Concept Mapping
Diunggah oleh
Malavika Jithin0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
40 tayangan6 halamanonline assignment
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inionline assignment
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
40 tayangan6 halamanConcept Mapping
Diunggah oleh
Malavika Jithinonline assignment
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
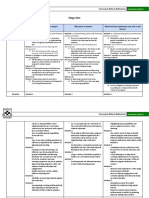
CONCEPT MAPPING
Concept maps provide a unique
graphical view of how students organize, connect and synthesis
information. They include concepts, usually enclosed in circles or
boxes of some type, and relationship between concepts indicated
by a connecting line linking two concepts. Words on the line
referred to as linking words or linking phrases, specify the
relationship between the two concepts.
Concept maps are developed on the
basis of Asubels theory of meaningful learning. Meaningful
learning refers to the concept that the learned knowledge is fully
understood by the individual and that individual knows how that
specific fact relate to other stored facts. According to Ausubel
meaningful learning requires three conditions:
1. The material to be learned must be conceptually clear and
presented with language and examples relatable to the
leaners prior knowledge.
2. Leaner must possess relevant prior knowledge.
3. The leaner must choose to learn meaningfully.
Characteristics of concept
Concept are represented in a hierarchical fashion with the
most inclusive, most general topics at the top of the map
and the more specific, less general hierarchically below.
Concept maps is the inclusion of cross-links. These are
relationships or links between concepts in different
segments or domains of the concept map. Cross-links help
us see how a concept in one domain of knowledge
represented on the map is related to a concept in another
domain shown on the map.
Concept maps is specific example of events or objects that
help to clarify the meaning of a given concept. Normally
these are not included in ovals or boxes, since they are
specific events or objects and do not represent concepts.
Advantages of concept mapping:
Concept mapping helps creative thinking.
Provides clarity to the concepts involved with each other.
It allows basic information on one page.
It is a good way to work to prepare for the exams.
It is easy to learn, teach and use.
It can be used for assessment.
Concept maps are student centered active methods for
students.
It is suitable for many different topics, instructional stage
and great level.
It can be used effectively for revision and students are able
to rank topics which they learned and provides easiness to
establish a link between topics.
It can encourage student-teacher interaction when they
create a map together by discussing.
The benefits of concept maps:
Concept mapping offers benefits to both student and
teachers. Concept maps give students an opportunity to;
Think about the connections between science terms
being learned.
Organize their thoughts and visualize the relationship
between key concepts in systematic way.
The steps of constructing a concept map:
Step 1: To construct a concept map, it is important to define
the context. A good way to define a context for construct
map is to construct a focus question, that is, a question that
clearly specifies the problem or issue the concept map
should help to resolve.
Step 2: Identify the key concept in a paragraph, research
report, and chapter; or simply think of the concepts of a
subject area and list them.
Step3: From the listed concepts, rank the concepts by
placing the broadest and most inclusive idea at the top of
the map.
Step 4: Work down the paper and add more specific
concepts and do hierarchical arrangement of concepts.
Step 5: Connect the concepts by lines. Label the lines with
action or linking words. These links between different
domains of knowledge on the concept map scan help to
illustrate how these domains are related to one another. The
connection creates meaning.
Step 6: Specific examples of the concepts can added below
the concept labels. But these are not included in ovals or
boxes. They are specific events or objects and do not
represent concepts.
Step 7: A concept map is never finished. After a preliminary
map is constructed, it is always necessary to revise this map.
Other concepts can be added.
Use of concept maps:
As method of learning: concept maps are a useful
learning tool in mathematics. Concept maps can
improve understanding of mathematics concepts and
help build connections among abstract concepts.
Concepts maps can also be used as a misconceptioncorrection tool.
As a teaching method: concept maps can help us
identify, understand, and organize concepts we plan to
teach. The instructor can present concept maps to the
whole class to highlight key concepts and connections.
As a curriculum and lesson planning method: in
curriculum planning, concept maps can be enormously
useful. The hierarchical organization of concept maps
suggest more optimal sequencing of instructional
material. If concept maps are used in planning
instruction and students are required to construct
concepts maps as they are learning , previously
unsuccessful students can become successful in
making sense out of mathematics.
As
an
evaluation
method
of
students
understanding of mathematical concepts: concept
mapping could be a key to developing strong
performance assessments that ought to be designed to
generate both an assessment of how students are
applying
concepts
and
to
assess
the
deep
understanding that students ae gaining.
Kinds of concept mapping
A spider concept map is a kind of map that is used to
investigate and enumerate various aspects of a single theme
or topic, helping the students to organize their thoughts. It
looks a bit like a spiders web, hence its name
The hierarchy concept map presents information in a
descending order of importance. The most important
information is placed on the top. Distinguishing factors
determine the placement of the information.
The flowchart concept map organizes information in a
linear format
The system concept map organizes information in a
format which is similar to a flowchart with the addition of
INPUTS and OUTPUTS
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Derbyshire Language Scheme AssessmentsDokumen3 halamanDerbyshire Language Scheme Assessmentshaya100% (1)
- Innovative Lesson Plan PDFDokumen3 halamanInnovative Lesson Plan PDFMalavika Jithin100% (3)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Department of Education Gammad National High SchoolDokumen3 halamanDepartment of Education Gammad National High SchoolJessica G. NaragBelum ada peringkat
- Recommendation Letter - Budi Waluyo - by LecturerDokumen1 halamanRecommendation Letter - Budi Waluyo - by LecturerSabrina Arfanindia DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDokumen8 halamanDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesapril joyBelum ada peringkat
- Way For Stimulating and Maintaing Interest in Learning in MathematicsDokumen5 halamanWay For Stimulating and Maintaing Interest in Learning in MathematicsMalavika JithinBelum ada peringkat
- Self Reflection PDFDokumen1 halamanSelf Reflection PDFMalavika JithinBelum ada peringkat
- Statistics: Frequency Table and MeanDokumen8 halamanStatistics: Frequency Table and MeanMalavika JithinBelum ada peringkat
- Pheromones LessonDokumen1 halamanPheromones Lessonapi-252539857Belum ada peringkat
- TKT Final TestDokumen9 halamanTKT Final TestJhonatan VélezBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Task 3 - IntroductionDokumen12 halamanPaper 2 Task 3 - IntroductionVitaBelum ada peringkat
- My Report - PPTX (Autosaved)Dokumen57 halamanMy Report - PPTX (Autosaved)ClaireXDBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Research 2 1Dokumen11 halamanPractical Research 2 1Phia Sheryn CarcellarBelum ada peringkat
- Dll-Types of ClaimsDokumen4 halamanDll-Types of ClaimsAllysa Marie Aguilar Borlado100% (1)
- Learning Plan: (Mapeh - Music)Dokumen11 halamanLearning Plan: (Mapeh - Music)Shiela Mea BlancheBelum ada peringkat
- He - Keeping Our Classroom CleanDokumen19 halamanHe - Keeping Our Classroom CleanNoumaan Ul Haq SyedBelum ada peringkat
- Key Words-Spatial Quality, Form, Space, Functions, OrganizationsDokumen3 halamanKey Words-Spatial Quality, Form, Space, Functions, OrganizationsYash SethiBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan in EnglishDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan in EnglishDarryl FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Ebook Psikologi Pendidikan J.W. SantrockDokumen12 halamanEbook Psikologi Pendidikan J.W. Santrockjofanianorma.23025Belum ada peringkat
- Micro PL Reflections 2023 - Curriculum Reform Stage 1Dokumen14 halamanMicro PL Reflections 2023 - Curriculum Reform Stage 1api-467854007Belum ada peringkat
- 2011 Demand of English Skills For Thai Nurses WorkingDokumen87 halaman2011 Demand of English Skills For Thai Nurses WorkingRadityo Tri NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- Substance DependenceDokumen27 halamanSubstance DependenceFranz Jonathan EgiptoBelum ada peringkat
- Pry 1 Week 1Dokumen1 halamanPry 1 Week 1Segun MajekodunmiBelum ada peringkat
- ENGLISH 8 Q4 w5Dokumen4 halamanENGLISH 8 Q4 w5Mycah DabuBelum ada peringkat
- Electron ConfigurationDokumen3 halamanElectron ConfigurationShyra May GalendezBelum ada peringkat
- Annex 1C To Deped Order No. 42, S.2016Dokumen4 halamanAnnex 1C To Deped Order No. 42, S.2016Kristia Mae CellonaBelum ada peringkat
- Student Industrial Attachment Log Book: Kenya Water InstituteDokumen6 halamanStudent Industrial Attachment Log Book: Kenya Water InstituteWashingtonChikengezhaBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly Home Learning Plan: Day/Time Learning Competency Learning Tasks Mode of DeliveryDokumen3 halamanWeekly Home Learning Plan: Day/Time Learning Competency Learning Tasks Mode of DeliveryEricha SolomonBelum ada peringkat
- General Bulletin 38-2022 - Teachers' Salary Scale 2021-2022Dokumen3 halamanGeneral Bulletin 38-2022 - Teachers' Salary Scale 2021-2022team TSOTAREBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Literacy and Metacognitive Strategy For Predicting Academic AchievementDokumen26 halamanReading Literacy and Metacognitive Strategy For Predicting Academic AchievementyayanBelum ada peringkat
- School Development Plan Overview 2021 22Dokumen1 halamanSchool Development Plan Overview 2021 22MARYCON G. GIRASOLBelum ada peringkat
- TTSC m9 Ruel Joyce Ann SantosDokumen2 halamanTTSC m9 Ruel Joyce Ann SantosJayacinthBelum ada peringkat
- Tesol Portfolio - Teaching Philosophy FinalDokumen6 halamanTesol Portfolio - Teaching Philosophy Finalapi-361319051Belum ada peringkat
- General Education 1001 Bullets 1Dokumen130 halamanGeneral Education 1001 Bullets 1Edilbert Bonifacio Gayo100% (2)