Ip Table 6 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta Campus
Diunggah oleh
Vhi Da Lyn0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan2 halamanUnder low family income (1,0005,000), the item number 6 "i respect the opinion of others" got the highest computed mean of 4. On the other hand, the family whose belong to the highest family income (6000 above) the item number 11 "we have a time to tutor each other" got the lowest computed means of 3.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
IP TABLE 6 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUS
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniUnder low family income (1,0005,000), the item number 6 "i respect the opinion of others" got the highest computed mean of 4. On the other hand, the family whose belong to the highest family income (6000 above) the item number 11 "we have a time to tutor each other" got the lowest computed means of 3.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan2 halamanIp Table 6 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta Campus
Diunggah oleh
Vhi Da LynUnder low family income (1,0005,000), the item number 6 "i respect the opinion of others" got the highest computed mean of 4. On the other hand, the family whose belong to the highest family income (6000 above) the item number 11 "we have a time to tutor each other" got the lowest computed means of 3.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
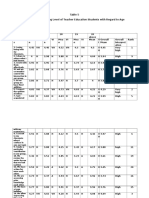
It could be gleaned from table 6 that under low family income (1,0005,000), the item number 6 I respect the
opinion of others got the highest
computed mean of 4.62 which is interpreted as very high cooperative
learning. On the other hand, item number 11 We have a time for tutor each
other got the lowest computed mean of 3.38 which is interpreted as
average.
On the other hand, the family whose belong to the highest family
income (6000 above) the item number 1 I enjoy being with my classmate
got the highest computed mean of 4.43 which interpreted as very high level
of cooperative learning. And the item number 11 we have a time to tutor
each other got the lowest computed mean of 3.23 which is interpreted as
average of cooperative learning.
Daly et al. (1994) stated that students from higher income families are
more comfortable asking questions and actively involving themselves in
classroom instruction. These observations present a challenge to Strong,
Silver, and Robinsons (1995) who positioned that students engagement in
the learning process promotes student to success, curiosity and originality,
as well as satisfying relationships, regardless of socioeconomic status.
Generally ,the cooperative learning of teacher education students as
according to their family income ,the item number 1 I enjoy being with my
classmate ranked no. 1 among cooperative learning questionnaire of
teacher education student which got the highest computed weighted
average mean of 4.48 which means very high. On the other hand, the item
we are assessing prior knowledge each other ranked no. 20 got the lowest
weighted average mean of 3.31 which interpreted as average.
It could be gleaned from table 6 that the respondent who belong to
family with low monthly income have computed weighted arithmetic mean of
3.95 which has an interpretation of high cooperative learning while the
respondent who belong to family who belong to family with high monthly
income have computed weighted arithmetic mean of 3.79 which has an
interpretation of high cooperative learning. Therefore, family income is a
contributory factor as regard to the cooperative learning of teacher
education students.
One study found that only 36 percent of low-income parents were
involved in three or more school activities on a regular basis, compared with
59 percent of parents above the poverty line (U.S. Department of Health and
Human Services, 2000). Goodman (2004) suggested that family income may
relate more to differences in coping styles and other interactional skills. The
data implies that poor families tend to have much quality time and
interactions to their siblings due to the occupations they have compared to
those with rich families who tend to be very busy on their careeres and work
place.
In summary the overall mean of cooperative learning of teacher
education students as regard to their monthly family income has computed
mean of 3.87 which is interpreted as high cooperative learning.
Table 7 shows the cooperative learning level of the Teacher Education
Students when grouped and as a whole
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Sample Web/Graphic Design QuestionnaireDokumen7 halamanSample Web/Graphic Design QuestionnaireTori Walker100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- 1 Chapter 4 Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of Data INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen5 halaman1 Chapter 4 Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of Data INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da Lyn100% (2)
- College Teaching Internship JournalDokumen11 halamanCollege Teaching Internship Journalapi-242908452100% (1)
- Etech WK1Dokumen4 halamanEtech WK1RonaBelum ada peringkat
- Integrating Business Management Processes - Volume 2 - Support and Assurance Processes (2022, Productivity Press) - Libgen - LiDokumen327 halamanIntegrating Business Management Processes - Volume 2 - Support and Assurance Processes (2022, Productivity Press) - Libgen - LiRihab FarhatBelum ada peringkat
- Surat Perjanjian Sewa Menyewa RukoDokumen3 halamanSurat Perjanjian Sewa Menyewa RukoMaamzkyBelum ada peringkat
- Lie To MeDokumen2 halamanLie To Meirish xBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Related Literature and Studies INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen12 halamanChapter 2 Related Literature and Studies INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da Lyn90% (20)
- Overall Interpretation INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen3 halamanOverall Interpretation INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUS Title PageDokumen7 halamanINTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUS Title PageVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 The Problem INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen74 halamanChapter 1 The Problem INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Table 6 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen4 halamanTable 6 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Interpretation of Age INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halaman2 Interpretation of Age INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Family Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen3 halamanFamily Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen6 halamanChapter 3 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da Lyn100% (1)
- Interpretation FAMILY INCOME INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halamanInterpretation FAMILY INCOME INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Wam INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen3 halamanWam INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- 1male and Female INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halaman1male and Female INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Table 5 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta CampusDokumen3 halamanTable 5 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta CampusVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- 2table 5 Ages INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen3 halaman2table 5 Ages INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- 1interpretation of Sex INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halaman1interpretation of Sex INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen8 halamanChapter 5 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Final Thesis INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen20 halamanFinal Thesis INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da Lyn100% (4)
- Complete Questionnaire INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen4 halamanComplete Questionnaire INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Ip Table 5 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta CampusDokumen2 halamanIp Table 5 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta CampusVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Final Presentation INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen21 halamanFinal Presentation INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Table 4INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen4 halamanTable 4INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Ip Table 4 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta CampusDokumen2 halamanIp Table 4 Interpersonal Skills of Elementary Education Students of Psu-Urdaneta CampusVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen6 halamanChapter 5 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- High Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen1 halamanHigh Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Low Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halamanLow Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Average Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halamanAverage Income INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Ages 15-17 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halamanAges 15-17 INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Ages 21 and Above INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen2 halamanAges 21 and Above INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Female Scale INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSDokumen1 halamanFemale Scale INTERPERSONAL SKILLS OF ELEMENTARY EDUCATION STUDENTS OF PSU-URDANETA CAMPUSVhi Da LynBelum ada peringkat
- Year 2 Daily Lesson Plans: Skills Pedagogy (Strategy/Activity)Dokumen5 halamanYear 2 Daily Lesson Plans: Skills Pedagogy (Strategy/Activity)Kalavathy KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Application Letter: Amirullah TanayDokumen4 halamanApplication Letter: Amirullah TanayAmirBelum ada peringkat
- Pattern Language RvsDokumen22 halamanPattern Language RvsRajni TanejaBelum ada peringkat
- Question: A 100 MM X 100 Mm. Vertical Cantilever Beam Xed at The BottoDokumen2 halamanQuestion: A 100 MM X 100 Mm. Vertical Cantilever Beam Xed at The Bottostructural mechanicsBelum ada peringkat
- T0021 HowtoConfigureMTG200withFreePBXDokumen11 halamanT0021 HowtoConfigureMTG200withFreePBXtomba2kBelum ada peringkat
- Panchel's Guide to Variables and Data Types in CDokumen14 halamanPanchel's Guide to Variables and Data Types in CUtkarsh AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- CBLM Participate in Workplace Comm. NC IiDokumen101 halamanCBLM Participate in Workplace Comm. NC IiErlene LinsanganBelum ada peringkat
- Absolut MarketingDokumen10 halamanAbsolut MarketingSaurabh AttalBelum ada peringkat
- Eng CompositionDokumen173 halamanEng CompositionVo SunnyBelum ada peringkat
- Comments On Society: Muntadas' Interventions: Nicolás Villegas HernándezDokumen5 halamanComments On Society: Muntadas' Interventions: Nicolás Villegas HernándezdirtyvermineBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Numeracy Through PlayDokumen4 halamanTeaching Numeracy Through Playpianoman3_1417750Belum ada peringkat
- Speech Act Theory ExplainedDokumen2 halamanSpeech Act Theory ExplainedEunice C. LoyolaBelum ada peringkat
- Communication in Everyday Life The Basic Course Edition With Public Speaking 2nd Edition Duck Test BankDokumen35 halamanCommunication in Everyday Life The Basic Course Edition With Public Speaking 2nd Edition Duck Test Bankredfinch.exedent.ti8uaz100% (13)
- GESL BriefingDokumen38 halamanGESL BriefingongjoelBelum ada peringkat
- Japanese Junior High School Girls' and Boys' First-Person Pronoun Use and Their Social WorldDokumen11 halamanJapanese Junior High School Girls' and Boys' First-Person Pronoun Use and Their Social WorldReposar ReynaldoBelum ada peringkat
- ID Model PDFDokumen20 halamanID Model PDFAbbasBelum ada peringkat
- I - CSCI - 2133 - 390 - 26585 - 201620 Introduction To JAVA - Online Spring 2016Dokumen7 halamanI - CSCI - 2133 - 390 - 26585 - 201620 Introduction To JAVA - Online Spring 2016William SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Sample of Action PlanDokumen32 halamanSample of Action PlanIl DalinaBelum ada peringkat
- Proposar Car Free WritingDokumen29 halamanProposar Car Free WritingWayan GandiBelum ada peringkat
- William Neal Clark CVDokumen2 halamanWilliam Neal Clark CVapi-234468987Belum ada peringkat
- KEYMILE Product TrainingDokumen64 halamanKEYMILE Product Trainingebg72900Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan - What Do You Want To TryDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan - What Do You Want To Tryapi-490600514Belum ada peringkat
- 16721-Article Text-46417-1-10-20220112Dokumen19 halaman16721-Article Text-46417-1-10-20220112Jessyl LiceraBelum ada peringkat
- Gracely Murphrey Resume - 01 18 16Dokumen2 halamanGracely Murphrey Resume - 01 18 16api-317060401Belum ada peringkat