Applications and Characteristics of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51)
Diunggah oleh
catalinccHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Applications and Characteristics of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51)
Diunggah oleh
catalinccHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
10/13/2014
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51) | EEP
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent
Relays (ANSI 50, 51)
P o s te d O C T 8 2 0 1 4 b y E DV A R D i n E NER GY A ND P O W ER , P R O TE CT IO N w i th 2 CO M M ENT S
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51)
50/51 and 50/51N relays
Overcurrent relays are the most commonly-used protective relay type.Time-overcurrent relays are
available with various timing characteristics to coordinate with other protective devices and to protect
specific equipment. Instantaneous overcurrent relays have no inherent time delay and are used for
fast short-circuit protection.
Figure 1 below shows the timing characteristics of several typical 51 time-overcurrent relay curve
types, along with the 50 instantaneous characteristic.
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/applications-and-characteristics-of-overcurrent-relays-ansi-50-51
1/6
10/13/2014
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51) | EEP
Figure 1 ANSI 50 and 51 overcurrent relay characteristics
The pickup level is set by the tap setting, which is usually set in CT secondary amperes but may be
set in primary amperes on some microprocessor-based relays.
Each relay curve has a time dial setting which allows the curve to be shifted up or down
on the time-current characteristic curve.
In Figure 1, the time dial settings are different to give enough space between the curves to show
their differences.
The above are IEEE-standard curves; others are available, depending upon the relay make and
model. A solid state electronic or microprocessor-based relay will have all of these curves available
on one unit; electromechanical relays must be ordered with a given characteristic that cannot be
changed.
The 50 instantaneous function is only provided with a pickup setting. The 30ms delay shown in figure
1 for the 50 function is typical and takes into account both the relay logic operation and the output
contact closing time.
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/applications-and-characteristics-of-overcurrent-relays-ansi-50-51
2/6
10/13/2014
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51) | EEP
Most microprocessor-based units will also have an adjustable delay for the 50
function; when an intentional time delay is added the 50 is referred to as a
definite-time overcurrent function. On solid-state electronic and microprocessorbased relays, the 50 function may be enabled or disabled.
On electromechanical relays, the 50 function can be added as an instantaneous
attachment to a 51 time-overcurrent relay. If a relay has both 50 and 51 functions
present and enabled is referred to as a 50/51 relay.
Typically, overcurrent relays are employed as one per phase. In solidly-grounded medium voltage
systems, the most common choice for ground fault protection is to add a fourth relay in the residual
connection of the CTs to monitor the sum of all three phase currents. This relay is referred to as
a residual ground overcurrent or 51N (or 50/51N) relay.
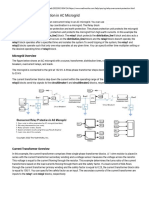
The CT arrangement for 50/51 and 50/51N relays for a solidly-grounded system is shown in Figure
2 below.
Figure 2 Overcurrent relay arrangement with CTs, including
50/51N
For a low-resistance-grounded system, the use of an overcurrent relay connected to a CT in the
service transformer or generator neutral is usually the best option. This CT should have a ratio
smaller than the phase CTs, and the relay pickup range in conjunction with the neutral CT should
allow a pickup as low as 10% of the neutral resistor rating.
For a feeder circuit downstream from the service transformer, a zero-sequence CT
is recommended, again with a ratio small enough to allow a pickup as low as 10% of the neutral
resistor rating.
When an overcurrent relay is utilized with a zero-sequence CT it is referred to as a 50G, 51G or
50/51G relay depending upon relay type used. Figure 3 shows typical arrangements for both these
applications.
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/applications-and-characteristics-of-overcurrent-relays-ansi-50-51
3/6
10/13/2014
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51) | EEP
Figure 3 Transformer neutral and zero-sequence ground relaying
applications for resistance-grounded systems
For ungrounded systems, the ground detection methods are recommended since little ground
current will flow during a single phase-to-ground fault. Low voltage solidly-grounded systems are
discussed below.
The typical application of phase and residual neutral ground overcurrent relays in one-line diagram
form is shown in figure 4.
Figure 4 Typical
application of overcurrent
relays
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/applications-and-characteristics-of-overcurrent-relays-ansi-50-51
4/6
10/13/2014
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51) | EEP
In Figure 4, the designation 52 is the IEEE Std. C37.2-1996 designationfor a circuit breaker.
The phase relays are designated 51 and the residual ground overcurrent relay is designated 51N
(both without instantaneous function). The bracketed denotes that there are three phase overcurrent
relays and three CTs. The dotted line from the relays to the circuit breaker denotes that the relays
are wired to trip the circuit breaker on an overcurrent condition.
Another type of overcurrent relay is the voltage-restrained overcurrent relay 51 V and
the voltage-controlled relay 51C. Both are used in generator applications to allow the
relay to be set below the generator full-load current due to the fact that the fault
contribution from a generator will decay to a value less than the full-load current of
the generator.
The 51C relay does not operate on overcurrent unless the voltage is below a preset value. The 51
V relay pickup current shifts as the voltage changes, allowing it to only respond to overcurrents at
reduced voltage. Both require voltage inputs, and thus require voltage transformers for operation.
OverCurrent Protection and Coordination (VIDEO)
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/applications-and-characteristics-of-overcurrent-relays-ansi-50-51
5/6
10/13/2014
Applications and Characteristics Of Overcurrent Relays (ANSI 50, 51) | EEP
Cant see this video? Click here to watch it on Youtube.
Reference: System Protection - Bill Brown, P.E., Square D Engineering Services
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/applications-and-characteristics-of-overcurrent-relays-ansi-50-51
6/6
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Applications and Characteristics of Overcurrent Relays ANSI 50 51Dokumen5 halamanApplications and Characteristics of Overcurrent Relays ANSI 50 51Pierre Enrique Carrasco FuentesBelum ada peringkat
- Relay Circuit Breaker ApplicationDokumen58 halamanRelay Circuit Breaker Applicationtenk_manBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Notes Overcurrent GroundFault Protection v1Dokumen7 halamanLab Notes Overcurrent GroundFault Protection v1srinivasaphanikiranBelum ada peringkat
- Motor ProtectionDokumen33 halamanMotor ProtectionMohamed RashidBelum ada peringkat
- Tranformer Protection GuideDokumen23 halamanTranformer Protection GuideSISWANTOBelum ada peringkat
- RelaysDokumen7 halamanRelaysRajeev RawatBelum ada peringkat
- Three Phase20three Level20voltage20source20inverterDokumen6 halamanThree Phase20three Level20voltage20source20inverterfarid kerroucheBelum ada peringkat
- Instrument Transformer Appli Guide AbbDokumen124 halamanInstrument Transformer Appli Guide AbbkapilBelum ada peringkat
- GE Power Relay Application GuideDokumen24 halamanGE Power Relay Application GuidehajianamirBelum ada peringkat
- Overcurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines TransformersDokumen7 halamanOvercurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines TransformersrobertoseniorBelum ada peringkat
- Protecciones Secundario SelectivoDokumen9 halamanProtecciones Secundario Selectivoelectric104Belum ada peringkat
- Numbering System For Protective Devices, Control and Indication Devices For Power SystemsDokumen6 halamanNumbering System For Protective Devices, Control and Indication Devices For Power SystemsDhiren PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Applications and Characteristics of Differential Relays ANSI 87Dokumen6 halamanApplications and Characteristics of Differential Relays ANSI 87Ricardo A VergaraBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTRONIC OVERCURRENT PROTECTION - PDFDokumen4 halamanELECTRONIC OVERCURRENT PROTECTION - PDFWisdom BasseyBelum ada peringkat
- Overcurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines CapacitorsDokumen4 halamanOvercurrent Coordination Setting Guidelines CapacitorsrobertoseniorBelum ada peringkat
- Phase Locked Loop System For FACTS: Dragan Jovcic, Member, IEEEDokumen8 halamanPhase Locked Loop System For FACTS: Dragan Jovcic, Member, IEEEPakde ZoelfaBelum ada peringkat
- Limongi 2007Dokumen8 halamanLimongi 2007NaqBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Protection Scheme For Power Transformers Based On IEC 61850 StandardDokumen10 halamanAdvanced Protection Scheme For Power Transformers Based On IEC 61850 StandardPHUC NGUYEN HUUBelum ada peringkat
- 221661A - QGX-CLP - Relay Coordination-Rev1Dokumen78 halaman221661A - QGX-CLP - Relay Coordination-Rev1HassenL100% (1)
- Applications & Characteristics of Differential Relays, ANSI 87Dokumen3 halamanApplications & Characteristics of Differential Relays, ANSI 87maungsoekhinBelum ada peringkat
- College Format DocumentDokumen74 halamanCollege Format DocumentRatnakarVarunBelum ada peringkat
- Protection Relay SettingsDokumen3 halamanProtection Relay SettingssmsbondBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Protection - Proven Technique For More Than 50 Years - EEPDokumen6 halamanDifferential Protection - Proven Technique For More Than 50 Years - EEPAbdul Mohid SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- 400KV Circuit BreakerDokumen128 halaman400KV Circuit BreakerRamakrishna67% (3)
- Trigged Current Limiters ApplicationsDokumen6 halamanTrigged Current Limiters ApplicationsVíctor RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Transient Overvoltages On Ungrounded Systems From Intermittent FaultsDokumen40 halamanTransient Overvoltages On Ungrounded Systems From Intermittent Faultsgeorge_cpp2Belum ada peringkat
- The ANSI/IEEE Code For Phase Sequence Relay Is 47 and of Phase Failure Relay Is 58Dokumen9 halamanThe ANSI/IEEE Code For Phase Sequence Relay Is 47 and of Phase Failure Relay Is 58ax33m144Belum ada peringkat
- Sel 421 r117 PTT User Manual EnuDokumen9 halamanSel 421 r117 PTT User Manual EnuioacymBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab PDFDokumen5 halamanMatlab PDFsubhasish deyBelum ada peringkat
- GET6600G Section 5 Rev 1 BookmarksDokumen10 halamanGET6600G Section 5 Rev 1 BookmarksMahmoud AbuziadBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Engineering IIDokumen8 halamanPower System Engineering IIAbdurrahman shuaibBelum ada peringkat
- Hydro Power Plant ControlDokumen5 halamanHydro Power Plant ControlHộpQuà TriÂnBelum ada peringkat
- Relay Interlocking Siemense Type NotesDokumen79 halamanRelay Interlocking Siemense Type NotesVikas Srivastav96% (23)
- Protective Device Coordination in An Industrial Power System With Multiple SourcesDokumen10 halamanProtective Device Coordination in An Industrial Power System With Multiple SourcestechtricBelum ada peringkat
- PSCAD EMTDC, FuzzyControl, HVDC Transmission, VoltageDependentCurrentOrderLimit VDCOLDokumen9 halamanPSCAD EMTDC, FuzzyControl, HVDC Transmission, VoltageDependentCurrentOrderLimit VDCOLKurniawan Indra LeksanaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Hi-Lo CO PDFDokumen7 halamanManual Hi-Lo CO PDFLeonel Zavarizi NetoBelum ada peringkat
- SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT LIMITATION TECHNIQUESDokumen13 halamanSHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT LIMITATION TECHNIQUESariefBelum ada peringkat
- Overcurrent Coordination StudyDokumen25 halamanOvercurrent Coordination StudyMohamed TalebBelum ada peringkat
- ! Over Current Coordination StudyDokumen25 halaman! Over Current Coordination Studybacuoc.nguyen356100% (1)
- Analysis and Design of Three-Phase AC-to-DC Converters With High Power Factor and Near-Optimum FeedforwardDokumen10 halamanAnalysis and Design of Three-Phase AC-to-DC Converters With High Power Factor and Near-Optimum FeedforwardTalha SadiqBelum ada peringkat
- Wayback Machine archive of MathWorks help page on relay overcurrent protection modelingDokumen7 halamanWayback Machine archive of MathWorks help page on relay overcurrent protection modelingGeorge CisnerosBelum ada peringkat
- Protection and Control Schemes: © 2009 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLCDokumen11 halamanProtection and Control Schemes: © 2009 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLCRonaldBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Pumping and Lockout RelaysDokumen7 halamanAnti Pumping and Lockout RelaysAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation For Short Circuit Current Calculation Using IEC / IEEE StandardDokumen11 halamanCalculation For Short Circuit Current Calculation Using IEC / IEEE StandardibmmoizBelum ada peringkat
- Article 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Dokumen6 halamanArticle 50 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Pradyumna PooskuruBelum ada peringkat
- Calculations of Protective Relay SettingsDokumen65 halamanCalculations of Protective Relay SettingsAngga Wira Pramana100% (12)
- Practical Switching Power Supply DesignDari EverandPractical Switching Power Supply DesignPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesDari EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDari EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsDari EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlDari EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Belum ada peringkat
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorDari EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorBelum ada peringkat
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesDari EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesBelum ada peringkat
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignDari EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Multimeter UNI-T Model UT33B-C-DDokumen42 halamanMultimeter UNI-T Model UT33B-C-Dcricketman2020Belum ada peringkat
- Importance of Transformer Inrush Current - EEPDokumen2 halamanImportance of Transformer Inrush Current - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Directional Overcurrent Relays Prevent Unneeded OutagesDokumen3 halamanDirectional Overcurrent Relays Prevent Unneeded OutagescatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- 6415 FundamentalsImprovements KZ-DC 20101025Dokumen12 halaman6415 FundamentalsImprovements KZ-DC 20101025rafeeque90Belum ada peringkat
- 12 Transformer Factory Tests Briefly Explained - EEPDokumen9 halaman12 Transformer Factory Tests Briefly Explained - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Which Type of Power Factor Correction To Use - EEPDokumen6 halamanWhich Type of Power Factor Correction To Use - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Relay Coordination GuideDokumen96 halamanRelay Coordination GuideShrimant Shanbhag80% (5)
- Antipumping Function in MVDokumen2 halamanAntipumping Function in MVcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- ABB B en Encl. Switch-Discon. IsolatorsDokumen30 halamanABB B en Encl. Switch-Discon. IsolatorscatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- What's Common For Beer Mug and Power Factor - EEPDokumen4 halamanWhat's Common For Beer Mug and Power Factor - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Roof - Photovoltaic TutorialDokumen19 halamanSolar Roof - Photovoltaic TutorialglobalrevolutionBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Periodic Inspections of A Substation Transformer - EEPDokumen4 halaman8 Periodic Inspections of A Substation Transformer - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Roof - Photovoltaic TutorialDokumen19 halamanSolar Roof - Photovoltaic TutorialglobalrevolutionBelum ada peringkat
- An Overview of Grounding System (Ungrounded) - EEPDokumen4 halamanAn Overview of Grounding System (Ungrounded) - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Main Means For The Generation of Reactive Power - EEPDokumen5 halaman4 Main Means For The Generation of Reactive Power - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Differences Between Shunt Reactor and Power Transformer - EEPDokumen5 halamanDifferences Between Shunt Reactor and Power Transformer - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- An Example of Transformer Tap-Changer Correct Adjustment - EEPDokumen3 halamanAn Example of Transformer Tap-Changer Correct Adjustment - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Transformer Types You Can See in Commercial Installations - EEPDokumen9 halaman6 Transformer Types You Can See in Commercial Installations - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- The Basics of Electrical Bus Protections - EEPDokumen8 halamanThe Basics of Electrical Bus Protections - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage Imbalance Protection of Synchronous Generator (ANSI Code 60) - EEPDokumen6 halamanVoltage Imbalance Protection of Synchronous Generator (ANSI Code 60) - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Power Plants On Board of Big Ships - Primary Distribution Schemes - EEPDokumen6 halamanPower Plants On Board of Big Ships - Primary Distribution Schemes - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Main Classes of Power Transformer - EEPDokumen8 halaman12 Main Classes of Power Transformer - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Heating of The Dry-Type Transformer - EEPDokumen4 halamanHeating of The Dry-Type Transformer - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Protection Schemes For Generators and Motors - EEPDokumen7 halamanProtection Schemes For Generators and Motors - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Using Latched Contactors To Switch Transformers - EEPDokumen2 halamanUsing Latched Contactors To Switch Transformers - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Protective Relay - Detecting Abnormal System Conditions - EEPDokumen6 halamanProtective Relay - Detecting Abnormal System Conditions - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Scott-T Transformer Connection OverviewDokumen6 halamanScott-T Transformer Connection OverviewcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Condition Monitoring of Transformers - EEPDokumen2 halamanCondition Monitoring of Transformers - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- Using Tap Changers To Match The System Voltage - EEPDokumen3 halamanUsing Tap Changers To Match The System Voltage - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Main Classes of Power Transformer - EEPDokumen8 halaman12 Main Classes of Power Transformer - EEPcatalinccBelum ada peringkat
- 7720 0554Dokumen3 halaman7720 0554KomalBelum ada peringkat
- RAB GensetDokumen3 halamanRAB GensetBintang Ersada JayaBelum ada peringkat
- GeneratorDokumen9 halamanGeneratordinukaeeBelum ada peringkat
- Compensated Drum LevelDokumen1 halamanCompensated Drum LevelFarrukh MajeedBelum ada peringkat
- (FOR VIEW) Renton 650 USB - User ManualDokumen33 halaman(FOR VIEW) Renton 650 USB - User ManualSky o skyBelum ada peringkat
- Spring'21 - IEC (I) - Quiz F02 - AC Circuit Analysis: PointsDokumen5 halamanSpring'21 - IEC (I) - Quiz F02 - AC Circuit Analysis: PointsShaian IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Bangladesh Power Sector OverviewDokumen42 halamanBangladesh Power Sector OverviewPratikBhowmickBelum ada peringkat
- Description: The Transformers With Other Specifications As The Detailed RequestDokumen2 halamanDescription: The Transformers With Other Specifications As The Detailed RequestViệt Hùng NghiêmBelum ada peringkat
- Ig5595 00 - en GBDokumen3 halamanIg5595 00 - en GBw automationBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 0-Introduction and Characteristic of Generating UnitsDokumen30 halamanLecture 0-Introduction and Characteristic of Generating UnitsVedaste Ndayishimiye100% (1)
- GisDokumen30 halamanGisAbdevil67% (3)
- NEC Table of Contents 2011 62pgsDokumen62 halamanNEC Table of Contents 2011 62pgsHassen LazharBelum ada peringkat
- ELEG 310L Prelab 3Dokumen3 halamanELEG 310L Prelab 3ghaliaBelum ada peringkat
- P.E.L Iec 60076-3-2000 2021-7-20Dokumen2 halamanP.E.L Iec 60076-3-2000 2021-7-20Luis Alfredo Ramos FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 797 KW Resistive Load Bank With Experium Controls: Dimensions (Entire Unit)Dokumen2 halaman797 KW Resistive Load Bank With Experium Controls: Dimensions (Entire Unit)Martin GoodnoughBelum ada peringkat
- EeeDokumen396 halamanEeebasavaraj100% (2)
- IEEE STD C37.20.4-2001Dokumen32 halamanIEEE STD C37.20.4-2001Teknik GresikBelum ada peringkat
- Protocol Database For Automatic Circuit Reclosers With Advanced ControllersDokumen205 halamanProtocol Database For Automatic Circuit Reclosers With Advanced ControllersCata CatalinBelum ada peringkat
- 230/460 and 460/575 Volt ModelsDokumen104 halaman230/460 and 460/575 Volt ModelsIan McNair100% (3)
- 05-Work Energy and Forces PDFDokumen6 halaman05-Work Energy and Forces PDFNazım Tola100% (1)
- Backup Box: Simple ReliableDokumen1 halamanBackup Box: Simple ReliableZhen SinBelum ada peringkat
- Addon Products From GiovenzanaDokumen11 halamanAddon Products From GiovenzanalifttecBelum ada peringkat
- Estifanos20Dagnew 2Dokumen115 halamanEstifanos20Dagnew 2daniel assefaBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Heating and CoolingDokumen11 halamanTransformer Heating and CoolingAli FarooqBelum ada peringkat
- Price List: Suny ElectronicDokumen18 halamanPrice List: Suny ElectronicPurevee PureveeBelum ada peringkat
- Installation and start up instructionsDokumen4 halamanInstallation and start up instructionsAndre FikasBelum ada peringkat
- EEET2274 3phase Rectifiers v1 2017Dokumen17 halamanEEET2274 3phase Rectifiers v1 2017Shahriar NowazBelum ada peringkat
- SREDA Module 3 Energy Efficiency in Electrical SystemsDokumen257 halamanSREDA Module 3 Energy Efficiency in Electrical SystemstowkirBelum ada peringkat
- Project 2Dokumen4 halamanProject 2amolmahajanBelum ada peringkat
- 120.515.309 - Profile Pro Safety 02Dokumen28 halaman120.515.309 - Profile Pro Safety 02johnBelum ada peringkat