HKIA Operation and Third Runway-New
Diunggah oleh
Nick TsangDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
HKIA Operation and Third Runway-New
Diunggah oleh
Nick TsangHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
5/20/2015
HKIA Operation and 3rd Runway
issues
Type of Airport
Role of Airport
Airport Management
Aeronautical and Non-aeronautical Revenue
HKIA challenges
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
3rd runway technical challenges
5/20/2015
Type of Airport
Aerodrome a defined area on land or water (including any
buildings, installations, and equipment) intended to be used either
wholly or in part for the arrival, departure and surface movement of
aircraft. (ICAO Definition Annex 14)
Airport a location where aircraft such as fixed wing aircraft,
helicopters and blimps take off and land. Aircraft may be stored or
maintained at an airport. An airport consists of at least one surface
such as a runway for a plane to take off and land, a helipad or water
for takeoffs and landings, and often includes buildings such as control
towers, hangars and terminal buildings.
Type:
International (CIQ: Customs, Immigration & Quarantine)
Domestic
General Aviation
Military
Role of Airport
Transport hub for
people and goods
Create jobs
Economy engine
Standard of living
Therefore, even
airport loses, we
still invest in
airport for the
overall benefit.
2008 (Actual)
2030
(estimate)
Economic
HK$ 78 billion
contribution
(Direct + indirect
+ induced)
HK$ 120 167
billion
% of GDP
4.6%
3.3% - 4.6%
Direct
employment
62,000
101,000-141,000
Indirect +
induced
employment
124,000
244,000
340,000
Source: Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA) (2011),
HKIA Master Plan 2030. Hong Kong: HKIA. p. 43
5/20/2015
Airport Management
Core Value
Safety passengers, employees and business partners
Security airport community
Efficiency
Environment
Quality
People
Airport Management
CEO
Corporate
Development
1. Training
2. Corporate
governance
Project
1. Engineering
2. 3rd Runway
Airport
Operations
1. Airfield
Business
2. Terminal
Business
Commercial
1. Airport
Property
2. Aviation
Logistics
3. Retail and
Advertising
Finance
1. Funding
2. Cost control
and budgeting
3. Debt
5/20/2015
Airport Management
Airport Operations
Airfield business
Maintain airfield infrastructure, including runway, taxiway, apron,
tunnels, airfield equipment, airbridge
Assignment of parking bay (parking bay allocation rule)
Marshalling service
Bird control
Apron ground traffic control
Baggage handling
Bus assignment and management
Airfield franchise management (Ground handling agent Fuel, water,
sewage, electricity, line maintenance, air conditioning)
Planning A380 parking, traffic impact (bus), rapid exit taxiway, etc
Airport Management
5/20/2015
Airport Management
Airport Management
http://www.safetypostershop.com/aviation-safetyposters/aircraft-marshalling-hand-signals/
5/20/2015
Airport Management
Airport Operations
Terminal Business
Check in counter allocation and management
Self check in system
Terminal facilities (lighting, signage, seats, resting area, toilets)
Trolley management
Ground transport (Bus, taxi, light goods vehicle)
Passenger facilitation:
CIQ and security arrangement
Terminal golf cart shuttle (WFS)
Airport Management
Commercial
5/20/2015
Airport Management
Commercial
Aviation logistics
Cargo terminal (HACTL, AAT & Cathay)
Marine cargo terminal
Airport Freight Forwarding Center
DHL Express
Airmail center
Fuel tank
Catering (Cathay, Lufthansa & Gate Gourmet)
Base Maintenance (CASL & HAECO)
Business Aviation Center
Franchise Management
Monitor operation & incident investigation
Maintain standards and safety
Audit
Airport Management
Commercial
Airport Properties
Golf course
Hotel
Land use planning
Commercial office?
Shopping mall?
Maintenance base?
5/20/2015
Airport Management
Commercial
Retail and Advertising
T1 and T2 shops
Down town price quaranteed
Food court and restaurant
Advertisement
Revenue
Fixed amount or % of revenue whichever
the higher or combination of both
Airport Management
CEO
Corporate
Development
1. Training
2. Corporate
governance
Expenditure
Project
1. Engineering
2. 3rd Runway
Expenditure
Airport
Operations
1. Airfield
Business
2. Terminal
Business
Revenue
Commercial
1. Airport
Property
2. Aviation
Logistics
3. Retail and
Advertising
Revenue
Finance
1. Funding
2. Cost control
and budgeting
3. Debt
Expenditure
5/20/2015
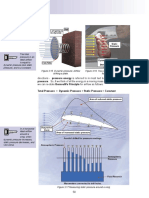
Aeronautical and Non-aeronautical Revenue
Aeronautical revenue: sources are those directly
associated with airport infrastructure related charges
such as aircraft landing, parking and passenger fees. It is
proportional with traffic volume. Usually higher traffic
volume, higher revenue.
Non-aeronautical revenue: sources indirectly associated
with airport infrastructure, such as rental, franchisee fee,
advertising, etc. It is not directly dependent on traffic
volume. Usually of higher profit margin.
Aeronautical and Non-aeronautical Revenue
Airport no longer only a transport hub
Turning into airport city
China, 134 out of 183 airports with deficit (2.9billion
RMB) (May 2013)
Too dependent on aeronautical revenue
5/20/2015
Aeronautical and Non-aeronautical Revenue
Disadvantage of reliance of Aeronautical
More nonrevenue:
aeronautical revenue
Less profit margin
Unstable source of income (affected by
seasonal)
Unattractive to passengers and airlines
More
airport
spending
Increasing non-aeronautical revenue
Singapore Changi Airport (AvsN) 50 : 50 (2012)
US airports (AvsN) 55.2 : 44.8 (2012)
Stable income for investment
Lower aeronautical charge to attract airliners
Lower
aeronautical
charge
More airline
higher
frequency
More
passengers
Aeronautical and Non-aeronautical Revenue
Air bridge
charge
Landing
charge
Parking
charge
Noise
surcharge
Passenger
charge
Aeronautical
Revenue
Lighting
charge
Security
charge
Baggage
Handling
Franchisee
charge
Terminal
check in
charge
Airside
service
franchisee
charge
10
5/20/2015
Aeronautical and Non-aeronautical Revenue
Airport Authority Ordinance (Chapter 483, The Laws of Hong
Kong)
Landing charge (MTOW Maximum Take-off Weight)
MTOW
Fixed Charge +
Rate per tonne
Up to 20 tonnes
HKD 2210.0
Nil
Over 20 tonnes
HKD 2210.0
HKD 63.0 over 20t.
B747 (MTOW) = 395t
HK$2210+63x(395-20)=HK$25,835
Parking charge per 15min
Terminal Frontal
HK$156
Remote Parking
HK$125
Cargo Apron
HK$99
Direct taxi-in/out
HK$99
Maintenance Parking
HK$80
Aeronautical and Non-aeronautical Revenue
Franchisee
fee
Land use
fee (golf
course)
Office
rental
Nonaeronautical
Revenue
Advertising
Retail shops
rental
11
5/20/2015
HKIA challenges
Limited capacity: parking, runway and
terminal facilities
Keen competition from PRD airports
Guangzhou: plan ultimately 5
runways+72 hrs visa free entry
China Southern Airline develop
Guangzhou Road
Shenzhen Airport 3 runway and 4
terminal in 2020
by A380
HKIA 2030 Master Plan
Close proximity of Macau/ Zhuhai airport
HKIA challenges
Threatening the role of Transfer hub
Competition from Seoul, Malaysia and Shanghai as transfer hub
Kangaroo route Singapore, Dubai
Approaching max capacity while increasing demand on air traffic
Runway capacity?
Passenger terminal capacity?
12
5/20/2015
Runway designator
-
Runway naming
a number between 01 and 36, which is generally one
tenth of the magnetic heading of the runway
HK Runway 073 or 253
07L/25R 07R/25L
Left / Center/ Right or even change the name to avoid
confusion
Runway summary
Airport
No. of
Runway
Name
Runway Heading
Hong Kong
(VHHH)
07L/25R & 07R/25L
073/253
Macau (VMMC)
16/34
163/343
Shenzhen
(ZGSZ)
15/33 & 16/34
155/335
Guangzhou
(ZGGG)
3*
(new
runway
open on 5
Feb 2015)
02L/20R, 02R/20L &
19/01
016/196
Zhuhai (ZGSD)
05/23
047/227
13
5/20/2015
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
Terrain
Limit airspace/airways
Affect departure and arrival turn
Affect missed approach
Lack of enough holding stack
Aircraft mix
70:30 Heavy vs Medium/small
Separation and wake turbulence separation problem
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
14
5/20/2015
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
Close proximity of PRD airports (GZ/SZ)
Invisible wall at BEKOL? (15,700ft)
=4800m
Possible Solution:
=>PRD Terminal
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
15
5/20/2015
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
16
5/20/2015
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
Constrain on HKIA Runway capacity
Close proximity of Macau/Zhuhai airport
Macau runway perpendicular to HK runway
Coordination required to avoid interference
One country two system
Different ATC procedures and standards
Coordination
17
5/20/2015
3rd Runway Technical Challenges
Background (by Consultant
report of HKIA)
Same direction 07/25 parallel
runway
North for Arrival, Middle for
Departure and South for Mixed
mode
New terminal linked by
Automated People Mover
3rd Runway Technical Challenges
Terrain
Restricted Area
over Tuen Mun
Castle Peak
(12,000ft)
SID and STAR
18
5/20/2015
3rd Runway Technical Challenges
STAR
3rd Runway Technical Challenges
STAR
19
5/20/2015
3rd Runway Technical Challenges
SID
3rd Runway Technical Challenges
Missed approach for 3rd runway?
No independent operation
Also the problem of extended final approach
20
5/20/2015
3rd Runway Technical Challenges
Shenzhen and Guangzhou departure and arrival cross in HK
Macau and Zhuhai airport
Airspace congestion
Runway interference
Efficiency ?
68 runway slots
102 runway slots?
Unless airspace redesign
Open PRD airspace
Centralized terminal air traffic control
Pros and Cons of 3rd Runway
Pros:
1. Contributing GDP
2. Increase employment
opportunities
3. Increase competitiveness of HK
4. Capture growing demand of air
travel
5. Changed air transport mode
leading early saturation of
airport
6. Relieve airport congestion and
improve services (airport
saturated)
7. Better slots and higher
frequency
Cons:
1. Pollution (air, noise)
2. Marine pollution due to
reclamation and endangering
white dolphin
3. Construction pollution
4. Huge cost (HKD$130200Billion)
5. Low efficiency
6. Airport not yet saturated
7. Air space congestion rather
than airport congestion
8. Not enough workforce
21
5/20/2015
Bibliography
Aeronautical Information Publication, Civil Aviation
Department, http://www.hkatc.gov.hk/
Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA) (2011),
HKIA Master Plan 2030.
HKIA Annual Report 2012/2013
HKIA 2030 Primary Traffic Forecast, Final report, 30
July 2010
Hong Kong International Airport Master Plan 2030 Technical Report
END
22
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Basic Radio Communication Handout PDFDokumen14 halamanBasic Radio Communication Handout PDFNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Flight Operation Inspectors ManualDokumen210 halamanFlight Operation Inspectors Manualvikash_kumar_thakurBelum ada peringkat
- Sales Manual: Vipul Brahmbhatt 10 Pavit Gandhi 25 Dolly Marvania 44 Jyoti Shau 73 Vivek Singh 101 Amrita Narang (MMS) 34Dokumen31 halamanSales Manual: Vipul Brahmbhatt 10 Pavit Gandhi 25 Dolly Marvania 44 Jyoti Shau 73 Vivek Singh 101 Amrita Narang (MMS) 34Trupti DaveBelum ada peringkat
- AtcDokumen48 halamanAtcfrancis GodoyBelum ada peringkat
- Airport CodeDokumen60 halamanAirport CodeGhannez Novaldi Loreza67% (3)
- Pilot - ATC CommunicationsDokumen24 halamanPilot - ATC Communicationsaske7sp8055100% (1)
- Air Traffic Control Manual of OperationsDokumen750 halamanAir Traffic Control Manual of OperationsRemiller CCNA100% (2)
- Air Trafit Control System SeminarDokumen14 halamanAir Trafit Control System SeminarMajestyBelum ada peringkat
- Heathrow Noise BlueprintDokumen7 halamanHeathrow Noise BlueprintlalbaghBelum ada peringkat
- ATM The Pilots EnvironmentDokumen25 halamanATM The Pilots EnvironmentNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- 001 - Air Law and ATC Procedures - 1-6 - PPL (A)Dokumen129 halaman001 - Air Law and ATC Procedures - 1-6 - PPL (A)sabina2424Belum ada peringkat
- Terminal Planning Spreadsheet ModelDokumen107 halamanTerminal Planning Spreadsheet ModelVivek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Annex 14-Aerodromes FinalDokumen71 halamanAnnex 14-Aerodromes FinalPorsche ChonthichaBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Airport Planning, and Site SelectionDokumen28 halaman03 Airport Planning, and Site SelectionjohnBelum ada peringkat
- Annexes 1 - 18Dokumen26 halamanAnnexes 1 - 18MIKHAEL YERIKHOBelum ada peringkat
- Nelson Airport Operations and Regulatory Review Redacted - Redacted - RSDokumen34 halamanNelson Airport Operations and Regulatory Review Redacted - Redacted - RSBillMetcalfeBelum ada peringkat
- ATM Enroute IFR ChartsDokumen28 halamanATM Enroute IFR ChartsNick Tsang100% (1)
- Spin AvoidanceDokumen28 halamanSpin AvoidanceNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Airport Runway Optimal Lengths and Isses in The Northwest TerritoriesDokumen98 halamanAirport Runway Optimal Lengths and Isses in The Northwest TerritoriesTim LinBelum ada peringkat
- Air Traffic Flow Management (ATFM)Dokumen27 halamanAir Traffic Flow Management (ATFM)Johari JeffreyBelum ada peringkat
- Plane Talking: A Guide To Good Radio UseDokumen48 halamanPlane Talking: A Guide To Good Radio UseNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Metaheuristics for Air Traffic ManagementDari EverandMetaheuristics for Air Traffic ManagementPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Aim 2019-TC PDFDokumen459 halamanAim 2019-TC PDFkaran dhanjal100% (1)
- Headset ProcedureDokumen50 halamanHeadset ProcedureElshaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Airport Terminals and Ground Access Part 2Dokumen13 halamanAirport Terminals and Ground Access Part 2Abdul HannanBelum ada peringkat
- Airport Layout ComponentsDokumen6 halamanAirport Layout ComponentsJohn Prashanth Vadlapati100% (1)
- Commercial Aviation Accidents 1958 - 2014: A Statistical AnalysisDokumen13 halamanCommercial Aviation Accidents 1958 - 2014: A Statistical AnalysisjouadiBelum ada peringkat
- TOR of Airport SampleDokumen5 halamanTOR of Airport SampleNal Bikram ThapaBelum ada peringkat
- Transport Canada AIM 2023Dokumen497 halamanTransport Canada AIM 2023Monika. Sassy100% (1)
- 62-00 ICAO+Doc+9137 Airport+Services+Manual Part+6+-+Control+of+Obstacles FR 110228 GanDokumen0 halaman62-00 ICAO+Doc+9137 Airport+Services+Manual Part+6+-+Control+of+Obstacles FR 110228 GanSubhash RamisettyBelum ada peringkat
- SME FSB Hangar Floor MarkingsDokumen11 halamanSME FSB Hangar Floor MarkingsMohamed ElfawalBelum ada peringkat
- GroundhandlngDokumen44 halamanGroundhandlnghuouinkyouma100% (1)
- Lec-1 Introduction, Airport ComponentsDokumen56 halamanLec-1 Introduction, Airport ComponentsUmar Naveed100% (1)
- LAPTER Airport Master Plan UpdateDokumen444 halamanLAPTER Airport Master Plan Updatemessy kollo100% (1)
- Dubai International AirportDokumen19 halamanDubai International AirportelcivilengBelum ada peringkat
- Apron SafetyDokumen20 halamanApron SafetyAmineHadjout100% (1)
- Airport EngineeringDokumen50 halamanAirport EngineeringPriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Aerodrome Safety For Airside DriversDokumen1 halamanAerodrome Safety For Airside DriversayamayamBelum ada peringkat
- Airport Operations Manual: August 20, 2020Dokumen73 halamanAirport Operations Manual: August 20, 2020hakan özcanBelum ada peringkat
- Airport CapacityDokumen18 halamanAirport CapacityAhsan AfzaalBelum ada peringkat
- Why Do Planes Need Pushback TrucksDokumen2 halamanWhy Do Planes Need Pushback TrucksMojdeh SoltaniBelum ada peringkat
- Approaches: U.S. Terminal Procedures ChartDokumen21 halamanApproaches: U.S. Terminal Procedures ChartNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- LGKR 20-2020Dokumen68 halamanLGKR 20-2020Tweed3ABelum ada peringkat
- Ground Support Equipment Safety Inspection Program 2014Dokumen25 halamanGround Support Equipment Safety Inspection Program 2014TonyBelum ada peringkat
- VFR MetDokumen56 halamanVFR MetNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Airport DesignDokumen6 halamanAirport DesignDIBYENDU MONDALBelum ada peringkat
- New Airport ReportDokumen743 halamanNew Airport Reportrgovindan123Belum ada peringkat
- Samsung C&T 2014 - Consolidated Financial StatementsDokumen126 halamanSamsung C&T 2014 - Consolidated Financial StatementsJinay ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Grid MapDokumen20 halamanGrid MapMd Arifur Rahman100% (1)
- Runway OrientationDokumen24 halamanRunway OrientationAbdulkareem Adeyinka100% (2)
- Cargo The Ambition of The Parisian Airports - September 2018Dokumen18 halamanCargo The Ambition of The Parisian Airports - September 2018Ilahe AslanBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Planning For Airport Capacity PDFDokumen8 halamanStrategic Planning For Airport Capacity PDFVkuzovlevaBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Runway LengthDokumen43 halamanAircraft Runway LengthAgung TrianshariBelum ada peringkat
- Air Traffic RouteDokumen16 halamanAir Traffic RouteLikeKangen LoveWaterBelum ada peringkat
- Airport Turnround CoordinatorDokumen1 halamanAirport Turnround CoordinatorAzeemBelum ada peringkat
- Statistics: Causes of Fatal Accidents by Decade (Percentage)Dokumen7 halamanStatistics: Causes of Fatal Accidents by Decade (Percentage)persadanusantaraBelum ada peringkat
- NZWNCharts PDFDokumen54 halamanNZWNCharts PDFThenady RiordanBelum ada peringkat
- Policy On Airport InfrastructureDokumen11 halamanPolicy On Airport InfrastructureRaja174100% (1)
- Long Island MacArthur Airport Master Plan UpdateDokumen22 halamanLong Island MacArthur Airport Master Plan UpdateNewsdayBelum ada peringkat
- Business Plan For Touch of Class Custom Air Service and TLC AirlinesDokumen59 halamanBusiness Plan For Touch of Class Custom Air Service and TLC AirlinesYahia Mustafa AlfazaziBelum ada peringkat
- Capacity Model For Two Intersecting Runways PDFDokumen6 halamanCapacity Model For Two Intersecting Runways PDFmxwbuaaBelum ada peringkat
- Wbs Final AirportDokumen8 halamanWbs Final AirportWASEEMZAHOOR100% (1)
- General Weight and BalanceDokumen30 halamanGeneral Weight and Balancehansen majayaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual On Collaborative Decision-Making (CDM) : Doc 9971 AN/485Dokumen48 halamanManual On Collaborative Decision-Making (CDM) : Doc 9971 AN/485Guido Fernandez NinaBelum ada peringkat
- Bangladesh BimanDokumen7 halamanBangladesh BimanMahmudur RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Dgca FunctionsDokumen60 halamanDgca FunctionsJeetendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Thames Estuary Airport Feasibility ReviewDokumen64 halamanThames Estuary Airport Feasibility ReviewMark PhyssasBelum ada peringkat
- Banalagay: Name: Rating: Subj-Sec: InstructorDokumen3 halamanBanalagay: Name: Rating: Subj-Sec: InstructorRaymond EdictoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Terminal Facility Requirements and AlternativesDokumen25 halamanChapter 4 - Terminal Facility Requirements and AlternativesBenito MosesBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Hire Rates: Aircraft Dual Solo Private CharterDokumen1 halamanAircraft Hire Rates: Aircraft Dual Solo Private CharterNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Emergencies: Emergency DeterminationDokumen10 halamanIntroduction To Emergencies: Emergency DeterminationNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Leadership Activities and Command Tasks 2012 PDFDokumen15 halamanLeadership Activities and Command Tasks 2012 PDFNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- ATM Strip MarkingDokumen25 halamanATM Strip MarkingNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Checkpoint - Test Platform, Structure and Scores - May 2017Dokumen10 halamanCheckpoint - Test Platform, Structure and Scores - May 2017Nick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- ATC Clearances: "Climb and Maintain " "Turn Right Heading Zero Six Zero." "Cleared For Takeoff."Dokumen11 halamanATC Clearances: "Climb and Maintain " "Turn Right Heading Zero Six Zero." "Cleared For Takeoff."Nick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- ATM VFR Charts and PublicationsDokumen26 halamanATM VFR Charts and PublicationsNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Atm Basic CommunicationDokumen27 halamanAtm Basic CommunicationNick Tsang100% (1)
- General Principles - Take-OffDokumen6 halamanGeneral Principles - Take-OffNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Form of The Earth: The Equator Is The Datum From Which Latitude North or South Is MeasuredDokumen4 halamanChapter 1: Form of The Earth: The Equator Is The Datum From Which Latitude North or South Is MeasuredNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- In Out and Around AucklandDokumen56 halamanIn Out and Around AucklandNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Level.: Aircraft Technical Book CompanyDokumen6 halamanLevel.: Aircraft Technical Book CompanyNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- DC Electrics BatteriesDokumen8 halamanDC Electrics BatteriesNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Sixteen IcingDokumen7 halamanChapter Sixteen IcingNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Fuselage, Wings and Stabilising Surfaces: Design PhilosophiesDokumen8 halamanFuselage, Wings and Stabilising Surfaces: Design PhilosophiesNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Flight Crew Licensing: Aircraft Technical Book CompanyDokumen7 halamanFlight Crew Licensing: Aircraft Technical Book CompanyNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Airframes: The Longitudinal AxisDokumen4 halamanChapter 1: Airframes: The Longitudinal AxisNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Unit or Service Call-Sign Suffix Example: Chapter 2: General Operating ProceduresDokumen4 halamanUnit or Service Call-Sign Suffix Example: Chapter 2: General Operating ProceduresNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Lift: Directions - We Can Re-StateDokumen4 halamanChapter 3: Lift: Directions - We Can Re-StateNick TsangBelum ada peringkat
- Ao PPT Presentation Lecture 9 Fall 2020 Dated 22 Oct 2020 Pax Terminal OpnDokumen37 halamanAo PPT Presentation Lecture 9 Fall 2020 Dated 22 Oct 2020 Pax Terminal OpnHassan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Lytv/Tiv Tivat, Montenegro: Lasti 1Rc (Las1Rc) Pinuk 1ra (Pin1Ra) RNP Arrivals (RWYS 14, 32)Dokumen25 halamanLytv/Tiv Tivat, Montenegro: Lasti 1Rc (Las1Rc) Pinuk 1ra (Pin1Ra) RNP Arrivals (RWYS 14, 32)Tweed3ABelum ada peringkat
- Circular 298 OACIDokumen20 halamanCircular 298 OACICésarAndrésTaleroFlórezBelum ada peringkat
- Target Start-Up Approval Time (TSAT) : How Is TSAT Calculated?Dokumen3 halamanTarget Start-Up Approval Time (TSAT) : How Is TSAT Calculated?jsesBelum ada peringkat
- ZBOP Catalogue Katalog PDFDokumen59 halamanZBOP Catalogue Katalog PDFGabriel TorrezBelum ada peringkat
- AIC Sup H25-18 'Holding Fuel Advice'Dokumen3 halamanAIC Sup H25-18 'Holding Fuel Advice'vonmanoBelum ada peringkat
- Eurocontrol Lssip 2022 MaastrichtDokumen130 halamanEurocontrol Lssip 2022 MaastrichtNeo PilBelum ada peringkat
- AIP Somali Part One (1) En-RouteDokumen80 halamanAIP Somali Part One (1) En-RouteabdirahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Kmsy (Armstrong New Orleans Intl) - R (06nov15) PDFDokumen25 halamanKmsy (Armstrong New Orleans Intl) - R (06nov15) PDFnabatmanBelum ada peringkat
- InstrumentationDokumen8 halamanInstrumentationGirish SreeneebusBelum ada peringkat
- Learn To Talk Like A Pilot ArticleDokumen4 halamanLearn To Talk Like A Pilot ArticleHazem KhafagaBelum ada peringkat
- Lung Surgery and Takeoff ProcedureDokumen4 halamanLung Surgery and Takeoff ProcedureCrystalBelum ada peringkat
- Easy Access Rules For Flight Crew Licencing (Part-FCL) PPL EUROPEAN FLYERSDokumen69 halamanEasy Access Rules For Flight Crew Licencing (Part-FCL) PPL EUROPEAN FLYERSjonathanaldazmBelum ada peringkat
- Narco Avionics: AT155 TSO TransponderDokumen27 halamanNarco Avionics: AT155 TSO TransponderElmer Villegas0% (1)
- 1961 4 EngDokumen15 halaman1961 4 EngTateBelum ada peringkat
- Ojai 20-2020Dokumen66 halamanOjai 20-2020Tweed3A100% (1)
- Hafisul Haq CV 1Dokumen4 halamanHafisul Haq CV 1Hafisul HaqBelum ada peringkat
- Kjfkkbos PDF 1679417293 PDFDokumen37 halamanKjfkkbos PDF 1679417293 PDFMarin DruckerBelum ada peringkat
- Adr Data Catalogue Annex A 0.4 PDFDokumen10 halamanAdr Data Catalogue Annex A 0.4 PDFpepegoesdigitalBelum ada peringkat
- ATO Business Plan 2010Dokumen154 halamanATO Business Plan 2010Bradford MorseBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Joyance Sprayer Drones CatalogDokumen9 halaman3 - Joyance Sprayer Drones CatalogDanijel ŽalacBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Industrial Building: A Project ReportDokumen59 halamanDesign of Industrial Building: A Project ReportKRishna KumalBelum ada peringkat
- Jeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDokumen63 halamanJeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitorionclassBelum ada peringkat
- CAP670Dokumen442 halamanCAP670Viorel CroitoruBelum ada peringkat
- PPL (A) : Part-FCL Question BankDokumen18 halamanPPL (A) : Part-FCL Question BankIbrahim MedBelum ada peringkat