IF_SES indicates the radio link severely errored second.
SES refers to a second in which 30% or more than 30% errored blocks exist or at least one
SDP exists. SDP is the period in which the BER of all the consecutive blocks in a period
of less than four consecutive blocks or 1 ms (the longer period is applied) is equal to or
higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
IF_CSES indicates the radio link consecutively severely errored second.
CSES refers to a second in which the SES occurs continuously for less than 10 seconds.
IF_UAS indicates the radio link unavailable second.
The unavailable time begins at the onset of 10 consecutive SESs, with the 10 SESs included.
When SESs disappear for 10 consecutive seconds, the available time begins from the
eleventh second, with the previous 10 seconds included.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
IF_BIP8
Unit
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
The MW_BER_SD or MW_BER_EXC alarm is reported when the BER crosses the specific
threshold.
Possible Causes
The system detects bit errors on the radio link through the bit error detection overheads in a radio
frame.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
669
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services for handling.
----End
C.3.10 LPBBE, LPES, LPSES, LPCSES, and LPUAS
Description
l
LPBBE indicates the lower order path background block error.
BBE refers to the errored blocks excluding the errored blocks in the unavailable and
severely errored seconds.
LPES indicates the lower order path errored second.
ES refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
LPSES indicates the lower order path severely errored second.
SES refers to a second in which 30% or more than 30% errored blocks exist or at least one
SDP exists. SDP is the period in which the BER of all the consecutive blocks in a period
of less than four consecutive blocks or 1 ms (the longer period is applied) is equal to or
higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
LPCSES indicates the lower order path consecutive severely errored second.
CSES refers to a second in which the SES occurs continuously for less than 10 seconds.
LPUAS indicates the lower order path unavailable second.
The unavailable time begins at the onset of 10 consecutive SESs, with the 10 SESs included.
When SESs disappear for 10 consecutive seconds, the available time begins from the
eleventh second, with the previous 10 seconds included.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
LPBIP2CNT
Unit
Block (LPBBE)
Second (LPES, LPSES, LPCSES, and
LPUAS)
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
When the LPBBE, LPES, LPSES, LPCSES, or LPUAS performance event crosses the preset
threshold, the LP_CROSSTR alarm is reported.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
670
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
LPBBE
1500
15000
LPES
50
100
LPSES
20
50
LPUAS
20
50
LPCSES
4 (number of consecutive SESs)
Possible Causes
The system detects lower order path bit errors through the BIP2 in the V5 byte (E1 interface
board or Hybrid IF board).
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.4 Troubleshooting Bit Errors in TDM Services for handling.
----End
C.3.11 LPFEBBE, LPFEES, LPFESES, LPFECSES, and LPFEUAS
Description
l
LPFEBBE indicates the lower order path far end background block error.
FEBBE indicates that the BBE occurs at the opposite end.
LPFEES indicates the lower order path far end errored second.
FEES indicates that the ES occurs at the opposite end.
LPFESES indicates the lower order path far end severely errored second.
FESES indicates that the SES occurs at the opposite end.
LPFECSES indicates the lower order path far end consecutive severely errored second.
FECSES indicates that the CSES occurs at the opposite end.
LPFEUAS indicates the lower order path far end unavailable second.
FEUAS indicates that the UAS occurs at the opposite end.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
LPFEBE
Unit
Block (LPFEBBE)
Second (LPFEES, LPFESES, LPFECSES,
and LPFEUAS)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
671
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than 10-3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
The LP_REI alarm is reported at the local end.
Possible Causes
The system detects the lower order path far end bit errors through bit 3 in the V5 byte.
Procedure
Step 1 Clear the corresponding performance event at the opposite end.
----End
C.3.12 E1_LCV_SDH, E1_LLOSS_SDH, E1_LES_SDH, and
E1_LSES_SDH
Description
l
The E1_LCV_SDH is a performance event indicating the E1 line side code violation count.
The E1_LLOSS_SDH is a performance event indicating the E1 line side loss-of-signal
seconds.
The E1_LES_SDH is a performance event indicating the E1 line side code violation errored
second.
ES refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
The E1_LSES_SDH is a performance event indicating the E1 line side code violation
severely errored second.
An SES refers to a certain second in which 30% or more errored blocks are detected or at
least one serious disturbance period (SDP) exists. The SDP refers to a period of at least
four consecutive blocks or 1 ms (taking the longer one) in which the BER of all the
consecutive blocks is equal to or higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
LCV_BPVCNT
Unit
None
Second
Impact on the System
If bit errors occur in the services, you need to find out the causes and troubleshoot the problem
in a timely manner. Otherwise, the signal transmission quality will be affected.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
672
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Related Alarms
None.
Possible Causes
l
External causes:
The fiber performance is degraded, and the fiber has extremely high attenuation.
The fiber connector is dirty or incorrect.
The equipment is improperly grounded.
A strong interference source is present near the equipment.
The working temperature is extremely high or extremely low, and the opposite
equipment cannot tolerate such temperature.
Equipment problems:
The service code types are incorrect.
The board becomes faulty, or the performance of the board is degraded.
Procedure
Step 1 First eliminate external causes, such as poor grounding, too high operating temperature, too low
or too high the receiving optical power of the line board.
Step 2 Check whether the correct E1 service code is selected. If not, modify the code of the services
received by a board by setting the code type of the board.
----End
C.3.13 TSL_MAX, TSL_MIN, TSL_CUR, and TSL_AVG
Description
l
TSL_MAX indicates the maximum radio transmitted signal level.
TSL_MIN indicates the minimum radio transmitted signal level.
TSL_CUR indicates the current radio transmitted signal level.
TSL_AVG indicates the average radio transmitted signal level.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
TSL
Unit
0.1dBm
Impact on System
When the radio transmitted signal level is very low or very high, the radio received signal level
at the opposite site is very low or very high. As a result, bit errors occur and even services are
interrupted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
673
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Related Alarms
If the radio transmitted signal level is not within the range supported by the ODU, the
RADIO_TSL_HIGH or RADIO_TSL_LOW alarm is reported.
C.3.14 RSL_MAX, RSL_MIN, RSL_CUR, and RSL_AVG
Description
l
RSL_MAX indicates the maximum radio received signal level.
RSL_MIN indicates the minimum radio received signal level.
RSL_CUR indicates the current radio received signal level.
RSL_AVG indicates the average radio received signal level.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
RSL
Unit
0.1dBm
Impact on System
When the radio received signal level is very low or very high, bit errors occur and even services
are interrupted.
Related Alarms
If the radio received signal level crosses the specific threshold, the RADIO_RSL_HIGH or
RADIO_RSL_LOW alarm is reported.
C.3.15 FEC_BEF_COR_ER, FEC_COR_BYTE_CNT and
FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT
Description
l
FEC_BEF_COR_ER indicates the BER before the FEC is performed.
This event indicates the impact of the external environment on the transmission.
FEC_COR_BYTE_CNT indicates the number of bytes corrected through the FEC.
This event indicates the impact of the FEC.
FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT indicates the number of frames that cannot be corrected
through the FEC.
This event indicates the number of blocks that cannot be corrected through the FEC.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
674
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
FECBEFCORER (FEC_BEF_COR_ER)
FECCORBYTECNT
(FEC_COR_BYTE_CNT)
FECUNCORBLOCKCNT
(FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT)
Unit
None (FEC_BEF_COR_ER)
None (FEC_COR_BYTE_CNT)
Block (FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT)
Impact on System
If the value of FEC_BEF_COR_ER is very high, residual bit errors exist in the service after the
FEC is performed.
If the value of FEC_UNCOR_BLOCK_CNT is not zero, it can be inferred that bit errors that
cannot be corrected exist on a radio link. Bit errors exist in the service accordingly.
Related Alarms
If a byte cannot be corrected, the MW_FEC_UNCOR alarm is reported.
C.3.16 QPSKWS, QAMWS16, QAMWS32, QAMWS64,
QAMWS128, and QAMWS256
Description
l
QPSKWS indicates the working duration of the QPSK modulation scheme.
QAMWS16 indicates the working duration of the 16QAM modulation scheme.
QAMWS32 indicates the working duration of the 32QAM modulation scheme.
QAMWS64 indicates the working duration of the 64QAM modulation scheme.
QAMWS128 indicates the working duration of the 128QAM modulation scheme.
QAMWS256 indicates the working duration of the 256QAM modulation scheme.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
675
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
QPSKWSSECOND (QPSKWS)
QAMWS16SECOND (16QAMWS)
QAMWS32SECOND (32QAMWS)
QAMWS64SECOND (64QAMWS)
QAMWS128SECOND (128QAMWS)
QAMWS256SECOND (256QAMWS)
Second
Unit
Impact on System
When the AM function is disabled, the performance event does not affect the system.
When the AM function is enabled, in normal cases, the seconds of the modulation scheme for
maximum capacity should account for a larger percentage. In the duration set for good weather,
if the seconds of the low-efficiency modulation scheme account for a larger percentage, the
performance of the radio link is abnormal.
Related Alarms
None.
C.3.17 ATPC_P_ADJUST and ATPC_N_ADJUST
Description
l
ATPC_P_ADJUST indicates the positive ATPC adjustment event.
This performance event indicates that the quality of a communication link declines.
Therefore, you must increase the transmit power of the ODU to maintain the
communication quality.
ATPC_N_ADJUST indicates the negative ATPC adjustment event.
This performance event indicates that the quality of a communication link becomes well
or the transmit power of the ODU is very large. Therefore, you can decrease the transmit
power of the ODU.
Attribute
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
ATPCPADJUST (ATPC_P_ADJUST) and
ATPCNADJUST (ATPC_N_ADJUST)
Unit
times
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
676
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Impact on the System
The ATPC adjustment indicates only the stability of a communication link and it does not affect
services. When the value of the performance event is larger, more adjustments are made.
When the factors that affect a communication link, such as sudden change of the weather, do
not exist, and when the ATPC adjustment count is very large, the communication link may be
faulty. You must check the communication link to prevent it from failure.
Related Alarms
None.
C.3.18 FB_AMDCNT and FB_AMUCNT
Description
l
FB_AMDCNT indicates the count of the AM downshifts on a board in the current
performance statistics period.
FB_AMUCNT indicates the count of the AM upshifts on a board in the current performance
statistics period.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
ACMDCNT(FB_AMDCNT) and
ACMUCNT(FB_AMUCNT)
Unit
times
Impact on System
l
When the value of the performance event is larger, more AM scheme are made.
When the factors that affect a communication link, such as sudden change of the weather,
do not exist, and when the AM scheme count is very large, the communication link may
be faulty. You must check the communication link to prevent it from failure.
Related Alarms
AM_DOWNSHIFT
Possible Causes
When the AM function is enabled, the transmission modulation scheme that the IF port on the
IF board uses varies according to the quality of the link. Accordingly, the system counts the
performance events of the modulation scheme shift. When the low-efficiency modulation
scheme is shifted to the high-efficiency modulation scheme, an upshift is recorded and one
FB_AMUCNT event is counted. Similarly, when the high-efficiency modulation scheme is
shifted to the low-efficiency modulation scheme, a downshift is recorded and one FB_AMDCNT
event is counted.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
677
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.3.19 RLHTT, RLLTT, TLHTT, TLLTT
Description
l
The RLHTT indicates the duration when the ODU at the local end has a receive power
lower than the upper threshold.
The RLLTT indicates the duration when the ODU at the local end has a receive power
lower than the lower threshold.
The TLHTT indicates the duration when the ODU at the local end has a transit power higher
than the upper threshold.
The TLLTT indicates the duration when the ODU at the local end has a transit power higher
than the lower threshold.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
RLHTS(RLHTT), RLLTS(RLLTT), TLHTS
(TLHTT), and TLLTS(TLLTT)
Unit
Second
Impact on System
None.
Related Alarms
None.
C.3.20 TPLMAX, TPLMIN, and TPLCUR
Description
l
TPLMAX indicates the maximum transmit optical power at an optical interface.
TPLMIN indicates the minimum transmit optical power at an optical interface.
TPLCUR indicates the current transmit optical power at an optical interface.
Attribute
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
OPM
Unit
0.1dBm
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
678
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Impact on System
In normal cases, the receive optical power should be 3 dB higher than the receiver sensitivity,
and 5 dB lower than the overload power.
If the transmit optical power is very low or very high, the receive optical power at the opposite
site is accordingly very low or very high. As a result, bit errors occur and even services are
interrupted.
Related Alarms
l
If the transmit optical power at the opposite site is lower than the receiver sensitivity, the
IN_PWR_LOW alarm is reported.
If the receive optical power at the opposite site is higher than the overload power, the
IN_PWR_HIGH alarm is reported.
C.3.21 RPLMAX, RPLMIN, and RPLCUR
Description
l
RPLMAX indicates the maximum receive optical power at an optical interface.
RPLMIN indicates the minimum receive optical power at an optical interface.
RPLCUR indicates the current receive optical power at an optical interface.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
IPM
Unit
0.1dBm
Impact on System
In normal cases, the receive optical power should be 3 dB higher than the receiver sensitivity,
and 5 dB lower than the overload power.
If the receive optical power is very low or very high, bit errors occur and even services are
interrupted.
Related Alarms
l
If the transmit optical power is lower than the receiver sensitivity, the IN_PWR_LOW
alarm is reported.
If the receive optical power is higher than the overload power, the IN_PWR_HIGH alarm
is reported.
C.3.22 BDTEMPMAX, BDTEMPMIN, and BDTEMPCUR
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
679
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Description
l
BDTEMPMAX indicates the maximum temperature of a board.
BDTEMPMIN indicates the minimum temperature of a board.
BDTEMPCUR indicates the current temperature of a board.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
XCS_TEMP
Unit
0.1C
Impact on System
If the temperature of a board is very high or very low, the performance of the board declines,
and bit errors or other faults occur.
Related Alarms
If the temperature of a board crosses the specific threshold, the TEMP_ALARM alarm is
reported.
C.3.23 XPIC_XPD_VALUE
Description
The XPIC_XPD_VALUE indicates the XPD value after the XPIC function is enabled.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
XPD
Unit
dB
Impact on System
l
When the XPIC function is disabled, the performance event does not affect the system.
When the XPIC function is enabled, a greater XPD value indicates less interference between
H and V polarization directions and better signaling environment; a smaller XPD value
indicates more interference and worse signaling environment. If the XPD value is smaller
than a specific threshold, errors and even interruptions occur on the radio link.
Related Alarms
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
680
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.3.24 PG_IF_BBE, PG_IF_ES, PG_IF_SES, PG_IF_CSES, and
PG_IF_UAS
Description
l
PG_IF_BBE indicates the protection group background block error.
Background block error (BBE) refers to the errored blocks excluding the errored blocks in
the unavailable and severely errored seconds.
PG_IF_ES indicates the protection group errored second.
Errored second (ES) refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
PG_IF_SES indicates the protection group severely errored second.
Severely errored second (SES) refers to a second in which 30% or more than 30% errored
blocks exist or at least one severely disturbed period (SDP) exists. SDP is the period in
which the BER of all the consecutive blocks in a period of less than four consecutive blocks
or 1 ms (the longer period is applied) is equal to or higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
PG_IF_CSES indicates the protection group consecutive severely errored second.
Consecutive severely errored second (CSES) refers to a second in which the SES occurs
continuously for less than 10 seconds.
PG_IF_UAS indicates the protection group unavailable second.
The unavailable time begins at the onset of 10 consecutive SESs, with the 10 SESs included.
When SESs disappear for 10 consecutive seconds, the available time begins from the
eleventh second, with the previous 10 seconds included.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
IF_BIP8
Unit
Block (PG_IF_BBE)
Second (PG_IF_ES, PG_IF_SES,
PG_IF_CSES, and PG_IF_UAS)
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than -3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
PG_IF_BBE
1500
15000
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
681
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
PG_IF_ES
50
100
PG_IF_SES
20
50
PG_IF_UAS
20
50
PG_IF_CSES
4 (number of consecutive SESs)
Possible Causes
The system detects the protection group bit errors.
Related Alarms
PG_LINK_FAIL, PG_PRT_DEGRADED
Procedure
Step 1 See PG_LINK_FAIL, PG_PRT_DEGRADED.
----End
C.3.25 E1_BBE, E1_ES, E1_SES, E1_CSES, and E1_UAS
Description
l
E1_BBE indicates the E1 background block error.
Background block error (BBE) refers to the errored blocks excluding the errored blocks in
the unavailable and severely errored seconds. This performance event can be detected only
when the E1 frame format is CRC-4.
E1_ES indicates the E1 errored second.
Errored second (ES) refers to a second in which one or more errored blocks are detected.
E1_SES indicates the E1 severely errored second.
Severely errored second (SES) refers to a second in which 30% or more than 30% errored
blocks exist or at least one severely disturbed period (SDP) exists. SDP is the period in
which the BER of all the consecutive blocks in a period of less than four consecutive blocks
or 1 ms (the longer period is applied) is equal to or higher than 10-2 or the signal is lost.
E1_CSES indicates the E1 consecutive severely errored second.
Consecutive severely errored second (CSES) refers to a second in which the SES occurs
continuously for less than 10 seconds.
E1_UAS indicates the E1 unavailable second.
The unavailable time begins at the onset of 10 consecutive SESs, with the 10 SESs included.
When SESs disappear for 10 consecutive seconds, the available time begins from the
eleventh second, with the previous 10 seconds included.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
682
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
E1CRC_ERR_CNT
Unit
Block (E1_BBE)
Second (E1_ES, E1_SES, E1_CSES, and
E1_UAS)
Impact on System
Excessive bit errors interrupt the service (the BER should be less than -3 for the voice service,
and 10-6 for the data service).
Related Alarms
None.
Performance Event
Default 15-Minute
Threshold
Default 24-Hour
Threshold
E1_BBE
1500
15000
E1_ES
50
100
E1_SES
20
50
E1_UAS
20
50
E1_CSES
4 (number of consecutive SESs)
Possible Causes
The system detects the E1 bit errors.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the frame format of the local E1 port is the same as that of the opposite port.
Step 2 Check whether the E1 cable is intact. If it is damaged, replace it.
Step 3 Use another E1 port.
Step 4 Troubleshoot the interconnected equipment.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
683
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
C.3.26 IF_SNR_MAX, IF_SNR_MIN, and IF_SNR_AVG
Description
l
IF_SNR_MAX indicates the maximum signal to noise ratio.
IF_SNR_MIN indicates the minimum signal to noise ratio.
IF_SNR_AVG indicates the average signal to noise ratio.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
IF_SNR(IF_SNR_MAX, IF_SNR_MIN)
IF_SNR_AVG_15M, and
IF_SNR_AVG_24H(IF_SNR_AVG)
Unit
dB
Impact on System
A greater SNR value indicates a steady radio link; a smaller SNR value indicates a worse radio
link, errors and even interruptions occur on the radio link.
Related Alarms
None.
C.3.27 OSPITMPMAX, OSPITMPMIN, and OSPITMPCUR
Description
l
OSPITMPMAX indicates the maximum temperature of a laser core.
OSPITMPMIN indicates the minimum temperature of a laser core.
OSPITMPCUR indicates the current temperature of a laser core.
Attribute
Attribute
Description
Performance event cell
TMP
Unit
Impact on System
If the temperature of a laser core is very high or very low, the performance of the laser degrades,
and bit errors or other faults occur.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
684
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
C Performance Event Reference
Relevant Alarms
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
685
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
RMON Event Reference
RMON events reflect the running of the Ethernet services. This chapter describes the possible
RMON events on the OptiX RTN 950 and how to handle these events.
D.1 List of RMON Alarm Entries
The RMON alarm entries refer to the table entries in the RMON alarm group.
D.2 List of RMON Performance Entries on the Packet-Plane
The RMON performance entries on the packet plane refer to the table entries in the RMON
statistics group or history group.
D.3 List of RMON Performance Entries on the EoS/EoPDH Plane
The ports that report RMON performance events on the EoPDH plane include PORT1 to PORT9,
and VCTRUNK1 to VCTRUNK16 on the EFP8 board. The ports that report RMON
performance events on the EoPDH plane include PORT1 to PORT8, and VCTRUNK1 to
VCTRUNK8 on the EMS6 board.
D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures
This chapter describes the RMON events that indicate Ethernet service abnormalities and how
to handle these events.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
686
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
D.1 List of RMON Alarm Entries
The RMON alarm entries refer to the table entries in the RMON alarm group.
Table D-1 List of RMON alarm entries
Alarm
Name
Description
ETHDROP
The number of packet loss events
crosses the threshold.
RXBBAD
The number of bytes in received bad
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHFCS
The number of frames that have FCS
check errors crosses the threshold.
Source
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2 and IFX2
Table D-2 List of RMON alarm entries
Alarm Name
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Description
ETHDROP
The number of packet loss events
crosses the threshold.
ETHEXCCO
L
The number of frames that fail to be
transmitted after continuous
collisions crosses the threshold.
ETHLATECO
L
The number of collisions that are
detected after a timeslot period
elapses crosses the threshold.
RXBBAD
The number of bytes in received bad
packets crosses the threshold.
TXDEFFRM
The number of frames whose
transmission is delayed crosses the
threshold.
ETHUNDER
The number of received undersized
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHOVER
The number of received oversized
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHFRG
The number of received fragmented
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHJAB
The number of received errored
oversized packets crosses the
threshold.
Source
EM6T, EM6F, EM6FA, EM6TA
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
687
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Alarm Name
D RMON Event Reference
Description
ETHFCS
The number of frames that have FCS
check errors crosses the threshold.
PORT_RX_B
W_UTILIZA
TION
Indicates the bandwidth utilization
at a port in the receive direction.
PORT_TX_B
W_UTILIZA
TION
Indicates the bandwidth utilization
at a port in the transmit direction.
Source
ISU2, ISX2, EM6T, EM6F,
EM6FA, EM6TA, IFU2 and IFX2
Table D-3 List of EMS6\EFP8 RMON alarm entries
Alarm Name
Description
ETHDROP
The number of packet loss events
crosses the threshold.
RXBBAD
The number of bytes in received bad
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHUNDER
The number of received undersized
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHOVER
The number of received oversized
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHFRG
The number of received fragmented
packets crosses the threshold.
ETHJAB
The number of received errored
oversized packets crosses the
threshold.
ETHFCS
The number of frames that have FCS
check errors crosses the threshold.
ETHALI
The number of alignment error
frames
Source
EMS6, EFP8
D.2 List of RMON Performance Entries on the Packet-Plane
The RMON performance entries on the packet plane refer to the table entries in the RMON
statistics group or history group.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
688
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Table D-4 Packet-Plane RMON Performance Entry List
Perfor
manc
e
Type
Basic
perfor
mance
Extend
ed
perfor
mance
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
Description
RXPKTS
Indicates the packets
received (packets).
ETHDROP
Indicates the packet loss
events (times).
RXOCTETS
Indicates the bytes
received (bytes).
RXMULCAST
Indicates the multicast
packets received
(packets).
RXBRDCAST
Indicates the broadcast
packets received
(packets).
ETHOVER
Indicates the oversized
packets received
(packets).
ETHJAB
Indicates the oversized
error packets received
(packets).
ETHUNDER
Indicates the undersized
packets received
(packets).
ETHFRG
Indicates the fragments
received (packets).
ETHCOL
Indicates the collisions
(times).
PORT_RX_BW_UTILIZATION
Indicates the bandwidth
utilization at a port in the
receive direction.
PORT_TX_BW_UTILIZATION
Indicates the bandwidth
utilization at a port in the
transmit direction.
ETHFCS
Indicates the FCS errored
frames (frames).
RXBGOOD
Indicates the bytes in
received good packets
(bytes).
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
EM6T, EM6F, EFP8,
IFU2, IFX2, ISU2, ISX2,
EM6FA, EM6TA, EMS6
EM6T, EM6F, EFP8,
EM6FA, EM6TA, EMS6
EM6T, EM6F, EM6FA,
EM6TA
EM6T, EM6F, EFP8,
IFU2, IFX2, ISU2, ISX2,
EM6FA, EM6TA, EMS6
689
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
D RMON Event Reference
Description
TXBGOOD
Indicates the bytes in
transmitted good packets
(bytes).
RXBBAD
Indicates the bytes in
received bad packets
(bytes).
TXUNICAST
Indicates the unicast
packets transmitted
(packets).
RXUNICAST
Indicates the unicast
packets received
(packets).
TXMULCAST
Indicates the multicast
packets transmitted
(packets).
TXBRDCAST
Indicates the broadcast
packets transmitted
(packets).
RXGOODFULLFRAME
SPEED
Indicates the rate of good
full-frame bytes received
(bytes/second).
TXGOODFULLFRAME
SPEED
Indicates the rate of good
full-frame bytes
transmitted (bytes/
second).
RXFULLBGOOD
Indicates the good fullframe bytes received
(bytes).
TXFULLBGOOD
Indicates the good fullframe bytes transmitted
(bytes).
RXPAUSE
Indicates the pause
frames received (frames).
TXPAUSE
Indicates the pause
frames transmitted
(frames).
ETHLATECOL
Indicates the late
collisions (times).
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
EM6T, EM6F, EFP8,
EM6FA, EM6TA, EMS6
EM6T, EM6F, EM6FA,
EM6TA
690
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
D RMON Event Reference
Description
ETHEXCCOL
Indicates the frames
unsuccessfully
transmitted after
consecutive collisions
(frames).
TXDEFFRM
Indicates the frames that
are deferred in
transmission (frames).
RXPKT64
Indicates the count of
received 64-byte packets
(errored packets
included)
RXPKT65
Indicates the count of
received packets with a
length of 65 to 127 bytes
(errored packets
included)
RXPKT128
Indicates the count of
received packets with a
length of 128 to 255 bytes
(errored packets
included)
RXPKT256
Indicates the count of
received packets with a
length of 256 to 511 bytes
(errored packets
included)
RXPKT512
Indicates the count of
received packets with a
length of 512 to 1023
bytes (errored packets
included)
RXPKT1024
Indicates the count of
received packets with a
length of 1024 to 1518
bytes (errored packets
included)
RXPKT1519
Indicates the count of
received packets with a
length of 1519 to MTU
bytes (errored packets
included)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
ISU2, ISX2
691
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
ATM
PWE3
perfor
mance
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
D RMON Event Reference
Description
TXPKT64
Indicates the count of
transmitted 64-byte
packets (errored packets
included)
TXPKT65
Indicates the count of
transmitted packets with a
length of 65 to 127 bytes
(errored packets
included)
TXPKT128
Indicates the count of
transmitted packets with a
length of 128 to 255 bytes
(errored packets
included)
TXPKT256
Indicates the count of
transmitted packets with a
length of 256 to 511 bytes
(errored packets
included)
TXPKT512
Indicates the count of
transmitted packets with a
length of 512 to 1023
bytes (errored packets
included)
TXPKT1024
Indicates the count of
transmitted packets with a
length of 1024 to 1518
bytes (errored packets
included)
TXPKT1519
Indicates the count of
transmitted packets with a
length of 1519 to MTU
bytes (errored packets
included)
ATMPW_SNDCELLS
Indicates the count of
transmitted cells.
ATMPW_RCVCELLS
Indicates the count of
received cells.
ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELLS
Indicates the count of
unknown cells.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
ML1, MD1
692
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
ATM/
IMA
perfor
mance
events
on the
access
side
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
D RMON Event Reference
Description
PORT_RX_BW_UTILIZATION
Indicates the bandwidth
utilization at a port in the
receive direction.
PORT_TX_BW_UTILIZATION
Indicates the bandwidth
utilization at a port in the
transmit direction.
ATM_CORRECTED_H
CSERR
Indicates the number of
correctable HCS error
cells received.
ATM_UNCORRECTED
_HCSERR
Indicates the number of
uncorrectable HCS error
cells received.
ATM_RCVCELLS
Indicates the total number
of received cells.
ATM_RCVIDLECELLS
Indicates the total number
of received idle cells.
ATM_SNDCELLS
Indicates the total number
of transmitted cells.
ATM_IF_INRATE_MA
X
Indicates the maximum
rate of normal cells
received on the port.
ATM_IF_INRATE_MIN
Indicates the minimum
rate of normal cells
received on the port.
ATM_IF_INRATE_AV
G
Indicates the average rate
of normal cells received
on the port.
ATM_IF_OUTRATE_M
AX
Indicates the maximum
rate of normal cells
transmitted on the port.
ATM_IF_OUTRATE_M
IN
Indicates the minimum
rate of normal cells
transmitted on the port.
ATM_IF_OUTRATE_A
VG
Indicates the average rate
of normal cells
transmitted on the port.
ATM_CELL_AVAILABILITY
Indicates the percentage
of valid cells.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
693
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
D RMON Event Reference
Description
PORT_RX_BW_UTILIZATION
Indicates the bandwidth
utilization rate (0.01%) of
the port in the receive
direction.
PORT_TX_BW_UTILIZATION
Indicates the bandwidth
utilization rate (0.01%) of
the port in the transmit
direction.
ATM_UNI1_INRATE_
MAX
Indicates the maximum
rate of receiving correct
cells on the UNI1 side of
ATM connections.
ATM_UNI1_INRATE_
MIN
Indicates the minimum
rate of receiving correct
cells on the UNI1 side of
ATM connections.
ATM_UNI1_INRATE_
AVG
Indicates the average rate
of receiving correct cells
on the UNI1 side of ATM
connections.
ATM_UNI1_OUTRATE
_MAX
Indicates the maximum
rate of transmitting
correct cells on the UNI1
side of ATM connections.
ATM_UNI1_OUTRATE
_MIN
Indicates the minimum
rate of transmitting
correct cells on the UNI1
side of ATM connections.
ATM_UNI1_OUTRATE
_AVG
Indicates the average rate
of transmitting correct
cells on the UNI1 side of
ATM connections.
ATM_UNI2_INRATE_
MAX
Indicates the maximum
rate of receiving correct
cells on the UNI2 side of
ATM connections.
ATM_UNI2_INRATE_
MIN
Indicates the minimum
rate of receiving correct
cells on the UNI2 side of
ATM connections.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
694
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
CES
perfor
mance
event
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
D RMON Event Reference
Performance Name
Description
ATM_UNI2_INRATE_
AVG
Indicates the average rate
of receiving correct cells
on the UNI2 side of ATM
connections.
ATM_UNI2_OUTRATE
_MAX
Indicates the maximum
rate of transmitting
correct cells on the UNI2
side of ATM connections.
ATM_UNI2_OUTRATE
_MIN
Indicates the minimum
rate of transmitting
correct cells on the UNI2
side of ATM connections.
ATM_UNI2_OUTRATE
_AVG
Indicates the average rate
of transmitting correct
cells on the UNI2 side of
ATM connections.
ATM_UNI1_INCELLS
Indicates the total number
of receiving correct cells
on the UNI1 side of ATM
connections.
ATM_UNI1_OUTCELLS
Indicates the total number
of transmitting correct
cells on the UNI1 side of
ATM connections.
ATM_UNI2_INCELLS
Indicates the total number
of receiving correct cells
on the UNI2 side of ATM
connections.
ATM_UNI2_OUTCELLS
Indicates the total number
of transmitting correct
cells on the UNI2 side of
ATM connections.
CES_MISORDERPKTS
Indicates the number of
lost disordered packets.
CES_STRAYPKTS
Indicates the number of
mis-connected packets.
CES_MALPKTS
Indicates the number of
deformed frames.
CES_JTRUDR
Indicates the number of
jitter buffer underflows.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
695
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
Description
CES_JTROVR
Indicates the number of
jitter buffer overflows.
CES_LOSPKTS
Indicates the number of
lost packets.
CES_RX_PKTS
Indicates the number of
received packets.
PW
perfor
mance
of
ATM/
CES
PW_RCVPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets received from
PWs.
PW_RCVBYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes received from PWs.
L2VP
Na
perfor
mance
VLAN_RCVPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets received at the VUNI VLAN.
VLAN_RCVBYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes in the packets
received at the V-UNI
VLAN.
VUNI_RCVPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets received on the
V-UNI.
VUNI_RCVBYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes received on the VUNI.
TUNNEL_REVERSE_R
CVPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets received in the
reverse tunnel.
TUNNEL_REVERSE_R
CVBYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes received in the
reverse tunnel.
TUNNEL_RCVPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets received in the
tunnel.
TUNNEL_RCVBYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes received in the
tunnel.
Tunnel
perfor
mance
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
D RMON Event Reference
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
CSH
696
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
PW
perfor
mance
of
L2VP
N
ETHO
AM
802.1a
g
Port
traffic
classifi
cation
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Performance Name
D RMON Event Reference
Description
PW_RCVPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets received on the
PW.
PW_RCVBYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes received on the PW.
PW_DROPPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets discarded on the
PW.
ETH_CFM_FLR
Indicates the E_Line
service packet loss ratio.
ETH_CFM_FL
Indicates the number of
discarded E_Line service
packets.
ETH_CFM_FD
Indicates the E_Line
service delay.
ETH_CFM_FDV
Indicates the E_Line
service delay variation.
QOS_PORTCAR_MarkedRedPKTS
Indicates the number of
red packets after traffic
monitoring is enabled.
QOS_PORTCAR_MarkedYellowPKTS
Indicates the number of
yellow packets after
traffic monitoring is
enabled.
QOS_PORTCAR_MarkedGreenPKTS
Indicates the number of
green packets after traffic
monitoring is enabled.
QOS_PORTSTRM_RC
VMATCHPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets received in the
matched flow.
QOS_PORTSTRM_SN
DMATCHPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets transmitted in the
matched flow.
PORTSTRM_SHAPING
_DROPPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets discarded due to
network congestion when
the traffic shaping
function is enabled in the
egress direction.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
EM6T, EM6F, IFU2,
IFX2, ISU2, ISX2,
EM6FA, EM6TA
697
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
Port
priorit
y
Port
DS
domai
n
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
D RMON Event Reference
Performance Name
Description
PORTSTRM_SHAPING
_DROPRATIO
Indicates the ratio of
packet loss due to
network congestion when
the traffic shaping
function is enabled in the
egress direction.
QOS_PORTCAR_MarkedRedRATIO
Indicates the proportion
of packets marked in red
when the traffic policing
function is enabled.
QOS_PORTQUEUE_D
ROPRATIO
Indicates the ratio of
packet loss due to
congestion in egress
queues with different
priorities.
QOS_PRI_DROPPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets discarded in the
services with different
priorities.
QOS_PRI_DROPBYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes discarded in the
services with different
priorities.
PORT_PRI_SNDPKTS
Indicates the number of
packets transmitted in
egress queues with
different priorities.
PORT_PRI_SNDBYTE
S
Indicates the number of
bytes in the packets
transmitted in egress
queues with different
priorities.
DS_CVLANPRI_PKTS
Indicates the number of
packets with matched CVLAN priorities in the
DS domain
DS_CVLANPRI_BYTE
S
Indicates the number of
bytes in the packets with
matched C-VLAN
priorities in the DS
domain.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source
698
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Perfor
manc
e
Type
D RMON Event Reference
Performance Name
Description
DS_SVLANPRI_PKTS
Indicates the number of
packets with matched SVLAN priorities in the
DS domain.
DS_SVLANPRI_BYTE
S
Indicates the number of
bytes in the packets with
matched S-VLAN
priorities in the DS
domain.
DS_DSCP_PKTS
Indicates the number of
packets with matched IP
DSCP priorities in the DS
domain.
DS_DSCP_BYTES
Indicates the number of
bytes in the packets with
matched IP DSCP
priorities in the DS
domain.
Source
NOTE
l a: L2VPN services include a variety of E-Line and E-LAN services supported by the equipment.
l VUNI represents virtual UNI, represents the sink or source of services on the UNI side.
l The E-LAN services transmitted by the OptiX RTN 950 do not support the VUNI-based RMON performance
statistics.
l Integrated IP radio ports support this parameter.
D.3 List of RMON Performance Entries on the EoS/EoPDH
Plane
The ports that report RMON performance events on the EoPDH plane include PORT1 to PORT9,
and VCTRUNK1 to VCTRUNK16 on the EFP8 board. The ports that report RMON
performance events on the EoPDH plane include PORT1 to PORT8, and VCTRUNK1 to
VCTRUNK8 on the EMS6 board.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
699
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Table D-5 List of RMON performance entries on the EoS/EoPDH plane
Categ
ory of
Perfor
manc
e
Entrie
s
Basic
perfor
mance
Extend
ed
perfor
mance
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Brief Name of a
Performance Entry
Full Name of a
Performance Entry
ETHUNDER
Undersized packets
received (packets)
ETHFRG
Fragments received
(packets)
RXPKT64
Packets received (64
bytes in length) (packets)
RXPKT65
Packets received (65-127
bytes in length) (packets)
RXPKT128
Packets received
(128-255 bytes in length)
(packets)
RXPKT256
Packets received
(256-511 bytes in length)
(packets)
RXPKT512
Packets received
(512-1023 bytes in
length) (packets)
RXPKT1024
Packets received
(1024-1518 bytes in
length) (packets)
RXCTLPKTS
Control frames received
(frames)
TXOCTETS
Bytes transmitted (bytes)
TXPKTS
Packets transmitted
(packets)
TXCTLPKTS
Control frames
transmitted (frame)
TXPKT64
Packets transmitted (64
bytes in length) (packets)
TXPKT65
Packets transmitted
(65-127 bytes in length)
(packets)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source Port
PORT1 to PORT8 on the
EFP8 board
PORT1 to PORT6 on the
EMS6 board
PORT1 to PORT9 on the
EFP8 board
PORT1 to PORT7 on the
EMS6 board
PORT1 to PORT9 on the
EFP8 board
PORT1 to PORT7 on the
EMS6 board
700
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Categ
ory of
Perfor
manc
e
Entrie
s
VCG
perfor
mance
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Brief Name of a
Performance Entry
D RMON Event Reference
Full Name of a
Performance Entry
TXPKT128
Packets transmitted
(128-255 bytes in length)
(packets)
TXPKT256
Packets transmitted
(256-511 bytes in length)
(packets)
TXPKT512
Packets transmitted
(512-1023 bytes in
length) (packets)
TXPKT1024
Packets transmitted
(1024-1518 bytes in
length) (packets)
ETHALI
Alignment error frames
(frames)
PKT64
Packets received and
transmitted (64 bytes in
length) (packets)
PKT65
Packets received and
transmitted (65-127 bytes
in length) (packets)
PKT128
Packets received and
transmitted (128-255
bytes in length) (packets)
PKT256
Packets received and
transmitted (256-511
bytes in length) (packets)
PKT512
Packets received and
transmitted (512-1023
bytes in length) (packets)
PKT1024
Packets received and
transmitted (1024-1518
bytes in length) (packets)
VCG_TXGOODPACKETS
Good packets transmitted
(packets)
VCG_TXPACKETS
Packets transmitted
(packets)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Source Port
VCTRUNK1 to
VCTRUNK16 on the
EFP8 board
701
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Categ
ory of
Perfor
manc
e
Entrie
s
Brief Name of a
Performance Entry
D RMON Event Reference
Full Name of a
Performance Entry
VCG_TXOCTETS
Bytes transmitted (bytes)
VCG_RXGOODPACKETS
Good packets received
(packets)
VCG_RXPACKETS
Packets received
(packets)
VCG_RXOCTETS
Bytes received (bytes)
VCG_TXSPEED
Speed of bytes
transmitted (bytes)
VCG_RXSPEED
Speed of bytes received
(bytes)
Source Port
VCTRUNK1 to
VCTRUNK8 on the
EMS6 board
D.4 RMON Events and Handling Procedures
This chapter describes the RMON events that indicate Ethernet service abnormalities and how
to handle these events.
D.4.1 ETHDROP
Description
ETHDROP indicates the number of events in which packet loss occurs due to resource deficiency
of Ethernet chips. An RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the number of packet
loss events is higher than the upper threshold or lower than the lower threshold.
NOTE
ETHDROP counts only the packets that are lost due to resource deficiency of Ethernet chips.
Impact on System
When packet loss occurs frequently, services are affected and the system is affected seriously.
Hence, you must rectify the fault immediately.
Possible Causes
This performance event indicates packet loss due to the full MAC buffer, FIFO overflow, or
backward pressure.
l
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
The lower threshold is not set to a non-zero value.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
702
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
The hardware at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle this alarm according to the specific performance event.
If...
Then...
The number is lower than the lower
threshold
Change the lower threshold to 0.
The number is higher than the upper
threshold
Manually decrease the traffic transmitted from
the opposite end. If the problem persists, go to
the next step.
Step 2 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
D.4.2 ETHEXCCOL
Description
ETHEXCCOL indicates the number of frames that fail to be transmitted due to continuous port
collisions. An RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the number of frames that fail
to be transmitted is higher than the upper threshold or lower than the lower threshold. Generally,
the value indicates that 16 port collisions occur continuously when the same frame is transmitted.
Impact on System
The opposite equipment fails to normally receive services.
Possible Causes
Generally, this event is caused when the local port is connected to a large number of devices
that work in half-duplex mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle this alarm according to the specific performance event.
If...
Then...
The number is lower than the lower threshold
Change the lower threshold to 0.
The number is higher than the upper threshold
Go to the next step.
Step 2 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
703
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
If...
Then...
The ports on the equipment at both ends
work in inconsistent modes, or any port
works in half-duplex mode
Set the working modes of the ports on the
equipment at both ends to full-duplex or autonegotiation, so that these ports work in
consistent modes.
The ports on the equipment at both ends
Go to the next step.
work in consistent modes and no ports work
in half-duplex mode
Step 3 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
D.4.3 ETHLATECOL
Description
ETHLATECOL indicates the number of collisions detected within a timeslot period after a
packet is transmitted. An RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the number of
collisions is higher than the upper threshold or lower than the lower threshold.
Impact on System
The opposite equipment fails to normally receive services.
Possible Causes
Generally, this performance event is caused by a large network diameter.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle this alarm according to the specific performance event.
If...
Then...
The number is lower than the lower threshold
Change the lower threshold to 0.
The number is higher than the upper threshold
Go to the next step.
Step 2 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
If...
Then...
The ports on the equipment at both ends
work in inconsistent modes, or any port
works in half-duplex mode
Set the working modes of the ports on the
equipment at both ends to full-duplex or autonegotiation, so that these ports work in
consistent modes.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
704
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
If...
Then...
The ports on the equipment at both ends
Go to the next step.
work in consistent modes and no ports work
in half-duplex mode
Step 3 Check whether the network diameter of the LAN is very large according to the networking
planning information.
If...
Then...
The network diameter is very large
Divide the network and deploy equipment to
different buses or physically shared devices (such as
hubs).
NOTE
In the case of the 10 Mbit/s port rate, the maximum Ethernet
diameter is 2000 m. In the case of the 100 Mbit/s port rate,
the maximum Ethernet diameter is 200 m.
The network diameter is appropriate Go to the next step.
Step 4 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
D.4.4 RXBBAD
Description
RXBBAD indicates the total number of bytes in received bad packets, excluding the framing
bit but including the FCS byte. An RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the total
number of bytes in received bad packets is higher than the upper threshold or lower than the
lower threshold.
Impact on System
A port discards bad packets. This may even interrupt system services.
Possible Causes
1.
Errors occur when the opposite end transmits packets.
2.
The transmission line is of the poor quality and bit errors exist.
3.
The hardware at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle this alarm according to the specific performance event.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
705
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
If...
Then...
The number is lower than the lower threshold
Change the lower threshold to 0.
The number is higher than the upper threshold
Go to the next step.
Step 2 Correct the errors that occur when the opposite end transmits packets.
Step 3 Handle the problem of poor quality of the transmission line.
Check whether the ETH_LOS alarm is reported at the local end because the external line is
damaged or over attenuated. If yes, see the related handling method to clear the alarm.
Step 4 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
D.4.5 TXDEFFRM
Description
TXDEFFRM indicates the number of frames the first transmission of which is delayed due to
the congestion on the transmission media, excluding the number of frames the first transmission
of which is delayed due to collisions. An RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the
number of frames that fail to be transmitted is higher than the upper threshold and lower than
the lower threshold.
Impact on System
The rate of frame transmission decreases, and therefore packets are congested at a port and the
throughput of the port decreases.
Possible Causes
Generally, this event is caused when the external port at the local end is connected to a large
number of devices that work in half-duplex mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle this alarm according to the specific performance event.
If...
Then...
The number is lower than the lower threshold
Change the lower threshold to 0.
The number is higher than the upper threshold
Go to the next step.
Step 2 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
706
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
If...
Then...
The ports on the equipment at both ends
work in inconsistent modes, or any port
works in half-duplex mode
Set the working modes of the ports on the
equipment at both ends to full-duplex or autonegotiation, so that these ports work in
consistent modes.
The ports on the equipment at both ends
Go to the next step.
work in consistent modes and no ports work
in half-duplex mode
Step 3 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
D.4.6 ETHUNDER
Description
ETHUNDER indicates that an RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the number of
packets that are shorter than 64 bytes and are received on the line side crosses the preset threshold.
Impact on System
The data frames whose length is not within the specific range are discarded. As a result, the
system services are affected.
Possible Causes
1.
The length of a data frame that is received at a port is shorter than 64 bytes.
2.
The hardware at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the opposite equipment transmits the packet that is shorter than 64 bytes.
If...
Then...
The opposite equipment transmits the packet Rectify the fault on the opposite equipment.
that is shorter than 64 bytes
The opposite end does not transmit the
packet that is shorter than 64 bytes
Go to the next step.
Step 2 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
707
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
D.4.7 ETHOVER
Description
ETHOVER indicates that an RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the number of
packets that are longer than 1518 bytes and are received at a port crosses the preset threshold.
Impact on System
If the length of the data frame received at a port is more than the preset maximum frame length,
the data frame is discarded and therefore the system services are affected.
Possible Causes
1.
The preset maximum frame length is less than the length of the frame that is received at a
port.
2.
The hardware at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the opposite equipment transmits the packet that is longer than the maximum
frame length set for the local equipment.
If...
Then...
The opposite equipment transmits the
packet that is longer than the maximum
frame length set for the local equipment
Notify the opposite equipment that the length
of transmitted frames should be changed.
The opposite equipment does not transmit Go to the next step.
the packet that is longer than the maximum
frame length set for the local equipment
Step 2 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
D.4.8 ETHFRG
Description
ETHFRG indicates that an RMON threshold-crossing event is reported when the number of
received packets that are shorter than 64 bytes and have FCS or alignment errors exceeds the
preset upper threshold.
Impact on System
Data transmission is delayed or packet loss occurs.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
708
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Possible Causes
l
The working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends are not consistent.
The hardware at the local end is faulty.
The ports on the equipment at both ends work in half-duplex mode, and the data traffic is
very heavy.
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends are consistent.
If...
Then...
The working modes are consistent
Go to the next step.
The working modes are not consistent Change the working mode of the local port so that
the ports on the equipment at both ends work in
consistent modes.
Step 2 Check whether the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends are set to the halfduplex mode.
If...
Then...
The working modes are not set to the half- Go to the next step.
duplex mode
The working modes are set to the halfduplex mode
Change the working modes of the ports on the
equipment at both ends to the full-duplex mode
or adaptive mode.
Step 3 Replace the involved part.
----End
D.4.9 ETHJAB
Description
ETHJAB indicates that an RMON threshold-crossing alarm is reported when the number of
received packets that are longer than 1518 bytes and have FCS or alignment errors is higher than
the upper threshold.
Impact on the System
Data transmission is delayed or packet loss occurs.
Possible Causes
l
The working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends are not consistent.
The hardware at the local end is faulty.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
709
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Procedure
Step 1 Check whether the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends are consistent.
If...
Then...
The working modes are consistent
Go to the next step.
The working modes are not consistent Change the working mode of the local port so that
the ports on the equipment at both ends work in
consistent modes.
Step 2 Replace the involved part.
----End
D.4.10 ETHCOL
Description
ETHCOL indicates the number of detected packet collisions. An RMON threshold-crossing
event is reported when the number of collisions is higher than the upper threshold or lower than
the lower threshold.
Impact on System
The opposite equipment fails to normally receive services.
Possible Causes
Generally, this event is caused when the local port is connected to a large number of devices
that work in half-duplex mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle this alarm according to the specific performance event.
If...
Then...
The number is lower than the lower threshold
Change the lower threshold to 0.
The number is higher than the upper threshold
Go to the next step.
Step 2 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
If...
Then...
The ports on the equipment at both ends
work in inconsistent modes, or any port
works in half-duplex mode
Set the working modes of the ports on the
equipment at both ends to full-duplex or autonegotiation, so that these ports work in
consistent modes.
The ports on the equipment at both ends
Go to the next step.
work in consistent modes and no ports work
in half-duplex mode
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
710
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Step 3 Replace the involved part.
----End
Reference
None.
D.4.11 ETHFCS
Description
ETHFCS indicates the number of received Ethernet data frames with FCS check errors at the
local end (excluding the oversized and undersized frames). An RMON threshold-crossing event
is reported when the number is higher than the upper threshold or lower than the lower threshold.
Impact on System
Most ports discard the packets with FCS check errors. The system services are interrupted in
the worst case.
Possible Causes
1.
The local port and opposite port work in inconsistent modes. For example, one port works
in full-duplex mode, and the opposite port works in half-duplex mode.
2.
The transmission line is of the poor quality and bit errors exist.
3.
The hardware at the local end is faulty.
Procedure
Step 1 Therefore, handle the alarm according to the specific performance event.
If...
Then...
The number is lower than the lower threshold
Change the lower threshold to 0.
The number is higher than the upper threshold
Go to the next step.
Step 2 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
If...
Then...
The ports on the equipment at both ends
work in inconsistent modes
Change the working modes of the ports on the
equipment at both ends so that they can work
in consistent modes
The ports on the equipment at both ends
work in consistent modes
Go to the next step.
Step 3 Replace the involved part.
----End
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
711
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Reference
None.
D.4.12 ATMPW_LOSPKTS
Description
The ATMPW_LOSPKTS is a performance event indicating the number of lost ATM PW
packets.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
1.
Signals on the radio link deteriorate.
2.
A strong interference source is present near the equipment.
3.
A board at the transmit or receive end is faulty.
4.
The operating temperature of the equipment is very high.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle the fault on the radio link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Remove the interference source near the equipment and then check whether the performance
event is cleared.
Step 3 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
Step 4 Replace the faulty board and then check whether the performance event is cleared.
Step 5 Rectify the fault in the fan so that the fan lowers the operating temperature of the equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.13 ATMPW_MISORDERPKTS
Description
The ATMPW_MISORDERPKTS is a performance event indicating the number of disordered
ATM PW packets.
Impact on the System
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
712
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Possible Causes
1.
Signals on the radio link deteriorate.
2.
A strong interference source is present near the equipment.
3.
A board at the transmit or receive end is faulty.
4.
The operating temperature of the equipment is very high.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle the fault on the radio link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Remove the interference source near the equipment and then check whether the performance
event is cleared.
Step 3 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
Step 4 Replace the faulty board and then check whether the performance event is cleared.
Step 5 Rectify the fault in the fan so that the fan lowers the operating temperature of the equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.14 ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELLS
Description
The ATMPW_UNKNOWNCELLS a performance event indicating the number of unknown
cells in an ATM PW service.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
1.
Signals on the radio link deteriorate.
2.
A strong interference source is present near the equipment.
3.
A board at the transmit or receive end is faulty.
4.
The operating temperature of the equipment is very high.
Procedure
Step 1 Handle the fault on the radio link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Remove the interference source near the equipment and then check whether the performance
event is cleared.
Step 3 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
713
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Step 4 Replace the faulty board and then check whether the performance event is cleared.
Step 5 Rectify the fault in the fan so that the fan lowers the operating temperature of the equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.15 ATM_CORRECTED_HCSERR
Description
The ATM_CORRECTED_HCSERR is a performance event indicating the number of cells that
are received by an ATM port and contain correctable header check sequence (HCS) errors.
Impact on the System
None.
Possible Causes
1.
A strong interference source is present near the equipment.
2.
A board at the transmit or receive end is faulty.
3.
The operating temperature of the equipment is very high.
Procedure
Step 1 Remove the interference source near the equipment and then check whether the performance
event is cleared.
Step 2 On the NMS, query the working modes of the ports on the equipment at both ends.
Step 3 Replace the faulty board and then check whether the performance event is cleared.
Step 4 Rectify the fault in the fan so that the fan lowers the operating temperature of the equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.16 ATM_UNCORRECTED_HCSERR
Description
The ATM_UNCORRECTED_HCSERR is a performance event indicating the number of cells
that are received by an ATM port and contain uncorrectable header check sequence (HCS) errors.
Impact on the System
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
714
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Possible Causes
1.
Signals on the radio link deteriorate.
2.
A strong interference source is present near the equipment.
3.
A board at the transmit or receive end is faulty.
4.
The operating temperature of the equipment is very high.
Procedure
Step 1 Refer to 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link and handle the fault on the radio link.
Step 2 Remove the interference source near the equipment and then check whether the performance
event is cleared.
Step 3 Replace the faulty board and then check whether the performance event is cleared.
Step 4 Rectify the fault in the fan so that the fan lowers the operating temperature of the equipment.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.17 CES_MISORDERPKTS
Description
The CES_MISORDERPKTS is a performance event indicating the count of lost disordered CES
PW packets.
Impact on the System
The packets are disordered. As a result, the packet loss rate increases and services are affected.
Possible Causes
1.
Signals degrade on the link.
2.
The link is looped.
3.
The link is congested.
Related Alarms
CES_MISORDERPKT_EXC
Procedure
Step 1 See 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Release the loop.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
715
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Step 3 Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.18 CES_STRAYPKTS
Description
The CES_STRAYPKTS is a performance event indicating the number of misconnected packets
in a period.
Impact on the System
The packets are discarded. As a result, the packet loss rate increases and services are affected.
Possible Causes
1.
Links are misconnected.
Related Alarms
CES_STRAYPKT_EXC
Procedure
Step 1 Check the link configuration and rectify the fault.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.19 CES_MALPKTS
Description
The CES_MALPKTS is a performance event indicating the number of deformed CES packets
in a period.
Impact on the System
The packets are discarded. As a result, the packet loss rate increases and services are affected.
Possible Causes
1.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
The RTP head enabling status is different between the two ends of the PW.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
716
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
2.
D RMON Event Reference
Bit errors occur on the link.
Related Alarms
CES_MALPKT_EXC
Procedure
Step 1 Set the RTP head enabling status to the same on the two ends of the PW. For details, see
Modifying CES Service Parameters.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.20 CES_JTRUDR
Description
The CES_JTRUDR is a performance event indicating the number of jitter buffer underflows.
Impact on the System
When no packets are transmitted from the jitter buffer, the buffer underflows.
Possible Causes
1.
Signals degrade on the link.
2.
The PSN network clocks used for the transmission of CES services are not synchronized.
3.
The link is looped.
4.
The link is congested.
5.
The size of buffer area is set to a low value.
Related Alarms
CES_JTRUDR_EXC
Procedure
Step 1 Troubleshoot the link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Synchronize the PSN network clock by setting clock synchronization, reducing transmission
nodes, and optimizing transmission routes.
Step 3 Release the loop.
Step 4 Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
Step 5 Query the size of buffer area. For details, see Querying CES Service Information.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
717
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Step 6 Determine whether the size can be increased according to network planning. If yes, change the
size to a greater value. For details, see Managing CES Services.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.21 CES_JTROVR
Description
The CES_JTROVR is a performance event indicating the number of jitter buffer overflows.
Impact on the System
The jitter buffer is insufficient. As a result, the buffer overflows.
Possible Causes
1.
The jitter buffer area is too small.
2.
The clocks are not synchronous.
3.
Link quality deteriorates, causing more jitters.
4.
There are too many hops of radio link on the network side, causing a large number of jitters.
Related Alarms
CES_JTROVR_EXC
Procedure
Step 1 Allocate a larger jitter buffer area.
Step 2 Check whether the LTI and other clock-related alarms are reported.
Step 3 Handle the fault on the radio link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 4 Determine whether the hops can be reduced according to network planning. If yes, reduce the
hops of radio link on the network side.
----End
Related Information
None.
D.4.22 CES_LOSPKTS
Description
The CES_LOSPKTS is a performance event indicating the number of CES packets lost in a
period.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
718
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
D RMON Event Reference
Impact on the System
When this alarm occurs, all 1s are inserted and services are interrupted.
Possible Causes
1.
The link transmission quality is poor.
2.
The link is configured as a loop.
3.
Link congestion occurs.
Related Alarms
CES_LOSPKT_EXC
Procedure
Step 1 Handle the fault on the radio link. For details, see 5.3 Troubleshooting the Radio Link.
Step 2 Release the loop.
Step 3 Check the bandwidth utilization. If the bandwidth is exhausted, increase the bandwidth or
eliminate any source that transmits a large amount of invalid data.
----End
Related Information
None.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
719
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
E Alarm Management
Alarm Management
The alarm management on the OptiX RTN 950 is classified into the NE alarm management and
board alarm management.
E.1 NE Alarm Management
The NE alarm management function set by user is applicable to all the boards on the NE.
E.2 Board Alarm Management
The board alarm management function is only applicable to the board on which users have
configured this function.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
720
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
E Alarm Management
E.1 NE Alarm Management
The NE alarm management function set by user is applicable to all the boards on the NE.
The equipment supports the following NE alarm management functions:
l
Settings of the alarm storage mode
Setting of the alarm delay
Setting of the alarm reversion mode
For details about these functions, see the manuals or online Help of the NMS.
E.2 Board Alarm Management
The board alarm management function is only applicable to the board on which users have
configured this function.
E.2.1 Setting the Alarm Severity
Alarms are classified into four levels: critical, major, minor, and warning, according to their
severities. The maintenance personnel can change the alarm severity by using the NMS.
This function is supported by all the boards.
l
Critical alarm: A critical alarm indicates a critical problem with the network. A critical
problem can be the failure, overload, or system restart of mission-critical boards. It must
be cleared immediately. Otherwise, system breakdown may occur.
Major alarm: A major alarm indicates failure of certain boards or links, such as
communication links. Urgent action is required to rectify the fault as this type of alarms
affects the QoS of the system.
Minor alarm: A minor alarm indicates a non-service affecting problem that needs to be
solved, for example, fan speed exceeds threshold alarm. This type of alarms does not affect
the QoS of the system, but you need to locate and remove these faults in time.
Warning alarm: A warning alarm indicates a potential error that may affect the QoS of the
system, for example, License file expiring precaution alarm. This type of alarms needs to
be handled based on actual conditions.
Critical alarms and major alarms need to be handled immediately to avoid system failures and
service interruptions.
E.2.2 Alarm Suppression
The maintenance personnel can change the alarm monitoring attribute by setting the alarm
suppression function. A board detects only the alarms that are not suppressed. The alarm
suppression function helps users to ignore their unconcerned alarms.
This function is supported by all the boards.
E.2.3 Alarm Auto-Report
If Alarm Auto-Report is set to Reported, all the detected alarms are reported to the NMS in a
timely manner. If Alarm Auto-Report is set to Not Report, the alarms are reported only when
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
721
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
E Alarm Management
alarm query is performed on the NMS. The maintenance personnel can change the setting on
the NMS.
This function is supported by all the boards.
E.2.4 Alarm Reversion
In the case of a port that is not configured with services, certain alarms may be reported. To filter
the alarms that users are not concerned, set these alarms to be reversed. In this manner, the alarm
status at this port is the opposite to the actual case. That is, the status is displayed as normal
when an alarm is actually reported.
The alarm reversion function is available in three modes, namely, non-reversion, automatic
reversion, and manual reversion.
l
Non-revertive
In this mode, the alarms are monitored by default and alarm reversion cannot be enabled
for a port.
Auto reversion
In this mode, alarm reversion can be enabled for a port where alarms are reported. After
alarm reversion is enabled at a port, alarms are not reported. When the current alarm is
cleared, the alarm reversion automatically changes to the disabled status. That is, it changes
to the non-reversion mode. Then, the alarm reporting status at the port is the same as the
actual status.
Manual reversion
In this mode, alarm reversion can be enabled for a port regardless of whether any alarms
are reported at the port. After alarm reversion is enabled, the alarm reporting status at the
port is opposite to the actual status. After alarm reversion is manually disabled, the alarm
reversion status changes to the non-reversion mode. Then, the alarm reporting status at the
port is the same as the actual status.
Pay attention to the following points when you set the alarm reversion function:
l
Alarm reversion does not change the actual status of alarms on the board, as well as the
indication status of the alarm indicators.
Alarm reversion is realized on the NE software. The alarm data is the same on the NE and
the NMS, which indicates the status after the alarm reversion. If you directly query the
alarm data of a board, however, the actual alarm status is returned.
Alarm reversion is set based on ports. It is supported by each port on the SL1D, SP3S,
SP3D, IFX2, IFU2, IF1, ISU2, ISX2, EM6TA, EM6FA, SL1DA, EM6T, and EM6F boards.
E.2.5 Setting of the Bit Error Alarm Threshold
When the number of bit errors detected by a board exceeds a specified number, the board
generates a bit error alarm. This specific number is the bit error alarm threshold, and the setting
of this threshold is supported by all the bit error threshold-crossing and degrading alarms on the
NE.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
722
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
E Alarm Management
Table E-1 Setting of the bit error alarm threshold
Alarm Name
Default Alarm Threshold
Applicable Board
B1_EXC
10-3
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
B1_SD
10-6
B2_EXC
10-3
B2_SD
10-6
B3_EXC
10-3
B3_SD
10-6
BIP_EXC
10-3
BIP_SD
10-6
MW_BER_EXC
10-3
MW_BER_SD
10-6
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
ISU2, ISX2, EFP8, EMS6,
SP3S, SP3D, IFU2, and IFX2
ISU2, ISX2, IFU2 and IFX2
E.2.6 AIS Insertion
AIS insertion can be set for certain alarms reported on a board. When the board detects the
alarms, it inserts all 1s into the lower level service to indicate the remote end that the service is
unavailable.
Table E-2 Setting of the AIS insertion
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Trigger Condition
Default Value
Applicable Board
B1_EXC
Enabled
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
B2_SD
Disabled
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
B2_EXC
Disabled
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
HP_LOM
Enabled
HP_TIM
Disabled
HP_SLM
Disabled
HP_UNEQ
Disabled
B3_EXC
Enabled
B3_SD
Disabled
B1_SD
Disabled
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
LP_TIM
Disabled
SP3S and SP3D
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
SL1DA, SL1D and IF1
723
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
E Alarm Management
Trigger Condition
Default Value
LP_UNEQ
Disabled
LP_SLM
Disabled
T_ALOS
Enabled
BIP_EXC
Disabled
BIP_SD
Disabled
MW_BER_EXC
Enabled
MW_BER_SD
Disabled
Applicable Board
ISU2, ISX2, IFX2 and IFU2
NOTE
l When the SL1D/SL1DA, board detects the R_LOS, R_LOF, MS_AIS, AU_AIS, or AU_LOP alarm,
it forcibly inserts the AIS.
l When the IF1 board detects the MW_LOF, MW_LIM, R_LOF, MS_AIS, AU_AIS, or AU_LOP
alarm, it forcibly inserts the AIS.
l When the ISU2, ISX2, IFX2 and IFU2 board detect the MW_LOF, MW_LIM, or R_LOF alarm, it
forcibly inserts the AIS.
E.2.7 UNEQ Insertion
When a board detects that the service path is not in use or that the LOS alarm exists, it inserts
all 0s into the service signal to notify the remote end that this signal is unavailable.
Table E-3 Setting of the UNEQ insertion
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Trigger Condition
Default Value
Applicable Board
T_ALOS
Disabled
SP3S and SP3D
Service path being not in use
Disabled
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
724
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
F Performance Event Management
Performance Event Management
The performance event management is classified into the NE performance event management
and board performance event management.
F.1 NE Performance Event Management
The NE performance event management function set by user is applicable to all the boards on
the NE.
F.2 Board Performance Event Management
The performance event management function is only applicable to the board on which users
have configured this function.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
725
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
F Performance Event Management
F.1 NE Performance Event Management
The NE performance event management function set by user is applicable to all the boards on
the NE.
The OptiX RTN 950 supports the following NE performance event management functions:
l
Setting NE performance event monitoring
Setting the start/end time of performance events
Enabling/Disabling the reporting of UAT events
For details about these functions, see the manuals or online Help of the NMS.
F.2 Board Performance Event Management
The performance event management function is only applicable to the board on which users
have configured this function.
Table F-1 Board performance event management function
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Function
Applicable Board
Setting 15-minute/24hour performance
monitoring
SL1DA, EMS6, SL1D, SP3S, SP3D, CSH, ODU, IFX2, IFU2,
ISU2, ISX2, ML1, MD1, EFP8, and IF1
Setting 15-minute/24hour performance event
auto-reporting
SL1DA, EMS6, SL1D, SP3S, SP3D, CSH, CST, ODU, IFX2,
IFU2, ISU2, ISX2, ML1, MD1, EFP8, and IF1
Setting performance
thresholds
SL1DA, EMS6, SL1D, SP3S, SP3D, IFX2, IFU2, ISU2, ISX2,
ML1, MD1, EFP8, and IF1
Resetting the
performance register
SL1DA, SL1D, SP3S, SP3D, ODU, IFX2, IFU2, ISU2, ISX2, and
IF1
Generating performance
threshold-crossing
alarms
SL1DA, EMS6, SL1D, SP3S, SP3D, ODU, IFX2, IFU2, ISU2,
ISX2, ML1, MD1, EFP8, and IF1
Monitoring UAT events
SL1DA, EMS6, SL1D, SP3S, SP3D, IFX2, IFU2, ISU2, ISX2,
EFP8, and IF1
Monitoring CSES
performance events
SL1DA, EMS6, SL1D, SP3S, SP3D, IFX2, IFU2, ISU2, ISX2,
EFP8, and IF1
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
726
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
G Alarm Suppression Relationship
Alarm Suppression Relationship
When the alarm suppression function is disabled on an NE, the root alarm and certain correlated
alarms are reported if a fault occurs on this NE. After the alarm suppression function is enabled,
the reporting of the correlated alarms is suppressed according to the relationship between alarms
when the root alarm is reported. The alarm suppression relationship can be classified into the
suppression relationship between intra-board alarms and suppression relationship between interboard alarms.
Table G-1 Suppression relationship between intra-board alarms
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Alarm Identifier
Identifier of the Suppressed Alarm
MW_LOF
R_LOS, R_LOF, R_LOC,
MW_FEC_UNCOR, MW_RDI,
MW_LIM, MS_AIS, B1_EXC, B1_SD,
MS_RDI, B2_EXC, B2_SD, MS_REI,
AU_AIS, AU_LOP, B3_EXC, B3_SD,
HP_TIM, HP_UNEQ, HP_SLM,
HP_RDI, HP_LOM, HP_REI,
MW_BER_EXC, and MW_BER_SD
MW_LIM
MW_RDI
MW_BER_EXC
MW_BER_SD
LSR_NO_FITED
R_LOS, R_LOC, R_LOF, J0_MM,
B1_EXC, B1_SD, MS_AIS, MS_RDI,
B2_EXC, B2_SD, MS_REI, AU_AIS,
AU_LOP, HP_TIM, HP_UNEQ,
HP_SLM, HP_RDI, B3_EXC, B3_SD,
HP_LOM, HP_REI, IN_PWR_LOW,
MW_RDI, and MW_LIM
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
727
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
G Alarm Suppression Relationship
Alarm Identifier
Identifier of the Suppressed Alarm
R_LOS or R_LOC
R_LOF, J0_MM, B1_EXC, B1_SD,
MS_AIS, MS_RDI, B2_EXC, B2_SD,
MS_REI, AU_AIS, AU_LOP, HP_TIM,
HP_UNEQ, HP_SLM, HP_RDI, B3_EXC,
B3_SD, HP_LOM, HP_REI,
IN_PWR_LOW, MW_RDI, and
MW_LIM
R_LOF
J0_MM, B1_EXC, B1_SD, MS_AIS,
MS_RDI, B2_EXC, B2_SD, MS_REI,
AU_AIS, AU_LOP, HP_TIM, HP_UNEQ,
HP_SLM, HP_RDI, B3_EXC, B3_SD,
HP_LOM, HP_REI, MW_RDI,
MW_LIM, MW_BER_EXC, and
MW_BER_SD
MS_AIS
B2_SD, MS_REI, MS_RDI, AU_AIS,
AU_LOP, HP_TIM, HP_UNEQ,
HP_SLM, HP_RDI, B3_EXC, B3_SD,
HP_LOM, HP_REI, and B2_EXC
MS_RDI
MS_REI
AU_AIS
AU_LOP, B3_EXC, B3_SD, HP_TIM,
HP_SLM, HP_UNEQ, HP_RDI,
HP_LOM, and HP_REI
AU_LOP
B3_EXC, B3_SD, HP_TIM, HP_SLM,
HP_UNEQ, HP_RDI, HP_LOM, and
HP_REI
HP_UNEQ
HP_TIM, HP_LOM, and HP_RDI
HP_RDI
HP_REI
LP_UNEQ
LP_TIM, LP_RDI, LP_RFI, LP_REI,
BIP_SD, and BIP_EXC
LP_RDI
LP_REI
B1_EXC
B1_SD, and MS_REI
B2_EXC
B2_SD, and MS_REI
B3_EXC
B3_SD
TU_AIS
LP_TIM, LP_UNEQ, LP_RDI, LP_REI,
LP_RFI, LP_R_FIFO, BIP_EXC,
BIP_SD, LP_SLM, TU_LOP, and
DOWN_E1_AIS
TU_LOP
LP_TIM, LP_UNEQ, LP_RDI, LP_REI,
LP_RFI, LP_R_FIFO, BIP_EXC,
BIP_SD, LP_SLM, and DOWN_E1_AIS
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
728
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
G Alarm Suppression Relationship
Alarm Identifier
Identifier of the Suppressed Alarm
T_ALOS
E1_LOS, DDN_LFA and UP_E1_AIS
E1_LOS
UP_E1_AIS
BIP_EXC
BIP_SD
LASER_MOD_ERR
ETH_LOS
UP_E1_AIS
LFA, DDN_LFA, and ALM_E1RAI
LFA
LMFA, ALM_IMA_LIF, and
ALM_E1RAI
LMFA
ALM_IMA_LIF
ALM_E1RAI
ALM_IMA_RFI, and
ALM_IMA_RE_RX_UNUSABLE
ETH_EFM_DF
ETH_EFM_REMFAULT
ETH_EFM_REMFAULT
ETH_EFM_EVENT
ALM_IMA_LIF
ALM_IMA_LODS
IMA_GROUP_LE_DOWN
VC_LOC, and VP_LOC
MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
MPLS_TUNNEL_UNKNOWN,
MPLS_TUNNEL_Excess, and
MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
MPLS_TUNNEL_SF
MPLS_TUNNEL_SD
MPLS_TUNNEL_FDI
MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
ETH_APS_PATH_MISMATCH
ETH_APS_LOST,
ETH_APS_TYPE_MISMATCH, and
ETH_APS_SWITCH_FAIL
ETH_APS_LOST
ETH_APS_TYPE_MISMATCH, and
ETH_APS_SWITCH_FAIL
MPLS_PW_LOCV
MPLS_PW_UNKNOWN,
MPLS_PW_Excess, and MPLS_PW_SF
MPLS_PW_SF
MPLS_PW_SD
PWAPSAPS_PATH_MISMATCH
PWAPS_LOST, PWAPS_TYPE_MISMATCH, and PWAPS_SWITCH_FAIL
PWAPS_LOST
PWAPS_TYPE_MISMATCH, and
PWAPS_SWITCH_FAIL
ETH_CFM_MISMERGE
ETH_CFM_LOC
CES_LOSPKT_EXC
CES_STRAYPKT_EXC,
CES_JTROVR_EXC, and
CES_JTRUDR_EXC
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
729
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
G Alarm Suppression Relationship
Alarm Identifier
Identifier of the Suppressed Alarm
CES_STRAYPKT_EXC
CES_MISORDERPKT_EXC, and
CES_MALPKT_EXC
PG_LINK_FAIL
PG_PRT_DEGRADED
Table G-2 Suppression relationship between intra-board alarms
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Alarm Identifier
Identifier of the Suppressed Alarm
R_LOS, R_LOC, MS_AIS, AU_AIS, or
AU_LOP
TU_AIS
MW_LOF or MW_LIM
TU_AIS
ETH_LOS
MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV,
MPLS_TUNNEL_OAMFAIL
MPLS_TUNNEL_LOCV
MPLS_PW_LOCV
MPLS_TUNNEL_BDI
MPLS_PW_BDI
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
730
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Indicators of Boards
Indicators of Boards
Table H-1 Status explanation for indicators on the CST
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the
board.
PROG
Blinks on (green) and off at
100 ms intervals
Software is being loaded to the board
during the power-on or resetting process
of the board.
Blinks on (green) and off at
300 ms intervals
The board software is in BIOS boot state
during the power-on or resetting process
of the board.
On (green)
l When the board is being powered on
or being reset, the upper layer
software is being initialized.
l When the board is running, the
software is running normally.
Blinks on (red) and off at
100 ms intervals
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
The BOOTROM self-check fails during
the power-on or resetting process of the
board.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
731
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
On (red)
l The memory self-check fails or
loading upper layer software fails
during the power-on or resetting
process of the board.
l The logic file or upper layer software
is lost during the running process of
the board.
l The pluggable storage card is faulty.
SYNC
SRV
On (green)
The clock is working properly.
On (red)
The clock source is lost or a clock
switchover occurs.
On (green)
The system is working properly.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
system.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm occurs in the
system.
Off
In an unprotected system, there is no
power supplied to the system.
In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the standby one.
ACT
On (green)
In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the active one.
In an unprotected system, the board has
been activated.
Off
In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the standby one.
In an unprotected system, the board is not
activated.
Table H-2 Status explanation for indicators on the CSH
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the
board.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
732
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Indicator
State
Meaning
PROG
Blinks on (green) and off at
100 ms intervals
Software is being loaded to the board
during the power-on or resetting process
of the board.
Blinks on (green) and off at
300 ms intervals
The board software is in BIOS boot state
during the power-on or resetting process
of the board.
On (green)
l When the board is being powered on
or being reset, the upper layer
software is being initialized.
l When the board is running, the
software is running normally.
Blinks on (red) and off at
100 ms intervals
The BOOTROM self-check fails during
the power-on or resetting process of the
board.
On (red)
l The memory self-check fails or
loading upper layer software fails
during the power-on or resetting
process of the board.
l The logic file or upper layer software
is lost during the running process of
the board.
l The pluggable storage card is faulty.
SYNC
SRV
On (green)
The clock is working properly.
On (red)
The clock source is lost or a clock
switchover occurs.
On (green)
The system is working properly.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
system.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm occurs in the
system.
Off
In an unprotected system, there is no
power supplied to the system.
In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the standby one.
ACT
On (green)
In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the active one.
In an unprotected system, the board has
been activated.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
733
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
Off
In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the standby one.
In an unprotected system, the board is not
activated.
Table H-3 Status explanation for indicators on the IF1
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working
properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power
supplied to the board.
SRV
LINK
ODU
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm
occurs in the services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm
occurs in the services.
On (green)
The radio link is normal.
On (red)
The radio link is faulty.
On (green)
The ODU is working
properly.
On (red)
l The ODU is reporting
critical or major alarms.
l There is no power
supplied to the ODU.
RMT
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
On (yellow)
The ODU is reporting minor
alarms.
Blinks on (yellow) and off at
300 ms intervals
The antennas are not aligned.
On (yellow)
The remote equipment is
reporting defects.
Off
The remote equipment is free
of defects.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
734
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Indicator
State
Meaning
ACT
On (green)
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
active one.
l In an unprotected system,
the board has been
activated.
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
standby one.
Off
l In an unprotected system,
the board is not activated.
Table H-4 Status explanation for indicators on the IFU2
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the board.
SRV
LINK
ODU
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm occurs in the
services.
On (green)
The radio link is normal.
On (red)
The radio link is faulty.
On (green)
The ODU is working properly.
On (red)
l The ODU is reporting critical or major
alarms.
l There is no power supplied to the ODU.
RMT
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
On (yellow)
The ODU is reporting minor alarms.
Blinks on (yellow)
and off at 300 ms
intervals
The antennas are not aligned.
On (yellow)
The remote equipment is reporting defects.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
735
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
ACT
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
Off
The remote equipment is free of defects.
On (green)
l In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the active one.
l In an unprotected system, the board has
been activated.
l In a 1+1 protected system, the board
works as the standby one.
Off
l In an unprotected system, the board is not
activated.
Table H-5 Status explanation for indicators on the ISU2
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working
properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power
supplied to the board.
SRV
LINK
ODU
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm
occurs in the services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm
occurs in the services.
On (green)
The radio link is normal.
On (red)
The radio link is faulty.
On (green)
The ODU is working
properly.
On (red)
l The ODU is reporting
critical or major alarms.
l There is no power
supplied to the ODU.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
On (yellow)
The ODU is reporting minor
alarms.
Blinks on (yellow) and off at
300 ms intervals
The antennas are not aligned.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
736
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Indicator
State
Meaning
RMT
On (yellow)
The remote equipment is
reporting defects.
Off
The remote equipment is free
of defects.
On (green)
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
active one.
ACT
l In an unprotected system,
the board has been
activated.
Off
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
standby one.
l In an unprotected system,
the board is not activated.
Table H-6 Status explanation for indicators on the IFX2
Indicator
State
Meaning
XPIC
On (green)
The XPIC input signal is
normal.
On (red)
The XPIC input signal is lost.
Off
The XPIC function is
disabled.
On (green)
The board is working
properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
STAT
l The board is not created.
l There is no power
supplied to the board.
SRV
LINK
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm
occurs in the services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm
occurs in the services.
On (green)
The radio link is normal.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
737
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
ODU
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
On (red)
The radio link is faulty.
On (green)
The ODU is working
properly.
On (red)
l The ODU is reporting
critical or major alarms.
l There is no power
supplied to the ODU.
RMT
ACT
On (yellow)
The ODU is reporting minor
alarms.
Blinks on (yellow) and off at
300 ms intervals
The antennas are not aligned.
On (yellow)
The remote equipment is
reporting defects.
Off
The remote equipment is free
of defects.
On (green)
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
active one.
l In an unprotected system,
the board has been
activated.
Off
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
standby one.
l In an unprotected system,
the board is not activated.
Table H-7 Status explanation for indicators on the ISX2
Indicator
State
Meaning
XPIC
On (green)
The XPIC input signal is
normal.
On (red)
The XPIC input signal is lost.
Off
The XPIC function is
disabled.
On (green)
The board is working
properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
STAT
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
738
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power
supplied to the board.
SRV
LINK
ODU
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm
occurs in the services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm
occurs in the services.
On (green)
The radio link is normal.
On (red)
The radio link is faulty.
On (green)
The ODU is working
properly.
On (red)
l The ODU is reporting
critical or major alarms.
l There is no power
supplied to the ODU.
RMT
ACT
On (yellow)
The ODU is reporting minor
alarms.
Blinks on (yellow) and off at
300 ms intervals
The antennas are not aligned.
On (yellow)
The remote equipment is
reporting defects.
Off
The remote equipment is free
of defects.
On (green)
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
active one.
l In an unprotected system,
the board has been
activated.
Off
l In a 1+1 protected system,
the board works as the
standby one.
l In an unprotected system,
the board is not activated.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
739
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Table H-8 Status explanation for indicators on the EM6T/EM6F
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the board.
SRV
PROG
On (green)
The system is working properly.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
system.
On (yellow)
A minor alarm occurs in the system.
Off
There is no power supplied to the system.
Blinks on (green) and off at
100 ms intervals
Software is being loaded to the board during
the power-on or resetting process of the
board.
Blinks on (green) and off at
300 ms intervals
The board software is in BIOS boot state
during the power-on or resetting process of
the board.
On (green)
l When the board is being powered on or
being reset, the upper layer software is
being initialized.
l When the board is running, the software
is running normally.
Blinks on (red) and off at 100
ms intervals
The BOOTROM self-check fails during the
power-on or resetting process of the board.
On (red)
l The memory self-check fails or loading
upper layer software fails during the
power-on or resetting process of the
board.
l The logic file or upper layer software is
lost during the running process of the
board.
l The pluggable storage card is faulty.
LINK1a
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
On (green)
The GE1 port is connected correctly and is
not receiving or transmitting data.
Blinking (green)
The GE1 port is receiving or transmitting
data.
Off
The GE1 port is not connected or is
connected incorrectly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
740
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Indicator
State
Meaning
LINK2a
On (green)
The GE2 port is connected correctly and is
not receiving or transmitting data.
Blinking (green)
The GE2 port is receiving or transmitting
data.
Off
The GE2 port is not connected or is
connected incorrectly.
NOTE
a: The LINK1 and LINK2 indicators are available only on the EM6F and indicate the states of the
corresponding GE ports.
Table H-9 Status explanation for indicators on the EM6TA/EM6FA
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the board.
SRV
PROG
On (green)
The system is working properly.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
system.
On (yellow)
A minor alarm occurs in the system.
Off
There is no power supplied to the system.
Blinks on (green) and off at
100 ms intervals
Software is being loaded to the board during
the power-on or resetting process of the
board.
Blinks on (green) and off at
300 ms intervals
The board software is in BIOS boot state
during the power-on or resetting process of
the board.
On (green)
l When the board is being powered on or
being reset, the upper layer software is
being initialized.
l When the board is running, the software
is running normally.
Blinks on (red) and off at 100
ms intervals
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
The BOOTROM self-check fails during the
power-on or resetting process of the board.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
741
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
On (red)
The memory self-check fails or loading
upper layer software fails during the poweron or resetting process of the board.
The logic file or upper layer software is lost
during the running process of the board.
The pluggable storage card is faulty.
L/A1a
L/A2a
On (green)
The GE1 port is connected correctly and is
not receiving or transmitting data.
Blinking (yellow)
The GE1 port is receiving or transmitting
data.
Off
The GE1 port is not connected or is
connected incorrectly.
On (green)
The GE2 port is connected correctly and is
not receiving or transmitting data.
Blinking (yellow)
The GE2 port is receiving or transmitting
data.
Off
The GE2 port is not connected or is
connected incorrectly.
NOTE
a: The L/A1 and L/A2 indicators are available only on the EM6FA and indicate the states of the
corresponding GE ports.
Table H-10 Status explanation for indicators on the EMS6
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the board.
PROG
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Blinks on (green) and off at
100 ms intervals
Software is being loaded to the board during
the power-on or resetting process of the
board.
Blinks on (green) and off at
300 ms intervals
The board software is in BIOS boot state
during the power-on or resetting process of
the board.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
742
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
On (green)
l The upper layer software is being
initialized during the power-on or
resetting process of the board.
l The software is running properly during
the running process of the board.
Blinks on (red) and off at 100
ms intervals
The BOOTROM self-check fails during the
power-on or resetting process of the board.
On (red)
l The memory self-check fails or loading
upper layer software fails during the
power-on or resetting process of the
board.
l The logic file or upper layer software is
lost during the running process of the
board.
l The pluggable storage card is faulty.
SRV
LINK1
ACT1
LINK2
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
On (green)
The system is working normally.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
system.
On (yellow)
A minor alarm occurs in the system.
Off
There is no power supplied to the system.
On (green)
The GE1 port is connected correctly.
Blinks on (red) and off at 300
ms intervals
The receive optical power at the GE1 optical
port is higher than the upper threshold.
Blinks 300 ms on (red) and 700
ms off
The receive optical power at the GE1 optical
port is lower than the lower threshold.
Off
The GE1 port is not connected or is
connected incorrectly.
Blinking (yellow)
The GE1 port is receiving or transmitting
data.
Off
The GE1 port is not receiving or
transmitting data.
On (green)
The GE2 port is connected correctly.
Blinks on (red) and off at 300
ms intervals
The receive optical power at the GE2 optical
port is higher than the upper threshold.
Blinks 300 ms on (red) and 700
ms off
The receive optical power at the GE2 optical
port is lower than the lower threshold.
Off
The GE1 port is not connected or is
connected incorrectly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
743
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Indicator
State
Meaning
ACT2
Blinking (yellow)
The GE2 port is receiving or transmitting
data.
Off
The GE2 port is not receiving or
transmitting data.
Table H-11 Status explanation for indicators on the EFP8
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the board.
PROG
Blinks on (green) and off at
100 ms intervals
Software is being loaded to the board during
the power-on or resetting process of the
board.
Blinks on (green) and off at
300 ms intervals
The board software is in BIOS boot state
during the power-on or resetting process of
the board.
On (green)
l When the board is being powered on or
being reset, the upper layer software is
being initialized.
l When the board is running, the software
is running normally.
Blinks on (red) and off at 100
ms intervals
The BOOTROM self-check fails during the
power-on or resetting process of the board.
On (red)
l The memory self-check fails or loading
upper layer software fails during the
power-on or resetting process of the
board.
l The logic file or upper layer software is
lost during the running process of the
board.
l The pluggable storage card is faulty.
SRV
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
On (green)
The system is working properly.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
system.
On (yellow)
A minor alarm occurs in the system.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
744
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
Off
There is no power supplied to the system.
Table H-12 Status explanation for indicators on the SL1D/SL1DA
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working
properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power
supplied to the board.
SRV
LOS1
LOS2
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm
occurs in the services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm
occurs in the services.
Off
The services are not
configured.
On (red)
The first port of the SL1D/
SL1DA is reporting the
R_LOS alarm.
Off
The first port of the SL1D/
SL1DA is free of R_LOS
alarms.
On (red)
The second port of the
SL1D/SL1DA is reporting
the R_LOS alarm.
Off
The second port of the
SL1D/SL1DA is free of
R_LOS alarms.
Table H-13 Status explanation for indicators on the SP3S/SP3D
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working
properly.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
745
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
H Indicators of Boards
Indicator
State
Meaning
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power
supplied to the board.
SRV
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm
occurs in the services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm
occurs in the services.
Off
The services are not
configured.
Table H-14 Status explanation for indicators on the ML1/MD1
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working
properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power
supplied to the board.
SRV
On (green)
The services are normal.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm
occurs in the services.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm
occurs in the services.
Off
The services are not
configured.
Table H-15 Status explanation for indicators on the AUX
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Indicator
State
Meaning
STAT
On (green)
The board is working properly.
On (red)
The board hardware is faulty.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
746
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
Indicator
H Indicators of Boards
State
Meaning
Off
l The board is not working.
l The board is not created.
l There is no power supplied to the
board.
SRV
On (green)
The system is working properly.
On (red)
A critical or major alarm occurs in the
system.
On (yellow)
A minor or remote alarm occurs in the
system.
Off
There is no power supplied to the system.
Table H-16 Status explanation for indicators on the PIU
Indicator
Status
Description
PWR
On (green)
The power supply is connected.
Off
There is no power supplied to the PIU or the power
supply is connected incorrectly.
Table H-17 Status explanation for indicators on the FAN
Indicator
State
Meaning
FAN
On (green)
The fan is working properly.
On (red)
The fan is faulty.
Off
The fan is not powered on or is not installed.
NOTE
The CRIT, MAJ, or MIN indicator on the front panel of the FAN indicates the current alarm severity of the
subrack.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
747
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
Glossary
Terms are listed in an alphabetical order.
I.1 0-9
This section provides the terms starting with numbers.
I.2 A-E
This section provides the terms starting with letters A to E.
I.3 F-J
This section provides the terms starting with letters F to J.
I.4 K-O
This section provides the terms starting with letters K to O.
I.5 P-T
This section provides the terms starting with letters P to T.
I.6 U-Z
This section provides the terms starting with letters U to Z.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
748
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
I.1 0-9
This section provides the terms starting with numbers.
1U
The standard electronics industries association (EIA) rack unit (44 mm/1.75 in.)
I.2 A-E
This section provides the terms starting with letters A to E.
A
ABR
See available bit rate
ACAP
See adjacent channel alternate polarization
access control list
A list of entities, together with their access rights, which are authorized to have access
to a resource.
ACL
See access control list
adaptive modulation
A technology that is used to automatically adjust the modulation scheme according to
the channel quality. When the channel quality is favorable, the equipment adopts a highefficiency modulation scheme to improve the transmission efficiency and the spectrum
utilization of the system. When the channel quality is degraded, the equipment adopts
the low-efficiency modulation scheme to improve the anti-interference capability of the
link that carries high-priority services.
ADC
See analog to digital converter
add/drop multiplexer
Network elements that provide access to all or some subset of the constituent signals
contained within an STM-N signal. The constituent signals are added to (inserted), and/
or dropped from (extracted) the STM-N signal as it passed through the ADM.
Address Resolution
Protocol
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is an Internet Protocol used to map IP addresses to
MAC addresses. It allows hosts and routers to determine the link layer addresses through
ARP requests and ARP responses. The address resolution is a process in which the host
converts the target IP address into a target MAC address before transmitting a frame.
The basic function of the ARP is to query the MAC address of the target equipment
through its IP address.
adjacent channel
alternate polarization
A channel configuration method, which uses two adjacent channels (a horizontal
polarization wave and a vertical polarization wave) to transmit two signals.
ADM
See add/drop multiplexer
administrative unit
The information structure which provides adaptation between the higher order path layer
and the multiplex section layer. It consists of an information payload (the higher order
VC) and an AU pointer which indicates the offset of the payload frame start relative to
the multiplex section frame start.
AF
See assured forwarding
aggregation
A collection of objects that makes a whole. An aggregation can be a concrete or
conceptual set of whole-part relationships among objects.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
749
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
AIS
I Glossary
See alarm indication signal
alarm automatic report When an alarm is generated on the device side, the alarm is reported to the Network
Management System (NMS). Then, an alarm panel prompts and the user can view the
details of the alarm.
alarm cascading
The shunt-wound output of the alarm signals of several subracks or cabinets.
Alarm Filtering
An NE reports the detected alarm to the element management system (EMS). Based on
the filter state of the alarm, the EMS determines whether to display or save the alarm
information. If the filter state of an alarm is set to Filter, the alarm is not displayed or
stored on the EMS. The alarm, however, is still monitored by the NE.
alarm indication signal A code sent downstream in a digital network as an indication that an upstream failure
has been detected and alarmed. It is associated with multiple transport layers.
alarm suppression
A function used not to monitor alarms for a specific object, which may be the
networkwide equipment, a specific NE, a specific board and even a specific function
module of a specific board.
AM
See adaptive modulation
analog to digital
converter
An electronic circuit that converts continuous signals to discrete digital numbers. The
reverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
APS
See automatic protection switching
ARP
See Address Resolution Protocol
assured forwarding
One of the four per-hop behaviors (PHB) defined by the Diff-Serv workgroup of IETF.
It is suitable for certain key data services that require assured bandwidth and short delay.
For traffic within the bandwidth limit, AF assures quality in forwarding. For traffic that
exceeds the bandwidth limit, AF degrades the service class and continues to forward the
traffic instead of discarding the packets.
Asynchronous
Transfer Mode
A protocol for the transmission of a variety of digital signals using uniform 53 byte cells.
A transfer mode in which the information is organized into cells; it is asynchronous in
the sense that the recurrence of cells depends on the required or instantaneous bit rate.
Statistical and deterministic values may also be used to qualify the transfer mode.
ATM
See Asynchronous Transfer Mode
ATM PVC
ATM permanent virtual circuit
ATPC
See automatic transmit power control
attenuator
A device used to increase the attenuation of an Optical Fiber Link. Generally used to
ensure that the signal at the receive end is not too strong.
AU
See administrative unit
automatic protection
switching
Capability of a transmission system to detect a failure on a working facility and to switch
to a standby facility to recover the traffic.
automatic transmit
power control
A method of adjusting the transmit power based on fading of the transmit signal detected
at the receiver
available bit rate
A kind of service categories defined by the ATM forum. ABR only provides possible
forwarding service and applies to the connections that does not require the real-time
quality. It does not provide any guarantee in terms of cell loss or delay.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
750
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
B
backward defect
indication
When detecting a defect, the sink node of an LSP uses backward defect indication (BDI)
to inform the upstream end of the LSP of a downstream defect along the return path.
bandwidth
A range of transmission frequencies that a transmission line or channel can carry in a
network. In fact, it is the difference between the highest and lowest frequencies the
transmission line or channel. The greater the bandwidth, the faster the data transfer rate.
base station controller
A logical entity that connects the BTS with the MSC in a GSM network. It interworks
with the BTS through the Abis interface, the MSC through the A interface. It provides
the following functions: radio resource management, base station management, power
control, handover control, and traffic measurement. One BSC controls and manages one
or more BTSs in an actual network.
base transceiver station A Base Transceiver Station terminates the radio interface. It allows transmission of traffic
and signaling across the air interface. The BTS includes the baseband processing, radio
equipment, and the antenna.
basic input/output
system
A firmware stored in the computer mainboard. It contains basic input/output control
programs, power-on self test (POST) programs, bootstraps, and system setting
information. The BIOS provides hardware setting and control functions for the computer.
BDI
See backward defect indication
BE
See best effort
BER
See bit error rate
best effort
A traditional IP packet transport service. In this service, the diagrams are forwarded
following the sequence of the time they reach. All diagrams share the bandwidth of the
network and routers. The amount of resource that a diagram can use depends of the time
it reaches. BE service does not ensure any improvement in delay time, jitter, packet loss
ratio, and high reliability.
binding strap
The binding strap is 12.7 mm wide, with one hook side (made of transparent
polypropylene material) and one mat side (made of black nylon material).
BIOS
See basic input/output system
BIP
See bit interleaved parity
bit error
An incompatibility between a bit in a transmitted digital signal and the corresponding
bit in the received digital signal.
bit error rate
Ratio of received bits that contain errors. BER is an important index used to measure the
communications quality of a network.
bit interleaved parity
A method of error monitoring. With even parity an X-bit code is generated by the
transmitting equipment over a specified portion of the signal in such a manner that the
first bit of the code provides even parity over the first bit of all X-bit sequences in the
covered portion of the signal, the second bit provides even parity over the second bit of
all X-bit sequences within the specified portion, etc. Even parity is generated by setting
the BIP-X bits so that there is an even number of 1s in each monitored partition of the
signal. A monitored partition comprises all bits which are in the same bit position within
the X-bit sequences in the covered portion of the signal. The covered portion includes
the BIP-X.
BPDU
See bridge protocol data unit
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
751
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
bridge protocol data
unit
The data messages that are exchanged across the switches within an extended LAN that
uses a spanning tree protocol (STP) topology. BPDU packets contain information on
ports, addresses, priorities and costs and ensure that the data ends up where it was
intended to go. BPDU messages are exchanged across bridges to detect loops in a
network topology. The loops are then removed by shutting down selected bridges
interfaces and placing redundant switch ports in a backup, or blocked, state.
broadcast
A means of delivering information to all members in a network. The broadcast range is
determined by the broadcast address.
BSC
See base station controller
BTS
See base transceiver station
buffer
A storage area used for handling data in transit. Buffers are used in inter-networking to
compensate for differences in processing speed between network devices. Bursts of data
can be stored in buffers until they can be handled by slower processing devices. In a
program, buffers are created to hold some amount of data from each of the files that will
be read or written. In a streaming media application, the program uses buffers to store
an advance supply of audio or video data to compensate for momentary delays.
C
cable tie
The tape used to bind the cables.
cable tray
N/A
cable trough
N/A
CAR
See committed access rate
CBR
See constant bit rate
CBS
See committed burst size
CC
See connectivity check
CCC
See circuit cross connect
CCDP
See co-channel dual polarization
CCM
See continuity check message
CE
See customer edge
central processing unit The computational and control unit of a computer. The CPU is the device that interprets
and executes instructions. The CPU has the ability to fetch, decode, and execute
instructions and to transfer information to and from other resources over the computer's
main data-transfer path, the bus.
CES
See circuit emulation service
CF
See compact flash
CGMP
See Cisco Group Management Protocol
channel
A telecommunication path of a specific capacity and/or at a specific speed between two
or more locations in a network. The channel can be established through wire, radio
(microwave), fiber or a combination of the three. The amount of information transmitted
per second in a channel is the information transmission speed, expressed in bits per
second. For example, b/s (100 bit/s), kb/s (103 bit/s), Mb/s (106 bit/s), Gb/s (109 bit/s),
and Tb/s (1012 bit/s).
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
752
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
CIR
See committed information rate
circuit cross connect
An implementation of MPLS L2VPN through the static configuration of labels.
circuit emulation
service
A function with which the E1/T1 data can be transmitted through ATM networks. At the
transmission end, the interface module packs timeslot data into ATM cells. These ATM
cells are sent to the reception end through the ATM network. At the reception end, the
interface module re-assigns the data in these ATM cells to E1/T1 timeslots. The CES
technology guarantees that the data in E1/T1 timeslots can be recovered to the original
sequence at the reception end.
Cisco Group
Management Protocol
N/A
CIST
See common and internal spanning tree
CIST root
A switch of the highest priority is elected as the root in an MSTP network.
clock tracing
The method to keep the time on each node being synchronized with a clock source in a
network.
co-channel dual
polarization
A channel configuration method, which uses a horizontal polarization wave and a vertical
polarization wave to transmit two signals. The Co-Channel Dual Polarization is twice
the transmission capacity of the single polarization.
coarse wavelength
division multiplexing
A signal transmission technology that multiplexes widely-spaced optical channels into
the same fiber. CWDM widely spaces wavelengths at a spacing of several nm. CWDM
does not support optical amplifiers and is applied in a short-distance chain network.
colored packet
A packet whose priority is determined by defined colors.
committed access rate
A traffic control method that uses a set of rate limits to be applied to a router interface.
CAR is a configurable method by which incoming and outgoing packets can be classified
into QoS (Quality of Service) groups, and by which the input or output transmission rate
can be defined.
committed burst size
committed burst size. A parameter used to define the capacity of token bucket C, that is,
the maximum burst IP packet size when the information is transferred at the committed
information rate. This parameter must be larger than 0. It is recommended that this
parameter should be not less than the maximum length of the IP packet that might be
forwarded.
committed information The rate at which a frame relay network agrees to transfer information in normal
rate
conditions. Namely, it is the rate, measured in bit/s, at which the token is transferred to
the leaky bucket.
common and internal
spanning tree
The single spanning tree calculated by STP and RSTP together with the logical
continuation of that connectivity by using MST Bridges and regions, calculated by MSTP
to ensure that all LANs in the bridged local area network are simply and fully connected.
compact flash
Compact flash (CF) was originally developed as a type of data storage device used in
portable electronic devices. For storage, CompactFlash typically uses flash memory in
a standardized enclosure.
concatenation
A process that combines multiple virtual containers. The combined capacities can be
used a single capacity. The concatenation also keeps the integrity of bit sequence.
connectivity check
Ethernet CFM can detect the connectivity between MEPs. The detection is achieved by
each MEP transmitting a Continuity Check Message (CCM) periodically.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
753
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
constant bit rate
A kind of service categories defined by the ATM forum. CBR transfers cells based on
the constant bandwidth. It is applicable to service connections that depend on precise
clocking to ensure undistorted transmission.
continuity check
message
CCM is used to detect the link status.
corrugated pipe
Used to protect optical fibers.
CPU
See central processing unit
CRC
See cyclic redundancy check
cross polarization
interference
cancellation
A technology used in the case of the Co-Channel Dual Polarization (CCDP) to eliminate
the cross-connect interference between two polarization waves in the CCDP.
customer edge
A part of BGP/MPLS IP VPN model. It provides interfaces for direct connection to the
Service Provider (SP) network. A CE can be a router, switch, or host.
CWDM
See coarse wavelength division multiplexing
cyclic redundancy
check
A procedure used in checking for errors in data transmission. CRC error checking uses
a complex calculation to generate a number based on the data transmitted. The sending
device performs the calculation before transmission and includes it in the packet that it
sends to the receiving device. The receiving device repeats the same calculation after
transmission. If both devices obtain the same result, it is assumed that the transmission
was error free. The procedure is known as a redundancy check because each transmission
includes not only data but extra (redundant) error-checking values.
D
data communication
network
A communication network used in a TMN or between TMNs to support the Data
Communication Function (DCF).
data communications
channel
The data channel that uses the D1-D12 bytes in the overhead of an STM-N signal to
transmit information on operation, management, maintenance and provision (OAM&P)
between NEs. The DCC channels that are composed of bytes D1-D3 is referred to as the
192 kbit/s DCC-R channel. The other DCC channel that are composed of bytes D4-D12
is referred to as the 576 kbit/s DCC-M channel.
Datagram
A kind of PDU which is used in Connectionless Network Protocol, such as IP datagram,
UDP datagram.
DC
See direct current
DC-C
See DC-return common (with ground)
DC-C
DC-return common (with ground)
DC-C
See DC-return common (with ground)
DC-I
See DC-return isolate (with ground)
DC-return common
(with ground)
A power system, in which the BGND of the DC return conductor is short-circuited with
the PGND on the output side of the power supply cabinet and also on the line between
the output of the power supply cabinet and the electric equipment.
DC-return common
(with ground)
A power system, in which the BGND of the DC return conductor is short-circuited with
the PGND on the output side of the power supply cabinet and also on the line between
the output of the power supply cabinet and the electric equipment.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
754
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
DC-return isolate (with A power system, in which the BGND of the DC return conductor is short-circuited with
ground)
the PGND on the output side of the power supply cabinet and is isolated from the PGND
on the line between the output of the power supply cabinet and the electric equipment.
DCC
See data communications channel
DCN
See data communication network
DDF
See digital distribution frame
DDN
See digital data network
DE
See discard eligible
differentiated services
A service architecture that provides the end-to-end QoS function. It consists of a series
of functional units implemented at the network nodes, including a small group of perhop forwarding behaviors, packet classification functions, and traffic conditioning
functions such as metering, marking, shaping and policing.
differentiated services
code point
A marker in the header of each IP packet that prompts network routers to apply
differentiated grades of service to various packet streams. It is specified by the DiffServ
policy proposed by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). This allows Internet and
other IP-based network service providers to offer different levels of service to customers.
DiffServ
See differentiated services
digital data network
A high-quality data transport tunnel that combines the digital channel (such as fiber
channel, digital microwave channel, or satellite channel) and the cross multiplex
technology.
digital distribution
frame
A type of equipment used between the transmission equipment and the exchange with
transmission rate of 2 to 155 Mbit/s to provide the functions such as cables connection,
cable patching, and test of loops that transmitting digital signals.
digital modulation
A digital modulation controls the changes in amplitude, phase, and frequency of the
carrier based on the changes in the baseband digital signal. In this manner, the
information can be transmitted by the carrier.
direct current
Electrical current whose direction of flow does not reverse. The current may stop or
change amplitude, but it always flows in the same direction.
discard eligible
A bit in the frame relay header. It indicates the priority of a packet. If a node supports
the FR QoS, the rate of the accessed FR packets is controlled. When the packet traffic
exceeds the specified traffic, the DE value of the redundant packets is set to 1. In the
case of network congestion, the packets with DE value as 1 are discarded at the node.
Distance Vector
Multicast Routing
Protocol
An Internet gateway protocol mainly based on the RIP. The protocol implements a typical
dense mode IP multicast solution. The DVMRP protocol uses IGMP to exchange routing
datagrams with its neighbors.
DS boundary node
A DS node that connects one DS domain to a node either in another DS domain or in a
domain that is not DS-capable.
DS domain
In the DifferServ mechanism, the DS domain is a domain consisting of a group of
network nodes that share the same service provisioning policy and same PHB. It provides
point-to-point QoS guarantees for services transmitted over this domain.
DS interior node
A DS node located at the center of a DS domain. It is a non-DS boundary node.
DS node
A DS-compliant node, which is subdivided into DS boundary node and ID interior node.
DSCP
See differentiated services code point
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
755
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
dual-polarized antenna An antenna intended to radiate or receive simultaneously two independent radio waves
orthogonally polarized.
DVMRP
See Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
E
E-Aggr
See Ethernet aggregation
E-LAN
See Ethernet LAN
E-Line
See Ethernet line
E-Tree
See Ethernet-tree
EBS
See excess burst size
ECC
See embedded control channel
EF
See expedited forwarding
electromagnetic
compatibility
Electromagnetic compatibility is the condition which prevails when telecommunications
equipment is performing its individually designed function in a common electromagnetic
environment without causing or suffering unacceptable degradation due to unintentional
electromagnetic interference to or from other equipment in the same environment.
electromagnetic
interference
Any electromagnetic disturbance that interrupts, obstructs, or otherwise degrades or
limits the effective performance of electronics/electrical equipment.
electrostatic discharge
The sudden and momentary electric current that flows between two objects at different
electrical potentials caused by direct contact or induced by an electrostatic field.
embedded control
channel
A logical channel that uses a data communications channel (DCC) as its physical layer,
to enable transmission of operation, administration, and maintenance (OAM)
information between NEs.
EMC
See electromagnetic compatibility
EMI
See electromagnetic interference
Engineering label
A mark on a cable, a subrack, or a cabinet for identification.
EPL
See Ethernet private line
EPLAN
See Ethernet private LAN service
equalization
A method of avoiding selective fading of frequencies. Equalization can compensate for
the changes of amplitude frequency caused by frequency selective fading.
ERPS
See Ethernet ring protection switching
ESD
See electrostatic discharge
ESD jack
Electrostatic discharge jack. A hole in the cabinet or shelf, which connect the shelf or
cabinet to the insertion of ESD wrist strap.
Ethernet
A technology complemented in LAN. It adopts Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision
Detection. The speed of an Ethernet interface can be 10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s, 1000 Mbit/
s or 10000 Mbit/s. The Ethernet network features high reliability and easy maintaining.
Ethernet
A technology complemented in LAN. It adopts Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision
Detection. The speed of an Ethernet interface can be 10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s, 1000 Mbit/
s or 10000 Mbit/s. The Ethernet network features high reliability and easy maintaining.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
756
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
Ethernet aggregation
A type of Ethernet service that is based on a multipoint-to-point EVC (Ethernet virtual
connection).
Ethernet LAN
A type of Ethernet service that is based on a multipoint-to-multipoint EVC (Ethernet
virtual connection).
Ethernet line
A type of Ethernet service that is based on a point-to-point EVC (Ethernet virtual
connection).
Ethernet private LAN
service
An Ethernet service type, which carries Ethernet characteristic information over a
dedicated bridge, point-to-multipoint connections, provided by SDH, PDH, ATM, or
MPLS server layer networks.
Ethernet private line
A type of Ethernet service that is provided with dedicated bandwidth and point-to-point
connections on an SDH, PDH, ATM, or MPLS server layer network.
Ethernet ring
protection switching
protection switching mechanisms for ETH layer Ethernet ring topologies.
Ethernet virtual
private LAN service
An Ethernet service type, which carries Ethernet characteristic information over a shared
bridge, point-to-multipoint connections, provided by SDH, PDH, ATM, or MPLS server
layer networks.
Ethernet virtual
private line
An Ethernet service type, which carries Ethernet characteristic information over shared
bandwidth, point-to-point connections, provided by SDH, PDH, ATM, or MPLS server
layer networks.
Ethernet-tree
An Ethernet service type that is based on a Point-to-multipoint Ethernet Virtual
Connection.
ETS
European Telecommunication Standards
ETSI
See European Telecommunications Standards Institute
European
Telecommunications
Standards Institute
A standards-setting body in Europe. Also the standards body responsible for GSM.
EVPL
See Ethernet virtual private line
EVPLAN
See Ethernet virtual private LAN service
excess burst size
A parameter related to traffic. In the single rate three color marker (srTCM) mode, the
traffic control is achieved by the token buckets C and E. Excess burst size is a parameter
used to define the capacity of token bucket E, that is, the maximum burst IP packet size
when the information is transferred at the committed information rate. This parameter
must be larger than 0. It is recommended that this parameter should be not less than the
maximum length of the IP packet that might be forwarded.
Exercise Switching
An operation to check if the protection switching protocol functions normally. The
protection switching is not really performed.
expansion
Connecting a storage system to more disk enclosures through connection cables,
expanding the capacity of the storage system.
expedited forwarding
The highest order QoS in the Diff-Serv network. EF PHB is suitable for services that
demand low packet loss ratio, short delay, and broad bandwidth. In all the cases, EF
traffic can guarantee a transmission rate equal to or faster than the set rate. The DSCP
value of EF PHB is "101110".
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
757
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
I.3 F-J
This section provides the terms starting with letters F to J.
F
failure
If the fault persists long enough to consider the ability of an item with a required function
to be terminated. The item may be considered as having failed; a fault has now been
detected.
fast Ethernet
Any network that supports transmission rate of 100Mbits/s. The Fast Ethernet is 10 times
faster than 10BaseT, and inherits frame format, MAC addressing scheme, MTU, and so
on. Fast Ethernet is extended from the IEEE802.3 standard, and it uses the following
three types of transmission media: 100BASE-T4 (4 pairs of phone twisted-pair cables),
100BASE-TX (2 pairs of data twisted-pair cables), and 100BASE-FX (2-core optical
fibers).
fast link pulse
The link pulse that is used to encode information during automatic negotiation.
FD
See frequency diversity
FDI
See forward defect indication
FE
See fast Ethernet
FEC
See forward error correction
FFD
fast failure detection
fiber patch cord
A kind of fiber used for connections between the subrack and the ODF, and for
connections between subracks or inside a subrack.
field programmable
gate array
A type of semi-customized circuit used in the Application Specific Integrated Circuit
(ASIC) field. It is developed on the basis of the programmable components, such as the
PAL, GAL, and EPLD. It not only remedies the defects of customized circuits, but also
overcomes the disadvantage of the original programmable components in terms of the
limited number of gate arrays.
FIFO
See First in First out
File Transfer Protocol
A member of the TCP/IP suite of protocols, used to copy files between two computers
on the Internet. Both computers must support their respective FTP roles: one must be an
FTP client and the other an FTP server.
First in First out
A stack management mechanism. The first saved data is first read and invoked.
Forced switch
For normal traffic signals, switches normal traffic signal to the protection section, unless
an equal or higher priority switch command is in effect or SF condition exists on the
protection section, by issuing a forced switch request for that traffic signal.
forward defect
indication
Forward defect indication (FDI) is generated and traced forward to the sink node of the
LSP by the node that first detects defects. It includes fields to indicate the nature of the
defect and its location. Its primary purpose is to suppress alarms being raised at affected
higher level client LSPs and (in turn) their client layers.
forward error
correction
A bit error correction technology that adds the correction information to the payload at
the transmit end. Based on the correction information, the bit errors generated during
transmission are corrected at the receive end.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
758
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
Forwarding plane
Also referred to as the data plane. The forwarding plane is connection-oriented, and can
be used in Layer 2 networks such as an ATM network.
FPGA
See field programmable gate array
fragment
Piece of a larger packet that has been broken down to smaller units.
Fragmentation
Process of breaking a packet into smaller units when transmitting over a network medium
that cannot support the original size of the packet.
frame
A frame, starting with a header, is a string of bytes with a specified length. Frame length
is represented by the sampling circle or the total number of bytes sampled during a circle.
A header comprises one or a number of bytes with pre-specified values. In other words,
a header is a code segment that reflects the distribution (diagram) of the elements prespecified by the sending and receiving parties.
frequency diversity
A diversity scheme that enables two or more microwave frequencies with a certain
frequency interval are used to transmit/receive the same signal and selection is then
performed between the two signals to ease the impact of fading.
FTP
See File Transfer Protocol
full-duplex
A full-duplex, or sometimes double-duplex system, allows communication in both
directions, and, unlike half-duplex, allows this to happen simultaneously. Land-line
telephone networks are full-duplex, since they allow both callers to speak and be heard
at the same time. A good analogy for a full-duplex system would be a two-lane road with
one lane for each direction.
G
gateway network
element
A network element that is used for communication between the NE application layer and
the NM application layer
GE
See gigabit Ethernet
generic framing
procedure
A framing and encapsulated method which can be applied to any data type. It has been
standardized by ITU-T SG15.
generic traffic shaping A traffic control measure that initiatively adjusts the output speed of the traffic. This is
to adapt the traffic to network resources that can be provided by the downstream router
to avoid packet discarding and congestion.
GFP
See generic framing procedure
gigabit Ethernet
GE adopts the IEEE 802.3z. GE is compatible with 10 Mbit/s and 100 Mbit/s Ethernet.
It runs at 1000 Mbit/s. Gigabit Ethernet uses a private medium, and it does not support
coaxial cables or other cables. It also supports the channels in the bandwidth mode. If
Gigabit Ethernet is, however, deployed to be the private bandwidth system with a bridge
(switch) or a router as the center, it gives full play to the performance and the bandwidth.
In the network structure, Gigabit Ethernet uses full duplex links that are private, causing
the length of the links to be sufficient for backbone applications in a building and campus.
Global Positioning
System
A global navigation satellite system. It provides reliable positioning, navigation, and
timing services to worldwide users.
GNE
See gateway network element
GPS
See Global Positioning System
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
759
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
graphical user interface A visual computer environment that represents programs, files, and options with
graphical images, such as icons, menus, and dialog boxes, on the screen.
GTS
See generic traffic shaping
GUI
See graphical user interface
guide rail
Components to guide, position, and support plug-in boards.
H
HA
See high availability
half-duplex
A transmitting mode in which a half-duplex system provides for communication in both
directions, but only one direction at a time (not simultaneously). Typically, once a party
begins receiving a signal, it must wait for the transmitter to stop transmitting, before
replying.
HDLC
See high level data link control
hierarchical quality of
service
A type of QoS that can control the traffic of users, and perform the scheduling according
to the priority of user services. HQoS has a perfect traffic statistics function, and the
administrator can monitor the usage of bandwidth of each service. Hence, the bandwidth
can be allocated reasonably through traffic analysis.
high availability
Typically, a scheme in which two modules operate in active/standby mode to achieve
high availability. When the active module fails, the standby module automatically takes
over the system functions of the active module.
high level data link
control
The HDLC protocol is a general purpose protocol which operates at the data link layer
of the OSI reference model. Each piece of data is encapsulated in an HDLC frame by
adding a trailer and a header.
High Speed Downlink
Packet Access
A modulating-demodulating algorithm put forward in 3GPP R5 to meet the requirement
for asymmetric uplink and downlink transmission of data services. It enables the
maximum downlink data service rate to reach 14.4 Mbit/s without changing the
WCDMA network topology.
higher order path
In an SDH network, the higher order path layers provide a server network from the lower
order path layers.
Hold priority
The priority of the tunnel with respect to holding resources, ranging from 0 (indicates
the highest priority) to 7. It is used to determine whether the resources occupied by the
tunnel can be preempted by other tunnels.
hop
A network connection between two distant nodes. For Internet operation a hop represents
a small step on the route from one main computer to another.
hot standby
A mechanism of ensuring device running security. The environment variables and
storage information of each running device are synchronized to the standby device. When
the faults occur on the running device, the standby device can take over the services in
the faulty device in automatic or manual way to ensure the normal running of the entire
system.
HP
See higher order path
HQoS
See hierarchical quality of service
HSB
See hot standby
HSDPA
See High Speed Downlink Packet Access
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
760
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
HSM
hitless switch mode
HTB
high tributary bus
hybrid radio
The hybrid transmission of Native E1 and Native Ethernet signals. Hybrid radio supports
the AM function.
I
ICMP
See Internet Control Message Protocol
IDU
See indoor unit
IEC
See International Electrotechnical Commission
IEEE
See Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IETF
See Internet Engineering Task Force
IF
See intermediate frequency
IGMP
See Internet Group Management Protocol
IGMP snooping
A multicast constraint mechanism running on a layer 2 device. This protocol manages
and controls the multicast group by listening to and analyze the Internet Group
Management Protocol (IGMP) packet between hosts and layer 3 devices. In this manner,
the spread of the multicast data on layer 2 network can be prevented efficiently.
IMA
See inverse multiplexing over ATM
indoor unit
The indoor unit of the split-structured radio equipment. It implements accessing,
multiplexing/demultiplexing, and IF processing for services.
Inloop
A method of looping the signals from the cross-connect unit back to the cross-connect
unit.
Institute of Electrical
and Electronics
Engineers
A society of engineering and electronics professionals based in the United States but
boasting membership from numerous other countries. The IEEE focuses on electrical,
electronics, computer engineering, and science-related matters.
intermediate frequency The transitional frequency between the frequencies of a modulated signal and an RF
signal.
Intermediate System
The basic unit in the IS-IS protocol used to transmit routing information and generate
routes.
Intermediate System to A protocol used by network devices (routers) to determine the best way to forward
Intermediate System
datagrams or packets through a packet-based network, a process called routing.
routing protocol
internal spanning tree
A segment of CIST in a certain MST region. An IST is a special MSTI whose ID is 0.
International
Electrotechnical
Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is an international and nongovernmental standards organization dealing with electrical and electronic standards.
International
Organization for
Standardization
An international association that works to establish global standards for communications
and information exchange. Primary among its accomplishments is the widely accepted
ISO/OSI reference model, which defines standards for the interaction of computers
connected by communications networks.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
761
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
International
Telecommunication
UnionTelecommunication
Standardization Sector
An international body that develops worldwide standards for telecommunications
technologies. These standards are grouped together in series which are prefixed with a
letter indicating the general subject and a number specifying the particular standard. For
example, X.25 comes from the "X" series which deals with data networks and open
system communications and number "25" deals with packet switched networks.
Internet Control
Message Protocol
A network-layer (ISO/OSI level 3) Internet protocol that provides error correction and
other information relevant to IP packet processing. For example, it can let the IP software
on one machine inform another machine about an unreachable destination. See also
communications protocol, IP, ISO/OSI reference model, packet (definition 1).
Internet Engineering
Task Force
A worldwide organization of individuals interested in networking and the Internet.
Managed by the Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG), the IETF is charged with
studying technical problems facing the Internet and proposing solutions to the Internet
Architecture Board (IAB). The work of the IETF is carried out by various working groups
that concentrate on specific topics, such as routing and security. The IETF is the publisher
of the specifications that led to the TCP/IP protocol standard.
Internet Group
Management Protocol
The protocol for managing the membership of Internet Protocol multicast groups among
the TCP/IP protocols. It is used by IP hosts and adjacent multicast routers to establish
and maintain multicast group memberships.
Internet Protocol
The TCP/IP standard protocol that defines the IP packet as the unit of information sent
across an internet and provides the basis for connectionless, best-effort packet delivery
service. IP includes the ICMP control and error message protocol as an integral part. The
entire protocol suite is often referred to as TCP/IP because TCP and IP are the two
fundamental protocols. IP is standardized in RFC 791.
Internet protocol
version 6
A update version of IPv4. It is also called IP Next Generation (IPng). The specifications
and standardizations provided by it are consistent with the Internet Engineering Task
Force (IETF). IPv6 is also called. It is a new version of the Internet Protocol, designed
as the successor to IPv4. The difference between IPv6 and IPv4 is that an IPv4 address
has 32 bits while an IPv6 address has 128 bits.
Internet protocol
version 6
A update version of IPv4. It is also called IP Next Generation (IPng). The specifications
and standardizations provided by it are consistent with the Internet Engineering Task
Force (IETF). IPv6 is also called. It is a new version of the Internet Protocol, designed
as the successor to IPv4. The difference between IPv6 and IPv4 is that an IPv4 address
has 32 bits while an IPv6 address has 128 bits.
inverse multiplexing
over ATM
The ATM inverse multiplexing technique involves inverse multiplexing and demultiplexing of ATM cells in a cyclical fashion among links grouped to form a higher
bandwidth logical link whose rate is approximately the sum of the link rates. This is
referred to as an IMA group.
IP
See Internet Protocol
IPV6
See Internet protocol version 6
IPv6
See Internet protocol version 6
IS-IS
See Intermediate System to Intermediate System routing protocol
ISO
See International Organization for Standardization
IST
See internal spanning tree
ITU-T
See International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication Standardization
Sector
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
762
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
J
Jitter
Short waveform variations caused by vibration, voltage fluctuations, and control system
instability.
I.4 K-O
This section provides the terms starting with letters K to O.
L
L2VPN
See Layer 2 virtual private network
label switched path
A sequence of hops (R0...Rn) in which a packet travels from R0 to Rn through label
switching mechanisms. A label-switched path can be chosen dynamically, based on
normal routing mechanisms, or through configuration.
label switching router
Basic element of MPLS network. All LSRs support the MPLS protocol. The LSR is
composed of two parts: control unit and forwarding unit. The former is responsible for
allocating the label, selecting the route, creating the label forwarding table, creating and
removing the label switch path; the latter forwards the labels according to groups
received in the label forwarding table.
LACP
See Link Aggregation Control Protocol
LAG
See link aggregation group
LAN
See local area network
LAN
See local area network
LAPS
link access protocol-SDH
Laser
A component that generates directional optical waves of narrow wavelengths. The laser
light has better coherence than ordinary light. The fiber system takes the semi-conductor
laser as the light source.
layer 2 switch
A data forwarding method. In LAN, a network bridge or 802.3 Ethernet switch transmits
and distributes packet data based on the MAC address. Since the MAC address is the
second layer of the OSI model, this data forwarding method is called layer 2 switch.
Layer 2 virtual private A virtual private network achieved by Layer 2 switching technologies in the packet
network
switched (IP/MPLS) network.
LB
See loopback
LCAS
See link capacity adjustment scheme
LCT
local craft terminal
line rate
The maximum packet forwarding capacity on a cable. The value of line rate equals the
maximum transmission rate capable on a given type of media.
line rate forwarding
The line rate equals the maximum transmission rate capable on a given type of media.
Link Aggregation
Control Protocol
A method of bundling a group of physical interfaces together as a logical interface to
increase bandwidth and reliability. For related protocols and standards, refer to IEEE
802.3ad.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
763
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
link aggregation group An aggregation that allows one or more links to be aggregated together to form a link
aggregation group so that a MAC client can treat the link aggregation group as if it were
a single link.
link capacity
adjustment scheme
LCAS in the virtual concatenation source and sink adaptation functions provides a
control mechanism to hitlessly increase or decrease the capacity of a link to meet the
bandwidth needs of the application. It also provides a means of removing member links
that have experienced failure. The LCAS assumes that in cases of capacity initiation,
increases or decreases, the construction or destruction of the end-to-end path is the
responsibility of the Network and Element Management Systems.
Link Protection
Protection provided by the bypass tunnel for the link on the working tunnel. The link is
a downstream link adjacent to the PLR. When the PLR fails to provide node protection,
the link protection should be provided.
LMSP
linear multiplex section protection
local area network
A network formed by the computers and workstations within the coverage of a few square
kilometers or within a single building. It features high speed and low error rate. Ethernet,
FDDI, and Token Ring are three technologies used to implement a LAN. Current LANs
are generally based on switched Ethernet or Wi-Fi technology and running at 1,000 Mbit/
s (that is, 1 Gbit/s).
local area network
A network formed by the computers and workstations within the coverage of a few square
kilometers or within a single building. It features high speed and low error rate. Ethernet,
FDDI, and Token Ring are three technologies used to implement a LAN. Current LANs
are generally based on switched Ethernet or Wi-Fi technology and running at 1,000 Mbit/
s (that is, 1 Gbit/s).
Locked switching
When the switching condition is satisfied, this function disables the service from being
switched from the working channel to the protection channel. When the service has been
switched, the function enables the service to be restored from the protection channel to
the working channel.
LOF
See Loss Of Frame
LOM
loss of multiframe
loopback
A troubleshooting technique that returns a transmitted signal to its source so that the
signal or message can be analyzed for errors.
LOP
See loss of pointer
LOS
See Loss Of Signal
Loss Of Frame
A condition at the receiver or a maintenance signal transmitted in the PHY overhead
indicating that the receiving equipment has lost frame delineation. This is used to monitor
the performance of the PHY layer.
loss of pointer
Loss of Pointer: A condition at the receiver or a maintenance signal transmitted in the
PHY overhead indicating that the receiving equipment has lost the pointer to the start of
cell in the payload. This is used to monitor the performance of the PHY layer.
Loss Of Signal
Loss of signal (LOS) indicates that there are no transitions occurring in the received
signal.
LP
lower order path
LPT
link-state pass through
LSP
See label switched path
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
764
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
LSR
I Glossary
See label switching router
M
MA
See maintenance association
MAC
See media access control
MAC
See media access control
MADM
multiple add/drop multiplexer
main topology
A interface that displays the connection relationships of NEs on the NMS (screen
display). The default client interface of the NMS, a basic component of the humanmachine interactive interface. The topology clearly shows the structure of the network,
the alarms of different NEs, subnets in the network, the communication status as well as
the basic network operation status. All topology management functions are accessed
here.
maintenance
association
That portion of a Service Instance, preferably all of it or as much as possible, the
connectivity of which is maintained by CFM. It is also a full mesh of Maintenance
Entities.
maintenance
association end point
A MEP is an actively managed CFM Entity, associated with a specific DSAP of a Service
Instance, which can generate and receive CFM frames and track any responses. It is an
end point of a single Maintenance Association, and terminates a separate Maintenance
Entity for each of the other MEPs in the same Maintenance Association.
maintenance domain
The network or the part of the network for which connectivity is managed by CFM. The
devices in an MD are managed by a single ISP.
maintenance point
Maintenance Point (MP) is one of either a MEP or a MIP.
management
information base
A type of database used for managing the devices in a communications network. It
comprises a collection of objects in a (virtual) database used to manage entities (such as
routers and switches) in a network.
manual switch
Switches normal traffic signal to the protection section, unless a failure condition exists
on other sections (including the protection section) or an equal or higher priority switch
command is in effect, by issuing a manual switch request for that normal traffic signal.
maximum transmission The largest packet of data that can be transmitted on a network. MTU size varies,
unit
depending on the network576 bytes on X.25 networks, for example, 1500 bytes on
Ethernet, and 17,914 bytes on 16 Mbps Token Ring. Responsibility for determining the
size of the MTU lies with the link layer of the network. When packets are transmitted
across networks, the path MTU, or PMTU, represents the smallest packet size (the one
that all networks can transmit without breaking up the packet) among the networks
involved.
MBS
maximum burst size
MCF
See message communication function
MD
See maintenance domain
MDI
See medium dependent interface
Mean Time Between
Failures
The average time between consecutive failures of a piece of equipment. It is a measure
of the reliability of the system.
Mean Time To Repair
The average time that a device will take to recover from a failure.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
765
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
media access control
A protocol at the media access control sublayer. The protocol is at the lower part of the
data link layer in the OSI model and is mainly responsible for controlling and connecting
the physical media at the physical layer. When transmitting data, the MAC protocol
checks whether to be able to transmit data. If the data can be transmitted, certain control
information is added to the data, and then the data and the control information are
transmitted in a specified format to the physical layer. When receiving data, the MAC
protocol checks whether the information is correct and whether the data is transmitted
correctly. If the information is correct and the data is transmitted correctly, the control
information is removed from the data and then the data is transmitted to the LLC layer.
media access control
A protocol at the media access control sublayer. The protocol is at the lower part of the
data link layer in the OSI model and is mainly responsible for controlling and connecting
the physical media at the physical layer. When transmitting data, the MAC protocol
checks whether to be able to transmit data. If the data can be transmitted, certain control
information is added to the data, and then the data and the control information are
transmitted in a specified format to the physical layer. When receiving data, the MAC
protocol checks whether the information is correct and whether the data is transmitted
correctly. If the information is correct and the data is transmitted correctly, the control
information is removed from the data and then the data is transmitted to the LLC layer.
medium dependent
interface
The electrical and mechanical interface between the equipment and the media
transmission.
MEP
See maintenance association end point
MEP
maintenance end point
message
communication
function
The MCF is composed of a protocol stack that allows exchange of management
information with their prs.
MIB
See management information base
MIP
maintenance intermediate point
mounting ear
A piece of angle plate with holes in it on a rack. It is used to fix network elements or
components.
MP
See maintenance point
MPID
maintenance point identification
MPLS
See Multiprotocol Label Switching
MPLS L2VPN
The MPLS L2VPN provides the Layer 2 VPN service based on an MPLS network. In
this case, on a uniform MPLS network, the carrier is able to provide Layer 2 VPNs of
different media types, such as ATM, FR, VLAN, Ethernet, and PPP.
MPLS OAM
The MPLS OAM provides continuity check for a single LSP, and provides a set of fault
detection tools and fault correct mechanisms for MPLS networks. The MPLS OAM and
relevant protection switching components implement the detection function for the CRLSP forwarding plane, and perform the protection switching in 50 ms after a fault occurs.
In this way, the impact of a fault can be lowered to the minimum.
MPLS TE
See multiprotocol label switching traffic engineering
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
766
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
MPLS TE tunnel
In the case of reroute deployment, or when traffic needs to be transported through
multiple trails, multiple LSP tunnels might be used. In traffic engineering, such a group
of LSP tunnels are referred to as TE tunnels. An LSP tunnel of this kind has two
identifiers. One is the Tunnel ID carried by the SENDER object, and is used to uniquely
define the TE tunnel. The other is the LSP ID carried by the SENDER_TEMPLATE or
FILTER_SPEC object.
MS
See multiplex section
MSP
See multiplex section protection
MSTP
See Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
MTBF
See Mean Time Between Failures
MTTR
See Mean Time To Repair
MTU
See maximum transmission unit
Multicast
A process of transmitting packets of data from one source to many destinations. The
destination address of the multicast packet uses Class D address, that is, the IP address
ranges from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. Each multicast address represents a multicast
group rather than a host.
Multiple Spanning
Tree Protocol
Multiple spanning tree protocol. The MSTP can be used in a loop network. Using an
algorithm, the MSTP blocks redundant paths so that the loop network can be trimmed
as a tree network. In this case, the proliferation and endless cycling of packets is avoided
in the loop network. The protocol that introduces the mapping between VLANs and
multiple spanning trees. This solves the problem that data cannot be normally forwarded
in a VLAN because in STP/RSTP, only one spanning tree corresponds to all the VLANs.
multiplex section
The trail between and including two multiplex section trail termination functions.
multiplex section
protection
A function, which is performed to provide capability for switching a signal between and
including two multiplex section termination (MST) functions, from a "working" to a
"protection" channel.
Multiprotocol Label
Switching
A technology that uses short tags of fixed length to encapsulate packets in different link
layers, and provides connection-oriented switching for the network layer on the basis of
IP routing and control protocols. It improves the cost performance and expandability of
networks, and is beneficial to routing.
multiprotocol label
switching traffic
engineering
N/A
N
N+1 protection
A radio link protection system composed of N working channels and one protection
channel.
NE
See network element
NE Explorer
The main operation interface, of the NMS, which is used to manage the
telecommunication equipment. In the NE Explorer, the user can query, manage and
maintain the NE, boards, and ports on a per-NE basis.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
767
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
network element
I Glossary
A network element (NE) contains both the hardware and the software running on it. One
NE is at least equipped with one system control and communication(SCC) board which
manages and monitors the entire network element. The NE software runs on the SCC
board.
Network Management A system in charge of the operation, administration, and maintenance of a network.
System
network service access A network address defined by ISO, through which entities on the network layer can
point
access OSI network services.
network to network
interface
An internal interface within a network linking two or more elements.
next hop
The next router to which a packet is sent from any given router as it traverses a network
on its journey to its final destination.
NLP
normal link pulse
NMS
See Network Management System
NNI
See network to network interface
node
A node stands for a managed device in the network. For a device with a single frame,
one node stands for one device. For a device with multiple frames, one node stands for
one frame of the device. Therefore, a node does not always mean a device.
Node Protection
A parameter of the FRR protection. It indicates that the bypass tunnel should be able to
protect the downstream node that is involved in the working tunnel and adjacent to the
PLR. The node cannot be a merge point, and the bypass tunnel should also be able to
protect the downstream link that is involved in the working tunnel and adjacent to the
PLR.
non-gateway network
element
A network element whose communication with the NM application layer must be
transferred by the gateway network element application layer.
non-GNE
See non-gateway network element
NSAP
See network service access point
NSF
not stop forwarding
O
OAM
See operation, administration and maintenance
ODF
See optical distribution frame
ODU
See outdoor unit
OM
Operation and maintenance
One-to-One Backup
A local repair method in which a backup tunnel is separately created for each protected
tunnel at a PLR.
open shortest path first A link-state, hierarchical interior gateway protocol (IGP) for network routing. Dijkstra's
algorithm is used to calculate the shortest path tree. It uses cost as its routing metric. A
link state database is constructed of the network topology which is identical on all routers
in the area.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
768
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
Open Systems
Interconnection
A framework of ISO standards for communication between different systems made by
different vendors, in which the communications process is organized into seven different
categories that are placed in a layered sequence based on their relationship to the user.
Each layer uses the layer immediately below it and provides a service to the layer above.
Layers 7 through 4 deal with end-to-end communication between the message source
and destination, and layers 3 through 1 deal with network functions.
operation,
administration and
maintenance
A group of network support functions that monitor and sustain segment operation,
activities that are concerned with, but not limited to, failure detection, notification,
location, and repairs that are intended to eliminate faults and keep a segment in an
operational state and support activities required to provide the services of a subscriber
access network to users/subscribers.
optic fiber connector
A device installed at the end of a fiber, optical source or receive unit. It is used to couple
the optical wave to the fiber when connected to another device of the same type. A
connector can either connect two fiber ends or connect a fiber end and an optical source
(or a detector).+
optical distribution
frame
A frame which is used to transfer and spool fibers.
orderwire
A channel that provides voice communication between operation engineers or
maintenance engineers of different stations.
OSI
See Open Systems Interconnection
OSPF
See open shortest path first
outdoor unit
The outdoor unit of the split-structured radio equipment. It implements frequency
conversion and amplification for RF signals.
Outloop
A method of looping back the input signals received at a port to an output port without
changing the structure of the signals.
Output optical power
The ranger of optical energy level of output signals.
I.5 P-T
This section provides the terms starting with letters P to T.
P
packet switched
network
A telecommunication network which works in packet switching mode.
Packing case
A case which is used for packing the board or subrack.
Path
A performance resource object defined in the network management system. The left end
of a path is a device node whose port needs to be specified and the right end of a path is
a certain IP address which can be configured by the user. By defining a path in the
network management system, a user can test the performance of a network path between
a device port and an IP address. The tested performance may be the path delay, packet
loss ratio or other aspects.
PBS
See peak burst size
PCB
See printed circuit board
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
769
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
PCI bus
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) bus. A high performance bus, 32-bit or 64-bit
for interconnecting chips, expansion boards, and processor/memory subsystems.
PDH
See plesiochronous digital hierarchy
PDU
See protocol data unit
PE
See provider edge
peak burst size
A parameter used to define the capacity of token bucket P, that is, the maximum burst
IP packet size when the information is transferred at the peak information rate. This
parameter must be larger than 0. It is recommended that this parameter should be not
less than the maximum length of the IP packet that might be forwarded.
peak information rate
A traffic parameter, expressed in bit/s, whose value should be not less than the committed
information rate.
penultimate hop
popping
Penultimate Hop Popping (PHP) is a function performed by certain routers in an MPLS
enabled network. It refers to the process whereby the outermost label of an MPLS tagged
packet is removed by a Label Switched Router (LSR) before the packet is passed to an
adjacent Label Edge Router (LER).
per-hop behavior
IETF Diff-Serv workgroup defines forwarding behaviors of network nodes as per-hop
behaviors (PHB), such as, traffic scheduling and policing. A device in the network should
select the proper PHB behaviors, based on the value of DSCP. At present, the IETF
defines four types of PHB. They are class selector (CS), expedited forwarding (EF),
assured forwarding (AF), and best-effort (BE).
PHB
See per-hop behavior
PHP
See penultimate hop popping
PIR
See peak information rate
PLA
physical link aggregation
plesiochronous digital
hierarchy
A multiplexing scheme of bit stuffing and byte interleaving. It multiplexes the minimum
rate 64 kit/s into the 2 Mbit/s, 34 Mbit/s, 140 Mbit/s, and 565 Mbit/s rates.
Point-to-Point Protocol A protocol on the data link layer, provides point-to-point transmission and encapsulates
data packets on the network layer. It is located in layer 2 of the IP protocol stack.
polarization
A kind of electromagnetic wave, the direction of whose electric field vector is fixed or
rotates regularly. Specifically, if the electric field vector of the electromagnetic wave is
perpendicular to the plane of horizon, this electromagnetic wave is called vertically
polarized wave; if the electric field vector of the electromagnetic wave is parallel to the
plane of horizon, this electromagnetic wave is called horizontal polarized wave; if the
tip of the electric field vector, at a fixed point in space, describes a circle, this
electromagnetic wave is called circularly polarized wave.
Power box
A direct current power distribution box at the upper part of a cabinet, which supplies
power for the subracks in the cabinet.
PPP
See Point-to-Point Protocol
PQ
See priority queue
PRBS
See pseudo random binary sequence
PRC
primary reference clock
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
770
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
printed circuit board
A board used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components
using conductive pathways, tracks, or traces, etched from copper sheets laminated onto
a non-conductive substrate.
priority queue
An abstract data type in computer programming that supports the following three
operations: (1) InsertWithPriority: add an element to the queue with an associated
priority (2) GetNext: remove the element from the queue that has the highest priority,
and return it (also known as "PopElement(Off)", or "GetMinimum") (3) PeekAtNext
(optional): look at the element with highest priority without removing it
protection ground
cable
A cable which connects the equipment and the protection ground bar. Usually, one half
of the cable is yellow; while the other half is green.
Protection path
A specific path that is part of a protection group and is labeled protection.
protocol data unit
It is a data packet at the network layer of the OSI model.
provider edge
A device that is located in the backbone network of the MPLS VPN structure. A PE is
responsible for VPN user management, establishment of LSPs between PEs, and
exchange of routing information between sites of the same VPN. During the process, a
PE performs the mapping and forwarding of packets between the private network and
the public channel. A PE can be a UPE, an SPE, or an NPE.
pseudo random binary A sequence that is random in a sense that the value of an element is independent of the
sequence
values of any of the other elements, similar to real random sequences.
pseudo wire
An emulated connection between two PEs for transmitting frames. The PW is established
and maintained by PEs through signaling protocols. The status information of a PW is
maintained by the two end PEs of a PW.
pseudo wire emulation A type of end-to-end Layer 2 transmitting technology. It emulates the essential attributes
edge-to-edge
of a telecommunication service such as ATM, FR or Ethernet in a Packet Switched
Network (PSN). PWE3 also emulates the essential attributes of low speed Time Division
Multiplexed (TDM) circuit and SONET/SDH. The simulation approximates to the real
situation.
PSN
See packet switched network
PTN
packet transport network
PW
See pseudo wire
PWE3
See pseudo wire emulation edge-to-edge
Q
QinQ
A layer 2 tunnel protocol based on IEEE 802.1Q encapsulation. It encapsulates the tag
of the user's private virtual local area network (VLAN) into the tag of the public VLAN.
The packet carries two layers of tags to travel through the backbone network of the
carrier. In this manner, the layer 2 virtual private network (VPN) is provided for the user.
QoS
See quality of service
QPSK
See quadrature phase shift keying
quadrature phase shift A modulation method of data transmission through the conversion or modulation and
keying
the phase determination of the reference signals (carrier). It is also called the fourth period
or 4-phase PSK or 4-PSK. QPSK uses four dots in the star diagram. The four dots are
evenly distributed on a circle. On these phases, each QPSK character can perform twobit coding and display the codes in Gray code on graph with the minimum BER.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
771
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
quality of service
I Glossary
A commonly-used performance indicator of a telecommunication system or channel.
Depending on the specific system and service, it may relate to jitter, delay, packet loss
ratio, bit error ratio, and signal-to-noise ratio. It functions to measure the quality of the
transmission system and the effectiveness of the services, as well as the capability of a
service provider to meet the demands of users.
R
radio frequency
A type of electric current in the wireless network using AC antennas to create an
electromagnetic field. It is the abbreviation of high-frequency AC electromagnetic wave.
The AC with the frequency lower than 1 kHz is called low-frequency current. The AC
with frequency higher than 10 kHz is called high-frequency current. RF can be classified
into such high-frequency current.
radio network
controller
A device in the RNS which is in charge of controlling the use and the integrity of the
radio resources.
random early detection A packet loss algorithm used in congestion avoidance. It discards the packet according
to the specified higher limit and lower limit of a queue so that global TCP synchronization
resulted in traditional Tail-Drop can be prevented.
Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
An evolution of the Spanning Tree Protocol, providing for faster spanning tree
convergence after a topology change. The RSTP protocol is backward compatible with
the STP protocol.
RDI
See remote defect indication
received signal level
The signal level at a receiver input terminal.
Received Signal
Strength Indicator
The received wide band power, including thermal noise and noise generated in the
receiver, within the bandwidth defined by the receiver pulse shaping filter, for TDD
within a specified timeslot. The reference point for the measurement shall be the antenna
Receiver Sensitivity
Receiver sensitivity is defined as the minimum acceptable value of average received
power at point R to achieve a 1 x 10-12 BER (The FEC is open).
RED
See random early detection
Reed-Solomon-Code
A forward error correction code located before interleaving that enables correction of
errors induced by burst noise. Widely used error correction scheme to fight transmission
errors at the receiver site.
REI
See remote error indication
remote defect
indication
A signal transmitted at the first opportunity in the outgoing direction when a terminal
detects specific defects in the incoming signal.
remote error indication A remote error indication (REI) is sent upstream to signal an error condition. There are
two types of REI alarms: Remote error indication line (REI-L) is sent to the upstream
LTE when errors are detected in the B2 byte. Remote error indication path (REI-P) is
sent to the upstream PTE when errors are detected in the B3 byte.
Request For Comments A document in which a standard, a protocol, or other information pertaining to the
operation of the Internet is published. The RFC is actually issued, under the control of
the IAB, after discussion and serves as the standard. RFCs can be obtained from sources
such as InterNIC.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
772
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
Resource Reservation
Protocol
The Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) is designed for Integrated Service and is
used to reserve resources on every node along a path. RSVP operates on the transport
layer; however, RSVP does not transport application data. RSVP is a network control
protocol like Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP).
reverse pressure
A traffic control method. In telecommunication, when detecting that the transmit end
transmits a large volume of traffic, the receive end sends signals to ask the transmit end
to slow down the transmission rate.
RF
See radio frequency
RFC
See Request For Comments
RIP
See Routing Information Protocol
RMON
remote network monitoring
RMON
remote network monitoring
RNC
See radio network controller
Root alarm
An alarm directly caused by anomaly events or faults in the network. Some lower-level
alarms always accompany a root alarm.
route
A route is the path that network traffic takes from its source to its destination. In a TCP/
IP network, each IP packet is routed independently. Routes can change dynamically.
route table
A mapping table that stores the relationship between the original address, destination
address, short message (SM) protocol type and account. The SMSC delivers an SM to
the designated account according to the information set in the route table.
Routing Information
Protocol
A simple routing protocol that is part of the TCP/IP protocol suite. It determines a route
based on the smallest hop count between source and destination. RIP is a distance vector
protocol that routinely broadcasts routing information to its neighboring routers and is
known to waste bandwidth.
routing table
A table that stores and updates the locations (addresses) of network devices. Routers
regularly share routing table information to be up to date. A router relies on the
destination address and on the information in the table that gives the possible routes--in
hops or in number of jumps--between itself, intervening routers, and the destination.
Routing tables are updated frequently as new information is available.
RSL
See received signal level
RSSI
See Received Signal Strength Indicator
RSTP
See Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
RSVP
See Resource Reservation Protocol
RTN
radio transmission node
S
SD
See space diversity
SDH
See synchronous digital hierarchy
SEMF
See synchronous equipment management function
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
773
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
service level agreement A service contract between a customer and a service provider that specifies the
forwarding service a customer should receive. A customer may be a user organization
(source domain) or another differentiated services domain (upstream domain). A SLA
may include traffic conditioning rules which constitute a traffic conditioning agreement
as a whole or partially.
Service Level
Agreement *
A management-documented agreement that defines the relationship between service
provider and its customer. It also provides specific, quantifiable information about
measuring and evaluating the delivery of services. The SLA details the specific operating
and support requirements for each service provided. It protects the service provider and
customer and allows the service provider to provide evidence that it has achieved the
documented target measure.
SES
See severely errored second
Setup Priority
The priority of the tunnel with respect to obtaining resources, ranging from 0 (indicates
the highest priority) to 7. It is used to determine whether the tunnel can preempt the
resources required by other backup tunnels.
severely errored second A one-second period which has a bit error ratio X 10-3 or at least one defect. Time
interval of one second during which a given digital signal is received with an error ratio
greater than 1 X 10 -3 (Rec. ITU R F. 592 needs correction).
SF
See signal fail
SFP
See small form-factor pluggable
side trough
The trough on the side of the cable rack, which is used to place nuts so as to fix the
cabinet.
signal cable
Common signal cables cover the E1 cable, network cable, and other non-subscriber
signal cable.
signal fail
A signal that indicates the associated data has failed in the sense that a near-end defect
condition (non-degrade defect) is active.
signal to noise ratio
The ratio of the amplitude of the desired signal to the amplitude of noise signals at a
given point in time. SNR is expressed as 10 times the logarithm of the power ratio and
is usually expressed in dB (Decibel).
Simple Network
Management Protocol
A network management protocol of TCP/IP. It enables remote users to view and modify
the management information of a network element. This protocol ensures the
transmission of management information between any two points. The polling
mechanism is adopted to provide basic function sets. According to SNMP, agents, which
can be hardware as well as software, can monitor the activities of various devices on the
network and report these activities to the network console workstation. Control
information about each device is maintained by a management information block.
simplex
Designating or pertaining to a method of operation in which information can be
transmitted in either direction, but not simultaneously, between two points.
SLA
See service level agreement
SLA*
See Service Level Agreement *
Slicing
To divide data into the information units proper for transmission.
small form-factor
pluggable
A specification for a new generation of optical modular transceivers.
SNC
See subnetwork connection
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
774
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
SNCP
See subnetwork connection protection
SNMP
See Simple Network Management Protocol
SNR
See signal to noise ratio
space diversity
A diversity scheme that enables two or more antennas separated by a specific distance
to transmit/receive the same signal and selection is then performed between the two
signals to ease the impact of fading. Currently, only receive SD is used.
Spanning Tree Protocol STP is a protocol that is used in the LAN to remove the loop. STP applies to the redundant
network to block some undesirable redundant paths through certain algorithms and prune
a loop network into a loop-free tree network.
SSM
See Synchronization Status Message
static virtual circuit
Static virtual circuit. A static implementation of MPLS L2VPN that transfers L2VPN
information by manual configuration of VC labels, instead of by a signaling protocol.
Statistical multiplexing A multiplexing technique whereby information from multiple logical channels can be
transmitted across a single physical channel. It dynamically allocates bandwidth only to
active input channels, to make better use of available bandwidth and allow more devices
to be connected than with other multiplexing techniques. Compare with TDM.
STM
See Synchronous Transport Module
STM-1
See synchronous transport mode-1
STM-N
See synchronous transport module of order N
STP
See Spanning Tree Protocol
sub-network
Sub-network is the logical entity in the transmission network and comprises a group of
network management objects. The network that consists of a group of interconnected or
correlated NEs, according to different functions. For example, protection subnet, clock
subnet and so on. A sub-network can contain NEs and other sub-networks. Generally, a
sub-network is used to contain the equipment located in adjacent regions and closely
related with one another, and it is indicated with a sub-network icon on a topological
view. The U2000 supports multilevels of sub-networks. A sub-network planning can
better the organization of a network view. On the one hand, the view space can be saved,
on the other hand, it helps the network management personnel focus on the equipment
under their management.
subnet mask
The technique used by the IP protocol to determine which network segment packets are
destined for. The subnet mask is a binary pattern that is stored in the client machine,
server or router and is matched with the IP address.
subnetwork connection A "transport entity" that transfers information across a subnetwork, it is formed by the
association of "ports" on the boundary of the subnetwork.
subnetwork connection A function, which allows a working subnetwork connection to be replaced by a protection
protection
subnetwork connection if the working subnetwork connection fails, or if its performance
falls below a required level.
SVC
See static virtual circuit
switch
To filter, forward frames based on label or the destination address of each frame. This
behavior operates at the data link layer of the OSI model.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
775
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
Synchronization Status A message that carries quality levels of timing signals on a synchronous timing link.
Message
Nodes on an SDH network and a synchronization network acquire upstream clock
information through this message. Then the nodes can perform proper operations on their
clocks, such as tracing, switching, or converting to holdoff, and forward the
synchronization information to downstream nodes.
synchronous digital
hierarchy
A transmission scheme that follows ITU-T G.707, G.708, and G.709. It defines the
transmission features of digital signals such as frame structure, multiplexing mode,
transmission rate level, and interface code. SDH is an important part of ISDN and BISDN. It interleaves the bytes of low-speed signals to multiplex the signals to high-speed
counterparts, and the line coding of scrambling is used only for signals. SDH is suitable
for the fiber communication system with high speed and a large capacity since it uses
synchronous multiplexing and flexible mapping structure.
synchronous
equipment
management function
The SEMF converts performance data and implementation specific hardware alarms into
object-oriented messages for transmission over DCCs and/or a Q interface.
synchronous transport Synchronous Transfer Mode at 155 Mbit/s.
mode-1
Synchronous
Transport Module
An STM is the information structure used to support section layer connections in the
SDH. It consists of information payload and Section Overhead (SOH) information fields
organized in a block frame structure which repeats every 125. The information is suitably
conditioned for serial transmission on the selected media at a rate which is synchronized
to the network. A basic STM is defined at 155 520 kbit/s. This is termed STM-1. Higher
capacity STMs are formed at rates equivalent to N times this basic rate. STM capacities
for N = 4, N = 16 and N = 64 are defined; higher values are under consideration.
synchronous transport A STM-N is the information structure used to support section layer connections in SDH.
See ITU-T Recommendation G. 707 for STM modules of order 1, 4, 16 and 64.
module of order N
T
tail drop
A type of QoS. When a queue within a network router reaches its maximum length,
packet drops can occur. When a packet drop occurs, connection-based protocols such as
TCP slow down their transmission rates in an attempt to let queued packets be serviced,
thereby letting the queue empty. This is also known as tail drop because packets are
dropped from the input end (tail) of the queue.
Tail drop
A congestion management mechanism, in which packets arrive later are discarded when
the queue is full. This policy of discarding packets may result in network-wide
synchronization due to the TCP slow startup mechanism.
TCI
tag control information
TCP
See Transmission Control Protocol
TDM
See time division multiplexing
TE
See traffic engineering
TEDB
See traffic engineering database
Telecommunication
A protocol model defined by ITU-T for managing open systems in a communications
Management Network network. An architecture for management, including planning, provisioning, installation,
maintenance, operation and administration of telecommunications equipment, networks
and services.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
776
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
TIM
trace identifier mismatch
time division
multiplexing
A multiplexing technology. TDM divides the sampling cycle of a channel into time slots
(TSn, n=0, 1, 2, 3, ...), and the sampling value codes of multiple signals engross time
slots in a certain order, forming multiple multiplexing digital signals to be transmitted
over one channel.
time to live
A technique used in best-effort delivery systems to prevent packets that loop endlessly.
The TTL is set by the sender to the maximum time the packet is allowed to be in the
network. Each router in the network decrements the TTL field when the packet arrives,
and discards any packet if the TTL counter reaches zero.
TMN
See Telecommunication Management Network
ToS priority
A ToS sub-field (the bits 0 to 2 in the ToS field) in the ToS field of the IP packet header.
TPS
See tributary protection switch
traffic engineering
A technology that is used to dynamically monitor the traffic of the network and the load
of the network elements, to adjust in real time the parameters such as traffic management
parameters, route parameters and resource restriction parameters, and to optimize the
utilization of network resources. The purpose is to prevent the congestion caused by
unbalanced loads.
traffic engineering
database
TEDB is the abbreviation of the traffic engineering database. MPLS TE needs to know
the features of the dynamic TE of every links by expanding the current IGP, which uses
the link state algorithm, such as OSPF and IS-IS. The expanded OSPF and IS-IS contain
some TE features, such as the link bandwidth and color. The maximum reserved
bandwidth of the link and the unreserved bandwidth of every link with priority are rather
important. Every router collects the information about TE of every links in its area and
generates TE DataBase. TEDB is the base of forming the dynamic TE path in the MPLS
TE network.
Traffic shaping
It is a way of controlling the network traffic from a computer to optimize or guarantee
the performance and minimize the delay. It actively adjusts the output speed of traffic
in the scenario that the traffic matches network resources provided by the lower layer
devices, avoiding packet loss and congestion.
Transmission Control
Protocol
The protocol within TCP/IP that governs the breakup of data messages into packets to
be sent via IP (Internet Protocol), and the reassembly and verification of the complete
messages from packets received by IP. A connection-oriented, reliable protocol (reliable
in the sense of ensuring error-free delivery), TCP corresponds to the transport layer in
the ISO/OSI reference model.
tributary protection
switch
Tributary protection switching, a function provided by the equipment, is intended to
protect N tributary processing boards through a standby tributary processing board.
trTCM
See two rate three color marker
TTL
See time to live
TU
tributary unit
Tunnel
A channel on the packet switching network that transmits service traffic between PEs.
In VPN, a tunnel is an information transmission channel between two entities. The tunnel
ensures secure and transparent transmission of VPN information. In most cases, a tunnel
is an MPLS tunnel.
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
777
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
two rate three color
marker
I Glossary
The trTCM meters an IP packet stream and marks its packets based on two rates, Peak
Information Rate (PIR) and Committed Information Rate (CIR), and their associated
burst sizes to be either green, yellow, or red. A packet is marked red if it exceeds the
PIR. Otherwise it is marked either yellow or green depending on whether it exceeds or
doesn't exceed the CIR.
I.6 U-Z
This section provides the terms starting with letters U to Z.
U
U-VLAN
A VLAN attribute indicating that the current VLAN is a user VLAN of an M-VLAN.
Multicast services are copied from the M-VLAN to the user VLAN.
UAS
unavailable second
UBR
See unspecified bit rate
UDP
See User Datagram Protocol
underfloor cabling
The cables connected cabinets and other devices are routed underfloor.
UNI
See user network interface
unicast
The process of sending data from a source to a single recipient.
unspecified bit rate
No commitment to transmission. No feedback to congestion. This type of service is ideal
for the transmission of IP datagrams. In case of congestion, UBR cells are discarded,
and no feedback or request for slowing down the data rate is delivered to the sender.
upload
An operation to report some or all configuration data of an NE to the NMS(Network
Management system). The configuration data then covers the configuration data stored
at the NMS side.
User Datagram
Protocol
A TCP/IP standard protocol that allows an application program on one device to send a
datagram to an application program on another. User Datagram Protocol (UDP) uses IP
to deliver datagrams. UDP provides application programs with the unreliable
connectionless packet delivery service. Therefore, UDP messages can be lost, duplicated,
delayed, or delivered out of order. UDP is used to try to transmit the data packet, that is,
the destination device does not actively confirm whether the correct data packet is
received.
user network interface The interface between user equipment and private or public network equipment (for
example, ATM switches).
V
V-UNI
See virtual user-network interface
variable bit rate
One of the traffic classes used by ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode). Unlike a
permanent CBR (Constant Bit Rate) channel, a VBR data stream varies in bandwidth
and is better suited to non real time transfers than to real-time streams such as voice calls.
VBR
See variable bit rate
VC
See virtual container
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
778
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
VCC
See virtual channel connection
VCG
See virtual concatenation group
VCI
See virtual channel identifier
VCTRUNK
A virtual concatenation group applied in data service mapping, also called the internal
port of a data service processing board
virtual channel
connection
The VC logical trail that carries data between two end points in an ATM network. A
logical grouping of multiple virtual channel connections into one virtual connection.
virtual channel
identifier
A 16-bit field in the header of an ATM cell. The VCI, together with the VPI, is used to
identify the next destination of a cell as it passes through a series of ATM switches on
its way to its destination.
virtual concatenation
group
A group of co-located member trail termination functions that are connected to the same
virtual concatenation link
virtual container
The information structure used to support path layer connections in the SDH. It consists
of information payload and path Overhead (POH) information fields organized in a block
frame structure which repeats every 125 or 500 s.
virtual local area
network
A logical grouping of two or more nodes which are not necessarily on the same physical
network segment but which share the same IP network number. This is often associated
with switched Ethernet.
virtual path identifier
The field in the Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) cell header that identifies to which
virtual path the cell belongs.
virtual private LAN
service
A type of point-to-multipoint L2VPN service provided over the public network. VPLS
enables geographically isolated user sites to communicate with each other through the
MAN/WAN as if they are on the same LAN.
virtual private network A system configuration, where the subscriber is able to build a private network via
connections to different network switches that may include private network capabilities.
virtual route forward
VRF performs the function of establishing multiple virtual routing devices on one actual
routing device. That is, the L3 interfaces of the device are distributed to different VRFs,
performing the function of establishing multiple virtual route forwarding instances on
the device.
virtual user-network
interface
A virtual user-network interface, works as an action point to perform service
classification and traffic control in HQoS.
VLAN
See virtual local area network
voice over IP
An IP telephony term for a set of facilities used to manage the delivery of voice
information over the Internet. VoIP involves sending voice information in a digital form
in discrete packets rather than by using the traditional circuit-committed protocols of the
public switched telephone network (PSTN).
VoIP
See voice over IP
VPI
See virtual path identifier
VPLS
See virtual private LAN service
VPN
See virtual private network
VRF
See virtual route forward
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
779
OptiX RTN 950 Radio Transmission System
Maintenance Guide (U2000)
I Glossary
W
wait to restore
The number of minutes to wait before services are switched back to the working line.
WAN
See wide area network
Web LCT
The local maintenance terminal of a transport network, which is located on the NE
management layer of the transport network
weighted fair queuing
A fair queue scheduling algorithm based on bandwidth allocation weights. This
scheduling algorithm allocates the total bandwidth of an interface to queues, according
to their weights and schedules the queues cyclically. In this manner, packets of all priority
queues can be scheduled.
weighted random early A packet loss algorithm used for congestion avoidance. It can prevent the global TCP
detection
synchronization caused by traditional tail-drop. WRED is favorable for the high-priority
packet when calculating the packet loss ratio.
weighted round Robin N/A
WFQ
See weighted fair queuing
wide area network
A network composed of computers which are far away from each other which are
physically connected through specific protocols. WAN covers a broad area, such as a
province, a state or even a country.
winding pipe
A tool for fiber routing, which acts as the corrugated pipe.
WRED
See weighted random early detection
WRR
See weighted round Robin
WTR
See wait to restore
X
XPIC
Issue 01 (2011-10-30)
See cross polarization interference cancellation
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
780
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Opti OSN 3800/6800/8800 Data ConfigurationDokumen85 halamanOpti OSN 3800/6800/8800 Data ConfigurationTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- OG For WDM ASON Network Management - (V100R006C02 - 01)Dokumen354 halamanOG For WDM ASON Network Management - (V100R006C02 - 01)Taha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- OTC107203 OptiX OSN 380068008800 NMS Side Operation and Maintenance ISSUE1.01Dokumen37 halamanOTC107203 OptiX OSN 380068008800 NMS Side Operation and Maintenance ISSUE1.01Taha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- Troja 2: X:Akta Stream TrainingDokumen31 halamanTroja 2: X:Akta Stream TrainingTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- TNMS ASON / Ethernet Manager 11.0: User Manual (UMN)Dokumen113 halamanTNMS ASON / Ethernet Manager 11.0: User Manual (UMN)Taha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- OTC107401 OptiX NG WDM Optical Layer Grooming ISSUE1.04Dokumen61 halamanOTC107401 OptiX NG WDM Optical Layer Grooming ISSUE1.04Taha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- CPCM High Level User Guide - 3V1Dokumen48 halamanCPCM High Level User Guide - 3V1Taha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- GSM EvolutionDokumen9 halamanGSM EvolutionTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- NSN RNC 2600 Npgep ExpansionDokumen50 halamanNSN RNC 2600 Npgep ExpansionTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- Relay Gmm/Sm/Sms GMM/SM SMS: UE RNS 3G-Sgsn I UDokumen18 halamanRelay Gmm/Sm/Sms GMM/SM SMS: UE RNS 3G-Sgsn I UTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- 922 Database SpecificationsDokumen162 halaman922 Database SpecificationsTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- 6100 CommandsDokumen5 halaman6100 CommandsTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- Iq RadiosDokumen43 halamanIq RadiosTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- Flexible WaveguideDokumen12 halamanFlexible WaveguideTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- RET Control UnitsDokumen7 halamanRET Control UnitsTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- ALCOMA ALxxF Class Carrier Radio DescriptionDokumen91 halamanALCOMA ALxxF Class Carrier Radio DescriptionTaha TounsiBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Table of Contents For Computer Architecture: A Minimalist PerspectiveDokumen6 halamanTable of Contents For Computer Architecture: A Minimalist PerspectiveWilliam GilreathBelum ada peringkat
- TFT Proview AY565 LCD Service MaunalDokumen30 halamanTFT Proview AY565 LCD Service MaunalMarienka JankovaBelum ada peringkat
- A320LEAP1A-B12-0008.5 Cont&Ind R1 220517Dokumen78 halamanA320LEAP1A-B12-0008.5 Cont&Ind R1 220517simsimsomBelum ada peringkat
- Technote On - Communication Between M340 and ATV312 Over Modbus Using READ - VAR and WRITE - VARDokumen14 halamanTechnote On - Communication Between M340 and ATV312 Over Modbus Using READ - VAR and WRITE - VARsimbamike100% (1)
- Pk232mbx Operating ManualDokumen266 halamanPk232mbx Operating ManualrdeagleBelum ada peringkat
- Udacity Enterprise Syllabus Enterprise Security nd0035Dokumen15 halamanUdacity Enterprise Syllabus Enterprise Security nd0035Saturnin DeglaBelum ada peringkat
- CP4P Week3 Course Preview ActivityDokumen4 halamanCP4P Week3 Course Preview ActivityPresiBelum ada peringkat
- P2P Technology User's ManualDokumen8 halamanP2P Technology User's ManualElenilto Oliveira de AlmeidaBelum ada peringkat
- Huawei AC6805 Wireless Access Controller Datasheet - 2Dokumen16 halamanHuawei AC6805 Wireless Access Controller Datasheet - 2irfanBelum ada peringkat
- Management Reporter Integration Guide For Microsoft Dynamics® AX - DynAXDataProvInstGuide - ENUSDokumen17 halamanManagement Reporter Integration Guide For Microsoft Dynamics® AX - DynAXDataProvInstGuide - ENUSUmesh PanditBelum ada peringkat
- AFF660 Flyer April 2015Dokumen2 halamanAFF660 Flyer April 2015Iulian BucurBelum ada peringkat
- Part III WirelessDokumen130 halamanPart III WirelessRalph Laurence G VisayaBelum ada peringkat
- Fuzzy Logic Control of Blood Pressure During AnesthesiaDokumen14 halamanFuzzy Logic Control of Blood Pressure During AnesthesiaChennai Samshan J100% (1)
- CCNA Exploration 2 - Module 4 Exam Answers Version 4.0Dokumen3 halamanCCNA Exploration 2 - Module 4 Exam Answers Version 4.0fun kollaBelum ada peringkat
- Embedded System and Matlab SIMULINK PDFDokumen31 halamanEmbedded System and Matlab SIMULINK PDFclaudiunicolaBelum ada peringkat
- Fastpath Configuration Guide v1.1 PDFDokumen110 halamanFastpath Configuration Guide v1.1 PDFMonowarul Alam MonirBelum ada peringkat
- Gri 418 Customer Privacy 2016 PDFDokumen9 halamanGri 418 Customer Privacy 2016 PDFsharmilaBelum ada peringkat
- Wayne Patterson, Cynthia E. Winston-Proctor - Behavioral Cybersecurity - Applications of Personality Psychology and Computer Science (2019, Taylor & Francis - CRC) - Libgen - LiDokumen291 halamanWayne Patterson, Cynthia E. Winston-Proctor - Behavioral Cybersecurity - Applications of Personality Psychology and Computer Science (2019, Taylor & Francis - CRC) - Libgen - Lisor ronBelum ada peringkat
- Asml 20110808 Careers Brochure ASML NLDokumen12 halamanAsml 20110808 Careers Brochure ASML NLerkin1989Belum ada peringkat
- FDokumen38 halamanFyuniar asmariniBelum ada peringkat
- Innovative Charts in Excel: Team Start Point Performance ScoreDokumen6 halamanInnovative Charts in Excel: Team Start Point Performance ScoreVictorBelum ada peringkat
- Python Go HackersDokumen23 halamanPython Go HackersAdaAdaAjeChanel33% (3)
- Seismic Processing - Noise Attenuation Techniques PDFDokumen3 halamanSeismic Processing - Noise Attenuation Techniques PDFDavid Karel AlfonsBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal 2014 BatchDokumen5 halamanProposal 2014 BatchimnithinBelum ada peringkat
- Priority ConservationDokumen6 halamanPriority Conservationapi-213428788Belum ada peringkat
- Z Remy SpaanDokumen87 halamanZ Remy SpaanAlexandra AdrianaBelum ada peringkat
- Pandapower PDFDokumen167 halamanPandapower PDFAlen TatalovićBelum ada peringkat
- BSNL Summer Traning ReportDokumen39 halamanBSNL Summer Traning ReportMohd MunzirBelum ada peringkat
- Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphDokumen15 halamanBlock Diagram and Signal Flow GraphAngelus Vincent GuilalasBelum ada peringkat
- Free License Keys of Kaspersky Internet Security 2017 Activation Code PDFDokumen20 halamanFree License Keys of Kaspersky Internet Security 2017 Activation Code PDFCaesar Catalin Caratasu0% (1)