19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration
Diunggah oleh
keyur.galaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration
Diunggah oleh
keyur.galaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 19 - Speed, velocity and acceleration (Answers)
Q.I) Multiple choice questions. Tick the correct answer from the options given below.
1. What A racing car is fitted with an on-board computer. Every time the car
passes the starting line, the computer records the distance travelled in the
next 2 seconds.
Which set of data shows that the car is increasing in speed during the 2
seconds?
2. A heavy metal ball falls vertically downwards through air past four equally
spaced levels J, K, L and M.
The times taken to fall from one level to the next are measured.
Where is the speed of the ball greatest and which time is shortest?
3. Which person is experiencing an acceleration?
A. a driver of a car that is braking to stop at traffic lights
B. a passenger in a train that is stationary in a railway station
C. a shopper in a large store ascending an escalator (moving stairs) at a
uniform rate
D. a skydiver falling at constant speed towards the Earth
4. A ball is thrown upwards.
What effect does the force of gravity have on the ball?
A. It produces a constant acceleration downwards.
B. It produces a constant acceleration upwards.
C. It produces a decreasing acceleration upwards.
D. It produces an increasing acceleration downwards.
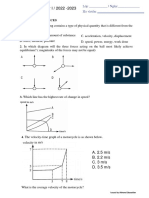
5. Which statement about a moving object is correct?
A. When an object is accelerating, the resultant force acting on it must
equal zero.
B. When an object is moving at a steady speed, the air resistance acting on
it must equal zero.
C. When an object is moving at a steady speed, the resultant force acting
on it must equal zero.
D. When an object is moving, there must be a resultant force acting on it.
6. A ship sends a pulse of sound vertically downwards to the sea bed. An echo
is heard 0.4 seconds later.
If the speed of sound in the water is 1200 m / s, how deep is the water below
the ship?
A. 240 m
B. 480 m
C. 1500 m
D. 3000 m
Q.II) Answer the following.
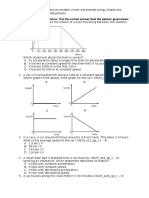
1. A hillside is covered with snow. A skier is travelling down the hill.
Fig 1.1
The table below gives the values of the acceleration of the skier at various heights
above the bottom of the hill.
(a) Describe what is happening, during the descent, to
(i) the acceleration of the skier,
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(ii) the speed of the skier.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(b) The acceleration becomes zero before the skier reaches the bottom of the hill.
Use ideas about forces to suggest why this happens.
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(c) Below a height of 50 m, further measurements show that the acceleration of the skier has
a negative value.
What does this mean is happening to the speed of the skier in the last 50 m?
...................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
(d) The skier has a mass of 60 kg.
Calculate the resultant force on the skier at a height of 250 m.
resultant force = .........................................................
2. A young athlete has a mass of 42 kg. On a day when there is no wind, she runs a 100 m
race in 14.2 s. A sketch graph (not to scale) showing her speed during the race is given
in Fig. 2.1.
(a) Calculate
(i) the acceleration of the athlete during the first 3.0 s of the race,
acceleration = .........................................................
(ii) the accelerating force on the athlete during the first 3.0 s of the race,
force = .........................................................
(iii) the speed with which she crosses the finishing line.
speed = .........................................................
(b) Suggest two differences that might be seen in the graph if there had been a strong wind
opposing the runners in the race.
1................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
2................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)Dokumen4 halaman19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)keyur.gala100% (1)
- HW3-Forces and motion-5 (学生版) - 022532Dokumen16 halamanHW3-Forces and motion-5 (学生版) - 022532Jun WuBelum ada peringkat
- P2 Resultant Forces Higher and IntermediateDokumen16 halamanP2 Resultant Forces Higher and IntermediatedownendscienceBelum ada peringkat
- HW6-Energy Stores and Transfers-1 (学生版) - 021544Dokumen12 halamanHW6-Energy Stores and Transfers-1 (学生版) - 021544Jun WuBelum ada peringkat
- Resultant Forces 1 QPDokumen21 halamanResultant Forces 1 QPTJBelum ada peringkat
- 10 IGCSE Physics Test 1 2014Dokumen12 halaman10 IGCSE Physics Test 1 2014pixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- P2.1-2 Physics: ForcesDokumen49 halamanP2.1-2 Physics: ForcesSteve Bishop100% (3)
- AE 11 02 2022 PhysicsDokumen5 halamanAE 11 02 2022 PhysicsĐặng Thái NhậtBelum ada peringkat
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling BodiesDokumen4 halamanSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling Bodieskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Y2 Workbook Final PDFDokumen177 halamanY2 Workbook Final PDFMelody RbayBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Deiseño SismicoDokumen5 halamanEjercicios Resueltos de Deiseño SismicoJuan Pablo Lemus IbacacheBelum ada peringkat
- W6.1 - Projectile Motion ProblemsDokumen8 halamanW6.1 - Projectile Motion ProblemsShiv NayakBelum ada peringkat
- USTH Exercise B1 Chapter1Dokumen5 halamanUSTH Exercise B1 Chapter1..--Belum ada peringkat
- 9th Grade Science ExamDokumen3 halaman9th Grade Science ExamSalve Gregorio AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- ForcesDokumen116 halamanForcesbloodymerlinBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment ChapterDokumen34 halamanAssessment ChapterfazilarazaliBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 NewDokumen5 halamanTutorial 1 NewAina BalqisBelum ada peringkat
- P2 Forces and Terminal Velocity FoundationDokumen13 halamanP2 Forces and Terminal Velocity Foundationdownendscience100% (1)
- Momentum 3 QPDokumen10 halamanMomentum 3 QPAroosha BaigBelum ada peringkat
- Momentum 3 QPDokumen10 halamanMomentum 3 QPRahul GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Calculating Power Needed to Transport Passengers in a LiftDokumen8 halamanCalculating Power Needed to Transport Passengers in a LiftSalman Farsi TaharatBelum ada peringkat
- Topic-Questions-Energy Work PowerDokumen8 halamanTopic-Questions-Energy Work PowerJoe Y. MathewBelum ada peringkat
- HW Worksheet 13Dokumen4 halamanHW Worksheet 13Marina ChamedesBelum ada peringkat
- U6 Work Energy Power Topic Test ADokumen14 halamanU6 Work Energy Power Topic Test ApixelhoboBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE General Physics Revision QuestionsDokumen34 halamanIGCSE General Physics Revision Questionsbriannamuham1249Belum ada peringkat
- CLASS 7 - Physics - Foces-TEST PAPER 3Dokumen15 halamanCLASS 7 - Physics - Foces-TEST PAPER 3lokapavani_senthilBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge O'Level Physics Batch 2023 - Examination 1 AugustDokumen8 halamanCambridge O'Level Physics Batch 2023 - Examination 1 AugustShrimal AbeyBelum ada peringkat
- Momentum - Worksheet: Section A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen5 halamanMomentum - Worksheet: Section A - Multiple Choice Questionshakky gamyBelum ada peringkat
- QB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power ADokumen11 halamanQB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power AmarufinoBelum ada peringkat
- 7energikinetik PDFDokumen16 halaman7energikinetik PDFGus EdiBelum ada peringkat
- Practice QuestionsDokumen8 halamanPractice QuestionsMohab MqattashBelum ada peringkat
- Motion Along A Straight Line QPDokumen8 halamanMotion Along A Straight Line QPSelina LIBelum ada peringkat
- Circular Motion QPDokumen9 halamanCircular Motion QPnechiemmaBelum ada peringkat
- Section A: Answer All The QuestionsDokumen14 halamanSection A: Answer All The QuestionsSam YiiBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT IV - Chapter 11 - 20230917 - 142042 - 0000Dokumen5 halamanUNIT IV - Chapter 11 - 20230917 - 142042 - 0000VanessaBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Term ReviewDokumen3 halamanMid Term ReviewMona AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- New Document 1Dokumen16 halamanNew Document 1R SBelum ada peringkat
- IB Mechanics PPQDokumen13 halamanIB Mechanics PPQemily100% (1)
- 21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)Dokumen4 halaman21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)keyur.gala100% (2)
- Forces and Motion Extended Writing Questions Higher and FoundationDokumen11 halamanForces and Motion Extended Writing Questions Higher and FoundationAika AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Formative Criterion A - EnergyDokumen4 halaman2nd Formative Criterion A - EnergySoha RamadanBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 Part 1 Physics and BiologyDokumen11 halaman2022 Part 1 Physics and BiologyFloraBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics Review Physics 11Dokumen2 halamanKinematics Review Physics 11Raymond NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- KS4 / Edexcel GCSE Additional Science / Topics P2.9 and P2.10 / Past Exam Questions Mar09Jun09Dokumen11 halamanKS4 / Edexcel GCSE Additional Science / Topics P2.9 and P2.10 / Past Exam Questions Mar09Jun09Paul BurgessBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics AssignmentDokumen6 halamanDynamics Assignmentsaed cabdiBelum ada peringkat
- Cameroon National Exam for Higher National Diploma in Physics - 2021Dokumen4 halamanCameroon National Exam for Higher National Diploma in Physics - 2021Alexandre CabrelBelum ada peringkat
- Constant velocity diagram physics tutorialDokumen1 halamanConstant velocity diagram physics tutorialnixleonBelum ada peringkat
- Leaving Cert Physics Long Questions 2002 - 2018Dokumen46 halamanLeaving Cert Physics Long Questions 2002 - 2018NorKamilahMakhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Form 4 Modul WAJADokumen14 halamanPhysics Form 4 Modul WAJARamanath RamBelum ada peringkat
- MODUL 1 FizikDokumen14 halamanMODUL 1 FizikMohd HafizuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Physics 122 Problem SetDokumen86 halamanPhysics 122 Problem SetCarmen DraghiaBelum ada peringkat
- Moments QPDokumen12 halamanMoments QPadmaBelum ada peringkat
- University Physics Chapter2Dokumen9 halamanUniversity Physics Chapter2Karlo OrnietaBelum ada peringkat
- p2 Revision Guide HigherDokumen66 halamanp2 Revision Guide Higherapi-320022467Belum ada peringkat
- Review Game FinalsDokumen31 halamanReview Game FinalseBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 Sec 3 Physics Term 2 WA 2Dokumen11 halaman2020 Sec 3 Physics Term 2 WA 2VinidraBelum ada peringkat
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Modulus FunctionDokumen2 halamanModulus Functionkeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- PolynomialsDokumen4 halamanPolynomialskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Q Names1 PDFDokumen4 halamanQ Names1 PDFClement Charles100% (1)
- Percentages (6 TH STD)Dokumen2 halamanPercentages (6 TH STD)keyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Profit and Loss - AnswersDokumen3 halamanProfit and Loss - Answerskeyur.gala100% (1)
- Organic NomenclatureDokumen12 halamanOrganic Nomenclatureitbwng100% (1)
- Matrices IGCSE QuestionsDokumen4 halamanMatrices IGCSE Questionskeyur.gala100% (2)
- Class Worksheet Date - Name: - Grade: 6th Unit: Ratio Subject: MathsDokumen4 halamanClass Worksheet Date - Name: - Grade: 6th Unit: Ratio Subject: Mathskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Advanced Trigonometry Part 1Dokumen4 halaman10 Advanced Trigonometry Part 1keyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Algebraic Expression (6th STD)Dokumen6 halamanAlgebraic Expression (6th STD)keyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Profit and Loss - AnswersDokumen3 halamanProfit and Loss - Answerskeyur.gala100% (1)
- 12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursDokumen1 halaman12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursJyoti ManwaniBelum ada peringkat
- MEP Y9 Practice Book B Sequences FormulaeDokumen28 halamanMEP Y9 Practice Book B Sequences FormulaeRahique ShuaibBelum ada peringkat
- Area and Trianle For KidsDokumen1 halamanArea and Trianle For Kidskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Interest - For KidsDokumen2 halamanSimple Interest - For Kidskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Interest - For KidsDokumen2 halamanSimple Interest - For Kidskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Area and Volume Word ProblemsDokumen2 halamanSurface Area and Volume Word Problemskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Q.I) Multiple Choice Questions. Tick The Correct Answer From The Options Given BelowDokumen4 halamanQ.I) Multiple Choice Questions. Tick The Correct Answer From The Options Given Belowkeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Quadratics ProblemsDokumen2 halamanQuadratics Problemskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- Venn Diagram Word Problems and Set Theory QuestionsDokumen2 halamanVenn Diagram Word Problems and Set Theory Questionskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursDokumen1 halaman12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursJyoti ManwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling BodiesDokumen4 halamanSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling Bodieskeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- 20 - Graphs and Equations (Answer)Dokumen5 halaman20 - Graphs and Equations (Answer)keyur.gala0% (1)
- 21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)Dokumen4 halaman21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)keyur.gala100% (2)
- Motion and Energy (Notes)Dokumen32 halamanMotion and Energy (Notes)keyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- 21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)Dokumen4 halaman21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)keyur.gala100% (2)
- Motion and EnergyDokumen43 halamanMotion and Energykeyur.galaBelum ada peringkat
- 13 - Moment and Levers (Answers)Dokumen7 halaman13 - Moment and Levers (Answers)keyur.gala100% (1)
- Women &literatureDokumen54 halamanWomen &literatureAicha ZianeBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules: BiologyDokumen32 halamanThe Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules: BiologyUyyykllBelum ada peringkat
- [4]Dokumen693 halaman[4]Ali Mohammed AlkafajyBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 006Dokumen50 halamanChap 006Martin TrịnhBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 GSFR General ChecklistDokumen12 halaman2021 GSFR General Checklistapi-584007256Belum ada peringkat
- Jurisidiction of MeTC, MTC, MCTC, MuTCDokumen3 halamanJurisidiction of MeTC, MTC, MCTC, MuTCKENEDY FLORESBelum ada peringkat
- Soal EnglishDokumen7 halamanSoal EnglishRieZky RamadhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Daß Ich Erkenne, Was Die Welt Im Innersten Zusammenhält (Lines 382-83) So That I Know What Holds The Innermost World TogetherDokumen2 halamanDaß Ich Erkenne, Was Die Welt Im Innersten Zusammenhält (Lines 382-83) So That I Know What Holds The Innermost World TogetherEmanuel MoşmanuBelum ada peringkat
- An Approach to Defining the Basic Premises of Public AdministrationDokumen15 halamanAn Approach to Defining the Basic Premises of Public AdministrationAlvaro CamargoBelum ada peringkat
- QDEGNSWDokumen2 halamanQDEGNSWSnehin PoddarBelum ada peringkat
- BSIA - Access ControlDokumen16 halamanBSIA - Access ControlSayed HashemBelum ada peringkat
- Pan or The DevilDokumen8 halamanPan or The DevilMarguerite and Leni Johnson100% (1)
- Petitioner Respondent: Civil Service Commission, - Engr. Ali P. DaranginaDokumen4 halamanPetitioner Respondent: Civil Service Commission, - Engr. Ali P. Daranginaanika fierroBelum ada peringkat
- Philo 12Dokumen2 halamanPhilo 12Rachel LaganBelum ada peringkat
- (Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Dokumen7 halaman(Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Naddy RetxedBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1Dokumen3 halamanAssignment 1Rabia Ahmad100% (1)
- Pathology PLE SamplexDokumen5 halamanPathology PLE SamplexAileen Castillo100% (1)
- Activity 13Dokumen13 halamanActivity 13Lielannie CarasiBelum ada peringkat
- Puregold SWOT AnalysisDokumen3 halamanPuregold SWOT AnalysisRizza Mae CabigasBelum ada peringkat
- Akhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihDokumen44 halamanAkhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihSauri ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Essays B1Dokumen6 halamanWriting Essays B1Manuel Jose Arias TabaresBelum ada peringkat
- Estimate of Channel Capacity in Rayleigh Fading EnvironmentDokumen3 halamanEstimate of Channel Capacity in Rayleigh Fading EnvironmentCung LevanBelum ada peringkat
- Set-2 Answer? Std10 EnglishDokumen13 halamanSet-2 Answer? Std10 EnglishSaiyam JainBelum ada peringkat
- Political Science Most Important Questions Part 1 PDFDokumen2 halamanPolitical Science Most Important Questions Part 1 PDFJayateerth KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Gaona BrianDokumen218 halaman1 Gaona BrianElias Nicol100% (1)
- PALS - Bar Ops Corporation Law Must Read CasesDokumen70 halamanPALS - Bar Ops Corporation Law Must Read CasesOnat PBelum ada peringkat
- Anita Desai PDFDokumen9 halamanAnita Desai PDFRoshan EnnackappallilBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test 4: Explorer's Rainforest Trip and Blind AdventurerDokumen6 halamanPractice Test 4: Explorer's Rainforest Trip and Blind AdventurerKhang Nguyen TienBelum ada peringkat
- Review Notes in ABG Interpretation - NCLEXDokumen1 halamanReview Notes in ABG Interpretation - NCLEXFilipino Nurses CentralBelum ada peringkat
- BOI Interim Report 2019 PDFDokumen122 halamanBOI Interim Report 2019 PDFAditya MukherjeeBelum ada peringkat















































































![[4]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/396226966/149x198/c657f32573/1545578422?v=1)