Blockages and Halo
Diunggah oleh
elumalaianithaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blockages and Halo
Diunggah oleh
elumalaianithaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Blockages and Halo
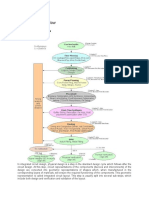
Blockages
Blockages are specified locations where placing cells are prevented or blocked. These act as
guidelines for placing standard cell* in the design. Blockages will not be guiding the
placement tool to place standard cell at some particular area, but it won't allow placement
tool to place standard cell at specified locations. This way blockages are act as guidelines to
placement tool.
*Standard cell: A standard cell is a group of transistors and interconnects structures that
provides a boolean logic function (e.g. AND, OR, XOR, XNOR, NOT) or a storage function
(flipflops or latch).
Types of blockages describes as below,
Soft (Non-buffer) blockage:
Soft blockage specifies a region where only buffer can be placed. That means standard cells
cannot be placed in this region. It blocks(prevents) the placement tool from placing nonbuffer cells such as std. cell in this region.
Hard blockage:
Hard blockage specifies a region where all standard cells and buffers cannot be placed. It
prevents the placement tool from placing standard cells and buffers in this region.
Hard blockage are mostly used to
Block standard cells to certain regions in the design,
Avoid routing congestion at macro conners,
Control power rail generations at macro cores.
Partial blockage:
The blockage factor for any blockage is 100% by default. So no cells can be placed in that
region, but the flexibility of blockages can be chosen by partial blockages.
Placement blockage:
Placement blockage prevent the placement tool from placing cells at specified regions.
Placement blockages are created at floor planning stage.
Placement blockage are used to
Define standard cells and macro* area,
Reserve channels for buffer insertion,
Prevent cells from being placed nearer to macros,
Prevent congestion near macros.
*Macros: Macros are intellectual properties that can be directly used in the design. These
are need not to be design. For example memories, processor core, PLL etc.
Routing blockage:
Routing blockages block routing resources on one or more layers. It can be created at any
point in the design.
Halo (keep-out-region):
Halo is the region around the boundary of fixed macro in the design in which no other
macro or standard cells can be placed. Halo allows placement of buffers and inverters in its
area.
Halos of two adjacent macros can be overlap.
If macro are moved from one place to another place, halos will also be moved. But in
case of blockages if the macros are moved from one place to another place the blockages
can't be moved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Iso 9001Dokumen6 halamanIso 9001IulianBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Perl and Tcl Training GuideDokumen29 halamanPerl and Tcl Training GuideelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Backend (Physical Design) Interview Questions and Answers - BipeenKulkarniDokumen34 halamanBackend (Physical Design) Interview Questions and Answers - BipeenKulkarnielumalaianitha100% (2)
- Fundamental of Loic SynthesisDokumen105 halamanFundamental of Loic SynthesiselumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Fiber Communication 10ec72 SolutionDokumen73 halamanOptical Fiber Communication 10ec72 Solutionshashank gupta100% (1)
- LinuxDokumen50 halamanLinuxelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- CmosDokumen23 halamanCmoselumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- ASIC Design Methodology Using Cadence SP&R FlowDokumen40 halamanASIC Design Methodology Using Cadence SP&R FlowstepannpBelum ada peringkat
- ASIC Design Methodology Using Cadence SP&R FlowDokumen40 halamanASIC Design Methodology Using Cadence SP&R FlowstepannpBelum ada peringkat
- Oriental Motor RK Series PDFDokumen28 halamanOriental Motor RK Series PDFTinesh ShanBelum ada peringkat
- VimDokumen25 halamanVimelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Design FlowDokumen42 halamanPhysical Design Flowelumalaianitha100% (1)
- 2012 Design Closure Within ICC PDFDokumen171 halaman2012 Design Closure Within ICC PDFelumalaianitha100% (1)
- 2012 Design Closure Within ICC PDFDokumen171 halaman2012 Design Closure Within ICC PDFelumalaianitha100% (1)
- Top Solar Energy Companies in IndiaDokumen9 halamanTop Solar Energy Companies in Indiaashokfriends0% (1)
- TCLDokumen1.690 halamanTCLelumalaianitha67% (3)
- Abhijat Equipments Pvt. LTDDokumen15 halamanAbhijat Equipments Pvt. LTDSatish PatilBelum ada peringkat
- IR Drop AnalysisDokumen9 halamanIR Drop AnalysisRohith Raj100% (1)
- Ex 02Dokumen14 halamanEx 02elumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Easy Corn Flour Halwa Recipe in Under 30 MinutesDokumen25 halamanEasy Corn Flour Halwa Recipe in Under 30 MinuteselumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- CH 05Dokumen46 halamanCH 05elumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Identify Quick Start GuideDokumen30 halamanIdentify Quick Start GuideelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling Digital Circuits Using Bottom-Up DesignDokumen77 halamanModeling Digital Circuits Using Bottom-Up DesignelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Cdnphysdes DsDokumen4 halamanCdnphysdes DselumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Backend Lecture 3Dokumen65 halamanBackend Lecture 3elumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- FabricationDokumen56 halamanFabricationshireesh12345Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Electronic & Transistor Circuits PDFDokumen54 halamanBasic Electronic & Transistor Circuits PDFSandeep GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Bar Swap End User Reference Manual v1.0Dokumen9 halamanBar Swap End User Reference Manual v1.0elumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Ramesh CoreEL VLSI VSAT Module1 2 (Compatibility Mode)Dokumen60 halamanRamesh CoreEL VLSI VSAT Module1 2 (Compatibility Mode)elumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electronic & Transistor Circuits PDFDokumen54 halamanBasic Electronic & Transistor Circuits PDFSandeep GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- FIX Section Update Ww20WTDokumen81 halamanFIX Section Update Ww20WTelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- IA Design Computing Env APAC Mar2004 PDFDokumen37 halamanIA Design Computing Env APAC Mar2004 PDFelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- Memory DesignDokumen4 halamanMemory DesignelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- IA Design Computing Env APAC Mar2004 PDFDokumen37 halamanIA Design Computing Env APAC Mar2004 PDFelumalaianithaBelum ada peringkat
- 75 W Single Output, Power-Factor Corrected LED Driver Using TOP250YNDokumen36 halaman75 W Single Output, Power-Factor Corrected LED Driver Using TOP250YNvladimir_p80Belum ada peringkat
- SCR 2n5061Dokumen8 halamanSCR 2n5061Gary NugasBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Devices and Circuit TheoryDokumen30 halamanElectronic Devices and Circuit TheoryIñaki Zuriel ConstantinoBelum ada peringkat
- SPS SeriesDokumen1 halamanSPS Seriesander2890Belum ada peringkat
- Ultra Compact High Voltage Power Supplies: SeriesDokumen4 halamanUltra Compact High Voltage Power Supplies: SeriesHari NurcahyadiBelum ada peringkat
- TPS3700 Window Supervisor With Internal Reference For Overvoltage and Undervoltage DetectionDokumen27 halamanTPS3700 Window Supervisor With Internal Reference For Overvoltage and Undervoltage DetectionRanveerPratapBelum ada peringkat
- MCC based on Rittal Ri4PowerDokumen2 halamanMCC based on Rittal Ri4PowerHungTruongBelum ada peringkat
- 1901 PC Monochrome Monitor Service Manual 314970-01 (1987 Apr)Dokumen22 halaman1901 PC Monochrome Monitor Service Manual 314970-01 (1987 Apr)Nicola BonettiBelum ada peringkat
- Deconstruction AssignmentDokumen5 halamanDeconstruction AssignmentJames TomyBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Voltage Regulating Relay EE 301-M: Instruction ManualDokumen22 halamanAutomatic Voltage Regulating Relay EE 301-M: Instruction ManualnarendragahlotBelum ada peringkat
- Exam4 - Solutions - S15 (1) .PdfvvipDokumen7 halamanExam4 - Solutions - S15 (1) .PdfvvipSaied Aly SalamahBelum ada peringkat
- Improvements to the NCP1012 Evaluation Board for Reduced Standby Power and EMIDokumen6 halamanImprovements to the NCP1012 Evaluation Board for Reduced Standby Power and EMIStasBelum ada peringkat
- Bias Tee Manual - 11612-90001Dokumen16 halamanBias Tee Manual - 11612-90001dataholderBelum ada peringkat
- A Three-Phase Grid-Connected Microinverter For Ac Photovoltaic Module ApplicationsDokumen4 halamanA Three-Phase Grid-Connected Microinverter For Ac Photovoltaic Module ApplicationsBrightworld ProjectsBelum ada peringkat
- Tfa9842bj DatasheetDokumen17 halamanTfa9842bj DatasheetJose BenavidesBelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Tecnica Cinta de Juntas 930-35-50Dokumen3 halamanFicha Tecnica Cinta de Juntas 930-35-50Carlos TarquinoBelum ada peringkat
- How To Make SMPS Pass Surge & Lightning TestDokumen10 halamanHow To Make SMPS Pass Surge & Lightning TestdcasdcasdcasdcBelum ada peringkat
- Top 500 SupercomputersDokumen63 halamanTop 500 SupercomputersOptimus PrimeBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Chemistry and Physics: Confinement of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Ordered Mesoporous Silica MCM-41Dokumen7 halamanMaterials Chemistry and Physics: Confinement of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Ordered Mesoporous Silica MCM-41Eliza ToteBelum ada peringkat
- Artificial EyeDokumen4 halamanArtificial EyeRinson RajBelum ada peringkat
- FT7900R ServDokumen50 halamanFT7900R ServRoberto ZenebreBelum ada peringkat
- MARLOG 2 Conference Explores Load Sharing of Parallel Generators on ShipsDokumen13 halamanMARLOG 2 Conference Explores Load Sharing of Parallel Generators on Shipsellie210879Belum ada peringkat
- DM00035129 - STM32F41xxxDokumen156 halamanDM00035129 - STM32F41xxxbatrung2906Belum ada peringkat
- HCF4068B: 8 Input Nand/And GateDokumen8 halamanHCF4068B: 8 Input Nand/And GateGoodLookingPirateBelum ada peringkat
- THHN Vs THWN 1Dokumen2 halamanTHHN Vs THWN 1bernardabatayoBelum ada peringkat