Three Phase Faults - Muhit - Part1 (Version1)
Diunggah oleh
Ismat AraJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Three Phase Faults - Muhit - Part1 (Version1)
Diunggah oleh
Ismat AraHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EEE4103 Power System Analysis
M.S.Muhit
4. Symmetrical 3 phase faults
4.1 Timing and protective systems
Time is measured in cycles where 1 cycle=1/60 of a second 0.0167 second. (f=60 Hz for this case).
Another important term is protection. A single protective system will have at least one circuit breaker,
one relay, and instrument transformers to measure electrical quantities on the power system.
Transmission lines generally have a protective system one each end of the line.
Following initiation of a fault, a properly operating circuit breaker will open the circuit after 4-8 cycles.
4.2 Fault and its types
A fault refers to a short circuit in a power system. Faults can be divided into two broad classes:
temporary and permanent faults.
Temporary faults cause momentary disruption, but the fault is cleared without protection operation.
The most common type of temporary faults are those from lightning.
Permanent faults cause sustained disruption if not cleared by protection. The most common permanent
fault types are associated with one or more of the following
Wind
Ice loading
Thermal heating and sag
Various rare events such as:
Trees growing into line
Automobile striking tower
Earthquakes
Flooding
Airplanes
The four most common ways are
1. Three phase (5%)
2. Single line to ground (70%)
3. Double line to ground (10%)
4. Line to line (15%)
Fault type 1 is special as it is symmetric (balanced 3 phases)! Whereas the other faults are asymmetrical
fault.
Problems caused by faults
Currents
Generator acceleration
Loss of component
EEE4103 Power System Analysis
M.S.Muhit
4.3 Transients in R-L circuits
A power transmission network is comprised of elements that have primarily resistance and inductance
only (there is some capacitance but it tends to be small compared to the inductance). It is informative,
therefore, to study the characteristics of an RL circuit. Our main goal in doing so is to see the
relationship between the DC and steady-state components of the current after a fault.
Fig 4.1 Typical R-L circuit
The current flowing when a generator is short circuited is similar to that flowing when an ac. Voltage is
suddenly applied to a R-L series circuit.
The solution of the equation after performing Laplace transformation, solving for , and taking partial
derivatives into account,
Where,
Time constant,
Dc offset + symmetrical (ac) =asymmetrical total
2
EEE4103 Power System Analysis
M.S.Muhit
The ms AC fault current,
Magnitude of dc offset depends on
When,
For the largest fault current,
Now, rms values of ,
Where,
EEE4103 Power System Analysis
M.S.Muhit
4.4 Three phase short circuit unloaded synchronous machine
If
, then we have no dc component.
So, When the switch is closed, very high current will flow instantly and after a few cycle the current will
be reduced due to the effect of back e.m.f of the armature.
Fig 4.2 Actual response of RL circuit with no dc component
Oa is maxm for the sustained short circuit current at steady state condition.
Nearer to O, the decrement is rapid for Ob. The transient current expression is given by,
The subtransient current is as follows:
Here,
EEE4103 Power System Analysis
M.S.Muhit
Problem 4.1
A bolted short circuit occurs in the series R-L circuit.
V=20 KV, R=0.8 , X=8
The breaker opens 3 cycle after the fault.
Find: (i) RMS ac fault current
(ii)
momentary for
cycle which pass
through the circuit breaker (CB) before it opens.
(iii) The RMS fault current which the breaker
interrupt.
GS
V
Solution:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Similarly,
Problem 4.2
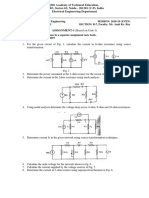
Two generators are connected in parallel to the low-voltage side of a three-phase transformer , as
shown in figure 1 .
G1
G2
Generator 1: 50 MVA, 13.8kV, X=25% .
Generator 2: 25 MVA, 13.8kV, X=25%
Transformer: 75 MVA, 13.8 /69 Y kV,X= 10% .
Beforethe fault occurs , the voltage on the high-voltage side of the transformer is 66 kV . The
transformer is unloaded and there is no circulating current between the generator .
Find the subtransient current in each generator when a three-phase short circuit occurs of the highvoltage side of the transformer.
5
EEE4103 Power System Analysis
M.S.Muhit
Solution:
Let us consider the transformer rating as the base.
For generator 1,
For generator 2,
As no circulating current flows, both
and
have the same magnitude.
For transformer,
Eg1
Eg2
For faulted condition, the switch S is closed.
Now,
Solving for eq. 1 and 2,
The actual subtransient fault current,
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDari EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- PSA - Lecture 6 - Symmetrical Fault Analysis (Part-1) - MAZSDokumen45 halamanPSA - Lecture 6 - Symmetrical Fault Analysis (Part-1) - MAZSAsikur Hasan SaumikBelum ada peringkat
- Further Electrical PowerDokumen18 halamanFurther Electrical PowerzzyyeeBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Balanced and Unbalanced FaultsDokumen117 halaman5 - Balanced and Unbalanced FaultsJuan Manuel VegaBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical Fault Analysis in Power SystemsDokumen14 halamanSymmetrical Fault Analysis in Power Systemsstudents answerBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDokumen35 halamanPower System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross Baldicka_r_vijayanand6550Belum ada peringkat
- Electrical Power System - Ii (2160908) : Active Learning AssignmentDokumen17 halamanElectrical Power System - Ii (2160908) : Active Learning AssignmentEzeldeen AgoryBelum ada peringkat
- Fault Analysis (Short-Circuit Analysis) Definition of FaultDokumen4 halamanFault Analysis (Short-Circuit Analysis) Definition of Faulthafiz_jaaffarBelum ada peringkat
- Calculations of Short Circuit CurrentsDokumen9 halamanCalculations of Short Circuit CurrentsCorneliusmusyokaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Fault Analysis 1.0 Timing, Protective Systems, and Fault TypesDokumen33 halamanIntroduction To Fault Analysis 1.0 Timing, Protective Systems, and Fault TypesAnonymous JzwlJ4snwlBelum ada peringkat
- SHORT CIRCUIT CALCULATIONSDokumen13 halamanSHORT CIRCUIT CALCULATIONSAmr EidBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit CalculationsDokumen10 halamanShort Circuit CalculationsvenkateshbitraBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical FaultsDokumen45 halamanSymmetrical FaultsTesfahun GirmaBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDokumen35 halamanPower System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickNnaabyendu SahaBelum ada peringkat
- EET301 2013 Chapter 6Dokumen51 halamanEET301 2013 Chapter 6Lee Boon HongBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical Faults and Transients in Power SystemsDokumen45 halamanSymmetrical Faults and Transients in Power SystemsPoor AdamBelum ada peringkat
- AC Machinery Lecture 1Dokumen52 halamanAC Machinery Lecture 1Derrick ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- How to Perform Short-Circuit Calculations (Part 1Dokumen4 halamanHow to Perform Short-Circuit Calculations (Part 1mshahidshaukatBelum ada peringkat
- Fault Analysis in Transmission System Using MatlabDokumen50 halamanFault Analysis in Transmission System Using MatlabSHIKHAR KHANDELWAL89% (46)
- Symmetrical FaultDokumen54 halamanSymmetrical FaultshinkazamaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit II Symmetrical Fault (Three Phase) Analysis: Transient On A Transmission LineDokumen12 halamanUnit II Symmetrical Fault (Three Phase) Analysis: Transient On A Transmission LinePankaj SarnobatBelum ada peringkat
- Protective Relay SettingsDokumen20 halamanProtective Relay SettingsChân Gà NướngBelum ada peringkat
- ESBI White Paper Delayed Zero Crossings Following Short Circuit PDFDokumen6 halamanESBI White Paper Delayed Zero Crossings Following Short Circuit PDFbgojkovic13Belum ada peringkat
- Fault Current Calculations in Electrical SystemsDokumen11 halamanFault Current Calculations in Electrical SystemsSureshraja9977Belum ada peringkat
- HT Switchgear RequirementsDokumen22 halamanHT Switchgear Requirementskankw879Belum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit Analysis Lecture NotesDokumen107 halamanShort Circuit Analysis Lecture NotesSankar MuthuswamyBelum ada peringkat
- EE369 Power Systems Fault AnalysisDokumen35 halamanEE369 Power Systems Fault AnalysisNima NiassatiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 18 - Power System AnalysisDokumen35 halamanLecture - 18 - Power System AnalysisAnonymous wIPMQ5rhBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDokumen35 halamanPower System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickAtabat AduduBelum ada peringkat
- Relay CoordinationDokumen68 halamanRelay CoordinationrajuBelum ada peringkat
- 022 TT Short-Circuit PDFDokumen4 halaman022 TT Short-Circuit PDFwwe_himanshuBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit CalculationDokumen41 halamanShort Circuit CalculationWilliamBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit Analysis of 33/11/0.4 KV Distribution System Using ETAPDokumen7 halamanShort Circuit Analysis of 33/11/0.4 KV Distribution System Using ETAPHamza KhalilBelum ada peringkat
- Ee 1004 Power Quality Two Mark Questions and AnswersDokumen12 halamanEe 1004 Power Quality Two Mark Questions and Answersscientistabbas100% (4)
- Lec 2Dokumen13 halamanLec 2Chamod DissanayakeBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit CalcsDokumen6 halamanShort Circuit Calcsapi-3759595100% (1)
- Transfo Reviewer V V T TDokumen19 halamanTransfo Reviewer V V T TcatherinejeanasBelum ada peringkat
- ProtectionDokumen53 halamanProtectionsantoshkumar100% (1)
- Section 01 (NXPowerLite)Dokumen44 halamanSection 01 (NXPowerLite)Ahmed FaragBelum ada peringkat
- Ee553 Chap 4 1 NewDokumen30 halamanEe553 Chap 4 1 NewWorl BossBelum ada peringkat
- Short CircuitDokumen30 halamanShort CircuitRa ArBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit CalDokumen7 halamanShort Circuit Caldian jaelaniBelum ada peringkat
- DK1913 CH10 PDFDokumen26 halamanDK1913 CH10 PDFManiraj PerumalBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical Fault Analysis PDFDokumen16 halamanSymmetrical Fault Analysis PDFlimkokchiang809Belum ada peringkat
- Derby U Faults Electrical PowerDokumen10 halamanDerby U Faults Electrical PowermsavoooBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit CalculationsDokumen44 halamanShort Circuit Calculationssasikumar100% (2)
- Learn About Short-Circuit Electrical CurrentsDokumen4 halamanLearn About Short-Circuit Electrical CurrentsBassem MostafaBelum ada peringkat
- Turn To Turn Fault For TransformerDokumen20 halamanTurn To Turn Fault For Transformerdeepak2628Belum ada peringkat
- How to Calculate Short Circuits Using the Point-to-Point MethodDokumen9 halamanHow to Calculate Short Circuits Using the Point-to-Point MethodMuhammad Irfan Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsDari EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesDari EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesBelum ada peringkat
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDari EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDari EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDari EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlDari EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- PDB Questions of 1998Dokumen5 halamanPDB Questions of 1998Ismat AraBelum ada peringkat
- SoundDokumen23 halamanSoundIsmat AraBelum ada peringkat
- Control System BasicDokumen11 halamanControl System BasicIsmat AraBelum ada peringkat
- 35 BCS Written RoutineDokumen4 halaman35 BCS Written RoutineIsmat AraBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics of Cls 7Dokumen156 halamanMathematics of Cls 7Ismat AraBelum ada peringkat
- Academic Calendar Full Dhaka University 2013Dokumen152 halamanAcademic Calendar Full Dhaka University 2013Ismat AraBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDokumen55 halamanElectrical and Electronics Engineering Interview Questions and Answerstowfiqeee87% (30)
- PAM Process Parameters and ApplicationsDokumen10 halamanPAM Process Parameters and ApplicationsLalaine EspiniliBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Safety in Mines: Work Regulations 1989. Approved Code of PracticeDokumen21 halamanElectrical Safety in Mines: Work Regulations 1989. Approved Code of PracticeAyu Wanda SaraswatiBelum ada peringkat
- As-3 REMOTE Tester For Arc Welding DB EngDokumen2 halamanAs-3 REMOTE Tester For Arc Welding DB Enga_velinovskiBelum ada peringkat
- Uninterruptible Power Supply Reference Design With A PIC-Www - CircuitdiagramDokumen60 halamanUninterruptible Power Supply Reference Design With A PIC-Www - Circuitdiagramirfan_ghani100% (1)
- Manual de Operacion y Mantenimiento Celdas de CargaDokumen70 halamanManual de Operacion y Mantenimiento Celdas de CargaDavidSamudioBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDokumen10 halamanElectrical Measuring InstrumentsKhen RamosBelum ada peringkat
- MCR3 - Manual de MantenimientoDokumen132 halamanMCR3 - Manual de MantenimientoMarcelo BeroldoBelum ada peringkat
- JSS Academy Electrical Engineering AssignmentDokumen2 halamanJSS Academy Electrical Engineering Assignmentamit621988Belum ada peringkat
- COMAND Error CodesDokumen1 halamanCOMAND Error CodesYael DemedetskayaBelum ada peringkat
- Superheterodyne Detector: What Heterodyning IsDokumen5 halamanSuperheterodyne Detector: What Heterodyning IsMiko BristolBelum ada peringkat
- MOD BUS: Digital Panel MeterDokumen2 halamanMOD BUS: Digital Panel MetertechnoprimeBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Receiving Inspection - Smart Grid Solutions - SiemensDokumen5 halamanTransformer Receiving Inspection - Smart Grid Solutions - Siemense.vicente.caballeroBelum ada peringkat
- Thermocouple: Seeback EffectDokumen8 halamanThermocouple: Seeback EffectMuhammadHadiBelum ada peringkat
- OETI Carpet Classification enDokumen4 halamanOETI Carpet Classification ensabry singerBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Market Characteristi Cs and Promoti On Strategy of Rooftop PVDokumen103 halamanAnalysis of Market Characteristi Cs and Promoti On Strategy of Rooftop PVSonu PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Demand Load & Voltage Drop CalculationDokumen1 halamanDemand Load & Voltage Drop CalculationKhizer Amin100% (1)
- Single Inductor Multi Output (SIMO) DC DCDokumen13 halamanSingle Inductor Multi Output (SIMO) DC DCamruthanarayananBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State Drives - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDokumen4 halamanSolid State Drives - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVBelum ada peringkat
- Dih 52Dokumen7 halamanDih 52Sourav Kumar GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 06-Problems PDFDokumen5 halamanHomework 06-Problems PDFElizabeth DouglasBelum ada peringkat
- f3sg R Series Safety Light Curtain ManualDokumen6 halamanf3sg R Series Safety Light Curtain ManualAlfonso GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- EeschDokumen12 halamanEeschMohana CBelum ada peringkat
- TPE - 322302 - AFABQQEFWB - Cipta MandiriDokumen5 halamanTPE - 322302 - AFABQQEFWB - Cipta MandiriTrisna RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Si-Tech Semiconductor Co.,Ltd: S80N10R/SDokumen8 halamanSi-Tech Semiconductor Co.,Ltd: S80N10R/SStefan IuscoBelum ada peringkat
- Guangzhou Hengchi Light Volt Power Generation SystemDokumen30 halamanGuangzhou Hengchi Light Volt Power Generation Systemsubaru WRX STIBelum ada peringkat
- 3.26.2020 I2C Unbounded - Solve Your 2-Wire ChallengesDokumen14 halaman3.26.2020 I2C Unbounded - Solve Your 2-Wire ChallengesMohsen haghighatBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Incident ReportDokumen33 halamanPower System Incident ReportmentongBelum ada peringkat
- VOTANO 100 PresentationDokumen26 halamanVOTANO 100 Presentationbcqbao100% (1)
- Battery Charger Testing MethodsDokumen6 halamanBattery Charger Testing Methodsmathew_john0077393Belum ada peringkat
- 256 MCDC506 eDokumen3 halaman256 MCDC506 eAndy KristiantoBelum ada peringkat