Quimica Organica Notas
Diunggah oleh
jordi17100 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
40 tayangan2 halamanquímica organica notas
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniquímica organica notas
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
40 tayangan2 halamanQuimica Organica Notas
Diunggah oleh
jordi1710química organica notas
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
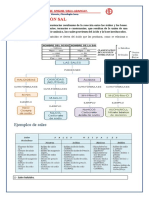
UNIDAD 11 QUMICA ORGNICA
Saber que un HIDROCARBON es un compuesto formado por CARBON, HYDROGEN
principalmente y OXYGEN
Saber que el Carbon puede establecer 4 enlaces
Saber que el Hydrogen siempre establece 1 enlace solo
Saber que el Oxygen puede establecer 2 enlaces
Saber que el CHAIN LENGHT determina las Physical Properties (P.332)
( Chain lenght m.p. y b.p. solubility)
Saber que el CHAIN TYPE determina las Chemical Properties (types of chemical
reactions the hydrocarbon will have) (P.332)
Definir FUNCTIONAL GROUP (an atom or group of atoms in the chain whose
reactions determine the properties of the whole chain) (p.333)
Definir HOMOLOGOUS SERIES (a group of compounds with the same functional
group (= chemical prop.) but different chain length ( physical prop.) (p.333)
Saber NOMBRAR los diferentes hidrocarburos segn la cantidad de carbonos y el
grupo funcional que tienen (p.334 table 30.2 y 30.3)
Chain Lenght
1C
2C
3C
First part of name
Meth-Eth-Prop--
Chain Length
4C
5C
6C
First part of name
But-Pent-Hex--
Number of bonds
Second part of name Functional group
Third part of name
between C
1 C-C
--ane
Alcohol -O-H
--ol
2 C=C
--ene
Carbonic Acid -C=O
--oic acid
O3 CC
--ine
H
Esters C=O
--ate
O-
Saber reconocer ALKANES (C-C) y nombrarlos.
Entender que son SATURATED HYDROCARBONS (each carbon in the chain has as
many hydrogens bonded onto it as possible, the carbons are all involved in single
covalent bonds) (p.341)
Saber reconocer ALKENES (C=C) y nombrarlos
Entender que son UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS (more atoms can be added to
the chain without breaking it) (p.341)
Saber que los ALKYNES tambin son insaturados
Saber en que tipos de reaccin esta involucrados estos 2 tipos de hidrocarburos
(p.341)
1. Saturated Hydrocarbons alkanes SUBSTITUTION
2. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons alkenes ADDITION
Saber que la Addition Reaction puede ser usada como Test de Reconocimiento de
Alquenos, al usar como aditivos a Br2 y KMnO4.(p.343)
Saber en que consiste la FRACTIONAL DISTILLATION OF OIL y bajo que criterios
se separan las diferentes fracciones (chain length and its different physical properties)
(p.337)
Conocer ligeramente las diferentes fracciones y sus usos (solamente las ms
comunes e importantes) (p.338 table 30.5)
Saber el concepto de PETROCHEMICALS (p.340)
Saber para que se usa el CRACKING (obtention of short saturated and unsaturated
hydrocarbons from long saturated chains that are useless) y porque es importante (2
ventajas) (p.342)
Saber que las ADDITION REACTIONS se usan para obtener saturated hydrocarbons de
unsaturated hydrocarbons (p.343)
Saber para que se usa POLYMERISATION (obtention of long saturated hydrocarbons
from short unsaturated chains) (p.344) saber por lo menos 1 ejemplo
Saber como se forman los ALCOHOLS, poder reconocerlos y nombrarlos (p.345)
Conocer los 2 mtodos de preparacin de ETANOL (p.346)
Methylated Spirits
Fermented Alcohol
Reacting ethane + water
Fermenting sugars with
Solvent, fuel
Beers, wine, spirits for
yeast
drinking
Saber como se forman los ORGANIC ACIDS, poder reconocerlos y nombrarlos
(p.347)
Conocer el mtodo de preparacin: Oxidation of Alcohols (p.347)
Conocer las caractersticas de los cidos orgnicos (son iguales a las de los
Oxocidos ya vistos!) (p.348)
Saber como se forman los ESTERS, poder reconocerlos y nombrarlos (p.349)
Conocer mtodo de preparacin de esteres (p.350)
Organic Acid + Alcohol Ester + Water (es una reaccin muy lenta!)
Complete Combustion of Methane CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O
Incomplete Combustion of Methane 4CH4 + 6O2 CO2 + 8H2O + 2CO + C
Bond breaking absorves energy and bond making releases it
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- APM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y AnatomiaDokumen44 halamanAPM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y Anatomiajordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- APM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y AnatomiaDokumen31 halamanAPM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y Anatomiajordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- APM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y AnatomiaDokumen44 halamanAPM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y Anatomiajordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- APM TEMA 2 - FarmacologiaDokumen13 halamanAPM TEMA 2 - Farmacologiajordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- TPDR Monchablon 31 Mayo 2017Dokumen3 halamanTPDR Monchablon 31 Mayo 2017jordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- Ateneo AT - MNG TBCDokumen22 halamanAteneo AT - MNG TBCjordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- TPDR Monchablon 31 Mayo 2017Dokumen3 halamanTPDR Monchablon 31 Mayo 2017jordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- APM TEMA 2 - FarmacologiaDokumen13 halamanAPM TEMA 2 - Farmacologiajordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- Guía de Estudio y Notas IGCSE CHEMISTRYDokumen7 halamanGuía de Estudio y Notas IGCSE CHEMISTRYjordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- Formuleo QuímicoDokumen2 halamanFormuleo Químicojordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- APM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y AnatomiaDokumen32 halamanAPM TEMA 1 - Bio Celular y Anatomiajordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- Pre Test - Adicciones en Atencion PrimariaDokumen2 halamanPre Test - Adicciones en Atencion Primariajordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- Escala de Hamilton para La AnsiedadDokumen2 halamanEscala de Hamilton para La Ansiedadjordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- FX PSIQUICAS CuadroDokumen1 halamanFX PSIQUICAS Cuadrojordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- Rec EtasDokumen2 halamanRec Etasjordi1710Belum ada peringkat
- Funcion Sales 3eroDokumen5 halamanFuncion Sales 3eroJuan Carrion CahuanaBelum ada peringkat
- Preparacion Del 2 Cloro 2 Metilpropano VDokumen6 halamanPreparacion Del 2 Cloro 2 Metilpropano VandresBelum ada peringkat
- Guía Unidad II. EstequiometríaDokumen35 halamanGuía Unidad II. EstequiometríaMayra LealBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluación Parcial 2Dokumen214 halamanEvaluación Parcial 2danielsuko64Belum ada peringkat
- Ácido Nítrico 12 %: Sección 1: Identificación Del ProductoDokumen12 halamanÁcido Nítrico 12 %: Sección 1: Identificación Del ProductoSergio Andrés Archila AbrilBelum ada peringkat
- Glosario de Palabras Quimica InorganicaDokumen8 halamanGlosario de Palabras Quimica InorganicaAriel CQBelum ada peringkat
- ISAE UNIVERSIDAD Español GabiDokumen14 halamanISAE UNIVERSIDAD Español Gabierick arauz mirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Guía de Ejercicios Química General I 2012 PDFDokumen91 halamanGuía de Ejercicios Química General I 2012 PDFDiego Gaston Enrich0% (1)
- Laboratorio Suelos Practica 8Dokumen17 halamanLaboratorio Suelos Practica 8Mallon Zuna Isaias GilbertoBelum ada peringkat
- Bioseguridad Dental PDFDokumen58 halamanBioseguridad Dental PDFBoliviano JaponesaBelum ada peringkat
- CAPITULO 1 - Química y MateriaDokumen2 halamanCAPITULO 1 - Química y MateriaLuis SandovalBelum ada peringkat
- Estructuras de LewisDokumen98 halamanEstructuras de LewisVitore MorleoneBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica Química 1-2Dokumen11 halamanPráctica Química 1-2Paulina MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Tecnica Esterilizador A Peroxido de Hidrogeno PHB EsDokumen5 halamanFicha Tecnica Esterilizador A Peroxido de Hidrogeno PHB EsAlemontse JiménezBelum ada peringkat
- Guia Estandar para Contaminacion de ComsbustiblesDokumen23 halamanGuia Estandar para Contaminacion de ComsbustiblesCARMENBelum ada peringkat
- Aplicacion de Los AlcanosDokumen5 halamanAplicacion de Los AlcanosAlvarez AntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Semillas para El Arca. EbookDokumen81 halamanSemillas para El Arca. EbookRoberto PitlukBelum ada peringkat
- Ácidos Carboxílicos y DerivadosDokumen31 halamanÁcidos Carboxílicos y DerivadosEliana GuardaBelum ada peringkat
- Radicales de Acidos Hidracidos y OxacidosDokumen10 halamanRadicales de Acidos Hidracidos y OxacidosSergio Driss Melèndez MartìnezBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Introduccion Al Proceso Del Gas NaturalDokumen45 halaman1 Introduccion Al Proceso Del Gas NaturalFreddy Ibañez Peña100% (1)
- Guia Rapida IrDokumen5 halamanGuia Rapida IrJuan Turmero AgapitoBelum ada peringkat
- Informe #1 Química OrgánicaDokumen7 halamanInforme #1 Química OrgánicaChristian Torres BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Diccionario de GeoquímicaDokumen22 halamanDiccionario de Geoquímicamenjhiu0% (1)
- AlcanosDokumen5 halamanAlcanosASDFBelum ada peringkat
- Tema 60Dokumen19 halamanTema 60Victor PereaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 DiccionariotecnologianuclearDokumen548 halaman2 DiccionariotecnologianuclearLa Cerrazón de WansBelum ada peringkat
- EL Origen de La VidaDokumen8 halamanEL Origen de La VidaPaulina CasarrubiasBelum ada peringkat
- Semana 1 Materia, Tabla P y EnlacesDokumen77 halamanSemana 1 Materia, Tabla P y EnlacesCaroline Ariana Sarmiento CurilloBelum ada peringkat