Test 1 Material BSC 315
Diunggah oleh
Melanie0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
17 tayangan2 halamanbiology, genetics
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inibiology, genetics
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
17 tayangan2 halamanTest 1 Material BSC 315
Diunggah oleh
Melaniebiology, genetics
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Test 1 Material BSC 315
4. Epistasismultigene traits
Polygenic inheritance: two (or more) genes control a phenotype
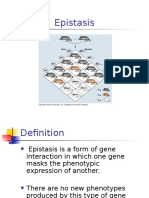
Epistasis: when two (or more) genes control a trait, one of the genes masks the effects of
the other(s).
Recessive epistasis: homozygous recessive at one gene hides phenotype of other genes
o Recessive epistasis in dog coat color:
B-E- black
bbE- brown
-- ee golden
Gene E is epistatic to B (genotype ee masks the effect of
B)
o Recessive epistasis in cats:
Genotype cc (albino) masks effects of all other coat color
genes
o Recessive epistasis can occur for two genes in the same
pathway
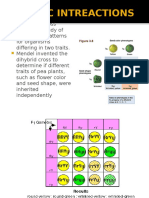
Dominant alleles are required for flower color
Results of a dihybrid selfcross: aa- - and - -bb genotypes give white flowers
Result: 9:7 purple:white
Dominant epistasis: dominant allele hides phenotype of another gene
o Dominant epistasis in chicken feather color
B- genotype is epistatis to A.
Allele A produceds pigment only in a bb genotype.
A-B- white feathers
aa- - white feathers
A-bb colored feathers
F2 progeny: 13:3 white: colored feathers
o Dominant epistasis in cats
W- (white dominant) genotype masks effects of all other coat color genes
Recessive alleles in different genes may produce the same phenotype
o Congenital deafness (recessive)
o Can two deaf parents have hearing children?
Yes, if the parents are homozygous for different genes. These genes
complement each other
No, if the parents are homozygous for same gene.
Additive effects
o Two genes contribute additively to lentil coat color:
4 genotype produce 4 different phenotypes
Dihybdrid selfcross: 9:3:3:1 ; A-B-:A-bb:aaB-:aabb ; brown:tan:grey:green
o Additive mechanism:
A allele produces tan
B allele produces grey
Grey + tan = brown
Alleles a and b are inactive no pigment
If neither grey nor tan no pigment in coat, so underlying green seed color by
virtue of chlorophyll
o Incomplete dominance of two genes gives 9 different phenotypes
Example: two different purple pigments. A contributes more pigment than B.
Continuous variation and additive genes
o Continuous traits are best modeled by several genes (polygenic inheritance) with
incomplete dominance and additive effects
Test 1 Material BSC 315
o Example: skin color in humans
Enrionmental variation
o Environmental conditions affect phenotype examples:
Humans: height, weight, skin color, cancer, etc.
Siamese cats: foot and face pigmentation (heat sensitive enzyme)
5.
Meiosis I
o Prophase I
o Metaphase I
o Anaphase I
Chromosomes do not split
Whole chromosomes segregate from each other!
Homologs separate and segregate
o Telophase I
Each daughter cell contains 2 chromosomes (n=haploid)
Each chromosome contains 2 chromatids
Meiosis II
o Prophase II
2 haploid cells
Each chromosome contains 2 chromatids
o Metaphase II
o Anaphase II
Chromosomes split into 2 chromatids
Chromatids segregate
o Telophase II/Result
4 haploid cells
Each chromosome contains 1 chromatid
Meiosis and Mendel
o Segregation explained:
5. Sexlinked inherit .
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fern Grower's Manual - Revised and Expanded Edition PDFDokumen605 halamanFern Grower's Manual - Revised and Expanded Edition PDFLuis Pedrero100% (6)
- 2016 Olympiad Training Genetics (Student)Dokumen73 halaman2016 Olympiad Training Genetics (Student)dimpledblissBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics Powerpoint JPDokumen31 halamanGenetics Powerpoint JPm wBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics PowerpointDokumen22 halamanGenetics PowerpointAditya VaishnavBelum ada peringkat
- Biology AdaptationDokumen2 halamanBiology Adaptation• LyaMew •Belum ada peringkat
- Lee Labrada Lean Body NutritionDokumen7 halamanLee Labrada Lean Body NutritionShakil AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Animal GeneticsDokumen33 halamanAnimal GeneticsOliver TalipBelum ada peringkat
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDokumen64 halamanNon Mendelian GeneticsDipanshi shahBelum ada peringkat
- Interactns Betwn GenesDokumen47 halamanInteractns Betwn GenesNOWAMANI RONALDBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics PowerpointDokumen39 halamanGenetics PowerpointcamsdelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- Where Did You Get the Color of Your Eyes? - Hereditary Patterns Science Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksDari EverandWhere Did You Get the Color of Your Eyes? - Hereditary Patterns Science Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Twice Baked Sweet Potato and Egg Recipe Recipe - LIVESTRONGDokumen20 halamanTwice Baked Sweet Potato and Egg Recipe Recipe - LIVESTRONGoiii88Belum ada peringkat
- Jeffrey Hamelman's Foreword To Home Baked by Hanne RisgaardDokumen3 halamanJeffrey Hamelman's Foreword To Home Baked by Hanne RisgaardChelsea Green Publishing25% (4)
- Module 11 Biointensive GardeningDokumen22 halamanModule 11 Biointensive GardeningMelikteBelum ada peringkat
- Year 11 Genetics Revision TestDokumen10 halamanYear 11 Genetics Revision Testapi-338606774Belum ada peringkat
- Ch04 2extensions PDFDokumen29 halamanCh04 2extensions PDFAakash SethiBelum ada peringkat
- Gene InteractionsDokumen28 halamanGene InteractionsZAMORA KEYBRENTBelum ada peringkat
- 4Dokumen38 halaman4Jason NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 10 - Extension Mendelian Genetics 2013Dokumen35 halamanLecture 10 - Extension Mendelian Genetics 2013Carina JLBelum ada peringkat
- 09 - PPT S2015Dokumen30 halaman09 - PPT S2015vysBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid CrossesDokumen25 halamanGenetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid CrossesAlam NuanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Genetic Intreactions: Dihybrid InheritanceDokumen18 halamanGenetic Intreactions: Dihybrid InheritanceHelpful HandBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Medelian Inheritance PDFDokumen12 halamanNon-Medelian Inheritance PDFbilly sauraBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Osama Al-Amer: Chapter Iii: Extension To Mendelian GeneticsDokumen29 halamanDr. Osama Al-Amer: Chapter Iii: Extension To Mendelian GeneticsBnDeRBelum ada peringkat
- Inheritance of GeneDokumen4 halamanInheritance of Genenan doeBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Mendelian Genetics: Inheritance Patterns That Don't Follow The RulesDokumen29 halamanNon-Mendelian Genetics: Inheritance Patterns That Don't Follow The RulesCza VerwinBelum ada peringkat
- GeneticsDokumen55 halamanGeneticsEl Cruz100% (1)
- Genetics Notes: Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsDokumen22 halamanGenetics Notes: Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsTevfik DoğanBelum ada peringkat
- General Biology 1 Gas GeneticsDokumen39 halamanGeneral Biology 1 Gas GeneticsDary SobrecareyBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To GeneticsDokumen23 halamanIntroduction To GeneticsShardul DalviBelum ada peringkat
- BIOL 3301 - Genetics Ch4B - Gene Interaction STDokumen58 halamanBIOL 3301 - Genetics Ch4B - Gene Interaction STChuongBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics Introduction and Recall SCDokumen32 halamanGenetics Introduction and Recall SCelyzaventura8Belum ada peringkat
- GCSE Biology Topic 6 NotesDokumen6 halamanGCSE Biology Topic 6 NotesRagavi KarunakaranBelum ada peringkat
- Bulldog Coat Colour PanelDokumen4 halamanBulldog Coat Colour PanelMiguelContrerasBelum ada peringkat
- BIO - 10 - 41 - V2 - DM - Interaction of Allelic and Non-Allelic GenesDokumen5 halamanBIO - 10 - 41 - V2 - DM - Interaction of Allelic and Non-Allelic GenesAlbina YulmukhametovaBelum ada peringkat
- Dihybrid Inheritance: Dihybrid Cross Problem SetDokumen16 halamanDihybrid Inheritance: Dihybrid Cross Problem SetHelpful HandBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics PowerpointDokumen22 halamanGenetics PowerpointMae MadronaBelum ada peringkat
- BIO2133 NotesDokumen20 halamanBIO2133 NotesSammie TdtBelum ada peringkat
- Extension of MendelismDokumen62 halamanExtension of MendelismTet LagazoBelum ada peringkat
- Modificationnof Mendelian RatioDokumen26 halamanModificationnof Mendelian RatioMonch LacedaBelum ada peringkat
- EpistasisDokumen26 halamanEpistasisy4heherBelum ada peringkat
- Unit III - GeneticsDokumen62 halamanUnit III - GeneticsErik BaldadoBelum ada peringkat
- Final GeneinteractionDokumen43 halamanFinal GeneinteractionNandini0% (1)
- Extensions of Mendelian InheritanceDokumen30 halamanExtensions of Mendelian InheritanceWONG JIE MIN MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics Patterns of Inheritance: Topics 7Dokumen39 halamanGenetics Patterns of Inheritance: Topics 7Heba TabchBelum ada peringkat
- Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsDokumen22 halamanIndependent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticshycherioneBelum ada peringkat
- Non MendelianDokumen13 halamanNon MendelianDave Christian Diaz BienBelum ada peringkat
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Genetics Some Basic FundamentalsDokumen9 halamanSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Genetics Some Basic FundamentalsMysterious SinghBelum ada peringkat
- M2P3 Mendelian Non Mendelian Genetics Part3Dokumen33 halamanM2P3 Mendelian Non Mendelian Genetics Part3heavenclaire.capangpanganBelum ada peringkat
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDokumen22 halamanNon Mendelian GeneticsJoraine Nichole Roquero VillajuanBelum ada peringkat
- The Genetics of Breed Color in The American Pit Bull TerrierDokumen6 halamanThe Genetics of Breed Color in The American Pit Bull TerrierhimselfBelum ada peringkat
- BIL250 Clicker QDokumen5 halamanBIL250 Clicker QsvBelum ada peringkat
- 10.2 Dihybrid Crosses HLDokumen7 halaman10.2 Dihybrid Crosses HLAbdelrahman HarrathBelum ada peringkat
- Extensions To Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype To PhenotypeDokumen27 halamanExtensions To Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype To PhenotypeWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics PowerpointDokumen17 halamanGenetics PowerpointestyBelum ada peringkat
- Deviation From Mendelian Genetic 1Dokumen38 halamanDeviation From Mendelian Genetic 1Yuliandini Pangestika Wiyono100% (1)
- Genetics Review#2 KeyDokumen4 halamanGenetics Review#2 KeyViggo GenereauxBelum ada peringkat
- Mendelian Genetics: Dominant & Recessive Review: Genotype: PP Genotype: PP Genotype: PPDokumen36 halamanMendelian Genetics: Dominant & Recessive Review: Genotype: PP Genotype: PP Genotype: PPangela0% (1)
- Bio120 Labex12 Genetics 1Dokumen30 halamanBio120 Labex12 Genetics 1api-525858524Belum ada peringkat
- MiscelleneousDokumen38 halamanMiscelleneousAbdul HananBelum ada peringkat
- University of Lahore (Sargodha Campus)Dokumen7 halamanUniversity of Lahore (Sargodha Campus)Ehtisham AslamBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonDokumen32 halamanGrade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonBenanBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics and Heredity - 240313 - 101549Dokumen17 halamanGenetics and Heredity - 240313 - 101549fuzilemarotya1Belum ada peringkat
- Epista SisDokumen16 halamanEpista SisSAMUELBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3Dokumen5 halamanModule 3Rhona Dianne VasquezBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Test 1 KeyDokumen7 halamanConcept Test 1 KeyMelanie100% (1)
- Quiz 20 Cell BiologyDokumen6 halamanQuiz 20 Cell BiologyMelanieBelum ada peringkat
- Test 3 Study Guide BSC 315Dokumen2 halamanTest 3 Study Guide BSC 315MelanieBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Notes BSC 315Dokumen4 halamanUnit 1 Notes BSC 315MelanieBelum ada peringkat
- Screw Oil Press/ Oil Expeller: Dr. Hammad KhanDokumen15 halamanScrew Oil Press/ Oil Expeller: Dr. Hammad KhanAhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Topping, Managing Suckers, and Using EthephonDokumen21 halamanTopping, Managing Suckers, and Using Ethephonnunik eka dianaBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Bibliography PDFDokumen454 halaman04 Bibliography PDFKevin MeyaseBelum ada peringkat
- GR6 Tle Q1 W5 D1-D5Dokumen10 halamanGR6 Tle Q1 W5 D1-D5Erdell BaronBelum ada peringkat
- Investigating Chinampa FarmingDokumen5 halamanInvestigating Chinampa FarmingDaniel JudyBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper ASAT VIIDokumen15 halamanSample Paper ASAT VIIThirumaleshwara M ShastryBelum ada peringkat
- Botanica Eorzea Vol 1Dokumen27 halamanBotanica Eorzea Vol 1Dr FalloutBelum ada peringkat
- Life Cycle of FunariaDokumen3 halamanLife Cycle of FunariaPalash Ghosh100% (1)
- Workbook AnswersDokumen16 halamanWorkbook AnswersNoelia UnamunoBelum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen7 halamanPDFAlex ParkBelum ada peringkat
- Damper System For Gas Turbine Exhaust Gas SystemDokumen2 halamanDamper System For Gas Turbine Exhaust Gas Systemjkhan_724384Belum ada peringkat
- Thinning Tree FruitDokumen2 halamanThinning Tree FruitSharad BhutoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Wood Combustion - CurkeetDokumen36 halamanWood Combustion - CurkeetzementheadBelum ada peringkat
- Solar DryingDokumen9 halamanSolar DryingNkem OkonkwoBelum ada peringkat
- Conservation of Ousteri Lake in Puducherry Draft Comprehensive Management Action Plan SACON 2011 PDFDokumen118 halamanConservation of Ousteri Lake in Puducherry Draft Comprehensive Management Action Plan SACON 2011 PDFvaishnavi sivaramakrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- 19 HTMDokumen6 halaman19 HTMSha-ReeBelum ada peringkat
- Pinnularia PresentationDokumen10 halamanPinnularia PresentationIjaz Ahmed100% (1)
- Cloning: For The Cloning of Human Beings, See - For Other Uses, SeeDokumen18 halamanCloning: For The Cloning of Human Beings, See - For Other Uses, Seemizz_liesaBelum ada peringkat
- PF 35 ReviewDokumen36 halamanPF 35 Reviewgiorgiana19Belum ada peringkat
- Horticultural Classification: Fruit Trees Common Name Scientific Name Family NameDokumen2 halamanHorticultural Classification: Fruit Trees Common Name Scientific Name Family NameNaifa CasanBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation EIL Project by JMV LPSDokumen59 halamanPresentation EIL Project by JMV LPSMahesh Chandra ManavBelum ada peringkat
- Cover Page: Describe The Male and Female Reproductive Parts of A Flowering PlantsDokumen19 halamanCover Page: Describe The Male and Female Reproductive Parts of A Flowering PlantsRowena DahiligBelum ada peringkat
- Adulteration and Evaluation of Crude DrugsDokumen48 halamanAdulteration and Evaluation of Crude DrugsVikash KushwahaBelum ada peringkat