Biological Timeline of Malaria
Diunggah oleh
Andrew PeckHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biological Timeline of Malaria
Diunggah oleh
Andrew PeckHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
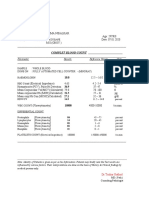
Timeline of Malaria
The symptoms of malaria have been recognised as far back as in
chinese mythology
(340CE), The anti fever properties of the Chinese qinghao plant were
first described
(2000 Y, Ago) The ancient greeks recognised it occuring in those that
lived near low, moist and hot districts near swamps. It was named
Malaria, meaning "bad air"
It was supposed that malaria might be caused by drinking swamp
water, or from the bites of swamp insects
The greeks and romans build drains to remove stagnant water, and
the incidence of the fever fell.
(1650) The first drug used to treat malaria was quinine.
(1880), Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran discovered the pathogen that
causes malaria while looking the blood of those who had contracted it.
(1885), Camillo Golgi, established that there were two or more forms of
the disease, one that causes a fever on alternate days, an another that
causes a fever every third day. It was also discovered that this
coincided with different production of new parasites and that the peak
of the gever coincided with the release of the merozites into the blood.
(1890), Giovanni Grassi and Raimondo Filetti named the two malaria
parasites discovered.
(1897), The name of the original parasite was changed to P. falciparum
(1898), Giovanni Grassi and Giuseppe Bastianelli showed that human
malaria is transmitted the sam way as malaria in birds.
(1898), The mosquito is shown to be responsible for the transmission
of malaria
Procedures are enacted to cull the vector, by draining stagnant
water, sprayed with oil and protective clothing was used.
(1901), Pyrethrum is used as an insectocide to kill mosquitos
(1922), A fourth human malaria parasite was discovered.
(1930), Anti malarial drug Atebrin was developed
(1944), Synthetic quinine was developed.
(1940+), Cloroquine was developed. Highly effevtive until new malaria
strains evolved resistance.
(1950), World Health Org. attempts to completely eradicate malaria.
This involves the use of the insectocide DDT to try to wipe out moquito
populations. It uses the intro duction of biological controls such as fish
that eat insect larvae.
(1970) The use of drugs such as prophylactics helps to prevent
contraction of the disease.
THe WHO program was initially very successful and numbers of
cases of malaria had dropped dramatically by the early 1970's.
(1971), Artemisisin was isolated from the qinhao plant.
(1970+), many idfferent anti malarial drugs have been used, but each
becomes ineffective as the parasite evolves into a resistant form. The
use of DDT was discontinued when mosquitos were found to be
resistant to it.
(1980), Resurgence of malaria
(1981), Search for malaria vaccine
(2000+), because of widespread development of drug resistant malaria
parasites, combination drug therapy that includes the highly effective
artemisinin is the only consistantly effective treatment.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Nurgle 1kDokumen2 halamanNurgle 1kAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Project Blue SkyDokumen40 halamanProject Blue SkyAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Reacpelent Et Ulu Dol Simgar Barlil. For Those Who Know Are in The Right To FindDokumen1 halamanReacpelent Et Ulu Dol Simgar Barlil. For Those Who Know Are in The Right To FindAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Assiufbiusldjfjksndkjfnsjndsdfa Sda Sdsas Admkjna SKLDNMKL Das DDokumen1 halamanAssiufbiusldjfjksndkjfnsjndsdfa Sda Sdsas Admkjna SKLDNMKL Das DAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Siufbiusldjfjksndkjfnsjndsdfa Sda Sdsas Admkjna SKLDNMKLSD AsDokumen1 halamanSiufbiusldjfjksndkjfnsjndsdfa Sda Sdsas Admkjna SKLDNMKLSD AsAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- FalseDokumen1 halamanFalseAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- This Is A Document - FnalsDokumen1 halamanThis Is A Document - FnalsAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- This Is A Bit of TextDokumen1 halamanThis Is A Bit of TextAndrew PeckBelum ada peringkat
- School ChildcareDokumen2 halamanSchool Childcarematt022005Belum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Immuno Notes LectureDokumen30 halamanImmuno Notes LectureSteph TabasaBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Coccidia: - Characterized by Thick-Walled OocystsDokumen26 halamanCoccidia: - Characterized by Thick-Walled Oocyststaty jatyBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Gram Negative BacilliDokumen108 halamanGram Negative Bacilliblue_blooded23100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- FOURTH MEETING RickyDokumen3 halamanFOURTH MEETING RickyQhie'yPhie ArdiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- DR - Savant ShirsoliDokumen1 halamanDR - Savant Shirsolijitendra karvandeBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Theories of Antibody FormationDokumen30 halamanTheories of Antibody FormationTarun0% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Chapter 10 BloodDokumen3 halamanChapter 10 BloodinitaygracileshayneBelum ada peringkat
- Literature ReviewDokumen3 halamanLiterature ReviewWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Andrew Moulden Interview - What You Were Never Told About VaccinesDokumen16 halamanDr. Andrew Moulden Interview - What You Were Never Told About VaccinesTiffany Torres100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Shang Han Lun - The Six StagesDokumen9 halamanShang Han Lun - The Six StagesFernândo SílvváBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Marrow Transplantation: Gargi M P Year MSC NursingDokumen35 halamanBone Marrow Transplantation: Gargi M P Year MSC NursingGargi MPBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral TherapyDokumen4 halamanAntiviral Therapyanand dubeyBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokumen21 halamanLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsEzekiel ArtetaBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Chronic Urticaria Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDokumen5 halamanChronic Urticaria Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsOgy SkillBelum ada peringkat
- Phmp-Finals RevDokumen22 halamanPhmp-Finals RevJay JayBelum ada peringkat
- SWT Microbiology DamsDokumen80 halamanSWT Microbiology DamsvamshidhBelum ada peringkat
- ROTAVIRUSDokumen16 halamanROTAVIRUSIkae NyamBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Patient Centred Surveillance of Drug Resistant PathogensDokumen19 halamanPatient Centred Surveillance of Drug Resistant PathogensHanna alexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology & Immune SystemDokumen81 halamanHematology & Immune SystemAmanuel Maru100% (1)
- 1526931449Dokumen123 halaman1526931449Lika KipshidzeBelum ada peringkat
- Cold AbscessDokumen3 halamanCold AbscessMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuBelum ada peringkat
- Hema Writen MidtermsDokumen12 halamanHema Writen Midtermsshinian_24Belum ada peringkat
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC)Dokumen19 halamanVernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC)api-3742497Belum ada peringkat
- Elisa & RiaDokumen4 halamanElisa & Riadihajum3Belum ada peringkat
- Blood DisordersDokumen4 halamanBlood DisordersShadrackBelum ada peringkat
- RadioimmunoassayDokumen16 halamanRadioimmunoassaysr_bakegBelum ada peringkat
- Molluscum ContagiosumDokumen2 halamanMolluscum ContagiosumMalueth AnguiBelum ada peringkat
- Communicable Diseases in The PhilippinesDokumen3 halamanCommunicable Diseases in The PhilippinesChevelle Valenciano-GaanBelum ada peringkat
- Mumps: Resurgence of A Once-Dormant Disease: Published Ahead-Of-PrintDokumen4 halamanMumps: Resurgence of A Once-Dormant Disease: Published Ahead-Of-Printanindya nandiniBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)