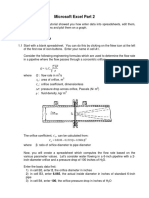
VDD and GND Power Analysis
Diunggah oleh
Divya MangeshkarDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
VDD and GND Power Analysis
Diunggah oleh
Divya MangeshkarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ECE 720 ESL & Physical Design
Lecture 25:
Power Rail Analysis
Spring 2013
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 1
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Announcements
Homework #8 Due Today
Project 2 Introduction Monday
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 2
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Todays Lecture
Power Rail Failure Modes
Rail Analysis with EPS/Voltage Storm
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 3
ECE 720
Spring 2013
The Power Rail Problem
Vdd
Vin
Vout
CL
Every time a gate switches, current flows
from the VDD rail or into the VSS/GND rail
Where does this current come from?
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 4
ECE 720
Spring 2013
A Typical Off-Chip I/O Plan
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 5
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Simplified Power Rail Model
Quarter
power pad
Rs
Rs
Rs
Rs
Rs
4Lp
Rs
Vdd
Quarter
4Lp ground pad
Rs
Rs
J ( s)xy
Source:
Huang, et al,
Elec. Comp.
& Tech. Conf.
2007
Cd xy
J(s) is a time-varying current source to model aggregate
current of many gates
Cd models wire capacitance, transistor source
capacitances, and added decoupling capacitance ("decap")
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 6
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Simplified Power Rail Model
Quarter
power pad
Rs
Rs
Rs
Rs
Rs
4Lp
Rs
Vdd
Quarter
4Lp ground pad
Rs
Rs
J ( s)xy
Source:
Huang, et al,
Elec. Comp.
& Tech. Conf.
2007
Cd xy
Inductors model bond wires
Typically very difficult to analyze by hand, due to large
number of resistors
Large matrix solvers or coarse analytical models needed
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 7
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Problem 1: IR-Drop
Also called "Voltage Droop"
Change in local supply voltage
Can cause intermittent
timing failures
Should static or dynamic analysis be used?
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 8
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Voltage Storm Static Analysis
Source: Cadence Encounter Power System
User Guide (wrapper for Voltage Storm and
other tools)
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 9
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Problem 2: Ldi/dt Noise
Also called "Simultaneous Switching Noise (SSN)"
or "Ground Bounce"
Bond-wire inductance causes
global ringing in the rail, which
can significantly increase
the change in rail voltage
Dynamic analysis needed
in Cadence Voltage Storm
to see these effects
Cadence claims this is necessary for sub 130nm techs
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Source: Gary Charles
Slide 10
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Cell-Based Analysis w/ VCD Files
Experiments show reasonably
good prediction of SSN using
currents from cell-based power
estimates from VCD files
Source: van Heijningen, Badaroglu. et al, JSSC 2002
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 11
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Problem 3: Electromigration
Mean Time to Failure
(Black's Equation: IEEE
Trans. Elec. Dev. 1969)
Ea
AT m kT
MTTF n e
j
Caused by collisions of
electrons with metal
atoms
Important to control
current density
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
j current density
Ea activation energy
T temperature
k Boltzmann's const.
Static or Dynamic Analysis?
Slide 12
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Todays Lecture
Power Rail Failure Modes
Rail Analysis with EPS/Voltage Storm
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 13
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Power Pad Location Files
Needed as input to specify where the power comes in
from off-chip
VDD.ppl
VDD 6.0 100.0 metal6
VDD
VSS
VSS.ppl
VSS 188.0 100.0 metal6
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 14
ECE 720
Spring 2013
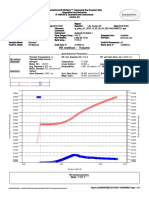
VDD Rail IR-Drop Analysis
Results for ir (linear filters):
================================
worst-case IR-drop of
*
0.336 mV
* Data filtering results for IR drop:
*
Overall data minimum: 0.949664V
*
Overall data average: 0.949806V
number of nodes
*
Overall data maximum:
0.95V
in extracted RC network
*
* Filter 1: 39791 of 39791 data values fell into this filter.
*
filtered data range:
0.949664V 0.95V
*
filtered data average: 0.949806V
*
366 values were in range 1: 0.949664V - 0.949706V
*
9060 values were in range 2: 0.949706V - 0.949748V
*
17298 values were in range 3: 0.949748V - 0.94979V
*
2837 values were in range 4: 0.94979V - 0.949832V
*
542 values were in range 5: 0.949832V - 0.949874V
*
1405 values were in range 6: 0.949874V - 0.949916V
*
4748 values were in range 7: 0.949916V - 0.949958V
*
3535 values were in range 8: 0.949958V 0.95V
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 15
ECE 720
Spring 2013
IR Drop Analysis Plots
Plots are "zoomed out" so that rails cover layout
completely
Why are the areas of greatest IR drop toward
the center?
VDD
rail
W. Rhett Davis
VSS
rail
NC State University
Slide 16
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Useful Debugging Plots
Instance Total Power Plot (ip)
100-1000 nW
10-100 nW
1-10 nW
show highest power towards
center and bottom
Instance Switching Power
Density (W/cm2) (ipd_s)
shows more switching towards
the center of chip
May be the cause of large IRdrop towards center
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 17
ECE 720
Spring 2013
VDD Rail Effective Resistance
Results for reff:
===============
worst-case IR-drop of
0.336 mV
*
* Data filtering results for effective resistance:
*
Overall data minimum: 16.7789Ohm
*
Overall data average: 44.6578Ohm
*
Overall data maximum: 91.6936Ohm
number of instances
*
* Filter 1: 9194 of 9194 data values fell into this filter.
*
filtered data range:
16.7789Ohm - 91.6936Ohm
*
filtered data average: 44.6578Ohm
*
158 values were in range 1: 82.3293Ohm - 91.6936Ohm
*
577 values were in range 2: 72.9649Ohm - 82.3293Ohm
*
1179 values were in range 3: 63.6006Ohm - 72.9649Ohm
*
977 values were in range 4: 54.2362Ohm - 63.6006Ohm
*
1410 values were in range 5: 44.8719Ohm - 54.2362Ohm
*
1480 values were in range 6: 35.5075Ohm - 44.8719Ohm
*
1511 values were in range 7: 26.1432Ohm - 35.5075Ohm
*
1902 values were in range 8: 16.7789Ohm - 26.1432Ohm
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 18
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Effective Resistance Plots
Effective Resistance of rail, from instance to pad
Instance power not considered
Helps to identify locations where decap can help
Decap can help up to a point, but adding additional
decap doesnt help if resistance is too high.
VDD
rail
W. Rhett Davis
VSS
rail
NC State University
Slide 19
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Other Useful Plots
Electromigration Risk (er)
Gaussian distribution assumed
around MTTF
Electromigration Models
not generated
Results appear to show areas
of large current density
Tap Current (er)
Current at each instance's
supply pin
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 20
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Notes
Dynamic Analysis not supported by this flow
Switching activity saved as a TCF (Toggle
Count File Cadence's version of SAIF)
TCF file used instead of VCD if it exists
allows discarding of VCD
No Decaps exist in our standard cell library
Power pad position, rail number/width are the only
things that we can change, currently
W. Rhett Davis
NC State University
Slide 21
ECE 720
Spring 2013
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- The Four Pillars of Assertion Based VerificationDokumen21 halamanThe Four Pillars of Assertion Based VerificationDivya MangeshkarBelum ada peringkat
- Read - Write Bus CyclesDokumen3 halamanRead - Write Bus CyclesDivya MangeshkarBelum ada peringkat
- Verdi-Quick Ref PDFDokumen7 halamanVerdi-Quick Ref PDFDivya Mangeshkar100% (1)
- SV Enum Datatypes Sample PDFDokumen4 halamanSV Enum Datatypes Sample PDFDivya MangeshkarBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- B.S.N.L: Telecom Technical Assistants Previous PaperDokumen10 halamanB.S.N.L: Telecom Technical Assistants Previous PaperPrasad NarvaneniBelum ada peringkat
- Hot Wheels Momentum LabDokumen3 halamanHot Wheels Momentum Labapi-360362467Belum ada peringkat
- The Periodic Table Webquest FinalDokumen3 halamanThe Periodic Table Webquest Finalapi-112724521Belum ada peringkat
- Excel Orifice FlowDokumen5 halamanExcel Orifice Flowkagaku090% (1)
- Physical Science ModuleDokumen35 halamanPhysical Science ModuleGajulin, April JoyBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Particle Testing: - One of The Most Effective Surface NDTDokumen29 halamanMagnetic Particle Testing: - One of The Most Effective Surface NDTharoub_nasBelum ada peringkat
- AS Physics: Number of Pixels X Bits Per Pixel and 1 Byte 8 BitsDokumen2 halamanAS Physics: Number of Pixels X Bits Per Pixel and 1 Byte 8 BitsAnanYasinBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Thiomersal Lidocaine and Phenylepherine in Their Ternary Mixture.2157 7064.1000199 PDFDokumen6 halamanDetermination of Thiomersal Lidocaine and Phenylepherine in Their Ternary Mixture.2157 7064.1000199 PDFiabureid7460Belum ada peringkat
- Advanced Material Modeling in AbaqusDokumen13 halamanAdvanced Material Modeling in AbaqusUdhamBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetism and Microwaves: Unit - IiDokumen30 halamanElectromagnetism and Microwaves: Unit - IiMukulKaushikBelum ada peringkat
- Discovery of Electron: The Atomic StructureDokumen3 halamanDiscovery of Electron: The Atomic Structurejohn100% (1)
- X-Ray Diffraction PrinciplesDokumen123 halamanX-Ray Diffraction Principlesatswalla100% (1)
- Silicon Nitride - Synthesis, Properties and Application (2012)Dokumen176 halamanSilicon Nitride - Synthesis, Properties and Application (2012)Daud BabaBelum ada peringkat
- Stat MechDokumen270 halamanStat MechRithish BarathBelum ada peringkat
- Radioactivity 1 QPDokumen9 halamanRadioactivity 1 QPShelly EdwardsBelum ada peringkat
- MSE 6130 Final Exam OutlineDokumen3 halamanMSE 6130 Final Exam Outlineredphoenix2k9Belum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Atomic and PEEDokumen6 halamanPaper 2 Atomic and PEEAnonymous oDx8RFfZBelum ada peringkat
- Combined Ad No 8-2021Dokumen7 halamanCombined Ad No 8-2021Abdul RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Activity 4Dokumen4 halamanPhysics Activity 4Ankit PanigrahiBelum ada peringkat
- Hasil XRDDokumen1 halamanHasil XRDAissyah LathifahBelum ada peringkat
- Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDokumen15 halamanCreated by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloremishaBelum ada peringkat
- Tic 106Dokumen4 halamanTic 106maiconandradecruzBelum ada peringkat
- Ultrasonic SolutionDokumen46 halamanUltrasonic Solutionsoumyadev86% (14)
- Stephen Hawking: The Life and Times ofDokumen7 halamanStephen Hawking: The Life and Times ofde sisilBelum ada peringkat
- LPXWeb ViewDokumen2 halamanLPXWeb ViewGeorge ZormpasBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel Chemistry Answers Combined FINALDokumen50 halamanEdexcel Chemistry Answers Combined FINALboobla100% (2)
- Assignment 1 & 2Dokumen2 halamanAssignment 1 & 2Ravindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Test-03 Quantum Numbers: B. C. D. E. F. GDokumen2 halamanTest-03 Quantum Numbers: B. C. D. E. F. GNishali Sam100% (1)
- SPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 BerjawapanDokumen18 halamanSPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar71% (7)
- QM16 SHOQuestionsDokumen10 halamanQM16 SHOQuestionsGaurav YadavBelum ada peringkat