Ccna Ipv6
Diunggah oleh
addislibroJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ccna Ipv6
Diunggah oleh
addislibroHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ccna-ipv6
Question 1
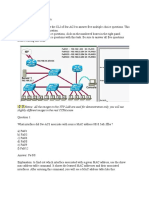
As a CCNA candidate, you must have a firm understanding of the IPv6 address structure. Refer to IPv6 address, could you tell me how many bits are included in each filed?
A - 24
B-4
C-3
D - 16
Answer: D
Explanation:
The format of a IPv6 address is X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X where X is a 16-bit hexadecimal field. For example: 110A:0192:190F:0000:0000:082C:875A:132c
Question 2
In practical IPv6 application, a technology encapsulates IPv6 packets inside IPv4 packets, this technology is called what?
A - tunneling
B - hashing
C - routing
D - NAT
Answer: A
Question 3
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the next-generation Internet Protocol version designated as the successor to IPv4 because IPv4 address space is being exhausted. Which one of the
following descriptions about IPv6 is correct?
A - Addresses are not hierarchical and are assigned at random.
B - Broadcasts have been eliminated and replaced with multicasts.
C - There are 2.7 billion available addresses.
D - An interface can only be configured with one IPv6 address.
Answer: B
Question 4
Which two of these statements are true of IPv6 address representation? (Choose two)
A - The first 64 bits represent the dynamically created interface ID.
B - A single interface may be assigned multiple IPV6 addresses of any type.
C - Every IPV6 interface contains at least one loopback address.
D - Leading zeros in an IPV6 16 bit hexadecimal field are mandatory.
Answer: B C
Explanation:
Leading zeros in IPv6 are optional do that 05C7 equals 5C7 and 0000 equals 0 -> D is not corect.
Question 5
Which three of the following are IPv6 transition mechanisms? (Choose three)
A - 6to4 tunneling
B - GRE tunneling
C - ISATAP tunneling
D - Teredo tunneling
E - VPN tunneling
F - PPP tunneling
Answer: A C D
Explanation:
Below is a summary of IPv6 transition technologies:
6 to 4 tunneling: This mechanism allows IPv6 sites to communicate with each other over the IPv4 network without explicit tunnel setup. The main advantage of this technology is that it
requires no end-node reconfiguration and minimal router configuration but it is not intended as a permanent solution.
ISATAP tunneling (Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol): is a mechanism for transmitting IPv6 packets over IPv4 network. The word "automatic" means that once an ISATAP
server/router has been set up, only the clients must be configured to connect to it.
Teredo tunneling: This mechanism tunnels IPv6 datagrams within IPv4 UDP datagrams, allowing private IPv4 address and IPv4 NAT traversal to be used.
In fact, GRE tunneling is also a IPv6 transition mechanism but is not mentioned in CCNA so we shouldn't choose it (there are 4 types of IPv6 transition mechanisms mentioned in CCNA; they
are: manual, 6-to-4, Teredo and ISATAP).
Question 6
Which two descriptions are correct about characteristics of IPv6 unicast addressing? (Choose two)
A - Global addresses start with 2000::/3.
B - Link-local addresses start with FF00::/10.
C - Link-local addresses start with FE00:/12.
D - There is only one loopback address and it is ::1.
Answer: A D
Explanation:
Below is the list of common kinds of IPv6 addresses:
Loopback address ::1
Link-local address FE80::/10
Site-local address FEC0::/10
Global address
2000::/3
Multicast address FF00::/8
(For more explanation about this question please read question 5 in http://9tut.net/ccna-operations)
Question 7
Select the valid IPv6 addresses. (Choose all apply)
A - ::192:168:0:1
B - 2002:c0a8:101::42
C - 2003:dead:beef:4dad:23:46:bb:101
D - ::
E - 2000::
F - 2001:3452:4952:2837::
Answer: A B C D F
Explanation:
Answers A B C are correct because A and B are the short form of 0:0:0:0:192:168:0:1 and 2002:c0a8:0101:0:0:0:0:0042 while C are normal IPv6 address.
Answer D is correct because "::" is named the "unspecified" address and is typically used in the source field of a datagram that is sent by a device that seeks to have its IP address configured.
Answer E is not correct because a global-unicast IPv6 address is started with binary 001, denoted as 2000::/3 in IPv6 and it also known as an aggregatable global
2000:: (in particular, 2000::/3) is just a prefix and is not a valid IPv6 address.
The entire global-unicast IPv6 address range is from 2000::/128 to 3FFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/128, resulting in a total usable space of over
42,535,295,865,117,307,932,921,825,928,971,000,000 addresses, which is only 1/8th of the entire IPv6 address space!
unicast address.The
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Blended Selections - Sept 16 2013 QTRDokumen4 halamanBlended Selections - Sept 16 2013 QTRaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Eclipse Java BeginnerDokumen45 halamanTutorial Eclipse Java BeginnerArnaldo Jr100% (2)
- Ccna Troubleshooting 2Dokumen4 halamanCcna Troubleshooting 2addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna OperationsDokumen6 halamanCcna OperationsaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 148 Blended WK##Dokumen5 halaman148 Blended WK##addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna-Lab-Sim0765 (CCNA NAT SIM Question 1)Dokumen4 halamanCcna-Lab-Sim0765 (CCNA NAT SIM Question 1)addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna WanDokumen6 halamanCcna WanaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- ATT 2 0 Online Attendance 2012 10 03Dokumen3 halamanATT 2 0 Online Attendance 2012 10 03addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- ICND1 and ICND2 Explained 9tutDokumen75 halamanICND1 and ICND2 Explained 9tutaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Verify Serial Cable Type on Router InterfaceDokumen7 halamanVerify Serial Cable Type on Router InterfaceaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna Operations 2Dokumen5 halamanCcna Operations 2addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna SubnettingDokumen4 halamanCcna SubnettingaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna Hotspot QuestionsDokumen6 halamanCcna Hotspot QuestionsaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna-Lab-Sim (CCNA Access List Sim 2)Dokumen6 halamanCcna-Lab-Sim (CCNA Access List Sim 2)addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna Drag and Drop 4Dokumen2 halamanCcna Drag and Drop 4addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna Drag and Drop 3Dokumen6 halamanCcna Drag and Drop 3addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna Access ListDokumen3 halamanCcna Access ListaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna Drag and Drop QuestionsDokumen11 halamanCcna Drag and Drop QuestionsaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 78 Ccna Access List Sim 2Dokumen4 halaman78 Ccna Access List Sim 2addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 70 Ccna Access List SimDokumen6 halaman70 Ccna Access List SimaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 64 Ccna Eigrp Lab QuestionDokumen3 halaman64 Ccna Eigrp Lab QuestionaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 66 Ccna Implementation SimDokumen5 halaman66 Ccna Implementation SimaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 52 Ccna Nat Sim QuestionDokumen2 halaman52 Ccna Nat Sim QuestionaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 64 Ccna Eigrp Lab QuestionDokumen3 halaman64 Ccna Eigrp Lab QuestionaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 59 Ccna Configuration Sim QuestionDokumen2 halaman59 Ccna Configuration Sim QuestionaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Instructor EPortfolio GuideDokumen17 halamanInstructor EPortfolio GuideaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 63 Ccna VTP Sim QuestionDokumen12 halaman63 Ccna VTP Sim QuestionaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- 57 Ccna Nat Sim Question 2Dokumen2 halaman57 Ccna Nat Sim Question 2addislibroBelum ada peringkat
- Alternative DocumentDokumen14 halamanAlternative DocumentaddislibroBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Studio 5000 Logix Designer - 35.00.01 (Released 2 - 2023)Dokumen17 halamanStudio 5000 Logix Designer - 35.00.01 (Released 2 - 2023)Everton PodencianoBelum ada peringkat
- User Manual - TDSL300W2Dokumen60 halamanUser Manual - TDSL300W2dugdugdugdugi67% (3)
- Is LBA Mandatory For SCAN Listener in Oracle RAC?Dokumen8 halamanIs LBA Mandatory For SCAN Listener in Oracle RAC?OrSklAcademyBelum ada peringkat
- Group PolicyDokumen45 halamanGroup PolicySubhasish PatnaikBelum ada peringkat
- Bizhub I-Series Is Smarter Working: Rethink ItDokumen4 halamanBizhub I-Series Is Smarter Working: Rethink ItGabiBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductor MemoriesDokumen63 halamanSemiconductor MemoriesNayanjyot SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Microprocessor and programming sample test papersDokumen6 halamanMicroprocessor and programming sample test papersHirkanipatilBelum ada peringkat
- 3SP WspeculationDokumen10 halaman3SP WspeculationAaryan gamitBelum ada peringkat
- Dis4 LabsDokumen445 halamanDis4 LabsBis Cuyt100% (1)
- Embedded System TestingDokumen2 halamanEmbedded System TestinguakragunathanBelum ada peringkat
- Index Item: Incident HandlingDokumen18 halamanIndex Item: Incident HandlingPetru Mihai Toma100% (1)
- System Center Configuration Manager - Administration Ebook v2Dokumen197 halamanSystem Center Configuration Manager - Administration Ebook v2RaphaelBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Secondary MemoryDokumen5 halamanIntroduction of Secondary MemorykhurramBelum ada peringkat
- Volte - Voice Over Lte: 3.1. Ims - Ip Multimedia SubsystemDokumen12 halamanVolte - Voice Over Lte: 3.1. Ims - Ip Multimedia SubsystemMiguel Angel Mamani ChahuaraBelum ada peringkat
- Ece Mini Project On Embedded Password Based Security Door Lock SystemDokumen45 halamanEce Mini Project On Embedded Password Based Security Door Lock SystemJaymin Patel100% (4)
- 1430-Opera Cluster Solution - InstallationDokumen60 halaman1430-Opera Cluster Solution - InstallationITDananjaya100% (2)
- PL Hikvision NVR Concept CCTVDokumen2 halamanPL Hikvision NVR Concept CCTVMuhibuddin FirmansahBelum ada peringkat
- Flex PodDokumen32 halamanFlex PodTom BakerBelum ada peringkat
- WST Macros Add-In InstructionsDokumen3 halamanWST Macros Add-In InstructionsTrader CatBelum ada peringkat
- Netra T4-1 Service Manual PDFDokumen290 halamanNetra T4-1 Service Manual PDFsaubhaagyapurnaBelum ada peringkat
- STG8000Dokumen73 halamanSTG8000Lucas PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- 001 Linux1Dokumen14 halaman001 Linux1Khairul AlomBelum ada peringkat
- Azure Stack Portfolio DatasheetDokumen3 halamanAzure Stack Portfolio DatasheetAnonymous N22tyB6UNBelum ada peringkat
- Hardware Troubleshooting: Course T302Dokumen19 halamanHardware Troubleshooting: Course T302Gajanan Chavhan100% (1)
- Orchestrating ContainersDokumen141 halamanOrchestrating ContainersCristhian Rey100% (3)
- Citrix XenServer 6.2.0 Installation GuideDokumen51 halamanCitrix XenServer 6.2.0 Installation GuideJohn ClaymanBelum ada peringkat
- 11p What Is Cloud ComputingDokumen46 halaman11p What Is Cloud ComputingSai TrilokBelum ada peringkat
- WindowsServer2012R2andWindows8 1GroupPolicySettingsDokumen699 halamanWindowsServer2012R2andWindows8 1GroupPolicySettingsalipcstechBelum ada peringkat
- Vi điều khiểnDokumen496 halamanVi điều khiểnPhuc ThinhBelum ada peringkat
- Compass Software: Features and HighlightsDokumen2 halamanCompass Software: Features and HighlightsHector Ernesto Cordero AmaroBelum ada peringkat