Light
Diunggah oleh
elorranHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Light
Diunggah oleh
elorranHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________
Ch 14:1
Light
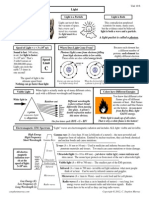
Light is a Wave
Light is a Particle
Light is Both
Light can travel
through the vacuum
of space, but waves
cant travel in a
vacuum. So light
must be a particle!
Light is refracted in lenses.
Light diffracting around two
fingers (look close) causes
lines of darkness: destructive interference.
Light must be a wave!
This contradiction perplexed
scientists for many, many years, but
the evidence must be believed:
light is both a wave and a particle.
Packets of light we call photons.
Speed of Light: 3 x 108 m/sec
Origins of Light and Color
Sound is fast: 340 m/sec, but
light is faster: 3 x 108 m/sec!
Thats 3 with 8 zeroes
or 300,000,000 m/sec.
Light can circle the earth
27 times in one second!
Photons (light) come from electrons falling
from high electron orbits to low orbits.
These orbits are also called energy levels.
Scientists now believe that
nothing can go faster than light.
The speed of light is the
ultimate speed limit.
Visible Light
White light in
8p
10
8p
10
Energy can raise an
electron to a higher
energy level.
When the electron
falls back, a photon
is given off: light!
What we call visible light is made up of many
different colors. Each color has a different
wavelength and a different frequency.
Rainbow out
Prism
photon
out
(blue)
energy in
Red
Orange
Yellow
Green
Blue
Indigo
Violet
Visible Light is a very small part of the entire Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum.
Infrared Visible UltraLight violet
Microwaves
Low Energy
Low Frequency
Long Wavelength
what we can see
Radio waves used to transmit radio and television signals.
Wavelengths range from hundreds of meters to less than a centimeter. This is why radio towers have to be so tall.
Microwaves used to cook food and by cell phones.
Wavelengths range from 30 cm to 1 mm.
Infrared (invisible heat) 1 mm to 700 nanometers
(700 billionths of a meter).
Visible (white) light from 700 to 400 nanometers.
cstephenmurray.com
You know that different
color flames give off different amounts of heat. Red
flames are the coolest and
blue flames are the hottest.
As you move from Red to
Blue, light GAINS energy.
White light is made up of all colors.
That is why a white flame is the hottest!
Red
Orange
Yellow
Green
Blue
Indigo
Violet
Radio waves
The sky is blue because
oxygen atoms give off
blue photons.
Colors have Different Energies
A prism uses
refraction to separate
the different
wavelengths (colors)
of visible light.
The first letters spell: ROY G BIV
EM Spectrum
Because each element has a
different number of protons,
each element has slightly
different electron energy
levels and gives off
different colors. From
their colors we can tell the
chemical makeup of stars.
X-rays
Gamma
Rays
High Energy
High Frequency
Short Wavelength
Ultraviolet light invisible wavelengths from 400 nanometers to
10 nanometers. Part of sunlight burns your skin and can cause
cancer. The ozone layer protects us from most of the suns
ultraviolet light.
X-rays Used in medicine and industry. Wavelengths are from
10 nanometers to .01 nanometers (10 trillionth of a meter).
Gamma rays the most powerful and dangerous form of radiation. Wavelengthsless than .01 nanometers. Emitted by
nuclear reactions, they can break chemical and nuclear bonds.
Copyright 2004, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Ch 14:1
Period: _____________________
Radio waves
A. Electromagnetic waves we feel as heat.
Infrared
B. Dangerous EM waves that have very
high energy and come from nuclear
reactions.
3.
Ultraviolet
C. EM waves that have very low energy and
long wavelengths.
D. Used to separate white light into its
colors.
4.
X-rays
D. EM waves that can pass through skin and
have short wavelengths.
EM Spectrum
E. A single particle or packet of light.
5.
Gamma rays
Energy Level
F. A wave that can travel through a vacuum.
E. EM waves with more energy than visible
light and can cause sunburns.
6.
Microwaves
F. Long wavelengths; used in cell phones.
1.
Photon
A. The fastest speed in the universe: the
speed of light.
2.
3 x 108 m/sec
B. An orbit of electrons. To move from low 2.
to high requires energy.
3.
Prism
4.
Light
5.
6.
C. All light: visible and invisible.
Is light a wave or a particle. Prove your answer:
1.
Put these three in order from slowest to fastest:
Light waves; sound waves; water waves.
__________________________________________
Where does light come from?
Put these from shortest to longest wavelengths
Radio waves
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Visible
Microwaves
___________________________________________________
Why do we see lightening and hear the thunder a few seconds
later?
Put these from least energy to most energy.
Radio waves
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Visible
Microwaves
___________________________________________________
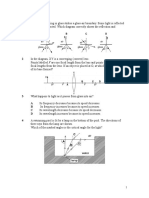
Find the period of a 10 Hz wave.
If a waves fifth harmonic has a frequency of 35 Hz, what is its
natural frequency and what is the frequency of H3?
A wave has these characteristics: 25 Hz and 8 m. Find speed.
Find its period: _______________________
A sound changes from 25 dB to 5 dB. How do we hear the
change?
What harmonic is this? _________________
Mark the nodes and anti-nodes.
You hear a thunder 3 seconds after you see the lightening. How
far away is the storm?
Mark one wavelength on the harmonic.
Can humans hear this frequency?__________
Find the fundamental frequency:
You are in a concert hall and yell up to the ceiling. It takes 1 second for the echo to come back to you. How high is the ceiling?
____________________________________
3rd harmonic frequency:
____________________________________
cstephenmurray.com
40 Hz
Copyright 2004, C. Stephen Murray
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Lesson Plan On SoundsDokumen31 halamanLesson Plan On SoundsTöňğ Geronimo100% (1)
- Work, potential and kinetic energy equationsDokumen8 halamanWork, potential and kinetic energy equationsGkid GkidBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect WorksheetDokumen2 halamanDoppler Effect WorksheetLawrenceOnthuga100% (2)
- Gravitation Class 9 Science Notes - Sarthaks Econnect - Largest Online Education CommunityDokumen12 halamanGravitation Class 9 Science Notes - Sarthaks Econnect - Largest Online Education Communitysmi_santhosh100% (1)
- Hearing Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanHearing Lesson Plannissi guingab0% (1)
- Wave PropertiesDokumen2 halamanWave PropertiesAshok Kumar Dondati100% (1)
- Heat, Light and SoundDokumen26 halamanHeat, Light and Soundsanober humairBelum ada peringkat
- Etkina TeacherContentKnowledgeDokumen28 halamanEtkina TeacherContentKnowledgeMrsriyansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 - Magnetic Fields and PolesDokumen4 halamanLesson 3 - Magnetic Fields and Polesapi-296195922100% (1)
- Learner's Material: ScienceDokumen14 halamanLearner's Material: ScienceElma MayBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Wave Anatomy Worksheet PDFDokumen1 halaman3 - Wave Anatomy Worksheet PDFJacob UnderwoodBelum ada peringkat
- 13 UCM GravityDokumen7 halaman13 UCM GravityeltytanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 27 Nuclear Physics (A2)Dokumen53 halamanChapter 27 Nuclear Physics (A2)Pathmanathan NadesonBelum ada peringkat
- A Level Physic 2 2017 PDFDokumen324 halamanA Level Physic 2 2017 PDFAref DahabrahBelum ada peringkat
- P2 Energy ReviseDokumen6 halamanP2 Energy ReviseSamuel ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesDokumen35 halamanChapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesBernardBelum ada peringkat
- Energy LessonDokumen6 halamanEnergy LessonKristenBalchBelum ada peringkat
- DP Physics Course Outline 2021Dokumen7 halamanDP Physics Course Outline 2021Mona Mohamed SafwatBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan #4 - Electrostatic ForceDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan #4 - Electrostatic Forcedmart033100% (1)
- Forces and Momentum Calculations for Unequal Mass SkatersDokumen9 halamanForces and Momentum Calculations for Unequal Mass SkatersMamun ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Balloons and Static Electricity and John Travoltage Remote LabDokumen6 halamanBalloons and Static Electricity and John Travoltage Remote LabAlexzandra Calderon0% (1)
- Grade 10 Physics (2020)Dokumen15 halamanGrade 10 Physics (2020)Mikail MoorajBelum ada peringkat
- How sound waves diffract around buildingsDokumen9 halamanHow sound waves diffract around buildingsnguyentrongtinBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Quarter Test - Physical ScienceDokumen4 halaman1st Quarter Test - Physical ScienceArven DulayBelum ada peringkat
- Seeing Sounds Worksheet: Tuning Fork StationDokumen2 halamanSeeing Sounds Worksheet: Tuning Fork StationEji AlcorezaBelum ada peringkat
- PLANETSDokumen2 halamanPLANETSIan JadeBelum ada peringkat
- Light by AndrewDokumen21 halamanLight by AndrewAndrew gadBelum ada peringkat
- 3.6 ConstellationsDokumen4 halaman3.6 ConstellationsCharles AbellanaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Physics Sound4Dokumen5 halamanLesson Plan Physics Sound4akhil100% (1)
- The Nature of Light WaveDokumen25 halamanThe Nature of Light WavepankajharitashBelum ada peringkat
- Subject Knowledge Audit - A Level PhysicsDokumen4 halamanSubject Knowledge Audit - A Level PhysicsW-d DomBelum ada peringkat
- Snell's Law VerificationDokumen13 halamanSnell's Law VerificationTamer A. Dakkak100% (1)
- Astronomy Project Report PDFDokumen8 halamanAstronomy Project Report PDFNooralhuda YousufBelum ada peringkat
- Sound Properties and CharacteristicsDokumen21 halamanSound Properties and CharacteristicsSwamy Nathan100% (1)
- Periodicity Review AnswersDokumen2 halamanPeriodicity Review Answersapi-263909505100% (1)
- North Atlanta High School: Chemistry SyllabusDokumen7 halamanNorth Atlanta High School: Chemistry Syllabusapi-325710836Belum ada peringkat
- Plate Tectonics Lecture NotesDokumen72 halamanPlate Tectonics Lecture Notesapi-27996976767% (3)
- The Nature of Sound WavesDokumen21 halamanThe Nature of Sound WavesJohn_2998Belum ada peringkat
- Constellation PresentationDokumen13 halamanConstellation PresentationGary Rose100% (2)
- Refraction and Reflection of Light at BoundariesDokumen11 halamanRefraction and Reflection of Light at BoundariesDewan Olin ChotepadaeBelum ada peringkat
- SNC1D1Dokumen9 halamanSNC1D1StarLink1Belum ada peringkat
- 113184208-Ppt-Properties of Light and The Image FormationDokumen50 halaman113184208-Ppt-Properties of Light and The Image FormationAzmi HolisBelum ada peringkat
- Solar System InquiryDokumen4 halamanSolar System Inquiryapi-232002863Belum ada peringkat
- Sound Waves ExplainedDokumen4 halamanSound Waves ExplainedUsman SirBelum ada peringkat
- Warping Spacetime: Testing Predictions of Black HolesDokumen30 halamanWarping Spacetime: Testing Predictions of Black HolesLIto LamonteBelum ada peringkat
- Push, Pull, Go: Force and Motion: 5 Day Unit Plan-Complete Draft Kensington Elementary School Second Grade Mrs. CrockerDokumen22 halamanPush, Pull, Go: Force and Motion: 5 Day Unit Plan-Complete Draft Kensington Elementary School Second Grade Mrs. Crockerapi-548689550Belum ada peringkat
- Sound WavesDokumen39 halamanSound WavesNurlailie Md JamilBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of LightDokumen2 halamanTheories of Lightdela2100% (2)
- MurraylightemDokumen2 halamanMurraylightemapi-26383090433% (3)
- Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Many Properties of Light Can Be Understood by Using A Wave Model of LightDokumen7 halamanGrade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Many Properties of Light Can Be Understood by Using A Wave Model of LightjomardsamBelum ada peringkat
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDokumen42 halamanSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiBelum ada peringkat
- Sci 10 PPT - em WavesDokumen27 halamanSci 10 PPT - em WavesDioscora S. GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDokumen152 halamanScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokumen15 halamanThe Electromagnetic Spectrumcindy lue parasBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Dokumen15 halamanScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaBelum ada peringkat
- Light Notes 1Dokumen31 halamanLight Notes 1api-233194737Belum ada peringkat
- Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation To Living Things and EnvironmentDokumen15 halamanEffects of Electromagnetic Radiation To Living Things and EnvironmentGeorcelle CarcillarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDokumen21 halamanUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter 2 Module 2Dokumen73 halamanQuarter 2 Module 2princesslayshoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 8 PhysicsDokumen7 halamanModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraBelum ada peringkat
- Scaffolding ProcessesDokumen1 halamanScaffolding ProcesseselorranBelum ada peringkat
- ArtsDokumen1 halamanArtselorranBelum ada peringkat
- Samsung HW-M450 AudioDokumen41 halamanSamsung HW-M450 AudioelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Vanilla: Expansion. The Format IsDokumen23 halamanVanilla: Expansion. The Format IselorranBelum ada peringkat
- Five Substances Are Possible - Beryl, Topaz, Chrysoberyl, Corindum or Sapphire, DiamondDokumen1 halamanFive Substances Are Possible - Beryl, Topaz, Chrysoberyl, Corindum or Sapphire, DiamondelorranBelum ada peringkat
- HD Cam Manual PDFDokumen15 halamanHD Cam Manual PDFelorranBelum ada peringkat
- TraditionallyDokumen1 halamanTraditionallyelorranBelum ada peringkat
- OdysseyDokumen5 halamanOdysseyelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Compare and Contrast Two Works of ArtDokumen3 halamanCompare and Contrast Two Works of ArtelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Omni SphereDokumen9 halamanOmni SphereelorranBelum ada peringkat
- The Virtual ClassroomDokumen17 halamanThe Virtual ClassroomelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Laokoön: An Essay On The Confusion of The Arts - in 1940 Clement Greenberg Used The ConceptDokumen3 halamanLaokoön: An Essay On The Confusion of The Arts - in 1940 Clement Greenberg Used The ConceptelorranBelum ada peringkat
- WhatDokumen5 halamanWhatelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Translations of The OdysseyDokumen1 halamanTranslations of The OdysseyelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Final Written ProjectDokumen7 halamanFinal Written ProjectelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Name - Date - PerDokumen2 halamanName - Date - PerelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Distinct Shadows Soft Shadows Barely Visible Shadows ShadowsDokumen1 halamanDistinct Shadows Soft Shadows Barely Visible Shadows ShadowselorranBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly Words From Forrest: Six Questions With Forrest Fenn: Over Five Years of The Thrill of The ChaseDokumen4 halamanWeekly Words From Forrest: Six Questions With Forrest Fenn: Over Five Years of The Thrill of The Chaseelorran100% (1)
- Your BibliographyDokumen2 halamanYour BibliographyelorranBelum ada peringkat
- PH POH & Concentration CalDokumen2 halamanPH POH & Concentration CalelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Mod 3-Amendment ProcessDokumen1 halamanMod 3-Amendment ProcesselorranBelum ada peringkat
- Hadrian's Wall (Osprey, Fortress #2)Dokumen65 halamanHadrian's Wall (Osprey, Fortress #2)elorran100% (16)
- How To Write An AbstractDokumen3 halamanHow To Write An AbstractYalda ShohaniBelum ada peringkat
- Burkholder Gray WaterDokumen1 halamanBurkholder Gray WaterelorranBelum ada peringkat
- The Gladius: By: Stephen PhillipsDokumen2 halamanThe Gladius: By: Stephen PhillipselorranBelum ada peringkat
- Your BibliographyDokumen3 halamanYour BibliographyelorranBelum ada peringkat
- Roman KingdomDokumen2 halamanRoman KingdomelorranBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Act StructureDokumen1 halaman3 Act StructureelorranBelum ada peringkat
- A Book in Every Home Edward LeedskalninDokumen16 halamanA Book in Every Home Edward Leedskalnindcbp2013Belum ada peringkat
- Effect of Materials on Sound AudibilityDokumen6 halamanEffect of Materials on Sound Audibilitynur aisyahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 16 - Electronics and Information and Communication Technology (Ict)Dokumen17 halamanChapter 16 - Electronics and Information and Communication Technology (Ict)Cikgu Shaiful KisasBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Physics B NotesDokumen10 halamanEngineering Physics B NotesBalagopal VBelum ada peringkat
- Advance Technology in Acoustical DesignDokumen9 halamanAdvance Technology in Acoustical Designjovelyn privadoBelum ada peringkat
- Taller 2Dokumen2 halamanTaller 2marcela galindoBelum ada peringkat
- 15.7: Forced Oscillations: Learning ObjectivesDokumen4 halaman15.7: Forced Oscillations: Learning ObjectivesSURESH SURAGANIBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect For Sound: and Review of WaveDokumen25 halamanDoppler Effect For Sound: and Review of WaveSHEENA MAE DALGUNTASBelum ada peringkat
- Oscillations TestDokumen3 halamanOscillations Testsunita singhalBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1.3 SoundDokumen10 halaman1.1.3 SoundAhsan WaheedBelum ada peringkat
- L1 ML Waves IDokumen67 halamanL1 ML Waves ISadiq QocayevBelum ada peringkat
- UIC Physics 105: Practice Final ExamDokumen7 halamanUIC Physics 105: Practice Final ExamnetrunnrBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 10: Physics Chapter 2: SoundDokumen3 halamanGrade 10: Physics Chapter 2: SoundKashif AliiiBelum ada peringkat
- Class VIII Science Worksheet SoundDokumen1 halamanClass VIII Science Worksheet SoundUmak50% (2)
- Dielectric Waveguides and Optical FibersDokumen191 halamanDielectric Waveguides and Optical FibersVijay JanyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Part Two: Oscillations, Waves & Fluids Examples, Mechanics & MotionDokumen32 halamanPart Two: Oscillations, Waves & Fluids Examples, Mechanics & MotionsteveBelum ada peringkat
- Antenna 4800 2L 4M 2.0m: Capacity Compact CoverageDokumen6 halamanAntenna 4800 2L 4M 2.0m: Capacity Compact CoveragelfgantiBelum ada peringkat
- Wave-Particle Duality: Light Explained in Terms of Waves and ParticlesDokumen1 halamanWave-Particle Duality: Light Explained in Terms of Waves and ParticlesjimbieBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3 Data and Signals Multiple Choice Questions and Answers MCQ PDF Data Communication and NetworkingDokumen11 halamanCH 3 Data and Signals Multiple Choice Questions and Answers MCQ PDF Data Communication and NetworkingRohit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Medidor ROEDokumen2 halamanMedidor ROEmazatlBelum ada peringkat
- Clem Waves Lesson02 NotesasDokumen1 halamanClem Waves Lesson02 NotesasKatelyn SmithBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Unit IV Phy110Dokumen51 halamanMCQ Unit IV Phy110Ansh ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration MachineDokumen7 halamanVibration Machinesajjad_naghdi241Belum ada peringkat
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Answer Sheet GuideDokumen2 halamanScience 10 Quarter 2 Answer Sheet Guidehughgwapo41 hughgwapo41Belum ada peringkat
- 4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion: 1a. (4 Marks)Dokumen21 halaman4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion: 1a. (4 Marks)xBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Sound WavesDokumen3 halamanPhysics Sound WavesAditya V NairBelum ada peringkat
- Data Sheet Antenas RFSDokumen9 halamanData Sheet Antenas RFSangel cesarBelum ada peringkat
- Millimeter-Wave Tech ModesDokumen5 halamanMillimeter-Wave Tech Modesgiri ssBelum ada peringkat
- IB PHYSICS HL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW ON WAVES & VIBRATIONSDokumen20 halamanIB PHYSICS HL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW ON WAVES & VIBRATIONSshammi nathanBelum ada peringkat
- General Wave Properties 3 MSDokumen3 halamanGeneral Wave Properties 3 MSAli SiddiqBelum ada peringkat
- CARA Test-CD: Tracks 1..28 (70 Sec/track) Track Frequency Track Frequency Track Frequency Track Frequency Track FrequencyDokumen1 halamanCARA Test-CD: Tracks 1..28 (70 Sec/track) Track Frequency Track Frequency Track Frequency Track Frequency Track FrequencyasdfasfqwerqwerBelum ada peringkat