Orthopedics Bone Dysplasias
Diunggah oleh
annapanna10 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
29 tayangan4 halamanOrthopedics Bone Dysplasias
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniOrthopedics Bone Dysplasias
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
29 tayangan4 halamanOrthopedics Bone Dysplasias
Diunggah oleh
annapanna1Orthopedics Bone Dysplasias
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
Bone Dysplasias: Definition: Generalized abnormality in growth or development.
Genetic aspects: variety of disorders (from single gene disorder to multifactorial
inheritance)
Classification of bone dysplasias:
1. Disorders around growth plate (epiphyseal or metaphyseal)
2. Changes in bone density (increased or decreased)
3. Cranio-tubular disorders
4. Cranio-facial abnormalities
5. Vertebral anomalies
6. Storage disorders
7. Anomalies of cartilage and fibrous tissue
8. Miscellaneous disorders
Disorders around growth plate (epiphyseal or metaphyseal):
Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia:
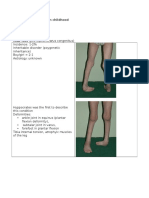
Flattening of epiphyses knee or hip abnormality
(genu varum, hip dysplasia similar epiphyseal changes of femoral epiphysis like
in Perthes disease)
Spondylo-epiphyseal dysplasia:
Dorsolumbar kyphosis due to wedge shaped vertebrae, disorder of ossification at
the hip (proximal femur)
ACHONDROPLASIA metaphyseal abnormality
Features: - DWARFISM
Disproportionately short limbs
Prominent forehead
Vertebral involvement- severe lordosis, spinal stenosis
typical disproportionate trunk- extremity relations in achondroplasia
Achondroplasia - x-ray features: short tubular bones, widened epiphyses
Changes in bone density
increased : OSTEOPETROSIS - thickening of diaphysis and metaphysis
Decreased: OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA fragilitas ossium
most severe form: congenital infants may die early from intracranial
haemorrhage
tarda form becomes manifest later , frequent fractures of long tubular
bones BLUE SCLERA
THIS TYPE MAY HEAL AT EARLY ADULTHOOD
OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA
Fracture fixation is a problem multiple fractures may occur repeatedly
telescoping nails should be used to fix the fractures as the child grows, nail
expands
Correction of femur curve in osteogenesis imperfecta
resection, rotation of curved segment and fixation
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia Morquio disease
Typical feature: growth of cartilage and ossification of cartilage are defective
Affected bones, joints: vertebrae, hips- knees
Manifestation: can be recognised at birth
Morquios syndrome typical appearance - gibbosity
Storage disorders:
Mucopolysacharidosis accumulation of mucopolysacharides in the cells and
subsequently in virtually all tissues of the body, with typical changes in the
skeleton
Example: GAUCHERS DISEASE large deposits of lypopolysacharids in the
skeleton, causing necrosis of femoral head
Anomalies of cartilage and fibrous tissue:
Enchondromatosis (Olliers disease): - aggregation of cartilage in the
metaphyses of long bones, producing deformities (forearm), growth disorder
(genu valgum or varum)
Exostosis cartilaginea multiplex exostoses at metaphyseal end of long
bones with a cartilage cap
Enchondromatosis:
Large chondral isles in proximal and distal epiphysis of tibia
Hyperchondroplasia Marphans syndrome (arachnodactyli)
Antoine Marphan French pediatrician 1896
Genetically inherited disorder of connective tissue
Feature: tall , lung upper limbs, reching near The knees, long thin fingers
(arachnodactyli- spiders fingers)
Risk: heart valve disorder!!
Multiple exostosis distal femur, proximal tibia
Ehler- Danlos syndrome
Hypermobility of joints
Vulnerable, white, extensile skin
rubber man
Cause: abnormal collagen fibers
Consequence: genu recurvatum, hip dislocation
Hyperlaxity of joints: thumb abducted into paralel position with forearm,
fingers hyperextended paralel with forearm
Importance: hyperlax joints are more vulnerable
Neurofibromatosis: (von Recklinghausens disease)
Typical feature: subcutanous nodules (neurofibroma), same nodules in spine
(causing severe form of scoliosis) cranium (compression of acoustic nerve)
Typical caf au lait skin patches
Cysts may lead to fractures
Fibrous dysplasia
Portions of endosteal bone are replaced by fibrous matrix
Two main types: monostotic (in one bone) and polyostotic
Consequence: pathological fracture, or deformity (curving) of bones
Vertebral anomalies:
Klippel- Feil syndrome
X-ray: fusion of several or all cervical vertebrae
Feature: short neck, posterior hairline is low
Sprengels deformity congenital elevationof scapula may be associated too
Klippel-Feil syndrome- clinical view, - risk: spinal cord compression
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Motivation SummariesDokumen3 halamanMotivation Summariesannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Ethical dilemma approaches for managersDokumen2 halamanEthical dilemma approaches for managersannapanna1100% (2)
- Residential Tenancies Act 2004Dokumen148 halamanResidential Tenancies Act 2004annapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics CDH, PerthesDokumen26 halamanOrthopedics CDH, Perthesannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- O1Dokumen5 halamanO1annapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Godfreygrant Ie Advice Advice For Tenants Utm Content BuffeDokumen8 halamanGodfreygrant Ie Advice Advice For Tenants Utm Content Buffeannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics Bone TumorsDokumen18 halamanOrthopedics Bone Tumorsannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics Cong. Disord.Dokumen13 halamanOrthopedics Cong. Disord.annapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics BoneDisordersDokumen20 halamanOrthopedics BoneDisordersannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics Club FootDokumen15 halamanOrthopedics Club Footannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics Bone ElongshortDokumen9 halamanOrthopedics Bone Elongshortannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics EeeDokumen1 halamanOrthopedics Eeeannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Fsi HungarianBasicCourse Volume1 StudentTextDokumen277 halamanFsi HungarianBasicCourse Volume1 StudentTextannapanna1100% (1)
- O5Dokumen2 halamanO5annapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- O4Dokumen8 halamanO4annapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Aptitude Test Application FormDokumen3 halamanAptitude Test Application Formannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Adult Spine Disorders and TreatmentsDokumen7 halamanAdult Spine Disorders and Treatmentsannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Patellar Friction Test - Pressing Patella Against Femur Patellar Apprehension Test: Pressing The Patella Laterally, While Flexing The Knee - IfDokumen6 halamanPatellar Friction Test - Pressing Patella Against Femur Patellar Apprehension Test: Pressing The Patella Laterally, While Flexing The Knee - Ifannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Dublin Public Transport MapDokumen2 halamanDublin Public Transport Mapannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Hungarian Language CourseDokumen32 halamanHungarian Language Courseannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Dublin Bus NetworkDokumen2 halamanDublin Bus NetworkDaniel RichmondBelum ada peringkat
- TMTH TG FinalDokumen322 halamanTMTH TG Finalruz_agnesBelum ada peringkat
- Qualification Recognition ManualDokumen16 halamanQualification Recognition Manualannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Criteria For Recognition of Physiotherapy Qualifications Acquired Outside The Republic of Ireland PDFDokumen3 halamanCriteria For Recognition of Physiotherapy Qualifications Acquired Outside The Republic of Ireland PDFJack JamalBelum ada peringkat
- Information For Physiotherapists Seeking Employment in The ROI For CouncilDokumen6 halamanInformation For Physiotherapists Seeking Employment in The ROI For Councilannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Physiotherapy Qualification Recognition FormDokumen24 halamanPhysiotherapy Qualification Recognition Formannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDokumen11 halamanFrequently Asked Questionsannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Predicting difficult employees through vocational interests and self-esteemDokumen34 halamanPredicting difficult employees through vocational interests and self-esteemannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- Moist Chocolate CakeDokumen1 halamanMoist Chocolate Cakeannapanna1Belum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Ashrae 62.1-2019Dokumen92 halamanAshrae 62.1-2019Alejandro Castillo100% (16)
- Overview of US Investment in NanotechnologyDokumen19 halamanOverview of US Investment in NanotechnologyMaterials Research InstituteBelum ada peringkat
- BCTG Guide-Love in The Time of CholeraDokumen21 halamanBCTG Guide-Love in The Time of CholeraBernard MasiphaBelum ada peringkat
- Error Codes (DTC) : 15 Electrical TroubleshootingDokumen13 halamanError Codes (DTC) : 15 Electrical TroubleshootingPoyraz PoyrazBelum ada peringkat
- RUDDER PLATING DIAGRAMDokumen1 halamanRUDDER PLATING DIAGRAMMuhammad Ilham AlfiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- GMSARN Conf: Design Criteria on Substation ProtectionDokumen6 halamanGMSARN Conf: Design Criteria on Substation Protectionbdaminda6701Belum ada peringkat
- Land Rover Range Rover Owners Manual 2007Dokumen358 halamanLand Rover Range Rover Owners Manual 2007PetreCaracaleanu0% (1)
- Anotações - Seminários em Língua Inglesa - Discurso LiterárioDokumen17 halamanAnotações - Seminários em Língua Inglesa - Discurso LiterárioAline MoraisBelum ada peringkat
- Audit Reveals Optimization Opportunities for Cement Ball Mill SystemDokumen19 halamanAudit Reveals Optimization Opportunities for Cement Ball Mill SystemVijay Bhan100% (2)
- TDS - RheoFIT 762Dokumen2 halamanTDS - RheoFIT 762Alexi ALfred H. TagoBelum ada peringkat
- SmogDokumen5 halamanSmogAlain MoratallaBelum ada peringkat
- ADAMHAND8A4Dokumen11 halamanADAMHAND8A4Elker José Camargo100% (1)
- 1625-De Dwks Parts ListDokumen69 halaman1625-De Dwks Parts ListSasan AbbasiBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer On Nervous System Grade VIDokumen4 halamanReviewer On Nervous System Grade VIKent Francis LayaguinBelum ada peringkat
- Axminster CarpetDokumen19 halamanAxminster Carpetrohit sinhaBelum ada peringkat
- IOM Paquetes DX Precedent RT-SVX22U-EN - 03072018Dokumen82 halamanIOM Paquetes DX Precedent RT-SVX22U-EN - 03072018Mario Lozano100% (1)
- Rec2009 025 PDFDokumen172 halamanRec2009 025 PDFEkaStaVTVBelum ada peringkat
- BSC Ag Syllabus 5th DeanDokumen150 halamanBSC Ag Syllabus 5th Deansaurabh rBelum ada peringkat
- PLOTINUS: On Beauty (Essay On The Beautiful)Dokumen12 halamanPLOTINUS: On Beauty (Essay On The Beautiful)Frederic LecutBelum ada peringkat
- Serospin Operating Manual 20100407Dokumen19 halamanSerospin Operating Manual 20100407Verdana50% (2)
- Fischer Carbene Complexes in Organic SynthesisDokumen9 halamanFischer Carbene Complexes in Organic SynthesisNorah AltayyarBelum ada peringkat
- SynopsisDokumen13 halamanSynopsisharivijay ranmaleBelum ada peringkat
- Estudio CarmenaDokumen11 halamanEstudio CarmenaAlfredo BalcázarBelum ada peringkat
- GadDokumen1 halamanGadFakhruddin DhilawalaBelum ada peringkat
- Raise The Limits: Eppendorf Research PlusDokumen12 halamanRaise The Limits: Eppendorf Research PlusZahia Slama Ep AchourBelum ada peringkat
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GuideDokumen12 halamanTherapeutic Drug Monitoring GuidePromise NcubeBelum ada peringkat
- Laplace Transform AssignmentDokumen1 halamanLaplace Transform AssignmentMohamad DuhokiBelum ada peringkat
- Toxicology Compendium PDFDokumen602 halamanToxicology Compendium PDFJUANBelum ada peringkat
- CQ B TECHNIQUESDokumen37 halamanCQ B TECHNIQUESeddie6355100% (3)
- Carbozinc 859: Selection & Specification Data Substrates & Surface PreparationDokumen2 halamanCarbozinc 859: Selection & Specification Data Substrates & Surface PreparationAmy JonesBelum ada peringkat