Electromagnetic Coil
Diunggah oleh
draganscribd12Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Electromagnetic Coil
Diunggah oleh
draganscribd12Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Electromagnetic coil
For other uses, see Coil.
Winding redirects here. For other uses, see Winding
(disambiguation).
An electromagnetic coil is an electrical conductor such
The direction of the magnetic eld produced by a coil can
be determined by the right hand grip rule. If the ngers of
the right hand are wrapped around the magnetic core of
a coil in the direction of conventional current through the
wire, the thumb will point in the direction the magnetic
eld lines pass through the coil. The end of a magnetic
core from which the eld lines emerge is dened to be the
North pole.
There are many dierent types of coils used in electric
and electronic equipment.
1 Windings and taps
I
The magnetic eld lines (green) of a current-carrying loop of
wire pass through the center of the loop, concentrating the eld
there
as a wire in the shape of a coil, spiral or helix.[1][2] Electromagnetic coils are used in electrical engineering, in applications where electric currents interact with magnetic
elds, in devices such as inductors, electromagnets,
transformers, and sensor coils. Either an electric current
is passed through the wire of the coil to generate a magnetic eld, or conversely an external time-varying mag- Diagram of typical transformer congurations
netic eld through the interior of the coil generates an
EMF (voltage) in the conductor.
The wire or conductor which constitutes the coil is called
A current through any conductor creates a circular mag- the winding.[5] The hole in the center of the coil is called
netic eld around the conductor due to Amperes law.[3] the core area or magnetic axis.[6] Each loop of wire is
The advantage of using the coil shape is that it increases called a turn.[2] In windings in which the turns touch,
the strength of magnetic eld produced by a given cur- the wire must be insulated with a coating of nonconducrent. The magnetic elds generated by the separate turns tive insulation such as plastic or enamel to prevent the
of wire all pass through the center of the coil and add current from passing between the wire turns. The wind(superpose) to produce a strong eld there.[3] The more ing is often wrapped around a coil form made of plasturns of wire, the stronger the eld produced. Conversely, tic or other material to hold it in place.[2] The ends of
a changing external magnetic ux induces a voltage in a the wire are brought out and attached to an external circonductor such as a wire, due to Faradays law of induc- cuit. Windings may have additional electrical connection.[3][4] The induced voltage can be increased by wind- tions along their length; these are called taps.[7] A winding the wire into a coil, because the eld lines intersect ing which has a single tap in the center of its length is
the circuit multiple times.[3]
called center-tapped.[8]
1
3 TYPES OF COILS
Coils can have more than one winding, insulated electrically from each other. When there are two or more
windings around a common magnetic axis, the windings
are said to be inductively coupled or magnetically coupled.[9] A time-varying current through one winding will
create a time-varying magnetic eld which passes through
the other winding, which will induce a time-varying voltage in the other windings. This is called a transformer.[10]
Magnetic core
Many electromagnetic coils have a magnetic core, a piece
of ferromagnetic material like iron in the center to inField coil electromagnet on the stator of an AC universal motor.
crease the magnetic eld.[11] The current through the coil
magnetizes the iron, and the eld of the magnetized material adds to the eld produced by the wire. This is called
Solenoid - an electromagnet in the form
a ferromagnetic-core or iron-core coil.[12] A ferromagof a straight hollow helix of wire
netic core can increase the magnetic eld of a coil by hun Motor and generator windings - iron core
dreds or thousands of times over what it would be without
electromagnets on the rotor or stator of
the core. A ferrite core coil is a variety of coil with a core
electric motors and generators which act
[13]
made of ferrite, a ferrimagnetic ceramic compound.
on each other to either turn the shaft (moFerrite coils have lower losses at high frequencies.
tor) or generate an electric current (genA coil without a ferromagnetic core is called an air-core
erator)
coil.[14] This includes coils wound on plastic or other
Field winding - an iron-core coil
nonmagnetic forms, as well as coils which actually have
which generates a steady magnetic
empty air space inside their windings.
eld to act on the armature winding.
Types of coils
Coils can be classied by the frequency of the current they
are designed to operate with:
Direct current or DC coils or electromagnets operate with a steady direct current
in their windings
Audio-frequency or AF coils, inductors
or transformers operate with alternating
currents in the audio frequency range,
less than 20 kHz
Radio-frequency or RF coils, inductors
or transformers operate with alternating
currents in the radio frequency range,
above 20 kHz
Coils can be classied by their function:
Armature winding - an iron-core
coil which is acted on by the magnetic eld of the eld winding to either create torque (motor) or induce
a voltage to produce power (generator)
Helmholtz coil, Maxwell coil - air-core
coils which serve to cancel an external
magnetic eld
Degaussing coil - a coil used to demagnetize parts
Voice coil - a coil used in a movingcoil loudspeaker, suspended between the
poles of a magnet. When the audio signal is passed through the coil, it vibrates,
moving the attached speaker cone to create sound waves.
3.2 Inductors
Main article: Inductor
3.1
Electromagnets
Inductors or reactors are coils which generate a magnetic
eld which interacts with the coil itself, to induce a back
EMF which opposes changes in current through the coil.
Electromagnets are coils that generate a magnetic eld Inductors are used as circuit elements in electrical cirfor some external use, often to exert a mechanical force cuits, to temporarily store energy or resist changes in curon something.[15] A few specic types:
rent. A few types:
Main article: Electromagnet
3.3
Transformers
Tank inductor in a tuned circuit in a shortwave radio transmitter
Tank coil - an inductor used in a tuned
circuit
Choke - an inductor used to block high
frequency AC while allowing through low
frequency AC.
Loading coil - an inductor used to add inductance to an antenna, to make it resonant, or to a cable to prevent distortion of
signals.
Variometer - an adjustable inductor consisting of two coils in series, an outer stationary coil and a second one inside it
which can be rotated so their magnetic
axes are in the same direction or opposed.
Flyback transformer - Although called a
transformer, this is actually an inductor
which serves to store energy in switching
power supplies and horizontal deection
circuits for CRT televisions and monitors
Saturable reactor - an iron-core inductor
used to control AC power by varying the
saturation of the core using a DC control
voltage in an auxiliary winding.
Inductive ballast - an inductor used
in gas-discharge lamp circuits, such as
uorescent lamps, to limit the current
through the lamp.
3.3
Transformers
Main article: Transformer
A transformer is a device with two or more magnetically
coupled windings (or sections of a single winding). A
time varying current in one coil (called the primary winding) generates a magnetic eld which induces a voltage
Transformer
in the other coil (called the secondary winding). A few
types:
Distribution transformer - A transformer
in an electric power grid which transforms the high voltage from the electric
power line to the lower voltage used by
utility customers.
Autotransformer - a transformer with
only one winding. Dierent portions of
the winding, accessed with taps, act as
primary and secondary windings of the
transformer.
Toroidal transformer - the core is in the
shape of a toroid. This is a commonly
used shape as it decreases the leakage
ux, resulting in less electromagnetic interference.
Induction coil or trembler coil - an early
transformer which uses a vibrating interrupter mechanism to break the primary
current so it can operate o of DC current.
Ignition coil - an induction coil used
in internal combustion engines to
create a pulse of high voltage to re
the spark plug which initiates the
fuel burning.
Balun - a transformer which matches a
balanced transmission line to an unbalanced one.
Bilar coil - a coil wound with two parallel, closely spaced strands. If AC currents
are passed through it in the same direction, the magnetic uxes will add, but if
equal currents in opposite directions pass
through the windings the opposite uxes
will cancel, resulting in zero ux in the
4
core. So no voltage will be induced in
a third winding on the core. These are
used in instruments and in devices like
Ground Fault Interrupters. They are also
used in low inductance wirewound resistors for use at RF frequencies.
Audio transformer - A transformer used
with audio signals. They are used for
impedance matching.
Hybrid coil - a specialized audio
transformer with 3 windings used
in telephony circuits to convert between two-wire and four-wire circuits
3.4
Transducer coils
REFERENCES
Recording head - a coil which is used
to create a magnetic eld to write data
to a magnetic storage medium, such as
magnetic tape, or a hard disk. Conversely
it is also used to read the data in the
form of changing magnetic elds in the
medium.
Induction heating coil - an AC coil used
to heat an object by inducing eddy currents in it, a process called induction heating.
Loop antenna - a coil which serves as a
radio antenna, to convert radio waves to
electric currents.
Rogowski coil - a toroidal coil used as an
AC measuring device
Musical instrument pickup - a coil used
to produce the output audio signal in an
electric guitar or electric bass.
Flux gate - a sensor coil used in a
magnetometer
Magnetic phonograph cartridge - a sensor
in a record player that uses a coil to translate vibration of a needle to an audio signal in playing vinyl phonograph records.
There are also types of coil which don't t into these categories.
4 References
[1] Stauer, H. Brooke (2005). NFPAs Pocket Dictionary of
Electrical Terms. Jones and Bartlett Learning. p. 36.
ISBN 0877655995.
[2] Laplante, Phillip A. (1999). Comprehensive Dictionary of
Electrical Engineering. Springer. pp. 114115. ISBN
3540648356.
[3] Arun, P. (2006). Electronics. Alpha Sciences International Ltd. pp. 7377. ISBN 1842652176.
[4] Newnes 2002, p. 129
[5] Stauer 2005, p. 273
The sensor coil of a metal detector.
These are coils used to translate time-varying magnetic
elds to electric signals, and vice versa. A few types:
[6] Amos, S W; Roger Amos (2002). Newnes Dictionary of
Electronics. Newnes. p. 191. ISBN 0080524052.
[7] Laplante 1999, p. 633
[8] Stauer 2005, p. 29
Sensor or pickup coils - these are used
to detect external time-varying magnetic
elds
[10] Newnes 2002, p. 326
Inductive sensor - a coil which senses
when a magnet or iron object passes near
it
[11] Laplante, Phillip A. (1998). Comprehensive Dictionary
of Electrical Engineering. Springer. p. 143. ISBN
3540648356.
[9] Newnes 2002, p. 167
[12] Laplante 1999, p. 346
[13] Laplante 1999, p. 243
[14] Laplante 1999, p. 19
[15] Newnes 2002, p. 113
Further reading
Querfurth, William, "Coil winding; a description of
coil winding procedures, winding machines and associated equipment for the electronic industry" (2d
ed.). Chicago, G. Stevens Mfg. Co., 1958.
Weymouth, F. Marten, "Drum armatures and commutators (theory and practice) : a complete treatise
on the theory and construction of drum winding, and
of commutators for closed-coil armatures, together
with a full rsum of some of the principal points involved in their design; and an exposition of armature
reactions and sparking". London, The Electrician
Printing and Publishing Co., 1893.
"Coil winding proceedings".
Winding Association.
International Coil
Chandler, R. H., "Coil coating review, 197076".
Braintree, R. H. Chandler Ltd, 1977.
External links
R. Clarke, "Producing wound components". Surrey.ac.uk, 2005 October 9
7 TEXT AND IMAGE SOURCES, CONTRIBUTORS, AND LICENSES
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
7.1
Text
Electromagnetic coil Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagnetic_coil?oldid=678954639 Contributors: Bryan Derksen, Rootbeer, Heron, Elhim, Patrick, JohnOwens, Stan Shebs, Mac, Curtisweyant~enwiki, CatherineMunro, Angela, Glenn, Samw, Hectorthebat,
Reddi, Nv8200pa, Robbot, David Hoeer, Twiin, Pengo, Giftlite, Wolfkeeper, BenFrantzDale, MSGJ, Bkonrad, BalthCat, Tweenk, Jrdioko, Sonett72, Deglr6328, Discospinster, Rich Farmbrough, Andros 1337, Meggar, Cmdrjameson, Stephen Bain, Avian, Wtshymanski,
DV8 2XL, Gene Nygaard, Nuno Tavares, Angr, Anilocra, SDC, Graham87, Josh Parris, Arnero, Sanbeg, Born2cycle, 6~enwiki, Bgwhite,
YurikBot, Borgx, RussBot, Red Slash, Shaddack, Wimt, NawlinWiki, THB, Mikeblas, Scottsher, SmackBot, C J Cowie, Eskimbot,
M stone, Anwar saadat, Chris the speller, Kurykh, Joerite, DMacks, BrownHairedGirl, Mgiganteus1, CyrilB, 16@r, JHunterJ, Iridescent,
Chetvorno, Neelix, Chrislk02, Narayanese, Barticus88, Gerry Ashton, Beta16, AlexOvShaolin, AntonellaD, VoABot II, Mondebleu, Swpb,
InvertRect, Jim.henderson, Kostisl, Pekaje, BigrTex, Bogey97, Rembecki, Tbone762, Hartvisarts, Idioma-bot, IWhisky, Philip Trueman,
Melsaran, Awl, Brenont, ClueBot, Bob1960evens, The Thing That Should Not Be, Rubin joseph 10, Grapeguy, Acsmith7, Rror, Addbot,
Some jerk on the Internet, Eh kia, Yobot, AnakngAraw, AnomieBOT, 1exec1, AdjustShift, Materialscientist, Neurolysis, Petropoxy (Lithoderm Proxy), 15mypic, Chipmunk2, A.amitkumar, GliderMaven, MetaNest, Dcshank, Suusion of Yellow, PleaseStand, TheArguer,
Alph Bot, DASHBot, Mjbarker1, Seikku Kaita, Cblambert, Teapeat, ClueBot NG, Widr, Titodutta, Northamerica1000, Op47, Rene1596,
Marrine magmanlac cacharro, Aisteco, BattyBot, Rokkistar, Mogism, Everymorning, SJ Defender, Gouge666, Monkbot, JREling1, DaveeBlahBlah, KasparBot and Anonymous: 107
7.2
Images
File:Magnetic_field_of_loop_3.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b7/Magnetic_field_of_loop_3.svg License: CC0 Contributors: Own work Original artist: Chetvorno
File:Metal_detecting_in_progress_on_a_Time_Team_dig.jpg Source:
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/ef/
Metal_detecting_in_progress_on_a_Time_Team_dig.jpg License: CC BY 2.0 Contributors: Metal detecting in progress on a Time Team
dig Original artist: Portable Antiquities Scheme from London, England
File:Stator_eines_Universalmotor.JPG Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/9c/Stator_eines_Universalmotor.
JPG License: CC BY-SA 3.0 Contributors: Own work Original artist: Marrrci
File:Trafo-innenleben.jpg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/76/Trafo-innenleben.jpg License: Public domain Contributors: Self-photographed Original artist: Stefan Riepl (Quark48)
File:Transformers.png Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4d/Transformers.png License: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Contributors: Transferred from en.wikipedia; transferred to Commons by User:Sfan00_IMG using CommonsHelper. Original artist: Original uploader was Reddi at en.wikipedia
File:Transmitter_tank_inductor.jpg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ac/Transmitter_tank_inductor.jpg
License: Public domain Contributors: Retrieved March 12, 2014 from <a data-x-rel='nofollow' class='external text' href='http://www.
americanradiohistory.com/Archive-Radio-News/30s/Radio-News-1938-05-R.pdf'>Radio News magazine, Zi-Davis Publishing Co.,
Chicago, Vol. 20, No. 11, May 1938, p. 31</a> American Radio History website Original artist: Unknown
File:Wiktionary-logo-en.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f8/Wiktionary-logo-en.svg License: Public
domain Contributors: Vector version of Image:Wiktionary-logo-en.png. Original artist: Vectorized by Fvasconcellos (talk contribs),
based on original logo tossed together by Brion Vibber
7.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsDari EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsBelum ada peringkat
- UsingAndUnderstandingMiniatureNeonLamps PDFDokumen132 halamanUsingAndUnderstandingMiniatureNeonLamps PDFbongoloidBelum ada peringkat
- Winding and Using ToroidsDokumen6 halamanWinding and Using ToroidsSararu OvidiuBelum ada peringkat
- A Star Close Up - Building A Dirod Electrostatic GeneratorDokumen11 halamanA Star Close Up - Building A Dirod Electrostatic GeneratorTomislav JovanovicBelum ada peringkat
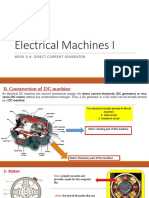
- Electrical Machines I: Week 3-4: Direct Current GeneratorDokumen18 halamanElectrical Machines I: Week 3-4: Direct Current Generatorkaloy33Belum ada peringkat
- Toroid NASA Design 19720015546 - 1972015546Dokumen21 halamanToroid NASA Design 19720015546 - 1972015546Niko Glamuzina100% (1)
- Directional Microphone Without Parabolic ReflectorDokumen3 halamanDirectional Microphone Without Parabolic Reflectordetroit_me2553Belum ada peringkat
- Basics of ElectricityDokumen88 halamanBasics of ElectricityKevin Haworth93% (15)
- Acoustic Levitator PDFDokumen26 halamanAcoustic Levitator PDFfranklin david100% (2)
- Introduction To Vacuum TubesDokumen22 halamanIntroduction To Vacuum TubesChrisTBelum ada peringkat
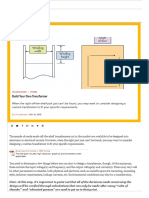
- Build Your Own TransformerDokumen11 halamanBuild Your Own Transformergumilang adienBelum ada peringkat
- Hammond SK1 ManualDokumen158 halamanHammond SK1 ManualRobert JaroviBelum ada peringkat
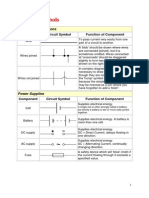
- Circuit Symbols: Wires and ConnectionsDokumen8 halamanCircuit Symbols: Wires and ConnectionsAnonymous BwLfvuBelum ada peringkat
- RadioKot - Effective Powerful Charging and Desulfation Device For Batteries of 10-100 A - HDokumen10 halamanRadioKot - Effective Powerful Charging and Desulfation Device For Batteries of 10-100 A - HLUis PEpeBelum ada peringkat
- 1998 AEMT Repair of Induction Motors Best Practices To Maintain Energy EfficiencyDokumen50 halaman1998 AEMT Repair of Induction Motors Best Practices To Maintain Energy EfficiencySing Yew LamBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Transistor FM RadioDokumen7 halaman1 Transistor FM RadiopalakqBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding UL508A Combination Motor Controller DataDokumen4 halamanUnderstanding UL508A Combination Motor Controller DataNoneya BidnessBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes 09Dokumen19 halamanLecture Notes 09nedian08Belum ada peringkat
- Xk3 ManualDokumen114 halamanXk3 ManualmichtalbotBelum ada peringkat
- Inventors.: LogicDokumen50 halamanInventors.: LogicSamuel KinsBelum ada peringkat
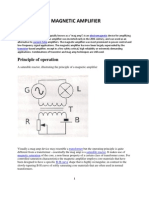
- Magnetic AmplifierDokumen2 halamanMagnetic Amplifierrintarejoy100% (1)
- LASER MicrophoneDokumen8 halamanLASER MicrophoneairylainBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Soldering Guide - How To Solder Electronic Components: June 11, 2020 Home AboutDokumen22 halamanBasic Soldering Guide - How To Solder Electronic Components: June 11, 2020 Home AboutDario PaladoBelum ada peringkat
- BK Precision CatalogDokumen118 halamanBK Precision CatalogTony WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Power Supply Unit For An Electric Discharge MachineDokumen6 halamanPower Supply Unit For An Electric Discharge MachineAhmed ShadeedBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Resonance AmplifierDokumen95 halamanMagnetic Resonance Amplifierspicerw100% (1)
- A Tutorial On Transistor Based Circuit DesignDokumen16 halamanA Tutorial On Transistor Based Circuit DesignSivaranjan Goswami100% (1)
- OCW MIT Edu ReferencesDokumen6 halamanOCW MIT Edu Referencespratut3335Belum ada peringkat
- Build Your Own Doug Coil MachineDokumen139 halamanBuild Your Own Doug Coil MachineЗорица Ћирић100% (1)
- WWW Talkingelectronics Com Projects LEDTorchCircuits LEDTorchCircuits P1 HTML PDFDokumen20 halamanWWW Talkingelectronics Com Projects LEDTorchCircuits LEDTorchCircuits P1 HTML PDFgleand latuniBelum ada peringkat
- Soldering ToolsDokumen7 halamanSoldering ToolsThamilselvan VengatasalamBelum ada peringkat
- Homebrew Lead Acid Battery DesulfatorDokumen5 halamanHomebrew Lead Acid Battery Desulfatorrosslovelady100% (1)
- Allied Radio Knight Crystal Set (1953) WWDokumen4 halamanAllied Radio Knight Crystal Set (1953) WWJan Pran100% (1)
- Vacuum TubesDokumen30 halamanVacuum TubesAira Mae CrespoBelum ada peringkat
- 1995 E36 328coupe LPG Conversion 0.6Dokumen58 halaman1995 E36 328coupe LPG Conversion 0.6Stig Stiggyness PoldenBelum ada peringkat
- Construction Article A Hi-Fi Vacuum Tube Phono PreampDokumen18 halamanConstruction Article A Hi-Fi Vacuum Tube Phono PreampΔημητριος Σταθης100% (1)
- Electric Motor LabDokumen9 halamanElectric Motor LabPhemi2580Belum ada peringkat
- Construction of DC GeneratorDokumen58 halamanConstruction of DC GeneratorRajeev ValunjkarBelum ada peringkat
- 47 Projects To Do With A 555Dokumen15 halaman47 Projects To Do With A 555Marius DanilaBelum ada peringkat
- The Beauty of The 6C33Dokumen9 halamanThe Beauty of The 6C33RastekHIBelum ada peringkat
- Homemade Magnetic AmplifiersDokumen8 halamanHomemade Magnetic AmplifiersVjekoslav NovoselBelum ada peringkat
- Vacuum TubesDokumen52 halamanVacuum TubesJoseGarciaRuiz100% (2)
- Chapter 6 - Audio AmplifierDokumen18 halamanChapter 6 - Audio Amplifierde_Petai84Belum ada peringkat
- Types of Electromechanical RelaysDokumen23 halamanTypes of Electromechanical RelaysJoseph B Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- EE3444LabManualV1 1Dokumen111 halamanEE3444LabManualV1 1aspen76rtBelum ada peringkat
- Guide To Fixing The Classic Westinghouse Model 556A AM Tabletop Tube Radio.Dokumen12 halamanGuide To Fixing The Classic Westinghouse Model 556A AM Tabletop Tube Radio.Gerry100% (2)
- ELECTRETDokumen3 halamanELECTRETchvar80100% (1)
- Pickup GuideDokumen2 halamanPickup GuidenoeryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Mendocino MotorDokumen16 halamanMendocino Motorfrancis_almazan_6100% (1)
- Hafler DH-220Dokumen21 halamanHafler DH-220ciohaniBelum ada peringkat
- 1881 Lecture by William George LemonDokumen12 halaman1881 Lecture by William George LemonTim LemonBelum ada peringkat
- Ed Lab Manual-2Dokumen82 halamanEd Lab Manual-2Akhil VinnakotaBelum ada peringkat
- E. WORKSHOP II by SemereDokumen93 halamanE. WORKSHOP II by SemereSami Ye KiyaBelum ada peringkat
- How Does A Transformer Work?Dokumen5 halamanHow Does A Transformer Work?Jane Anne Rica BasasBelum ada peringkat
- Dps MegaDokumen14 halamanDps MegaJitendra PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Term PaperDokumen19 halamanTerm PaperAdeel Ashraf100% (1)
- REVIEWER ACDC SUMMATIVE 1 M1-M3 PDFDokumen7 halamanREVIEWER ACDC SUMMATIVE 1 M1-M3 PDFDiether PaderoBelum ada peringkat
- Dielectric StrengthDokumen3 halamanDielectric Strengthdraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- Electrical BreakdownDokumen4 halamanElectrical Breakdowndraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- Numerical AnalysisDokumen7 halamanNumerical Analysisdraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- First Serbian UprisingDokumen6 halamanFirst Serbian Uprisingdraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- CapacitorDokumen21 halamanCapacitordraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- Serbian LiteratureDokumen3 halamanSerbian Literaturedraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- List of Unsolved Problems in PhysicsDokumen11 halamanList of Unsolved Problems in Physicsdraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- Quantum OpticsDokumen4 halamanQuantum Opticsdraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- 07 Petrovic PDFDokumen14 halaman07 Petrovic PDFdraganscribd12Belum ada peringkat
- Commercial Unit Coolers Cubic Series Type: S3HC 59 E 65 N. Units: 1Dokumen2 halamanCommercial Unit Coolers Cubic Series Type: S3HC 59 E 65 N. Units: 1hamzehBelum ada peringkat
- Alpha ParticleDokumen12 halamanAlpha ParticlechristineBelum ada peringkat
- 1 SMDokumen6 halaman1 SMDejan DoslicBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - I Dynamics of Electric Drives: Electrical Power Transmission SystemsDokumen4 halamanUnit - I Dynamics of Electric Drives: Electrical Power Transmission Systemsyemane gebremichalBelum ada peringkat
- SANS5847 - Flakiness Index of Course AggregatesDokumen7 halamanSANS5847 - Flakiness Index of Course AggregatesAndrew MwindililaBelum ada peringkat
- K.T. Chau, R.H.C. Wong, T.-f. Wong (Auth.), STAVROS K. KOURKOULIS (Eds.) - Fracture and Failure of Natural Building Stones_ Applications in the Restoration of Ancient Monuments-Springer Netherlands (2Dokumen581 halamanK.T. Chau, R.H.C. Wong, T.-f. Wong (Auth.), STAVROS K. KOURKOULIS (Eds.) - Fracture and Failure of Natural Building Stones_ Applications in the Restoration of Ancient Monuments-Springer Netherlands (2Daniel Ruperto CanoBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes For Sinotruk HOWO Engines PDFDokumen4 halamanDiagnostic Trouble Codes For Sinotruk HOWO Engines PDFhektor AtkinsonBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Huawei 3g Capacity OptimizationDokumen39 halaman1 Huawei 3g Capacity OptimizationCharles W GitahiBelum ada peringkat
- Theodore Sider - Logic For Philosophy PDFDokumen377 halamanTheodore Sider - Logic For Philosophy PDFAnonymous pYK2AqH100% (1)
- Wärtsilä NOXDokumen35 halamanWärtsilä NOXDeepesh MerchantBelum ada peringkat
- HMT16 MarksDokumen12 halamanHMT16 MarkstagoreboopathyBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Prototyping PPT SeminarDokumen32 halamanRapid Prototyping PPT SeminarShantha Kumar G C0% (1)
- FITEL Fusion Splicer Catalog PDFDokumen25 halamanFITEL Fusion Splicer Catalog PDFAbdelilah CharboubBelum ada peringkat
- Physics: FiitjeeDokumen1.319 halamanPhysics: FiitjeeBISWAJEET100% (2)
- U Series: Vortex ImpellerDokumen12 halamanU Series: Vortex ImpellerNichamon NBelum ada peringkat
- ISORIA 20 BrochureDokumen16 halamanISORIA 20 BrochuremariodalBelum ada peringkat
- Math Ed 04: TrigonometryDokumen5 halamanMath Ed 04: TrigonometryCharles SilerioBelum ada peringkat
- Sci Problem SolutionsDokumen10 halamanSci Problem SolutionsVS PUBLIC SCHOOL BangaloreBelum ada peringkat
- 2WDokumen8 halaman2WSuneel ChinchanikarBelum ada peringkat
- MATH 10 - Q4 - WEEK 1 - MODULE 1 - Illustrating-The-Measures-Of-Position-Quartiles-Deciles-And-PercentilesDokumen23 halamanMATH 10 - Q4 - WEEK 1 - MODULE 1 - Illustrating-The-Measures-Of-Position-Quartiles-Deciles-And-PercentilesLyle Isaac L. Illaga67% (27)
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDokumen2 halamanAtomic Absorption SpectrosSirTonz100% (1)
- Bok:978 94 017 9664 4Dokumen215 halamanBok:978 94 017 9664 4fivalen1_443898619100% (2)
- Características Clínicas y Resultados de Los Pacientes Con COVID-19 Con Ventilación Invasiva en ArgentinaDokumen10 halamanCaracterísticas Clínicas y Resultados de Los Pacientes Con COVID-19 Con Ventilación Invasiva en ArgentinaSMIBA MedicinaBelum ada peringkat
- Users Manual ACS 501 PDFDokumen94 halamanUsers Manual ACS 501 PDFmodelador3dBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM101 051 Old-Exam Second-Major Master-KeyDokumen10 halamanCHEM101 051 Old-Exam Second-Major Master-KeyalwafiBelum ada peringkat
- MATLAB AssignmentsDokumen12 halamanMATLAB AssignmentsnilimaBelum ada peringkat
- TK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsDokumen34 halamanTK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsMuhammad IkbalBelum ada peringkat
- ME201 Material Science & Engineering: Imperfections in SolidsDokumen30 halamanME201 Material Science & Engineering: Imperfections in SolidsAmar BeheraBelum ada peringkat
- Transformers 2023Dokumen36 halamanTransformers 2023dgongorBelum ada peringkat
- Efficiency Analysis of An Aerospike Nozzle: Dipak J. Choudhari, Uday V. AsolekarDokumen5 halamanEfficiency Analysis of An Aerospike Nozzle: Dipak J. Choudhari, Uday V. AsolekarAswith R ShenoyBelum ada peringkat