IMPAC Alviz 1
Diunggah oleh
Yaj CruzadaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IMPAC Alviz 1
Diunggah oleh
Yaj CruzadaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1 INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
Prepared by: Archie D. Alviz, R.N., R.M. | manofsteel_archie@yahoo.com| facebook fan
page: Sir Archie D. Alviz
INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
IMPAC STRATEGIES:
antenatal care
normal delivery care assisted by a skilled birth attendant
treatment for complications of pregnancy (including hemorrhage, obstructed labour, eclampsia, sepsis, abortion complications)
neonatal care
family planning advice
management of sexually transmitted infections.
IMPAC TARGETS:
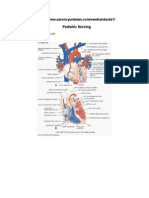
IMPAC FLOWCHART:
ASK, CHECK RECORD
LOOK, LISTEN, FEEL
SIGNS
CLASSIFY
TREAT
Why did you come?
for yourself?
for the baby?
How old is the
baby?
What is the
concern?
Is the woman being
wheeled or
carried in or:
bleeding vaginally
convulsing
looking very ill
unconscious
in severe pain
in labour
delivery is imminent
If the woman is or has:
unconscious (does not
answer)
convulsing
bleeding
severe abdominal pain or
looks very ill
headache and visual
disturbance
severe difficulty breathing
fever
severe vomiting.
Emergency
FOR WOMAN
Transfer woman to a
treatment room for Rapid
assessment and management
B3-B7 .
Call for help if needed.
Reassure the woman that
she will be taken care of
immediately.
Ask her companion to stay.
Imminent delivery or
Labour
Labour
Transfer the woman to the
labour ward.
Call for immediate
assessment.
If the baby is or has:
very small
convulsions
difficult breathing
just born
any maternal concern.
Emergency
for baby
Transfer the baby to the
treatment room for
immediate Newborn care J1J11 .
Ask the mother to stay.
Check if baby is or has:
very small
convulsing
2 INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
Prepared by: Archie D. Alviz, R.N., R.M. | manofsteel_archie@yahoo.com| facebook fan
page: Sir Archie D. Alviz
breathing difficulty
Pregnant woman, or after
delivery,
with no danger signs
A newborn with no danger
signs or
maternal complaints.
Routine care
Keep the woman and baby
in the waiting room for
routine care.
WHO Recommended Interventions for Improving Maternal and Newborn Health
Routine essential care
Situational care
Additional care
Specialized care
Care to all women and babies
Care dependent on disease patterns in the community.
Care to women and babies with moderately severe diseases or complications
Care to women and babies with severe diseases or complications.
Table 1. Care in pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum period for mother and newborn infant
Routine care
Additional care
(offered to all women and babies)
(for women and babies with moderately
severe diseases and complications)
FORBIDDEN SEALS:
ALL ABOUTNORMAL PREGNANCY
FORBIDDEN SEALS:
1. Pregnancy Confirmation
ALL ABOUTPROMPT TREATMENT
2. Pregnancy Monitoring
1. Early treatment
3. Pregnancy Detection
2. Referrals
Complications, Diagnostics
4. Nutrition
Specialized - obstetrical and
neonatal care
(for women and babies with severe
diseases and complications)
FORBIDDEN SEALS:
ALL ABOUTSEVERE
COMPLICATIONS
Pregnancy care
4 visits
Essential
Confirmation of pregnancy
Monitoring of progress of pregnancy
and assessment of maternal and fetal
well-being
Detection of problems complicating
pregnancy (e.g., anaemia, hypertensive
disorders, bleeding, malpresentations,
multiple pregnancy
Respond to other reported complaints.
Tetanus immunization, anaemia
prevention and control (iron and folic
acid supplementation)
Information and counselling on self
care at home, nutrition, safer sex,
breastfeeding, family planning, healthy
lifestyle
Birth and emergency planning, advice
on danger signs and emergency
preparedness
Recording and reporting
Syphilis testing
Treatment of mild to moderate
pregnancy complications:
- mild to moderate anaemia
- urinary tract infection
- vaginal infection
Post abortion care and family planning
Pre-referral treatment of severe
complications
- pre-eclampsia
- eclampsia
- bleeding
- infection
- complicated abortion
Support for women with special needs
e.g. adolescents, women living with
violence
Treatment of syphilis (woman and her
partner)
Treatment of severe pregnancy
complications:
- anaemia
- severe pre-eclampsia
- eclampsia
- bleeding
- infection
- other medical complications
Treatment of abortion complications
Situational
HIV testing and counselling
Antimalarial Intermittent preventive
treatment (IPT) and promotion of
insecticide treated nets (ITN)
Deworming
Assessment of female genital
mutilation (FGM)
Prevention of mother to child
transmission of HIV (PMTCT) by
antiretroviral treatment (ART), infant
feeding counselling, mode of delivery
advice
Treatment of mild to moderate
opportunistic infections
Treatment of uncomplicated malaria
Treatment of severe HIV infection
Treatment of complicated malaria
Childbirth Care
(labour, delivery,
and
immediate
postpartum)
Essential
Care during labour and delivery
- Diagnosis of labour
- Monitoring progress of labour,
maternal and fetal well-being with
partograph
- Providing supportive care and pain
Treatment of abnormalities and
complications (e.g. prolonged
labour, vacuum extraction; breech
presentation, episiotomy, repair of
genital tears, manual removal of
placenta)
Treatment of severe complications
in childbirth and in the immediate
postpartum period, including caesarean
section, blood transfusion and
hysterectomy):
- obstructed labour
3 INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
Prepared by: Archie D. Alviz, R.N., R.M. | manofsteel_archie@yahoo.com| facebook fan
page: Sir Archie D. Alviz
relief
- Detection of problems
and complications (e.g.
malpresentations, prolonged and/or
obstructed labour, hypertension,
bleeding, and infection)
- Delivery and immediate care of
the newborn baby, initiation of
breastfeeding
- Newborn resuscitation
- Active management of third stage
of labour
Immediate postpartum care of mother
- Monitoring and assessment of
maternal well being, prevention
and detection of complications (e.g.
hypertension, infections, bleeding,
anaemia)
- Treatment of moderate posthaemorrhagic
anaemia
- Information and counselling on
home self care, nutrition, safe sex,
breast care and family planning
- Advice on danger signs, emergency
preparedness and follow-up
Recording and reporting
Pre-referral management of serious
complications (e.g. obstructed labour,
fetal distress, preterm labour, severe
peri- and postpartum haemorrhage)
Emergency management of
complications if birth imminent
Support for the family if maternal
death
- malpresentations
- eclampsia
- severe infection
- bleeding
Induction and augmentation of labour
Situational
Vitamin A administration
Prevention of mother-to-child
transmission of HIV by mode of
delivery, guidance and support for
chosen infant feeding option
Management of complications related
to FGM
Postpartum
maternal
care (up to 6
weeks)
Essential
Assessment of maternal wellbeing
Prevention and detection of
complications (e.g. infections, bleeding,
anaemia)
Anaemia prevention and control (iron
and folic acid supplementation)
Information and counselling on
nutrition, safe sex, family planning
and provision of some contraceptive
methods
Advice on danger signs, emergency
preparedness and follow-up
Provision of contraceptive methods
Treatment of some problems (e.g. mild
to moderate anaemia, mild puerperal
depression)
Pre-referral treatment of some
problems (e.g. severe postpartum
bleeding, puerperal sepsis)
Treatment of all complications
- severe anaemia
- severe postpartum bleeding
- severe postpartum infections
- severe postpartum depression
Female sterilization
Situational
Promotion of ITN use
Treatment of uncomplicated malaria
Treatment of complicated malaria
Newborn care
(birth and
immediate
postnatal)
Essential
Promotion, protection and support for
breastfeeding
Monitoring and assessment of
wellbeing, detection of complications
(breathing, infections, prematurity, low
birthweight, injury, malformation)
Infection prevention and control,
rooming-in
Eye care
Information and counselling on home
care, breastfeeding, hygiene
Advice on danger signs, emergency
preparedness and follow-up
Immunization according to the national
guidelines (BCG, HepB, OPV-0)
Care if moderately preterm, low
birth weight or twin: support for
breastfeeding, warmth, frequent
assessment of wellbeing and detection
of complications e.g. feeding difficulty,
jaundice, other perinatal problems
Kangaroo Mother Care follow-up
Treatment of mild to moderate
- local infections (cord, skin, eye,
thrush)
- birth injuries
Pre-referral management of infants
with severe problems:
- very preterm babies and/or birth
weight very low
- severe complications
- malformations
Supporting mother if perinatal death.
Management of severe newborn
problems - general care for the sick
newborn and management of specific
problems:
- preterm birth
- breathing difficulty
- sepsis
- severe birth trauma and asphyxia
- severe jaundice
- Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC)
Management of correctable
malformations
4 INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
Prepared by: Archie D. Alviz, R.N., R.M. | manofsteel_archie@yahoo.com| facebook fan
page: Sir Archie D. Alviz
Situational
Promotion of sleeping under ITN
Presumptive treatment of congenital
syphilis
Prevention of mother-to-child
transmission of HIV by ART
Support for infant feeding of maternal
choice
Treatment of:
- congenital syphilis
- neonatal tetanus
Postnatal
newborn care
(visit from/at
home)
Essential
Assessment of infants wellbeing and
breastfeeding
Detection of complications and
responding to maternal concerns
Information and counselling on home
care
Additional follow-up visits for high
risk babies (e.g. preterm, after severe
problems, on replacement feeding)
Management of:
- minor to moderate problems and
- feeding difficulties
Pre-referral management of severe
problems:
- convulsions
- inability to feed
Supporting the family if perinatal death
Management of severe newborn
problems:
- sepsis
- other infections
- jaundice
- failure to thrive
Table 2 lists the places where care should be provided through health services, the type of providers required and the recommended
interventions and commodities at each level.
Table 2. Place of care, providers, interventions and commodities
Health care
Level of
Venue / place
health care
Provider
Interventions and
commodities
Pregnancy
(antenatal)
care
Routine
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Outpatient clinic of a hospital
Outreach home visit
Health worker with midwifery
skills*
On site tests (Hb, syphilis)
Maternal health record
Vaccine
Basic oral medicines
Situational
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Outpatient clinic of a hospital
Outreach home visits
Health worker with midwifery
skills*
On site tests (HIV)
Insecticide treated nets (ITN)
Additional
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Outpatient clinic of a hospital
Health worker with midwifery
and
selected obstetric and
neonatal
skills*
IV fluids
Parenteral drugs (antibiotics,
MgSO4, antimalarial)
Manual Vacuum Aspiration (MVA)
Anti-retroviral therapy (ART)
Specialized
Secondary
Hospital
Team of doctors, midwives
and
nurses
All of the above plus:
Blood transfusion
Surgery
Laboratory tests
Obstetric care
Routine
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Maternity ward of a hospital
Outreach home care
Health worker with midwifery
skills*
Delivery set
Oxytocin
Partograph
Situational
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Maternity ward of a hospital
Outreach home care
Health worker with midwifery
skills*
ART
Additional
Primary
Health centre in the
Health worker with midwifery
Vacuum extraction
Childbirth
(mother and
baby)
5 INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
Prepared by: Archie D. Alviz, R.N., R.M. | manofsteel_archie@yahoo.com| facebook fan
page: Sir Archie D. Alviz
community
Maternity ward of a hospital
and
selected obstetric and
neonatal
skills*
Manual removal of placenta
Repair of genital tears
IV fluids
MgSO4, parenteral uterotonics,
and
antibiotics
Newborn resuscitation
Specialized
Mother
Secondary
Hospital
Team of doctors, midwives
and
nurses with neonatal care
skills
All of the above plus:
Surgery
Blood transfusion
Specialized
Newborn
Secondary
Hospital
Team of doctors and nurses
with
obstetric and nursing skills
Oxygen
IV fluids
Parenteral antebiotics
Blood transfusion
Laboratory - biochemical and
microbiology (small blood samples)
Routine
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Outpatient clinic of a hospital
Outreach home visit
Health worker with midwifery
skills*
On site tests (Hb, syphilis)
Vaccines
Basic oral medicines
Situational
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Outpatient clinic of a hospital
Health worker with midwifery
skills*
On site tests (HIV)
ART
Additional
Primary
Health centre in the
community
Outpatient clinic of a hospital
Health worker with midwifery
and
selected obstetric and
neonatal
skills*
IV fluids
Parenteral drugs (antibiotics,
MgSO4, antimalarial)
Manual removal of placenta
Specialized
Mother
Secondary
Hospital
Team of doctors, midwives
and
nurses
All of the above plus:
Blood transfusion
Surgery
Laboratory tests
Obstetric care
Specialized
Newborn
Secondary
Hospital
Team of doctors, midwives
and
nurses with neonatal skills
Oxygen
IV fluids
Parenteral antebiotics
Blood transfusion
Laboratory - biochemical and
microbiology (small samples)
Postpartum
(mother),
postnatal
(newborn
infant)
Table 3. Home care, family, community and workplace support for the woman during pregnancy and childbirth and for the newborn
infant
Home/family
Community and workplace
Pregnancy
Safe and nutritive diet
Safe sexual practices
Support for quitting smoking
Protection from passive tobacco smoking
Support for avoiding hard work
Planning for birth, and emergencies -mother and baby
Knowledge and support for the birth and emergency plan
Recognition of labour and danger signs
Maternity protection
Time off for antenatal care visits
Safe and clean workplace
Tobacco free working environment
Pregnant adolescents kept at school
6 INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
Prepared by: Archie D. Alviz, R.N., R.M. | manofsteel_archie@yahoo.com| facebook fan
page: Sir Archie D. Alviz
Support for compliance with preventive treatments
Support / accompaniment for pregnancy care visits
Adolescent girls encouraged to continue going to school
Participation in improving quality of services
Participation in transport and financing scheme
Situational
Support for taking ART and for coping with its side effects
Support for HIV positive women
Childbirth
Accompanying and supporting the woman in childbirth
Support and care for the rest of the family
Organize transport and financial support
Support for the family during childbirth and
immediate
postpartum
Postpartum and
beyond
Support for exclusive breastfeeding/replacement feeding
Personal hygiene
Safe disposal / washing of pads
Support for rest and less work load
Safe and nutritive diet
Safe sexual practices
Motivation for prescribed treatments
Recognition of dangers signs, including blues / depression
Optimal pregnancy spacing
Reporting birth and death (vital registration)
Participation in improving quality of services
Participation in transport and financing scheme
Maternity leave
Breastfeeding breaks
Time off for postpartum and baby care visits
If mother referred to hospital, support that
she is accompanied
with the baby
Newborn and young
infant
Exclusive breastfeeding
Hygiene (cord care, washing, clothes)
Avoiding contacts with sick family members
Clean, warm and quiet place, tobacco and fire smoke free
Extra care for small babies (preterm, low birth weight)
including KMC
Support for routine and follow up visits
Motivation for home treatment of minor problems
Recognition of danger signs
Safe disposal of baby stool
Care seeking at health facility or hospital
Promotion, protection and support for
breast feeding.
Keeping mother with the baby in hospital for
breastfeeding
Supporting the family during maternal
absence
Support for referral care for sick newborn.
Situational
Sleeping under ITN
Table 4. Care for the woman before and between pregnancies
Care by health services
Home/family
Community and workplace
Education
Information on prevention of
HIV and
STI infections
Adolescence
Immunization according to national
policy (tetanus and rubella)
Family planning
HIV prevention including VCT
Delayed childbearing
Healthy lifestyle
Balanced diet, including iodized
salt
All women of
reproductive age
Family planning
Assessment and management of STIs
HIV prevention including testing and
counselling
Optimal pregnancy timing
Table 5. Pregnant women not wanting child
Care by health services
Pregnant woman not
wanting child
Safe abortion (where legal)
Post-abortion care and family
planning
Home/family
Care for unwanted pregnancy
Community and workplace
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- NP1 BulletsDokumen17 halamanNP1 BulletsJea VesagasBelum ada peringkat
- TRA Psychiatric NursingDokumen10 halamanTRA Psychiatric NursingGil GanibanBelum ada peringkat
- Public Health Nursing in Schools and the WorkplaceDokumen9 halamanPublic Health Nursing in Schools and the WorkplaceJoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- Top Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingDokumen3 halamanTop Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZBelum ada peringkat
- Bullets: "Victory Belongs To Those Who Are Most Persevering. Ad Majorem Dei Gloriam."Dokumen15 halamanBullets: "Victory Belongs To Those Who Are Most Persevering. Ad Majorem Dei Gloriam."Johnmer Avelino100% (1)
- Nursing Licensure Exam Practice QuestionsDokumen11 halamanNursing Licensure Exam Practice QuestionsPaul Lexus Gomez LorenzoBelum ada peringkat
- Nle Tips For OrthopedicDokumen2 halamanNle Tips For OrthopedicCharie OcampoBelum ada peringkat
- MS PERI OPushjDokumen13 halamanMS PERI OPushjEmeroot RootBelum ada peringkat
- Goal 3: Good Health and Well-: Placed in The Center of The Public Health BagDokumen26 halamanGoal 3: Good Health and Well-: Placed in The Center of The Public Health BagHed KcamBelum ada peringkat
- Prelims Pedia 102Dokumen10 halamanPrelims Pedia 102quidditch07Belum ada peringkat
- TRA Pediatric Nursing 1Dokumen4 halamanTRA Pediatric Nursing 1Gil GanibanBelum ada peringkat
- Preboard Exam Np3 Medical Surgical NursingDokumen19 halamanPreboard Exam Np3 Medical Surgical NursingBhie Bhie100% (1)
- Funda Prac QDokumen11 halamanFunda Prac QAngelica Murillo Ang-AngcoBelum ada peringkat
- June 2008 NleDokumen71 halamanJune 2008 NleCharm TanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewerDokumen8 halamanPsychiatric Nursing ReviewerDarren Mae MosadaBelum ada peringkat
- My Reviewer On Funda Epaphras Joel T. MilitarDokumen82 halamanMy Reviewer On Funda Epaphras Joel T. MilitarEpaphras Joel MilitarBelum ada peringkat
- Q&A Random - 2Dokumen18 halamanQ&A Random - 2Filipino Nurses CentralBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro Post TestDokumen4 halamanNeuro Post TestAhrisJeannine EscuadroBelum ada peringkat
- PNLE III For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsDokumen10 halamanPNLE III For Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsANGELINE PALATINO100% (1)
- NCM 102 OB Abnormal 2Dokumen113 halamanNCM 102 OB Abnormal 2Maria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IIBelum ada peringkat
- Professional Adjustment and Nursing EthicsDokumen13 halamanProfessional Adjustment and Nursing EthicsGaea Angela MACATANGAYBelum ada peringkat
- IFSU PretestDokumen29 halamanIFSU PretestTerzky TerceroBelum ada peringkat
- Compt - Appraisal Prelim 2 Glenda CasundoDokumen19 halamanCompt - Appraisal Prelim 2 Glenda CasundoJoanne Bernadette AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Disorders Guide: Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal GlandsDokumen5 halamanEndocrine Disorders Guide: Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal GlandsMiss GBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Practice IVDokumen11 halamanNursing Practice IVapi-3718174100% (1)
- PNLE I Nursing PracticeDokumen8 halamanPNLE I Nursing PracticeDanielle KayeBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Dokumen3 halamanPediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Jonah MaasinBelum ada peringkat
- 43 Questions NLE Dec 2011Dokumen15 halaman43 Questions NLE Dec 2011Lyka Cuanan CorcueraBelum ada peringkat
- Bulacan State University College of Nursing Final Exam ReviewDokumen7 halamanBulacan State University College of Nursing Final Exam ReviewDemiar Madlansacay QuintoBelum ada peringkat
- PNLE June 2007 With Key AnswersDokumen82 halamanPNLE June 2007 With Key AnswersJustin CubillasBelum ada peringkat
- GI System OverviewDokumen20 halamanGI System OverviewJoshua DelantarBelum ada peringkat
- Community Health Nursing Part 1 & 2Dokumen35 halamanCommunity Health Nursing Part 1 & 2mark OrpillaBelum ada peringkat
- June 2009 Nursing Practice 1Dokumen9 halamanJune 2009 Nursing Practice 1Karl Gabriel BonifacioBelum ada peringkat
- Final Diagnostic ExamDokumen28 halamanFinal Diagnostic ExamAlfred Benjamin CajitaBelum ada peringkat
- November 2008 PreboardDokumen84 halamanNovember 2008 PreboardYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- CD-RESPI TBDokumen3 halamanCD-RESPI TBNae OrdanozoBelum ada peringkat
- New Bon-NleDokumen3 halamanNew Bon-NleCristina L. JaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Registered Nurse Rushed to Help Injured Elderly Woman Hit by MotorcycleDokumen26 halamanRegistered Nurse Rushed to Help Injured Elderly Woman Hit by MotorcycleNina OaipBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Practice IDokumen11 halamanNursing Practice IEulamarie TevesBelum ada peringkat
- Pfinal Pedia With AnswerDokumen5 halamanPfinal Pedia With AnswerplmokjniBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Practice 1 (Dec 2006)Dokumen12 halamanNursing Practice 1 (Dec 2006)ɹǝʍdןnos100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing ReviewerDokumen16 halamanMaternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewerjoyce.feir03Belum ada peringkat
- My Courses: Dashboard RMC Cap 2 Prelim Medical Surgical Nursing 4 Post Test 2Dokumen9 halamanMy Courses: Dashboard RMC Cap 2 Prelim Medical Surgical Nursing 4 Post Test 2Fraylle AbongBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Nursing GastroDokumen3 halamanPediatric Nursing GastronieacatleyaBelum ada peringkat
- PNLE I Foundation of Nursing ReviewDokumen52 halamanPNLE I Foundation of Nursing ReviewDarnell Adrian EstobioBelum ada peringkat
- Top Q&a - Chn-Imci-Cd-Ob-Pedia-LmDokumen5 halamanTop Q&a - Chn-Imci-Cd-Ob-Pedia-LmWilmaBongotanPadawilBelum ada peringkat
- Scope of Nle1116aDokumen413 halamanScope of Nle1116aericBelum ada peringkat
- SOALANDokumen92 halamanSOALANSyafiqAziziBelum ada peringkat
- Pentagon CDDokumen12 halamanPentagon CDJohnBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Common Board QuestionsDokumen66 halamanIntegrated Common Board QuestionsBorja MyatBelum ada peringkat
- HTTP://WWW - Aaroncyuntalan.com/newhandouts1/ Pediatric NursingDokumen99 halamanHTTP://WWW - Aaroncyuntalan.com/newhandouts1/ Pediatric Nursingchelljynxie100% (2)
- Anc For C1Dokumen41 halamanAnc For C1Henok Y KebedeBelum ada peringkat
- Maternal and Child Health (MCH)Dokumen20 halamanMaternal and Child Health (MCH)Redw AnBelum ada peringkat
- Manage High-Risk PregnanciesDokumen33 halamanManage High-Risk PregnanciesDakshayini MbBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal CareDokumen17 halamanAntenatal CareARIESGA, NICOLE FRANCINE M.Belum ada peringkat
- Cne On MCHDokumen30 halamanCne On MCHPraachii SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Preventive ObstetricsDokumen8 halamanPreventive ObstetricsAnn Merlin JobinBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis of Pregnancy & Focussed Antenatal CareDokumen29 halamanDiagnosis of Pregnancy & Focussed Antenatal CareHomeground entertainmentBelum ada peringkat
- Maternal & Child Health CareDokumen209 halamanMaternal & Child Health CareAhsan Ul Kayum Bhuiyan100% (1)
- Practice Questions in Physics ScienceDokumen21 halamanPractice Questions in Physics ScienceYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Content Update-PhysicsDokumen10 halamanContent Update-PhysicskirtveluzBelum ada peringkat
- NotesDokumen1 halamanNotesYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Developing Competitivenes ProposalDokumen17 halamanDeveloping Competitivenes ProposalYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Facilitating Human LearningDokumen8 halamanFacilitating Human LearningYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Ok Na NQT Teaching Math To The FIRSTMATH ClassDokumen8 halamanOk Na NQT Teaching Math To The FIRSTMATH ClassYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Preboard Civil ServiceDokumen26 halamanPreboard Civil ServiceYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science Notes-2Dokumen78 halamanPhysical Science Notes-2Yaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science Notes-1Dokumen216 halamanPhysical Science Notes-1Yaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- CPA EXAM QsDokumen34 halamanCPA EXAM QsYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Developing CompetitivenessDokumen17 halamanDeveloping CompetitivenessYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Developing Competitivenes ProposalDokumen17 halamanDeveloping Competitivenes ProposalYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Pre & Post Observation Interview and EvaluationDokumen5 halamanIntegrated Pre & Post Observation Interview and EvaluationYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- NTQ Curriculum Ok NaDokumen5 halamanNTQ Curriculum Ok NaYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Ok Na TEACHER - Observation CONSENT - FORM - FirstmathDokumen1 halamanOk Na TEACHER - Observation CONSENT - FORM - FirstmathYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Ok Na Firstmath Clasroom Observation Protocol 201112Dokumen26 halamanOk Na Firstmath Clasroom Observation Protocol 201112Yaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Nov 22 Message 2 of 3Dokumen1 halamanNov 22 Message 2 of 3Yaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Pre & Post Observation Interview and EvaluationDokumen5 halamanIntegrated Pre & Post Observation Interview and EvaluationYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 7 EditedDokumen32 halamanModule 7 EditedYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 9Dokumen23 halamanModule 9Maria TracyBelum ada peringkat
- Journals Publication DBSDokumen2 halamanJournals Publication DBSYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Pre TestDokumen2 halamanAssessment Pre TestYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Pie and Bar Graphs (2011 and 2012)Dokumen3 halamanPie and Bar Graphs (2011 and 2012)Yaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Faculty Development Plan - DMDokumen2 halamanFaculty Development Plan - DMYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Faculty Development Plan DBSDokumen1 halamanFaculty Development Plan DBSYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Question No. 2Dokumen3 halamanQuestion No. 2Yaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Faculty Development Plan Department: ICTDokumen1 halamanFaculty Development Plan Department: ICTYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- A Link ExchangDokumen2 halamanA Link ExchangYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Linkages Final Aug 29Dokumen55 halamanLinkages Final Aug 29Yaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- Research Topics Global Competitiveness Internationalization EducationDokumen2 halamanResearch Topics Global Competitiveness Internationalization EducationYaj CruzadaBelum ada peringkat
- EMS Drug DilutionDokumen21 halamanEMS Drug Dilutionthompson godfreyBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Pustaka KolelitiasisDokumen2 halamanDaftar Pustaka KolelitiasisReni IstiarBelum ada peringkat
- Bu SuryaniDokumen68 halamanBu SuryaniMaulana SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- MidazolamDokumen18 halamanMidazolamHarnugrahanto AankBelum ada peringkat
- Teva PharmaceuticalDokumen17 halamanTeva PharmaceuticalGanesh VedhachalamBelum ada peringkat
- Dry SocketDokumen20 halamanDry SocketHosuru SwethaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacoeconomics - Part IIIDokumen29 halamanPharmacoeconomics - Part IIISima JabbariBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter33Walker2015 PDFDokumen12 halamanChapter33Walker2015 PDFMai AngelBelum ada peringkat
- Fphar 12 768268Dokumen25 halamanFphar 12 768268Araceli Anaya AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Intravenous Pamidronate Treatment in Children With Osteogenesis ImperfectaDokumen5 halamanEffect of Intravenous Pamidronate Treatment in Children With Osteogenesis Imperfectavikash singhBelum ada peringkat
- R - MN R - 1 Z: Mkg-Xixltechlib/1 T/06Dokumen48 halamanR - MN R - 1 Z: Mkg-Xixltechlib/1 T/06Jhantu MazumderBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Case in Contact Lenses, 1e - 2001Dokumen205 halamanClinical Case in Contact Lenses, 1e - 2001Miguel PalaciosBelum ada peringkat
- CelecoxibDokumen2 halamanCelecoxibLaromac RolandBelum ada peringkat
- IRB Definitions (Is It Research? and Definitions of Exempt, Expedited and Full)Dokumen4 halamanIRB Definitions (Is It Research? and Definitions of Exempt, Expedited and Full)analyn123Belum ada peringkat
- CPV/CCV Ag (3 Lines) : VcheckDokumen2 halamanCPV/CCV Ag (3 Lines) : VcheckFoamfab WattikaBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Disorders - Ay NewDokumen46 halamanJoint Disorders - Ay NewPraisingson SyiemliehBelum ada peringkat
- Obama Mind ControlDokumen68 halamanObama Mind Controlkdnkgljfg67% (3)
- Nurture and ConnectionDokumen4 halamanNurture and Connectionparents021100% (1)
- Growth PredictionDokumen101 halamanGrowth PredictionKristty Magallanes100% (1)
- Lesson 6 (New) Medication History InterviewDokumen6 halamanLesson 6 (New) Medication History InterviewVincent Joshua TriboBelum ada peringkat
- (ANES) Mon 01 Epidural For Labor Analgesia (A2021)Dokumen3 halaman(ANES) Mon 01 Epidural For Labor Analgesia (A2021)Miguel SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Atlantis Implant Compatibility Chart 79214-US-1107Dokumen2 halamanAtlantis Implant Compatibility Chart 79214-US-1107Jean-Christophe PopeBelum ada peringkat
- Adr FormDokumen2 halamanAdr FormSachin Kumar PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Compartment SyndromeDokumen29 halamanCompartment SyndromeFazmial UjirBelum ada peringkat
- Pembimbing: Dr. Dr. Maria Regina Rachmawati, Pa (K), SPKFR Presentan: DR Ratna EkawatiDokumen27 halamanPembimbing: Dr. Dr. Maria Regina Rachmawati, Pa (K), SPKFR Presentan: DR Ratna EkawatiratnaekawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Juvenile Sex Offenders A Complex PopulationDokumen6 halamanJuvenile Sex Offenders A Complex PopulationRoberto GalleguillosBelum ada peringkat
- Severe Gastric ImpactionDokumen4 halamanSevere Gastric ImpactionNanda Ayu Cindy KashiwabaraBelum ada peringkat
- R3 Vital Pulp Therapy With New MaterialsDokumen7 halamanR3 Vital Pulp Therapy With New MaterialsWening TyasBelum ada peringkat
- Autologous Transfusion Strategies to Reduce Allogeneic Blood UseDokumen31 halamanAutologous Transfusion Strategies to Reduce Allogeneic Blood Usethalida24100% (1)
- Unit 5 Hospital EquipmentDokumen3 halamanUnit 5 Hospital EquipmentALIFIABelum ada peringkat
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- The Menopause Manifesto: Own Your Health With Facts and FeminismDari EverandThe Menopause Manifesto: Own Your Health With Facts and FeminismPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (18)
- ADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementDari EverandADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- The Strength and Conditioning Bible: How to Train Like an AthleteDari EverandThe Strength and Conditioning Bible: How to Train Like an AthleteBelum ada peringkat
- All in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayDari EverandAll in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- The 21-Day Self-Love Challenge: Learn How to Love Yourself Unconditionally, Cultivate Confidence, Self-Compassion and Self-WorthDari EverandThe 21-Day Self-Love Challenge: Learn How to Love Yourself Unconditionally, Cultivate Confidence, Self-Compassion and Self-WorthBelum ada peringkat
- The Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouDari EverandThe Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfDari EverandBrain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- What No One Tells You: A Guide to Your Emotions from Pregnancy to MotherhoodDari EverandWhat No One Tells You: A Guide to Your Emotions from Pregnancy to MotherhoodPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (30)
- A Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersDari EverandA Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (71)
- Perimenopause Power: Navigating your hormones on the journey to menopauseDari EverandPerimenopause Power: Navigating your hormones on the journey to menopausePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- What to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Dari EverandWhat to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Younger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondDari EverandYounger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (110)
- The Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenDari EverandThe Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (153)
- Hypnobirthing Meditations: Relaxation And Mindfulness Techniques For Expectant Mothers To Experience A Natural And Positive ChildbirthDari EverandHypnobirthing Meditations: Relaxation And Mindfulness Techniques For Expectant Mothers To Experience A Natural And Positive ChildbirthPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Dark Feminine Energy: Free Your Femme Fatale Ignite Your Irresistible Allure Through Mystique, Sexuality, Femininity, and Elegance to Become the Dark Diva No One Can IgnoreDari EverandDark Feminine Energy: Free Your Femme Fatale Ignite Your Irresistible Allure Through Mystique, Sexuality, Femininity, and Elegance to Become the Dark Diva No One Can IgnorePenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Sacred Womb Healing Meditation Divine feminine alignment: heal ancestral traumas deep wounds, release blocked sexual energies, flow to creativity, overcome the energies of birthing, joy love happyDari EverandSacred Womb Healing Meditation Divine feminine alignment: heal ancestral traumas deep wounds, release blocked sexual energies, flow to creativity, overcome the energies of birthing, joy love happyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- I'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionDari EverandI'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (123)
- Breaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodDari EverandBreaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (33)
- Menopause: All you need to know in one concise manualDari EverandMenopause: All you need to know in one concise manualPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (11)
- Rediscover Your Sparkle: Nourish Your SoulDari EverandRediscover Your Sparkle: Nourish Your SoulPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- I'm So Effing Hungry: Why We Crave What We Crave – and What to Do About ItDari EverandI'm So Effing Hungry: Why We Crave What We Crave – and What to Do About ItBelum ada peringkat
- ROAR: How to Match Your Food and Fitness to Your Unique Female Physiology for Optimum Performance, Great Health, and a Strong, Lean Body for LifeDari EverandROAR: How to Match Your Food and Fitness to Your Unique Female Physiology for Optimum Performance, Great Health, and a Strong, Lean Body for LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (44)
- Women, Food, And Hormones: A 4-Week Plan to Achieve Hormonal Balance, Lose Weight, and Feel Like Yourself AgainDari EverandWomen, Food, And Hormones: A 4-Week Plan to Achieve Hormonal Balance, Lose Weight, and Feel Like Yourself AgainPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (14)
- Skinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!Dari EverandSkinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!Penilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (488)
- Getting My Bounce Back: How I Got Fit, Healthier, and Happier (And You Can, Too)Dari EverandGetting My Bounce Back: How I Got Fit, Healthier, and Happier (And You Can, Too)Belum ada peringkat
- Bumpin': The Modern Guide to Pregnancy: Navigating the Wild, Weird, and Wonderful Journey From Conception Through Birth and BeyondDari EverandBumpin': The Modern Guide to Pregnancy: Navigating the Wild, Weird, and Wonderful Journey From Conception Through Birth and BeyondPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (38)
- After Birth: What Nobody Tells You - How to Recover Body and MindDari EverandAfter Birth: What Nobody Tells You - How to Recover Body and MindPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Mindful Birthing: Training the Mind, Body, and Heart for Childbirth and BeyondDari EverandMindful Birthing: Training the Mind, Body, and Heart for Childbirth and BeyondPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (24)
- The Better Period Food Solution: Eat Your Way to a Lifetime of Healthier CyclesDari EverandThe Better Period Food Solution: Eat Your Way to a Lifetime of Healthier CyclesBelum ada peringkat