Parallel Operation of Transformers III
Diunggah oleh
Gideon MoyoHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Parallel Operation of Transformers III
Diunggah oleh
Gideon MoyoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Parallel Operation Of Transformers
By Kiran Daware Transformer
Sometimes, it becomes necessary to connect more than one transformers in parallel, for
example, for supplying excess load of the rating of existing transformer. If two or more
transformers are connected to a same supply on the primary side and to a same load on the
secondary side, then it is called as parallel operation of transformers.
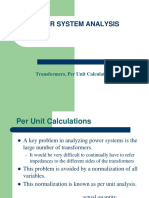
Necessity Of Parallel Operation Of Transformers
Why parallel operation of transformers is needed?
Increased Load: When load is increased and it exceeds the capacity of existing
transformer, another transformer may be connected in parallel with the existing
transformer to supply the increased load.
Non-availability of large transformer: If a large transformer is not available which can
meet the total requirement of load, two or more small transformers can be connected
in parallel to increase the capacity.
Increased reliability: If multiple transformers are running in parallel, and a fault occurs
in one transformer, then the other parallel transformers still continue to serve the load.
And the faulty transformer can be taken out for the maintenance.
Transportation is easier for small transformers: If installation site is located far away,
then transportation of smaller units is easier and may be economical.
Conditions For Parallel Operation
When two or more transformers are to be operated in parallel, then certain conditions have
to be met for proper operation. These conditions are
Voltage ratio of all connected transformers must be same.
If the voltage ratio is not same, then the secondaries will not show equal voltage even
if the primaries are connected to same busbar. This results in a circulating current in
secondaries, and hence there will be reflected circulating current on the primary side
also. In this case, considerable amount of current is drawn by the transformers even
without load.
The per unit (pu) impedance of each transformer on its own base must be same.
Sometimes, transformers of different ratings may be required to operate in parallel.
For, proper load sharing, voltage drop across each machine must be same. That is,
larger transformer has to draw equivalent large current. That is why per unit
impedance of the connected transformers must be same.
The polarity of all connected transformers must be same in order to avoid circulating
currents in transformers. Polarity of a transformer means the instantaneous direction of
induced emf in secondary. If polarity is opposite to each other, huge circulating current
flows.
The phase sequence must be identical of all parallel transformers.
This condition is relevant to poly-phase transformers only. If the phase sequences are
not same, then transformers can not be connected in parallel.
The short-circuit impedances should be approximately equal (as it is very difficult to
achieve identical impedances practically).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsDari EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsBelum ada peringkat
- Parallel Operation of TransformersDokumen10 halamanParallel Operation of TransformersMMK29100% (1)
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityDari EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityBelum ada peringkat
- Parallel Operation of Transformers - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDokumen6 halamanParallel Operation of Transformers - Electrical Notes & ArticlesaaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer DesigneDokumen6 halamanTransformer Designemhm770077Belum ada peringkat
- Vector Group of Transformer - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDokumen28 halamanVector Group of Transformer - Electrical Notes & ArticlesRamanjaneyulu KBelum ada peringkat
- Generator and distribution transformer connections: Star and delta configurationsDokumen34 halamanGenerator and distribution transformer connections: Star and delta configurationsAnonymous ufMAGXcskMBelum ada peringkat
- Parallel Con - For TransformersDokumen6 halamanParallel Con - For Transformersmahmoud shalabiBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Vector Group of TransformerDokumen13 halamanUnderstanding Vector Group of TransformerNagendra Babu100% (1)
- Tertiary Winding of TransformerDokumen3 halamanTertiary Winding of TransformerHamayoun MurtazaBelum ada peringkat
- VTU NOTES Load Flow AnalysisDokumen33 halamanVTU NOTES Load Flow AnalysisRakshitha VBelum ada peringkat
- PowerWorld Transmission Line Parameter Calculator - TransLineCalcHelp1Dokumen17 halamanPowerWorld Transmission Line Parameter Calculator - TransLineCalcHelp1Suresh UmadiBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation - Method - ULF Unbalanced Load Flow ETAP PDFDokumen8 halamanCalculation - Method - ULF Unbalanced Load Flow ETAP PDFZulqibalBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Per Unit CalculationsDokumen19 halamanTransformer Per Unit CalculationsOwais Afzal Jan100% (1)
- Guide to DC Decay of Fault Currents and X/R RatiosDokumen10 halamanGuide to DC Decay of Fault Currents and X/R RatiosMiko F. RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- OLTC Control of Parallel TransformersDokumen31 halamanOLTC Control of Parallel Transformersskylimit.skylimitBelum ada peringkat
- Zero Sequence DiagramDokumen2 halamanZero Sequence DiagramVerukv007Belum ada peringkat
- Travelling Wave Fault Location in HV LinesDokumen8 halamanTravelling Wave Fault Location in HV LinesSuginoMarwotoBelum ada peringkat
- Testing Directional Overcurrent ProtectionDokumen2 halamanTesting Directional Overcurrent ProtectionZokiBelum ada peringkat
- Lowering The Limits For Earth-Fault Detection: Abstract-Current Flowing To Earth Has Only TwoDokumen5 halamanLowering The Limits For Earth-Fault Detection: Abstract-Current Flowing To Earth Has Only TwoDeepak GehlotBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer voltage regulation and efficiencyDokumen15 halamanTransformer voltage regulation and efficiencyJhiGz Llausas de GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- ETAP Workshop Notes on Slow Bus ChangeoverDokumen7 halamanETAP Workshop Notes on Slow Bus ChangeoverPandiyan100% (1)
- Paralleling Module APM2000 PDFDokumen4 halamanParalleling Module APM2000 PDFsareluis30Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding Transformer PolarityDokumen3 halamanUnderstanding Transformer PolarityVENKATESAN R100% (1)
- Case Studies On Paralleling of TransformersDokumen7 halamanCase Studies On Paralleling of Transformersmuaz_aminu1422Belum ada peringkat
- DISCUSSION Load Flow AnalysisDokumen4 halamanDISCUSSION Load Flow AnalysisKu WhereBelum ada peringkat
- High Set 1 (Is-HS1) & High Set 2 (Is-HS2) and Its Calculation - Electrical ConceptsDokumen5 halamanHigh Set 1 (Is-HS1) & High Set 2 (Is-HS2) and Its Calculation - Electrical ConceptsAdam AbrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage ControlDokumen25 halamanVoltage Controlbenson215100% (1)
- Load Flow Analysis of 66 KV Substation Using ETAP SoftwareDokumen4 halamanLoad Flow Analysis of 66 KV Substation Using ETAP SoftwareNasser SabrBelum ada peringkat
- EDOC-Surge Arrester Sizing For SubDokumen14 halamanEDOC-Surge Arrester Sizing For SubEl Comedor BenedictBelum ada peringkat
- Fault Analysis On LVDokumen15 halamanFault Analysis On LVVENKATESAN RBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis and Application of Scott ConnectionDokumen11 halamanAnalysis and Application of Scott ConnectionRam Uday MandalBelum ada peringkat
- Wye-Wye Transformers & Tertiary WindingsDokumen5 halamanWye-Wye Transformers & Tertiary WindingssasahitoBelum ada peringkat
- Vector Group of Transformer Electrical Notes & ArticlesDokumen22 halamanVector Group of Transformer Electrical Notes & Articlesvprochocky0% (1)
- Eeda 512 - Ac/Dc Machinery (Lecture) Lesson 3: Transformers and RegulatorsDokumen4 halamanEeda 512 - Ac/Dc Machinery (Lecture) Lesson 3: Transformers and RegulatorsPatrick NavaBelum ada peringkat
- CT-PT burden calculation for 110kV substationDokumen5 halamanCT-PT burden calculation for 110kV substationunnvishnuBelum ada peringkat
- Improve Power Factor by Capacitive VAR CompensationDokumen15 halamanImprove Power Factor by Capacitive VAR CompensationMalith DeemanthaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit III-reactive Powerûvoltage ControlDokumen58 halamanUnit III-reactive Powerûvoltage ControlLalith Krishnan100% (2)
- Protection Systems and Devices (Protective Relays) : Dr. Ahmed SaberDokumen31 halamanProtection Systems and Devices (Protective Relays) : Dr. Ahmed SaberMichael AshrafBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Nigerian Grid Using MATLABDokumen8 halamanAnalysis of Nigerian Grid Using MATLABOgunranti RasaqBelum ada peringkat
- Percentage ImpedanceDokumen2 halamanPercentage Impedancetaha88Belum ada peringkat
- Ferro Resonance in Power SystemDokumen3 halamanFerro Resonance in Power SystemYash BhattiproluBelum ada peringkat
- Back Up Impedance ProtectionDokumen3 halamanBack Up Impedance ProtectionNeelakandan MasilamaniBelum ada peringkat
- Losses in TransformerDokumen15 halamanLosses in TransformerAnkit SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Long Transmission Lines Explained: Ferranti Effect, Surge Impedance & MoreDokumen5 halamanLong Transmission Lines Explained: Ferranti Effect, Surge Impedance & MorePratik RanjanBelum ada peringkat
- Power Transformer Connections PDFDokumen22 halamanPower Transformer Connections PDFRanjith Kumar100% (2)
- Course PC3, Dubai Applic Ation of Prote Ctive Relayi NG To Distri Bution and Sub-Trans Missi On Syste MsDokumen41 halamanCourse PC3, Dubai Applic Ation of Prote Ctive Relayi NG To Distri Bution and Sub-Trans Missi On Syste MsMahmoud Al-QudahBelum ada peringkat
- Switchgear Battery Sizing by HandDokumen4 halamanSwitchgear Battery Sizing by HandNia KurniawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Fault Analysis: Kibrom GDokumen37 halamanFault Analysis: Kibrom Gmillion100% (1)
- Transformers 17.7.14Dokumen7 halamanTransformers 17.7.14TharinduBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Transformer Impedance (ZDokumen2 halamanUnderstanding Transformer Impedance (ZAnonymous vcadX45TD7Belum ada peringkat
- Arrestor Energy Calculation PDFDokumen6 halamanArrestor Energy Calculation PDFpartha_gang4526Belum ada peringkat
- Contingency Analysis of Power Systems PDFDokumen4 halamanContingency Analysis of Power Systems PDFbenitogaldos19gmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- Over Fluxing in Transformer - Electrical EngineeringDokumen5 halamanOver Fluxing in Transformer - Electrical Engineeringsriramv93Belum ada peringkat
- 1MRK508019-BEN A en Fuse Supervisory Relays RXBA 4 RXETB 1 PDFDokumen6 halaman1MRK508019-BEN A en Fuse Supervisory Relays RXBA 4 RXETB 1 PDFUmanshu PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Starting Methods of Induction MotorsDokumen8 halamanStarting Methods of Induction MotorsChathuranga Nagasinghe100% (1)
- Restricted Earth-Fault Protection in REF 542plus: Application and Setting GuideDokumen20 halamanRestricted Earth-Fault Protection in REF 542plus: Application and Setting GuideSandeep PanigrahiBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions of Ac - DC Power Flow.-1Dokumen15 halamanSolutions of Ac - DC Power Flow.-1Krishna Reddy100% (1)
- Parallel Operation of TransformersDokumen3 halamanParallel Operation of TransformersHARIHARANBelum ada peringkat
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker or VCB and Vacuum InterruptersDokumen5 halamanVacuum Circuit Breaker or VCB and Vacuum InterruptersGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- DC Generator CharacteristicsDokumen10 halamanDC Generator CharacteristicsGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Project Mangement Tutorial On Critical PathDokumen30 halamanProject Mangement Tutorial On Critical PathGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Porter Value Chain AiDokumen1 halamanPorter Value Chain AiGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Construction of Circle DiagramDokumen18 halamanConstruction of Circle DiagramGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Standardization Guidelines For ResearchDokumen37 halamanStandardization Guidelines For ResearchGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Operating Characteristics of Synchronous Machine ExplainedDokumen8 halamanOperating Characteristics of Synchronous Machine ExplainedGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- HR Expectancy theory VroomDokumen2 halamanHR Expectancy theory VroomGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Droop Speed ControlDokumen4 halamanDroop Speed ControldskymaximusBelum ada peringkat
- Compiler and AssemblerDokumen21 halamanCompiler and AssemblerGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Cooling Methods and LossesDokumen12 halamanTransformer Cooling Methods and LossesGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Transfer Functions Examples Part 1Dokumen21 halamanTransfer Functions Examples Part 1Gideon Moyo0% (1)
- Compiler and AssemblerDokumen21 halamanCompiler and AssemblerGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Apportioning Loads On Paralleled Generator Sets - August 2010 - Kenneth L. Lovorn PDFDokumen7 halamanApportioning Loads On Paralleled Generator Sets - August 2010 - Kenneth L. Lovorn PDFpevareBelum ada peringkat
- Transfer Functions Examples Part 1Dokumen21 halamanTransfer Functions Examples Part 1Gideon Moyo0% (1)
- Protecting Oil Type Transformer With Buchholz RelayDokumen10 halamanProtecting Oil Type Transformer With Buchholz RelayGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Principle Operation of Synchronous MotorDokumen9 halamanPrinciple Operation of Synchronous MotorGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Phasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadDokumen3 halamanPhasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadAdnan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Relays and ContactorsDokumen9 halamanRelays and ContactorsGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of RelaysDokumen13 halamanClassification of RelaysGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Construction and Operation of Three Phase Induction MotorDokumen14 halamanConstruction and Operation of Three Phase Induction MotorGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Q and Bandwidth of A Resonant CircuitDokumen8 halamanQ and Bandwidth of A Resonant CircuitGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Models of Two-Port Networks Z, Y, H, ParametersDokumen17 halamanModels of Two-Port Networks Z, Y, H, ParametersGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Inverse hybrid (g) parameters circuit analysisDokumen2 halamanInverse hybrid (g) parameters circuit analysisGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- AC Vs DC Transmission On Super Grids GridsDokumen3 halamanAC Vs DC Transmission On Super Grids GridsGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Equivalent Circuit of Transformer Referred To PrimaryDokumen5 halamanEquivalent Circuit of Transformer Referred To PrimaryGideon Moyo100% (1)
- High Voltage SwitchgearDokumen5 halamanHigh Voltage SwitchgearGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Alloyed Copper Overhead Line ConductorsDokumen9 halamanMicro Alloyed Copper Overhead Line ConductorsGideon MoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate heating and cooling loads for buildingsDokumen8 halamanCalculate heating and cooling loads for buildingsdpadrianBelum ada peringkat
- Ps 1 SolDokumen3 halamanPs 1 SolPang XsBelum ada peringkat
- Determining The Redundancy FactorDokumen6 halamanDetermining The Redundancy FactorEdris Salehi GolsefidiBelum ada peringkat
- Wacker Neuson-Dpu - 25 KNDokumen3 halamanWacker Neuson-Dpu - 25 KNMilutin BožovićBelum ada peringkat
- Correlation Study and Regression Analysis of Water Quality Assessment of Nagpur City, IndiaDokumen5 halamanCorrelation Study and Regression Analysis of Water Quality Assessment of Nagpur City, IndiaShakeel AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of The Spectral Properties of Rhodamine (6G&B) Dyes Mixture Dissolved in ChloroformDokumen14 halamanA Study of The Spectral Properties of Rhodamine (6G&B) Dyes Mixture Dissolved in ChloroformNoureddine BarkaBelum ada peringkat
- NIKI V4 Infusion Pump Service ManualDokumen54 halamanNIKI V4 Infusion Pump Service ManualIgor Simonelli BermudesBelum ada peringkat
- Bottom Ash HopperDokumen8 halamanBottom Ash HopperBhargav ChaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 9001 ChecklistDokumen3 halamanISO 9001 Checklistthanh571957Belum ada peringkat
- Strength and Insulating Properties of Building Blocks Made From Waste MaterialsDokumen7 halamanStrength and Insulating Properties of Building Blocks Made From Waste Materialsmjrobust05Belum ada peringkat
- Dow Corning (R) 200 Fluid, 50 Cst.Dokumen11 halamanDow Corning (R) 200 Fluid, 50 Cst.Sergio Gonzalez GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- End All Red Overdrive: Controls and FeaturesDokumen6 halamanEnd All Red Overdrive: Controls and FeaturesBepe uptp5aBelum ada peringkat
- Civil 3 8sem PDFDokumen43 halamanCivil 3 8sem PDFG0utham100% (1)
- Dacnewppt p4Dokumen21 halamanDacnewppt p4vmspraneethBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling of SO2 Scrubbing in Spray TowersDokumen16 halamanModeling of SO2 Scrubbing in Spray Towersrebelde96100% (1)
- Friction Factor For Turbulent Pipe Flow: January 2006Dokumen17 halamanFriction Factor For Turbulent Pipe Flow: January 2006John AnthoniBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis, Specification and Estimate On Road WorksDokumen71 halamanAnalysis, Specification and Estimate On Road WorksAnonymous BACdUNvPZ280% (5)
- Pull Test Procedure - Chile Cabildo & Villa Seca 3MW-SkyLineDokumen7 halamanPull Test Procedure - Chile Cabildo & Villa Seca 3MW-SkyLinecnuneza4Belum ada peringkat
- Usn LM2500 Asme Paper GT2010-22811 61410 JalDokumen7 halamanUsn LM2500 Asme Paper GT2010-22811 61410 Jalferrerick0% (1)
- Struts by Kamalakar DanduDokumen237 halamanStruts by Kamalakar DanduKamalakar DanduBelum ada peringkat
- January2016page1to36 Layout 1Dokumen36 halamanJanuary2016page1to36 Layout 1c737Belum ada peringkat
- Cyber Security Research Proposal - SandboxingDokumen23 halamanCyber Security Research Proposal - SandboxingAnonymous Sa6jc83D100% (4)
- Inventory Management PreetDokumen28 halamanInventory Management PreetKawalpreet Singh MakkarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 - Software Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDokumen12 halamanUnit 4 - Software Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inNazma QureshiBelum ada peringkat
- Luran S KR2868C: Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate / Polycarbonate (ASA/PC)Dokumen3 halamanLuran S KR2868C: Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate / Polycarbonate (ASA/PC)rosebifBelum ada peringkat
- FG - BDER-78 Technical Catalogue - Technical - UNDokumen8 halamanFG - BDER-78 Technical Catalogue - Technical - UNAnh Le NgocBelum ada peringkat
- Propeller DesignDokumen74 halamanPropeller DesignBambang Teguh Setiawan75% (4)
- Lab5 AnswerSheetDokumen3 halamanLab5 AnswerSheetnislam57Belum ada peringkat
- HalideDokumen195 halamanHalidejadecolourBelum ada peringkat
- Interaction & Bank EffectDokumen6 halamanInteraction & Bank EffectAkash KandwalBelum ada peringkat
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideDari EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuidePenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Prevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryDari EverandPrevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryBelum ada peringkat
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresDari EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresBelum ada peringkat
- Pipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationDari EverandPipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualDari EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (7)
- The Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastDari EverandThe Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (76)
- Oil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionDari EverandOil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (16)
- Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesDari EverandInternal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDari EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (22)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDari EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Deepwater Drilling: Well Planning, Design, Engineering, Operations, and Technology ApplicationDari EverandDeepwater Drilling: Well Planning, Design, Engineering, Operations, and Technology ApplicationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Hydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisDari EverandHydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisBelum ada peringkat
- Fire in the Night: The Piper Alpha DisasterDari EverandFire in the Night: The Piper Alpha DisasterPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (5)
- Risk Management in the Oil and Gas Industry: Offshore and Onshore Concepts and Case StudiesDari EverandRisk Management in the Oil and Gas Industry: Offshore and Onshore Concepts and Case StudiesBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsDari EverandPractical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Black Gold Stranglehold: The Myth of Scarcity and the Politics of OilDari EverandBlack Gold Stranglehold: The Myth of Scarcity and the Politics of OilBelum ada peringkat
- Oil & Gas Design Engineering Guide Book: Useful Practices and Equipment & SystemsDari EverandOil & Gas Design Engineering Guide Book: Useful Practices and Equipment & SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Subsea Valves and Actuators for the Oil and Gas IndustryDari EverandSubsea Valves and Actuators for the Oil and Gas IndustryPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Compression Machinery for Oil and GasDari EverandCompression Machinery for Oil and GasKlaus BrunPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)