FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 15 - Reading 51
Diunggah oleh
RafaelDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 15 - Reading 51
Diunggah oleh
RafaelHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
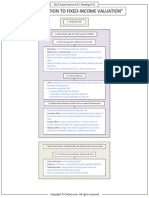
2015 Study Session # 15, Reading # 51
FIXED-INCOME SECURITIES: DEFINING ELEMENTS
FI = Fixed Income
CFs = Cash Flows
1. INTRODUCTION
FI security an instrument that allow governments, companies &
other types of issuers to borrow money from investors.
Adding FI securities to portfolio adds diversification benefits.
2. OVERVIEW OF A FIXED-INCOME SECURITY
Three important elements of bond investing:
The bonds features
Legal, regulatory & tax consideration.
Contingency provisions.
2.1 Basic Features of a Bond
2.1.1 Issuer
2.1.2 Maturity
Major types of bond issuer include:
Supranational organizations e.g. World Bank.
Sovereign governments e.g. UK, USA.
Non-sovereign governments.
Quasi-govt. entities.
Corporate issuers.
Credit risk risk of loss resulting from the issuer
failing to make full & timely payment of
interest/principal.
Maturity date date when the issuer is
obligated to redeem the bond by paying
the outstanding principal.
Tenor time remaining until maturity
date.
Money market securities maturities at
issuance of one year or less.
Capital market securities FI securities
with maturity > 1 year.
2.1.3 Par Value
2.1.4 Coupon Rate and Frequency
Principal or par value amount that the issuer
agrees to repay the bondholder on maturity date
Coupon/nominal rate interest rate that
the issuer agrees to pay every year until
maturity.
Plain vanilla bond fixed rate bond.
Floaters bonds with floating rate
coupon.
Zero coupon bonds issued at discount
to par & redeemed at par.
2.1.5 Currency Denomination
Dual currency bonds pay interest in one
currency & principal in another currency.
Currency option bonds single currency
bond+ foreign currency option.
2.2 Yield Measures
Yield to maturity (YTM) internal rate of return on a
bonds expected cash flows.
Lower IR scenario anticipation, lower YTM demand.
Copyright FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
2015 Study Session # 15, Reading # 51
3. LEGAL, REGULATORY, AND TAX CONSIDERATIONS
3.1 Bond Indenture
Trust deed (indenture) legal contract that describe:
Bond form
Issuers obligations.
Bondholders rights.
Collateral assets or financial guarantees above &
beyond the issuers promise to pay.
Credit enhancements provisions to reduce the
credit risk of the bond issue.
Covenants clauses that define bond-holders rights
and an issuers actions.
3.1.1 Legal Identity of the Bond Issuer and its Legal Form
Bond issuer is legally obliged to make contractual
payments.
3.1.2 Source of Repayment Proceeds
Supranational organization either the
repayment of previous loans or the paid-in-capital
from its members.
Sovereign bonds tax revenue & print money is
the major source of repayment.
Non-sovereign govt. debt:
Tax
Cash flow of project (financed with bond
issue).
Special tax or fees.
Corporate bonds issuers ability to generate
CFs from operations.
Securitization CFs generated by one or more
underlying financial assets.
3.2 Legal and Regulatory
FI securities are subject to legal & regulatory
requirements.
National bond market bonds that are issued &
traded in a specific county.
Euro bonds bond issued & traded on euro bond
market.
Bearer bonds trustee doesnt keep records
of bonds ownership.
Registered bonds ownership is recorded by
either name or serial number.
3.1.3 Asset or Collateral Backing
3.1.3.1 Seniority Ranking
Secured bonds backed by assets or financial
guarantees pledged to ensure debt repayment in
case of default.
Unsecured bonds no collateral bond.
Debentures types of bond that can be
unsecured.
3.1.3.2 Types of Collateral Backing
Collateral trust bonds secured by securities
such as shares other bonds or financial assets.
Equipment trust certificates bonds secured by
specific types of equipment or physical assets.
Mortgage-backed securities debt obligations
that represent claims to the CFs from pools of
mortgage loans.
Covered bonds debt backed by a segregated
pool of assets called cover pool
3.1.4 Credit Enhancement
Credit enhancement variety of provisions that
can be used to the credit risk of a bond issue.
3.1.4.1 Internal credit enhancement
subordination ordering of claim priorities for
ownership or interest in an asset.
Junior tranche function as credit protection
for senior tranche.
Excess spread difference b/w CF received
from the assets used to secured issue & the
interest paid to investors.
3.1.4.2 External credit enhancement.
Surety bond issued by a rated & regulated
insurance company.
Letter of credit provided by a financial
institution.
Less common form.
3.1.5 Covenants
Bond covenants legally enforceable rules that
borrowers & lenders agree on at the time of a
new bond issue.
Affirmative covenants what issuers required to
do (admin nature).
Negative covenants what issuers are
prohibited from doing (costly & do materially
constrain the issuers potential business decision).
Examples restrictions on debt, negative
pledges. Restriction on prior claims
restrictions on investments etc.
Copyright FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
2015 Study Session # 15, Reading # 51
3.3 Tax Considerations
Income portions of a bond investment taxed at
ordinary income tax rate.
Capital gain/loss if the price is likely to have changed
compared with the purchase price.
Different tax rate for long term & short term capital
gains in different countries.
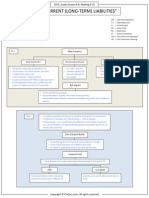
4. STRUCTURE OF A BOND'S CASH FLOWS
4.1 Principal Repayment Structures
4.1.1 Bullet, Fully Amortized, and Partially Amortized Bonds
Bullet bond entire principal payment occurs at maturity.
Amortizing bond periodic payments of interest &
repayment of principal.
Partially amortized bond fixed periodic payments until
maturity & a portion of the principal at maturity date.
Balloon payment payment to retire the bonds
outstanding principal at maturity.
4.1.2 Sinking Fund Arrangements
Sinking fund an issuers plan to set aside funds
over time to retire the bond.
Benefit:
Formal plan to retire the debt.
Disadvantage:
Reinvestment risk
Issuer may have option to repurchase bonds
at below market prices.
4.2 Coupon Payment Structures
Coupon interest payment that the bond issuer
makes to the bondholder.
Usually coupon is paid semi-annually for sovereign &
corporate bonds.
4.2.1 Floating-Rate Notes
4.2.2 Step-Up Coupon Bonds
Coupon rate is linked to an external reference
rate e.g. LIBOR.
Quarterly coupons.
Typical coupon rate = 3M LIBOR+---BPS (spread).
Variable rate note spread is not fixed.
Little interest rate risk.
Additional features may include a floor or cap.
Inverse floater inverse relationship to the
reference rate.
Fixed or floating coupon which by specified
margins at specified dates.
Provides some protection against rising interest
rates.
4.2.3 Credit-Linked Coupon Bonds
4.2.4 Payment-in-Kind Coupon Bonds
Coupon rate change when bonds credit rating
change.
Attractive to investors who are concerned about
the future credit worthiness of the issuer.
Coupon is paid in the form of additional amounts
of the bonds issue rather than as a cash payment.
Favored when issuers future cash flows will be
questionable.
Copyright FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
2015 Study Session # 15, Reading # 51
4.2 Coupon Payment Structures
4.2.5 Deferred Coupon Bonds
4.2.6 Index-Linked Bonds
These bonds:
Paid no coupon for first few years & pays
higher than normal coupon for the remainder
of its life.
Common in project financing.
Priced at significant discount to par.
Coupon &/or principal repayments are linked to a
specific index.
Example inflation linked bonds.
Real interest rate = nominal interest rate
inflation.
Equity-linked note final payment is based on
the return of an equity index.
5. BONDS WITH CONTINGENCY PROVISIONS
Contingency provision clause in legal document that allows for some
action if the event does occur.
Embedded option various contingency provisions found in the indenture.
5.1 Callable Bonds
Callable bond gives the issuer the right to redeem all or part of the bond before maturity date.
Provide protection to issuer in declining interest rate environment.
The yield & price compensate the bondholders for the value of the call option to the issuer.
Bermuda-style call issuer has the right to call bonds on specified dates following the call protection period.
5.2 Putable Bonds
Put provisions provide right to the bondholder to sell the bond back to the issuer at a predetermined price on specified dates.
Pre-specified selling price of put able bond provide benefit to bond holder.
Lower yield on these bonds compensate the issuer for the value of the put option to the
investor.
5.3 Convertible Bonds
Convertible bond hybrid security with both debt & equity features (bond holder has a right to
exchange the bond for specified number of shares in issuing company).
Convertible bond may further include call provision.
Advantages for investor:
Investor can participate in equity upside.
Investor receives downside protection.
Price of convertible bond cant fall below the price of the straight bond.
Price of a convertible bond is than the price of the bond without this provision.
Conversion price price per share at which the convertible bond can be converted into shares.
Conversion ratio number of common shares that each bond can be converted into.
Conversion value current share price conversion ratio.
Copyright FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2Dari EverandFixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2Belum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 15 - Reading 52Dokumen5 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 15 - Reading 52RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 17 - Reading 57Dokumen4 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 17 - Reading 57RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 25Dokumen6 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 25RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 4 - Reading 14Dokumen5 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 4 - Reading 14RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 18 - Reading 60Dokumen14 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 18 - Reading 60Rafael0% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 6 - Reading 21Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 6 - Reading 21RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 5 - Reading 17Dokumen4 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 5 - Reading 17RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 1 - Reading 1Dokumen17 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 1 - Reading 1RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 7 - Reading 23Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 7 - Reading 23Rafael0% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 26Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 26RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 1 - Reading 4Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 1 - Reading 4RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 1, Reading 1Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 1, Reading 1Taha OwaisBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 31Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 31RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 49Dokumen6 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 49Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 32Dokumen6 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 32RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Dokumen7 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 50Dokumen4 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 50Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 44Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 44RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 2 - Reading 6Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 2 - Reading 6RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 4 - Reading 15Dokumen7 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 4 - Reading 15RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- The Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual For InvestorsDokumen6 halamanThe Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual For InvestorsRafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 1, Reading 2Dokumen15 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 1, Reading 2Taha OwaisBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 30Dokumen5 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 30RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 10 - Reading 34Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 10 - Reading 34RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 28Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 28RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- Fintree CFA LI 2018 Curriculum ChangesDokumen2 halamanFintree CFA LI 2018 Curriculum ChangesMohamed GamalBelum ada peringkat
- Usgaap, Igaap & IfrsDokumen7 halamanUsgaap, Igaap & IfrsdhangarsachinBelum ada peringkat
- Elan Cfa ReviewDokumen34 halamanElan Cfa Reviewabd nassBelum ada peringkat
- 11-Level 1 Smart Summaries PDFDokumen273 halaman11-Level 1 Smart Summaries PDFBadAss Babbar100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 2, Reading 5Dokumen1 halamanFinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 2, Reading 5Sankalp Jain0% (1)
- Akin SecurityAnalysisPresentation2014 1p80bskDokumen50 halamanAkin SecurityAnalysisPresentation2014 1p80bskgarych72Belum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 4, Reading 10Dokumen5 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 4, Reading 10Tam T NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- BEC 1 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewDokumen4 halamanBEC 1 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewGabriel100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 3, Reading 9Dokumen7 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary, Study Session 3, Reading 9Tam T NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Investment and Portfolio ManageemntDokumen2 halamanInvestment and Portfolio Manageemntumair aliBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 3, Reading 5Dokumen10 halamanFinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 3, Reading 5faseeBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Summary Income Taxes CFADokumen3 halamanSmart Summary Income Taxes CFAKazi HasanBelum ada peringkat
- FRM Currency FutureDokumen48 halamanFRM Currency FutureParvez KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Fra MindmapDokumen10 halamanFra MindmapNghĩaTrầnBelum ada peringkat
- A&J Flashcards For Exam SOA Exam FM/ CAS Exam 2Dokumen39 halamanA&J Flashcards For Exam SOA Exam FM/ CAS Exam 2anjstudymanualBelum ada peringkat
- Level I Volume 5 2019 IFT NotesDokumen258 halamanLevel I Volume 5 2019 IFT NotesNoor QamarBelum ada peringkat
- CFA Level 2 One Pagers v3 - Class Notes - Free Online ClassDokumen18 halamanCFA Level 2 One Pagers v3 - Class Notes - Free Online ClassShivgan JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate Finance Fundamentals - Course PresentationDokumen85 halamanCorporate Finance Fundamentals - Course PresentationAngie WandyBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 20 CFA Level I Curriculum ChangesDokumen20 halaman2019 20 CFA Level I Curriculum ChangesNadia JBelum ada peringkat
- Alternative Invesmtents For Pension FundsDokumen35 halamanAlternative Invesmtents For Pension FundsQuantmetrixBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate RestructuringDokumen46 halamanCorporate RestructuringMilu Mathew MoorkkattilBelum ada peringkat
- Ta CN TCNH - Unit 2 - Time Value of MoneyDokumen19 halamanTa CN TCNH - Unit 2 - Time Value of MoneyPhương NhiBelum ada peringkat
- Adidas Group Equity Valuation Thesis - João Francisco Menezes - 152114017-1 PDFDokumen43 halamanAdidas Group Equity Valuation Thesis - João Francisco Menezes - 152114017-1 PDFNancy NanBelum ada peringkat
- CPA BEC - BudgetingDokumen15 halamanCPA BEC - Budgetingpambia2000Belum ada peringkat
- CFA Financial Statement Analysis Flashcards - Chegg - Com1Dokumen16 halamanCFA Financial Statement Analysis Flashcards - Chegg - Com1anissa claritaBelum ada peringkat
- Export FinancingDokumen61 halamanExport FinancingkanikaBelum ada peringkat
- Bloomberg Equity Research and Analysis CheatsheetDokumen2 halamanBloomberg Equity Research and Analysis Cheatsheetanshuljain785Belum ada peringkat
- Cfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsDokumen4 halamanCfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsSanjay RathiBelum ada peringkat
- FRM NotesDokumen13 halamanFRM NotesNeeraj LowanshiBelum ada peringkat
- M1-1 MGT Accounting & OrgDokumen19 halamanM1-1 MGT Accounting & OrgKetoisophorone WongBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate BondsDokumen4 halamanCorporate BondsWaseem ManshaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Two: Non - Current LiabilitiesDokumen10 halamanChapter Two: Non - Current LiabilitiesJuan KermaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 HomeworkDokumen3 halamanChapter 7 HomeworkSarah MoonBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 15 - Reading 53Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 15 - Reading 53Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 55Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 55Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 17 - Reading 59Dokumen1 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 17 - Reading 59RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Dokumen7 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 44Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 44RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 49Dokumen6 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 49Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 13 - Reading 47Dokumen4 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 13 - Reading 47RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 48Dokumen4 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 48Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 10 - Reading 34Dokumen2 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 10 - Reading 34RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 50Dokumen4 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 14 - Reading 50Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 37Dokumen4 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 37RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 43Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 43RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 13 - Reading 45Dokumen6 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 13 - Reading 45RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 39Dokumen13 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 39Rafael100% (1)
- The Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual For InvestorsDokumen6 halamanThe Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual For InvestorsRafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 41Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 41RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 36Dokumen5 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 36RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 35Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 35RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 38Dokumen5 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 11 - Reading 38RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 42Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 12 - Reading 42Rafael100% (1)
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 32Dokumen6 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 32RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 31Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 31RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 29Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 29RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 28Dokumen3 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 28RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 30Dokumen5 halamanFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 30RafaelBelum ada peringkat
- MARKETING STRATEGY OF - HDFC Mutual FundDokumen114 halamanMARKETING STRATEGY OF - HDFC Mutual Fundsuryakantshrotriya100% (1)
- JPM Guide To The Markets 2020Dokumen71 halamanJPM Guide To The Markets 2020John PBelum ada peringkat
- BKM Chapter14Dokumen5 halamanBKM Chapter14Vishakha DarbariBelum ada peringkat
- Fixed Income Chapter3Dokumen51 halamanFixed Income Chapter3sosnBelum ada peringkat
- FDGFDSGDFGDokumen3 halamanFDGFDSGDFGJesus Colin CampuzanoBelum ada peringkat
- Welling ReprintDokumen9 halamanWelling ReprintDealCurryBelum ada peringkat
- ACG3141 Chap 14 PDFDokumen35 halamanACG3141 Chap 14 PDFLexter Dave C EstoqueBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental Equity Analysis & Analyst Recommendations - STOXX Large 200 Index ComponentsDokumen401 halamanFundamental Equity Analysis & Analyst Recommendations - STOXX Large 200 Index ComponentsQ.M.S Advisors LLCBelum ada peringkat
- FIN303 Exam-Type Questions For Midterm 2Dokumen10 halamanFIN303 Exam-Type Questions For Midterm 2bi2345Belum ada peringkat
- FNCE 623 Financial Management: Mid Term Exam 3 June 2020 Time: 7:00 P.M. To 9:00 P.MDokumen3 halamanFNCE 623 Financial Management: Mid Term Exam 3 June 2020 Time: 7:00 P.M. To 9:00 P.Mleili fallahBelum ada peringkat
- Nism Mutual Fund VaDokumen24 halamanNism Mutual Fund VaKanikaa B KaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Interest Rates and Bond ValuationDokumen65 halamanInterest Rates and Bond Valuationgusti dianBelum ada peringkat
- SapmDokumen87 halamanSapmpriya031Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Credit Risk PDFDokumen53 halamanChapter 4 Credit Risk PDFSyai GenjBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Corporate Finance: Aswath Damodaran For Material Specific To This Package, Go ToDokumen72 halamanApplied Corporate Finance: Aswath Damodaran For Material Specific To This Package, Go TomeidianizaBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Markets and Institutions 8th Edition by Frederic S Mishkin Ebook PDFDokumen42 halamanFinancial Markets and Institutions 8th Edition by Frederic S Mishkin Ebook PDFdon.anderson433100% (37)
- Fixed Income BulletinDokumen12 halamanFixed Income BulletinfaiyazadamBelum ada peringkat
- Uti Mutual Fund Project 2022Dokumen45 halamanUti Mutual Fund Project 2022Anuja DekateBelum ada peringkat
- Ben Graham Calculations Template - FinboxDokumen8 halamanBen Graham Calculations Template - FinboxDario RBelum ada peringkat
- Investment Planning Mock TestDokumen20 halamanInvestment Planning Mock Testjayaram_polaris100% (2)
- Summary On An Intelligent Investor by Benjamin GrahamDokumen31 halamanSummary On An Intelligent Investor by Benjamin GrahamvssrjBelum ada peringkat
- Value Investor Insight - 3.31.14 Kopernik PDFDokumen11 halamanValue Investor Insight - 3.31.14 Kopernik PDFJohn Hadriano Mellon FundBelum ada peringkat
- Equity Analysis of Automobile CompaniesDokumen58 halamanEquity Analysis of Automobile Companiesyogesh patilBelum ada peringkat
- 5) Exam Is Due Back Before Midnight (EST) On Nov 5: WWW - Federalreserve.govDokumen3 halaman5) Exam Is Due Back Before Midnight (EST) On Nov 5: WWW - Federalreserve.govTrevor TwardzikBelum ada peringkat
- Irc Kit Part F (Business Valuations)Dokumen16 halamanIrc Kit Part F (Business Valuations)Amir ArifBelum ada peringkat
- QEIC Tech - CGI Group Pitch - FinalDokumen16 halamanQEIC Tech - CGI Group Pitch - FinalAnonymous Ht0MIJBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Corporate Finance QuizDokumen5 halamanPrinciples of Corporate Finance QuizKalonBelum ada peringkat
- IdeasDokumen158 halamanIdeashabbas1Belum ada peringkat
- Awp Examination Guide For Exams From 1 May 2016 Up To 30 April 2017Dokumen22 halamanAwp Examination Guide For Exams From 1 May 2016 Up To 30 April 2017Piere Christofer Salas HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- MAS 2023 Module 10 - Risk Leverage and Cost of CapitalDokumen9 halamanMAS 2023 Module 10 - Risk Leverage and Cost of CapitalPurple KidBelum ada peringkat