Biol137mt1 f01 PDF
Diunggah oleh
وان أحمدDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biol137mt1 f01 PDF
Diunggah oleh
وان أحمدHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biology 137 Introduction to Toxicology
Midterm Exam 1
Name
Fall Semester 2001
Part I. Multiple choice. Two points each.
1.
Toxicology is the study of
A. prevalence of disease and death in a population B. adverse effects of chemicals on
living organisms C. the appearance of symptoms produced by infectious agents D. word
origins E. none of the above
2.
In the human body, toxicological processes ultimately take place at which level?
A. cell B. tissue C. organ D. organ system E. the whole organism
3.
Which type of toxicologist is concerned with the use of toxicants by the public and in the
workplace?
A. descriptive toxicologist B. mechanistic toxicologist C. regulatory toxicologist
4.
Which is the best definition of the term toxicant?
A. a chemical that causes no adverse effects B. a substance produced as a result of human
activities C. a branch of toxicology D. an agent that neutralizes the effects of a poison
E. a substance that is naturally produced
5.
The statement, "All substances are poisons; there is none which is not a poison. Only the
dose determines that a thing is not a poison" , is attributed to which of the following?
A. Hippocrates B. Theophrastus C. Mithridates D. Paracelsus E. Catherine
DiMedici
6.
Toxicity is recognized when on the administration of a chemical an observable and
quantifiable
is identified.
A. mutagen B. waste product C. dose D. end-effect or response E. safety factor
7.
A substance that is being tested for toxicity is injected intramuscularly mixed with peanut
oil. The term vehicle in this case refers to:
A. the syringe used B. the needle type used C. the manner in which the substance was
transported to the lab D. the peanut oil E. none of the above
For the following (8-12) select the most appropriate answer in column B for each item in
column A below.
Column A
Column B
8.
acute toxicity
A. Symptoms restricted to the site of initial
exposure
9.
systemic toxicity
B. Toxicity occurring within less that 24 hours
10.
local toxicity
C. toxic effects occur within the body, at sites
far removed from exposure site
11.
delayed toxicity
D. dead and lost cells replaced by cell division
12.
reversible toxic effect E. the appearance of cancerous tumors 25-30 years after
exposure to a toxin.
13.
The sigmoid (s) dose response curve for a toxicant indicates a threshold dose below which
no effects are observed. A threshold occurs because of
A. saturation of biotransformation pathways. B. saturation of protein binding sites.
C. saturation of receptor sites. D. depletion of cofactors. E. All of the above are possible
reasons.
1
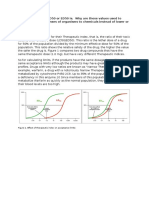
14.
In the figure above, toxin A is
than toxin B and toxin C is
than toxin D.
A. less potent, less efficacious B. more potent, more efficacious C. less potent, more
efficacious D. more potent, less efficacious
15.
The sigmoid (s) dose response curve is usually converted into a probit probability
presentation. Each probit unit of the transformed data represents
A. 50% of the population B. 99.7% of the population. C. one standard deviation.
D. two standard deviations. E. the LD50 value obtained from the plot.
16.
A weak organic acid with a pKa of 5.5 would be expected to be
A. more ionized at low pH B. more ionized at high pH C. non-ionized at low pH
D. non-ionized at high pH E. both (B) and (C) are true
17.
A contaminant in the local drinking water is at a concentration of 0.2 mg/ml. What will be
the average daily dose (mg/kg) of the contaminant for a mouse. Mouse water consumption
per day is 5 ml and the mouse weight is 30 grams.
A. 6.66 mg/kg B. 33.33 mg/kg C. 0.033 mg/mouse D. 6.55 mg/ml E. 0.66 mg
For the following (18-21) match the item in column B with the item in column A.
Column A
Column B
18.
Additive effects
A. equal to the sum of effects of each agent given
alone.
19.
Potentiation effects
B. combined effect of two chemicals is greater than
the sum of effects of each.
20.
Antagonistic effects
C. one substance is not toxic but when added to
another toxic chemical it makes that chemical
more toxic
21.
Synergistic effects
D. when two chemicals interfere with each other's
actions
22.
The "first pass effect" refers to
A. rejection on a first date B. a toxicant passing through the circulation for one cycle
C. elimination of a toxicant before it is distributed by the blood stream D. successfully
completing this course the first time E. none of the above
23.
For a gas with a high solubility in plasma, absorption in the lungs depends more on
respiration rate than on pulmonary blood flow.
A. True
B. False
24.
Chemicals are more readily absorbed through the skin or GI tract if they are
A. polar compounds B. ionic compounds C. lipid soluble D. non-ionic, neutral
compounds E. both (C) and (D)
25.
Metalothionein is a special protein that binds metals in the
A. liver B. GI tract C. type I pneumocytes D. nasal passages
26.
With respect to excretion of toxic substances which of the following is the correct order of
importance of the three major routes?
A. fecal>lung>kidney B. lung>fecal>kidney C. fecal>kidney>lung
D. kidney>fecal>lung
27.
Which of the following processes or interactions would interfere with the delivery of the
ultimate toxicant to its target site (intracellular molecule) where it produces the toxic
effect?
A. increased porosity of capillaries B. reabsorption C. specialized membrane
transporters D. activation of the toxicant (toxication) E. excretion
28.
Excretion of weak organic bases by the kidney is favored by
and
reabsorption of weak organic acids by the kidney tubule epithelium is favored by
in the forming urine.
A. high pH, high pH B. low pH, low pH C. high pH, low pH D. low pH, high pH
29.
Which of the following would be considered a detoxication biotransformation process?
A. formation of electrophiles B. formation of free radicals C. conjugation with
glucuronic acid D. formation of redox-active reactants E. Both (A) and (B)
30.
Dysregulation of gene expression can result from
by the toxicant.
A. disruption of DNA transcription B. interference with promoter regions of genes
C. interference with phosphorylation networks involved in signal transduction D.
interference with signal production E. all of the above.
31.
Class B substances that are excreted by the liver have a bile to plasma concentration ratio
that is greater than 1. These substances are probably
A. excreted by passive processes if they are lipophilic. B. actively transported by the
hepatocytes. C. reabsorbed in the bile ducts. D. not excreted rapidly.
32.
Which of the following would enhance the absorption of a toxicant through the various
skin layers.
A. hydrophilicity B. lipophilicity C. active transport mechanisms D. hydration of the
skin E. Both (B) and (D)
33.
Toxins get across the placenta to the developing fetus
A. by active transport processes B. by simple diffusion C. by paracellular transport
D. through fenestrated capillaries E. with difficulty because the placenta acts as a barrier
much like the blood brain barrier.
3
34
The most important contributing source for excretion of toxicants via the fecal route is
A. intestinal secretion. B. exfoliation of intestinal cells. C. biliary excretion.
D. pancreatic excretion. E. none of the above.
35.
Disposition refers to the
of toxic substances.
A. absorption B. distribution C. biotransformation D. excretion
processes.
E. All of these
Part II Short essay. You must answer questions 36 and 37 and choose one more from the
remaining three. Ten points each.
36.
It is found that a toxin is more toxic when it is given in one large dose than when it is
administered in small doses given at 6-8 hour intervals. It takes a larger total dose to
produce the same effect when it is given in small increments than when the toxin is given
as one large dose. Give at least three reasons to explain this phenomenon.
37.
Repair is an important process that may ultimately determine whether or not a chemical
will manifest toxicity. Describe briefly the three levels of repair and give an example of
each.
38.
Discuss four major anatomic and physiological properties that are responsible for the
"blood brain barrier" in the central nervous system.
39.
Explain what an LD50 or ED50 is. Why are these values used to compare toxic responses of
organisms to chemicals instead of lower or higher values?
40.
Describe four potential storage depots for toxicants. Provide an example of a storage
mechanism or a type of toxicant that is stored in each depot.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pharmaceutics Exam 1 - This Semester!Dokumen6 halamanPharmaceutics Exam 1 - This Semester!api-372361284% (19)
- Pharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - CompressedDokumen289 halamanPharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - Compressed09Dhawal PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Biopharmaceutics VIOLET PACOPDokumen35 halamanBiopharmaceutics VIOLET PACOPLilian Daria100% (8)
- Toxicologie Question PaperDokumen20 halamanToxicologie Question Paperboskii2u100% (2)
- ToxicologyDokumen29 halamanToxicologyAniey Mohd Nor100% (1)
- Question Bank Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics (Choice Based) FH 2022Dokumen12 halamanQuestion Bank Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics (Choice Based) FH 2022Usman Khan100% (5)
- Biology Model Exam Grade 12Dokumen13 halamanBiology Model Exam Grade 12All in One Tube100% (5)
- Chapter 26Dokumen14 halamanChapter 26Mhmad MokdadBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 192 Lab Report #1 BivalveDokumen8 halamanBIO 192 Lab Report #1 BivalveBen KillamBelum ada peringkat
- More TipsDokumen6 halamanMore Tipslalilu07Belum ada peringkat
- TOXICOLOGY MCQ -[1]Dokumen11 halamanTOXICOLOGY MCQ -[1]farhanyasser34Belum ada peringkat
- Ami and Rosyel Question Chap 2Dokumen7 halamanAmi and Rosyel Question Chap 2Mallari, John JesterBelum ada peringkat
- Farmacologia y Toxicologia FINAL EXAMDokumen3 halamanFarmacologia y Toxicologia FINAL EXAMAlfredo SarachoBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Health Risk AssessmentDokumen9 halamanEnvironmental Health Risk AssessmentYuniar WidyaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology MCQS For 3rd Yr ZSMUDokumen116 halamanPharmacology MCQS For 3rd Yr ZSMUDrRaghavender Reddy88% (8)
- Pharmacology and Neurochemistry Question BankDokumen12 halamanPharmacology and Neurochemistry Question BankAHER SANKETBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacodynamics Multiple Choice Questions PDF - Top Drug MechanismsDokumen6 halamanPharmacodynamics Multiple Choice Questions PDF - Top Drug MechanismsLibby Khalid100% (1)
- 1st Comprehensive Examination PHARMADokumen9 halaman1st Comprehensive Examination PHARMANdor BariboloBelum ada peringkat
- Practice-Midterm 1 Biol 1101Dokumen6 halamanPractice-Midterm 1 Biol 1101Megadirectioner 21Belum ada peringkat
- PHARMACODYNAMICS MCQDokumen8 halamanPHARMACODYNAMICS MCQyan219100% (3)
- Practice Midterm 1Dokumen6 halamanPractice Midterm 1Zaineb SalehBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 1 - MCQDokumen16 halamanCHP 1 - MCQNida RidzuanBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Base Clinical Pharmacology PDFDokumen30 halamanMCQ Base Clinical Pharmacology PDFTesfa HopeBelum ada peringkat
- VET 313 Study MCQsDokumen4 halamanVET 313 Study MCQsChiku Mtegha100% (2)
- Dr. Yousif MCQsDokumen11 halamanDr. Yousif MCQsM7md AllahhamBelum ada peringkat
- UACE BIOLOGY PAPER 1 2019 GuideDokumen11 halamanUACE BIOLOGY PAPER 1 2019 Guidek75544863Belum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology Test QuestionsDokumen7 halamanPharmacology Test QuestionsMedawar CarpetsBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23Dokumen7 halamanLecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23wafae moutanaBelum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen12 halaman1Gaanappriya Mohan Yogesh100% (4)
- ZSMU, Ukraine Pharmacology MCQs by Gankidi Raghavender Reddy,,,Used For Preparation of FMGE (Mci Screening Test) TooDokumen117 halamanZSMU, Ukraine Pharmacology MCQs by Gankidi Raghavender Reddy,,,Used For Preparation of FMGE (Mci Screening Test) Toogrreddy836100% (2)
- A. B. C. D.: Name: Date: ScoreDokumen6 halamanA. B. C. D.: Name: Date: ScoreGynesis Lim RoqueroBelum ada peringkat
- The Biology Model Examination For Grade 12 in 2009/2017Dokumen16 halamanThe Biology Model Examination For Grade 12 in 2009/2017koket negash100% (2)
- BBO 2011 Round 2Dokumen16 halamanBBO 2011 Round 2martynapetBelum ada peringkat
- General Pharmacology Revision Questions Level 100 ShareDokumen15 halamanGeneral Pharmacology Revision Questions Level 100 ShareFortune MiyagueBelum ada peringkat
- PPSC EXAMS PAST PAPER 10Dokumen9 halamanPPSC EXAMS PAST PAPER 10Muhammad RawasBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs on Pharmacokinetics and PharmacogenomicsDokumen29 halamanMCQs on Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacogenomicsbaker samuelBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma Exam MasterDokumen636 halamanPharma Exam MastercheenuBelum ada peringkat
- New Biology Booklet ACTDokumen152 halamanNew Biology Booklet ACTNatalieBelum ada peringkat
- Questions - Answer Bassam QQ 1Dokumen14 halamanQuestions - Answer Bassam QQ 1Bassam SaifBelum ada peringkat
- Ain Shams University - Pharmacology MCQ Ain Shams (2019 - 2020)Dokumen144 halamanAin Shams University - Pharmacology MCQ Ain Shams (2019 - 2020)Cristian C BecerraBelum ada peringkat
- All MCQDokumen136 halamanAll MCQWajiha ZahraBelum ada peringkat
- Bio5A Midterm2 (2012U)Dokumen5 halamanBio5A Midterm2 (2012U)Nicholas ChewBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs TOXICOLOGYEXAMPLESDokumen15 halamanMCQs TOXICOLOGYEXAMPLESesraaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology g12 Model Exam 2016Dokumen15 halamanBiology g12 Model Exam 2016Getahun AbebawBelum ada peringkat
- Block 1Dokumen17 halamanBlock 1Toni-Krys HardyBelum ada peringkat
- BIOPHARMACEUTICS MCQsDokumen38 halamanBIOPHARMACEUTICS MCQsShahrukh SindhiBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Questions 1 PhotosynthesisDokumen17 halamanPractice Questions 1 Photosynthesis사나Belum ada peringkat
- S.6 Bio P1Dokumen14 halamanS.6 Bio P1Mwesigwa HannahBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 1 Post-Test: DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheDokumen3 halamanBiology 1 Post-Test: DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheGette AcupanBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology Holroyd WithkeyDokumen39 halamanPharmacology Holroyd Withkeykathryn ongBelum ada peringkat
- BPK Question BankDokumen11 halamanBPK Question Bankwritters2023Belum ada peringkat
- Test3 AnsDokumen38 halamanTest3 AnsKavitha Suresh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Neonetal and midwiferyDokumen2 halamanNeonetal and midwiferygemechu gebisaBelum ada peringkat
- Medi Chem MCQ With Ans-1Dokumen74 halamanMedi Chem MCQ With Ans-109Dhawal Patil100% (2)
- Biology 2A03 Quiz 1 Version 1 Answers Feb 2013Dokumen8 halamanBiology 2A03 Quiz 1 Version 1 Answers Feb 2013JeevikaGoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Итоговое 2020 MCQDokumen62 halamanИтоговое 2020 MCQmohammad farooque razaa100% (4)
- 01 Test BankDokumen16 halaman01 Test BankNaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecotoxicology: New Challenges and New ApproachesDari EverandEcotoxicology: New Challenges and New ApproachesElisabeth GrossBelum ada peringkat
- Essays in Toxicology: Volume 1Dari EverandEssays in Toxicology: Volume 1Frank R. BloodPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (6)
- 3Dokumen3 halaman3وان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Moody Robotics Ebooks 0Dokumen19 halamanMoody Robotics Ebooks 0وان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- How To Make A MiloDokumen11 halamanHow To Make A Miloوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Seven Chapter Seven: Gears GearsDokumen13 halamanChapter Seven Chapter Seven: Gears Gearsوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Glass Bottle Specs Diagrams OI Anchor Glass PDFDokumen2 halamanGlass Bottle Specs Diagrams OI Anchor Glass PDFوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Shah AhmedDokumen6 halamanShah Ahmedوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Tamba HanDokumen1 halamanTamba Hanوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Front View MomDokumen3 halamanFront View Momوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- 3.0 Research Methodology: Detail DesignDokumen7 halaman3.0 Research Methodology: Detail Designوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Toxicology SummaryDokumen19 halamanPrinciples of Toxicology SummaryUrugonda VenumadhavBelum ada peringkat
- 3.0 Research Methodology: Detail DesignDokumen7 halaman3.0 Research Methodology: Detail Designوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Lab C 5Dokumen3 halamanLab C 5وان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 6Dokumen2 halamanLab 6وان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 6Dokumen2 halamanLab 6وان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- 17 Packaging PDFDokumen28 halaman17 Packaging PDFNiki SanBelum ada peringkat
- Food Packaging-Roles, Materials, and Environmental Issues: R: Concise Reviews/Hypotheses in Food ScienceDokumen17 halamanFood Packaging-Roles, Materials, and Environmental Issues: R: Concise Reviews/Hypotheses in Food ScienceHafie JayBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Toxicology SummaryDokumen19 halamanPrinciples of Toxicology SummaryUrugonda VenumadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Eee PC User ManualDokumen62 halamanEee PC User ManualAli BoerhannoeddinBelum ada peringkat
- Horlicks Packaging Product Pricing Placement PromotionDokumen1 halamanHorlicks Packaging Product Pricing Placement Promotionوان أحمدBelum ada peringkat
- Non-symbiotic Nitrogen FixersDokumen21 halamanNon-symbiotic Nitrogen Fixersrajiv pathakBelum ada peringkat
- The Science of NeglectDokumen20 halamanThe Science of NeglectdrdrtsaiBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0141022999001556 MainDokumen21 halaman1 s2.0 S0141022999001556 MainRenata ScoralickBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Medical Terminology Verified AnswersDokumen5 halamanChapter 2 Medical Terminology Verified AnswersGregg ProducerBelum ada peringkat
- Parts, Functions and Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDokumen32 halamanParts, Functions and Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsZephie100% (1)
- Chemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanDokumen7 halamanChemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanSkyle VoBelum ada peringkat
- Lec.6.Varietal & Hybrid Seed Production in RiceDokumen75 halamanLec.6.Varietal & Hybrid Seed Production in RiceAmirthalingam KamarajBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 IECR P3 Q1 v2 PDFDokumen9 halaman0610 IECR P3 Q1 v2 PDFGAIA Educators - Home TuitionBelum ada peringkat
- Presented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyDokumen20 halamanPresented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyCristine EchaveBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDokumen17 halamanBiology Investigatory ProjectAnmol Dhungel100% (6)
- Effects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiDokumen7 halamanEffects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiAngela ValdiviesoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Bioinformatics: Database Search (FASTA)Dokumen35 halamanIntroduction To Bioinformatics: Database Search (FASTA)mahedi hasanBelum ada peringkat
- Biomimicry Avjeet SinghDokumen21 halamanBiomimicry Avjeet SinghAvjeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Lipid Movement BiochemDokumen9 halamanLipid Movement BiochemCrowBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Lab ReportDokumen7 halamanSample Lab ReportPutri Syalieyana0% (1)
- Zoologija VrsteDokumen16 halamanZoologija VrsteДушан МарковићBelum ada peringkat
- Botany AssignmentDokumen35 halamanBotany AssignmentLakshmiBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Replication Practice PDFDokumen2 halamanDNA Replication Practice PDFKim100% (1)
- Geology of Malta and GozoDokumen6 halamanGeology of Malta and GozoCarolina Pérez P.Belum ada peringkat
- Turbidimetry and Nephelometry1Dokumen3 halamanTurbidimetry and Nephelometry1maxim_crank6101100% (1)
- Summary of Qualitative Tests (Pharmacognosy)Dokumen8 halamanSummary of Qualitative Tests (Pharmacognosy)kidsaintfineBelum ada peringkat
- Adolescent Reproductive and Sexual HealthDokumen42 halamanAdolescent Reproductive and Sexual HealthMuhammad Abbas WaliBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Concepts of Care in Evidence Based Practice 8th Edition Townsend Test BankDokumen36 halamanPsychiatric Mental Health Nursing Concepts of Care in Evidence Based Practice 8th Edition Townsend Test Bankquemefuloathableilljzf100% (26)
- E-Portfolio Injection Study GuideDokumen7 halamanE-Portfolio Injection Study Guideapi-366034042Belum ada peringkat
- Adlerian Psychotherapy: Prioritizing RelationshipsDokumen24 halamanAdlerian Psychotherapy: Prioritizing RelationshipsJayanth MamundiBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Sleep Deprivation among Students in Saint Francis of Assisi CollegeDokumen50 halamanEffects of Sleep Deprivation among Students in Saint Francis of Assisi College• Cielo •Belum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Perkecambahan Biji PDFDokumen14 halamanJurnal Perkecambahan Biji PDFKinad Danik50% (2)
- Uits PDFDokumen36 halamanUits PDFCrystal ParkerBelum ada peringkat
- MDU Open Elective 3rd Sem Date Sheet May 2019Dokumen1 halamanMDU Open Elective 3rd Sem Date Sheet May 2019Ratan DeshBelum ada peringkat










![TOXICOLOGY MCQ -[1]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/719796107/149x198/ba934880af/1712180735?v=1)