ECG Lesson 1
Diunggah oleh
Marwan M.0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
127 tayangan5 halamanHak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
127 tayangan5 halamanECG Lesson 1
Diunggah oleh
Marwan M.Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
The standard 12-lead electrocardiogram is a
representation of the heart's electrical activity recorded
from electrodes on the body surface. This section
describes the basic components of the ECG and the
lead system used to record the ECG tracings.
Topics for study:
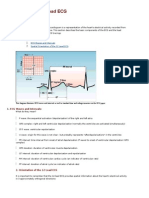
This diagram illustrates ECG waves
and intervals as well as standard
time and voltage measures on the
click to view ECG paper.
1. ECG Waves and Intervals
2. Spatial Orientation of the 12 Lead ECG
1. ECG Waves and Intervals:
What do they mean?
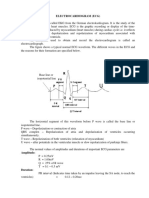
P wave: the sequential activation (depolarization) of the right and left atria
QRS complex: right and left ventricular depolarization (normally the ventricles
are activated simultaneously)
ST-T wave: ventricular repolarization
U wave: origin for this wave is not clear - but probably represents "after
depolarization" in the ventricles
PR interval: time interval from onset of Atrial depolarization (P wave) to onset of
ventricular depolarization (QRS complex)
QRS duration: duration of ventricular muscle depolarization
QT interval: duration of ventricular depolarization and repolarization
RR interval: duration of ventricular cardiac cycle (an indicator of ventricular
rate)
PP interval: duration of Atrial cycle (an indicator of Atrial rate)
2. Orientation of the 12 Lead ECG: It is important to remember that the
12-lead ECG provides spatial information about the heart's electrical
activity in 3 approximately orthogonal directions:
Right Left
Superior Inferior
Anterior Posterior
Each of the 12 leads represents a particular orientation in space,
as indicated below (RA = right arm; LA = left arm, LF = left foot):
Bipolar limb leads (frontal plane):
• Lead I: RA (-) to LA (+) (Right Left, or lateral)
Lead II: RA (-) to LF (+) (Superior Inferior
Lead III: LA (-) to LF (+) (Superior Inferior)
• Augmented unipolar limb leads (frontal plane):
• Lead aVR: RA (+) to [LA & LF] (-) (Rightward)
• Lead aVL: LA (+) to [RA & LF] (-) (Leftward)
• Lead aVF: LF (+) to [RA & LA] (-) (Inferior)
Unipolar (+) chest leads (horizontal plane):
• Leads V1, V2, and V3: (Posterior Anterior)
• Leads V4, V5, V6 :( Right Left or lateral)
Click here to see:
Lead Placement
Diagrams
Behold: Einthoven's Triangle! Each of the 6 frontal plane leads has a negative and
positive orientation (as indicated by the '+' and '-' signs). It is important to
recognize that Lead I (and to a lesser extent Leads aVR and aVL) are right Ûleft in
orientation. Also, Lead aVF (and to a lesser extent Leads II and III) are superior
Ûinferior in orientation. The diagram below further illustrates the frontal plane
hookup.
LOCATION OF CHEST ELECTRODES IN 4TH AND 5TH INTERCOSTAL SPACES:
V1: right 4th intercostal space
V2: left 4th intercostal space
V3: halfway between V2 and V4
V4: left 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line
V5: horizontal to V4, anterior axillary line
V6: horizontal to V5, mid-axillary line
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationDari EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- 17 CRISP PhysiologyDokumen5 halaman17 CRISP PhysiologySyed Aijaz44% (9)
- EcgDokumen57 halamanEcgenii_ta100% (9)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsDari EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsBelum ada peringkat
- I. The Standard 12 Lead ECGDokumen2 halamanI. The Standard 12 Lead ECGapi-376925250% (2)
- Elektrokardiogramm) Is A Graphic Produced by An ElectrocardiographDokumen5 halamanElektrokardiogramm) Is A Graphic Produced by An ElectrocardiographReverie ManalaysayBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Waves and Intervals:: Simultaneously)Dokumen2 halamanECG Waves and Intervals:: Simultaneously)blade157721Belum ada peringkat
- Bipolar Limb Leads (Frontal Plane)Dokumen7 halamanBipolar Limb Leads (Frontal Plane)jonna casumpangBelum ada peringkat
- Orientation of The 12 Lead ECGDokumen1 halamanOrientation of The 12 Lead ECGLwin Maung Maung ThikeBelum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDokumen76 halamanElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduBelum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Base Line or Isopotential LineDokumen15 halamanElectrocardiogram (Ecg) : Base Line or Isopotential Linegyspsunshine girlBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Waves and Intervals Spatial Orientation of The 12 Lead ECGDokumen31 halamanECG Waves and Intervals Spatial Orientation of The 12 Lead ECGiah_18Belum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg) Introduction of Basic Principles: Dian Puspita SariDokumen47 halamanElectrocardiogram (Ecg) Introduction of Basic Principles: Dian Puspita SariArie Krisnayanti Ida AyuBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg Reading Made EasyDokumen59 halamanEcg Reading Made EasyAngealyn GaviolaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding An ECGDokumen1 halamanUnderstanding An ECGCecil-An DalanonBelum ada peringkat
- 9 EcgDokumen12 halaman9 EcgTommy CharwinBelum ada peringkat
- Auskultation. ECG - LastDokumen5 halamanAuskultation. ECG - LastAndreyBelum ada peringkat
- A Seminar On ECGDokumen16 halamanA Seminar On ECGVibha C PrabhuBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Fisiologi Kardiovaskuler: DR .H. Sonny Pamuji Laksono M.Kes, AifmDokumen135 halamanSistem Fisiologi Kardiovaskuler: DR .H. Sonny Pamuji Laksono M.Kes, AifmAnonymous RPcFL6OVW1Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0Dokumen84 halamanIntroduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0TrickyRooBelum ada peringkat
- REAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALDokumen15 halamanREAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALSHANKARBelum ada peringkat
- ECG InterpretationDokumen48 halamanECG InterpretationKervayse St.ClairBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg in DogsDokumen107 halamanEcg in DogsPLABITA GOSWAMI100% (2)
- Electrocardiography: DR Budi EnochDokumen115 halamanElectrocardiography: DR Budi EnochAriyanaBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Made Easy by Mallareddy SripujaDokumen46 halamanECG Made Easy by Mallareddy Sripujagrreddy836100% (3)
- A Brief Introduction To The Standard 12-Lead ECG (EKG)Dokumen29 halamanA Brief Introduction To The Standard 12-Lead ECG (EKG)Lazar BoskovicBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg FileDokumen29 halamanEcg Fileneha miriBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idDokumen12 halamanElectrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idlemon kyuteaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3c Interpretation of ECG - The Heart Model EM Theory & Applications II Spring Semester 2006Dokumen27 halamanLecture 3c Interpretation of ECG - The Heart Model EM Theory & Applications II Spring Semester 2006hebaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiography Basic: DR Budi EnochDokumen49 halamanElectrocardiography Basic: DR Budi EnochYohanes Malindo Wiyaa DBs-uno100% (1)
- ElectrocardiogramDokumen52 halamanElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhBelum ada peringkat
- 05 - ElektrokardiogramDokumen39 halaman05 - ElektrokardiogramNauval Zilal FananyBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 EcgDokumen49 halaman2020 EcgHannah HalimBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Made EasyDokumen82 halamanECG Made EasyBobby SodhiBelum ada peringkat
- ECG EKG InterpretationDokumen11 halamanECG EKG InterpretationGunma AkagiBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomi 1Dokumen54 halamanAnatomi 1Fany LainamaBelum ada peringkat
- EKGDokumen153 halamanEKGOsmy JuniorBelum ada peringkat
- ElectrocardiogramDokumen52 halamanElectrocardiogramMona AlhindiBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg PresentationDokumen27 halamanEcg Presentationanish3189Belum ada peringkat
- 12 Lead EKG 101Dokumen84 halaman12 Lead EKG 101zul fatmah100% (1)
- A El Outline June 2007Dokumen82 halamanA El Outline June 2007neysaonlineBelum ada peringkat
- 4cardiovascular SystemDokumen18 halaman4cardiovascular SystemJack OneBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg Physio LectureDokumen60 halamanEcg Physio LectureAninze Chidera100% (1)
- Ecg Engl Large 126Dokumen125 halamanEcg Engl Large 126Andreea-Sânziana StanciuBelum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiogram Asyik GuysDokumen29 halamanElectrocardiogram Asyik Guysdesinta mrBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg (Ekg) : Dr. Jamal Dabbas Interventional Cardiologist & InternistDokumen87 halamanEcg (Ekg) : Dr. Jamal Dabbas Interventional Cardiologist & Internistsara rababahBelum ada peringkat
- CVS Physiology (Assignment) : Abu BakarDokumen6 halamanCVS Physiology (Assignment) : Abu BakarAbu BakarBelum ada peringkat
- ElectrocardiogramDokumen24 halamanElectrocardiogramShamsuzzaman SharifBelum ada peringkat
- ECG EKG: BasicsDokumen191 halamanECG EKG: BasicsSabio DenmenBelum ada peringkat
- 16 Analyzing EKG Vectors and MEADokumen50 halaman16 Analyzing EKG Vectors and MEAEnrique Téllez CentenoBelum ada peringkat
- Cute Interpretation of Ecg PDFDokumen157 halamanCute Interpretation of Ecg PDFNers SenBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Interpretation ECG Interpretation Basics & Quick Guide PDFDokumen157 halamanECG Interpretation ECG Interpretation Basics & Quick Guide PDFNers SenBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Laboratory Activit1Dokumen9 halamanECG Laboratory Activit1Leiraset WuBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg + Ventricular Tachycardia and FibrillationDokumen9 halamanEcg + Ventricular Tachycardia and Fibrillationsakkiyy154Belum ada peringkat
- Ecg Tutorial PDFDokumen82 halamanEcg Tutorial PDFpacpacpac123Belum ada peringkat
- Ecg Utah EduDokumen87 halamanEcg Utah EduMos Viorel DanutBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideDari EverandUnderstanding Intracardiac EGMs: A Patient Centered GuideBelum ada peringkat
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasDari EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Epilepsy and Loss of ConsciousnessDokumen11 halamanEpilepsy and Loss of ConsciousnessMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Multiple SclerosisDokumen4 halamanMultiple SclerosisMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- HeadacheDokumen4 halamanHeadacheMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- MRCP EndocrineDokumen94 halamanMRCP EndocrineMarwan M.100% (3)
- Movement Disorders: Akinetic-Rigid SyndromesDokumen8 halamanMovement Disorders: Akinetic-Rigid SyndromesMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Investigations:) - To Diagnose Lesions in The Oesophageal orDokumen4 halamanInvestigations:) - To Diagnose Lesions in The Oesophageal orMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- The Acute AbdomenDokumen7 halamanThe Acute AbdomenMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 27: Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDokumen26 halamanChapter 27: Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Stroke and Cerebrovascular DiseaseDokumen14 halamanStroke and Cerebrovascular DiseaseMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- G.I Diseases.Dokumen3 halamanG.I Diseases.Marwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Functional Gastrointestinal DisordersDokumen6 halamanFunctional Gastrointestinal DisordersMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Osmotic Diarrhoea: Difficile)Dokumen4 halamanOsmotic Diarrhoea: Difficile)Marwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Acute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingDokumen7 halamanAcute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingMarwan M.100% (1)
- Atlas Sectiuni AnatomieDokumen55 halamanAtlas Sectiuni AnatomieManuela UrlanBelum ada peringkat
- Chest Pain: (See Also Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17 Edition, Chapter 13)Dokumen10 halamanChest Pain: (See Also Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17 Edition, Chapter 13)Marwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Fluid and Elctrolyte Balance.... Power PointDokumen40 halamanFluid and Elctrolyte Balance.... Power PointMarwan M.100% (1)
- Postpartum Hemorrhage 12-01Dokumen50 halamanPostpartum Hemorrhage 12-01pkmmanaluBelum ada peringkat
- Gallstones - Treatment in AdultsDokumen4 halamanGallstones - Treatment in AdultsMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Hepatiti Viral - NdjekjaDokumen13 halamanHepatiti Viral - NdjekjaKreshnik HAJDARIBelum ada peringkat
- Angela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterDokumen32 halamanAngela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Dokumen12 halamanChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Marwan M.100% (1)
- Abg AnalysisDokumen26 halamanAbg Analysissridhar100% (11)
- Hypertension GuidelinesDokumen30 halamanHypertension GuidelinesLucky PermanaBelum ada peringkat
- Warfarin RecordDokumen2 halamanWarfarin RecordMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Asthma Education andDokumen440 halamanNational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Asthma Education andMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Overweight, Obesity and Physical InactivityDokumen13 halamanOverweight, Obesity and Physical InactivityMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Earth and Life ScienceDokumen14 halamanEarth and Life ScienceEms TeopeBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of Antipyretic DrugsDokumen19 halamanPharmacology of Antipyretic DrugsPretty HiaBelum ada peringkat
- Occupational Therapy - Play, SIs and BMTsDokumen3 halamanOccupational Therapy - Play, SIs and BMTsAnnbe Barte100% (1)
- LeafanatomyDokumen18 halamanLeafanatomyTeach FrezBelum ada peringkat
- The MoneraDokumen19 halamanThe MoneraNaufal Taufiq AmmarBelum ada peringkat
- Thomas K. Rayhawk: Graduate Coursework in Medicinal Pharmacology & Physiology University of Missouri-ColumbiaDokumen3 halamanThomas K. Rayhawk: Graduate Coursework in Medicinal Pharmacology & Physiology University of Missouri-ColumbiaThomas RayhawkBelum ada peringkat
- Kristal Pada UrineDokumen4 halamanKristal Pada UrineyholicBelum ada peringkat
- Gbio 2122 Week 1 10 by Kuya CharlesDokumen18 halamanGbio 2122 Week 1 10 by Kuya CharlesChoe Yoek Soek100% (2)
- Good BooksDokumen16 halamanGood BooksFbihansip bancel100% (1)
- MODUL Praktikum Anatomi Dan HistologiDokumen20 halamanMODUL Praktikum Anatomi Dan HistologiandikaBelum ada peringkat
- Jaw RelationDokumen48 halamanJaw RelationBharanija100% (1)
- PT, Aptt, TTDokumen44 halamanPT, Aptt, TTswaraj sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Different Approaches in Pharmacological ResearchDokumen3 halamanDifferent Approaches in Pharmacological ResearcharcherselevatorsBelum ada peringkat
- 47pages METHAMPHETAMINE TOXICITY AND MESSENGERS OF DEATHDokumen47 halaman47pages METHAMPHETAMINE TOXICITY AND MESSENGERS OF DEATHDenise MathreBelum ada peringkat
- SEPTEMBER 6, 2021 Hematology Assessment: Characteristic FeaturesDokumen23 halamanSEPTEMBER 6, 2021 Hematology Assessment: Characteristic FeaturesChristian John V. CamorahanBelum ada peringkat
- Common Board QuestionDokumen17 halamanCommon Board QuestionJonathan Renier VerzosaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiology I WorkbookDokumen68 halamanCardiology I WorkbookPharmacist DinaBelum ada peringkat
- Argaud Et Al. - 2018 - Facial Emotion Recognition in Parkinson's Disease A Review and New HypothesesDokumen14 halamanArgaud Et Al. - 2018 - Facial Emotion Recognition in Parkinson's Disease A Review and New HypothesesAleja ToPaBelum ada peringkat
- LC Biology GuideDokumen90 halamanLC Biology GuideBassel BitarBelum ada peringkat
- PM Artifacts WEBDokumen20 halamanPM Artifacts WEBSalman MemonBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy, Lecture 11, The Peritoneum (Lecture Notes)Dokumen11 halamanAnatomy, Lecture 11, The Peritoneum (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (1)
- TCM Student Study GuideDokumen40 halamanTCM Student Study GuideHomework PingBelum ada peringkat
- Antigen & AntibodiesDokumen16 halamanAntigen & AntibodiesYing Ming TangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12 - Cardiovascular EmergenciesDokumen47 halamanChapter 12 - Cardiovascular EmergenciesJunx TripoliBelum ada peringkat
- Davis's NCLEX-RN® Success 3E (2012) - MEMORY AIDS - IMPORTANTDokumen4 halamanDavis's NCLEX-RN® Success 3E (2012) - MEMORY AIDS - IMPORTANTMaria Isabel Medina MesaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen7 halamanEndocrine SystemSolita PorteriaBelum ada peringkat
- URRADokumen3 halamanURRAMubashir RafiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Recommended TextbooksDokumen8 halamanRecommended TextbooksShi Lin Lau0% (1)
- (Physio A) ECG (Javier)Dokumen4 halaman(Physio A) ECG (Javier)AliBelum ada peringkat