1 - Restless Earth UPDATED
Diunggah oleh
MROHANLONHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1 - Restless Earth UPDATED
Diunggah oleh
MROHANLONHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Dynamic Planet - Restless Earth - 1
Restless Earth
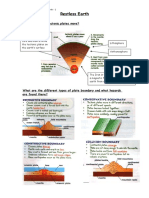
How and why do tectonic plates move?
Convection currents
from the hot outer
core and mantle move
the tectonic plates on
the earths surface
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
The Iron in the outer core produces
a magnetic field which protects the
earth from radiation from space
What are the different types of plate boundary and what hazards
are found there?
Dynamic Planet - Restless Earth - 1
Volcano
Montserrat, Caribbean (LEDC)
Montserrat is found on a destructive plate boundary
Primary Effects
Social
Economic
Environmental
Secondary Effects
23 people died in 1997
50% of the population were
evacuated to the north of the
island to live in makeshift shelters
Plymouth - the capital became a
ghost town
Many schools and hospitals were
destroyed
Homes were destroyed and
abandoned
Infrastructure, including the
airport, was destroyed - 2/3 of
the island was covered in ash
Farmland was destroyed
Tourism came to a halt
Unemployment rose as tourism
industry declined
More than half Montserrat
become uninhabitable.
Pyroclastic flows destroyed
everything in their path
Floods as valleys blocked by
ash
Forest fires caused by
pyroclastic flows
Scientists monitored the volcano and
set up warning systems via radio,
loudhailer and sirens
The UK government sent 17 million of
emergency aid, including temporary
buildings and water purification systems
Charities like the Red Cross set up
temporary schools
People were evacuated to the north of
the island, and then to other countries
Immediate Responses
Health problems were
reported (due by volcanic ash
containing quartz that can then
cause silicosis)
Ageing population as many
young people have left the
island
Over half the population left
the island and have not
returned (many went to the
UK)
Long Term Responses
Ten years later the South of the island
is still out of bounds, and scientists are
still monitoring the volcano
The UK government funded a three year
re-development plan. It is building
homes, schools, infrastructure and
hospitals
The Red Cross have built a home for the
elderly
Tourists may come back and the volcano
itself could become a tourist attraction
Prediction
Seismometers: to monitor earthquakes as magma rises to the surface
Tiltmeters: to monitor the volcano swelling as it fills with magma
Aircraft: To measure the amount of gas given off by the volcano
Protection
Concrete channels: To divert dangerous lahar mudflows
Concrete shelters: To protect people from volcanic bombs and ash
Evacuation routes: Clearly signposted. People also have regular drills
Dynamic Planet - Restless Earth - 1
Earthquakes in MEDCs and LEDCs
Haiti (LEDC)
Haiti is found on a conservative plate boundary. The earthquake in 2010. Magnitude 7
Primary (caused directly by the earthquake)
Secondary (result from primary effects)
316,000 people were killed and 1 million people
were made homeless.
1 in 5 people lost their jobs because so many
buildings were destroyed.
250,000 homes and 30,000 other buildings,
including the Presidents Palace were either
destroyed or badly damaged
The large number of deaths meant that
hospitals and morgues became full and bodies
then had to be piled up on the streets
Transport and communication links were also
badly damaged by the earthquake
The large number of bodies meant that diseases,
especially cholera, became a serious problem
Hospitals (50+) and schools (1,300+) were
badly damaged, as was the airports control
tower
It was difficult getting aid into the area
because of issues at the airport and generally
poor management of the situation
The main prison was destroyed and 4,000
inmates escaped
People were squashed into shanty towns or onto
the streets because their homes had been
destroyed leading to poor sanitation and health,
and looting became a real problem
Immediate Responses
Long Term Responses
$100 million in aid given by the USA and $330
million by the European Union
98% of the rubble on the roads hadnt been
cleared restricting aid access
Lack of immediate aid through poor planning,
management and access meant that people had
to try and rescue each other
1 million people still without houses after 1 year
so still have to live in aid camps
115,000 tents and 1,000,000+ tarpaulin
Support for people without jobs, which equates
shelters provided, 810,000 people placed in aid to nearly 70% of the population, through
camps. Healthcare supplies provided to limit
cash/food-for-work projects
disease
Earthquake proof
design in the developing
world.
Japan (MEDC)
Dynamic Planet - Restless Earth - 1
Japan is found on a destructive plate boundary. The earthquake in 2011. Magnitude 9
Primary (caused directly by the earthquake)
Secondary (result from primary effects)
Ground shaking: parts of Japan were shifted
2.4 metres further east.
Tsunami: this was caused by a 58 metre up
thrust along a 180 km long section of the
seabed.
Ground subsidence: a 400 km stretch of
coastline dropped vertically by 0.6 metres,
which allowed the tsunami to overtop defences
and travel further and faster inland.
Flooding: there was massive coastal flooding as
a consequence of the tsunami flowing inland
Soil liquefaction: this was found to have
occurred in areas of reclaimed land around
Tokyo, damaging more than a thousand
buildings.
The economic impact on the region and on Japan
as a whole is severe. The Japanese government
estimated that the damage alone could cost
US$300 billion. By June that year, 209
companies in Japan had been forced into
bankruptcy by the disaster.
15,845 killed
128,479 properties totally destroyed
3,918 roads damaged
78 bridges damaged.
Nuclear power plants were damaged. In the
Fukushima region over 200,000 residents were
evacuated and are still unable to return to the
area.
Immediate Responses
Long Term Responses
Text messages were sent and TV broadcasts
interrupted to warn people of the potential
tsunami following the earthquake
Long term planning: They have regular
earthquake drills to educate people. Emergency
services practice how to rescue people. People
keep emergency kits at home (torch, food, radio)
The nuclear power plant at Fukoshima was
automatically shut down
Many buildings in Japan are earthquake proof
deep foundations, strong, flexible steel frames,
and shock absorbers in the buildings frame.
Emergency rescue teams were mobilised
quickly and effectively to reach and rescue
affected people.
Earthquake proof design in the
developed world. E.g. Japan
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Japan Tsunami Case StudyDokumen2 halamanJapan Tsunami Case Studykristianbourke08Belum ada peringkat
- Aqa Geography Case StudiesDokumen18 halamanAqa Geography Case StudiesVishnu SelvakumarBelum ada peringkat
- MT PinatuboDokumen2 halamanMT Pinatuboapi-228716866Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Energy Sources 2Dokumen20 halaman1 Energy Sources 2Mohamed RiazBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 GCSE Geography NotesefsfDokumen86 halaman2022 GCSE Geography NotesefsfLix FNBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel B Geography Unit 1 Revision BookletDokumen45 halamanEdexcel B Geography Unit 1 Revision BookletIlayda UludagBelum ada peringkat
- Geography case studies of deadly earthquakes and tsunamisDokumen36 halamanGeography case studies of deadly earthquakes and tsunamisLotus MbambyBelum ada peringkat
- LEDC Volcano Case StudyDokumen14 halamanLEDC Volcano Case StudyleobutterflyBelum ada peringkat
- Chile and Nepal Earthquake 10BDokumen2 halamanChile and Nepal Earthquake 10BTanvirH.ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Japan Earthquake, Tsunami and Nuclear Crisis: / Nætʃ.ɚ. L Dɪ Zæs - TɚDokumen9 halamanJapan Earthquake, Tsunami and Nuclear Crisis: / Nætʃ.ɚ. L Dɪ Zæs - TɚAldanaBelum ada peringkat
- Japan Earthquake, Tsunami and Nuclear Crisis: / Nætʃ.ɚ. LD Ɪ Zæs - TɚDokumen6 halamanJapan Earthquake, Tsunami and Nuclear Crisis: / Nætʃ.ɚ. LD Ɪ Zæs - TɚLillis SarahBelum ada peringkat
- Let's Make The Change Protect The Environment - June 4 2009 Veracruz, MexicoDokumen9 halamanLet's Make The Change Protect The Environment - June 4 2009 Veracruz, MexicoLong Kuan - Lohas QueenBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Geographical PhenomenaDokumen6 halamanThe Impact of Geographical PhenomenaKristof Stuven100% (1)
- Effects of Natural Disasters On TourismDokumen11 halamanEffects of Natural Disasters On TourismAnonymous TR7KLlARBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquakes in Chile and NepalDokumen6 halamanEarthquakes in Chile and NepalMysticalBelum ada peringkat
- GeographyDokumen17 halamanGeographyTedesia AssanahBelum ada peringkat
- The Boxing Day Tsunami: by Chelsea SutherlandDokumen12 halamanThe Boxing Day Tsunami: by Chelsea SutherlandAssignment GirlBelum ada peringkat
- Created by Pankaj Kumar BBA IV Semester Disaster ManagementDokumen5 halamanCreated by Pankaj Kumar BBA IV Semester Disaster ManagementPankaj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Keynote Disasters in Coastal AreasDokumen39 halamanKeynote Disasters in Coastal AreasPratul RanaBelum ada peringkat
- Geography Snapshot Notes DYNPLDokumen31 halamanGeography Snapshot Notes DYNPLSkye G-s100% (2)
- Paper 1 CS BookletDokumen12 halamanPaper 1 CS BookletrbtjhfgwnbBelum ada peringkat
- 20th century disasters: major events 1900-1999Dokumen3 halaman20th century disasters: major events 1900-1999KaremVulgarinRugelBelum ada peringkat
- Case Studies - iGCSE GeographyDokumen21 halamanCase Studies - iGCSE GeographyAmalia Korakaki100% (1)
- International Notes Earthquake Disaster - Luzon EarthquakeDokumen6 halamanInternational Notes Earthquake Disaster - Luzon EarthquakeMelek BencanaBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Disasters in The Top 10 Richest CountriesDokumen7 halamanNatural Disasters in The Top 10 Richest Countrieszainrasheedpk7986Belum ada peringkat
- Good Essay ChernobylDokumen2 halamanGood Essay ChernobylmillreefBelum ada peringkat
- Japan Earthquake & Tsunami: Natural Made Hazards 11/03/11Dokumen4 halamanJapan Earthquake & Tsunami: Natural Made Hazards 11/03/11JaybeeBelum ada peringkat
- EST MPDokumen19 halamanEST MPpbange084Belum ada peringkat
- First Assignment: ADokumen6 halamanFirst Assignment: Ahuma tariqBelum ada peringkat
- Background Music:we Are The WorldDokumen15 halamanBackground Music:we Are The WorldRoss Adrales GeleraBelum ada peringkat
- Japan Earthquake and Tsunami of 2011Dokumen3 halamanJapan Earthquake and Tsunami of 2011Vicky MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Lesson 3Dokumen7 halamanUnit 1 Lesson 3Kenzie ButtowskiBelum ada peringkat
- Activity (DRR)Dokumen11 halamanActivity (DRR)Tricia Maxine DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Top 10 Countries On The Ring of FireDokumen19 halamanTop 10 Countries On The Ring of FirewsfgsadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 12Dokumen13 halamanPresentation 12diliniBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Hazards in The Environment.: 1: Hurricane KatrinaDokumen2 halamanNatural Hazards in The Environment.: 1: Hurricane KatrinaPath WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 - Natural Hazards, Mitigation and AdaptationDokumen9 halamanChapter 3 - Natural Hazards, Mitigation and AdaptationAxelBelum ada peringkat
- Tsunami Destruction: What Causes A Tsunami?Dokumen4 halamanTsunami Destruction: What Causes A Tsunami?Isabella persadBelum ada peringkat
- Haiti Earthquake 2010: by Shiv Mirpuri + Will MatthewsDokumen12 halamanHaiti Earthquake 2010: by Shiv Mirpuri + Will MatthewsKishanBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 Tohoku Earthquake and TsunamiDokumen79 halaman2011 Tohoku Earthquake and Tsunamiralkad22Belum ada peringkat
- Textbook Geoactive 2 Chapter 3Dokumen36 halamanTextbook Geoactive 2 Chapter 3Flame ShineBelum ada peringkat
- 1natural Disasters ExercisesDokumen15 halaman1natural Disasters ExercisesTatyana BuseBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Management AssignmentDokumen20 halamanDisaster Management AssignmentSukhman AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Mount St. Helens Case Study NotesDokumen3 halamanMount St. Helens Case Study Notesfaryal khanBelum ada peringkat
- The Restless EarthDokumen164 halamanThe Restless Earthb_osborneBelum ada peringkat
- Individual Paper-2Dokumen6 halamanIndividual Paper-2Rana AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster ManagmentDokumen21 halamanDisaster ManagmentNEFSYA KAMALBelum ada peringkat
- Typhoon HaiyanDokumen4 halamanTyphoon Haiyanshraddhabakshi12Belum ada peringkat
- Running Head: Tohoku EarthquakeDokumen9 halamanRunning Head: Tohoku Earthquakeapi-300550974Belum ada peringkat
- PGS506coursenotes 2Dokumen20 halamanPGS506coursenotes 2VishalBelum ada peringkat
- ES3205 Student Text Chapter 1Dokumen25 halamanES3205 Student Text Chapter 1Msus HughesBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Care in The Management of The Lake Nyos Gas Disaster of 1986Dokumen7 halamanMedical Care in The Management of The Lake Nyos Gas Disaster of 1986Ijahss JournalBelum ada peringkat
- Envi Sci Lesson 2Dokumen25 halamanEnvi Sci Lesson 2Rod P. Cabico Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Contingency PlanDokumen112 halamanContingency PlanAira RonquilloBelum ada peringkat
- Case Studies TectonicsDokumen9 halamanCase Studies TectonicsLavankaBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake in Turkey 5Dokumen3 halamanEarthquake in Turkey 5Ajla ŠahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Typhoon Haiyan 2013Dokumen2 halamanTyphoon Haiyan 2013iGotheInfoBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Restless Earth UPDATED1Dokumen5 halaman1 - Restless Earth UPDATED1MROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Restless Earth UPDATEDDokumen4 halaman1 - Restless Earth UPDATEDMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- Eco Garden OpeningDokumen1 halamanEco Garden OpeningMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Consuming ResourcesDokumen5 halaman2 - Consuming ResourcesMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- Globalisation: People and The Planet - Globalisation - 3Dokumen5 halamanGlobalisation: People and The Planet - Globalisation - 3MROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- News From The Eco Garden - May 2014Dokumen1 halamanNews From The Eco Garden - May 2014MROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 6 - The Challenges of An Urban WorldDokumen5 halaman6 - The Challenges of An Urban WorldMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Consuming ResourcesDokumen4 halaman2 - Consuming ResourcesMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - The Changing Economy of The UKDokumen4 halaman5 - The Changing Economy of The UKMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Development DilemmasDokumen4 halaman4 - Development DilemmasMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Population DynamicsDokumen3 halaman1 - Population DynamicsMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Consuming ResourcesDokumen5 halaman2 - Consuming ResourcesMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Water WorldDokumen3 halaman4 - Water WorldMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Population DynamicsDokumen3 halaman1 - Population DynamicsMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - GlobalisationDokumen5 halaman3 - GlobalisationMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- News From The Garden - March 2014Dokumen1 halamanNews From The Garden - March 2014MROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Consuming ResourcesDokumen4 halaman2 - Consuming ResourcesMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Population DynamicsDokumen3 halaman1 - Population DynamicsMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- News From The Eco Garden - New CropsDokumen1 halamanNews From The Eco Garden - New CropsMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - River Processes and PressuresDokumen4 halaman5 - River Processes and PressuresMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Battle For The BiosphereDokumen2 halaman3 - Battle For The BiosphereMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 6 - Oceans On The EdgeDokumen2 halaman6 - Oceans On The EdgeMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Climate and ChangeDokumen3 halaman2 - Climate and ChangeMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- Eco News This Term - March 2014Dokumen1 halamanEco News This Term - March 2014MROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Restless EarthDokumen3 halaman1 - Restless EarthMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 6 - The Challenges of An Urban WorldDokumen9 halaman6 - The Challenges of An Urban WorldMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- Crowded Coasts Exam QuestionsDokumen1 halamanCrowded Coasts Exam QuestionsMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - The Changing Economy of The UKDokumen7 halaman5 - The Changing Economy of The UKMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - GlobalisationDokumen5 halaman3 - GlobalisationMROHANLONBelum ada peringkat
- North Eastern Atlantic Mediterranean Tsunami Warning SystemDokumen1 halamanNorth Eastern Atlantic Mediterranean Tsunami Warning SystemJoaquin EnriqueBelum ada peringkat
- Frontal RainfallDokumen3 halamanFrontal RainfallFatin AnisahBelum ada peringkat
- Sultanate of Oman D.G. of Meteorology: General Weather ForecastDokumen3 halamanSultanate of Oman D.G. of Meteorology: General Weather Forecastதுரைராஜ் இலட்சுமணன்Belum ada peringkat
- Uzb SeismicDokumen1 halamanUzb SeismicKyungYong Park100% (1)
- Hydro Meteorological Phenomena and HazardsDokumen39 halamanHydro Meteorological Phenomena and HazardsJess Maglunob80% (5)
- Tropical CycloneDokumen1 halamanTropical CycloneVince CastorBelum ada peringkat
- DepEd RADaR Report FormsDokumen2 halamanDepEd RADaR Report FormsBrown Cp50% (2)
- Relief OperationDokumen10 halamanRelief OperationgeramerBelum ada peringkat
- Function Notation Real World Application Problems 2017-2018Dokumen12 halamanFunction Notation Real World Application Problems 2017-2018api-366582437Belum ada peringkat
- CIGRE Technical Brochure 256Dokumen48 halamanCIGRE Technical Brochure 256shoboru100% (2)
- Port Coogee Coastal Monitoring - D HamiltonDokumen18 halamanPort Coogee Coastal Monitoring - D HamiltondanBelum ada peringkat
- National Weather Service in Wakefield, VADokumen2 halamanNational Weather Service in Wakefield, VALaura EmeryBelum ada peringkat
- Bangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD)Dokumen32 halamanBangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD)raduBelum ada peringkat
- MagazineArticle WeatherDokumen5 halamanMagazineArticle WeatherMargarita AlcevskaBelum ada peringkat
- Copy Reading & Headline Writing - Copy (1) .PPSXDokumen32 halamanCopy Reading & Headline Writing - Copy (1) .PPSXCharisel Jeanne Casala100% (1)
- Sample Cause Effect Essay ClimateDokumen2 halamanSample Cause Effect Essay ClimateingridguerreroocampoBelum ada peringkat
- Major Tornado Hits OklahomaDokumen4 halamanMajor Tornado Hits Oklahomaapi-213899712Belum ada peringkat
- Beaufort Wind ScaleDokumen2 halamanBeaufort Wind Scalegiannis2Belum ada peringkat
- Mayon VolcanoDokumen12 halamanMayon VolcanoJuan UnoBelum ada peringkat
- TornadoDokumen51 halamanTornadobambang aconkBelum ada peringkat
- Forecast Created By: Anthony SicilianoDokumen5 halamanForecast Created By: Anthony Sicilianoapi-309523265Belum ada peringkat
- 757 Apd 5 ErosionscourDokumen8 halaman757 Apd 5 ErosionscourAny NurhasanahBelum ada peringkat
- What causes Cyclones and LandslidesDokumen3 halamanWhat causes Cyclones and LandslidesshajmalikBelum ada peringkat
- Day 1 - Dr. Lourdes Tibig Climate Outlook PDFDokumen35 halamanDay 1 - Dr. Lourdes Tibig Climate Outlook PDFlipBelum ada peringkat
- DRRM in SchoolsDokumen22 halamanDRRM in SchoolsSalvador Dagoon Jr100% (2)
- Poručnićki - EngleskiDokumen2 halamanPoručnićki - EngleskiCorto Maltese100% (1)
- Geography ReflectionDokumen4 halamanGeography Reflectionapi-253260812Belum ada peringkat
- WEATHER AND CLIMATEDokumen1 halamanWEATHER AND CLIMATEHorváth LillaBelum ada peringkat
- EpicenterDokumen2 halamanEpicenterAlcazar Renz JustineBelum ada peringkat
- Remote Sensing ApplicationsDokumen14 halamanRemote Sensing ApplicationsShivaniSharmaBelum ada peringkat