Theory
Diunggah oleh
Prashant SharmaHak Cipta
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniTheory
Diunggah oleh
Prashant SharmaNetwork Analysis
Node & SuperNode Analysis
Theory
NODE ANALYSIS
Nodal analysis states that the algebraic sum of currents meeting at
junction/ node is zero.
It is completely based on KCL
This analysis is carried out to determine voltages of different nodes with
respect to reference node.
Reference node/ Datum node is also one type of node in the network.
After determination of node voltages, currents in all the branches can be
determined. This method is useful where number of loops is large and
mesh analysis is bit complicated.
Steps for Nodal analysis:
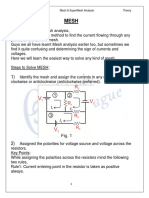
Step 1) Mark all the nodes in the given network.
Here, there are 4 nodes.
Step 2) Select one of the node as reference/ datum node.
Network Analysis
Node & SuperNode Analysis
Theory
NOTE:
1) On observing, we come to know that the Node 3 and Node 4 are
actually the same. Because there is no voltage drop between them due to
any resistor. So both Node 3 and Node 4 can be considered as reference
node.
2) If we consider Note 2 as the reference node, then in this case there
is no other node whose potential will be same as node 2 point. So unlike
point (1) only node 2 will be the reference node.
KEY NOTE: Generally the lower nodes in the network are considered as
reference node to avoid any sort of mistake.
Step 3) Assign the unknown potentials of all nodes with respect to the
reference node.
As Vc and Reference node have zero potential, so we need not consider
Vc.
Step 4) At each node (excluding reference node), assume the unknown
currents and mark their directions arbitrarily. (It's recommended that
consider all the currents moving away from the respective node)
Network Analysis
Node & SuperNode Analysis
Theory
Step 5) Apply the KCL at each node and write the equations in terms of
node voltages.
At node VA:
1 0
1
0
4
=0
All the voltage drop in each term is with respect to reference node.
But VC is same as reference node. Therefore, Vc = 0V.
The equations becomes,
1
i.e.
1
1
1
+
+
1
2
4
1
2
=0
1
1
-----(1)
-----(2)
At node VB:
0
2
0
5
2
3
But Vc = 0V
3
= 0 ----(3)
Network Analysis
Node & SuperNode Analysis
Theory
=0
2
5
3
2
1
1
1
1
+
+
+
=
2
2
5
3
3
-----(4)
Step 6) Solve the equations (2) and (4) to get VA and VB.
SUPERNODE ANALYSIS
Nodes that are connected to each other by voltage sources, but not to the
reference node by a path of voltage source form a super node.
To solve supernode problem, we need one current equation that is KCL
equation and the remaining node voltage equations that is KVL
equations.
Examples of SuperNode:-
Here, V2 & V3 forms a Supernode.
Network Analysis
Node & SuperNode Analysis
Theory
Steps for Supernode analysis:
Step 1) Identify the super node.
Here, V2 and V3 forms a supernode.
Step 2) Apply KCL to the remaining node/s.
Here, V1 is the remaining node. So,
-I +
i.e. V1
1
1
1 2
1
2
=0
2
2
= I -------(1)
Step 3) Write the voltage equation for supernode.
V 2- V 3 = V A
------(2)
Step 4) Apply KCL to supernode.
2 1
2
2
3
1
1
1
+ 2
+
1
2
3
+ 3
4
1
1
+
4
5
3
5
=0
----(3)
NOTE: Observe the KCL equation of supernode properly.
Step 5) Solve the equations and find the node voltages (V1, V2 & V3).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Change Your MotionDokumen4 halamanChange Your MotionreynandcpcBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 3 (Nodal and Mesh Analysis)Dokumen15 halamanLab 3 (Nodal and Mesh Analysis)Jing Heng0% (1)
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsDari EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsBelum ada peringkat
- Pivot Interactives Motion Graphing A Dry Ice Puck On A RampDokumen2 halamanPivot Interactives Motion Graphing A Dry Ice Puck On A RampSophia0% (1)
- DC Circuit Analysis - Part 2Dokumen29 halamanDC Circuit Analysis - Part 2temesgen adugnaBelum ada peringkat
- Eee-121 Electric Circuit Analysis Week#7/ Lecture#7 /chapter #3Dokumen20 halamanEee-121 Electric Circuit Analysis Week#7/ Lecture#7 /chapter #3sumya khanBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 2 - Circuit AnalysisDokumen22 halamanChap 2 - Circuit AnalysisYang Yew RenBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal AnalysisDokumen6 halamanNodal AnalysisJerome BricenioBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 4 - Techniques of CKT AnalysisDokumen34 halamanChapter - 4 - Techniques of CKT AnalysisKopano MalomboBelum ada peringkat
- SUPERNODE Circuit Analysis (@B)Dokumen5 halamanSUPERNODE Circuit Analysis (@B)shivamBelum ada peringkat
- Esc201 - L4Dokumen26 halamanEsc201 - L4synthesis 1507Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 - Node and Mesh Analysis - Part 1Dokumen22 halamanChapter 3 - Node and Mesh Analysis - Part 1fayBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No.9: Nodal Theorem ObjectDokumen3 halamanExperiment No.9: Nodal Theorem Objectsensie NakaBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal AnalysisDokumen4 halamanNodal AnalysisinfistudeeeeBelum ada peringkat
- NT UNIT - I Lecture 4Dokumen26 halamanNT UNIT - I Lecture 4girish mishraBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal AnalysisDokumen28 halamanNodal AnalysisSantosh Singh YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Node Voltage Analysis TechniquesDokumen8 halamanNode Voltage Analysis TechniquesAqil SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- Ece 201 Exam 2 ReviewDokumen12 halamanEce 201 Exam 2 ReviewkarlrodBelum ada peringkat
- M1L2 DC Network TheoremsDokumen64 halamanM1L2 DC Network TheoremsUDhayBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal AnalysisDokumen15 halamanNodal AnalysisRBelum ada peringkat
- Esc201: Introduction To Electronics: Amit Verma Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurDokumen26 halamanEsc201: Introduction To Electronics: Amit Verma Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurPrakhar chhalotreBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 9 1Dokumen14 halamanExperiment No. 9 1Kent Gerard SolanoBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal AnalysisDokumen25 halamanNodal AnalysisFreezing FlamesBelum ada peringkat
- M1L2 DC Network TheoremsDokumen57 halamanM1L2 DC Network TheoremsChandan Pandey super cricket gamesBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 4 Nodal & Mesh AnalysisDokumen2 halamanChap 4 Nodal & Mesh AnalysisIrtaza Nasir ßhattiBelum ada peringkat
- DC Circuits:: DET 101/3 Basic Electrical Circuit 1Dokumen150 halamanDC Circuits:: DET 101/3 Basic Electrical Circuit 1guna6986Belum ada peringkat
- Nodal Analysis NotesDokumen2 halamanNodal Analysis Notesapi-288751705Belum ada peringkat
- Bee Report1Dokumen5 halamanBee Report1Rajeev kumarBelum ada peringkat
- EEELec12 Nodal-Analysis OkDokumen12 halamanEEELec12 Nodal-Analysis OkMau DimapilisBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Analysis TechniquesDokumen14 halamanCircuit Analysis TechniquesSanthoshBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 03Dokumen10 halamanLecture 03IfhamBelum ada peringkat
- NodalDokumen21 halamanNodalStrife Ci-ZeusBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal AnalysisDokumen30 halamanNodal AnalysisPuji LestariBelum ada peringkat
- Mesh Nodal Analysis 1Dokumen20 halamanMesh Nodal Analysis 1subasriramiahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Three: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Part 1: Nodal & Mesh AnalysisDokumen68 halamanChapter Three: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Part 1: Nodal & Mesh Analysis01 PrOdUcTiOnBelum ada peringkat
- FEI 3103 Circuit TheoryDokumen16 halamanFEI 3103 Circuit TheorySyafnie NinieBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Analysis - CH3Dokumen23 halamanMethods of Analysis - CH3Rifah Shanjida MomoBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuits Chapter 3 MethodsDokumen77 halamanFundamentals of Electric Circuits Chapter 3 MethodsasfasBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal analysisDokumen3 halamanNodal analysisRana IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal Analysis Guide: Label Nodes, KCL Equations & MoreDokumen80 halamanNodal Analysis Guide: Label Nodes, KCL Equations & MorembloexBelum ada peringkat
- BIT CA2 Report on Nodal AnalysisDokumen6 halamanBIT CA2 Report on Nodal AnalysisAbhradeep SenguptaBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Curcuit Chapter 2.Dokumen25 halamanElectronic Curcuit Chapter 2.AbcdBelum ada peringkat
- 4 SuperNode-2fSupermesh NoteDokumen2 halaman4 SuperNode-2fSupermesh NoteShihabul Milah IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 6Dokumen5 halamanLab 6Stephen BridgesBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Theory 1 C3 Analysis MethodsDokumen54 halamanCircuit Theory 1 C3 Analysis Methodshaseeb tBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter2-28node and Mesh Analysis-291Dokumen5 halamanChapter2-28node and Mesh Analysis-291Amirul SyazwanBelum ada peringkat
- Nodal Analysis Collection 2Dokumen21 halamanNodal Analysis Collection 2Manoj ManmathanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3. Circuit Analysis Techniques: EE 131 Electric Circuit Theory IDokumen27 halamanLecture 3. Circuit Analysis Techniques: EE 131 Electric Circuit Theory INiza YatazaBelum ada peringkat
- V8 - Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis - Delta Wye - TE 58 A - B and CDokumen74 halamanV8 - Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis - Delta Wye - TE 58 A - B and CMubashir KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDokumen27 halamanChapter 3 Mesh and Nodal Analysisthines raveentraanBelum ada peringkat
- Module 10Dokumen17 halamanModule 10Ferdinand Marcelo AbantoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 - Method Analysis - Teaching ModeDokumen27 halamanLecture 3 - Method Analysis - Teaching ModeYip Tuck WaiBelum ada peringkat
- Beee PPT - 5Dokumen24 halamanBeee PPT - 5Girish Shankar MishraBelum ada peringkat
- CH 2meshandnodeanalysis-Jameel23oct23Dokumen30 halamanCH 2meshandnodeanalysis-Jameel23oct23Gorin GorinBelum ada peringkat
- Week 6Dokumen38 halamanWeek 6IGIHOZO HeritierBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 EEE121 Part 2Dokumen9 halamanChapter 2 EEE121 Part 2Ashraf RezaBelum ada peringkat
- 11. Circuit Analysis Techniques 4Dokumen65 halaman11. Circuit Analysis Techniques 4Shibly SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Dari EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Belum ada peringkat
- Transient Phenomena in Electrical Power Systems: Problems and IllustrationsDari EverandTransient Phenomena in Electrical Power Systems: Problems and IllustrationsPenilaian: 1.5 dari 5 bintang1.5/5 (3)
- TheoryDokumen3 halamanTheoryPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Network Analysis Mesh & Supermesh Analysis TheoryDokumen5 halamanNetwork Analysis Mesh & Supermesh Analysis TheoryPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 4) Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDokumen4 halaman4) Maximum Power Transfer TheoremPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- TheoryDokumen7 halamanTheoryPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Rules of Dot ConventionDokumen2 halamanRules of Dot ConventionPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Network Analysis: Krichoff's LawsDokumen2 halamanNetwork Analysis: Krichoff's LawsPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Network Theorems: 1) Superposition TheoremDokumen7 halamanNetwork Theorems: 1) Superposition TheoremPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- TheoryDokumen5 halamanTheoryPrashant Sharma100% (1)
- Realization of RL Functions:: Points To Keep in MindDokumen2 halamanRealization of RL Functions:: Points To Keep in MindPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Ladder & Non Ladder NetworksDokumen6 halamanLadder & Non Ladder NetworksPrashant Sharma100% (1)
- TheoryDokumen5 halamanTheoryPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction & Types of NnetworksDokumen4 halamanIntroduction & Types of NnetworksPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- TheoryDokumen7 halamanTheoryPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Laplace Transform & It'S ApplicationDokumen2 halamanLaplace Transform & It'S ApplicationPrashant SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- HW1Dokumen8 halamanHW1Anonymous fXSlye100% (1)
- SMS LteaDokumen11 halamanSMS LteaArdi CikaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Engineering Magazine Abril 2009 PDFDokumen108 halamanChemical Engineering Magazine Abril 2009 PDFFélix Vargas Santillán100% (1)
- DMCR Detection Measurement Control RelayDokumen5 halamanDMCR Detection Measurement Control RelayMuhammad AbuzarBelum ada peringkat
- Precision Thermometers CatalogueDokumen44 halamanPrecision Thermometers CataloguemarthaBelum ada peringkat
- Activity MergedDokumen9 halamanActivity MergedSoham MondalBelum ada peringkat
- Is 7246Dokumen10 halamanIs 7246Gaurav AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Energy in Somaliland Novia Thesis - Editing PDFDokumen25 halamanEnergy in Somaliland Novia Thesis - Editing PDFAbdirahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Signature RedactedDokumen49 halamanSignature RedactedG Pavan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Wiring DiagramDokumen24 halamanWiring DiagramReji Raju0% (1)
- DWC ElecConduit Is 16205 P24 2018Dokumen11 halamanDWC ElecConduit Is 16205 P24 2018Vamsi Manoj60% (5)
- E-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)Dokumen3 halamanE-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)darling deanBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Design Basis 1.1 Material and Properties 1.1 Material and PropertiesDokumen13 halaman1 Design Basis 1.1 Material and Properties 1.1 Material and PropertiesDarshan PanchalBelum ada peringkat
- Adrian Stan MFQMCourseHsL2006Dokumen60 halamanAdrian Stan MFQMCourseHsL2006禿公Belum ada peringkat
- Factors that Determine Paper StrengthDokumen23 halamanFactors that Determine Paper StrengthNur Ariesman Salleh100% (2)
- Shoot For Your Grade Lab Write UpDokumen5 halamanShoot For Your Grade Lab Write Upapi-254812059Belum ada peringkat
- Astm F1717-21Dokumen11 halamanAstm F1717-21wenhsiaochuanBelum ada peringkat
- FTTH Accessories PDFDokumen10 halamanFTTH Accessories PDFdannyalcivarBelum ada peringkat
- Review: Modeling Damping in Mechanical Engineering StructuresDokumen10 halamanReview: Modeling Damping in Mechanical Engineering Structuresuamiranda3518Belum ada peringkat
- 2019 Hydropower Status Report 0Dokumen56 halaman2019 Hydropower Status Report 0Titos Nicosio ComéBelum ada peringkat
- IS 516 (Part-2) Sec-1 - 2018Dokumen16 halamanIS 516 (Part-2) Sec-1 - 2018Sai Pavan100% (9)
- Mid-Term Math Exam for Grade 5Dokumen18 halamanMid-Term Math Exam for Grade 5李安逸Belum ada peringkat
- SABIC Innovative Plastics Lexan® 940 PC Data SheetDokumen3 halamanSABIC Innovative Plastics Lexan® 940 PC Data SheetMRC RailBelum ada peringkat
- Newton's Laws of Motion Worksheet.Dokumen2 halamanNewton's Laws of Motion Worksheet.Llama jennerBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Nanorobotics and Their ApplicationsDokumen25 halamanIntroduction to Nanorobotics and Their ApplicationsSharifa RahamadullahBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical and Optical Properties of Indium-Tin Oxide (ITO) Films by Ion-Assisted Deposition (IAD) at Room TemperatureDokumen6 halamanElectrical and Optical Properties of Indium-Tin Oxide (ITO) Films by Ion-Assisted Deposition (IAD) at Room Temperaturereza mirzakhaniBelum ada peringkat
- The Statistical Imagination: Chapter 7. Using Probability Theory To Produce Sampling DistributionsDokumen18 halamanThe Statistical Imagination: Chapter 7. Using Probability Theory To Produce Sampling DistributionsVictoria LiendoBelum ada peringkat