Ecuaciones Exactas
Diunggah oleh
Diacono10Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ecuaciones Exactas
Diunggah oleh
Diacono10Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
[ECUACIONES EXACTAS] Unidad I
Ecuaciones Exactas
Definicin de una expresin diferencial
M ( x, y)dx N ( x, y)dy 0
Es una diferencial exacta en una regin R
del plano xy
si
corresponde a la diferencial total alguna funcin. Una ecuacin:
M ( x, y)dx N ( x, y)dy
Se dice que es exacta si la expresin del miembro izquierdo es una
diferencial exacta.
El siguiente teorema es un criterio para determinar si una diferencial
es exacta.
Teorema
Supongamos que M ( x, y) y N ( x, y) son continuas y tienen derivadas
parciales de primer orden continuas en una regin del plano xy .
Entonces una condicin necesaria y suficiente para que
M ( x, y)dx N ( x, y)dy
Sea una diferencial exacta es que
M N
y
x
Mtodo de solucin
Primero demuestre que
M N
y
x
Suponga entonces que
f
M ( x, y )
x
As podremos encontrar integrando M ( x, y) con respecto a x
mientras se mantiene y constante. Escribimos
Prof. Gerson Villa Gonzlez
Pgina 1
[ECUACIONES EXACTAS] Unidad I
f ( x, y) M ( x, y)dx g ( y)
Donde la funcin arbitraria g ( y)
Derive
ahora
(1.1)
con
(1.1)
es la constante de integracin.
respecto
suponga
que
M ( x, y)dx g '( y) N ( x, y)
y y
De esto resulta
g '( y ) N ( x, y )
M ( x, y )dx
y
(1.2)
Nota. En el procedimiento anterior podramos perfectamente haber
empezado por suponer que
f
N ( x, y )
y
Las anlogas de (1.1) y (1.2) seran:
f ( x, y ) N ( x, y )dy h( x)
y
h '( x) M ( x, y )
N ( x, y )dy
x
Respectivamente.
Prof. Gerson Villa Gonzlez
Pgina 2
[ECUACIONES EXACTAS] Unidad I
Problemas Propuestos
En los problemas siguientes determine si la ecuacin respectiva es
exacta. Si lo es resulvala.
Problema 1
y
1 ln x dx 1 ln x dy
x
y
M ( x, y ) 1 ln x
x
M 1
y x
N ( x, y ) 1 ln x
N 1
x x
En consecuencia la ecuacin es exacta por lo tanto existe una funcin
f ( x, y) tal que
f
y
1 ln x
x
x
f
1 ln x
y
Al integrar la segunda de estas ecuaciones obtenemos:
f y
y
h '( x) 1 ln x
x x
x
h '( x) 1 ln x
h '( x) 1 ln x dx
h( x) x x ln x x
h( x) x ln x
Sustituyendo tenemos
C y y ln x x ln x
Prof. Gerson Villa Gonzlez
Pgina 3
[ECUACIONES EXACTAS] Unidad I
Problema 2
1 1
t
y
t
dt
ye
dy 0
2
t 2 y2
t 2 y2
t t
1 1
y
M ( x, y ) 2 2
t t
t y2
2
2
M t y 1 y 2 y 2 y 2 t 2 y 2
y2 t 2
2
2
2
y
t 2 y2
t 2 y 2 t 2 y 2
N ( x, y ) ye y
t
t y2
2
2
2
N t y 1 t 2t
y2 t 2
2
2
2 2
t
t
t 2 y 2
En consecuencia es exacta por lo tanto existe una funcin f ( x, y) tal
que
f 1 1
y
2 2
t t t
t y2
f
t
ye y 2
y
t y2
Al integrar la primera de estas ecuaciones obtenemos:
f ( x, y ) M ( x, y )dt h( y )
1 1
y
f ( x, y ) 2 2
dt h( y )
2
t
t
t
1
f ( x, y ) ln t tan 1
t
Prof. Gerson Villa Gonzlez
t
h( y )
y
Pgina 4
[ECUACIONES EXACTAS] Unidad I
La integral en azul se desarrolla a continuacin
y
a 2 x 2 a sec u
t 2 y 2 dt tan u x / a bien x a tan u
t 2 y 2 a 2 sec2 u
t 2 y 2 y 2 sec2 u
t y tan u dt y sec 2 udu
u tan 1
y
2
1
y
sec
u
du
du
tan
y 2 sec2 u
Calculamos la derivada parcial con respecto a y
e igualamos el
resultado a N ( x, y) y obtenemos
t
Dy
f x, y
y h '( y ) ye y t
2
y
t 2 y2
t
1
y
t
f x, y
t
y2
2 2 h ' y ye y 2
y t
y
t y2
y2
f x, y
t
t
2 2 h ' y ye y 2
y
y t
t y2
h '( y ) ye y
h( y ) ye y e y
t
1
ln t tan 1 ye y e y C
t
y
Prof. Gerson Villa Gonzlez
Pgina 5
[ECUACIONES EXACTAS] Unidad I
Problemas Suplementarios
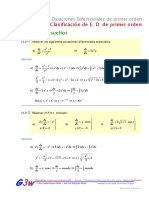
1. 4t 3 y 15t 2 y dt t 4 3 y 2 t dy 0 sol. t 4 y 5t 3 ty y 3 C
2.
3. x
y 2dx x 2 2 xy dy 0 sol. no es exacta
dy
2 xe x y 6 x 2 sol. ln x e y / x 1
dx
Prof. Gerson Villa Gonzlez
Pgina 6
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Conceptos Mecánica de FluidosDokumen2 halamanConceptos Mecánica de FluidosNagiri leonBelum ada peringkat
- Sistemas Dinamicos DiscretosDokumen2 halamanSistemas Dinamicos DiscretosCristian Sarmiento SBelum ada peringkat
- Cauchy EulerDokumen17 halamanCauchy EulerCarlos Rojas SernaBelum ada peringkat
- Integrales ImpropiasDokumen14 halamanIntegrales Impropiasasuid100% (1)
- Qué Es La Impresión 3DDokumen22 halamanQué Es La Impresión 3DPILAR LOARTEBelum ada peringkat
- Clases de MatricesDokumen2 halamanClases de MatricesPORTEGACAMPOVERDEBelum ada peringkat
- Sistemas de Ecuaciones 1Dokumen8 halamanSistemas de Ecuaciones 1fx_itachiBelum ada peringkat
- Mate II-funciones de Varias Variables-FabiolaDokumen35 halamanMate II-funciones de Varias Variables-FabiolaChristian Villalobos100% (1)
- Equilibrio de Cuerpos RígidosDokumen5 halamanEquilibrio de Cuerpos RígidosAdrian Cuellar SampayoBelum ada peringkat
- Unidad 4. La Derivada PDFDokumen7 halamanUnidad 4. La Derivada PDFIrisOrozcoFonsecaBelum ada peringkat
- Mètodo de Diferencias Divididas de NewtonDokumen5 halamanMètodo de Diferencias Divididas de NewtonMuxaxa marynhaBelum ada peringkat
- Algoritmo de Denavit HartenbergDokumen6 halamanAlgoritmo de Denavit HartenbergGil Robles LoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Derivación NuméricaDokumen11 halamanDerivación Numéricaman101100Belum ada peringkat
- Investigacion Unidad 2 Ecuaciones DifDokumen15 halamanInvestigacion Unidad 2 Ecuaciones DifCristian Ramirez Herrera100% (1)
- Teoría de errores y aproximaciones numéricasDokumen34 halamanTeoría de errores y aproximaciones numéricasMontoya JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Procesos Que Provocan Desprendimiento de VirutaDokumen23 halamanProcesos Que Provocan Desprendimiento de VirutaJoseiito Jesus DBelum ada peringkat
- Mecanizado básico: torneado, fresado, taladrado y roscadoDokumen8 halamanMecanizado básico: torneado, fresado, taladrado y roscadoNelson MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Flujo de FluidosDokumen68 halamanFlujo de FluidosJRPAVELONBelum ada peringkat
- LímitesDokumen6 halamanLímitesfrancozamora0100Belum ada peringkat
- Potencia ElectricaDokumen15 halamanPotencia Electricam contrerasBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuación DiferencialDokumen12 halamanEcuación DiferencialJose Vasquez Vargas100% (1)
- 19 Derivadas ParcialesDokumen13 halaman19 Derivadas ParcialesGinoJEspiNozaL0% (1)
- 7-Análisis VectorialDokumen49 halaman7-Análisis VectorialLuis Miguel Mendoza GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- P2.6.2 Ecuacion Diferencial Lineal Homogenea Con Coeficientes Constantes.Dokumen21 halamanP2.6.2 Ecuacion Diferencial Lineal Homogenea Con Coeficientes Constantes.Ana Karen Ramirez Dolores100% (1)
- Movimiento de Cuerpos Rígidos - Métodos de La Energía y La Cantidad de MovimientoDokumen30 halamanMovimiento de Cuerpos Rígidos - Métodos de La Energía y La Cantidad de MovimientoRaul PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Uso de La Tabla de La Distribucion Normal ZDokumen4 halamanUso de La Tabla de La Distribucion Normal ZFran OverdickBelum ada peringkat
- Sistemas de Ecuaciones Diferenciales Lineales Parte 1Dokumen6 halamanSistemas de Ecuaciones Diferenciales Lineales Parte 1Michael Martines IzquierdoBelum ada peringkat
- Unidad I. Vectores en El EspacioDokumen10 halamanUnidad I. Vectores en El EspacioJose fernandoBelum ada peringkat
- FUNCIONESDokumen32 halamanFUNCIONESLuis David Espinoza CadenasBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones Lineales en Una VariableDokumen4 halamanEcuaciones Lineales en Una VariableClemen AlarconBelum ada peringkat
- Informe TorsionDokumen9 halamanInforme TorsionCristhian Flores QuevedoBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales Lineales de Primer OrdenDokumen4 halamanEcuaciones Diferenciales Lineales de Primer Ordenleonardo2994Belum ada peringkat
- Antecedentes de Sistemas de Ecuaciones Diferenciales LinealesDokumen6 halamanAntecedentes de Sistemas de Ecuaciones Diferenciales LinealesJhassminBelum ada peringkat
- Unidad-IV Sistemas de Ecuaciones LinealesDokumen16 halamanUnidad-IV Sistemas de Ecuaciones LinealesCerchJimenezBelum ada peringkat
- Resumen Rotación de Cuerpos RígidosDokumen3 halamanResumen Rotación de Cuerpos RígidosgonzaloshookBelum ada peringkat
- Guia11. Metodo de Coeficientes IndeterminadosDokumen13 halamanGuia11. Metodo de Coeficientes IndeterminadosGerman Ramos PerezBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Sucesiones ConvergenciaDokumen15 halaman2.1 Sucesiones ConvergenciaAlfredo Lázaro GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- Función de Distribución Acumulada. Valor Esperado.Dokumen1 halamanFunción de Distribución Acumulada. Valor Esperado.Alejandro Olea DíazBelum ada peringkat
- Metodos Numericos Metodo de EulerDokumen6 halamanMetodos Numericos Metodo de EulerJesus Asaf Mtanous RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Calculadora ecuaciones diferenciales MATLABDokumen4 halamanCalculadora ecuaciones diferenciales MATLABArturino14Belum ada peringkat
- 4.sistemas de Ecuaciones Lineales Con MathematicaDokumen5 halaman4.sistemas de Ecuaciones Lineales Con MathematicadanielBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones Exactas y HomogéneasDokumen10 halamanEcuaciones Exactas y HomogéneasCarlosRodriguezArtetaBelum ada peringkat
- Calculo Vectorial Resumen 2da UnidadDokumen30 halamanCalculo Vectorial Resumen 2da UnidadSakers 1wacrewBelum ada peringkat
- Métodos de Métodos de Integración Integración: Proyecto 1Dokumen60 halamanMétodos de Métodos de Integración Integración: Proyecto 1Camila CincoBelum ada peringkat
- Unidad IDokumen24 halamanUnidad Ijoab100% (1)
- Mecanismos U1 Parte 1 1Dokumen52 halamanMecanismos U1 Parte 1 1Fernando HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Tensor de CurvaturaDokumen7 halamanTensor de CurvaturaJavier Garcia RajoyBelum ada peringkat
- Transformada de Laplace: Introducción, definición y propiedadesDokumen8 halamanTransformada de Laplace: Introducción, definición y propiedadesgianco_x12Belum ada peringkat
- Practica 1. Operaciones Lógicas y Tablas de VerdadDokumen8 halamanPractica 1. Operaciones Lógicas y Tablas de VerdadJorge VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Solución de Ecuaciones Diferenciales en MapleDokumen4 halamanSolución de Ecuaciones Diferenciales en MapleJorge LaraBelum ada peringkat
- Cauchy EulerDokumen7 halamanCauchy EulerAngel Julisses Valderrama ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Análisis Cualitativo de Sistemas Autónomos LinealesDokumen2 halamanAnálisis Cualitativo de Sistemas Autónomos Linealesbartle290171Belum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales Unidad 4Dokumen28 halamanEcuaciones Diferenciales Unidad 4Jason Clemente0% (1)
- Cálculo vectorial IPNDokumen26 halamanCálculo vectorial IPNAndrea LoBelum ada peringkat
- Ecua Dif8 (Primerordenoexactas)Dokumen13 halamanEcua Dif8 (Primerordenoexactas)Jimmy GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios EDE ResueltosDokumen9 halamanEjercicios EDE ResueltosJoze Antonio Mejia RoncalBelum ada peringkat
- ED exactas factor integranteDokumen9 halamanED exactas factor integranteMarco SánchezBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios ED UNADDokumen8 halamanEjercicios ED UNADKenBelum ada peringkat
- Ies Ipn UvgDokumen10 halamanIes Ipn UvgDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Desafíos y Temas Críticos de La EducaciónDokumen8 halamanDesafíos y Temas Críticos de La EducaciónDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Humano Impredecible o PredecibleDokumen4 halamanHumano Impredecible o PredecibleDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Guia Fundamentos de Programación Segundo Parcial AlumnoDokumen5 halamanGuia Fundamentos de Programación Segundo Parcial AlumnoDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Actividad Integradora Trabajo Integrador. Elaboración de Un Blog - GVGDokumen8 halamanActividad Integradora Trabajo Integrador. Elaboración de Un Blog - GVGDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Guia Segundo Examen Parcial 2016 GVG MNDokumen4 halamanGuia Segundo Examen Parcial 2016 GVG MNDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Problemario de Calculo Diferencial e IntregralDokumen24 halamanProblemario de Calculo Diferencial e IntregralDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Ies Ipn GVGDokumen9 halamanIes Ipn GVGDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Ies Ipn GVG PDFDokumen9 halamanIes Ipn GVG PDFDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Problemario de Ecuaciones DiferencialesDokumen21 halamanProblemario de Ecuaciones DiferencialesDiacono100% (1)
- Practica 01 Arduino y LCDDokumen14 halamanPractica 01 Arduino y LCDDiacono1067% (3)
- Practica Arduino Con MatlabDokumen24 halamanPractica Arduino Con MatlabDiacono10100% (2)
- Guia Segundo Examen Parcial 2016 GVG MNDokumen4 halamanGuia Segundo Examen Parcial 2016 GVG MNDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- ¿Sacrificamos Libertad Por Seguridad?Dokumen5 halaman¿Sacrificamos Libertad Por Seguridad?Diacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Guia Primer Parcial Lai 2016Dokumen4 halamanGuia Primer Parcial Lai 2016Diacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Guia Primer Parcial MN 2016Dokumen3 halamanGuia Primer Parcial MN 2016Diacono10Belum ada peringkat
- La Mentira Es La Base para La Fe y EsperanzaDokumen5 halamanLa Mentira Es La Base para La Fe y EsperanzaDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Guia Final Simulacion 2016-2 Grupo Sc09s GVGDokumen2 halamanGuia Final Simulacion 2016-2 Grupo Sc09s GVGDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Guia Bimestral Simulación 2016-1 Grupo Sc09sDokumen3 halamanGuia Bimestral Simulación 2016-1 Grupo Sc09sDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Práctica 5 Sensores de Proximidad Por InfrarojosDokumen5 halamanPráctica 5 Sensores de Proximidad Por InfrarojosDiacono1067% (3)
- Tecnicas de Escaneo MasivoDokumen56 halamanTecnicas de Escaneo MasivoDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Solucion Tarea Practica 1Dokumen6 halamanSolucion Tarea Practica 1Diacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Norma MexicanaDokumen3 halamanNorma MexicanaDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Honey PotsDokumen13 halamanHoney PotsDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Web Services en Sistemas DistribuidosDokumen15 halamanWeb Services en Sistemas DistribuidosDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Recomendaciones de SeguridadDokumen18 halamanRecomendaciones de SeguridadDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- HebrasDokumen21 halamanHebrasDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Como Preparar Un BosquejoDokumen10 halamanComo Preparar Un BosquejoDiacono10Belum ada peringkat
- Mate Matic AsDokumen43 halamanMate Matic AsCeSaar AlaRcon50% (2)
- Formulario de cálculo diferencialDokumen1 halamanFormulario de cálculo diferencialIchigo miyamizuBelum ada peringkat
- Vías Terrestres 1Dokumen6 halamanVías Terrestres 1Ricardo MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuación Diferencial LaplaceDokumen3 halamanEcuación Diferencial LaplaceRazorBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuacion Diferencial de Bernoulli.Dokumen7 halamanEcuacion Diferencial de Bernoulli.Anonymous iThQNMBelum ada peringkat
- Operador LaplaceDokumen7 halamanOperador LaplacetomBelum ada peringkat
- Cuadernillo de Analisis Integral de FuncionesDokumen35 halamanCuadernillo de Analisis Integral de FuncionesRenglones En BlancoBelum ada peringkat
- GUÍA - DEL - ESTUDIANTE - 2023 - 1 - Matemática II - Parte IDokumen72 halamanGUÍA - DEL - ESTUDIANTE - 2023 - 1 - Matemática II - Parte IInfante Fernandez EdwinBelum ada peringkat
- Matemática III: Integrales de Superficie, Teoremas de Divergencia y StokesDokumen3 halamanMatemática III: Integrales de Superficie, Teoremas de Divergencia y StokesRodrigo Alejandro Prudencio AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicio de Calculo VectorailDokumen4 halamanEjercicio de Calculo VectorailAlexander QuezadaBelum ada peringkat
- Deber Ci Matlab 1 ParcialDokumen3 halamanDeber Ci Matlab 1 ParcialKel-ler HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- Modulo Calculo DiferencialDokumen104 halamanModulo Calculo DiferencialBrayan Esteban Ceron PastesBelum ada peringkat
- Universidad Autónoma de ChiapasDokumen4 halamanUniversidad Autónoma de ChiapasJose Luis Lopez GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Actividad de Aprendizaje 2 (Aproximaciones Por Defecto)Dokumen5 halamanActividad de Aprendizaje 2 (Aproximaciones Por Defecto)adolfo diazBelum ada peringkat
- Semana 3 - Curvas ParametricasDokumen8 halamanSemana 3 - Curvas ParametricasDavid Andres NINO WALTEROSBelum ada peringkat
- Taller 2 Cálculo MultivariadoDokumen26 halamanTaller 2 Cálculo Multivariadojhon chaconBelum ada peringkat
- Rojas CalculoDokumen375 halamanRojas CalculoPeter VallejoBelum ada peringkat
- Universidad Nacional de San Antonio Abad Del Cusco: Escuela de Posgrado M Maestria en Ciencias: Mención MatemáticasDokumen110 halamanUniversidad Nacional de San Antonio Abad Del Cusco: Escuela de Posgrado M Maestria en Ciencias: Mención MatemáticasWilser Aldair Condori HolgadoBelum ada peringkat
- 518 2013 11 12 Integrales2Dokumen25 halaman518 2013 11 12 Integrales2Sergio Del CarpioBelum ada peringkat
- Medidores de Flujo de HidrocarburosDokumen11 halamanMedidores de Flujo de HidrocarburosAndrésTorres100% (1)
- Suma de Riemann para x^2+x en 1,2 con partición de 8Dokumen2 halamanSuma de Riemann para x^2+x en 1,2 con partición de 8Yoshi CoreBelum ada peringkat
- Regla de la cadena, tangente y costo marginalDokumen27 halamanRegla de la cadena, tangente y costo marginalEsmeralda Caballero Ponte100% (2)
- Evaluacion Final - Escenario 8: Historial de IntentosDokumen5 halamanEvaluacion Final - Escenario 8: Historial de IntentosLeonardo EcheverriBelum ada peringkat
- Solemne 2 Parte 1Dokumen3 halamanSolemne 2 Parte 1Mauricio Baeza100% (1)
- Ejercicios de ecuaciones diferencialesDokumen12 halamanEjercicios de ecuaciones diferencialesNinjanautaBelum ada peringkat
- Derivadas ParcialesDokumen1 halamanDerivadas ParcialesJose Francisco Barros RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Malla SonidoDokumen1 halamanMalla SonidoLuis Solvial100% (1)
- Plan Anual Matematica 8vo.Dokumen11 halamanPlan Anual Matematica 8vo.Ana Pazmiño de Torres0% (1)
- Universidad Marista Lic. ActuariaDokumen2 halamanUniversidad Marista Lic. ActuariaFelipe GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones diferenciales de primer ordenDokumen7 halamanEcuaciones diferenciales de primer ordenSilvia Verónica Varillas FioriBelum ada peringkat