Calculate Raw Material Costs for Garments
Diunggah oleh
Anonymous KuELCsMGDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Calculate Raw Material Costs for Garments
Diunggah oleh
Anonymous KuELCsMGHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Methods of garment costing
Material cost is a major cost component of garment manufacturing costs and a correct cost calculation metho
give one a better projection of garment cost for a style, explains Vishnu Pareek.
Since the industrial beginnings, textiles and apparel have been the leaders in terms of cost awareness as well as
product innovations. Textile costing includes all the activities like purchase of raw materials and accessories,
knitting fabrics, processing and finishing of fabrics, sewing and packing of
garments, transport and conveyance, shipping, overheads, banking charges and
commissions, etc.
To do perfect garment costing, one must know about all these activities
thoroughly about their costs, procedures, advantages and risk factors. Also he
must know how to solve the problems when they occur and to take suitable
alternate decision immediately in time.
There are always fluctuations in the costs of raw materials and accessories,
charges of knitting, processing, finishing, sewing and packing, charges of transport and conveyance. Hence
knowledge update is required about the latest prices and charges, latest procedures, methods and quality system
market prices and availability, transportation (road, sea, air) and freight charges, etc.
Quality depends on price; price depends on quality. Each product will have different price according to its qua
Different Costing methods include:
Job Costing.
Batch Costing.
Contract or Terminal Costing.
Single or Output Costing.
Process Costing.
Operation Costing.
Operating Costing.
Departmental Costing.
Multiple Costing.
Job Costing
Job Costing is done, as the name suggests, on job works which may differ from case to case basis. By giving
different job numbers and debiting the costs on the jobs, cost of each job work can be ascertained.
Batch Costing or Batch Costing method
Batch Costing is similar to job costing but pertains to batches.
Contract Costing or Terminal Costing
Contract costing is done for large contracts. Such businesses need not maintain costs separately as financial
accounting will indicate the costs and expenses. In such contracting firms, the cost sheets are maintained for
individual contracts. In the absence of expense budgets, inefficiencies are often hidden in such cost sheets.
Single or Output Costing
Single Costing is done when the end product is single like a colliery or a power station. Cost sheets are mainta
Process Costing
Process Costing is useful when a product passes through various processes, yielding different by products of
commercial value. This is useful in industries like refineries.
Operation Costing
Operation Costing is followed by mechanical engineering industries which make products or parts. Each
manufacturing operation cost is taken into account. There is no difference between this and process costing.
Departmental Costing
When an end product is ultimately manufactured by different departments this method can be useful.
Multiple Costing
Multiple Costing is useful when a product is manufactured in an assembly line like an automobile. It is import
choose the most appropriate method of costing for your business or industry. Most businesses do not like to en
cost accountants and leave it to financial accountants to take care of this job. It is not recommended. There are
free lance cost accountants available and they can be engaged on need basis.
How to Calculate Raw Material Cost for Garments?
Material cost is the major cost component of a garment manufacturing costs. A correct cost calculation method
give you better projection of garment cost for a style. In this article how to calculate direct materials cost have
explained in details. Raw materials required for making a garment is sourced from suppliers. Main materials ar
fabric, labels, sewing thread, hang tags, trims, etc. So to have correct material cost you must have price knowle
of each item.
Steps used for material costing are: Preparation of material requirement sheet; Material price listing; Preparatio
material cost sheet.
Prepare material requirement sheet
List down all items required and calculate consumption per unit for all materials to be used in garments.
For an example, let us say you are going to calculate material cost for a polo shirt. To make polo you need knit
fabric - Single jersey/pique, cuff and collar rib. Sourcing of knitted fabric can be done in three ways:
You can directly purchase dyed fabric, or
You can source yarn, knit fabric and process the knitted fabric as per your requirement, or
Purchase dyed yarn and knit.
Let us consider you will purchase yarn and get knitting and dyeing processes done by job workers. To go throu
this process collect the pricing list of different types of yarn (or at least for the yarn that you will purchase for y
product), knitting cost, knitting loss%, dyeing cost per kg and process loss% from suppliers.
Material Price listing
Collect material price quote for all the material you need to purchase from different vendors. Prepare database
the current market price of raw materials.
For example here is one Price List Yarn: The costs for different yarns are 20s Combed - Rs 105/kg, 30s Combe
115/kg, 50s Combed - Rs 140 - 145/kg, 2/60s Combed - Rs 200/Kg, 2/60s dyed yarn - Rs 420/kg dark shade.
Knitting cost: For Single Jersey - Rs.15/kg; For Rib - Rs 18/kg; For Interlock - Rs 30 - 35/kg.
Knitting loss: 2%; Dyeing cost: Rs 80/kg for dark shades; Process loss (Dyeing): 6%.
Fabric cost: Ready to use fabric cost is calculated using basic calculation as shown in the following Table. Co
the knit fabric is represented in price per kg.
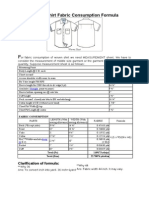
Fabric Consumption: Next step is to find requirement of fabric for the polo. Suppose for this polo shirt you n
shell fabric 0.32 kg and ribs for cuff and collar 0.080 kg. Read how to calculate fabric consumption for a knitte
garment to know fabric consumption calculation.
Prepare material cost sheet: Once you find fabric cost and fabric consumption prepare material cost sheet
including all other material required to make a garment ready for sale. An example of material cost sheet has b
shown below:
So, the total fabric cost is Rs 128.37 and including other material costs the total cost of the material for making
Polo is Rs 142.87.
Now for each item, merchants generally purchased extra quantity of inventory (from 2% to 7%) as buffer. This
excess cost due to extra purchase of material is added to the garment costing.
References
1. Prasad Kulkarni: Overview of Fashion Brand.
2. Nikhil Bhosale: Textile Progress.
Vishnu Pareek
DKTE Society's Textile & Engineering Institute
Rajwada, PO Box No 130
Ichalkaranji, Maharashtra-416 115.
Email:vishnudkte@gmail.com.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cost Sheet of Garment (By Pooja Kumari)Dokumen11 halamanCost Sheet of Garment (By Pooja Kumari)Pooja KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Fashion Merchandising: Garment CostingDokumen9 halamanFashion Merchandising: Garment CostingGopalakrishnan PalaniappanBelum ada peringkat
- Garment CostingDokumen12 halamanGarment Costingjoreva10_257827399100% (1)
- Costing of SkirtDokumen16 halamanCosting of SkirtmishrarBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Sheet GarmentDokumen9 halamanCost Sheet GarmentAnonymous uHT7dDBelum ada peringkat
- Costing Techiniques in Garment IndustryDokumen17 halamanCosting Techiniques in Garment Industrymahe_ftBelum ada peringkat
- Garment CostingDokumen17 halamanGarment CostingEmranul Islam ShovonBelum ada peringkat
- Fabric Consumption of A Basic ShirtDokumen7 halamanFabric Consumption of A Basic ShirtEmdad ApmBelum ada peringkat
- Diploma in Apparel Merchandising (LANKA CLOTHING)Dokumen23 halamanDiploma in Apparel Merchandising (LANKA CLOTHING)shahdhk100% (1)
- Formula of Garments Costing CalculationDokumen3 halamanFormula of Garments Costing CalculationShahedBelum ada peringkat
- Sweaters and Costing of A SweaterDokumen14 halamanSweaters and Costing of A SweaterViveek Rules67% (3)
- Cost Control Apparel IndustryDokumen20 halamanCost Control Apparel IndustryjitinsharmanewBelum ada peringkat
- Thread Consumption MethodsDokumen5 halamanThread Consumption MethodsRejaal100% (1)
- Product Analysis and Developement: Presented by Parul Vashist Divya Rani DFT Sem ViiDokumen29 halamanProduct Analysis and Developement: Presented by Parul Vashist Divya Rani DFT Sem Viimaduvats100% (1)
- Cutting Room Planning: ATDC, BhubaneswarDokumen37 halamanCutting Room Planning: ATDC, BhubaneswarBinoy MundaBelum ada peringkat
- The Six Month Merchandise PlanDokumen6 halamanThe Six Month Merchandise PlanJudy Ann CaubangBelum ada peringkat
- Garment L-IDokumen70 halamanGarment L-Isiyoum negashBelum ada peringkat
- Intellectual Capital On Sustainability For Garment IndustryDokumen8 halamanIntellectual Capital On Sustainability For Garment Industryraghu7676Belum ada peringkat
- Fashion Designer OSDokumen30 halamanFashion Designer OSSudi ForFrndzBelum ada peringkat
- 18.estimating Thread ConsumptionDokumen4 halaman18.estimating Thread ConsumptionSugar Lipss0% (1)
- GPT and FPT - 10Dokumen2 halamanGPT and FPT - 10satexBelum ada peringkat
- Cutting and Spreading Fabric EfficientlyDokumen7 halamanCutting and Spreading Fabric EfficientlyAlemu HaileBelum ada peringkat
- 1c. Cutting TrainingDokumen1 halaman1c. Cutting Trainingjahazi1Belum ada peringkat
- Unit-4 - Merchandising Mix ElementsDokumen33 halamanUnit-4 - Merchandising Mix ElementsSricharan ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- BGMF Fabric Cost DetailsDokumen5 halamanBGMF Fabric Cost DetailsAsif NewtonBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning 18 StepsDokumen19 halamanProduction Planning 18 StepsFaraz AliBelum ada peringkat
- Planning Process and Capacity Calculations in Clothing ManufactureDokumen11 halamanPlanning Process and Capacity Calculations in Clothing ManufactureSivakumar KBelum ada peringkat
- Garment Inspection Criteria CodesDokumen9 halamanGarment Inspection Criteria CodesKarthick Jayaram Karthick JayaramBelum ada peringkat
- Item Projects Production Folder ContentsDokumen2 halamanItem Projects Production Folder Contentsjammyb123Belum ada peringkat
- Costing of TDokumen7 halamanCosting of TJatin MandhyanBelum ada peringkat
- Cut Order PlanningDokumen12 halamanCut Order PlanningShirisha Bala100% (3)
- Polo ShirtDokumen1 halamanPolo ShirtMehedi Hasan100% (2)
- Marker EfficiencyDokumen8 halamanMarker EfficiencyMeeta Arora100% (1)
- Marker EfficiencyDokumen2 halamanMarker EfficiencyGaurav ShakyaBelum ada peringkat
- Thread Consumption GuideDokumen6 halamanThread Consumption GuideMohammad Saleh MusaBelum ada peringkat
- Course Guide Book of Garment CostingDokumen5 halamanCourse Guide Book of Garment Costingwendosen seifeBelum ada peringkat
- Fabric Consumption FormulaDokumen6 halamanFabric Consumption FormulaYeamin SufiBelum ada peringkat
- Productivity in Apparel ManufacturingDokumen7 halamanProductivity in Apparel ManufacturingAmar Nath PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Smeda-Jica Industry Support Program: Small and Medium Enterprises Development AuthorityDokumen65 halamanSmeda-Jica Industry Support Program: Small and Medium Enterprises Development AuthoritySAILAYS100% (2)
- 1.1 Garment Industry Preproduction Works 01Dokumen6 halaman1.1 Garment Industry Preproduction Works 01maya_muthBelum ada peringkat
- SMV Calculation in Garments Industry:: Standard Minute ValueDokumen2 halamanSMV Calculation in Garments Industry:: Standard Minute Valuesarwar jahanBelum ada peringkat
- Knitwear Technology (Cutting & Sewing) - APM 7402 - Note Book-1Dokumen25 halamanKnitwear Technology (Cutting & Sewing) - APM 7402 - Note Book-1shahinrezaBelum ada peringkat
- Improving Productivity of Garment Industry With Time Study October 2017Dokumen6 halamanImproving Productivity of Garment Industry With Time Study October 2017rasel miahBelum ada peringkat
- Industry Visit Report of Sai Baba Garments: BY - Ashish Bhuwania BFT/17/381Dokumen8 halamanIndustry Visit Report of Sai Baba Garments: BY - Ashish Bhuwania BFT/17/381ravikantBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Wise Sewing Thread Consumption and Sewing Thread Consumption per BodyDokumen3 halamanMachine Wise Sewing Thread Consumption and Sewing Thread Consumption per BodyAhsanul SumonBelum ada peringkat
- The Toyota Way (Overview)Dokumen7 halamanThe Toyota Way (Overview)Desrizal ABelum ada peringkat
- Raw Material Consumption Calculation in Apparel Industry - Clothing IndustryDokumen5 halamanRaw Material Consumption Calculation in Apparel Industry - Clothing IndustryQad BestmplBelum ada peringkat
- IE SOP - Standard Operating Procedure of Industrial Engineering Department - Garments-InfoDokumen3 halamanIE SOP - Standard Operating Procedure of Industrial Engineering Department - Garments-InfoSayed Aasim JawaidBelum ada peringkat
- L-5 (Marker Making)Dokumen17 halamanL-5 (Marker Making)Kashfmm100% (1)
- Pom 040: Production and Operations ManagementDokumen37 halamanPom 040: Production and Operations Managementcharles makasabiBelum ada peringkat
- Apparel Merchandising & Sourcing and Costing of Apparel ProductsDokumen34 halamanApparel Merchandising & Sourcing and Costing of Apparel Productssrishty dhanukaBelum ada peringkat
- How To Calculate SAM of A Garment?Dokumen21 halamanHow To Calculate SAM of A Garment?Rakesh ts AcharBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Layout Assignment 1Dokumen12 halamanPlant Layout Assignment 1Debdeep GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Factory Report 2Dokumen6 halamanFactory Report 2Chen Wei Sassei-KetsuBelum ada peringkat
- Planning and Scheduling in Apparel IndustryDokumen5 halamanPlanning and Scheduling in Apparel IndustryshailyrastogiBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Apparel Manufacturing ManagementDokumen27 halamanAdvanced Apparel Manufacturing ManagementPrachi YashBelum ada peringkat
- Carr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDari EverandCarr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDavid J. TylerPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Fashion Merchandising: Garment CostingDokumen9 halamanFashion Merchandising: Garment Costingvigtex2Belum ada peringkat
- Important Costing Tips for GarmentsDokumen5 halamanImportant Costing Tips for GarmentsKhandaker Sakib FarhadBelum ada peringkat
- Costing of Men's ShirtDokumen12 halamanCosting of Men's ShirtChahakNagpal100% (2)
- Chapter 29 Capital BudgetingDokumen28 halamanChapter 29 Capital BudgetingAnonymous KuELCsMGBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Management KangraDokumen12 halamanFinancial Management Kangramanik_chand_patnaikBelum ada peringkat
- Women EmpowermentDokumen21 halamanWomen EmpowermentAnonymous KuELCsMGBelum ada peringkat
- Mba IV Rural Marketing (12mbamm415) Notes - UnlockedDokumen121 halamanMba IV Rural Marketing (12mbamm415) Notes - UnlockedJohn Patterson100% (1)
- Marketing: Add To Flashcards Save To Favorites See ExamplesDokumen1 halamanMarketing: Add To Flashcards Save To Favorites See ExamplesAnonymous KuELCsMGBelum ada peringkat
- Costing TypesDokumen1 halamanCosting TypesAnonymous uHT7dDBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Sheet For HoodyDokumen11 halamanCost Sheet For HoodyfooboapparelBelum ada peringkat
- Presentacion FinsaDokumen25 halamanPresentacion FinsaEngineering Office ShahrakBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On Textured YarnsDokumen13 halamanAssignment On Textured YarnsdelwarBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Plan CharcoalDokumen2 halamanQuality Plan CharcoalPT. Estupedo Agri MakmurBelum ada peringkat
- Textile Design Lecture 2Dokumen10 halamanTextile Design Lecture 2Muhammad Usama WaseemBelum ada peringkat
- 956 Article Text 2459 1 10 20210615Dokumen4 halaman956 Article Text 2459 1 10 20210615VBelum ada peringkat
- Stanley Kochanek - CompressedDokumen26 halamanStanley Kochanek - CompressedVinayak ChaturvediBelum ada peringkat
- GRADE 8 ART HandoutsDokumen2 halamanGRADE 8 ART HandoutsJulie Ann SaquilayanBelum ada peringkat
- In-Plant Training Report PresentationDokumen60 halamanIn-Plant Training Report Presentationrajhossie9335100% (3)
- Natural Fibres 2Dokumen26 halamanNatural Fibres 2Kebede kasaBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae: Work ExperienceDokumen5 halamanCurriculum Vitae: Work Experiencetimatech solutionsBelum ada peringkat
- SAEJ30Dokumen38 halamanSAEJ30Jose Luis AusinBelum ada peringkat
- Sbi Project ReportDokumen102 halamanSbi Project Reportankit161019893980Belum ada peringkat
- Inernship Project at BhagyarekhaDokumen40 halamanInernship Project at BhagyarekhaVishal MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Learn Textile0Dokumen208 halamanLearn Textile0Hassan ShahzadBelum ada peringkat
- LETRA English Grade 9Dokumen20 halamanLETRA English Grade 9paomaiabadBelum ada peringkat
- Kohinoor Mills Limted: Outside The CountryDokumen5 halamanKohinoor Mills Limted: Outside The CountryAFTAB GAMBHIRBelum ada peringkat
- Rajasthan Culture PDFDokumen100 halamanRajasthan Culture PDFgaurav khandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University May/June 2007 Exam TimetableDokumen2 halamanAnna University May/June 2007 Exam Timetablevino1393Belum ada peringkat
- CV of MD Yousuf HasanDokumen2 halamanCV of MD Yousuf HasanTazina ShamsBelum ada peringkat
- Pakistan Textiles Industry Challenges and SolutionsDokumen12 halamanPakistan Textiles Industry Challenges and SolutionsMuqadas RehmanBelum ada peringkat
- Kids Clothing Safety Manual 2022Dokumen85 halamanKids Clothing Safety Manual 2022mdfazle165Belum ada peringkat
- Pn7-Rajesh Mehta-Textile & Apparel TradeDokumen7 halamanPn7-Rajesh Mehta-Textile & Apparel TradeAnuj SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Managerial Accounting 10th Edition Crosson Solutions ManualDokumen36 halamanManagerial Accounting 10th Edition Crosson Solutions Manualmortgagechoric3yh7100% (24)
- Things Kept in Mind While Purchasing ReadyDokumen3 halamanThings Kept in Mind While Purchasing ReadyAshish SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Tasago Aroma Ingredient Compendium 2022Dokumen65 halamanTasago Aroma Ingredient Compendium 2022Giovanni MagnoBelum ada peringkat
- Masood Textile Mills LTD.: Supply Chain ManagementDokumen11 halamanMasood Textile Mills LTD.: Supply Chain ManagementTàlhà Bïn TàrïqBelum ada peringkat
- Impact of Textile Production On EnvironmentDokumen23 halamanImpact of Textile Production On Environmentchikoti vakyapriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Internship report on production processes at Nishat Apparel LahoreDokumen39 halamanInternship report on production processes at Nishat Apparel LahoreQareena ChBelum ada peringkat
- 04 - Thiết Bị Đưa Vải VàoDokumen2 halaman04 - Thiết Bị Đưa Vải VàoPhan Quốc ThịnhBelum ada peringkat