Redox Calculations #2
Diunggah oleh
Christian MirandaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Redox Calculations #2
Diunggah oleh
Christian MirandaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Redox calculations
A piece of limestone weighing 0.1965 g was allowed to react with an excess of HCl. The calcium
in it was precipitated as CaC2O4. The precipitate was dissolved in H2SO4 and the ethanedioate ions
in the solution needed 35.6 cm of a 0.0200 M solution of potassium permanganate for titration.
Calculate the percentage of CaCO3 in the limestone.
25.0 cm of a sodium sulphite solution require 45.0 cm of a 0.0200 M potassium permanganate
2.
solution for oxidation. What is the concentration of the sodium sulphite solution.
What volume of acidified potassium permanganate solution of concentration 0.0200 M is
3.
decolorized by 100 cm of hydrogen peroxide of concentration 0.0100 M?
Manganese(II) sulphate is oxidized to manganese(IV) oxide by potassium permanganate in acid
4.
solution. A flocculant is added to settle the solid manganese(IV) oxide so that it does not obscure
the colour of the potassium permanganate. If 25.0 cm of manganese(II) sulphate solution require
22.5 cm of 0.0200M potassium permanganate solution, what is the concentration of
manganese(II) sulphate.
2.83 g of a sample of haematite iron ore [iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3] were dissolved in concentrated
5.
hydrochloric acid and the solution diluted to 250 cm3. 25.0 cm3 of this solution was reduced with
tin(II) chloride (which is oxidised to Sn4+ in the process) to form a solution of iron(II) ions. This
solution of iron(II) ions required 26.4 cm3 of a 0.0200 mol dm3 potassium dichromate(VI)
solution for complete oxidation back to iron(III) ions. Calculate the percentage of iron(III) oxide
in the ore.
10.0 g of iron(II) ammonium sulphate crystals were made up to 250 cm3 of acidified aqueous
6.
solution. 25.0 cm3 of this solution required 21.25 cm3 of 0.0200 mol dm3 potassium
dichromate(VI) for oxidation. Calculate x in the formula FeSO4.(NH4)2S04.xH2O
Given the halfreaction NO3(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2e ==> NO2(aq) + H2O(l)
7.
(a) give the ionic equation for potassium manganate(VII) oxidising nitrate(III) to nitrate(V)
(b) 24.2 cm3 of sodium nitrate(III) [sodium nitrite] solution, added from a burette, were needed to
discharge the colour of 25.0 cm3 of an acidified 0.0250 mol dm3 KMnO4 solution.
What was the concentration of the nitrate(III) solution in grammes of anhydrous salt per dm3?
1.01g of an impure sample of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, was dissolved in dil. sulphuric
8.
acid and made up to250 cm3 in a calibrated volumetric flask. A 25.0 cm3 aliquot of this solution
pipetted into a conical flask and excess potassium iodide solution and starch indicator were added.
The liberated iodine was titrated with 0.100 mol dm3 sodium thiosulphate and the starch turned
colourless after 20.0 cm3 was added. Calculate the total mass of potassium dichromate(VI) in the
original sample and hence its % purity.
Given the halfcell reaction IO3(aq) + 6H+(aq) + 5e ==> 1/2I2(aq) + 3H2O(l)
9.
(a) Deduce the redox equation for iodate(V) ions oxidising iodide ions.
(b) What volume of 0.0120 mol dm3 iodate(V) solution reacts with 20.0 cm3 of 0.100 mol
dm3 iodide solution?
(c) 25.0 cm3 of the potassium iodate solution were added to about 15 cm3 of a 15% solution of
potassium iodide (ensures excess iodide ion). On acidification, the liberated iodine
needed 24.1 cm3 of 0.0500 mol dm3 sodium thiosulphate solution to titrate it.
(i) Calculate the concentration of potassium iodate(V) in g dm3
(ii) What indicator is used for this titration and what is the colour change at the endpoint?
10. Ammonium iron(II) sulphate crystals have the following formula: (NH4)2.FeSO4.nH20. In an
experiment to determine n, 8.492 g of the salt were dissolved and made up to 250 cm of solution
with distilled water and dilute sulphuric acid. A 25.0 cm portion of the solution was further
acidified and titrated against potassium manganate(VII) solution of concentration 0.0150 mol dm3
. A volume of 22.5 cm was required. Find the value of n. [10]
1.
11.
1.01g of an impure sample of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, was dissolved in dil. sulphuric
acid and made up to250 cm3 in a calibrated volumetric flask. A 25.0 cm3 aliquot of this solution
pipetted into a conical flask and excess potassium iodide solution and starch indicator were added.
The liberated iodine was titrated with 0.100 mol dm3 sodium thiosulphate and the starch turned
colourless after 20.0 cm3 was added. Calculate the total mass of potassium dichromate(VI) in the
original sample and hence its % purity. [10]
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chem Stoichio QnsDokumen9 halamanChem Stoichio Qnsemily_liu_5Belum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresDari EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- 5.3 Exercise 1 - Manganate VII TitrationsDokumen1 halaman5.3 Exercise 1 - Manganate VII TitrationsCayden DasilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Name: - Class: - DateDokumen3 halamanName: - Class: - DateDaniel MateusBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 123 HWK Back and Redox TitrationsDokumen3 halamanCHE 123 HWK Back and Redox TitrationsJuiloBelum ada peringkat
- Titration Questions and AnswersDokumen29 halamanTitration Questions and Answersngah lidwineBelum ada peringkat
- Chemsheets - co.UkIron Redox QuestionsDokumen1 halamanChemsheets - co.UkIron Redox QuestionsdoggiesrcuteBelum ada peringkat
- S7 11012021 Acid Base Titrations WS With ANSWERSDokumen7 halamanS7 11012021 Acid Base Titrations WS With ANSWERSFatima Ahmed-VeriterBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017Dokumen3 halamanForm 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017khangsiean89Belum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen12 halamanSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryNikhil BhattBelum ada peringkat
- Redox MCQ Cie + AnswersDokumen1 halamanRedox MCQ Cie + Answersby7777Belum ada peringkat
- Question 18: 1.01g of An Impure Sample of Potassium Dichromate (VI), K CR O Aliquot of This Sodium Thiosulphate and The StarchDokumen1 halamanQuestion 18: 1.01g of An Impure Sample of Potassium Dichromate (VI), K CR O Aliquot of This Sodium Thiosulphate and The StarchGirish SreeneebusBelum ada peringkat
- Take Home QuizDokumen1 halamanTake Home QuizArgel Linard Francisco MabagaBelum ada peringkat
- Titrations Practice ProblemsDokumen3 halamanTitrations Practice ProblemsbenitonziratimaanaBelum ada peringkat
- Molarity CalculationDokumen3 halamanMolarity CalculationhahaBelum ada peringkat
- Acid N Salt RevisionDokumen6 halamanAcid N Salt RevisionTennarasu PannirselvamBelum ada peringkat
- Iodine Thiosulfate Titration QuestionsDokumen13 halamanIodine Thiosulfate Titration QuestionsWeb Books100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Dokumen6 halamanTutorial 4Jayakumar SankaranBelum ada peringkat
- MoleDokumen7 halamanMoleplayboy_suruBelum ada peringkat
- Redox Titration 2017 With AnswersDokumen4 halamanRedox Titration 2017 With Answersjohn78% (9)
- 1.2 Exercise 2 - SolutionsDokumen2 halaman1.2 Exercise 2 - Solutions123456Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsDokumen7 halamanUnit 1 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsVeraBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Chapter 1 and 2 Model ADokumen10 halamanExam Chapter 1 and 2 Model AMuhamed MahmoudBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 01 - Assignment 3 - Titration - Tutors Copy (2013)Dokumen4 halamanTopic 01 - Assignment 3 - Titration - Tutors Copy (2013)Turfy YanBelum ada peringkat
- Back TitrationsDokumen3 halamanBack TitrationsChristine Angelica EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 StoichiometryDokumen15 halaman5 StoichiometryNimeshBelum ada peringkat
- Mole Concept ExerciseDokumen2 halamanMole Concept Exercisechong56100% (1)
- Worked Egs - Titration CalculationsDokumen3 halamanWorked Egs - Titration CalculationsJez Leith-RossBelum ada peringkat
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 4Dokumen9 halamant2 Chem Revision Ex 4Nicholas OwBelum ada peringkat
- TAREA GRUPAL Tercer Parcial.2p2014Dokumen3 halamanTAREA GRUPAL Tercer Parcial.2p2014Grecia ObandoBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Moles and StoichiometryDokumen6 halaman1 - Moles and StoichiometryArvin LiangdyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Calc (1) .Problems (Volumetric Analysis)Dokumen28 halamanChemical Calc (1) .Problems (Volumetric Analysis)Peter Yin100% (4)
- Moles-Questions-Mixed Topic 1 Ib Chemistry PracticeDokumen2 halamanMoles-Questions-Mixed Topic 1 Ib Chemistry PracticeHana BessalahBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation in ACDokumen4 halamanCalculation in AC23005852Belum ada peringkat
- PsDokumen2 halamanPsMichael James Menor QuerosBelum ada peringkat
- Honors Chemistry WKSHT Solution Stoichiometry With Some ANSWERSDokumen5 halamanHonors Chemistry WKSHT Solution Stoichiometry With Some ANSWERSIan CacciatoreBelum ada peringkat
- Acid-Base TitrationDokumen10 halamanAcid-Base TitrationajaxBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 40 Redox TitrationDokumen2 halamanExp 40 Redox TitrationCherylBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 2 Exercise 2 - SolutionsDokumen2 halamanTopic 2 Exercise 2 - SolutionsSalman ZaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz StoichiometryDokumen3 halamanQuiz StoichiometrychampionBelum ada peringkat
- 1.2 Exercise 6 - More Complex CalculationsDokumen1 halaman1.2 Exercise 6 - More Complex CalculationslingarajugowdaBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Exercise Ch.15 (Concentration 2)Dokumen5 halamanRevision Exercise Ch.15 (Concentration 2)Tse Ho YinBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation in AC-2Dokumen36 halamanCalculation in AC-223005852Belum ada peringkat
- Salts-Answer ChemistryDokumen15 halamanSalts-Answer ChemistryAngie Kong Su MeiBelum ada peringkat
- StoichiometryDokumen3 halamanStoichiometrylinnbrownieBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Complex Formation TitrationDokumen1 halaman3 Complex Formation TitrationMiguel SantosBelum ada peringkat
- BacktitrationDokumen2 halamanBacktitrationChrisBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM 1235 Volumetric QuizDokumen1 halamanCHEM 1235 Volumetric QuizJesseca Calaunan QuintoBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Grade 9 GeneralDokumen7 halamanChemistry Grade 9 GeneralkamalBelum ada peringkat
- Stoichiometry AP Exam QuestionsDokumen12 halamanStoichiometry AP Exam QuestionsAllen Jerry AriesBelum ada peringkat
- Pharm AnalysisDokumen6 halamanPharm AnalysisMirumbi Kefa MomanyiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 HW Set (09-10)Dokumen19 halamanChapter 4 HW Set (09-10)David StainesBelum ada peringkat
- Volumetric Analysis QuestionsDokumen3 halamanVolumetric Analysis QuestionsJake Robinson100% (8)
- AttachmentDokumen6 halamanAttachmentVarsha VasthaviBelum ada peringkat
- Common Foundation Physical Q in A Level (Repaired)Dokumen39 halamanCommon Foundation Physical Q in A Level (Repaired)黄维燕Belum ada peringkat
- Finding The Percentage Purity of Iron Wire PDFDokumen2 halamanFinding The Percentage Purity of Iron Wire PDFKrishna SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Ideas - Concentrations of Solutions - ANSWERSDokumen7 halamanChemical Ideas - Concentrations of Solutions - ANSWERSAnshu MovvaBelum ada peringkat
- Stoichiometry WorksheetDokumen9 halamanStoichiometry Worksheetdizzy057765Belum ada peringkat
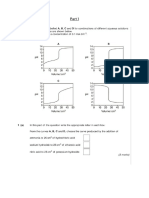
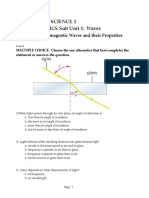
- Integrated Science 1 UNIT 4: PHYSICS Sub Unit 1: Waves Test 2Dokumen16 halamanIntegrated Science 1 UNIT 4: PHYSICS Sub Unit 1: Waves Test 2Charina May Lagunde-SabadoBelum ada peringkat
- Add Math KINEMATICS (20 PTS) 2012Dokumen4 halamanAdd Math KINEMATICS (20 PTS) 2012Christian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
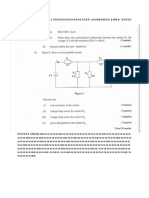
- Electricity PastPapers (200 gdrtfg5 2013)Dokumen13 halamanElectricity PastPapers (200 gdrtfg5 2013)Christian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Light - Reflection - Refraction - Diffraction - ReviewDokumen42 halamanLight - Reflection - Refraction - Diffraction - ReviewLester MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Science 1 UNIT 4: PHYSICS Sub Unit 1: Waves Test 2Dokumen16 halamanIntegrated Science 1 UNIT 4: PHYSICS Sub Unit 1: Waves Test 2Charina May Lagunde-SabadoBelum ada peringkat
- Add Math KINEMATICS (20 PTS) 2012Dokumen4 halamanAdd Math KINEMATICS (20 PTS) 2012Christian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Specimen Paper 1 AnswersDokumen26 halamanSpecimen Paper 1 AnswersChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Handout Triacs, LEDS & SCRSDokumen4 halamanHandout Triacs, LEDS & SCRSChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen1 halaman2Christian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- QWQWDD D Sadv SVDokumen3 halamanQWQWDD D Sadv SVChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Ewrwrev KJDokumen4 halamanEwrwrev KJChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen1 halaman2Christian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Labs Mark SchemesDokumen4 halamanLabs Mark SchemesChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- VVVVVVVVVVV VDokumen1 halamanVVVVVVVVVVV VChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- DataDokumen1 halamanDataChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- QWQWV VDokumen3 halamanQWQWV VChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Use ThermometerDokumen1 halamanUse ThermometerChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Sheet: Name Class DateDokumen4 halamanAnswer Sheet: Name Class DateChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- EntrepreneurshipDokumen11 halamanEntrepreneurshipChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Total TotalDokumen1 halamanTotal TotalChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- NNNDokumen2 halamanNNNChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- IrvcvcvcvcDokumen2 halamanIrvcvcvcvcChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- AmirDokumen2 halamanAmirChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Applications of Amino Acids in MedicineDokumen1 halamanApplications of Amino Acids in MedicineChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Epistasis PracticeDokumen1 halamanEpistasis PracticeChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Culture BacteriaDokumen1 halamanCulture BacteriaChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- SJCJC NewDokumen41 halamanSJCJC NewChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Title Page APADokumen2 halamanTitle Page APAChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- CC 4-6Dokumen3 halamanCC 4-6Christian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- As SPANISH Indpnt Study ChecklistDokumen1 halamanAs SPANISH Indpnt Study ChecklistMaxim SerkovBelum ada peringkat
- Earth Science (Metamorphic Rocks)Dokumen8 halamanEarth Science (Metamorphic Rocks)MA. ALEXIS LAURENBelum ada peringkat
- Final Thesis - Aris PotliopoulosDokumen94 halamanFinal Thesis - Aris PotliopoulosCristinaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Nice9000v A04Dokumen151 halamanManual Nice9000v A04hoang tamBelum ada peringkat
- Intumescent Paint For Steel NZ - Coating - Co.nzDokumen8 halamanIntumescent Paint For Steel NZ - Coating - Co.nzPeter ThomsonBelum ada peringkat
- iPQ-Center Webvideo Star TTB MA R1 42 en PDFDokumen32 halamaniPQ-Center Webvideo Star TTB MA R1 42 en PDFHamid KharazmiBelum ada peringkat
- Southwest Airlines Final ReportDokumen16 halamanSouthwest Airlines Final Reportapi-427311067Belum ada peringkat
- The Ieee Test System Methods: Reliability ofDokumen11 halamanThe Ieee Test System Methods: Reliability ofFsdaSdsBelum ada peringkat
- History of Flash Part - 2Dokumen7 halamanHistory of Flash Part - 2YOGESHWER NATH SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- Ask A Monk EnlightenmentDokumen16 halamanAsk A Monk EnlightenmentPetruoka EdmundasBelum ada peringkat
- Contact Inform 2002 PDFDokumen24 halamanContact Inform 2002 PDFFrank AlmeidaBelum ada peringkat
- Ii 2015 1Dokumen266 halamanIi 2015 1tuni santeBelum ada peringkat
- CE Review GEOMETRY 2Dokumen6 halamanCE Review GEOMETRY 2Paul Gerard AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- ChipmunkDokumen19 halamanChipmunkema.nemec13Belum ada peringkat
- Orofacial Complex: Form and FunctionDokumen34 halamanOrofacial Complex: Form and FunctionAyushi Goel100% (1)
- ANS: (2.59807m/s2 Horizontal) (1.5m/s2 Vertical) (12.93725 Degree Angle That The Water Surface Makes With The Horizontal)Dokumen5 halamanANS: (2.59807m/s2 Horizontal) (1.5m/s2 Vertical) (12.93725 Degree Angle That The Water Surface Makes With The Horizontal)Lolly UmaliBelum ada peringkat
- Generative Shape DesignDokumen195 halamanGenerative Shape DesignAdi Fiera100% (1)
- Class 12 - Maths - MatricesDokumen87 halamanClass 12 - Maths - MatricesAishwarya MishraBelum ada peringkat
- (G. Lakshmi Narasaiah) Finite Element Analysis PDFDokumen349 halaman(G. Lakshmi Narasaiah) Finite Element Analysis PDFmoljaime1326Belum ada peringkat
- Dizziness - Vertigo and HomoeopathyDokumen38 halamanDizziness - Vertigo and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomBelum ada peringkat
- How To Eat WellDokumen68 halamanHow To Eat WelleledidiBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Choice Enzymes Plant and Animal NutritionDokumen44 halamanMultiple Choice Enzymes Plant and Animal Nutritionliufanjing07Belum ada peringkat
- Engineering Structures: C.X. Dong, A.K.H. Kwan, J.C.M. HoDokumen14 halamanEngineering Structures: C.X. Dong, A.K.H. Kwan, J.C.M. HoElieser SinagaBelum ada peringkat
- Donna Hay Magazine 2014-10-11 PDFDokumen172 halamanDonna Hay Magazine 2014-10-11 PDFlekovic_tanjaBelum ada peringkat
- Efficient Rice Based Cropping SystemDokumen24 halamanEfficient Rice Based Cropping Systemsenthilnathan100% (1)
- Illuminati TruthsDokumen27 halamanIlluminati TruthsDonnaveo ShermanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecotopia Remixed II-FormattedDokumen54 halamanEcotopia Remixed II-FormattedthisisdarrenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 04 Product and ServDokumen43 halamanChapter 04 Product and ServAlireza AlborziBelum ada peringkat
- Fret Position Calculator - StewmacDokumen1 halamanFret Position Calculator - StewmacJuan Pablo Sepulveda SierraBelum ada peringkat
- Army Aviation Digest - Nov 1978Dokumen52 halamanArmy Aviation Digest - Nov 1978Aviation/Space History Library100% (1)
- Furuno CA 400Dokumen345 halamanFuruno CA 400Димон100% (3)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDari EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDari EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDari EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (90)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDari EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDari EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (21)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDari EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDari EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TablePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (22)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDari EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (146)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDari EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDari EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDari EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookDari EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathDari EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Dari EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDari EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)