Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4
Diunggah oleh
phoenixchiaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4
Diunggah oleh
phoenixchiaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Yearly Lesson Plan
FORM FOUR
ENGINEERING DRAWING
YEARLY LESSON PLAN
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Yearly Lesson Plan
UNIT 1 : INTRODUCTION
LEARNING AREA
1.1
1.2
Evolution of
drawing, system
and standardization
Definition and
importance of
Engineering
Drawing
a.
Compariso
n of
Engineering
Drawing,
illustration and
LEARNING OUTCOMES
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Level 1
Narrate the
development of
Engineering
Drawing.
Explain the
current development
of Computer -Aided
Drafting (CAD).
Identify the
classification of the
projection systems.
Identify the
importance of
standardization.
State the
agencies related to
standardization.
Gather charts/graphic material
about engineering
Prepare material to explain the
current development of Computer
Aided Drafting (CAD).
Prepare the classification of the
projection systems charts.
Provide examples to expose
students the importance of
standardization and its related
agencies.
Discuss career prospects in
Engineering Drawing.
Students observe and compare
CAD on CAD drawing
In Groups, students discuss the
importance of standardization
and its related agencies.
Prepare charts to define
engineering drawing and its
relations.
Gather and exhibit samples of
Engineering Drawing, Illustration
and Fine-Arts.
Gather captions of news
papers/magazines related to
engineering drawing
Compare Engineering Drawing,
Illustration and Fine-Art
Level 1
Define
Engineering
Drawing.
Relate the
importance of
Engineering
Drawing as a basis
for higher learning in
the fields of
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
WEEK / DATE
Resources:
1.
Samples of Engineering
Drawing, CAD, illustration and
fine-arts.
2.
Drawing equipment and
materials
Resources:
Samples of Engineering Drawing,
illustration and fine-arts.
Yearly Lesson Plan
fine-arts
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OUTCOMES
1.3
Types of
Engineering
Drawing
a.
b.
Geometrical
Drawing
i.
Plane
Geometry
ii.
Solid
Geometry
Related
Drawings
i.
Mechanical
Drawing
ii.
Building
Drawing
iii.
Piping Drawing
iv.
engineering.
Relate
engineering drawing
in career
opportunity.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Differentiate
between
engineering
drawing, illustration
and fine- arts.
Level 1
Explain the
types of Engineering
Drawing.
Differentiate
between
Geometrical
Drawing and
Related Drawing.
Explain the
Geometrical
Drawing and
Related Drawing.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Prepare Fraction Charts of plane
geometry and solid geometry.
Distribute and explain samples of
geometrical and other related
drawings.
Compare Plane Geometry
drawings and Solid Geometry
Drawings.
Link the related drawings to
engineering.
Resources:
Fraction chart of Engineering
Drawing
Yearly Lesson Plan
Electrical
Drawing
v.
Electronic
Drawing
LEARNING AREA
1.4
Equipment and
materials
a.
Use, maintenance
and safety of
drawing
equipment and
materials
1.5
Setting up of
drawing paper
a.
Placing of paper on
drawing board
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify drawing
equipment and
related materials.
Practise proper
use of equipment
and drawing
materials.
Use appropriate
and safe
equipments and
drawing materials.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Demonstrate and introduce actual
drawing equipment and materials.
Explain proper application and
maintenance of equipments.
Prepare a simple paper work of
drawing complete with borders and
title block.
Demonstrate how to divide
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
WEEK / DATE
Students name the equipment.
Using/handling the equipment
/tools correctly
Construct horizontal line using
T-Square.
Construct vertical and inclined
lines using set square.
Construct curve and arc using
compass and French curve.
Erase unnecessary text and
lines using eraser shield.
Resources:
Drawing equipments and
materials.
Level 1
Setup drawing paper
on the drawing
board.
Prepare border lines
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Place paper on drawing board.
Draw border and title block
areas.
Plan drawing layout.
4
Yearly Lesson Plan
and title block.
b.
Preparation of
border lines
and title block
Plan the drawing
position on the
drawing paper.
drawing paper with borders, title
blocks and drawing layout
accurately.
c.
Planning of
drawing layout
LEARNING AREA
1.6
Career
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify related
career to
Engineering
Drawing.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Prepare video recordings, career
pamphlets and brochures that
exemplify related career.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Watch video recordings.
Gather captions of news
papers/magazines related to
career opportunity.
Resources:
Career pamphlet and brochure.
Yearly Lesson Plan
UNIT 2 : SKETCHING
LEARNING AREA
2.1
Principles of
Sketching
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Explain
principles of
sketching.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Explain principles of
sketching correctly.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Students identify principles
of Sketching correctly.
Resources:
1. Grid paper.
2. Samples of sketches.
2.2
Sketching
Techniques
a.
Straight
lines
b.
Circles, arcs
and curves
c.
Shapes
Level 1
Sketch straight
lines, circles, arcs,
curves and shapes
correctly.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Explain the technique of
sketching correctly.
Demonstrate methods of
sketching
- straight line
- circle
- arc line
- curve line
- show the sketching on
blank and grid paper
Sketch on a grid paper.
Sketch on a blank paper.
Activities:
Sketching on grid paper.
Techniques:
1. Holding a pencil.
2. Making approximate
proportions
6
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
2.3
2.4
Techniques in
Determining
Proportion
Types of Sketches
a.
Orthogr
aphic
Projection
b.
Isometr
ic
c.
Obliqu
e
d.
Perspe
ctive
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Determine
sketching
proportions
correctly.
Level 1
Identify types of
sketches.
Ortho
graphic
Projection
Isome
tric
Obliqu
e
Persp
ective
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Demonstrate methods of
making estimation of
proportional diagram
correctly.
Prepare samples of full size
sketching and proportion.
Prepare sketching samples
- Orthographic Projection
- Isometric, Oblique and
Perspectives
Explain and distribute
sketching samples of
Orthographic Projection
Isometric, Oblique and
Perspectives
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Estimate proportional
sketching diagram.
Sketch straight lines,
circle, arc, curve and
shapes.
Identify samples and give
explanation about
sketching.
WEEK / DATE
Yearly Lesson Plan
UNIT 3 : LINES AND LETTERINGS
LEARNING AREA
3.1
Alphabet of Lines
a. Object line
b. Hidden line
c. Centre line
d. Border line
e. Constructio
n line
f. Guide line
g. Dimension
al line
h. Sectioning
line
i. Extension
line
j. Cutting
plane
k. Projection
line
l. Phantom
line
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Identify alphabet of lines and
their usages
Identify alphabet
of lines and their
application
in
Engineering
Drawing
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
3.2
Characteristics of
Alphabet of
Lines
a. Shapes
b. Line
darkness
c. Application
3.3
Types of lines
a. Vertical
lines
b. Horizontal
lines
c. Inclined
lines
d. Parallel
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify
and
apply
the
characteristics
of alphabet of
lines correctly.
Level 1
Draw
parallel
lines
(vertical,
horizontal,
inclined
and
perpendicular
lines)
with
uniform line
Darkness and gauge
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Prepare sample charts or
transparencies
with
alphabets
of
lines
characteristics
Explain and demonstrate
steps to construct alphabet
of lines accurately
Practice draw the different
accurately basing on the
following characteristics
- Shape
- Darkness
- Application
Prepare samples charts
or transparencies on type
of lines
Construct
and
demonstrate
correct
methods to draw straight
lines (vertical, horizontal,
Use T-Square to construct
vertical lines and inclined lines
WEEK / DATE
Use T-Square and set square to
construct Horizontal lines
Use T-Square and se square to
construct perpendicular lines
9
Yearly Lesson Plan
lines
e. Perpendicu
lar lines
using
appropriate
drawing equipments.
LEARNING AREA
3.4
Types of Lettering
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify shapes
of letters
Standard
upright
lettering
Standard
lettering
3.5
Techniques of
Lettering
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Use T-Square and set square to
construct inclined lines
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
inclined
Write letters with
correct lettering
technique using
guidelines
Apply
inclined
and
perpendicular)
with
uniform darkness and
thickness using standard
drawing instruments.
Prepare transparencies or
charts to demonstrate type
of lines and their usages
Explain and demonstrate
type of lines and their
usages in Engineering
Drawings
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Prepare
examples
of
charts or transparencies
on types of letterings
Explain shapes of upright
lettering
and
inclined
letterings
Using
guide line to
produce standard lettering
to apply correct technique
to
produce
standard
letterings
Follow standard lettering guide
lines using guide lines to
produce standard lettering
Use
correct
technique
to
10
Yearly Lesson Plan
appropriate
spacing between
letters
and
between words.
3.6
Tracing and Inking
a.
Instrument
and Inking
I. tracing paper
ii.
Technical
pen
b.
Tracing
and
inking
methods
produce
sizes
standard
lettering
Level 1
Identify
instrument and
materials.
Explain correct
tracing
and
inking methods.
UNIT 6 : ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION
LEARNING AREA
6.1
Concepts and
Symbols of First and
Third Angle
Projections
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Explain the concepts
and symbols of first
and third angle
projections.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Demonstrate and explain first
and third angles projection for
solid models on chart/
transparencies.
Demonstrate and explain
symbols for first and third
angles projection.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Compare and construct
concepts and symbols of
first and third angles
projection.
Draw first and third angles
projection symbols.
Resources:
Related solid models.
Activities:
Draw Orthographic Projection
of simple solid.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
11
Yearly Lesson Plan
6.
2
6.3
Principle of
Quadrants in the
First and Third Angle
Projections
Level 2
Explain the principle of
quadrants in the first
and third angle
projections.
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Construction of
Third Angle
Orthographic
Projection
Level 1
Construct third angle
orthographic
projection of
geometrical solids
as follows:
solid
flat surface only
solid
inclined surface
solid
circle surface
Level 2
Demonstrate on transparencies
the principles of quadrant for
first and third angles projection.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Demonstrate method of
constructing flat, inclined and
circle surface in third angles
orthographic projection.
Construct and demonstrate
orthographic projection of
geometrical solid on oblique
and solid curve surfaces.
Compare first and third
angles projection principle.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Construct flat, inclined and
circle surface drawings by
orthographic projection.
Construct oblique and
curve surfaces by
orthographic projection.
Construct third angle
orthographic
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
12
Yearly Lesson Plan
projection of
geometrical solids
as follows:
Solid with oblique
surface
Solid with curve
surface
6.4
Dimensioning of
Orthographic
Projections
Concept and use of
dimensioning
a.
Components
of dimensioning
b.
Types of
dimension
LEARNING AREA
c.
Techniques
of dimensioning
Level 1
Explain the
concept and
dimensioning in
orthographic
projections:
Unidirectional
system
Aligned system
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Use extension
line dimension line,
arrow head and
leaders according to
standard guidelines
Identify types of
dimension:
size
location
-
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Prepared orthographic
drawing hand-out.
Explain the concepts and
components of dimensions.
Demonstrate and explain
methods of
- unidirectional system
- aligned system
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Compare the unidirectional
system to aligned system
dimensioning.
Dimensioning the
orthographic drawing using:
- unidirectional system
- aligned system
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
13
Yearly Lesson Plan
radius
circle
angle
text
Level 2
Apply
dimensioning
techniques on
Orthographic
Projection Drawing.
6.5
Application of
Orthographic
Projection in
engineering field
Level 1
Apply
orthographic
projection in
engineering fields.
On charts/ graphic materials
demonstrate how orthographic
projection drawing are used in
engineering in Mechanical
drawing, Building drawing and
etc.
In groups students observe
and discuss how
orthographic drawing are
being applied in engineering
.
UNIT 7 : ADDITIONAL VIEWS
LEARNING AREA
7.1
Concepts of
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Identify the concept of
14
Yearly Lesson Plan
Additional Views
7.2
Types of Additional
Views
a.
Auxiliar
y view
b.
Revolv
ed view
LEARNING AREA
7.3
Construction of
Auxiliary Views
Explain the
concepts of
Additional View.
Differentiate
between Additional
View and
Orthographic
Projection.
Level 1
Explain different
types of additional
views
Auxiliary view
Revolved view
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 2
Construct
auxiliary views for
geometrical solid
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Prepare drawing to explain the
concepts of additional views.
additional views.
Relate an orthographic
projection and additional views.
Prepare/collect samples of
additional view and orthographic
projection drawing
Resources:
1.
Orthographic
projection drawing of solid having
inclined surface.
2.
Model of solid
having inclined surface
Explain types of additional views:
- Auxiliary views
- Revolved views
Explain and show the
differentiation between auxiliary
views and revolved views.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Explain and show the methods to
draw auxiliary views of Height,
Width and Depth.
Identify the concepts of
additional views.
Relate an orthographic
projection and additional views.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Draw an auxiliary views of
Height, Width and Depth based
on exercises given
Determine the true length
15
Yearly Lesson Plan
based on :
- auxiliary views
of Height
- auxiliary views
of Width
- auxiliary views
of Depth
7.4
Application of
Auxiliary Views in
engineering field
based on exercises given.
Use of auxiliary
views to determine
- True length
- True angle
- True shape
Level 3
Explain and show the methods to
determine :
True length
True angle
True shape
Use of Auxiliary
views in engineering
fields.
Show charts / transparency the
use of auxiliary views in
engineering fields.
UNIT 8 : ISOMETRIC DRAWING
LEARNING AREA
8.1
Concepts of
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Students draw diagram
16
Yearly Lesson Plan
Isometric Drawing
a.
I
sometric axis
b.
C
haracteristics of
Isometric
Drawing
LEARNING AREA
8.2
Construction of
Isometric Drawing
on Normal Axis
Explain the
concept of
Isometric:
- normal axis
- horizontal axis
- reversed axis
Identify
Isometric Drawing
characteristics:
- isometric line
- non-isometric
line
- angle in
isometric
- circle in
isometric
- curve in
isometric
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Construct
Isometric Drawing of
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Explain concept of isometric
projection.
Explain isometric axes:
- Normal axis
- Longitudinal axis
- Reversed axis
Demonstrate characteristics of
isometric drawing
- Isometric lines
- Non Isometric lines
- Isometric angle
- Isometric circle
- Curves in isometric
- Arcs/circles in isometric
- Isometric planes
- Non isometric planes
related to isometric
projection concept.
Students identify and
differentiate various types of
isometric axis
- Normal/regular axis
- Longitudinal axis
- Reversed axis
Identify isometric drawing
characteristics.
Resources:
1.
Sampl
es of drawings
2.
Model
from various
engineering fields.
Activities:
Draw Isometric Drawing
from Orthographic
Projections.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Demonstrate and describe
methods to construct
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Students draw simple block
using box and frame
17
Yearly Lesson Plan
a.
Box
method
b.
Frame
method
geometrical solid by:
- Box method
- Frame method
Construct
isometric circles
using four-centre
method.
Construct
curves in isometric
plane using
coordinate method.
Construct
Isometric Drawing of
geometrical solid
having surfaces:
- Flat
- Inclined
- Rounded
Level 2
Construct
Isometric Drawing of
geometrical solid
having:
- oblique surface
- curved surface
LEARNING AREA
8.3
Dimensioning of
Isometric Drawing
LEARNING OUTCOMES
isometric drawing by
- Box method
- Frame method
Demonstrate and explain
ways to construct
- Isometric circle/arc using
four centred method.
- Isometric curve using
ordinate method.
Demonstrate and explain
ways to determine position of
isometric drawing from the
angle given.
method.
Students draw isometric
circle/arc using four centred
method.
Students draw using
coordinate method.
Students identify and
determine direction of
isometric drawing.
Students draw isometric
drawing of block with flat,
inclined and round
surfaces.
Students construct
isometric drawing for block
an oblique curved surface
using frame method.
Students construct
isometric drawing according
to correct orientation view.
Demonstrate and explain
ways to draw isometric
drawing on block/solid with
flat, inclined and
round surfaces.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Level 1
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
18
Yearly Lesson Plan
8.4
Application of
Isometric Drawing
in engineering field
Dimension
Isometric Drawing.
Explain and demonstrate
method of dimensioning
Isometric drawing on board/
transparencies.
Dimensioning Isometric
Drawing based on alligned
and unidirectional system.
Explain and demonstrate how
to construct exploded view of
objects or components from
various engineering range of
learning.
Construct exploded
Isometric drawing for
objects or components and
of various engineering
range of learning based on
exercises or questions
given by teacher.
Level 2
Construct Isometric
Drawing including
exploded view of
objects or
components from
various engineering
field.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
19
Yearly Lesson Plan
UNIT 9 : OBLIQUE DRAWING
LEARNING AREA
9.1
Concepts of
Oblique Drawing
a. Oblique
axis
b. Circles,
arcs and
curves in
Oblique
Drawing
c. Characteris
tic of
Oblique
Drawing
9.2
Types of Oblique
Drawing
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify
- oblique axis
- receding axis
- horizontal axis
- vertical axis
Explain the concept
of circles, arcs and
curves in Oblique
Drawing
Identify
characteristics of
Oblique Drawing
- oblique lines
- non-oblique lines
- angles in oblique
- circles in oblique
- arcs in oblique
Level 1
Identify types of
Oblique
Drawing:
- Common
Oblique
- Cavalier
Oblique
- Cabinet
Oblique
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Prepare samples of drawing
explain axes in Oblique
Drawing
- oblique axis
- receding axis
- vertical axis
Describe concept of circle,
curve and arc in Oblique
Drawing
Exhibit samples of common
oblique, cavalier oblique and
cabinet oblique
Use OHP to narrate concept of
Oblique Drawing
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Identify axis of oblique drawing
Understand concept of circles,
arc and curve in Oblique
Drawing
Identify the characteristics of
oblique drawing
Construct three types of
Oblique Drawings.
20
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OUTCOMES
9.3
Selection of
orientation of
oblique drawing
Level 2
Select the best
orientation
to
produce oblique
drawing
9.4
Constructions of
oblique drawing
a. Box
method
b. Frame
method
Level 1
Construct
oblique drawing
of geometrical
solids using:
- Box Method
- Frame Method
Level 2
Draw circles on
oblique axis:
-four-centered
method
- coordinate
method
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Explain
and
display
methods
of
selecting
suitable orientation based
on the characteristics of
oblique drawing on OHP
Students select and determine
the most suitable oblique
drawing orientation
Explain
and
show
methods
to
construct
oblique drawing by using
- Box Method
- Frame Method
Students construct
drawing by using:
Box Method
Frame Method
Show
methods
to
construct
circles
on
oblique axes by using
- four-centered method
- coordinate method
WEEK / DATE
oblique
Students construct
oblique
drawing by using
Box Method
Frame Method
Students answer questions that
teacher has prepared
21
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
9.5
Dimensioning of
oblique drawing
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
9.6
Application of
oblique drawing in
engineering field
Dimension oblique
drawing
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Distribute oblique drawing
questions for dimensioning
Explain and demonstrate
method
of
dimensioning
oblique drawing by using
unidirectional and aligned
system
Explain and demonstrate
Oblique Drawing on charts or
OHP
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Students use
unidirectional
and
aligned
system
to
demonstrate Oblique Drawing
Level 2
Apply oblique
drawing for objects
or components in
various engineering
fields.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
22
Yearly Lesson Plan
UNIT 5 : COMPUTER AIDED DRAFTING ( CAD ) I
LEARNING AREA
5.1
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Introduction to CAD
Level 1
Define CAD.
a.
F
Identify the
acilities of CAD
facilities of CAD
System
system.
Use PC Hardware
b.
A
I
dvantage and
nput device
Disadvantage of
O
CAD
utput device
P
c.
C
rinter
AD Software
P
lotter
Explain the
advantage and
disadvantage of
CAD with regards to
the conventional
method.
Level 2
Familiarize with
CAD Software and
its functions.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Distribute notes;
-
Define CAD (Computer
Aided Drafting).
- Computer hardware
(output device, input,
printer and plotter).
- Example of AutoCAD
drawing.
- Example of
conventional drawing.
Explain ang demonstrate
actual hardware.
Explain and prepare simple
diagram of AutoCAD drawing.
- Demonstration of
AutoCAD advantage.
Discuss the advantages and
disadvantages between
conventional drawing and CAD
system.
Distribute notes of AutoCAD
introduction and its functions.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Students define CAD.
Students prepare a list of
input hardware such as;
- Scanner
- Digitizer Pen
- Keyboard
- Mouse
Students prepare a list of
output hardware:
- Printer and plotter
- LCD Projector
Students prepare a list
of AutoCADs advantages:
- Easier to edit and
modify.
- Accuracy
- Template (Basic symbol
aid)
- Size or scale could be
adjusted.
- Direction of view could
be adjusted.
- Shapes of solid could
be reconstructed.
Disadvantages of AutoCAD:
- Higher cost.
- Lower skills.
Students prepare a list of
the different type of Auto
CAD softwares.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
WEEK / DATE
23
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
5.2
AutoCAD Software
Commands
Management
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Use drawing file
command :
New
Open
Limit
Qsave
Quit/Exi
t/End
Use Auto CAD
Software command:
a.
Drawing
Line
Circl
e
Eras
e
Oop
s
Arc
b.
Modify
Eras
e
Trim
c.
Osnap
Tan
gent
Cen
ter
Per
pendicular
Mid
Oth
er Osnap
Command
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Distribute commands notes
AutoCAD file operation.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Students use AutoCAD file
operation commands.
Students use AutoCAD
software commands as
listed.
Explain and distribute notes of
AutoCAD software commands
as listed.
Explain AutoCAD software
commands using pull-down
menu and icon.
- Drawing
- Modify
- Osnap
24
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
5.3
AutoCAD
application in
producing simple
plane diagram
LEARNING OUTCOMES
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Level 2
Constru
ct simple plane
diagram using
familiarized
command.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Charts or transperancy of
simple plane diagrams.
Distribute notes of AutoCAD
drawing steps using
commands that have been
learned.
Students draw based on the
instruction acquired and
follow the given steps.
25
Yearly Lesson Plan
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
26
Yearly Lesson Plan
FORM 5 - UNIT 2 : COMPUTER AIDED DRAFTING ( CAD ) II
LEARNING AREA
2.1
Application of
Various Command
to Construct Block
Drawing
a.
b.
Orthograph
ic Projection
Drawing in
Computer
Aided Drafting
(CAD)
Isometric
Drawing
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Use Auto CAD
software commands:
Snap
Grid
Trim
Undo
Redo
Block
Insert
Dist
Offset
Polygon
Ellipse
Dtext
Pline
Draw title block
Level 2
Apply Layers
Use AutoCad
Software command
to construct 2D
block diagrams:
orthogra
phic projection
drawing
isometri
c drawing
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Preparation of equipment.
A set of computer equipment
with the latest AutoCAD
software.
Printer / plotter
Distribute AutoCAD printed
notes commands.
Teacher prepares a simple
drawing module in diskettes.
Appendix 11/1
Complete the orthographic
drawing using AutoCAD
software commands.
Appendix 11/2
Complete the isometric
drawing using AutoCAD
software commands.
Appendix 11/3
Complete the isometric
drawing using AutoCAD
software commands.
Prepare an example of a
simple block drawing using
AutoCAD commands.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Students use pre-recorded
diskette to complete
drawing according to
AutoCAD software
commands.
Students use the AutoCAD
software commands to
complete drawing exercises
in the diskette.
Students prepare title block
using the format available
in AutoCAD.
Students draw based on
instructions acquired in title
block and refer to the given
example.
27
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
2.2
CAD Text and
Dimensioning
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 2
2.3
Printing the
Computer Aided
Drafting Drawing
Use of text
commands and
dimension in
Computer Aided
Drafting drawing:
Mtext
Dtext
Dim
Level 1
Explain Print
command.
Print computer
aided drafting
assignment.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Student uses the drawing in
the diskette according to
AutoCAD software
commands.
Identify the commands
used to print from a given
or available file.
WEEK / DATE
Appendix 11/4
Layers application in
Orthographic Drawing.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Prepare example of a block
drawing in diskettes for text
commands and dimensioning.
Distribute text commands and
dimensioning printed notes.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Teacher prepares printing
output on different types of
paper. Example:
- Transparency paper.
- Card paper.
- A3 paper.
Distribute printing manual
notes.
Teacher prepares diskettes or
student AutoCAD Drawing
output.
28
Yearly Lesson Plan
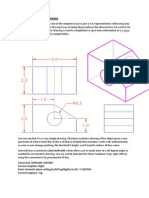
UNIT 4 : GEOMETRY
LEARNING AREA
4.1
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Graphic elements
Level 1
a.
Co
ncept of point
b.
Co
ncept of line
c.
Co
ncept of plane
Explain basic
concepts of point,
line and plane.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Prepare transparencies for
graphic element
Explain and display the type of
common points used in
geometrical drawing:
-
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Mark the type of points
Construct a line from a
point to a point
Straight line intersecting
straight line.
Straight line intersecting
curved line
Curved line intersecting
curved line
Explain line concept, that is, a
point that move evenly
(straight line) or move un
evenly (curved line)
Explain plane concept, which
is, a flat surface of various
shapes with no thickness
measurement
Make use a piece of paper as
a sample plane
Appendix 4/1:
Method of marking points and
types of lines
29
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
4.2
Lines
a.
Constr
uction of lines
b.
Divisio
n of lines
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Construct
various types of
lines
- Parallel lines.
- Perpendicular
lines.
Divide lines
according to given
criteria:
- Bisect a line.
- Divide into
equal division.
- Divide
according to
given ratio.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
Exhibit sample picture that
shows parallel line in:
- Fence grill
- Stadium track
Captions of paper of
various shape to
understand the plane
concept.
Construct horizontal,
vertical and incline parallel
lines using various drawing
instruments.
Explain the parallel lines
concept.
Demonstrate how a parallel
line can be constructed by a T
square and set square.
Demonstrate how to construct
perpendicular line on
horizontal, vertical and
inclination lines
Demonstrate how to divide a
line of two equal
sections and divide into
several length.
Demonstrate how to divide a
line.
WEEK / DATE
Construct perpendicular
line on horizontal, vertical
and inclination lines
o Construct the parallel
line on a perpendicular
line.
Divide the given line into
two section by geometrical
method.
Divide a line into several
equal section of the same
length .
Divide a line base on the
ratio given.
30
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
4.3
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Angles
Level 1
a.
Identify various
types of angles.
Construct
various types of
angles.
Divide angles
into equal parts.
Types
of angles
b.
Constr
uction of
angles
c.
Divisio
n of angles
Transfer angles.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Explain types of angle and its
characteristics and also samples
of angle:
Right angle
acute angle
Obtuse angle
Complementary angle
Explementary angle
Reflex angle
Demonstrate how to construct
90,60 ,30,15 and 75angles
using geometrical/plane methods.
Demonstrate the division of angle.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Construct various type of
angles by combining 30,45,
60 and a square.
Use geometrical method to
construct 90,60,30,15 and
75 angles.
Divide an angle into two equal
parts.
use set square to divide 180
angle into six parts.
use set square to divide 360
angle into 12 parts
Transfer angle to a new
location.
Demonstrate how to divide the
same angle can be transferred to
another location.
Appendix 4/2
Types of angle
4.4
Triangles
Level 1
a.
b.
Ty
pes and
characteristics
of triangles
Co
nstruction of
triangles
Identify types
and characteristics
of triangles:
Equila
teral
Isosce
les
Right
triangle
Scale
ne
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
On charts prepare types of
triangle.
Appendix 4/3
Triangular terms
Demonstrate how to construct
various triangles :
Three sided
Two sided and an Included
angle or based angle
Two sided and a based
angle
Base and two based angle
Identify types and
characteristics of triangle on
worksheet given.
Construct various triangle:
Three sided
Two sided and an
included angle.
Base and two based
angles.
Resources:
1.
Types
and characteristics of triangle
chart
31
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Construct
triangles based on
given criteria:
Three
sides.
Two
sides and one
angle.
Two
sides and
one
included
angle.
Two
sides and
base angle.
Base and two base
angles.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Demonstrate how to construct
triangles using three median
method.
Demonstrate how to construct
triangles using the criteria given.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Use perimeter and side
proportion given to construct
triangles.
Use right angle, hypotenuse
and a side given to construct
triangle.
Use base length, angle and
vertex given to construct
triangle.
Use base length, vertex angle
and height given
to construct triangle.
Use perimeter, height and
vertex given to construct
triangle.
Use three medians given to
construct triangle.
Level 2
Construct
triangles based on
given criteria:
Perimeter and side
proportion.
Right angle,
hypotenuse and
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
32
Yearly Lesson Plan
one side.
Base, one angle and
vertex angle.
Base, vertex angle
and height.
Perimeter, height
and vertex
angle.
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OUTCOMES
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Level 3
4.5
Quadrilaterals
a.
Level 1
Ty
pes and
characteristics
of quadrilateral
b.
Construct
triangles based on:
- three medians
Co
nstruction of
quadrilaterals
Identify types
and characteristics
of quadrilaterals:
- Square
- Rectangle
- Parallelogram
- Rhombus
- Trapezium
- Kite shape
Construct
square and
rectangle based on
given criteria:
- Sides
- Diagonal
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
With a side and diagonal
measurement given,
construct a square and a
rectangle
With adjacent sides given ,
construct a parallelograms
and dimension of the
following :
Explain and display a chart or
trenparency yype and
charactics of rectangular
Explain side and diagonal of
quadrilateral plane
Demonstrate how to construct a
various types of quadrilateral
Include angle
Diagonal
Construct a rhombhus
when sides and anglesare
given
33
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
4.6
Polygons
a.
Types and
characteristics
of polygons
b.
Constructio
n of regular
polygons
Construct
parallelogram given
two adjacent sides:
- Included angles
- Diagonal
Construct
rhombus based on
given criteria:
- Sides
- Angles
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify types of:
Regular
polygons
Irregular
polygons
Construct regular
pentagon based on
given criteria:
Sides
Circums
cribed circle.
Construct regular
hexagon based on
given criteria:
Sides
Length
across flats
Length
across corners.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
On charts/transparencies explain
and exhibit types and
characteristics of polygon.
Explain the differences between
regular and irregular polygons.
Demonstrate how to construct
regular pentagon, hexagon and
octagon.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Construct a regular pentagon
with one side length given.
Construct a regular pentagon in
circumscribed circle.
Construct a regular hexagon
with one side length given.
Construct a regular hexagon
with
Length across flats given
Construct a regular hexagon
with
Length across corners given.
Construct a regular octagon
with one side given.
Construct a regular octagon in
circumscribed circle.
Construct a regular octagon in
a square given.
Resources:
Types and characteristics polygon
34
Yearly Lesson Plan
chart.
LEARNING AREA
4.7
Scale
a.
Types of
scale
b.
Ways of
stating scale
c.
Application
of scale ruler
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify types of
scale:
Commo
n scale
Diagona
l scale
Mention scale by:
Ratio
Fraction
Stateme
nt
Level 2
4.8
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Explain types of scale commonly
used and ways to state them.
Guided by a map scale, explain
how scale is used.
Show actual scale rule and explain
how to read the scale on the ruler.
Explain how to measure using a
scale rule.
State that scale can also be done
by ratio representative fraction and
statement. This can be done on
charts or orally
Distribute scale ruler for
observation and discussion in
groups.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Students discuss and observe
the scales line on the scale
ruler by group.
Resources:
Scale ruler
Use correct
technique of scale
ruler with certain
ratio.
Reduction and
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Level 1
35
Yearly Lesson Plan
Enlargement
Explain the concept
of reduction and
enlargement.
Explain and demonstrate two
plane diagrams, of a similar
shapes but different in sizes.
Differentiate the
reduction or
enlargement
between side ratio
and area ratio.
Explain and differentiate two plane
diagrams.
LEARNING AREA
Construct reduced
or enlarged plane
diagram with:
-given side ratio.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Draw enlarged or reduced
plane diagram based on given
side ratio.
Draw enlarged or reduced
plane diagram based on given
area ratio.
Explain the differences of
reduction or enlargement as in
side ratio and area ratio and their
relations.
Demonstrate methods to construct
reduced or enlarged plane
diagram based on given area ratio
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Level 2
4.9
Figure of Equal
Area
a.
Concept of
Area according
to stage of
transformation
Constru
ct reduced or
enlarged plane
diagram with given:
- Area ratio.
Level 1
Explain the
concept of equal
area.
Identify
diagrammatic
transformation of
shape of equal area.
Construct
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Explain equal area concept for
triangles and quadrilaterals of the
same base located between two
parallel lines.
Demonstrate how to change a
shape of a triangle to a rectangle.
Demonstrate how to construct
rectangle to square of equal area.
Demonstrate how to change a
polygon to triangle of equal area.
Construct diagrams of equal
area:
- Triangle to another
triangle with one of its
side given.
- Triangle to rectangle.
- Rectangle to square.
Construct a triangle equal in
area to another triangle with
36
Yearly Lesson Plan
various diagram of
equal area.
- Polygon to
triangle.
- Triangle to
rectangle.
- Rectangle to
square.
Distribute worksheets to students.
Present and demonstrate how to
construct triangle with one of its
side given.
Present and demonstrate how to
construct a triangle to another
triangle with one of its side given.
one of its side given.
Construct a quadrilateral equal
in area to another quadrilateral
based on one side given.
Construct a quadrilateral which
is equal in area to a polygon.
.
Level 2
Construct
various diagrams of
equal area.
Triangle to
triangle with one
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OUTCOMES
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
side
given.
4.10
Circles
Quadrila
teral to
quadrilateral
with one side
given.
Develop
sequential
transformation of
polygon to square.
Level 1
Identify terms and
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Use Transparencies or graphic
Use two chords method to
37
Yearly Lesson Plan
a.
b.
Ter
ms and
characteristics
of circles
Co
nstruction of
circles and arcs
LEARNING AREA
4.11
Ellipse And
Parabola
a.
Characteris
tics of ellipse
and parabola
b.
Constructio
n of ellipse
c.
Constructio
n of parabola
characteristics of
circles.
Determine centre of
circle or arcs using
two chords.
Construct a circle or
arcs based on given
criteria:
Radius
Diamete
r
3 points.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 1
Identify the
characteristics of
ellipse and parabola.
Construct ellipse
using concentric
circle method.
Construct
parabola using
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
materials to explain the terms and
characteristics of circles.
Explain and show how to
determine centre of circle or an
arc using two chords.
Explain and show how to construct
a circle based on given criteria:
Radius
Diameter
3 points.
-
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Explain the characteristics of
ellipse, parabola and the
differences between them using
OHP or graphic materials.
Demonstrate how to construct
ellipse by concentric circle
method.
Show how to construct parabola by
rectangular method
determine centre of a circle or
an arc.
Students draw a circle based
on the criteria given.
Resources:
Chart of terms and characteristics
of circle
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Construct ellipse on major and
minor axis.
Construct ellipse in rectangle.
Construct parabola by
rectangular method.
Resources:
Model representation of ellipse
and parabola.
38
Yearly Lesson Plan
rectangular method.
4.12
Identify the
difference between
ellipse and parabola.
Tangents
Level 1
a.
Concepts
and
characteristics
of tangent
b.
Constructio
n of line
tangential to a
circle
c.
Constructio
n of circle
tangential to a
line
d.
Constructio
n of circle
tangential to a
circle
LEARNING AREA
Explain the
concepts and
characteristics of
tangency
Tangent
between line
and circle.
Tangent
between circle
and another
circle.
Level 2
Explain the concept of tangent line
(straight line touching to circle or
curve).
Explain how tangential occur on
two curves or two circles.
Explain when internal and external
touches each other.
Explain and show the methods to
construct a circle touching a
straight line.
Draw a circle tangential to a
line
Resources:
1.
Video show/CDROM related to tangent.
2.
Illustrations related
to tangent.
Locate the point of
tangency:
Between
circle
LEARNING OUTCOMES
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
and line.
Between
two lines and
circle.
Between
a line and two
circles (inside or
outside).
Between
two circles
touching
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
a line tangential to a circle.
Draw a common tangent line
touching two circles externally.
Explain and show how to construct
a common tangential line
internally.
Explain and show how to construct
two circles tangential to a line
.
Explain and show how to construct
a circle through a point and
Draw a circle tangential to two
lines.
Draw a line tangential to a
circle.
Draw a common tangential line
touching two circles externally.
Draw a common tangential line
internally.
Draw two circles tangential to a
line.
WEEK / DATE
39
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
internally or
externally.
Between
straight line and
two circles
internally or
externally.
Construct a line
tangential to:
A point
on the
circumference
of a circle.
A point
outside a circle.
Construct a circle
tangential to:
A line
given the radius
of the circle.
Two
lines given the
radius of the
circle.
Construct a circle
tangential to:
another
circle
LEARNING OUTCOMES
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
tangential to a line at a given
point.
Explain and show how to construct
a circle from a point and tangential
to a given line and point.
Explain and show how to construct
a circle touching another circle
externally.
Explain and show how to construct
a circle touching another circle
internally.
Explain and show how to construct
a tangential circle touching
another circle externally at T and
through point P.
Explain and show how to construct
a circle touching another circle
and line at point P.
Explain and distribute worksheet
related to tangent exercises.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Draw a circle through a point
and tangential to a given line
and point.
Draw a circle through point P
and tangential to the given two
lines.
Draw a circle touching another
circle externally.
Draw a circle touching another
circle internally.
Draw a tangential circle
touching another circle
externally at T and through
point P.
Draw a circle touching another
circle and line at point P.
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
and tangential to
it externally.
another
circle and
tangential to it
40
Yearly Lesson Plan
-
internally.
Two
other circles and
tangential to
both internally.
Two
other circles and
tangential to
both externally.
Level 3
Construct a circle
tangential to:
another
circle through
the given point
internally.
another
circle through
the given point
externally.
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
41
Yearly Lesson Plan
FORM 5 - UNIT 7 : BUILDING DRAWING
LEARNING AREA
7.1
Introduction
LEARNING OUTCOMES
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Level 1
a.
Ty
pes of building
drawing
b.
Sta
ndard
architectural
symbols
Identify and
differentiate types
of building drawing
plan
drawing
elevatio
n/view drawing
sectiona
l drawing
detailed
drawing
Identify the use
of standard
architectural
symbols in building
drawing
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Collect and prepare example
of building drawing.
Show example of Building
Drawng and explain the
differences between:
- Layout drawing
- Elevation Drawing
- Sectional Drawing
- Detailed Drawing
Students discuss the
different types of Building
Drawing.
Show and explain standard
architectural symbols in
Building Drawing and clarify
their uses.
Students draw symbols
basing on actual objects
and macth suitability.
42
Yearly Lesson Plan
LEARNING AREA
7.2
Application of
Building Drawings
of Single and
Double-Storey
Residential
Building
a.
Sc
ale in Building
Drawing (1:50 ,
1:100)
b.
Ele
vation/View
drawing
c.
Flo
or plan
d.
Ro
of plan
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Level 2
Draw
Orthographic
Projection of single
and double-storey
residential building.
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
a.
Plan
Drawing
floor
plan
roof
plan
b.
Elevatio
n/View Drawing
Level 3
Draw Building
Drawing using
appropriate scale for
single and doublestorey residential
building.
a.
Plan
Drawing
floor
plan
roof
plan
b.
Elev
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
Prepare a single-storey
building model complete with
roof which could be opened.
Prepare Ortographic
Projection questions to
complete the views/elevation.
Prepare answers on
transperancies.
Model aided, teacher explains
types of roof such as;
- Hip roof ( limas )
- Gable roof ( tebeng layar )
- Lean to roof ( pisang
sesikat )
SUGGESTED LEARNING
ACTIVITIES
WEEK / DATE
Draw and complete the
Orthographic Views (singlestorey building).
Draw building drawing
according to the scale (floor
plan or roof plan).
Draw View/Elevation
Drawing according to scale.
Prepare actual plan and
instruct students to recopy
basing on a certain scale.
Appendix 16/1
a ) Location plan.
b ) Floor plan.
c ) Roof plan
Appendix 16/2
Floor Plan and Accessories
Appendix 16/3
Views/Elevation Drawing
Appendix 16/4
Detailed Drawing
43
Yearly Lesson Plan
ation/view
Drawing
ENGINEERING DRAWING FORM 4
44
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Design And Technology A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandDesign And Technology A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Reading and Comprehension in the African Context: A Cognitive EnquiryDari EverandReading and Comprehension in the African Context: A Cognitive EnquiryBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan DraftDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan Draftapi-283139107Belum ada peringkat
- Final Project Presentation - Grading RubricDokumen2 halamanFinal Project Presentation - Grading Rubricapi-435394354Belum ada peringkat
- Draft Elevations and SectionsDokumen16 halamanDraft Elevations and SectionsKing Rey YapBelum ada peringkat
- Technology Lesson PlansDokumen10 halamanTechnology Lesson Plansapi-287683180Belum ada peringkat
- Q4 MODULE7 G10 Technical DraftingDokumen12 halamanQ4 MODULE7 G10 Technical DraftingIrine IrineBelum ada peringkat
- Drafting Handouts and QuestionsDokumen6 halamanDrafting Handouts and QuestionsCherryn Dorotayo QuiminsaoBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Performance ExpectationsDokumen5 halamanTeaching Performance Expectationsgeorge millerBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of 1st Angle and 3rd AngleDokumen14 halamanOverview of 1st Angle and 3rd AngleM SureshBelum ada peringkat
- Technology Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanTechnology Lesson Planapi-331637419Belum ada peringkat
- Multiview Drawings: Unit 5Dokumen14 halamanMultiview Drawings: Unit 5Nur SidikBelum ada peringkat
- Cartooning Unit Plan Grade 9Dokumen12 halamanCartooning Unit Plan Grade 9api-242221534Belum ada peringkat
- TLE 10 TD 3.docx FinalDokumen11 halamanTLE 10 TD 3.docx FinalSandara HongBelum ada peringkat
- KPRUT-What To Know... ? Procees? Reflect? Understand? and Transfer?Dokumen19 halamanKPRUT-What To Know... ? Procees? Reflect? Understand? and Transfer?Gilbert BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanLesson PlaneirielssBelum ada peringkat
- Artifact ReflectionDokumen3 halamanArtifact Reflectionapi-455790828Belum ada peringkat
- Drafting - G9Dokumen40 halamanDrafting - G9Neil Cody A. JeliangBelum ada peringkat
- Drawing Syllabus Fall 16Dokumen6 halamanDrawing Syllabus Fall 16api-249573286Belum ada peringkat
- Flowchart LessonDokumen3 halamanFlowchart LessonApril Ann OliverosBelum ada peringkat
- CHAP. 3 Principles of Orthographic ProjectionsDokumen45 halamanCHAP. 3 Principles of Orthographic Projectionshidayatullah100% (2)
- Tle Tech Drafting 10 q1 m3Dokumen15 halamanTle Tech Drafting 10 q1 m3Shitsui Uchiha100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Forces On Structures 4Dokumen3 halamanLesson Plan - Forces On Structures 4api-399406916Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutDokumen25 halamanChapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutTeshome Bekele100% (1)
- DLP Demo TeachingDokumen8 halamanDLP Demo TeachingChristopher GalivoBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Fiction Non Fiction Text BilingualDokumen31 halamanSummary of Fiction Non Fiction Text Bilingualapi-237154393Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Engineering DrawingDokumen4 halaman1 Engineering DrawingRovil BeridoBelum ada peringkat
- TM 1 TemplatesDokumen61 halamanTM 1 Templateslina angeloBelum ada peringkat
- TOPIC Prepare Architectural Job RequirementDokumen9 halamanTOPIC Prepare Architectural Job Requirementf agbBelum ada peringkat
- 3 View Orthographic DrawingDokumen3 halaman3 View Orthographic DrawingMuhammad FitriBelum ada peringkat
- Orthographic Projection Lesson RevisedDokumen87 halamanOrthographic Projection Lesson RevisedVictor M. MorcilloBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Drafting 10 SLHT Q2 WK 3 4Dokumen9 halamanTechnical Drafting 10 SLHT Q2 WK 3 4Donna EnopiquezBelum ada peringkat
- EDU TAHlookinside DraftingDokumen2 halamanEDU TAHlookinside DraftingwolfvorBelum ada peringkat
- Year 2 The-Arts Visual-Arts Judging Standards Assessment-PointersDokumen3 halamanYear 2 The-Arts Visual-Arts Judging Standards Assessment-Pointersapi-287660266Belum ada peringkat
- Ict Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanIct Lesson Planapi-281784618Belum ada peringkat
- Module Week 3Dokumen6 halamanModule Week 3Yzel Gyle YrayBelum ada peringkat
- Structures and Forces Unit PlanDokumen21 halamanStructures and Forces Unit Planapi-335715006Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12 Working DrawingDokumen63 halamanChapter 12 Working DrawingLhen Mediante AsuncionBelum ada peringkat
- GENG 111 - Lecture 05 - Orthographic ProjectionDokumen38 halamanGENG 111 - Lecture 05 - Orthographic ProjectionNaeem NasserBelum ada peringkat
- First Day of School PlanDokumen8 halamanFirst Day of School Planapi-457623745Belum ada peringkat
- Procedural Text Lesson SequenceDokumen4 halamanProcedural Text Lesson Sequenceapi-238051278100% (1)
- (MYP5 Design) Designing For Connectedness (EPortfolio) (TSC)Dokumen6 halaman(MYP5 Design) Designing For Connectedness (EPortfolio) (TSC)tamararox2008Belum ada peringkat
- Engineering Drawing (Graphics) Technical DrawingDokumen47 halamanEngineering Drawing (Graphics) Technical DrawingErhan TokBelum ada peringkat
- Ojeda Co1 Dlp-SptveDokumen5 halamanOjeda Co1 Dlp-SptveZan OjedaBelum ada peringkat
- 15 Week Planner Unit 4Dokumen14 halaman15 Week Planner Unit 4api-318222702Belum ada peringkat
- Multiplying Binomials Lesson Plan (Access Version)Dokumen15 halamanMultiplying Binomials Lesson Plan (Access Version)RichardRaquenoBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2Dokumen3 halamanWeek 2Angeline EspantonBelum ada peringkat
- Alphabet of LineDokumen9 halamanAlphabet of LineCONCEPTO RICONBelum ada peringkat
- My Art CurriculumDokumen22 halamanMy Art Curriculumapi-273005472Belum ada peringkat
- Alphabet LinesDokumen2 halamanAlphabet LinesElla ParadoBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson #3: Introduction To Environment and Market Lesson#4: Product and Concept DevelopmentDokumen22 halamanLesson #3: Introduction To Environment and Market Lesson#4: Product and Concept DevelopmentCatherine Bercasio Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 7 Dimensioning Views Tolerance QuizDokumen5 halamanUnit 7 Dimensioning Views Tolerance Quizapi-240153916100% (1)
- 1 Point Perspective Lesson Plan MsteenhartDokumen4 halaman1 Point Perspective Lesson Plan Msteenhartapi-451208805Belum ada peringkat
- Technical Drawing 7: Q 1 Week: 1Dokumen9 halamanTechnical Drawing 7: Q 1 Week: 1Rosemarie G. HermosoBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Developing A ProductDokumen11 halamanConcepts of Developing A ProductJustine MontoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Cad Orthographic RubricDokumen2 halamanCad Orthographic Rubricapi-331833215Belum ada peringkat
- Lanie A. Arcangel: San Antonio National High School 8 Mechanical Drafting FourthDokumen4 halamanLanie A. Arcangel: San Antonio National High School 8 Mechanical Drafting FourthLjoval Lanie AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- TLE-generating Business IdeasDokumen32 halamanTLE-generating Business IdeasMike ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Enkbkbkngineering Drawing Form FourDokumen25 halamanEnkbkbkngineering Drawing Form FourorangramaiBelum ada peringkat
- Yearly Lesson Plan LK Form 4Dokumen36 halamanYearly Lesson Plan LK Form 4Nur'ain Abd RahimBelum ada peringkat
- GRADE 7 Third PT DivisionDokumen4 halamanGRADE 7 Third PT DivisionKingGamer 4595100% (1)
- Plane & Shperical Tirgonometry by Kells, Kern, Bland PDFDokumen529 halamanPlane & Shperical Tirgonometry by Kells, Kern, Bland PDFJason StaleBelum ada peringkat
- B.sc. (H) Mathematics Analysis IIDokumen47 halamanB.sc. (H) Mathematics Analysis IIRenu ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Trigo PDFDokumen71 halamanTrigo PDFRaushan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Date: 09-01-2019: Chater # 7 VECTORS (7.1 - 7.3)Dokumen2 halamanDate: 09-01-2019: Chater # 7 VECTORS (7.1 - 7.3)MashaviaBelum ada peringkat
- Quant Mega Quiz For SSC CGL Tier - 2: WWW - Careerpower.inDokumen6 halamanQuant Mega Quiz For SSC CGL Tier - 2: WWW - Careerpower.inRahul SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Math10 - Q2 - Module 6 - Lessons 1-4 - v2Dokumen106 halamanMath10 - Q2 - Module 6 - Lessons 1-4 - v2erraBelum ada peringkat
- FreeStyle Shaper and OptimizerDokumen234 halamanFreeStyle Shaper and OptimizerPrathameshNalawdeBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Nine (9) Summative Assessment 9.4.3 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Correct Letter of Each ItemDokumen3 halamanMathematics Nine (9) Summative Assessment 9.4.3 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Correct Letter of Each ItemGen-GenAlcantaraBaldadoBelum ada peringkat
- Ms&E 302 Lecture W# 3: Strains: Ødisplacement Field Øcalculation of Strains Øprincipal Strains and Strain InvariantsDokumen5 halamanMs&E 302 Lecture W# 3: Strains: Ødisplacement Field Øcalculation of Strains Øprincipal Strains and Strain Invariantsİlke Candan BengiBelum ada peringkat
- Projectile MotionDokumen5 halamanProjectile MotionDJ AaryanBelum ada peringkat
- Higher Mathematics-01 EnglishDokumen4 halamanHigher Mathematics-01 EnglishSainder Pankaj DasBelum ada peringkat
- ECE 5233 - Lecture 2 (Orbital Mechanics)Dokumen11 halamanECE 5233 - Lecture 2 (Orbital Mechanics)John JohnstonBelum ada peringkat
- T Chart WeeblyDokumen1 halamanT Chart Weeblyapi-449513893Belum ada peringkat
- Tracing of Polar Curves - DR - KR PDFDokumen48 halamanTracing of Polar Curves - DR - KR PDFGundappa SwamyBelum ada peringkat
- WWW Scribd Com Document 356032044 Cape Pure Mathematics UnitDokumen114 halamanWWW Scribd Com Document 356032044 Cape Pure Mathematics UnithiBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric PowersDokumen29 halamanTrigonometric PowersJasmin PagpaguitanBelum ada peringkat
- Applied - Physics - Notes 1Dokumen248 halamanApplied - Physics - Notes 1Ashutosh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 10 Math ReviewDokumen7 halamanGrade 10 Math ReviewnobBelum ada peringkat
- Shinglee EmathTxt 6thedtDokumen216 halamanShinglee EmathTxt 6thedtMethodology OfStudies88% (8)
- Acceleration Calculation Description Result Unit 9.81Dokumen12 halamanAcceleration Calculation Description Result Unit 9.81venkateswaranBelum ada peringkat
- PMR Perak Math 2010 AnswerDokumen8 halamanPMR Perak Math 2010 AnswerwaichunkoBelum ada peringkat
- Experiential Learning Theory: A Dynamic, Holistic Approach To Management Learning, Education and DevelopmentDokumen59 halamanExperiential Learning Theory: A Dynamic, Holistic Approach To Management Learning, Education and DevelopmentamiBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3: 4.6 (C) Iwbat Apply Knowledge of Right Angles To Identify Acute, Right, and Obtuse TrianglesDokumen7 halamanLesson 3: 4.6 (C) Iwbat Apply Knowledge of Right Angles To Identify Acute, Right, and Obtuse TrianglesSamantha HolmesBelum ada peringkat
- Review Exam 2-NewDokumen29 halamanReview Exam 2-NewJabeenAhmedBelum ada peringkat
- New Curriculum History PDFDokumen105 halamanNew Curriculum History PDFGlaiza Gilamon CadagBelum ada peringkat
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers:: Eighth EditionDokumen32 halamanVector Mechanics For Engineers:: Eighth EditionkeanshengBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3-BalancingDokumen30 halamanChapter 3-BalancingHafzal GaniBelum ada peringkat
- UCM and Projectile MotionDokumen80 halamanUCM and Projectile MotionMarlyne VillarealBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry Formula Sheet: Geometric FormulasDokumen13 halamanGeometry Formula Sheet: Geometric Formulasaerogem618Belum ada peringkat