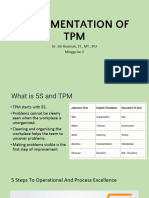
Total Productive Maintenance
Diunggah oleh
Mahi FatimaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Total Productive Maintenance
Diunggah oleh
Mahi FatimaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Total Productive Maintenance
Comprehensive, life cycle approach
Minimizes equipment failures, production defects and accidents
Involves everyone
A method to achieve maximum equipment effectiveness through employee involvement
Objectives of TPM
Ideal goals: Zero failure, zero defects and zero accidents
Continuously improve availability and prevent degradation
TPM Concepts
Autonomous Maintenance
Equipment operators performing some routine maintenance tasks
Daily cleaning, inspecting, tightening, lubricating
Operators to quickly notice anomalies
Maintenance staff trains operators
Special safety awareness training provided to operators
Implementation includes use of visual controls
Planned Maintenance
Activities scheduled to repair equipments before they breakdown
Production schedule to accommodate planned downtime
Maintenance Reduction
Consists of equipment design and predictive maintenance
Working with equipment suppliers
Maintenance knowledge incorporated into next generation of equipment designs
Equipment manufacturer even includes visual control markings and labels
Special equipment analysis to collect data to predict equipment failure
Thermography, Ultrasound, Vibration analysis
Equipment Effectiveness
Equipment effectiveness is not only equipment availability
Overall equipment effectiveness that also includes equipment efficiency and quality rate
Equipment Availability
Equipment availability = Actual Operating Time/ Net available Run Time
Performance Efficiency
Performance Efficiency = [(Design Cycle Time x Total output for Operating Time) /
Actual Operating Time] x 100
Quality Rate
Quality Rate = [(Total output for Operating Time - Rejects)/ Total output for Operating
Time] x 100
Overall Equipment Effectiveness
Overall Equipment Effectiveness = Equipment Availability x Performance Efficiency x
Quality Rate
Ready for maintenance?
Assignment 1: Wednesday, 30th September
2015
Quiz 1: Wednesday, 30th September 2015
Eliminating Process Losses
Losses Due to Downtime
Breakdowns
Proactive replacement during scheduled maintenance
Setup and Adjustment
Internal setup and external setup
Losses Due to Poor Performance
Reduced Speed
Excessive equipment wear
Idling and Minor Stops
Equipment jams
Losses Due to Poor Quality
Process Defects
Improving equipment
Startup Losses
Product waste until operating temperature
Benefits of Total Productive Maintenance
Increased Productivity
Less unscheduled downtime
More time to value added tasks
Workers also increase productivity
Reduced Maintenance Costs
Proactive improvement
Firefighting approach to extra staff members
Autonomous maintenance
Reduced Inventory
Unreliable equipment results in large stocks of finished goods
Reduced spare parts inventory
Improved Safety
Safety of operators
Improved Morale
Operators in drivers seat
Maintenance technicians time for equipment analysis and designers
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Maintenance FunctionsDokumen41 halamanMaintenance FunctionsAryyaka SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- TPMDokumen32 halamanTPMdavegrohl127Belum ada peringkat
- Total Productive MaintenanceDokumen48 halamanTotal Productive MaintenanceSajid Chaudhary100% (1)
- Design For Ease of MaintenanceDokumen24 halamanDesign For Ease of MaintenancePrabu BalakrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- TPM Pillars and OEEDokumen15 halamanTPM Pillars and OEESenthil KumaarBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance ManagementDokumen21 halamanMaintenance ManagementRahul WaghmareBelum ada peringkat
- What is Total Productive Maintenance? (TPMDokumen48 halamanWhat is Total Productive Maintenance? (TPMArvind ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- M M Sanoop: Prepared ByDokumen36 halamanM M Sanoop: Prepared Byvappichi00Belum ada peringkat
- Maintenance ManagementDokumen4 halamanMaintenance ManagementAnand MauryaBelum ada peringkat
- MaintenanceDokumen89 halamanMaintenancelp mishra100% (4)
- Unit IV - Maintenance, System Reliability & TQMDokumen64 halamanUnit IV - Maintenance, System Reliability & TQMcoxshulerBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance ManagementDokumen18 halamanMaintenance ManagementPrasanna KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-3-1 Maintenance ManagementDokumen36 halamanChapter-3-1 Maintenance ManagementneelakantamtatiBelum ada peringkat
- Manage assets & production with maintenanceDokumen4 halamanManage assets & production with maintenanceAnand MauryaBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Maintenance CLOs and Troubleshooting FundamentalsDokumen37 halamanMechanical Maintenance CLOs and Troubleshooting FundamentalsNazuan NazriBelum ada peringkat
- IntroDokumen16 halamanIntroKarunakaran DBelum ada peringkat
- Introductory Concepts: Basics of MaintenanceDokumen47 halamanIntroductory Concepts: Basics of Maintenancetewodros mihretBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 5 - MOMDokumen27 halamanChap 5 - MOMladdooparmarBelum ada peringkat
- Total Productive MaintenanceDokumen41 halamanTotal Productive Maintenancejeff090288Belum ada peringkat
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) : Prepared By: M.Ganesh MuruganDokumen56 halamanTotal Productive Maintenance (TPM) : Prepared By: M.Ganesh MuruganPriscila Villas Boas TonãoBelum ada peringkat
- TPM and Oee: Mauri e O'BrieDokumen51 halamanTPM and Oee: Mauri e O'Brieprashanth191182Belum ada peringkat
- Total Productive Maintenance: Failure PreventionDokumen12 halamanTotal Productive Maintenance: Failure PreventionTrue BarcaFanBelum ada peringkat
- Engr. John Lumenick Peñas: Total Productive ManufacturingDokumen54 halamanEngr. John Lumenick Peñas: Total Productive ManufacturingXype LanderBelum ada peringkat
- Operations Management - Maintenance Types, Objectives & AnalysisDokumen7 halamanOperations Management - Maintenance Types, Objectives & AnalysisVijay Singh ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- TPM by AnupDokumen27 halamanTPM by AnupArif NaikwadeBelum ada peringkat
- CalibrationDokumen155 halamanCalibrationBhegz Escalona100% (3)
- TPM OEE EBook - LBSPartners 2015 PDFDokumen51 halamanTPM OEE EBook - LBSPartners 2015 PDFpsychic_jason0071319Belum ada peringkat
- 5) OEE Measuring PerformanceDokumen34 halaman5) OEE Measuring PerformanceM. Munir FahmiBelum ada peringkat
- Total Productive MaintenanceDokumen10 halamanTotal Productive MaintenanceMohamed KhaledBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorDokumen37 halamanMaintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorHajra AamirBelum ada peringkat
- Plant MaintenanceDokumen10 halamanPlant MaintenanceGatut SulianaBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To MaintenanceDokumen24 halamanIntro To MaintenanceMushfiqur Rahman AshiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Total Productive MaintenanceDokumen2 halamanTotal Productive Maintenanceanadinath sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- RSM 1Dokumen2 halamanRSM 1Kamal Prasad SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Foro CARLOS ORTEGA AYALA PDFDokumen2 halamanForo CARLOS ORTEGA AYALA PDFBryan CEBelum ada peringkat
- Otal Roductive Aintenance: Designed by Danish Zakria Hafiz Abdul MananDokumen11 halamanOtal Roductive Aintenance: Designed by Danish Zakria Hafiz Abdul MananManan IFtikharBelum ada peringkat
- Breakdown Prevention Maintenance TipsDokumen18 halamanBreakdown Prevention Maintenance Tipsm_alodat6144Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9 Maintenance Management SystemDokumen35 halamanChapter 9 Maintenance Management SystemIbrahim AbduBelum ada peringkat
- TQM ToolsDokumen11 halamanTQM ToolsShanky JainBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Maintenance and RepairingDokumen32 halamanIntroduction To Maintenance and RepairingR.W. SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- The TPM Guide: Total Productive MaintenanceDokumen38 halamanThe TPM Guide: Total Productive Maintenanceusmanafzal246Belum ada peringkat
- TPMen InglesDokumen6 halamanTPMen InglesMargarita Bautista PastorBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Maintenance: P-115-3 Juruteknik Kenderaan MotorDokumen27 halamanIntroduction To Maintenance: P-115-3 Juruteknik Kenderaan MotorZaleq YunosBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance ManagementDokumen22 halamanMaintenance Managementafree_khan1990100% (1)
- New Topic 1 Introduction To Maintenance ManagementDokumen41 halamanNew Topic 1 Introduction To Maintenance ManagementNurul Nabila Sahri100% (1)
- Total Productive MaintenanceDokumen21 halamanTotal Productive Maintenancedr_tripathineerajBelum ada peringkat
- Tqm Unit 4 Lecture 5 TpmDokumen22 halamanTqm Unit 4 Lecture 5 TpmtamilselvansambathBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3A MaintenanceDokumen43 halamanLecture 3A Maintenancemoyo josephBelum ada peringkat
- GGGGG 111Dokumen21 halamanGGGGG 111FraolBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance EngineeringDokumen67 halamanMaintenance EngineeringV.Muthu KumarBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)Dokumen10 halamanAn Introduction To Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)Ravi AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- 1 IntroduccionDokumen28 halaman1 IntroduccionFilosofia BernalistaBelum ada peringkat
- CalibrationDokumen155 halamanCalibrationdarrel_julio100% (1)
- Strategic Importance of Maintenance and ReliabilityDokumen5 halamanStrategic Importance of Maintenance and ReliabilitybrennestevezBelum ada peringkat
- MG 443 Lesson 6 Maintenance StrategiesDokumen27 halamanMG 443 Lesson 6 Maintenance StrategiesZegera Mgendi0% (1)
- Introduction to Total Productive Maintenance (TPMDokumen16 halamanIntroduction to Total Productive Maintenance (TPMAman SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Kpi BHPDokumen27 halamanKpi BHPAdalberto Gomes100% (1)
- 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes Instructions and Grading For CFD Lab ReportDokumen2 halaman57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes Instructions and Grading For CFD Lab ReportSaad Al HelyBelum ada peringkat
- To Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesDokumen2 halamanTo Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Distance Learning AddDokumen6 halamanDistance Learning AddMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0376738802003058 Main - 2Dokumen12 halaman1 s2.0 S0376738802003058 Main - 2Mahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Holy Quran para 2Dokumen28 halamanHoly Quran para 2Rabia Tabassum Dhanotar94% (32)
- To Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesDokumen2 halamanTo Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample CritiqueDokumen9 halamanSample CritiqueNajwaZainuddin100% (1)
- 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes Instructions and Grading For CFD Lab ReportDokumen2 halaman57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes Instructions and Grading For CFD Lab ReportSaad Al HelyBelum ada peringkat
- 2003 JMembr Sci KumarDokumen15 halaman2003 JMembr Sci KumarMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- To Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesDokumen2 halamanTo Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- 9Dokumen2 halaman9Mahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Dewaxing ProcessesDokumen19 halamanDewaxing ProcessesMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceramics Lec 2Dokumen20 halamanCeramics Lec 2Mahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- To Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesDokumen2 halamanTo Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- To Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesDokumen2 halamanTo Prevent The Formation of Mineral Scale On MembranesMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Holy Quran para 2Dokumen28 halamanHoly Quran para 2Rabia Tabassum Dhanotar94% (32)
- 10 - RateLawDokumen32 halaman10 - RateLawMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Petroleum Refinery Engineering: Dr. M. Saif Ur RehmanDokumen37 halamanPetroleum Refinery Engineering: Dr. M. Saif Ur RehmanMahi Fatima100% (1)
- ResidDokumen10 halamanResidMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Assign-1Dokumen1 halaman1 - Assign-1Mahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Holy Quran para 2Dokumen28 halamanHoly Quran para 2Rabia Tabassum Dhanotar94% (32)
- 0109 Mar 019Dokumen7 halaman0109 Mar 019Mahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- ResidDokumen10 halamanResidMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Petrochemical Engineering-Lect05 - Primary Raw MaterialsDokumen8 halamanPetrochemical Engineering-Lect05 - Primary Raw MaterialsMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Individual Vs Group ReplacementDokumen2 halamanIndividual Vs Group ReplacementMahi Fatima0% (1)
- Test DocumentDokumen1 halamanTest DocumentMahi FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Space Gass 12 5 Help Manual PDFDokumen841 halamanSpace Gass 12 5 Help Manual PDFNita NabanitaBelum ada peringkat
- Appointment Letter JobDokumen30 halamanAppointment Letter JobsalmanBelum ada peringkat
- Blank Character StatsDokumen19 halamanBlank Character Stats0114paolBelum ada peringkat
- L16 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDokumen25 halamanL16 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyBelum ada peringkat
- Dompet Digital Di Kota SemarangDokumen10 halamanDompet Digital Di Kota SemarangRikson TandelilinBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2: Science, Technology, and Society in Human Condition Lesson 1: Human FlourishingDokumen5 halamanChapter 2: Science, Technology, and Society in Human Condition Lesson 1: Human FlourishingJcBelum ada peringkat
- Vocabulary Prefixes ExercisesDokumen2 halamanVocabulary Prefixes ExercisesMarina García CarrascoBelum ada peringkat
- Pedestrian Safety in Road TrafficDokumen9 halamanPedestrian Safety in Road TrafficMaxamed YusufBelum ada peringkat
- Shaft design exercisesDokumen8 halamanShaft design exercisesIvanRosellAgustíBelum ada peringkat
- 10 1016@j Ultras 2016 09 002Dokumen11 halaman10 1016@j Ultras 2016 09 002Ismahene SmahenoBelum ada peringkat
- Trendline Mastery: Course Outline: 3. Interview of Peter Bain by Frank PaulDokumen5 halamanTrendline Mastery: Course Outline: 3. Interview of Peter Bain by Frank PaulnacareBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustDokumen16 halamanDigital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustAtifMinhasBelum ada peringkat
- S32 Design Studio 3.1: NXP SemiconductorsDokumen9 halamanS32 Design Studio 3.1: NXP SemiconductorsThành Chu BáBelum ada peringkat
- Paaralan Tungo Sa Magandang Kinabukasan" The Campaign Kicked Off in All The PublicDokumen7 halamanPaaralan Tungo Sa Magandang Kinabukasan" The Campaign Kicked Off in All The PublicJOHN FRANCIS OCTAVIANOBelum ada peringkat
- 07CRMDokumen81 halaman07CRMsangramlifeBelum ada peringkat
- NMIMS MBA Midterm Decision Analysis and Modeling ExamDokumen2 halamanNMIMS MBA Midterm Decision Analysis and Modeling ExamSachi SurbhiBelum ada peringkat
- Omega Fluid PDFDokumen2 halamanOmega Fluid PDFapatzinfedBelum ada peringkat
- Viola Jones AlgorithmDokumen4 halamanViola Jones AlgorithmBhumika GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- Subject and Power - FoucaultDokumen10 halamanSubject and Power - FoucaultEduardo EspíndolaBelum ada peringkat
- 5.mpob - LeadershipDokumen21 halaman5.mpob - LeadershipChaitanya PillalaBelum ada peringkat
- Es E100091 Pi PDFDokumen1 halamanEs E100091 Pi PDFCarlos Humbeto Portillo MendezBelum ada peringkat
- Factors That Affect Information and Communication Technology Usage: A Case Study in Management EducationDokumen20 halamanFactors That Affect Information and Communication Technology Usage: A Case Study in Management EducationTrần Huy Anh ĐứcBelum ada peringkat
- Finger Relaxation Technique Reduces Post-Appendectomy PainDokumen13 halamanFinger Relaxation Technique Reduces Post-Appendectomy PainIan ClaxBelum ada peringkat
- Mitchell 1986Dokumen34 halamanMitchell 1986Sara Veronica Florentin CuencaBelum ada peringkat
- Instruction Manual For National Security Threat Map UsersDokumen16 halamanInstruction Manual For National Security Threat Map UsersJan KastorBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFDokumen65 halamanChapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFTiên Nguyễn100% (1)
- 2-Eagan Model of CounsellingDokumen23 halaman2-Eagan Model of CounsellingVijesh V Kumar100% (4)
- Investigation of Water Resources Projects - Preparation of DPRDokumen148 halamanInvestigation of Water Resources Projects - Preparation of DPRN.J. PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam: Functional Performance Testing: Technical vs. Process CommissioningDokumen9 halamanFinal Exam: Functional Performance Testing: Technical vs. Process CommissioningBen MusimaneBelum ada peringkat
- BUDDlab Volume2, BUDDcamp 2011: The City of Euphemia, Brescia / ItalyDokumen34 halamanBUDDlab Volume2, BUDDcamp 2011: The City of Euphemia, Brescia / ItalyThe Bartlett Development Planning Unit - UCLBelum ada peringkat
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (22)
- Overcoming Fake Talk: How to Hold REAL Conversations that Create Respect, Build Relationships, and Get ResultsDari EverandOvercoming Fake Talk: How to Hold REAL Conversations that Create Respect, Build Relationships, and Get ResultsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverDari EverandThe Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (186)
- TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingDari EverandTED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (210)
- Follow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipDari EverandFollow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (122)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDari EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- The First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsDari EverandThe First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (55)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeDari EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolDari EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (702)
- Think Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceDari EverandThink Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceBelum ada peringkat
- Billion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsDari EverandBillion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (52)
- How to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobDari EverandHow to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (36)
- Summary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEODari EverandSummary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Cultures of Growth: How the New Science of Mindset Can Transform Individuals, Teams, and OrganizationsDari EverandCultures of Growth: How the New Science of Mindset Can Transform Individuals, Teams, and OrganizationsBelum ada peringkat
- Creating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsDari EverandCreating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- An Ugly Truth: Inside Facebook's Battle for DominationDari EverandAn Ugly Truth: Inside Facebook's Battle for DominationPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (33)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Dari EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Belum ada peringkat
- Crucial Conversations by Kerry Patterson, Joseph Grenny, Ron McMillan, and Al Switzler - Book Summary: Tools for Talking When Stakes Are HighDari EverandCrucial Conversations by Kerry Patterson, Joseph Grenny, Ron McMillan, and Al Switzler - Book Summary: Tools for Talking When Stakes Are HighPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (97)
- Spark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessDari EverandSpark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (130)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDari EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeoplePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2564)
- How to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersDari EverandHow to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (150)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleDari EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeoplePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6509)
- Entreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesDari EverandEntreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (186)
- The 21 Indispensable Qualities of a Leader: Becoming the Person Others Will Want to FollowDari EverandThe 21 Indispensable Qualities of a Leader: Becoming the Person Others Will Want to FollowPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (38)
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxDari EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (155)
- Living the 7 Habits: Powerful Lessons in Personal ChangeDari EverandLiving the 7 Habits: Powerful Lessons in Personal ChangePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (70)
- Leadership Skills that Inspire Incredible ResultsDari EverandLeadership Skills that Inspire Incredible ResultsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (11)
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldDari Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (19)