Glaucoma
Diunggah oleh
adimHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Glaucoma
Diunggah oleh
adimHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Glaucoma
INTRODUCTION
Glaucoma, group of eye diseases characterized by increased pressure within the eye and resulting
loss of vision. Although the vision loss caused by glaucoma is irreversible, medication or surgery
can usually control the pressure within the eye and slow or halt the progression of the disease. If
glaucoma is diagnosed in its early stages, it can be treated effectively, and vision can usually be
preserved.
Glaucoma occurs in two main varieties, known as chronic simple and acute glaucoma. In chronic
simple glaucoma, pressure within the eye rises gradually, and vision loss progresses over a period
of years. In acute glaucoma, the pressure inside the eye rises suddenly and immediate medical
treatment is necessary to preserve vision. Acute glaucoma is also known as narrow-angle or angleclosure glaucoma, because the angle between the cornea (the transparent layer of tissue at the
front of the eye) and the iris (the colored part of the eye) becomes smaller than normal. Chronic
simple glaucoma is also known as open-angle glaucoma because the angle between the cornea and
iris remains normal. This article focuses on chronic simple glaucoma, which accounts for 95 percent
of all cases of glaucoma.
Worldwide, approximately 6.7 million people have significant vision loss in both eyes due to
glaucoma, making this condition the second leading cause of blindness. About 120,000 people in
the United States alone have significant bilateral vision loss due to glaucoma, and the condition is
the leading cause of preventable blindness in the nation. More than 2 million people are currently
being treated for glaucoma, and an estimated 1 million additional cases of the disease are
undiagnosed.
II
CAUSE
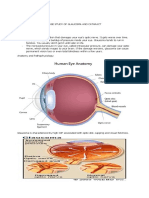
The front part of the eye is filled with a watery fluid, known as the aqueous humor. This fluid helps
the eye maintain its shape and delivers oxygen and nutrients to the cornea and the lens, the eye
structure that refracts light to form images. The aqueous humor is produced by the ciliary body, a
small gland located just behind the lens. The fluid percolates through the pupil and circulates
through the front chamber of the eye. It then drains away through a network of tiny channels,
called the trabecular meshwork, located at the front of the eye where the cornea and iris meet.
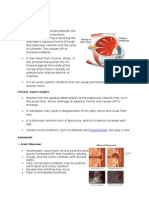
When the aqueous humor does not drain properly, the fluid backs up, causing the pressure inside
the eye to increase, and glaucoma develops. The increased pressure inside the eye compresses
and damages the optic nerve, the bundle of nerve cells that transmit visual information from the
eye to the brain. This damage to the optic nerve results in vision loss. In chronic simple glaucoma,
the aqueous humor drains through the trabecular meshwork more slowly than normal, much as a
sink empties more slowly when the drain is clogged.
Age is a primary risk factor for glaucoma: The condition strikes about 2 percent of people over age
40, and about 8 percent of people over age 70. The disease tends to run in families, although it is
not inherited in a regular, predictable pattern. Glaucoma affects six to eight times as many blacks
as whites, and blacks may develop glaucoma at a younger age and suffer more severe vision loss
than whites. Other factors that increase the risk of glaucoma include diabetes, nearsightedness,
high blood pressure, and long-term use of cortisone or other steroid medication. Although risk
factors for the disease are well understood, the cause of glaucoma remains unknown.
III
SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSIS
In its early stages, glaucoma is symptomless. The gradual increase of pressure inside the eye does
not cause any pain or discomfort. As the disease progresses, however, vision begins to deteriorate.
The deterioration usually begins with the peripheral visionsight at the outer edges of the visual
field. If glaucoma is left untreated, the field of vision continues to shrink until a person becomes
blind.
Glaucoma can be detected before vision loss occurs by a tonometry test, which is a simple,
painless part of a routine eye exam. An instrument called a tonometer blows a puff of air into the
eye to measure the pressure inside the eye. Some tonometers measure pressure by means of a
small plastic prism that is pressed lightly against the surface of the eye. Tests to measure
peripheral vision help detect vision loss due to glaucoma. Finally, an instrument called an
ophthalmoscope permits examination of the inside of the eye to detect damage to the optic nerve
(see Ophthalmology).
IV
TREATMENT
Most cases of glaucoma can be controlled with medication in the form of eyedrops or pills. These
medications reduce the pressure inside the eye either by decreasing the amount of aqueous humor
produced or by increasing the rate at which the fluid drains from the eye.
When the pressure inside the eye cannot be controlled by medication, surgery may be necessary.
In laser surgery, a high-energy laser beam is aimed at the eye to help stretch the trabecular
meshwork and make it easier for fluid to flow out of the eye. Sometimes patients who already have
had laser surgery develop increased pressure inside the eye again. At that point, conventional
surgery is often performed to create a new channel through which fluid can leave the eye. A valve
may be surgically implanted in the eye to help control the pressure.
ACUTE GLAUCOMA
Acute glaucoma is most common in Asians and in people who are farsighted. It tends to run in
families and can develop at any age. An acute attack can be brought on by entering a darkened
room, stress, and certain medications. The pressure inside the eye increases because the iris is
suddenly pushed down over the trabecular meshwork, much as a stopper is put in a drain. The
pressure increases very rapidly within a matter of a few hours. Symptoms develop suddenly and
include severe headache, nausea, sensitivity to light, redness of the eyes, blurred vision, and
seeing rainbowlike halos around lights. The pressure inside the eye must be lowered within 24
hours to prevent severe vision loss. Medications to decrease the production of aqueous humor and
to constrict the pupil are used to treat acute glaucoma. Laser surgery is another common
treatment. A test called gonioscopy can be performed as part of an eye exam to predict a persons
chance of having an acute attack.
Contributed By:
Mitchell H. Friedlaender
Microsoft Encarta 2009. 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- GlaucomaDokumen15 halamanGlaucomapreethijojo20035582100% (5)
- Glaukoma CSDokumen13 halamanGlaukoma CSKevinVun100% (4)
- Acupuncture Intake FormDokumen2 halamanAcupuncture Intake FormMeraki MaryBelum ada peringkat
- ABO Incompatibility Disease of The NewbornDokumen10 halamanABO Incompatibility Disease of The NewbornSha CapiliBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Glaucoma?Dokumen9 halamanWhat Is Glaucoma?Subhash Digambar VisalBelum ada peringkat
- GLAUCOMa Edited2Dokumen8 halamanGLAUCOMa Edited2Maki CabuenaBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Eye Eye Glaucoma Brain Vision Loss: Symptoms Open-Angle GlaucomaDokumen2 halamanGlaucoma Eye Eye Glaucoma Brain Vision Loss: Symptoms Open-Angle Glaucomavandana singhBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma and Your EyesDokumen4 halamanGlaucoma and Your EyesclubsanatateBelum ada peringkat
- GLAUCOMADokumen5 halamanGLAUCOMArocioisabelacamposBelum ada peringkat
- A Project ReportDokumen80 halamanA Project ReportShakun VidyottamaBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Word FileDokumen34 halamanGlaucoma Word Fileanon_784834955100% (1)
- Glaucoma and Cataract - ContentannDokumen20 halamanGlaucoma and Cataract - ContentannDR. KUMARASWAMI HEALTH CENTRE COLLEGE OF NURSING KANYAKUMARIBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Is Optic Nerve Damage (Often, But Not Always, Associated With Increased Eye Pressure) That Leads To Progressive, Irreversible Loss of VisionDokumen7 halamanGlaucoma Is Optic Nerve Damage (Often, But Not Always, Associated With Increased Eye Pressure) That Leads To Progressive, Irreversible Loss of VisionKusum RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma What Is Glaucoma?Dokumen4 halamanGlaucoma What Is Glaucoma?Marini Christin PanjaitanBelum ada peringkat
- American Optometric Association. Glaucoma HTTP - WWW - Aoa.org - Glaucoma - Xml.Dokumen8 halamanAmerican Optometric Association. Glaucoma HTTP - WWW - Aoa.org - Glaucoma - Xml.Adriana FallaBelum ada peringkat
- Cataracts Diabetes Diuretics EyeDokumen4 halamanCataracts Diabetes Diuretics Eyevandana singhBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, and TreatmentDokumen7 halamanGlaucoma: Causes, Symptoms, Risks, and TreatmentGraitaaBelum ada peringkat
- How the Eye Works and What is GlaucomaDokumen34 halamanHow the Eye Works and What is GlaucomaNanik Herlina MarwanBelum ada peringkat
- Cataract and Glaucoma Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen6 halamanCataract and Glaucoma Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSairileenDoradoBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Case StudyDokumen5 halamanGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Case StudyDokumen5 halamanGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Booklet: Presented by The Eye Digest: Authored by University of Illinois Eye & Ear Infirmary PhysiciansDokumen25 halamanGlaucoma Booklet: Presented by The Eye Digest: Authored by University of Illinois Eye & Ear Infirmary PhysiciansThe Eye Digest100% (2)
- Age-Related Cataract & GlaucomaDokumen26 halamanAge-Related Cataract & Glaucomasweetyeyal2002Belum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Diagnosis & Treatment GuideDokumen42 halamanGlaucoma Diagnosis & Treatment GuideSaha DirllahBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma: DR - Nugraha Wahyu Cahyana, SPMDokumen16 halamanGlaucoma: DR - Nugraha Wahyu Cahyana, SPMArdy SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Guide: Symptoms, Types, TreatmentDokumen8 halamanGlaucoma Guide: Symptoms, Types, TreatmentShannen Narace100% (2)
- Glacoma What You Should KnowDokumen26 halamanGlacoma What You Should KnowTaranisaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Glaucoma ENDokumen44 halamanUnderstanding Glaucoma ENTheophilus Oduro-NyarkoBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma 2 PDFDokumen16 halamanGlaucoma 2 PDFAgus HrtBelum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen2 halamanGlaucomagaurang03Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 - Introduction To GlaucomaDokumen16 halamanChapter 3 - Introduction To Glaucoma1330658Belum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma: by Tekia BuntynDokumen18 halamanGlaucoma: by Tekia BuntynTekia BuntynBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma: DefinitionDokumen5 halamanGlaucoma: DefinitionDani PhilipBelum ada peringkat
- GlucomaDokumen14 halamanGlucomametalheavy9993Belum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen9 halamanGlaucomat2ybrkm5hwBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma OverviewDokumen4 halamanGlaucoma OverviewSurya Cahyadi JunusBelum ada peringkat
- Eye Care Surgery and Laser: Open Angle GlaucomaDokumen2 halamanEye Care Surgery and Laser: Open Angle GlaucomaABDUL HADI ABD LATIFBelum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen3 halamanGlaucomaAgustinus BethaBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Glaucoma Group 1Dokumen27 halamanMakalah Glaucoma Group 1VeronicaBelum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen4 halamanGlaucomaMohammed Shamiul ShahidBelum ada peringkat
- Signs and Symptoms of Macular DegenerationDokumen19 halamanSigns and Symptoms of Macular DegenerationJayveersinh JadejaBelum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen6 halamanGlaucomaBasit AliBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma - A Eye Disorder Its Causes, Risk Factor, Prevention and MedicationDokumen16 halamanGlaucoma - A Eye Disorder Its Causes, Risk Factor, Prevention and MedicationDea MaulidiaBelum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen8 halamanGlaucomaapi-303064624Belum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma Types, Causes and Treatment ExplainedDokumen6 halamanGlaucoma Types, Causes and Treatment ExplainedZolfa AlhelaniBelum ada peringkat
- CataractDokumen6 halamanCataractKarel LuBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired VisionDokumen3 halamanImpaired VisionJannelle Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Activity2 (Glaucoma)Dokumen7 halamanActivity2 (Glaucoma)Gabbii CincoBelum ada peringkat
- Laser Iridotomy and GlaucomaDokumen2 halamanLaser Iridotomy and Glaucomajo_jo_maniaBelum ada peringkat
- The Healthy Eye: Structure, Function and Common Eye DiseasesDokumen38 halamanThe Healthy Eye: Structure, Function and Common Eye DiseasesHasnain Ahmad KhanBelum ada peringkat
- E GlaucomaDokumen3 halamanE GlaucomaMohammed Mahmoud Abd ElhalemBelum ada peringkat
- GLAUCOMADokumen10 halamanGLAUCOMAcarls burg a. resurreccionBelum ada peringkat
- Concept MapDokumen4 halamanConcept MapCasison Mark ArrysonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter One Mohamed - SeadDokumen12 halamanChapter One Mohamed - SeadAbdirahman Hassan MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Glaucoma: Polatkhan Aruzhan GM18-36-2aDokumen12 halamanGlaucoma: Polatkhan Aruzhan GM18-36-2aAruzhan PolatkhanBelum ada peringkat
- Open Angle Glaucoma OverviewDokumen7 halamanOpen Angle Glaucoma OverviewLoren GayudanBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Glaucoma?: Glaucoma American Academy of OphthalmologyDokumen5 halamanWhat Is Glaucoma?: Glaucoma American Academy of OphthalmologymenisBelum ada peringkat
- Endpd PDFDokumen29 halamanEndpd PDFNaveen AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Two Major Forms of Glaucoma: Acute and ChronicDokumen5 halamanTwo Major Forms of Glaucoma: Acute and ChronicKath CuevasBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Angle Closure GlaucomaDokumen17 halamanAcute Angle Closure GlaucomaOvidiu RusuBelum ada peringkat
- Cataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureDokumen16 halamanCataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureAmandeep Singh GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsDari EverandDiabetic Retinopathy: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsBelum ada peringkat
- Moving MamasDokumen9 halamanMoving MamasMindy MichaelsBelum ada peringkat
- Complementary Therapies in Clinical PracticeDokumen9 halamanComplementary Therapies in Clinical PracticeKurnia NuriBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Teaching 4PEUPERAL SEPSISDokumen5 halamanClinical Teaching 4PEUPERAL SEPSISAjit M Prasad PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- 1000113 EUS教學 (7) 重點式急診婦產科超音波之應用Dokumen114 halaman1000113 EUS教學 (7) 重點式急診婦產科超音波之應用juice119100% (4)
- Clinical Case Study-Lung CancerDokumen14 halamanClinical Case Study-Lung Cancerapi-299403846100% (1)
- PathologyDokumen31 halamanPathologyStudy Usmle100% (1)
- RH D Immunoglobulin (Anti-D)Dokumen4 halamanRH D Immunoglobulin (Anti-D)Ywagar YwagarBelum ada peringkat
- Efficacy and Safety of Minoxidil 3% Lotion For BeardDokumen2 halamanEfficacy and Safety of Minoxidil 3% Lotion For BeardPedro SauloBelum ada peringkat
- Volume 15, Number 1 January 2011Dokumen233 halamanVolume 15, Number 1 January 2011Nicolai BabaliciBelum ada peringkat
- Conization of CervixDokumen4 halamanConization of Cervixdrnareshkumar3281Belum ada peringkat
- Evidence Based PediatricDokumen463 halamanEvidence Based Pediatricsetyo pranotoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 32 - Anesthesia For Genitourinary SurgeryDokumen20 halamanChapter 32 - Anesthesia For Genitourinary SurgeryfewBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Pustaka Penelitian 2019Dokumen6 halamanDaftar Pustaka Penelitian 2019maithakeloayBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthetic Considerations in Polytrauma PatientsDokumen8 halamanAnaesthetic Considerations in Polytrauma PatientsMileidys LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebellopontine Angle Tumor Surgery HistoryDokumen12 halamanCerebellopontine Angle Tumor Surgery HistoryIndah KhairunnisaBelum ada peringkat
- Template AnalysisDokumen49 halamanTemplate AnalysisChirag Patil100% (1)
- Acupuncture Boosts IVF Success RatesDokumen10 halamanAcupuncture Boosts IVF Success RatesWolfgang Rb100% (1)
- Ny KhairaniDokumen16 halamanNy KhairaniHaris KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Divine Intervention Episode 36 Usmle OphthalmologyDokumen15 halamanDivine Intervention Episode 36 Usmle OphthalmologySwisskelly1Belum ada peringkat
- LogbookDokumen38 halamanLogbookniranjan sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Christa Maki Letter of Recommednation 4Dokumen2 halamanChrista Maki Letter of Recommednation 4api-491578633Belum ada peringkat
- BF 01888530Dokumen2 halamanBF 01888530Tsedic ZegeyeBelum ada peringkat
- ASEAN Mutual Recognition Arrangement For Indonesian Nurses: Is It A Promise?Dokumen4 halamanASEAN Mutual Recognition Arrangement For Indonesian Nurses: Is It A Promise?Krisha JacobBelum ada peringkat
- List of Professional Organization and Associations of Nurses in The PhilippinesDokumen1 halamanList of Professional Organization and Associations of Nurses in The PhilippinesLen Bernabe RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Alternative Method For Fabrication of Power ArmDokumen2 halamanAlternative Method For Fabrication of Power ArmVikas VatsBelum ada peringkat
- Australian Product Information - Oripro (Progesterone) Pessaries 1 Name of The Medicine 2 Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionDokumen14 halamanAustralian Product Information - Oripro (Progesterone) Pessaries 1 Name of The Medicine 2 Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionKirubakaranBelum ada peringkat
- Trauma Ginjal: Sub Bagian Urologi Bagian/Smf Bedah FK Uns/Rsud Dr. MoewardiDokumen39 halamanTrauma Ginjal: Sub Bagian Urologi Bagian/Smf Bedah FK Uns/Rsud Dr. MoewardiAtika SugiartoBelum ada peringkat
- CCES PUB SubstanceClassification EDokumen55 halamanCCES PUB SubstanceClassification Efree121Belum ada peringkat