Hydrochloric Acid MSDS
Diunggah oleh
madmelzarJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hydrochloric Acid MSDS
Diunggah oleh
madmelzarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
47A
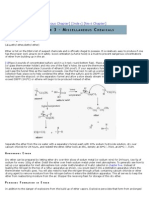
Hydrochloric acid and other hydrohalic acids
Hydrochloric acid
Corrosive
Hydrobromic acid
Corrosive
Hydroiodic acid
Corrosive
These substances
are dangerous
with:
C
C
HCl (aq)
R34: Causes burns. R37: Irritating to respiratory system.
-3
Solutions equal to or stronger than 6.5 mol dm should be labelled CORROSIVE.
-3
-3
Solutions equal to or stronger than 2 mol dm but weaker than 6.5 mol dm should be
labelled IRRITANT.
-3
WEL (mg m ): 2 (LTEL), 8 (STEL).
HBr(aq)
R34: Causes burns. R37: Irritating to respiratory system.
-3
Solutions equal to or stronger than 4.5 mol dm should be labelled CORROSIVE.
-3
-3
Solutions equal to or stronger than 1.2 mol dm but weaker than 4.5 mol dm should
be labelled IRRITANT.
-3
WEL (mg m ): 10 (STEL).
Purchase the 48% (w/w) acid.
HI(aq)
R34: Causes burns.
-3
Solutions equal to or stronger than 0.7 mol dm should be labelled CORROSIVE.
-3
-3
Solutions equal to or stronger than 0.3 mol dm but weaker than 0.7 mol dm should
be labelled IRRITANT. Purchase the 55% (w/w) acid.
ALUMINIUM, MAGNESIUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM and many other reactive metals. A vigorous or
violent reaction occurs.
PHOSPHORIC(V) ACID. Hydrogen halide gas is released.
POTASSIUM MANGANATE(VII). Explosions can occur.
SULFURIC ACID. Hydrogen halide gas is released.
Store: CLa
Store large containers at a low level, preferably in a tray to contain spills. Once bottles are
opened, gases can leak into the store; this accelerates the corrosion of metals. The gases can
also diffuse through plastic so that labels on the containers fade and disintegrate. The gases
react with ammonia and amines to deposit a white powder over bottles.
For emergencies, see Hazcard E as well as more detailed information which may be on this Hazcard.
Disposal: W1, W4
W4:
Use a fume
cupboard.
CLEAPSS 2007
47A
Hydrochloric acid and other hydrohalic acids
Activity
User
Control measures
Use of dilute
acids
Y7
Wear eye protection.
Use of concentrated acids
Y9
Preparation of
chlorine
Preparation of
solutions
Y12
Wear goggles.
Use a fume cupboard.
Wear disposable nitrile gloves.
Wear goggles.
Use a fume cupboard.
Wear goggles.
Use a fume cupboard.
Wear chemical-resistant gloves.
Large-scalepreparation of
chlorine
TT
Wear goggles or a face shield.
Use a fume cupboard.
Wear chemical-resistant gloves.
Aqua Regia for
use in analysis
of alloys
TT
Wear goggles or a face shield.
Use a fume cupboard.
Wear chemical-resistant gloves.
Y12
Model risk assessments
Experimental points
-3
This refers to solutions equal to or less than 2 mol dm . Use the mostdilute solution which produces the desired result. Guidance can be
found in L195, Safer Chemicals, Safer Reactions.
-3
Acids, more concentrated than 2 mol dm , may be used with careful
supervision. Security is important; bottles of concentrated acids have
been stolen.
-3
See Hazcard 89 for a safe, controllable method using 5 mol dm
hydrochloric acid. See Handbook 13.3.
See Recipe Card 31 for hydrochloric acid.
-3
3
A 1 mol dm solution is prepared by diluting 113 cm of 48% hydrobromic acid to 1 litre with water.
-3
3
A 1 mol dm solution is prepared by diluting 137 cm of 55% hydroiodic
acid to 1 litre with water.
The reaction between concentrated hydrochloric acid and potassium
manganate(VII) has caused several accidents by the inadvertent use of
the wrong acid. If this method is used, double check that the correct
acid is available and cover the potassium manganate(VII) with water
first. An explosion has occurred when potassium manganate(VII) and
concentrated hydrochloric acid were mixed but it seems neither
sulfuric(VI) acid nor a tube blockage could have been responsible. It
could possibly have been caused by the production of chlorine oxides;
see J C Curry, SSR, 1965, 46 (160), 770.
See Handbook 13.3 for details of equipment.
3
This very corrosive mixture is made by adding 5 cm fresh concen3
trated nitric(V) acid to 15 cm concentrated hydrochloric acid in a clean
container. If the acids are warm, cool them before mixing. Do not
attempt to stopper and store; any darkening beyond a yellow colour
indicates appreciable decomposition.
Disposal: W4: Immediately after use, in a fume cupboard and proceed
very slowly.
For emergencies, see Hazcard E as well as more detailed information which may be on this Hazcard.
CLEAPSS 2007
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Sulfuric Acid 98% DSDokumen2 halamanSulfuric Acid 98% DSbandarBelum ada peringkat
- AOCS CD 1-25 Iodine Value of Fats and Oils - Wijs MethodDokumen4 halamanAOCS CD 1-25 Iodine Value of Fats and Oils - Wijs Methodedshe67% (3)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisDari EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- D 1957 Hydroxyl ValueDokumen3 halamanD 1957 Hydroxyl ValueJean Carlos NoriegaBelum ada peringkat
- Cromato AmarilloDokumen3 halamanCromato Amarillohumbertotorresr100% (1)
- D1385 PDFDokumen4 halamanD1385 PDFAlejandra HernándezBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Practicals First YearsDokumen65 halamanChemistry Practicals First YearsWaleed EmaraBelum ada peringkat
- AOCS CD 1b 87 IV PDFDokumen4 halamanAOCS CD 1b 87 IV PDFzarlyBelum ada peringkat
- Diels Alder ReactionDokumen6 halamanDiels Alder ReactionSornkamnird.S92% (12)
- Chemistry Practicals First YearsDokumen65 halamanChemistry Practicals First YearsJAMES MIRICHOBelum ada peringkat
- Índice de Iodo - D 1959Dokumen4 halamanÍndice de Iodo - D 1959Sofia Fasolo CunhaBelum ada peringkat
- Pas Sop Sigma AldrichDokumen2 halamanPas Sop Sigma AldrichRajeev PareekBelum ada peringkat
- The Complete Book of EcstacyDokumen56 halamanThe Complete Book of EcstacyMagikFungus86% (7)
- Chemistry Labaratory Manual For First Years: Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyDokumen65 halamanChemistry Labaratory Manual For First Years: Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technologymark njeru ngigi100% (1)
- Chemistry Practicals First Years 87-3 PDFDokumen63 halamanChemistry Practicals First Years 87-3 PDFoscarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (Cod)Dokumen8 halamanChemical Oxygen Demand (Cod)evreddy05100% (4)
- Usp36-Nf31 01 38Dokumen2 halamanUsp36-Nf31 01 38Salsabil Nurazizah TABelum ada peringkat
- Astm 4458-94Dokumen3 halamanAstm 4458-94Roberto Eduardo Salvador MonteroBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of %age Purity NaClDokumen6 halamanDetermination of %age Purity NaClRana NaveedBelum ada peringkat
- D1072 (Total Sulfur in Fuel Gases by Combustion and Barium)Dokumen6 halamanD1072 (Total Sulfur in Fuel Gases by Combustion and Barium)Ale Hurtado MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Miscellaneous ChemicalsDokumen8 halamanMiscellaneous Chemicalsgbonger100% (8)
- Sodium and Potassium Chlorate The Complete Guide v1.0 PDFDokumen7 halamanSodium and Potassium Chlorate The Complete Guide v1.0 PDFDavid MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Iodine ValueDokumen4 halamanIodine ValueRobert Gilmore100% (4)
- D 4278 - 02 Rdqynzg - PDFDokumen3 halamanD 4278 - 02 Rdqynzg - PDFRufo CascoBelum ada peringkat
- Methoxyl Groups in Wood and Related Materials: Standard Test Method ForDokumen4 halamanMethoxyl Groups in Wood and Related Materials: Standard Test Method ForArnold RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Aliphatic AldehydesDokumen10 halamanAliphatic AldehydesMohammed AliraqiBelum ada peringkat
- Water-Soluble Chlorides Present As Admixtures in Graded Aggregate Road MixesDokumen3 halamanWater-Soluble Chlorides Present As Admixtures in Graded Aggregate Road MixesIgor RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Astm D 1121-07 Rezerva Alcalinitate AntigelDokumen3 halamanAstm D 1121-07 Rezerva Alcalinitate AntigelCorina StanculescuBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM D 512 - Standard Test Methods For Chloride Ion in WaterDokumen7 halamanASTM D 512 - Standard Test Methods For Chloride Ion in WaterGianinaRoncalChávezBelum ada peringkat
- Cfns Experiment 79 - Flame Tests (Wooden Splint Method) - 2Dokumen2 halamanCfns Experiment 79 - Flame Tests (Wooden Splint Method) - 2inconspicuousannieBelum ada peringkat
- 020-Gravim CL PDFDokumen6 halaman020-Gravim CL PDFInarah SulinaiBelum ada peringkat
- Astm D 890 98Dokumen3 halamanAstm D 890 98panzervausfeBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of ChloridesDokumen4 halamanDetermination of Chloridesawaaan100% (1)
- Peroxide ProcessDokumen10 halamanPeroxide ProcessAdrian Bermudez LoeraBelum ada peringkat
- Equilibrium ..... MDokumen3 halamanEquilibrium ..... MharetasakurausagiiBelum ada peringkat
- BleachingDokumen11 halamanBleachingPRATEEKMAHAJAN02Belum ada peringkat
- Acid Content of VinegarDokumen5 halamanAcid Content of VinegaramyBelum ada peringkat
- Adi Pic AcidDokumen8 halamanAdi Pic AcidTwas AnassinBelum ada peringkat
- Esterification Oil of WintergreenDokumen8 halamanEsterification Oil of WintergreenMaria MahusayBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-2: Materials and MethodsDokumen13 halamanChapter-2: Materials and Methodsdalton2003Belum ada peringkat
- Organic Chemistry Final 1Dokumen18 halamanOrganic Chemistry Final 1Tenny AbioyeBelum ada peringkat
- Lead Azide p004872Dokumen7 halamanLead Azide p004872Anthony SimonaitisBelum ada peringkat
- Chloride Ion in Water: Standard Test Methods ForDokumen8 halamanChloride Ion in Water: Standard Test Methods Forsantty1617Belum ada peringkat
- Making Soaps and DetergentsDokumen4 halamanMaking Soaps and Detergentsrachel CunananBelum ada peringkat
- Kodak Chemicals and FormulaeDokumen48 halamanKodak Chemicals and Formulaebtyler9100% (1)
- Core Practical 5 and 6Dokumen4 halamanCore Practical 5 and 6Adam EchikrBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrochloric AcidDokumen4 halamanHydrochloric AcidcventanBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrochloric Acid - 3Dokumen1 halamanHydrochloric Acid - 3True StoryBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium Hydride 60 Percent in OilDokumen3 halamanSodium Hydride 60 Percent in Oilbhawanisr@gmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- Galmet Industrial Primer (GOAC & ROAC) - ITW Polymers & FluidsDokumen5 halamanGalmet Industrial Primer (GOAC & ROAC) - ITW Polymers & FluidsBiju_PottayilBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of TalcDokumen5 halamanAnalysis of Talcalexander_suarez_19Belum ada peringkat
- AOCS - CD - 8-53 Peroxido Con CLDokumen2 halamanAOCS - CD - 8-53 Peroxido Con CLmanuelsnic100% (5)
- Silicon-mediated Transformations of Functional GroupsDari EverandSilicon-mediated Transformations of Functional GroupsBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion and Fouling Control in Desalination IndustryDari EverandCorrosion and Fouling Control in Desalination IndustryBelum ada peringkat
- Water Softening with Potassium Chloride: Process, Health, and Environmental BenefitsDari EverandWater Softening with Potassium Chloride: Process, Health, and Environmental BenefitsBelum ada peringkat
- Recover Gold from Gold Plated Items, And Turn It Into 99.995% Pure GoldDari EverandRecover Gold from Gold Plated Items, And Turn It Into 99.995% Pure GoldBelum ada peringkat
- Manual of Formulas - Recipes, Methods & Secret ProcessesDari EverandManual of Formulas - Recipes, Methods & Secret ProcessesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Produced Water Treatment Field ManualDari EverandProduced Water Treatment Field ManualPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (5)
- Hydrochloric Acid MSDSDokumen2 halamanHydrochloric Acid MSDSmadmelzarBelum ada peringkat
- AntacidDokumen40 halamanAntacidmadmelzarBelum ada peringkat
- Extension - QuadraticsDokumen3 halamanExtension - QuadraticsmadmelzarBelum ada peringkat
- ADifferentLookAtTheWelfareTrapI PreviewDokumen10 halamanADifferentLookAtTheWelfareTrapI PreviewmadmelzarBelum ada peringkat
- SAT January 2014Dokumen47 halamanSAT January 2014madmelzar100% (1)
- Win Configure Updated Title "Recommended Settings Updated"Dokumen2 halamanWin Configure Updated Title "Recommended Settings Updated"dams6797Belum ada peringkat
- Sat May 2011Dokumen27 halamanSat May 2011madmelzarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Learning JournalDokumen1 halamanChemistry Learning JournalmadmelzarBelum ada peringkat
- August 2013: Day Early AM Later AM Early PM Later PM Early Eve Later Eve MondayDokumen17 halamanAugust 2013: Day Early AM Later AM Early PM Later PM Early Eve Later Eve MondaymadmelzarBelum ada peringkat
- Astm d7503 - 10 CicDokumen5 halamanAstm d7503 - 10 CicMatiasFuentealbaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry KSSM Form 5 Textbook AnswerDokumen64 halamanChemistry KSSM Form 5 Textbook AnswerJason Teh59% (66)
- Calorimetry and Hess LawDokumen4 halamanCalorimetry and Hess LawchuralaBelum ada peringkat
- Black 2Dokumen14 halamanBlack 2KashyapBelum ada peringkat
- Science - Form 4 - Chapter 5Dokumen12 halamanScience - Form 4 - Chapter 5Marcia PattersonBelum ada peringkat
- Beet Root4Dokumen36 halamanBeet Root4abhishek padhy100% (1)
- Catalogo de Estimulacion SLBDokumen34 halamanCatalogo de Estimulacion SLBpetanteloBelum ada peringkat
- Formularium KF 58 - EviDokumen8 halamanFormularium KF 58 - EviNurul Evi kurniatiBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency Medicines List 2014Dokumen38 halamanEmergency Medicines List 2014Michael Silva100% (3)
- Science Focus 4Dokumen343 halamanScience Focus 4meetpatel9739100% (3)
- Secondary NutrientsDokumen18 halamanSecondary NutrientsMessiBelum ada peringkat
- Aalco Metals LTD Aluminium Alloy 5754 H22 Sheet and Plate 153Dokumen2 halamanAalco Metals LTD Aluminium Alloy 5754 H22 Sheet and Plate 153a1528347Belum ada peringkat
- Gomayadi GhanvatiDokumen1 halamanGomayadi GhanvatiBharatiyulamBelum ada peringkat
- Proposta RicetteDokumen14 halamanProposta Ricetteامل ابراهيمBelum ada peringkat
- Acid and AlkaliDokumen9 halamanAcid and Alkali云吸仓鼠吉尼斯保持者Belum ada peringkat
- PEKA Experiment Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 To 5Dokumen9 halamanPEKA Experiment Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 To 5James Chua Hong Kheng67% (6)
- 9701 s15 QP 22 PDFDokumen8 halaman9701 s15 QP 22 PDFAl BeruniBelum ada peringkat
- Nordin 1997 Effluent Treatment System PDFDokumen10 halamanNordin 1997 Effluent Treatment System PDFVivek KapadiaBelum ada peringkat
- The Essential Facts On PDFDokumen10 halamanThe Essential Facts On PDFMbahBelum ada peringkat
- Dioxido de Titanio Monografía USPDokumen2 halamanDioxido de Titanio Monografía USPsigridborjaBelum ada peringkat
- Tips For Growing OrchidsDokumen16 halamanTips For Growing OrchidsIsroi.comBelum ada peringkat
- Metal and Acids Lessons Year 8Dokumen13 halamanMetal and Acids Lessons Year 8Sara KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Multiple-Choice and Bimodal Questions: Diff: 3 Page Ref: Sec. 2.1Dokumen74 halaman2.1 Multiple-Choice and Bimodal Questions: Diff: 3 Page Ref: Sec. 2.1Uday Prakash SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Village Disaster Management Plan Nalbari 0Dokumen36 halamanVillage Disaster Management Plan Nalbari 0Lalit JainBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 The Reactivity SeriesDokumen15 halamanChapter 10 The Reactivity SeriesSumi VjBelum ada peringkat
- Chemicals: Mnemonic List For 110 ElementsDokumen31 halamanChemicals: Mnemonic List For 110 ElementsKenneth DayritBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Two Methods To Evaluate Matrix Acidizing Using Real-Time Skin Effect in Saudi Arabia - SPE 73703, 2002Dokumen7 halamanApplication of Two Methods To Evaluate Matrix Acidizing Using Real-Time Skin Effect in Saudi Arabia - SPE 73703, 2002alizareiforoushBelum ada peringkat
- 17 - All Reaction Types Worksheet AnswersDokumen8 halaman17 - All Reaction Types Worksheet AnswersCubicatBelum ada peringkat
- Solvay - Sulphur Sf6Dokumen50 halamanSolvay - Sulphur Sf6Rudolf SteinerBelum ada peringkat
- Specification For Water Softening Plant and Online Self Cleaning FilterDokumen16 halamanSpecification For Water Softening Plant and Online Self Cleaning Filterkatepol8264100% (1)