Softwares Fstat Ver.2.9.3.2
Diunggah oleh
Iseng IsengHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Softwares Fstat Ver.2.9.3.2
Diunggah oleh
Iseng IsengHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
FSTAT
FSTAT is a computer package for PCs which estimates and tests gene
diversities and differentiation statistics from codominant genetic markers. It
computes both Nei and Weir & Cockerham families of estimators of gene
diversities and F-statistics, and tests them using randomisation methods.
Jackknife and Bootstrap confidence intervals are also provided. The windows
version also estimates statistics developed for the stepwise mutation model
(Rst and the like).
HIERFSTAT
hierfstat is a package for R allowing to estimate F-statistics and variance
components with the methods of moments for any number of levels in a
hierarchy. The package also allows to test the significance of population
differentiation using the likelihood ratio G-statistic or the variance
components.
quantiNEMO
quantiNEMO is an individual-based, genetically explicit stochastic simulation
program. It was developed to investigate the effects of selection, mutation,
recombination, and drift on quantitative traits with varying architectures in
structured populations connected by migration and located in a
heterogeneous habitat. quantiNEMO is highly flexible at various levels:
population, selection, trait(s) architecture, genetic map for QTL and/or
markers, environment, demography, mating system, etc.
PCAGEN
PCAGEN is a computer package for Windows which performs Principal
Component Analysis (PCA) on gene frequency data. Graphical ordinations of
samples are provided and graphs can be saved. Using randomizations, the
program also tests the significance of total inertia as well as individual axes
inertia.
BIASDISP
BIASDISP is now included in FSTAT.
A software developed by Jrme Goudet.
FSTAT is a computer package for PCs which estimates and tests gene diversities
and differentiation statistics from codominant genetic markers. It computes both
Nei and Weir & Cockerham families of estimators of gene diversities and Fstatistics, and tests them using randomisation methods. The current version
(Feb. 2002) is 2.9.3.2. Previous versions are not maintained anymore. However,
if you still run DOS, you can still download the old version (1.2) below.
To install FSTAT 2.9.3, double click the file fstat293dist.exe once you have
downloaded it. This will create under the folder you have chosen the following
architecture of folders and files:
Fstat293.exe
Fstat293.hlp
Fstat293.cnt
Readme.txt
Readme.doc
In order to read the help file, you will need to install winhlp32.exe
The following folders contain data and example files, use of which is detailed in the
help file:
.\data
.\data\bias dispersal
.\data\multiple regression
What FSTAT does
From a data set of codominant or haploid genetic markers, FSTAT calculates the
following:
- Number of individuals per sample and loci.
- Allele frequency estimated per sample and overall.
- Observed and expected number of each genotype per sample and locus.
- Unbiased gene diversity per sample and locus.
- Number of alleles sampled per locus and sample, as well as overall.
- [NEW] Allelic richness per locus and sample, as well as overall samples
- Fis per locus and sample, as well as a test of whether it is significantly positive or
negative (significant deficit and excess of heterozygotes respectively).
- Nei's (1987) estimators of gene diversities and differentiation.
- Weir & Cockerham (1984) Capf (Fit), theta (Fst) and smallf (Fis) estimated per
allele, per locus and overall. FSTAT also calculates Hamilton's (1971) relatedness
relat=2Fst/(1+Fit), calculated using an estimator strictly equivalent to Queller and
Goodnight's (1989). This measure is the average relatedness of individuals within
samples when compared to the whole data set.
Confidence intervals based on resampling schemes are provided for Weir &
Cockerham statistics:
- Jackknifing per locus over samples is performed. The resampling unit are the
different samples. This procedure is only carried out if there are more than 4
samples.
- Jackknifing over loci. In this case, the resampling units are the different loci. This
procedure is only carried out if there are more than 4 loci.
- Bootstrapping over loci. Bootstrapping over loci is performed only when there is
more than 4 loci in the data set.
- Estimation of R- statistics (Slatkin, 1995), specifically designed for microsatellite
undergoing stepwise mutations.
- Estimation of Fst (theta) per pair of samples.
- Overall test whether each sample at each locus is in HW equilibrium.
- Test whether the entire data set is in HW equilibrium.
- Test whether samples are differentiated assuming either that there is HW within
samples or that there is not (Only one of these 2 tests can be carried out).
- Test whether each sample at each locus is in Hardy-Weinberg (HW) equilibrium.
- Test whether each pair of samples is differentiated. The tests do not assume
random mating within samples. A table of significant pairwise differentiation after
corrections for multiple testing is produced.
- [NEW] Test whether each pair of loci in each sample and overall is at genotypic
equilibrium
- [NEW] Test whether groups of samples differ for a large panel of statistics
- [NEW] Test whether categories of individuals differ in dispersal rates (four
different tests)
- [NEW] Convert FSTAT format to GENEPOP and vice- versa
- [NEW] Performs multiple regression or Partial Mantel tests
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- GooglepreviewDokumen69 halamanGooglepreviewtarunchatBelum ada peringkat
- Lambika YogaDokumen2 halamanLambika Yogavsyamkumar100% (3)
- GA Toolbox in MatlabDokumen105 halamanGA Toolbox in MatlabSoy GuajiroBelum ada peringkat
- Application in Establishing Epidemiology and Variability: Genome & Protein " Sequence Analysis Programs"Dokumen23 halamanApplication in Establishing Epidemiology and Variability: Genome & Protein " Sequence Analysis Programs"Dr. Rajesh Kumar100% (3)
- R GWAS PackagesDokumen18 halamanR GWAS PackagesmnstnBelum ada peringkat
- Chich The ChickenDokumen23 halamanChich The ChickenSil100% (4)
- Aquaculture BiotechnologyDokumen31 halamanAquaculture BiotechnologyIseng Iseng100% (1)
- Design of Helical Antennas For 433 MHZ Radio Telemetry Ground Station and Uav (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)Dokumen7 halamanDesign of Helical Antennas For 433 MHZ Radio Telemetry Ground Station and Uav (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)Tiara Nira SariBelum ada peringkat
- Methods Available For The Analysis of Data From Dominant Molecular MarkersDokumen6 halamanMethods Available For The Analysis of Data From Dominant Molecular MarkersEduardo RuasBelum ada peringkat
- Fstat HelpDokumen12 halamanFstat Helpsbspu100% (1)
- Arlequin (Version 3.0) : An Integrated Software Package For Population Genetics Data AnalysisDokumen4 halamanArlequin (Version 3.0) : An Integrated Software Package For Population Genetics Data AnalysisRahmat FauziBelum ada peringkat
- Manual FBAT 2009Dokumen50 halamanManual FBAT 2009evaldoamaralBelum ada peringkat
- Arlequin Software Package for Population Genetics AnalysisDokumen4 halamanArlequin Software Package for Population Genetics AnalysisSara MagoBelum ada peringkat
- Asap Poster SibdaysDokumen1 halamanAsap Poster SibdaysAdrian ShajkofciBelum ada peringkat
- StrafDokumen12 halamanStraftauhidjBelum ada peringkat
- Patterns of Molecular Evolution in Pathogenesis-Related ProteinsDokumen9 halamanPatterns of Molecular Evolution in Pathogenesis-Related ProteinsFrontiersBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Signature of Metastasis in Primary Solid TumorsDokumen4 halamanMolecular Signature of Metastasis in Primary Solid TumorsjimakosjpBelum ada peringkat
- Mascot: Take The Guesswork Out of Protein Identification..Dokumen12 halamanMascot: Take The Guesswork Out of Protein Identification..mikeydiBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Sequence RepeatsDokumen1 halamanSimple Sequence Repeatsmilove_88003272Belum ada peringkat
- Felsenstein (1985)Dokumen9 halamanFelsenstein (1985)Marita AndreaBelum ada peringkat
- 2.exome Variant Interpretation SNVs CNVsDokumen9 halaman2.exome Variant Interpretation SNVs CNVsfilda d5Belum ada peringkat
- Lost in Parameter Space: A Road Map For: Josephine R. Paris, Jamie R. Stevens and Julian M. CatchenDokumen14 halamanLost in Parameter Space: A Road Map For: Josephine R. Paris, Jamie R. Stevens and Julian M. CatchenAlejandro JijónBelum ada peringkat
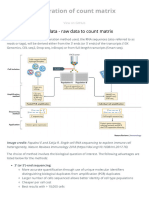
- Generation of Count Matrix - Introduction To Single-Cell RNA-seqDokumen9 halamanGeneration of Count Matrix - Introduction To Single-Cell RNA-seqYanelisa PulaniBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Finger PrintingDokumen21 halamanDNA Finger PrintingMeylinda EnggiBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Genes Skills Database Comparison of GenesDokumen2 halaman3.1 Genes Skills Database Comparison of GenesBig CinemaBelum ada peringkat
- Detecting signatures of selection from DNA sequences using DatamonkeyDokumen31 halamanDetecting signatures of selection from DNA sequences using DatamonkeyRebriarina HapsariBelum ada peringkat
- Manual StimateDokumen48 halamanManual StimateAna García GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- E Cient Enumeration of Phylogenetically Informative SubstringsDokumen17 halamanE Cient Enumeration of Phylogenetically Informative Substringsmuhammad ahmadBelum ada peringkat
- TCS1 21Dokumen8 halamanTCS1 21amparoparanoiaBelum ada peringkat
- MUMmer PDFDokumen8 halamanMUMmer PDFRohith AthreyaBelum ada peringkat
- SPADE UserGuideDokumen71 halamanSPADE UserGuidewildwildlifeBelum ada peringkat
- STRBase: A Short Tandem Repeat DNA DatabaseDokumen16 halamanSTRBase: A Short Tandem Repeat DNA DatabaseArindi AmirantiBelum ada peringkat
- BT Practical SpotterDokumen2 halamanBT Practical SpotterAnkit AthreyaBelum ada peringkat
- Bioinformatics:: Guide To Bio-Computing and The InternetDokumen34 halamanBioinformatics:: Guide To Bio-Computing and The InternetZoran BogoeskiBelum ada peringkat
- DAVID TutorialDokumen34 halamanDAVID TutorialData ScrewBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of The Wild-Type: C. Elegans TranscriptomeDokumen27 halamanAnalysis of The Wild-Type: C. Elegans TranscriptomeFeseha AbebeBelum ada peringkat
- Nucl. Acids Res. 2004 Stanke W309 12Dokumen4 halamanNucl. Acids Res. 2004 Stanke W309 12Shashank YadavBelum ada peringkat
- User's Guide For Program SPADE (Species Prediction and Diversity Estimation)Dokumen71 halamanUser's Guide For Program SPADE (Species Prediction and Diversity Estimation)Jorge Valencia HerverthBelum ada peringkat
- Perdido en El Sapcio StackDokumen22 halamanPerdido en El Sapcio StackAlejandro JijónBelum ada peringkat
- ESTWeb Bioinformatics Services For ESTDokumen2 halamanESTWeb Bioinformatics Services For ESTタ ー タBelum ada peringkat
- 1996 The Natural Way To Evolve HardwareDokumen4 halaman1996 The Natural Way To Evolve HardwareZxBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises For Phylogeny: Exercise 1. Parsimony and Rooted Versus Unrooted TreesDokumen11 halamanExercises For Phylogeny: Exercise 1. Parsimony and Rooted Versus Unrooted TreesNeeru RedhuBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Experiments For The NIPS 2003 Variable Selection BenchmarkDokumen30 halamanDesign of Experiments For The NIPS 2003 Variable Selection BenchmarkBayu Adhi NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- V5i9 0221Dokumen4 halamanV5i9 0221Anmol SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Criticizing The ArticleDokumen4 halamanCriticizing The ArticleRizalyn MertoBelum ada peringkat
- W. James Kent - BLAT-The BLAST-Like Alignment ToolDokumen10 halamanW. James Kent - BLAT-The BLAST-Like Alignment ToolYopghm698Belum ada peringkat
- Alternative Splicing DatabasesDokumen5 halamanAlternative Splicing DatabasesKanupriya TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- A Generic Framework For Population-Based Algorithms, Implemented On Multiple FpgasDokumen13 halamanA Generic Framework For Population-Based Algorithms, Implemented On Multiple FpgasAnonymous PsEz5kGVaeBelum ada peringkat
- PIIS0002929707618473Dokumen3 halamanPIIS0002929707618473Gayathri ViswanathanBelum ada peringkat
- Private Book Headingss SecretDokumen20 halamanPrivate Book Headingss Secretinspectiv5Belum ada peringkat
- Private Book HeadingDokumen20 halamanPrivate Book Headinginspectiv5Belum ada peringkat
- "ScriptAlert (1) :scriptDokumen20 halaman"ScriptAlert (1) :scriptxssBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Sequence Alignment ThesisDokumen8 halamanMultiple Sequence Alignment Thesisvalerielohkamprochester100% (2)
- BMC Genomics: Fourmidable: A Database For Ant GenomicsDokumen5 halamanBMC Genomics: Fourmidable: A Database For Ant GenomicsywurmBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Local Alignment Search ToolDokumen8 halamanBasic Local Alignment Search ToolfacefaceBelum ada peringkat
- SC Perthub Single Cell OmicsDokumen34 halamanSC Perthub Single Cell OmicsGANYA U 2022 Batch,PES UniversityBelum ada peringkat
- Rosen et al 2012Dokumen16 halamanRosen et al 2012Claudia MaturanaBelum ada peringkat
- B1 BioinfoDokumen7 halamanB1 BioinfoJohn Kent0% (1)
- Algoritmo Genético para MatlabDokumen105 halamanAlgoritmo Genético para Matlabbonmarche28Belum ada peringkat
- Using BLAST: FASTA FormatDokumen3 halamanUsing BLAST: FASTA Formatnurul nabilah bt khairul anuar0% (1)
- Data RetrievalDokumen17 halamanData RetrievalAyesha Khan50% (2)
- (IJCST-V1I2P7) : T.Shanmugavadivu, T.RavichandranDokumen3 halaman(IJCST-V1I2P7) : T.Shanmugavadivu, T.RavichandranIJETA - EighthSenseGroupBelum ada peringkat
- Gene Expression Programming: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDari EverandGene Expression Programming: Fundamentals and ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Bioinformatics, Sequence and Genome AnalysisDari EverandIntroduction to Bioinformatics, Sequence and Genome AnalysisBelum ada peringkat
- Detection and Use of QTLDokumen7 halamanDetection and Use of QTLIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas RancobDokumen2 halamanTugas RancobIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Conjoint AnalysisDokumen12 halamanConjoint AnalysisIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- BOLD TaxonID Tree for BOLD:AAD8153Dokumen2 halamanBOLD TaxonID Tree for BOLD:AAD8153Iseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- BOLD TaxonID Tree for BOLD:AAD8153Dokumen2 halamanBOLD TaxonID Tree for BOLD:AAD8153Iseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- TPSDokumen8 halamanTPSIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Sex ReversalDokumen7 halamanSex ReversalIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Reaksi BiokimiaDokumen1 halamanSkema Reaksi BiokimiaIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Arogenate dehydratase enzyme reaction and referencesDokumen1 halamanArogenate dehydratase enzyme reaction and referencesIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Accepted Name: Arogenate Dehydrogenase (NAD (P) Reaction:: Click HereDokumen1 halamanAccepted Name: Arogenate Dehydrogenase (NAD (P) Reaction:: Click HereIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Penelitian PerikananDokumen8 halamanPenelitian PerikananIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Cover Essential StatisticsDokumen1 halamanCover Essential StatisticsIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Body Size-Mating StrategyDokumen9 halamanBody Size-Mating StrategyIseng IsengBelum ada peringkat
- Food 8 - Part 2Dokumen7 halamanFood 8 - Part 2Mónica MaiaBelum ada peringkat
- Eca Important QuestionsDokumen3 halamanEca Important QuestionsSri KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Viscosity IA - CHEMDokumen4 halamanViscosity IA - CHEMMatthew Cole50% (2)
- Iwwusa Final Report IdsDokumen216 halamanIwwusa Final Report IdsRituBelum ada peringkat
- Pure Quality Pure Natural: Calcium Carbonate Filler / MasterbatchDokumen27 halamanPure Quality Pure Natural: Calcium Carbonate Filler / MasterbatchhelenBelum ada peringkat
- Beuys Begleitheft en ScreenDokumen18 halamanBeuys Begleitheft en Screensofijawt0% (1)
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA Biology Investigatory ProjectDokumen28 halamanKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA Biology Investigatory Projectvishali GBelum ada peringkat
- Schedule FinalDokumen6 halamanSchedule FinalJamora ManilynBelum ada peringkat
- Macbeth Introduction0Dokumen40 halamanMacbeth Introduction0MohammedelamineBelum ada peringkat
- Hempathane Topcoat 55219 Base 5521967280 En-UsDokumen11 halamanHempathane Topcoat 55219 Base 5521967280 En-UsSantiago Rafael Galarza JacomeBelum ada peringkat
- Single-phase half-bridge inverter modes and componentsDokumen18 halamanSingle-phase half-bridge inverter modes and components03 Anton P JacksonBelum ada peringkat
- RRC Igc1Dokumen6 halamanRRC Igc1kabirBelum ada peringkat
- Etoposide JurnalDokumen6 halamanEtoposide JurnalShalie VhiantyBelum ada peringkat
- Year 2 - Push and Pull FPDDokumen18 halamanYear 2 - Push and Pull FPDRebecca LBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment No. 8 (Culture 1) : Discuss The Significance of Montessori Cultural Exercises.? Hfodhfsfnsfsfsajk AnsDokumen10 halamanAssignment No. 8 (Culture 1) : Discuss The Significance of Montessori Cultural Exercises.? Hfodhfsfnsfsfsajk Anseman zahraBelum ada peringkat
- ARTS 9 Q4 Week 1Dokumen3 halamanARTS 9 Q4 Week 1Elaissa MaglanqueBelum ada peringkat
- Format For Handout - Comparative Models of EducationDokumen5 halamanFormat For Handout - Comparative Models of EducationAdrian AsiBelum ada peringkat
- Flow Through Pipes: Departmentofcivilengineering Presidency University, Bangalore-64 BY Santhosh M B Asstistant ProfessorDokumen15 halamanFlow Through Pipes: Departmentofcivilengineering Presidency University, Bangalore-64 BY Santhosh M B Asstistant ProfessorSanthoshMBSanthuBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Processes: Lesson 3Dokumen3 halamanPlant Processes: Lesson 3Kayla Ta’jaeBelum ada peringkat
- Gizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsDokumen5 halamanGizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsEuropaBelum ada peringkat
- Bimbo Marketing ResearchDokumen27 halamanBimbo Marketing Researcheman.konsouhBelum ada peringkat
- TG KPWKPDokumen8 halamanTG KPWKPDanmar CamilotBelum ada peringkat
- Learner's Activity Sheet: English (Quarter 4 - Week 5)Dokumen5 halamanLearner's Activity Sheet: English (Quarter 4 - Week 5)Rufaidah AboBelum ada peringkat
- JASA SREVIS LAPTOP Dan KOMPUTERDokumen2 halamanJASA SREVIS LAPTOP Dan KOMPUTERindimideaBelum ada peringkat
- Encrypt and decrypt a file using AESDokumen5 halamanEncrypt and decrypt a file using AESShaunak bagadeBelum ada peringkat