GN
Diunggah oleh
JohnBedaLatawanMalecdan0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan3 halamanrenal disease
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inirenal disease
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan3 halamanGN
Diunggah oleh
JohnBedaLatawanMalecdanrenal disease
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
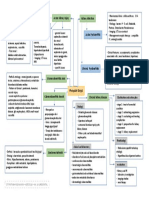
Glomerular disease
Tubular and interstitial
disease
Azotemia
Pre-renal azotemia
Most are immunologically mediated
Most are caused by toxic or infections
- elevation of:
BUN
Creatinine
- decrease in GFR
- consequence of many renal disorders, and some extrarenal
- happens when theres hypoperfusion of the kidneys
caused by:
Hemorrhage
Shock
Volume depletion
CHF
- this hypoperfusion of the kidneys could impair renal
function in the absence of parenchymal damage
Post renal azotemia
Uremia
- seen when urine flow is obstructed
- term used when azotemia is associated with
costellation of S/Sx and biochemical abnormalities
- failure of renal excretory function, metabolic and
endocrine alteration
Peripheral neuropathy
- uremia in peripheral nerve
Uremic fibrinous
pericarditis
Nephrotic Syndrome
(NoS)
- uremia in the heart
Nephritic syndrome (NiS)
- due to glomerular disease
- dominated by acute onset of gross hematuria
- mild-moderate proteinuria and HPN
- classic presentation of acute post strep
glomerulonephritis
- NiS with rapid decline of GFR (hours to days)
Rapidly progressing
Glomerulonephritis
Acute renal failure
Due to glomrular disease
heavy proteinuria
hypoalbuminemia
severe edema
hyperlipidemia
lipiduria
- oliguria and anuria
- reduced or no urine flow
- recent onset of azotemia
- can result from injury of glomerulus, interstitial injury,
vascular and tubular injury
- rapid and reversible detoriation of kidney
Chronic renal failure
prolonged S/Sx of uremia
end result of chronic renal parenchymal disease
end result of variety of renal disease
major cause of death from renal disease
Renal tubular disease
- polyurea, nocturia and electrolyte disorders (m.
acidosis)
- can be caused by medullary cystic disease
UTI
- bacteriuria and pyuria (leukocytes in the urine)
- can be symptomatic or assymtomatic
- may result to nephritis or cystitis
Nephrolithiasis
- Renal stone
- manifested by:
Renal Colic - renal spasm of pain ()
Hematuria
Stone reccurence
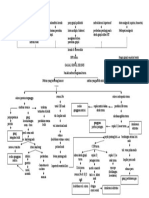
Stages of chronic renal
failure
Stage
1 : Diminished renal reverse
GFR is 50% normal
BUN and creatinine are normal
Susceptible to developing anemia
Asymptomatic
Stage
2 : renal insufficiency
GFR is 20-50% normal
Azotemia appears, with anemia and HPN
Polyuria and nocturia are present
Stage 3: Chronic Renal Failure
Less than 20% normal GFR
Kidney cant regulate volume and solute
composition
Develops edema, hyperkalemia
With GIT, cardio, neuro complications
Stage 4: ESRD
CHRONIC
GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Primary
glomerulonephritis
Secondary
glomerulonephritis
Nodular
Glomerulosclerosis
CHAPTER 20: The Kidney
GFR is less than 5% normal
Terminal stage
CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
- most common cause of chronic kidney disease in
humans
- only the kidney is involved
- glomerulonephritis that is caused by:
SLE
HPN
DM
Fabrys disease
Seen in DM
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Groundbreaking ProgramDokumen1 halamanGroundbreaking ProgramJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology Eent - Derm PDFDokumen2 halamanPharmacology Eent - Derm PDFJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- How Did Rizal Develop His Nationalist AspirationsDokumen3 halamanHow Did Rizal Develop His Nationalist AspirationsJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Burns: Dr. Shiara Ortiz-Pujols Burn Fellow NC Jaycee Burn CenterDokumen75 halamanPathophysiology of Burns: Dr. Shiara Ortiz-Pujols Burn Fellow NC Jaycee Burn CenterJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- EENT Outline 4ADokumen2 halamanEENT Outline 4AJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- Ex2 Glucocorticoids: Study Online atDokumen3 halamanEx2 Glucocorticoids: Study Online atJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- Preterm Birth Post Term Growth Restriction Still BirthDokumen12 halamanPreterm Birth Post Term Growth Restriction Still BirthJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- Local Anesthetics: Richard D. Minshall, PHD Tobias Piegeler, MDDokumen40 halamanLocal Anesthetics: Richard D. Minshall, PHD Tobias Piegeler, MDJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- EENT - Nose - Mouth PDFDokumen3 halamanEENT - Nose - Mouth PDFJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- Eent - Ear - LCCWDokumen3 halamanEent - Ear - LCCWBeda MalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- EENT - Lecture 4bDokumen3 halamanEENT - Lecture 4bJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- Local Anesthetics: Richard D. Minshall, PHD Tobias Piegeler, MDDokumen40 halamanLocal Anesthetics: Richard D. Minshall, PHD Tobias Piegeler, MDJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanBelum ada peringkat
- ENT Lecture 1Dokumen2 halamanENT Lecture 1JohnBedaLatawanMalecdan100% (1)
- KDIGO 2021 Glomerular Diseases GuidelineDokumen276 halamanKDIGO 2021 Glomerular Diseases GuidelineAmbulatório Dieta Cetogênica HUBBelum ada peringkat
- Glomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2Dokumen67 halamanGlomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2ibnbasheer100% (12)
- Acute Kidney Injury Kidney Infection: ClasificationDokumen1 halamanAcute Kidney Injury Kidney Infection: ClasificationSiti RuchjayaniBelum ada peringkat
- GLomerulus DiseaseDokumen5 halamanGLomerulus DiseaseMEDS easyBelum ada peringkat
- Glomerular Disorders - Part I & Part II (ARI NOTES)Dokumen144 halamanGlomerular Disorders - Part I & Part II (ARI NOTES)Laiba FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research Centre: Specimen Nature: Specimen SiteDokumen3 halamanShaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research Centre: Specimen Nature: Specimen Siteshahid.bhai877605Belum ada peringkat
- SLE Kidney Disease GuideDokumen6 halamanSLE Kidney Disease GuidenehaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathway CKDDokumen1 halamanPathway CKDocsitaocsitulBelum ada peringkat
- Renal DiseaseDokumen4 halamanRenal DiseaseApril Lady Faith P. PaundogBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Disease 2023Dokumen9 halamanRenal Disease 2023MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen2 halamanDaftar PustakaDasep PadilahBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Pustaka Bab IV Tentang Glomerulonephritis Pada AnakDokumen1 halamanDaftar Pustaka Bab IV Tentang Glomerulonephritis Pada AnakFany LainamaBelum ada peringkat
- Mortality and Morbidity Conference: Service Census January 2019Dokumen63 halamanMortality and Morbidity Conference: Service Census January 2019AnneCanapiBelum ada peringkat
- KDIGO GD Membranous NephropathyDokumen1 halamanKDIGO GD Membranous NephropathyF AudreyBelum ada peringkat
- Wikipedia - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (CHECKED)Dokumen7 halamanWikipedia - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (CHECKED)pixoguiasBelum ada peringkat
- Glomerular Diseases My NotesDokumen5 halamanGlomerular Diseases My Notesmalar_km43Belum ada peringkat
- Pathology of Urinary SystemDokumen384 halamanPathology of Urinary SystemNzau MuangeBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen35 halamanNephrotic SyndromesudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Glomerular Diseases: Assistant Professor Dr. Shumaila Rafi MedicineDokumen17 halamanGlomerular Diseases: Assistant Professor Dr. Shumaila Rafi MedicineMuhammad MakkiBelum ada peringkat
- PHS4300 Kennedy Sample MCQs 1Dokumen4 halamanPHS4300 Kennedy Sample MCQs 1iDNEBelum ada peringkat
- PKC AryanDokumen62 halamanPKC AryanAryan PurohitBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0011.Dokumen180 halamanWa0011.Mohamed AbdelmoniemBelum ada peringkat
- Renal PathologyDokumen2 halamanRenal PathologySiddhant KotaBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkuman Terminologi MedisDokumen6 halamanRangkuman Terminologi MedisAlissa RevoliusBelum ada peringkat
- Renal System and Its Disorders: Key PointsDokumen19 halamanRenal System and Its Disorders: Key PointsskBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Hematuria and Proteinuria in ChildrenDokumen52 halamanApproach To Hematuria and Proteinuria in ChildrenMysheb SS100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : by Primary DiseasesDokumen5 halamanDifferential Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : by Primary DiseasesElisa SalakayBelum ada peringkat
- 1035 Pathway CKDDokumen1 halaman1035 Pathway CKDeka pandeBelum ada peringkat
- Progression To End Stage Renal Disease in Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis (PSGN) - Chandigarh StudyDokumen6 halamanProgression To End Stage Renal Disease in Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis (PSGN) - Chandigarh StudyAubrey PerezBelum ada peringkat
- CV M Sjaifullah NoerDokumen6 halamanCV M Sjaifullah Noersatrio clarkBelum ada peringkat