Tepzz 59 Za - T: European Patent Application
Diunggah oleh
dangtuan27Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tepzz 59 Za - T: European Patent Application
Diunggah oleh
dangtuan27Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
TEPZZ59ZA_T
(19)
(11)
EP 2 592 320 A1
EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
(12)
(43) Date of publication:
(51) Int Cl.:
F16L 3/10 (2006.01)
15.05.2013 Bulletin 2013/20
F16L 55/035 (2006.01)
(21) Application number: 12192562.2
(22) Date of filing: 14.11.2012
(84) Designated Contracting States:
(72) Inventor: Utay, Arthur W.
AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB
GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO
PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR
Designated Extension States:
BA ME
(30) Priority: 14.11.2011 US 201113295687
South Windsor, CT Connecticut 06074 (US)
(74) Representative: Tomlinson, Kerry John
Dehns
St Brides House
10 Salisbury Square
London
EC4Y 8JD (GB)
(71) Applicant: United Technologies Corporation
Hartford, CT 06101 (US)
(54)
(57)
Duct clamp
a plurality of flat sides (20) constructed to bow in contact
with a duct (D). The fastener holds the two clamp halves
together. The mounting piece is attached to the polygonal
clamp, and configured to attach to a support structure.
EP 2 592 320 A1
A duct clamp assembly (10, 10B) comprises a
polygonal clamp (12, 12B), a fastener (16, 16B), and a
mounting piece (14, 14B). The polygonal clamp is a
clamp formed from two clamp halves (18), each having
Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)
EP 2 592 320 A1
Description
BACKGROUND
[0001] The present invention relates generally to duct
clamps, and more particularly to lightweight duct clamp
assemblies tuned to handle specific vibration conditions.
[0002] Cylindrical ducts are used in a wide range of
applications, including aircraft air systems. These ducts
are conventionally secured via circular or semicircular
duct clamps with deformable clamp pads. Conventional
clamps are attached with mounting pieces to an immobile
support structure such as a case or wall, so that secured
ducts cannot shift or detach.
[0003] Conventional duct clamps have rigid cylindrical
or ring-shaped frames typically constructed of two or
more pieces of cast, forged, or machined metal connected by hinges or bolts. The inner surfaces of these rigid
cylindrical frames are covered by deformable clamp
pads, which are usually formed of rubber. Clamp pads
fit inside duct clamp frames, between the rigid frame of
the clamp and a duct to be secured. When this kind of
duct clamp is closed and tightened about a duct (with,
for instance, a latch or bolt), the clamp pad is squeezed
and deformed about the duct. Duct clamps of this construction provide limited protection against duct vibration
and translation, and typically comprise a plurality of parts
which add considerable cost and weight to the duct assembly. There exists a need for lighter, more cost-effective duct clamps capable of increased vibration control.
10
15
20
25
30
SUMMARY
[0004] The present invention is directed toward a duct
clamp assembly having a polygonal clamp, a fastener,
and a mounting piece. The polygonal clamp is clamp
formed from two clamp halves, each having a plurality of
flat sides constructed to bow in contact with a duct. The
fastener holds the two clamp halves together. The mounting piece is attached to the polygonal clamp, and configured to attach to a support structure.
35
40
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
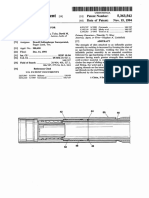
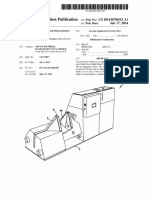
[0005] FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a duct clamp
assembly attached to a duct.
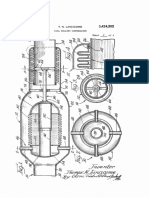
[0006] FIG. 2A is an exploded perspective view of one
embodiment of the duct clamp assembly of FIG. 1
[0007] FIG. 2B is an unexploded perspective view of
the duct clamp assembly of FIG. 1.
[0008] FIG. 3 is a perspective view of an exemplary
alternative duct clamp assembly of the present invention.
45
50
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
55
[0009] FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of duct clamp
assembly 10 supporting and restraining duct D. Duct
clamp assembly 10 comprises polygonal clamp 12,
mounting pieces 14, and fasteners 16. Polygonal clamp
12 is formed of two clamp halves 18 (including top half
18a and bottom half 18b), each having a plurality of
straight sides 20, and two bolt tabs 22 with bolt holes 24.
[0010] Each clamp half 18 is formed in a single piece.
In some embodiments, clamp halves 18 are stamped
from sheet metal. Clamp halves 18 fit together such that
bolt tabs 22 of each clamp half 18 meet, and straight
sides 20 form a regular polygon. In the depicted embodiment, polygonal clamp 12 has eight straight sides 20
(four to each clamp half 18), although other embodiments
may use other numbers of sides (e.g. hexagonal or decagonal clamps). In some embodiments, clamp halves
12 are substantially identical pieces for manufacturing
efficiency. In other embodiments, clamp halves 12 may
exhibit differences such as different threading at bolt
holes 24 or different gussets or tuning holes 34, as described below.
[0011] Fasteners 16, which may for instance be screws
or bolts, pass through bolt holes 24 to secure top half
18a to bottom half 18b, clamping polygonal clamp 12
about duct D. Duct D is a rigid duct, such as found in an
aircraft air system. Duct D may be formed of a non-rusting
metal such aluminum or stainless steel. As depicted in
FIG. 1, one fastener 16 has been inserted, while another
has not. In some embodiments fasteners 16 may include
both a bolt and a nut, as shown; in other embodiments,
fasteners 16 may be screws which thread directly into
clamp halves 18. When polygonal clamp 12 is closed,
each straight side 20 abuts duct D at a tangent point tp,
as shown. Each tangent point tp is located at the center
of a straight side 20. Straight sides 20 may bow slightly
about tangent points tp when in contact with duct D. This
bowing produces a spring force which increases the
clamping strength of polygonal clamp 12 by increasing
the force exerted by straight sides 20 on duct D at tangent
points tp. In this way, polygonal clamp 12 is able to provide a tight clamp without a conventional clamp pad. Polygonal clamp 12 is clamped about duct D by arranging
clamp halves 18 around duct D and tightly securing fastener 16 through bolt holes 24 of tabs 22.
[0012] Polygonal clamp 12 is connected to a support
structure such as a case or wall (not shown) via mounting
pieces 14, as described below with respect to FIGs. 2
and 3. Each mounting piece 14 is an elongated arm
formed from a single piece. In some embodiments,
mounting pieces 14 are stamped from sheet metal. In
the embodiment depicted in FIG. 1, mounting pieces 14
are formed in one piece with clamp half 18b. In other
embodiments, mounting pieces 14 may be formed separately and affixed to polygonal clamp 12 by bolts or
screws, welds, or other conventional attachment mechanisms. In some embodiments, fasteners 16 may attach
mounting pieces 14 to polygonal clamp 12, in additional
to securing clamp halves 18 together. Mounting pieces
14 are constructed with features such as flanges, gussets, and holes to restrain duct D with required or desired
stiffness along relevant axes, as described below with
EP 2 592 320 A1
respect to FIGs. 2A and 2B.
[0013] Polygonal clamp 12 and mounting piece 14 together provide a low-cost, high-strength, low-weight
mechanism for securing duct D against vibration or translation, particularly along axes against which mounting
piece 14 is strengthened.
[0014] FIGs. 2A and 2B are perspective views of duct
clamp assembly 10. FIG. 2A is an exploded view of duct
clamp assembly 10, while FIG. 2B is an unexploded view
of the same. Duct clamp assembly 10 comprises polygonal clamp 12, mounting pieces 14, and fasteners 16.
Polygonal clamp 12 is formed of two clamp halves 18,
each having a plurality of straight sides 20, and two bolt
tabs 22 with bolt holes 24. Each mounting pieces 14 has
piece body 26, clamp connection point 28, structural attachment location 30, and ribs or flanges 32. Polygonal
clamp 12 and mounting pieces 14 may both have a plurality of gussets or tuning holes 34.
[0015] As described above with respect to FIG. 1, fasteners 16 secure clamp halves 18 together to clamp duct
D. Mounting pieces 14 extend from polygonal clamp 12
to a case or wall to secure duct D against translation or
vibration. Each mounting piece 14 is attached to at least
one clamp half 18 at clamp connection point 28. As depicted, mounting pieces 14 are stamped sheet metal extensions of one clamp half 18, such that clamp connection
point 28 is a strip of shared sheet metal joining clamp
half 18 with mounting piece 14. In other embodiments,
mounting pieces 14 are separate components welded or
bolted to at least one clamp half 18 at clamp connection
point 28 (see FIG. 3). Each mounting pieces 14 attaches
to a flange, boss, or similar element of a support structure
such as a case or wall at structural attachment locations
30. As shown, structural attachment locations 30 are flat
plates with bolt holes for screwing or bolting mounting
pieces 14 to said flange or boss. In other embodiments,
structural attachment locations 30 may be weld locations,
secondary clamps, or other features which allow mounting pieces 14 to be affixed to a support structure.
[0016] Mounting pieces 14 must support the weight of
any duct held by polygonal clamp 12. Some degree of
flexibility may be desirable in mounting pieces 14, to allow
for slight duct movements. In many cases, however,
mounting pieces 14 must restrain ducts against translation and vibration. Where directions of vibration or translation are known, mounting pieces 14 can be tuned to
provide greater stiffness in these directions. Ribs or flanges 32 are portions of each mounting piece 14 which extend from and are angled relative to body 26 of mounting
piece 14. As shown, ribs or flanges 32 increase the stiffness of mounting pieces 14 along vibration axis VA, helping to limit duct translation or vibration along that axis.
Other embodiments of mounting pieces 14 may be constructed according to the same principles, to restrict duct
movement in other or additional dimensions (see, e.g.
FIG. 3, below). The stiffness provided by ribs or flanges
32 is a function of the angle of each rib or flange 32 relative
to piece body 26, with the greater stiffness where rib or
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
flange 32 is close to perpendicular to piece body 26, and
comparatively little stiffness where rib or flange 32 is only
slightly angled relative to piece body 26. The stiffness of
mounting pieces 14 can thus be tuned along desired axes
by varying the angles of ribs or flanges 32. Stiffness can
be further tuned by adding holes or gussets 34 to the
piece body 26, as shown. Gussets provide increased
stiffness, while holes decrease stiffness, as is well known
in the art. Holes or gussets 34 may also be added to
polygonal clamp 12 to increase clamp stiffness.
[0017] FIG. 3 is a perspective view of duct clamp assembly 10B, an alternative embodiment of duct clamp
assembly 10 of FIGs 2A and 2B. Duct clamp assembly
10B includes polygonal clamp 12B, mounting piece 14B,
and fasteners 16B. Polygonal clamp 12B is substantially
identical to polygonal clamp 12 (see FIGs. 2A and 2B),
and is comprised of two halves joined together by fasteners 16B. Although polygonal clamp 12B is depicted
as a decagonal clamp, polygonal clamp 12B may have
any suitable number of regular sides, including eight (see
polygonal clamp 12 in FIGs 1, 2A and 2B).
[0018] Mounting piece 14B has piece body 26B, clamp
connection points 28B, structural attachment locations
30B, and ribs or flanges 32B. Where duct clamp assembly 10 comprised two mounting pieces 14 formed as integral extensions of clamp half 18b, duct clamp assembly
10B comprises a single separate mounting piece 14B
which is separately attached to polygonal clamp 12 clamp
connection points 28B. Body piece 26B abuts at least a
portion of polygonal clamp 12. In the depicted embodiment, clamp connection points 28B are welds along the
interface of mounting piece 14B and polygonal clamp
12B. In alternative embodiments, clamp connection
points 28B may be bolts or other attachment mechanisms
which affix mounting piece 14B to polygonal clamp 12B.
Structural attachment locations 30B are flat plates fastenable to an adjacent support structure such as a case or
wall. In the depicted embodiment, structural attachment
locations 30B feature bolt holes for screws or bolts. In
other embodiments, structural attachment locations 30B
may be welded directly to the adjacent support structure.
[0019] Mounting piece 14B includes ribs or flanges
32B, which extend from body piece 26B to structural attachment locations 30B. In some embodiments, ribs or
flanges 32B may be welded or otherwise attached to
structural attachment locations 30B, to further strengthen
mounting piece 14B. Ribs or flanges 32B increase the
rigidity of duct clamp assembly 10B, retaining duct D (see
FIG. 1) against translation and vibration. Ribs or flanges
32B provide greater rigidity than ribs or flanges 32, restraining duct D against motion in all directions.
[0020] The duct assemblies of the present invention
retain duct D against translation and vibration along at
least one axis. Different mounting pieces (e.g. 14, 14B)
provide different degrees of retention stiffness in different
directions. These duct assemblies (e.g. 10, 10B) are
formed of stamped sheet metal, and are therefore both
light and inexpensive. Polygonal clamps (e.g. 10, 10B)
EP 2 592 320 A1
provide strong clamping without need for clamp pads or
complex clamping rings.
[0021] While the invention has been described with reference to an exemplary embodiment(s), it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes may
be made and equivalents may be substituted for elements thereof without departing from the scope of the
invention, which is defined by the claims. In addition,
many modifications may be made to adapt a particular
situation or material to the teachings of the invention without departing from the essential scope thereof. Therefore, it is intended that the invention not be limited to the
particular embodiment(s) disclosed, but that the invention will include all embodiments falling within the scope
of the appended claims.
9.
The duct clamp assembly of any preceding claim,
wherein the mounting piece includes strengthening
flanges or ribs (32,32B) selected to provide the
mounting piece with rigidity along at least one axis
of vibrational (VA) or translational concern.
10
10. The duct clamp assembly of any preceding claim,
wherein at least one of the mounting piece or the
polygonal clamp has holes or gussets (34) selected
to increase or decrease rigidity by a desired amount.
11. A duct assembly comprising the duct clamp assembly of any preceding claim, further comprising a rigid
cylindrical duct (D), and wherein:
15
Claims
1.
A duct clamp assembly (10,10B) comprising:
a polygonal clamp (12,12B) formed from two
clamp halves (18), each having a plurality of flat
sides (20) constructed to bow in contact with a
duct (D);
a fastener (16,16B) which holds the two clamp
halves together; and
a mounting piece (14,14B) attached to the polygonal clamp and configured to attach to a support structure.
2.
20
25
30
The duct clamp assembly of claim 1, wherein the
polygonal clamp and the mounting piece are formed
from stamped sheet metal.
the two clamp halves comprise a first polygonal
clamp half (18a) having a first plurality of flat
sides (20) and a first bolt tab (22); and a second
polygonal clamp half (18b) having a second plurality of flat sides and a second bolt tab (22);
the fastener is configured to secure the first bolt
tab to the second bolt tab, thereby clamping the
first polygonal clamp half and the second polygonal clamp half about the rigid cylindrical duct,
such that each of the first plurality of flat sides
and the second plurality of flat sides bows outward in contact with the rigid cylindrical duct; and
the mounting piece is configured to affix at least
one of the first polygonal clamp half and the second polygonal clamp half to the support structure.
12. The duct assembly of claim 11, wherein the mounting
piece further comprises:
35
3.
The duct clamp assembly of claim 2, wherein one
clamp half and the mounting piece are formed from
a single continuous piece of stamped sheet metal.
4.
The duct clamp assembly of claim 1 or 2, wherein
the polygonal clamp and the mounting piece are attached by a weld.
5.
The duct clamp assembly of claim 1 or 2, wherein
the polygonal clamp and the mounting piece are attached by a threaded fastener, and preferably
wherein the threaded fastener is the fastener which
holds the two clamp halves together.
6.
The duct clamp assembly of any preceding claim,
wherein the fastener is a bolt secured by a nut.
7.
The duct clamp assembly of any of claims 1 to 5,
wherein the fastener is a screw threaded into at least
one clamp half.
8.
40
45
50
55
The duct clamp assembly of any preceding claim,
wherein the polygonal clamp has 8 or 10 sides.
a structural attachment location (30,30B) configured to attach to the support structure;
a clamp connection point which (28,28B) attaches to the first polygonal clamp half; and
a body (26,26B) which extends from the structural attachment location to the clamp connection point.
13. The duct assembly of claim 12, wherein the rib or
flange is welded to the structural attachment location.
14. The duct assembly of claim 12 or 13, wherein the
structural attachment location is a flat plate with a
bolt hole for screwing or bolting the mounting piece
to the support structure.
15. The duct assembly of any of claims 11 to 14, wherein
each flat side from the first and second pluralities of
flat sides contacts the rigid cylindrical duct at a tangent point (tp) located at the center of the flat side.
EP 2 592 320 A1
EP 2 592 320 A1
EP 2 592 320 A1
EP 2 592 320 A1
EP 2 592 320 A1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- I Like To Draw Cars and Trucks PDFDokumen35 halamanI Like To Draw Cars and Trucks PDFdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- HVAC Procedures Forms ManualDokumen279 halamanHVAC Procedures Forms Manualgeneroso67100% (12)
- On Blu-Ray Combo Pack and Disney HD Digital October 2Dokumen17 halamanOn Blu-Ray Combo Pack and Disney HD Digital October 2Juliya AyobBelum ada peringkat
- On Blu-Ray Combo Pack and Disney HD Digital October 2Dokumen17 halamanOn Blu-Ray Combo Pack and Disney HD Digital October 2Juliya AyobBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 ConnectionDokumen30 halamanChapter 6 ConnectionIvy SeahBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Shop Trade Secrets: Second EditionDari EverandMachine Shop Trade Secrets: Second EditionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (7)
- Ci3503crsi - Column Tie ConfigurationsDokumen7 halamanCi3503crsi - Column Tie ConfigurationsNono_geotecBelum ada peringkat
- MS For Mechanical Piping System Installation WorkDokumen22 halamanMS For Mechanical Piping System Installation WorkUmut Eren63% (8)
- Analyzing Taper Fits For ManufacturingDokumen7 halamanAnalyzing Taper Fits For Manufacturingsalgado_24Belum ada peringkat
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsDari EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Panel - S MCB - Cable Size Calculation (1.1.19)Dokumen29 halamanElectrical Panel - S MCB - Cable Size Calculation (1.1.19)Nikhilesh PatelBelum ada peringkat
- M2 CV ST D 002 (R0)Dokumen13 halamanM2 CV ST D 002 (R0)ksshashidhar100% (1)
- Bolted Joints-ExamplesDokumen14 halamanBolted Joints-Examplesmandregomes100% (1)
- Bonded Slab Post-Tension SystemDokumen7 halamanBonded Slab Post-Tension SystemMaris BauersBelum ada peringkat
- Minimum Thickness of MetalDokumen15 halamanMinimum Thickness of MetalswatiBelum ada peringkat
- Design For Snapfit Revi-10Dokumen26 halamanDesign For Snapfit Revi-10Arasu Pandian100% (1)
- All-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceDari EverandAll-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenancePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- BS 476 24 PDFDokumen29 halamanBS 476 24 PDFJIDUBelum ada peringkat
- MovinCool Spot Cooling CatalogueDokumen16 halamanMovinCool Spot Cooling CatalogueKhizerBelum ada peringkat
- ADDC Specs For LV - MV CablesDokumen39 halamanADDC Specs For LV - MV Cableskarviz100% (1)
- Bs-Iso 12241Dokumen61 halamanBs-Iso 12241juninho7050% (2)
- (Heating Ventilation & Air Conditioning System) : Career Scope Course HighlightsDokumen2 halaman(Heating Ventilation & Air Conditioning System) : Career Scope Course HighlightsMilind KshirsagarBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Fan Systems and AuditDokumen72 halaman4 - Fan Systems and AuditTamer Fathy100% (5)
- Chicken Operations Manual - Multi Stage PDFDokumen198 halamanChicken Operations Manual - Multi Stage PDFWinson90% (10)
- Elevator Guide Rails Installation and AlignmentDokumen12 halamanElevator Guide Rails Installation and Alignmentdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Types of DampersDokumen7 halamanTypes of DampersOA Aoo0% (1)
- Ventilation Design for Small WorkshopDokumen4 halamanVentilation Design for Small WorkshoplaichmailBelum ada peringkat
- TEPZZ - 4 885B - T: European Patent SpecificationDokumen10 halamanTEPZZ - 4 885B - T: European Patent SpecificationshamsBelum ada peringkat
- Bus Bar k0186 MC 10 Busbar Systems 2013 IinfoDokumen47 halamanBus Bar k0186 MC 10 Busbar Systems 2013 IinfoManish ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- Bar BendingDokumen142 halamanBar Bendingjaffna100% (4)
- Manual Alup VarioDokumen52 halamanManual Alup VarioMauricio Rúa Cáceres100% (1)
- Tube Saport PDFDokumen4 halamanTube Saport PDFjr110livecomBelum ada peringkat
- Cement BasketDokumen4 halamanCement Basketराजकुमार यादवBelum ada peringkat
- European Patent Specification F01D 11/00: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)Dokumen10 halamanEuropean Patent Specification F01D 11/00: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)shamsBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For Collect DesignDokumen24 halamanGuidelines For Collect DesignArun LeleBelum ada peringkat
- Uhlted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 4,579,373: Neal Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1986Dokumen5 halamanUhlted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 4,579,373: Neal Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1986daniel_iosif_glBelum ada peringkat
- 915 9000 990 112 /// 325 Aaa 3002 295 022 225 464 710 965 150 DWWDokumen15 halaman915 9000 990 112 /// 325 Aaa 3002 295 022 225 464 710 965 150 DWWMetin MehelBelum ada peringkat
- United States Patent (191: RandallDokumen6 halamanUnited States Patent (191: RandallluiscremaschiBelum ada peringkat
- Pipe Sealing PATENTDokumen23 halamanPipe Sealing PATENTDaniel InemughaBelum ada peringkat
- Method of Increasing Strength of Welded Slat Assembly for Inflatable PackersDokumen6 halamanMethod of Increasing Strength of Welded Slat Assembly for Inflatable Packersmohammadreza91Belum ada peringkat
- Umted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,642,778: Gentry (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 1, 1997Dokumen15 halamanUmted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,642,778: Gentry (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 1, 1997aegosmithBelum ada peringkat
- Tài liệu5Dokumen12 halamanTài liệu5Hoàng ĐứcBelum ada peringkat
- Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,430,626 B1Dokumen9 halamanUlllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,430,626 B1shamsBelum ada peringkat
- Dresser Industries, Inc. v. The United States, R. H. Baker & Company, Inc., Graver Tank and Manufacturing Co., and Western-Knapp Engineering Company, Third-Party, 432 F.2d 787, 3rd Cir. (1970)Dokumen21 halamanDresser Industries, Inc. v. The United States, R. H. Baker & Company, Inc., Graver Tank and Manufacturing Co., and Western-Knapp Engineering Company, Third-Party, 432 F.2d 787, 3rd Cir. (1970)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- United States Patent: Sultan Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008Dokumen7 halamanUnited States Patent: Sultan Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008aqil_shamsiBelum ada peringkat
- Siled Sept. 8, 1966: T, N. NccomeDokumen5 halamanSiled Sept. 8, 1966: T, N. NccomeliBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Riveted JointDokumen12 halamanDesign of Riveted JointYogesh DandekarBelum ada peringkat
- United States PatentDokumen5 halamanUnited States PatentJagannathan ArumugamBelum ada peringkat
- Barrel CouplingsDokumen16 halamanBarrel Couplingsamariei_niculinaBelum ada peringkat
- Inflatable Packer Reinforcement MethodDokumen5 halamanInflatable Packer Reinforcement Methodmohammadreza91Belum ada peringkat
- Us20140196515 PDFDokumen23 halamanUs20140196515 PDFnangkarak8201Belum ada peringkat
- TEPZZ 6 Z956A - T: European Patent ApplicationDokumen10 halamanTEPZZ 6 Z956A - T: European Patent ApplicationDumitru ScortanuBelum ada peringkat
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0153034 A1Dokumen25 halamanPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0153034 A1Paballo MontleBelum ada peringkat
- Method for constructing and assembling a multiple valve unitDokumen4 halamanMethod for constructing and assembling a multiple valve unitscibduser001Belum ada peringkat
- Elemenst of Union in DesignDokumen4 halamanElemenst of Union in Designcal2_uniBelum ada peringkat
- Dec. 24, 1963 A. K. Kline 3,115,186: Gln/I301. '6 Bym Fda LDokumen5 halamanDec. 24, 1963 A. K. Kline 3,115,186: Gln/I301. '6 Bym Fda LcheesewizzBelum ada peringkat
- Glulam Handbook-02 PDFDokumen90 halamanGlulam Handbook-02 PDFBanuta GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Pinned Base Plates 7Dokumen1 halamanPinned Base Plates 7pawkomBelum ada peringkat
- Development Length: CE A433 - RC Design T. Bart Quimby, P.E., PH.DDokumen22 halamanDevelopment Length: CE A433 - RC Design T. Bart Quimby, P.E., PH.DJatinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Riveted Joints: StructureDokumen10 halamanUnit 4 Riveted Joints: StructureDilip ChavdaBelum ada peringkat
- Us 5360355Dokumen6 halamanUs 5360355kimscribd66Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 3 - Strength Calculation and Dimensioning of JointsDokumen24 halamanChapter - 3 - Strength Calculation and Dimensioning of Jointsfedila jemalBelum ada peringkat
- FGR Eadips Ebook 04.2011 10 ChapterDokumen10 halamanFGR Eadips Ebook 04.2011 10 ChapterIvor VlahovićBelum ada peringkat
- United States Patent (19) : Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentDokumen10 halamanUnited States Patent (19) : Patent Number: (45) Date of PatentMichael JordanBelum ada peringkat
- Tension MemberDokumen35 halamanTension MemberLUGHANO NGAJILOBelum ada peringkat
- TEPZZ - 4 - 45 A - T: European Patent ApplicationDokumen10 halamanTEPZZ - 4 - 45 A - T: European Patent ApplicationdaveBelum ada peringkat
- Modular Hydraulic System ComponentsDokumen12 halamanModular Hydraulic System ComponentsharisupayBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6 Shaft Coupling and Pipe Joints: StructureDokumen11 halamanUnit 6 Shaft Coupling and Pipe Joints: StructureNandini BiswasBelum ada peringkat
- Socket and Spigot JointDokumen5 halamanSocket and Spigot Jointsarath.kumarnmk930Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen30 halamanUnit 1balachandran143Belum ada peringkat
- Equipment Design Chapter 3Dokumen30 halamanEquipment Design Chapter 3Miguel Magat JovesBelum ada peringkat
- Drilling constant curvature well boresDokumen7 halamanDrilling constant curvature well boresandreBelum ada peringkat
- Buckstay SystemDokumen15 halamanBuckstay SystemAssistente Engenharia HNRBelum ada peringkat
- Cotter JointDokumen7 halamanCotter Jointsarath.kumarnmk930Belum ada peringkat
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 441, June 14, 1884.Dari EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 441, June 14, 1884.Belum ada peringkat
- Vinata member schedule working-off systemDokumen3 halamanVinata member schedule working-off systemdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Selection of 3P-TPN-4P MCB & Distribution BoardDokumen4 halamanSelection of 3P-TPN-4P MCB & Distribution Boarddangtuan27100% (1)
- Disney Coloring BookDokumen900 halamanDisney Coloring BookGabriela95% (21)
- Tu Dien Cau DuongDokumen132 halamanTu Dien Cau DuongNguyên HạnhBelum ada peringkat
- Cleanroom Design in 10 Easy StepsDokumen8 halamanCleanroom Design in 10 Easy StepsEdgar Alejandro Barajas RuizBelum ada peringkat
- WHO TRS-970-46th-2012Dokumen250 halamanWHO TRS-970-46th-2012shonuneenu100% (1)
- Lift Machine Room Code PDFDokumen19 halamanLift Machine Room Code PDFAvinash Pathania100% (1)
- Kids Coloring Dancers Coloring BookDokumen34 halamanKids Coloring Dancers Coloring Bookdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Material Safety Data Sheet Product Name: Pva Adhesive PRODUCT CODE: 8711, 8712Dokumen4 halamanMaterial Safety Data Sheet Product Name: Pva Adhesive PRODUCT CODE: 8711, 8712dangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- FactoryDokumen5 halamanFactorySumera AslamBelum ada peringkat
- Catalog Thang Mang Cap enDokumen20 halamanCatalog Thang Mang Cap endangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Coloring BookDokumen10 halamanColoring Bookdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- BW11 Introduction Catalogue - TCBMDokumen2 halamanBW11 Introduction Catalogue - TCBMdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Bs 7671 Bristol Cibse Dec 2012Dokumen41 halamanBs 7671 Bristol Cibse Dec 2012dangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Thesis For The Degree of Licentiate of EngineeringDokumen155 halamanThesis For The Degree of Licentiate of Engineeringdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- BLD Permit Insp Checklist PipelineInspectionDokumen3 halamanBLD Permit Insp Checklist PipelineInspectionMadhan RamamoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- Method Statement: Site Set Up: Compound, Parking & Material StorageDokumen17 halamanMethod Statement: Site Set Up: Compound, Parking & Material Storagedangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Method Statement For Test and Inspection of An Existing Lightning Protection/Earthing SystemDokumen4 halamanMethod Statement For Test and Inspection of An Existing Lightning Protection/Earthing Systemdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Site Setup Plan - Hatton Road, CroydonDokumen2 halamanSite Setup Plan - Hatton Road, Croydondangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- 01 CPT DOT PresentationDokumen30 halaman01 CPT DOT PresentationJamie MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Dampers: KD-T Non Return DamperDokumen2 halamanDampers: KD-T Non Return Damperdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Cable Tray & Trunking ModelDokumen1 halamanCable Tray & Trunking ModelmanimaranguruBelum ada peringkat
- 2013 PW Catalog Spreads-Metallicladder-SsDokumen3 halaman2013 PW Catalog Spreads-Metallicladder-Ssdangtuan27Belum ada peringkat
- Hvac Survey & Calculation Report: Site NameDokumen17 halamanHvac Survey & Calculation Report: Site NameMehdi Hasan TararBelum ada peringkat
- Erelis 150: General DataDokumen22 halamanErelis 150: General DataJun TanBelum ada peringkat
- Dryer: User ManualDokumen120 halamanDryer: User ManualCarlosBelum ada peringkat
- Signature Series Detector Application BulletinDokumen36 halamanSignature Series Detector Application BulletinShahina MirashBelum ada peringkat
- AlstomDokumen68 halamanAlstomMauricio AguilonBelum ada peringkat
- MEP Bill of QuantitiesDokumen70 halamanMEP Bill of Quantitiessaifhorani95Belum ada peringkat
- Sizing Guide: Type B Gas Vent All Fuel ChimneyDokumen32 halamanSizing Guide: Type B Gas Vent All Fuel ChimneyJuan PabloBelum ada peringkat
- PCVVN1520 VRV4SDokumen36 halamanPCVVN1520 VRV4SPepe PradaBelum ada peringkat
- HVAC ASSIGNMENT - HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENTSDokumen29 halamanHVAC ASSIGNMENT - HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENTSNeerajaBelum ada peringkat
- OSHJ-GL-12 Local Exhaust Ventilation Version 1 EnglishDokumen17 halamanOSHJ-GL-12 Local Exhaust Ventilation Version 1 Englishsajin100% (1)
- C4 Specific PDFDokumen44 halamanC4 Specific PDFNadim JilaniBelum ada peringkat
- 3M HT-401 / HT-402 Visors: Care and MaintenanceDokumen1 halaman3M HT-401 / HT-402 Visors: Care and MaintenanceMichael TadrosBelum ada peringkat
- Code of Practice For The Installation & Inspection of Fire Resisting Duct SystemsDokumen23 halamanCode of Practice For The Installation & Inspection of Fire Resisting Duct SystemsNguyen Trung KienBelum ada peringkat
- Air Conditioning Duct Design-Lecture 38Dokumen20 halamanAir Conditioning Duct Design-Lecture 38Mrityunjay TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Amerex: Design, Installation, Maintenance & Recharge Manual NO. 20150 Restaurant Fire Suppression SystemDokumen186 halamanAmerex: Design, Installation, Maintenance & Recharge Manual NO. 20150 Restaurant Fire Suppression SystemBany Isai Villar QuispeBelum ada peringkat
- EagleBurgmann - KE-Flex Expansion Joints - ENDokumen4 halamanEagleBurgmann - KE-Flex Expansion Joints - ENANSHORI PAGANBelum ada peringkat
- Patents Absorption and drying towersDokumen6 halamanPatents Absorption and drying towerspavijayaBelum ada peringkat
- 7ha Constructability Pitch ExternalDokumen51 halaman7ha Constructability Pitch ExternalSofianeLeksir0% (1)
- Mat Cscec 12 Me HD 0072 04Dokumen270 halamanMat Cscec 12 Me HD 0072 04Mostafa ElsammanBelum ada peringkat
- English Lectrobar 26may2021Dokumen3 halamanEnglish Lectrobar 26may2021SCHAEFFER CAPITAL ADVISORSBelum ada peringkat